6e8b260276b4cbc1a759dddfcfc364d2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Economics, Global, and Other Issues in Electronic Commerce

Learning Objectives • • Identify the major impacts of Web-based economics Describe the major components of Web-based economics Analyze the impact of online markets on competition Describe the impacts and industry structure on intermediation • Describe the role and impact of virtual communities • Evaluate the issues involved in global electronic commerce
Marketplace Vs. Marketspace • Markets have three main functions – Matching buyers and sellers – Facilitating the exchange of information, goods, services and payments – Providing an institutional infrastructure • Electronic Marketplaces = Marketspaces – Increase effectiveness – Lower distribution costs – ‘Friction-free’ markets

Marketplace Vs. Marketspace (cont. ) • Regular and EC economics are completely different – EC involves gathering, selecting, synthesizing, and distributing information – Economics of EC starts with supply and demand, and ends with pricing and competition

Components of E-Economics • • Digital Products The Consumers The Sellers The Infrastructure Companies The Intermediaries The Support Services Content Creators

Competition in E-Commerce • Impacts on competition – Lower buyers’ search cost – Speedy comparisons – Differentiation – Lower price – Customer service – Digital products lack normal wear and tear

Competition in E-Commerce • Perfect competition – Enable many buyers and sellers to enter the market at little or no cost (no barriers to entry) – Not allow any buyers and sellers to individually influence the market – Make certain products homogeneous (no product differentiation) – Supply buyers and sellers with perfect information about the products and the market participants and conditions

Competition in E-Commerce • Observations regarding competitiveness – – – There will be many new entrants The bargaining power of buyers is likely to increase There will be more substitute products and services The bargaining power of suppliers may decrease The number of industry competitors in one location will increase
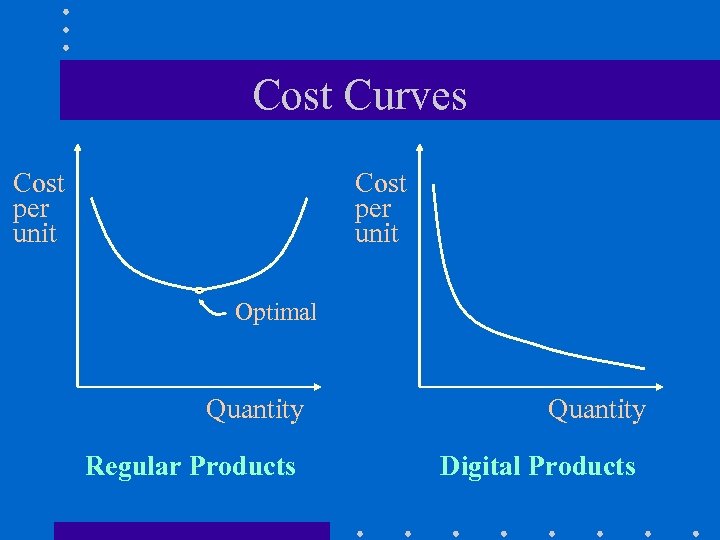
Cost Curves Cost per unit Optimal Quantity Regular Products Quantity Digital Products

The Need for a Critical Mass of Buyers • Reasons for the need for critical mass of buyers – Fixed cost of EC is high, need many customers to cover it. – Strong and fair competition can be developed • Estimated Internet users worldwide : – Small number as compared with an estimated 1. 3 billion TVs • No need to wait a few years before starting EC – Look at the microlevel segmentation of the market you are trying to reach

Quality Uncertainty and Quality Assurance • Price is becoming the major factor influencing many Web purchases • Quality is extremely important in many situations • Issue of quality is related to issue of trust • Quality assurance by a trusted 3 rd party is needed – For example : Trust-e and Better Business Bureau (BBB)

Quality Uncertainty and Quality Assurance (cont. ) • Solutions for quality uncertainty – Provide free samples • clear signal that the vendor is confident about the quality – Return if you are not satisfied • providing a guarantee, or a full refund, for dissatisfied customers is facilitating EC • returns not feasible for digital products – many digital products such as information, knowledge, or educational material, are fully consumed when they are viewed by consumers – returning a product or refunding a purchase price may be impractical due to transaction costs

Pricing on the Internet • Price Discovery – Electronic marketplaces enable new types of price discovery • Web-based auctions at Onsale. com and e. Bay. com • Intermediaries such as Priceline (www. priceline. com) • Agents such as Kasbah (ecomerce. medis. mit. edu/kasbah) The ability to customize price products discriminate

Online Vs. Offline Pricing • How to price the online vs. the offline products or services • Pacific Brokerage Services (www. tradepbs. com) – a discount broker – offered almost 50% commission discount for online services • Banking Industry – most do not offer any discounts for going online – some even charge additional online fixed monthly service fee – some, whose strategy is to aggressively go online, provide discount • Retailers – no clear strategy

Contributors to Electronic Market Success • Product characteristics – Digitizable products; low priced items; computers; electronics, consumer products; and even cars • Industry characteristics – The need for a transaction broker exists (e. g. , stocks) • Seller characteristics – In oligopolistic situations, sellers can maintain an environment of lower volume, higher profit margin transactions • Consumer characteristics – Patient and analytical consumers
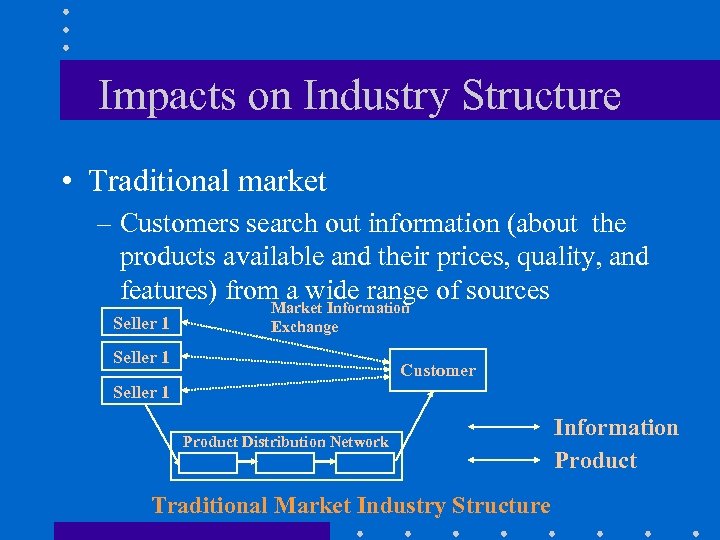
Impacts on Industry Structure • Traditional market – Customers search out information (about the products available and their prices, quality, and features) from a wide range of sources Market Information Seller 1 Exchange Seller 1 Customer Seller 1 Product Distribution Network Traditional Market Industry Structure Information Product
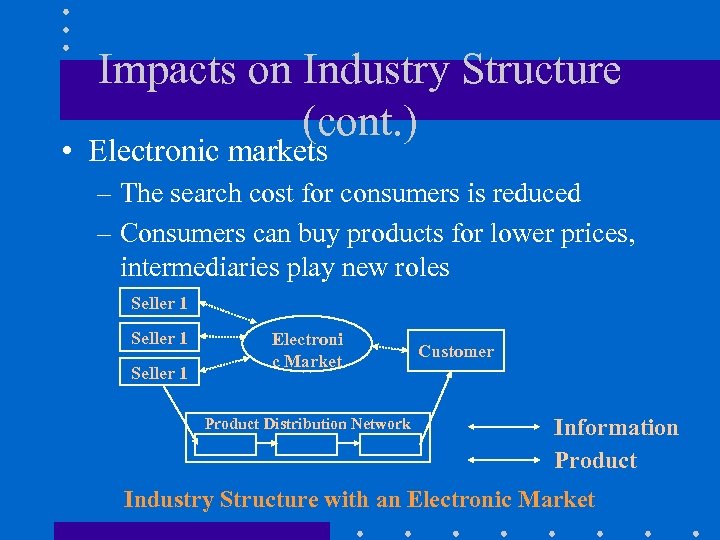
Impacts on Industry Structure (cont. ) • Electronic markets – The search cost for consumers is reduced – Consumers can buy products for lower prices, intermediaries play new roles Seller 1 Electroni c Market Product Distribution Network Customer Information Product Industry Structure with an Electronic Market

Winners and Losers in EC • Winners • • • Proprietary network owners • Internet access providers Midsize manufacturers • Portal providers Technology suppliers • A few large resellers Market makers Online dedicated companies • EC software companies Conventional retailers that use online extensively Providers of diversified Internet services Advertisement and target marketing companies Security, special infrastructure, and payment systems providers

Potential Losers in EC • • Most wholesalers, especially small ones Brokers Salespeople Non-differentiated manufacturers

Virtual Communities • The Internet Communities – Web is being transformed into a social Web of communities – Types of communities • Communities of transactions – facilitate buying and selling • Communities of interest – place for people to interact with each other on a specific topic • Communities of relations – be organized around certain life experiences • Communities of fantasy – place for participants to create imaginary environments
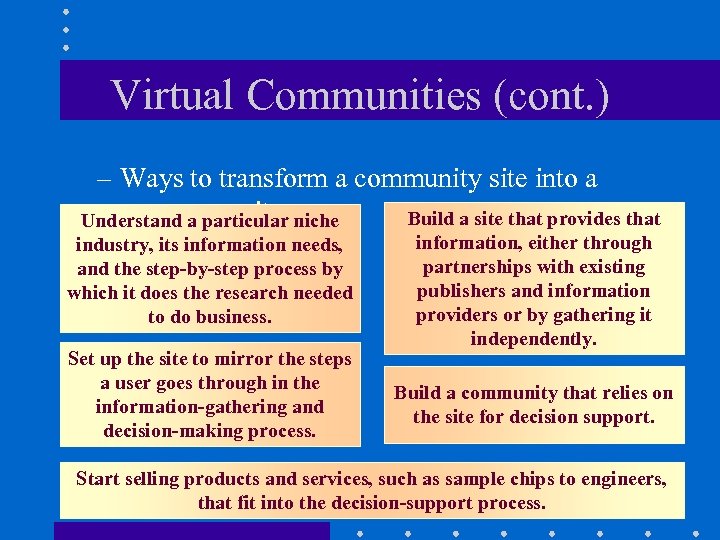
Virtual Communities (cont. ) – Ways to transform a community site into a commerce site: Build a site that provides that Understand a particular niche industry, its information needs, and the step-by-step process by which it does the research needed to do business. Set up the site to mirror the steps a user goes through in the information-gathering and decision-making process. information, either through partnerships with existing publishers and information providers or by gathering it independently. Build a community that relies on the site for decision support. Start selling products and services, such as sample chips to engineers, that fit into the decision-support process.

Virtual Communities (cont. ) • The Expected Payback – Customer loyalty increases – Increased sales – Customer participation and feedback increases – Increased repeat traffic to site – Drive new traffic to the site

Virtual Communities (cont. ) • Creating economic value – Members input useful information in the form of comments, feedback, elaborating their attitudes and beliefs, and information needs of the community – The community brings together consumers of specific demographic and interest – Communities charge members content fees for downloading certain articles, music, or pictures

Global Electronic Commerce • While geographical market boundaries may be falling, global interest-based communities will spring up • Mainly in support of business-to-business financial and other repetitive, standard transactions, e. g. EFT & EDI • The emergence of the Internet and the extranets resulted in an inexpensive and flexible infrastructure that can greatly facilitate global trade

Barriers to Global Electronic Commerce • Legal Issues – Uncoordinated actions must be avoided an international policy of cooperation should be encouraged • Market Access Issues – Companies starting e-commerce need to evaluate bandwidth needs by analyzing the data required, time constraints, access demands, and user technology limitations • Financial Issues – Customs and taxation – electronic payment systems

Barriers to Global Electronic Commerce (cont. ) • Other Issues – – – – Identification of buyers and sellers Trust Security ( for example, viruses) Cultural diversity International agreements (multi-lateral agreements) Role of government Purchasing in local currencies Language and translation

The U. S. Policy Regarding Global Electronic Commerce • The private sector should lead • Governments should avoid undue restrictions on electronic commerce • Where government involvement is needed, its aim should be to support and enforce a predictable minimalist, consistent and simple legal environment for commerce • Governments should recognize the unique qualities of the Internet • Electronic commerce on the Internet should be facilitated on a global basis

Managerial Research Issues – Advertisement • measuring the effectiveness, integration and coordination – Applications • creating a methodology of finding EC business applications – Strategy • designing strategic advantage strategy for EC • initiating “Where to market” strategy • finding way to Integrate EC into organizations – Impacts • identify the necessary organization structure and culture • integration with ERP and SCM
6e8b260276b4cbc1a759dddfcfc364d2.ppt