a7ad8d869ff7f6eb0cfbd7cd36cf00a4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78
 • “Economics may never strike you as particularly interesting until that moment you wake up at 4 A. M. asking yourself this big question: Hey, Where Has All My Money Gone? ” David J. Fike and Gregg Stebben
• “Economics may never strike you as particularly interesting until that moment you wake up at 4 A. M. asking yourself this big question: Hey, Where Has All My Money Gone? ” David J. Fike and Gregg Stebben
 “MOST OF ECONOMICS CAN BE SUMMARIZED IN FOUR WORDS: “PEOPLE RESPOND TO INCENTIVES. ” THE REST IS COMMENTARY. ” ― STEVEN E. LANDSBURG, ARMCHAIR ECONOMIST: ECONOMICS AND EVERYDAY EXPERIENCE
“MOST OF ECONOMICS CAN BE SUMMARIZED IN FOUR WORDS: “PEOPLE RESPOND TO INCENTIVES. ” THE REST IS COMMENTARY. ” ― STEVEN E. LANDSBURG, ARMCHAIR ECONOMIST: ECONOMICS AND EVERYDAY EXPERIENCE
 WHAT IS ECONOMICS? • Economics is the study of choices • Studies how people decide to resolve conflict between unlimited wants & limited resources. • Tries to explain how limited resources are used to satisfy people’s wants.
WHAT IS ECONOMICS? • Economics is the study of choices • Studies how people decide to resolve conflict between unlimited wants & limited resources. • Tries to explain how limited resources are used to satisfy people’s wants.

 GOODS VS. SERVICE
GOODS VS. SERVICE

 Scarcity: SCARCITY: • The reason we make decisions, exists in all places at all times • Implies limited quantity of resources relative to human wants • BUT: The fact that there is small quantity of a good does not make it scarce. People have to want it! • http: //www. newyorker. com/magazine/2017/05/29/the-world-isrunning-out-of-sand
Scarcity: SCARCITY: • The reason we make decisions, exists in all places at all times • Implies limited quantity of resources relative to human wants • BUT: The fact that there is small quantity of a good does not make it scarce. People have to want it! • http: //www. newyorker. com/magazine/2017/05/29/the-world-isrunning-out-of-sand
 SCARCITY V. SHORTAGE: • Scarcity is not same as a shortage • Shortages -short term supply can’t/won’t meet consumer demand • Can you think of any examples of shortages? • Scarcity always exists because our needs & wants are always greater than our resources http: //www. foxnews. com/us/2017/08/26/hurricane-harveyprice-gouging-complaints-include-99 -for-water. html
SCARCITY V. SHORTAGE: • Scarcity is not same as a shortage • Shortages -short term supply can’t/won’t meet consumer demand • Can you think of any examples of shortages? • Scarcity always exists because our needs & wants are always greater than our resources http: //www. foxnews. com/us/2017/08/26/hurricane-harveyprice-gouging-complaints-include-99 -for-water. html
 CHICKEN WINGS CASE ON SUPERBOWL SUNDAY
CHICKEN WINGS CASE ON SUPERBOWL SUNDAY
 ALLOCATION / HTTP: //WWW. FOODANDWINE. COM/NEWS http: //www. huffingtonpost. com/ entry/59344 dc 3 e 4 b 00573 ab 57 a 491 How do we decide who gets what? http: //www. huffingtonpost. com/entry/59344 dc 3 e 4 b 00573 ab 57 a 491
ALLOCATION / HTTP: //WWW. FOODANDWINE. COM/NEWS http: //www. huffingtonpost. com/ entry/59344 dc 3 e 4 b 00573 ab 57 a 491 How do we decide who gets what? http: //www. huffingtonpost. com/entry/59344 dc 3 e 4 b 00573 ab 57 a 491
 FACTORS OF PRODUCTION(RESOURCES): • Inputs used in production: • Necessary to produce goods & services • Include: • Natural resources (land) • Labor • Capital • Entrepreneurship
FACTORS OF PRODUCTION(RESOURCES): • Inputs used in production: • Necessary to produce goods & services • Include: • Natural resources (land) • Labor • Capital • Entrepreneurship
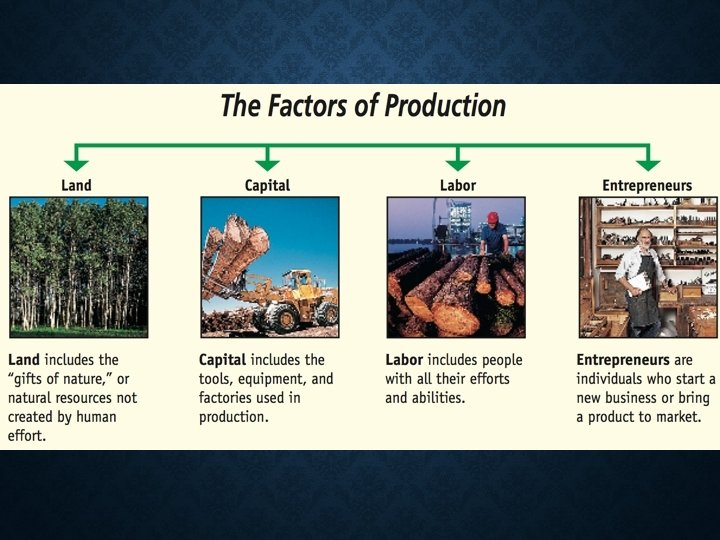
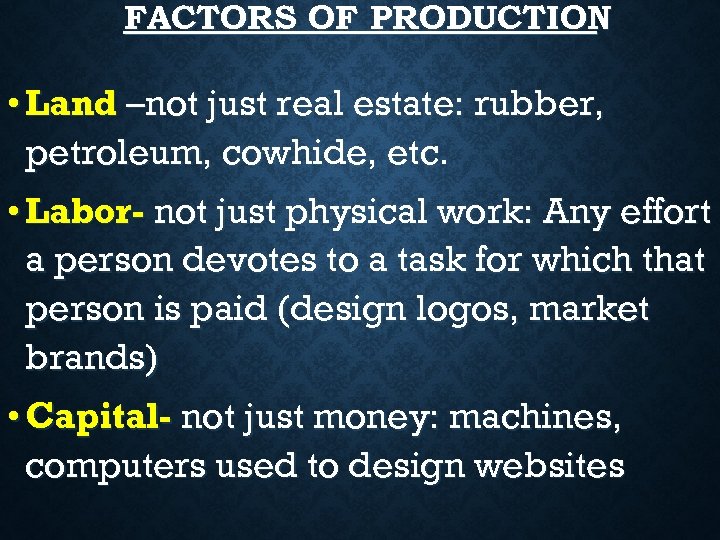 FACTORS OF PRODUCTION • Land –not just real estate: rubber, petroleum, cowhide, etc. • Labor- not just physical work: Any effort a person devotes to a task for which that person is paid (design logos, market brands) • Capital- not just money: machines, computers used to design websites
FACTORS OF PRODUCTION • Land –not just real estate: rubber, petroleum, cowhide, etc. • Labor- not just physical work: Any effort a person devotes to a task for which that person is paid (design logos, market brands) • Capital- not just money: machines, computers used to design websites
 TYPES OF CAPITAL: Physical Capital: Human-made objects used to create other goods & services. (Important: saves time & money) Human Capital: knowledge & skills a worker gains w/ education & experience. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=b. XM 3 a 1 d. SIh. M Financial Capital: Money used to purchase factors of production.
TYPES OF CAPITAL: Physical Capital: Human-made objects used to create other goods & services. (Important: saves time & money) Human Capital: knowledge & skills a worker gains w/ education & experience. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=b. XM 3 a 1 d. SIh. M Financial Capital: Money used to purchase factors of production.
 WHAT WILL YOUR HUMAN CAPITAL BE?
WHAT WILL YOUR HUMAN CAPITAL BE?
 LABOR SKILLED UNSKILLED
LABOR SKILLED UNSKILLED
 WHAT FACTORS OF PRODUCTION WENT INTO THIS GOOD? ___Land_______Labor_______Capital____
WHAT FACTORS OF PRODUCTION WENT INTO THIS GOOD? ___Land_______Labor_______Capital____
 ORGANIZING THE FACTORS Think of the most innovative company, business, good/service you have encountered.
ORGANIZING THE FACTORS Think of the most innovative company, business, good/service you have encountered.
 ENTREPRENEUR : • business innovator who sees opportunity to profit from a new product, process, or unexploited raw material • brings together land, labor, & capital to exploit opportunity to create new goods or services. Takes risk & reaps benefits of creating new goods or services. • How it’s made • Scrub Daddy • Update
ENTREPRENEUR : • business innovator who sees opportunity to profit from a new product, process, or unexploited raw material • brings together land, labor, & capital to exploit opportunity to create new goods or services. Takes risk & reaps benefits of creating new goods or services. • How it’s made • Scrub Daddy • Update

 A BUCK WELL SPENT? • https: //www. ispot. tv/ad/Atn 2/taco-bell-crunchwrap-sliders-abuck-wasted-digital-dolphin
A BUCK WELL SPENT? • https: //www. ispot. tv/ad/Atn 2/taco-bell-crunchwrap-sliders-abuck-wasted-digital-dolphin
 WHAT IS SOMETHING ELSE YOU COULD BE DOING RIGHT NOW? • Sheldon’s Dilemma • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Tjvb-Wh 5 Gs 8
WHAT IS SOMETHING ELSE YOU COULD BE DOING RIGHT NOW? • Sheldon’s Dilemma • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Tjvb-Wh 5 Gs 8
 EVERY CHOICE HAS CONSEQUENSES: • Scarcity forces people to make choices Trade off- an alternative we sacrifice when we make a choice Examples: • Making a 5 cars instead of a tank out of steel. • Going on a vacation instead of working over the week long spring break • Watching Netflix instead of studying for economics • http: //channel. nationalgeographic. com/the-numbers-game/episodes/do-you-live-on-the-edge /
EVERY CHOICE HAS CONSEQUENSES: • Scarcity forces people to make choices Trade off- an alternative we sacrifice when we make a choice Examples: • Making a 5 cars instead of a tank out of steel. • Going on a vacation instead of working over the week long spring break • Watching Netflix instead of studying for economics • http: //channel. nationalgeographic. com/the-numbers-game/episodes/do-you-live-on-the-edge /

 EVERY CHOICE HAS CONSEQUENCES: Opportunity Cost- most desirable alternative given up as the result of a decision • What is the best possible thing I am giving up; stated in a positive way? v. Choice: What to do with a block of wood? v. Use it as a chair? v. Use it as a door stop? v https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=d 6 z. MY 0 cfzfc
EVERY CHOICE HAS CONSEQUENCES: Opportunity Cost- most desirable alternative given up as the result of a decision • What is the best possible thing I am giving up; stated in a positive way? v. Choice: What to do with a block of wood? v. Use it as a chair? v. Use it as a door stop? v https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=d 6 z. MY 0 cfzfc

 WHAT IS THE OPPORTUNITY COST OF SUPERMAN SAVING A CAT?
WHAT IS THE OPPORTUNITY COST OF SUPERMAN SAVING A CAT?
 HONYECON
HONYECON
 OPPORTUNITY COST PRACTICE: • What is the best possible thing given up in the following scenarios? • Spending $100. 00 on a pair of new jeans • Skipping class • Playing in a basketball game • Cutting down an apple orchard to make room for a new apartment complex https: //qz. com/895101/in-the-time-you-spend-on-social-media-eachyear-you-could-read-200 -books/
OPPORTUNITY COST PRACTICE: • What is the best possible thing given up in the following scenarios? • Spending $100. 00 on a pair of new jeans • Skipping class • Playing in a basketball game • Cutting down an apple orchard to make room for a new apartment complex https: //qz. com/895101/in-the-time-you-spend-on-social-media-eachyear-you-could-read-200 -books/
 WHAT IS THE OPPORTUNITY COST OF: 1. building a turf athletic field in an area currently occupied by low income housing apartments? 2. Going to the movies instead of cleaning your room? 3. Eating a slice of cake even though you know it is going to hurt your stomach? 4. Fixing your car instead of going on vacation? 5. Using 20% of our countries resources on the armed forces?
WHAT IS THE OPPORTUNITY COST OF: 1. building a turf athletic field in an area currently occupied by low income housing apartments? 2. Going to the movies instead of cleaning your room? 3. Eating a slice of cake even though you know it is going to hurt your stomach? 4. Fixing your car instead of going on vacation? 5. Using 20% of our countries resources on the armed forces?
 THINKING AT THE MARGIN: • http: //www. bazinganomics. com/bazinganomics //more-isnt-always-merrier • Examining additional benefits of an activity compared to additional costs incurred by that same activity. • deciding whether to do or use one additional unit of some resource. • Thinking at the margin with Monty Python: • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=0 BAMv 6 l. V 2 t 4
THINKING AT THE MARGIN: • http: //www. bazinganomics. com/bazinganomics //more-isnt-always-merrier • Examining additional benefits of an activity compared to additional costs incurred by that same activity. • deciding whether to do or use one additional unit of some resource. • Thinking at the margin with Monty Python: • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=0 BAMv 6 l. V 2 t 4


 THINKING AT THE MARGIN • When making a decision you should think at the margin —don’t make all or nothing decisions! • Companies use marginal analysis as a decision-making tool to help them maximize their potential profits. • Individuals unconsciously use marginal analysis as well, to make a host of everyday decisions • PPFs help us visualize and make decisions at the margin
THINKING AT THE MARGIN • When making a decision you should think at the margin —don’t make all or nothing decisions! • Companies use marginal analysis as a decision-making tool to help them maximize their potential profits. • Individuals unconsciously use marginal analysis as well, to make a host of everyday decisions • PPFs help us visualize and make decisions at the margin
 DIMINISHING MARGINAL RETURNS: • WHY DOESN’T THE LAST VEGGIE ON YOUR PLATE EVER TASTE AS GOOD AS THE FIRST?
DIMINISHING MARGINAL RETURNS: • WHY DOESN’T THE LAST VEGGIE ON YOUR PLATE EVER TASTE AS GOOD AS THE FIRST?
 CRASH COURSE 1: 20 - 4: 15 • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=3 mida. Qqm 7 NM&list=PL 8 d. Puua. Lj. Xt. PNZwz 5_o_5 uir. J 8 g. QXnh. EO&index=18
CRASH COURSE 1: 20 - 4: 15 • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=3 mida. Qqm 7 NM&list=PL 8 d. Puua. Lj. Xt. PNZwz 5_o_5 uir. J 8 g. QXnh. EO&index=18
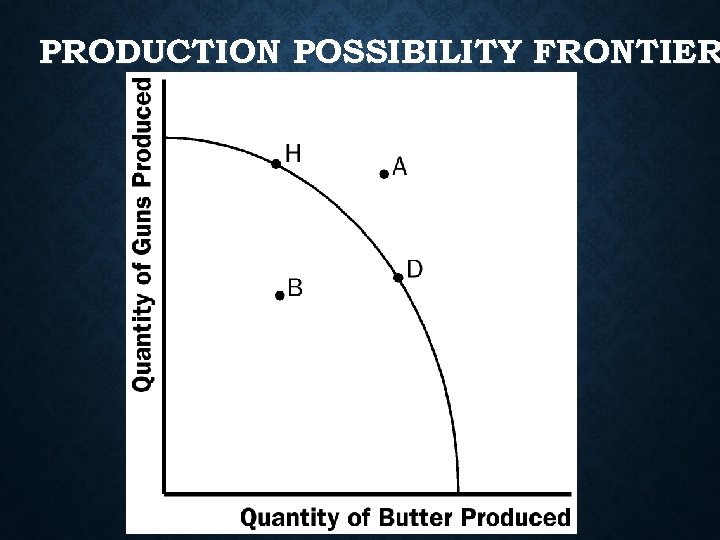
 PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY FRONTIER: • A PPF is a visual representation of trade-offs & opportunity costs • graph that shows what economy can produce with present resources • shows what we can make with what we have. • Illustrates different maximum output combinations of goods/services than can be obtained from a fixed amount of resources
PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY FRONTIER: • A PPF is a visual representation of trade-offs & opportunity costs • graph that shows what economy can produce with present resources • shows what we can make with what we have. • Illustrates different maximum output combinations of goods/services than can be obtained from a fixed amount of resources
 PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY FRONTIER
PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY FRONTIER
 What does a PPF tell us? • If the economy is at a point on the line, then it is making full use of its resources- efficient • If economy is at a point inside boundary it is not using all its resources efficientlyunderutilization. • It’s impossible to be at point outside PPF boundary/line unless increase in factors of production– Growth/Unattainable
What does a PPF tell us? • If the economy is at a point on the line, then it is making full use of its resources- efficient • If economy is at a point inside boundary it is not using all its resources efficientlyunderutilization. • It’s impossible to be at point outside PPF boundary/line unless increase in factors of production– Growth/Unattainable
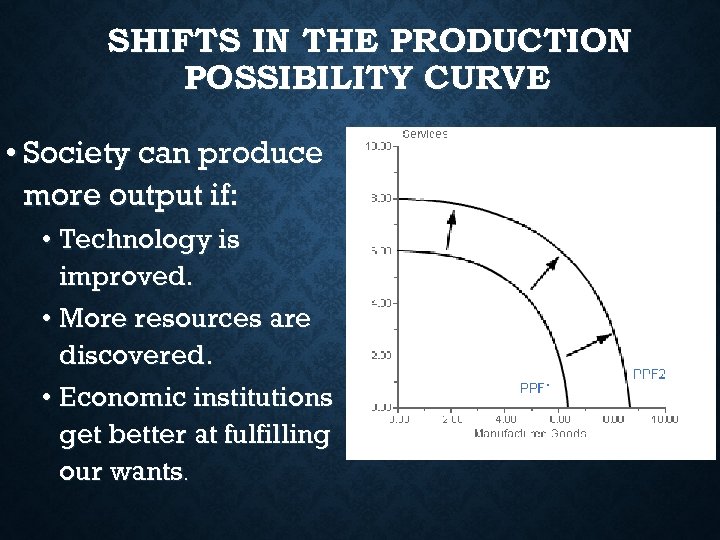 SHIFTS IN THE PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY CURVE • Society can produce more output if: • Technology is improved. • More resources are discovered. • Economic institutions get better at fulfilling our wants.
SHIFTS IN THE PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY CURVE • Society can produce more output if: • Technology is improved. • More resources are discovered. • Economic institutions get better at fulfilling our wants.
 WHAT ELSE CAUSES GROWTH? • Influx of immigrants • New inventions • More/better education • More/better health care
WHAT ELSE CAUSES GROWTH? • Influx of immigrants • New inventions • More/better education • More/better health care
 WHAT PUSHES CURVE TO THE LEFT? • Aging population • War • Strikes • Poor healthcare • Poor education/bad schools • Less resources (oil spill)
WHAT PUSHES CURVE TO THE LEFT? • Aging population • War • Strikes • Poor healthcare • Poor education/bad schools • Less resources (oil spill)
 EFFICIENCY OR GIMMICK HTTP: //DIRKMATEER. COM/MEDI A/OFFICE+HOURS/EFFICIENCYOR-GIMMICK-YOU-DECIDE
EFFICIENCY OR GIMMICK HTTP: //DIRKMATEER. COM/MEDI A/OFFICE+HOURS/EFFICIENCYOR-GIMMICK-YOU-DECIDE
 LAW OF INCREASING COSTS: • As production switches from one item to another more & more resources necessary to increase production of 2 nd item. • “Guns or Butter”- phrase that refers to a trade-off between producing military or consumer goods • Opportunity cost increases b/c Some resources better suited to one alternative over the other
LAW OF INCREASING COSTS: • As production switches from one item to another more & more resources necessary to increase production of 2 nd item. • “Guns or Butter”- phrase that refers to a trade-off between producing military or consumer goods • Opportunity cost increases b/c Some resources better suited to one alternative over the other
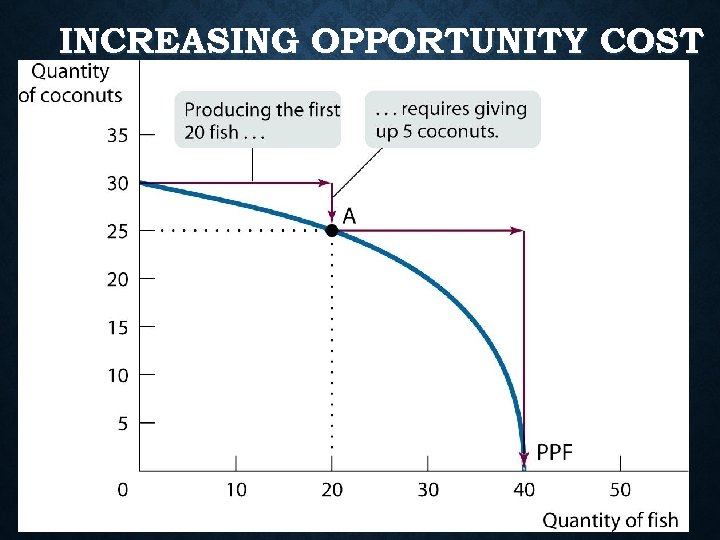 INCREASING OPPORTUNITY COST
INCREASING OPPORTUNITY COST
 MONSTERS INC. & THE PPF • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=t. W 4 G 5 IPpz. FY
MONSTERS INC. & THE PPF • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=t. W 4 G 5 IPpz. FY
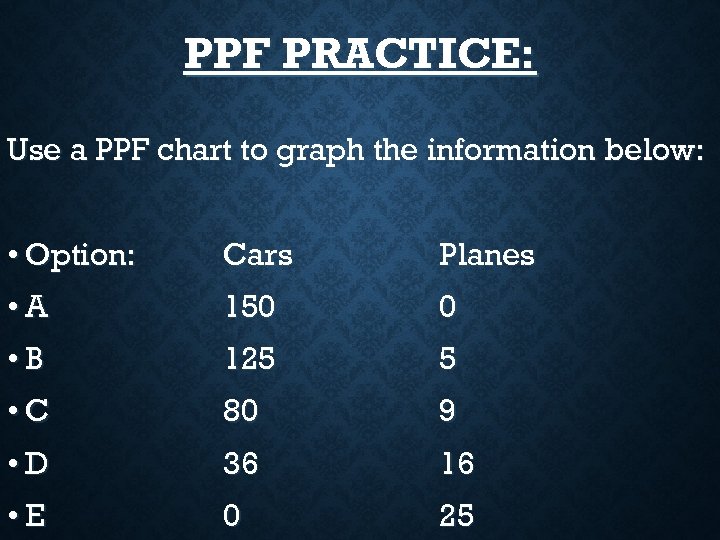 PPF PRACTICE: Use a PPF chart to graph the information below: • Option: Cars Planes • A 150 0 • B 125 5 • C 80 9 • D 36 16 • E 0 25
PPF PRACTICE: Use a PPF chart to graph the information below: • Option: Cars Planes • A 150 0 • B 125 5 • C 80 9 • D 36 16 • E 0 25
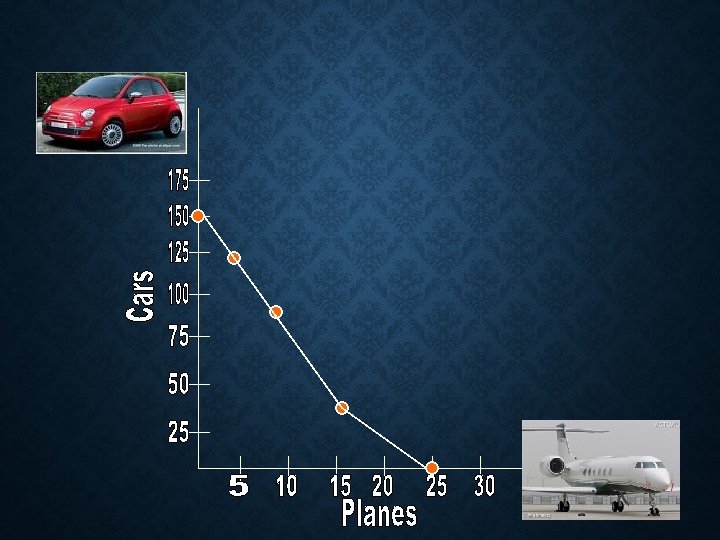
 MAKING CHOICES: • About how many cars can be produced when five planes are made? • About how many planes can be produced when 36 cars are produced?
MAKING CHOICES: • About how many cars can be produced when five planes are made? • About how many planes can be produced when 36 cars are produced?
 1. 125 2. 16
1. 125 2. 16
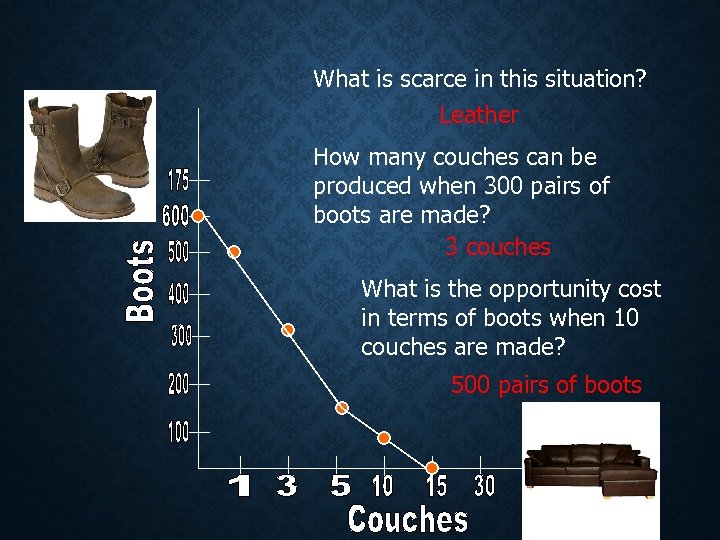 What is scarce in this situation? Leather How many couches can be produced when 300 pairs of boots are made? 3 couches What is the opportunity cost in terms of boots when 10 couches are made? 500 pairs of boots
What is scarce in this situation? Leather How many couches can be produced when 300 pairs of boots are made? 3 couches What is the opportunity cost in terms of boots when 10 couches are made? 500 pairs of boots
 PEPE LE PEW IN LOVE • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=_w. Rfik. O 99 qo
PEPE LE PEW IN LOVE • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=_w. Rfik. O 99 qo
 EXTERNALITIES • An externality is a consequence of an economic activity experienced by unrelated third parties; it can be either positive or negative.
EXTERNALITIES • An externality is a consequence of an economic activity experienced by unrelated third parties; it can be either positive or negative.
 HTTP: //ECONOMICSOFTHEOFFICE. COM/ALL/? JEL=D 62 The Proposal Jim pays for fireworks at Toby's farewell party so that he can propose to Pam, creating a positive externality for everyone at the party.
HTTP: //ECONOMICSOFTHEOFFICE. COM/ALL/? JEL=D 62 The Proposal Jim pays for fireworks at Toby's farewell party so that he can propose to Pam, creating a positive externality for everyone at the party.
 POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES • Immunizations (flu shot, etc. ) - help prevent spread of illness in general public. • Specialized training -company benefited by increased production which also benefits customers. Benefits society as a whole by increasing level of education, quality of life, etc. • Significant home improvements raises property value, but also increase values of homes nearby. • Improving driving habits decreases risk of accidents for everyone on the road as well as eventually reducing insurance premiums of the driver. • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=x 78 Pn. Pd-V-A
POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES • Immunizations (flu shot, etc. ) - help prevent spread of illness in general public. • Specialized training -company benefited by increased production which also benefits customers. Benefits society as a whole by increasing level of education, quality of life, etc. • Significant home improvements raises property value, but also increase values of homes nearby. • Improving driving habits decreases risk of accidents for everyone on the road as well as eventually reducing insurance premiums of the driver. • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=x 78 Pn. Pd-V-A
 EXAMPLES OF POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES • a beautiful garden on a busy street • the safer neighborhood for others that results from some residents hiring private security patrols
EXAMPLES OF POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES • a beautiful garden on a busy street • the safer neighborhood for others that results from some residents hiring private security patrols
 NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Factory pollution - causes health problems & erodes quality of life & property values in a community: • A power plant burns coal to generate electricity emits pollution. • More electricity demanded by customers increases amount of coal burned to generate electricity • Can lead to global warning, acid rain, & smog. • http: //www. criticalcommons. org/Members/sarahjenyk/clips/sriracha-hot-sauce-creating-a-negative-externality • http: //www. criticalcommons. org/Members/jtierney 86/clips/the-big-bang-theory-negative-externalities-of-a/view
NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Factory pollution - causes health problems & erodes quality of life & property values in a community: • A power plant burns coal to generate electricity emits pollution. • More electricity demanded by customers increases amount of coal burned to generate electricity • Can lead to global warning, acid rain, & smog. • http: //www. criticalcommons. org/Members/sarahjenyk/clips/sriracha-hot-sauce-creating-a-negative-externality • http: //www. criticalcommons. org/Members/jtierney 86/clips/the-big-bang-theory-negative-externalities-of-a/view
 NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES: • A loud party next door • an unmowed lawn • automobile exhaust • Second-hand smoke What is the cost of a Chip? • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=ljr. BEd g-QU 4
NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES: • A loud party next door • an unmowed lawn • automobile exhaust • Second-hand smoke What is the cost of a Chip? • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=ljr. BEd g-QU 4
 PLASTIC BAG TAX IS FUELLING SPREAD OF FOOD POISONING IN UK
PLASTIC BAG TAX IS FUELLING SPREAD OF FOOD POISONING IN UK
 SECOND-HAND CIGARETTE SMOKE CAUSES HEALTH PROBLEMS IN PEOPLE OTHER THAN SMOKER. A LOUD PARTY NEXT DOOR CAN CAUSE THOSE NOT INVOLVED IN THE FESTIVITIES TO LOSE SLEEP. • Colbert Report • http: //www. criticalcommons. org/Members/JJWooten/clips/ev an-osnos-on-the-colbert-report/view
SECOND-HAND CIGARETTE SMOKE CAUSES HEALTH PROBLEMS IN PEOPLE OTHER THAN SMOKER. A LOUD PARTY NEXT DOOR CAN CAUSE THOSE NOT INVOLVED IN THE FESTIVITIES TO LOSE SLEEP. • Colbert Report • http: //www. criticalcommons. org/Members/JJWooten/clips/ev an-osnos-on-the-colbert-report/view
 EXTERNALITIES EXPLAINED • http: //www. stlouisfed. org/education_resources/economiclowdown-video-companion-series/episode-5 -externalities/
EXTERNALITIES EXPLAINED • http: //www. stlouisfed. org/education_resources/economiclowdown-video-companion-series/episode-5 -externalities/
 THE LORAX • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=56 LTGBUNT 5 c
THE LORAX • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=56 LTGBUNT 5 c
 OH NO, CIRCULAR FLOW!
OH NO, CIRCULAR FLOW!
 What is a market - Arrangement that allows buyers & sellers to exchanges things Why? Nobody is self-sufficient Can I barter at Wegmans? • Specialization • Concentration of productive efforts of individuals • www. criticalcommons. org/Members/jtierney 86/clips/project-runway-specialization
What is a market - Arrangement that allows buyers & sellers to exchanges things Why? Nobody is self-sufficient Can I barter at Wegmans? • Specialization • Concentration of productive efforts of individuals • www. criticalcommons. org/Members/jtierney 86/clips/project-runway-specialization
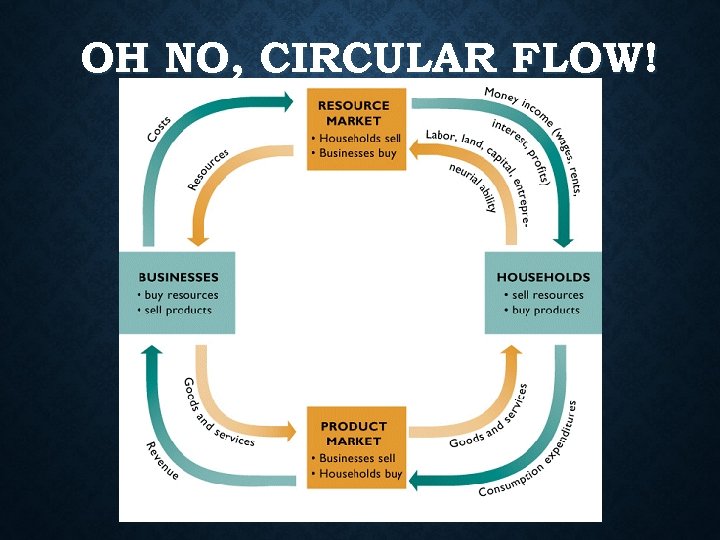
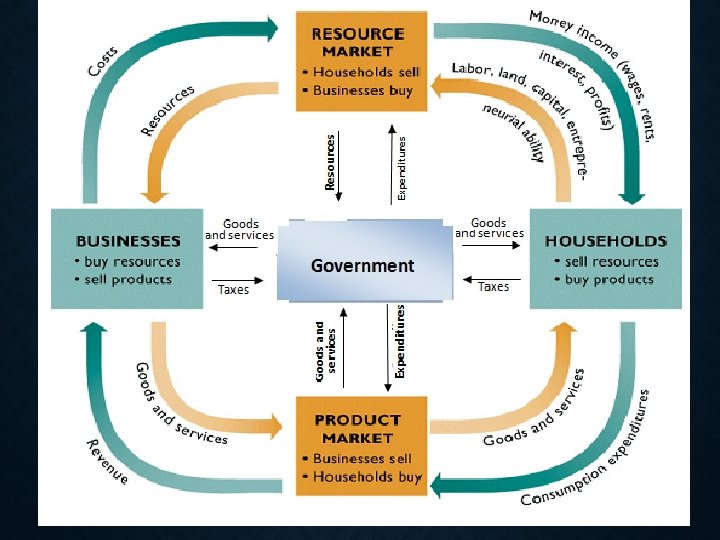
 THE 2 STAKEHOLDERS IN A NATION’S ECONOMY THAT ARE PORTRAYED IN CIRCULAR FLOW ARE: • Household • Person or group living in same residence • Own land, labor, capital (factors of production) • Firm • Organization that uses resources to produce a product. Combines Land, Labor, & Capital. • Transforms “inputs” into “outputs”
THE 2 STAKEHOLDERS IN A NATION’S ECONOMY THAT ARE PORTRAYED IN CIRCULAR FLOW ARE: • Household • Person or group living in same residence • Own land, labor, capital (factors of production) • Firm • Organization that uses resources to produce a product. Combines Land, Labor, & Capital. • Transforms “inputs” into “outputs”
 • Firms demand (want) REOURCES from households • Households demand (want)PRODUCTS from firms. Factor Market • where firms purchase the factors of production from households • Most notably, labor • Product Market • Where households purchase goods and services that firms produce
• Firms demand (want) REOURCES from households • Households demand (want)PRODUCTS from firms. Factor Market • where firms purchase the factors of production from households • Most notably, labor • Product Market • Where households purchase goods and services that firms produce
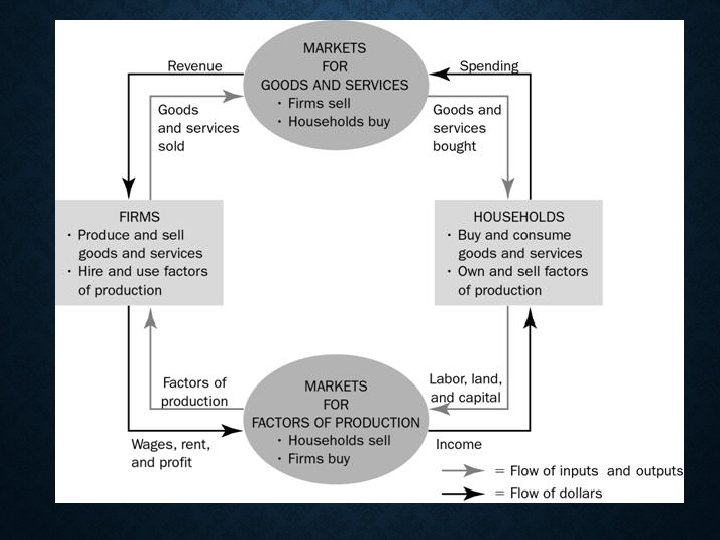
 WHAT’S GOING ON? • Resources flow from households to firms, are turned into goods & services, then flow from firms to households • Money flows in opposite direction; first from firms to households in the form of Wages, Interest, Rent & Profit (income payments for resources owned by households), then from households to firms in form of expenditures(payments) on goods & services
WHAT’S GOING ON? • Resources flow from households to firms, are turned into goods & services, then flow from firms to households • Money flows in opposite direction; first from firms to households in the form of Wages, Interest, Rent & Profit (income payments for resources owned by households), then from households to firms in form of expenditures(payments) on goods & services
 WHY DOES IT ALL WORK? • Self-Interest: • "It is not from the benevolence of the butcher, the brewer, or the baker, that we can expect our dinner, but from their regard to their own interest. " – A. Smith • Acting in our own self interest to satisfy needs and wants • Not the same as selfish
WHY DOES IT ALL WORK? • Self-Interest: • "It is not from the benevolence of the butcher, the brewer, or the baker, that we can expect our dinner, but from their regard to their own interest. " – A. Smith • Acting in our own self interest to satisfy needs and wants • Not the same as selfish
 COMPETITION • Competition –struggle among producers for the dollars of consumers • http: //www. gasbuddy. com/
COMPETITION • Competition –struggle among producers for the dollars of consumers • http: //www. gasbuddy. com/
 INVISIBLE HAND How the market regulates itself “He intends only his own gain, and he is in this, as in many other cases, led by an invisible hand to promote an end which was no part of his intention. Nor is it always the worse for the society that it was not part of it. By pursuing his own interest he frequently promotes that of the society more effectually than when he really intends to promote it. ” – A. Smith, Wealth of Nations
INVISIBLE HAND How the market regulates itself “He intends only his own gain, and he is in this, as in many other cases, led by an invisible hand to promote an end which was no part of his intention. Nor is it always the worse for the society that it was not part of it. By pursuing his own interest he frequently promotes that of the society more effectually than when he really intends to promote it. ” – A. Smith, Wealth of Nations
 60 SECOND ECON- INVISIBLE HAND • http: //www. open. edu/openl earn/society/politics-policypeople/economics/60 second-adventureseconomics-the-invisiblehand
60 SECOND ECON- INVISIBLE HAND • http: //www. open. edu/openl earn/society/politics-policypeople/economics/60 second-adventureseconomics-the-invisiblehand
 I PENCIL • https: //www. youtube. com/w atch? v=IYO 3 t. Oq. DISE
I PENCIL • https: //www. youtube. com/w atch? v=IYO 3 t. Oq. DISE
 GOVT. AND CIRCULAR FLOW: • Like a firm, govt. purchases land, labor, & capital from households in the product market • Transfer of money: • Taxes • Paying benefits (social security)
GOVT. AND CIRCULAR FLOW: • Like a firm, govt. purchases land, labor, & capital from households in the product market • Transfer of money: • Taxes • Paying benefits (social security)
 • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=m. N 5 HPJYJzus
• https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=m. N 5 HPJYJzus
 “WHAT GOES AROUND COMES AROUND” Households: Start w/factors of production— Sell them to firms for money—w/ money you buy Goods/Services (AKA: “ECONOS”). The more ECONOS you have the wealthier you are. Firms: Start w/ $1, 000, (loan) to buy factors of production, Exchange 1 land, 1 labor, 1 capital for ECONOS (goods and services), Lastly sell the ECONOS back to household. Goal: • Households: Acquire as many “ECONOS” as possible • Firms: Acquire as much money as possible
“WHAT GOES AROUND COMES AROUND” Households: Start w/factors of production— Sell them to firms for money—w/ money you buy Goods/Services (AKA: “ECONOS”). The more ECONOS you have the wealthier you are. Firms: Start w/ $1, 000, (loan) to buy factors of production, Exchange 1 land, 1 labor, 1 capital for ECONOS (goods and services), Lastly sell the ECONOS back to household. Goal: • Households: Acquire as many “ECONOS” as possible • Firms: Acquire as much money as possible


