8e99e9c503e3a5b2bdb9e48b9d843d93.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Economics, Unit 4 Chapter 4 Demand
Economics, Unit 4 Chapter 4 Demand
 Activating Question • When you prepare to buy something, what influences your decision the most?
Activating Question • When you prepare to buy something, what influences your decision the most?
 Demand – The desire to own something and the ability to pay for it. – When a good’s price is lower, consumers will buy more and when a good’s price is higher, consumers will buy less of it. – Whether your income is $10. 00 or $10, 000, the price of a good will strongly influence your decision to buy. – Example: Would you buy a slice of pizza for $1. 00? $2. 00? $10. 00?
Demand – The desire to own something and the ability to pay for it. – When a good’s price is lower, consumers will buy more and when a good’s price is higher, consumers will buy less of it. – Whether your income is $10. 00 or $10, 000, the price of a good will strongly influence your decision to buy. – Example: Would you buy a slice of pizza for $1. 00? $2. 00? $10. 00?
 Law of Demand – It is a result of two separate behavior patterns that overlap. – They explain why an increase in price decreases quantity of purchases. – These two behavior patterns are: Substitution Effect and Income Effect.
Law of Demand – It is a result of two separate behavior patterns that overlap. – They explain why an increase in price decreases quantity of purchases. – These two behavior patterns are: Substitution Effect and Income Effect.
 Substitution Effect – When a consumer reacts to a rise in price of one good by consuming less of that good and more of a substitute good. – OR Price drops and a good becomes cheaper, consumers will buy more causing quantity of the good demanded to rise. – Example: Price of pizza , , so buy tacos instead – Price of pizza , buy less tacos & more pizza
Substitution Effect – When a consumer reacts to a rise in price of one good by consuming less of that good and more of a substitute good. – OR Price drops and a good becomes cheaper, consumers will buy more causing quantity of the good demanded to rise. – Example: Price of pizza , , so buy tacos instead – Price of pizza , buy less tacos & more pizza
 Income Effect – Rising prices makes us feel poorer so we cut back on purchases of some goods. We buy fewer slices of pizza AND we do NOT substitute other goods. – NOTE: Economists measure consumption in the amount of a good that is BOUGHT, NOT the amount of money spent to buy it.
Income Effect – Rising prices makes us feel poorer so we cut back on purchases of some goods. We buy fewer slices of pizza AND we do NOT substitute other goods. – NOTE: Economists measure consumption in the amount of a good that is BOUGHT, NOT the amount of money spent to buy it.
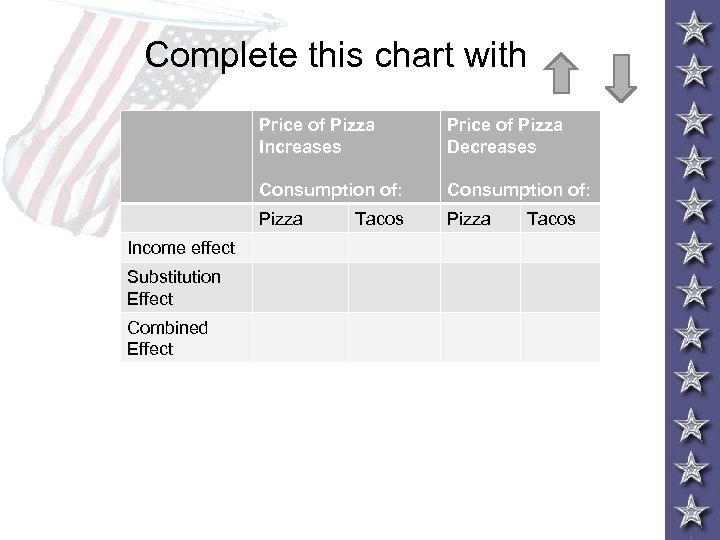 Complete this chart with Price of Pizza Increases Consumption of: Substitution Effect Combined Effect Consumption of: Pizza Income effect Price of Pizza Decreases Pizza Tacos
Complete this chart with Price of Pizza Increases Consumption of: Substitution Effect Combined Effect Consumption of: Pizza Income effect Price of Pizza Decreases Pizza Tacos
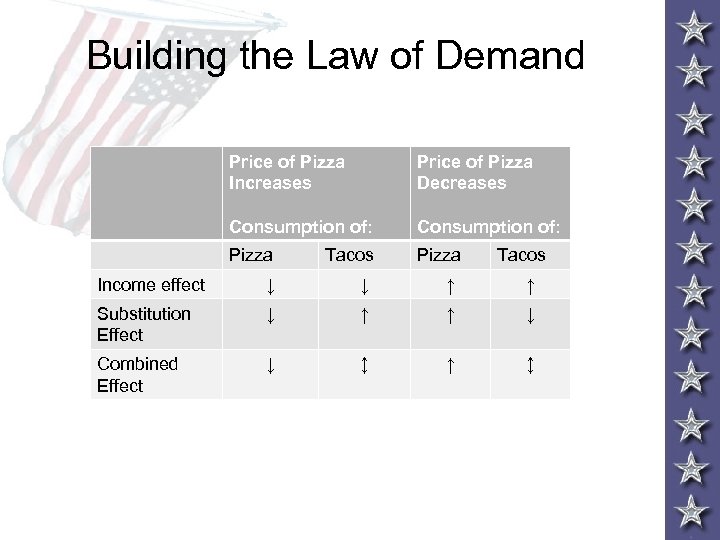 Building the Law of Demand Price of Pizza Increases Price of Pizza Decreases Consumption of: Pizza Tacos Income effect ↓ ↓ ↑ ↑ Substitution Effect ↓ ↑ ↑ ↓ Combined Effect ↓ ↕ ↑ ↕
Building the Law of Demand Price of Pizza Increases Price of Pizza Decreases Consumption of: Pizza Tacos Income effect ↓ ↓ ↑ ↑ Substitution Effect ↓ ↑ ↑ ↓ Combined Effect ↓ ↕ ↑ ↕
 Demand Schedules – To have demand for a good, you must be willing and able to buy it at the specified price. – You want the good and can afford it. – If you want a car, and can’t truly afford it, then you do NOT demand it Sorry. – A Demand Schedule show the good that a person will purchase at each price in a market.
Demand Schedules – To have demand for a good, you must be willing and able to buy it at the specified price. – You want the good and can afford it. – If you want a car, and can’t truly afford it, then you do NOT demand it Sorry. – A Demand Schedule show the good that a person will purchase at each price in a market.
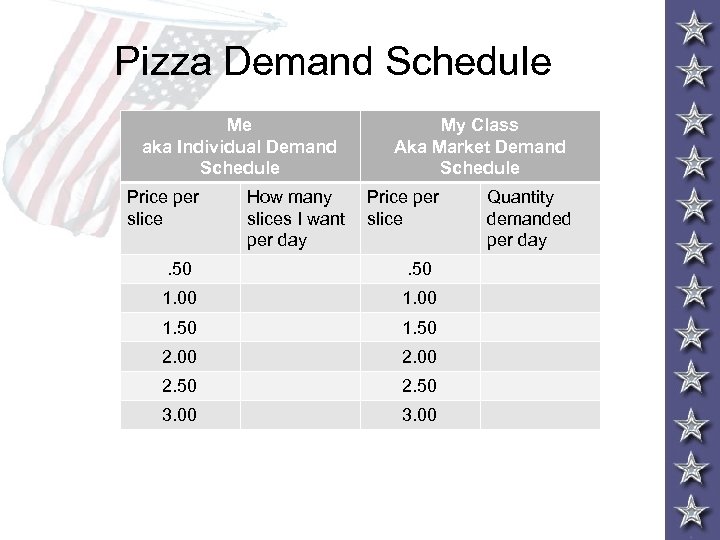 Pizza Demand Schedule Me aka Individual Demand Schedule Price per slice How many slices I want per day My Class Aka Market Demand Schedule Price per slice . 50 1. 00 1. 50 2. 00 2. 50 3. 00 Quantity demanded per day
Pizza Demand Schedule Me aka Individual Demand Schedule Price per slice How many slices I want per day My Class Aka Market Demand Schedule Price per slice . 50 1. 00 1. 50 2. 00 2. 50 3. 00 Quantity demanded per day
 Demand Curves • If take your demand schedule graph from the previous slide and plot it, you will have created a DEMAND CURVE. • Y-axis: Price per slice (in dollars) start at 0 and go up to $3. 00 • X-axis: Slices per day (0 – 5) • Try it.
Demand Curves • If take your demand schedule graph from the previous slide and plot it, you will have created a DEMAND CURVE. • Y-axis: Price per slice (in dollars) start at 0 and go up to $3. 00 • X-axis: Slices per day (0 – 5) • Try it.
 Demand Curves • The graph shows the relationship between price of one good and quantity a person will purchase ALL other factors held constant (price of other goods, your income, quality of pizza) • The graph curves down to right. Why?
Demand Curves • The graph shows the relationship between price of one good and quantity a person will purchase ALL other factors held constant (price of other goods, your income, quality of pizza) • The graph curves down to right. Why?
 Demand Curve Limitations • Used to predict how ppl will change their buying habits when price of a good rises or falls. • ONLY accurate for one very specific set of market conditions. Example: nearby factory closes, less ppl at lunch, sell less pizza even though price is the same.
Demand Curve Limitations • Used to predict how ppl will change their buying habits when price of a good rises or falls. • ONLY accurate for one very specific set of market conditions. Example: nearby factory closes, less ppl at lunch, sell less pizza even though price is the same.
 Question • Which of the following is plotted on the vertical axis of a demand curve? A. Demand schedule B. Price C. Quantity D. Market demand schedule
Question • Which of the following is plotted on the vertical axis of a demand curve? A. Demand schedule B. Price C. Quantity D. Market demand schedule
 Homework • Page 83, #’s 5 and 6 • Freyer Model: demand, substitution effect and income effect
Homework • Page 83, #’s 5 and 6 • Freyer Model: demand, substitution effect and income effect


