44797a458532a8f5ff3c889c4f32fca6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Economics
Economics
 Do Now: What do you think this quote means? “There’s no such thing as a free lunch. ”
Do Now: What do you think this quote means? “There’s no such thing as a free lunch. ”
 1) Everything has a cost to it 2) The cost can come from you or someone else 3) The cost can be money, time, and the things you are NOT getting
1) Everything has a cost to it 2) The cost can come from you or someone else 3) The cost can be money, time, and the things you are NOT getting
 What is Economics? 1) The study of how people satisfy their needs and wants through the choices that they make 2) Study of the production and consumption of goods and services Includes: jobs/employment trade business/commerce money (and how it is spent)
What is Economics? 1) The study of how people satisfy their needs and wants through the choices that they make 2) Study of the production and consumption of goods and services Includes: jobs/employment trade business/commerce money (and how it is spent)
 Needs vs. Wants Need – basic requirement for survival Needs can also be immaterial (love, acceptance, success)
Needs vs. Wants Need – basic requirement for survival Needs can also be immaterial (love, acceptance, success)
 Want – a means of expressing a need (Ex. Food is a need, Pizza is a want) EVERYTHING ELSE that is not a need (ex: cell phones, cars) Often, wants are advertised as needs (we think that our wants are things we need)
Want – a means of expressing a need (Ex. Food is a need, Pizza is a want) EVERYTHING ELSE that is not a need (ex: cell phones, cars) Often, wants are advertised as needs (we think that our wants are things we need)
 Is it a Need or a Want?
Is it a Need or a Want?
 Resources Goods – something that can be touched Services – work performed However, there a limited amount of resources available
Resources Goods – something that can be touched Services – work performed However, there a limited amount of resources available
 The Basic Economic Problem Unlimited Wants Limited Resources SCARCITY
The Basic Economic Problem Unlimited Wants Limited Resources SCARCITY
 Scarcity Because of scarcity, people must make choices on how to spend/distribute resources 1) WHAT to use the resources for 2) HOW to use the resources 3) WHO will have the resources
Scarcity Because of scarcity, people must make choices on how to spend/distribute resources 1) WHAT to use the resources for 2) HOW to use the resources 3) WHO will have the resources
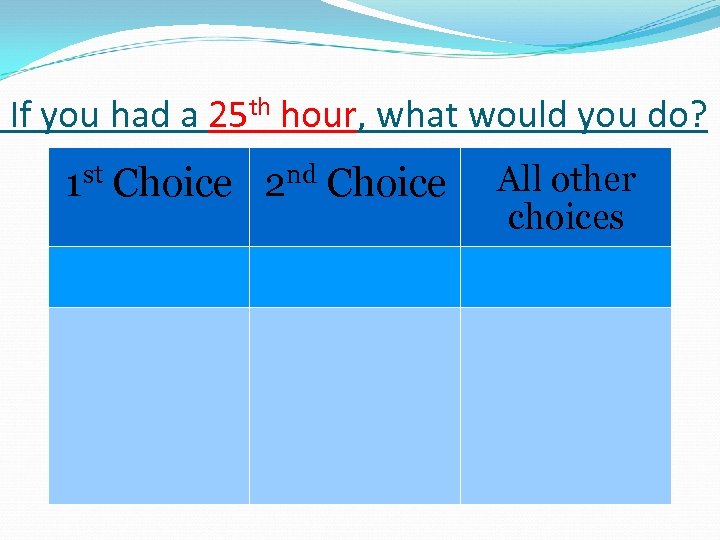 If you had a 25 th hour, what would you do? 1 st Choice 2 nd Choice All other choices
If you had a 25 th hour, what would you do? 1 st Choice 2 nd Choice All other choices
 Opportunity Cost • What you are giving up (the cost of the opportunity) • The value of the runner-up, the second choice • It can be both positive and negative 1 st Choice 2 nd Choice Opportunity Cost All other choices
Opportunity Cost • What you are giving up (the cost of the opportunity) • The value of the runner-up, the second choice • It can be both positive and negative 1 st Choice 2 nd Choice Opportunity Cost All other choices
 Ex. You have $300 = (Opportunity Cost)
Ex. You have $300 = (Opportunity Cost)
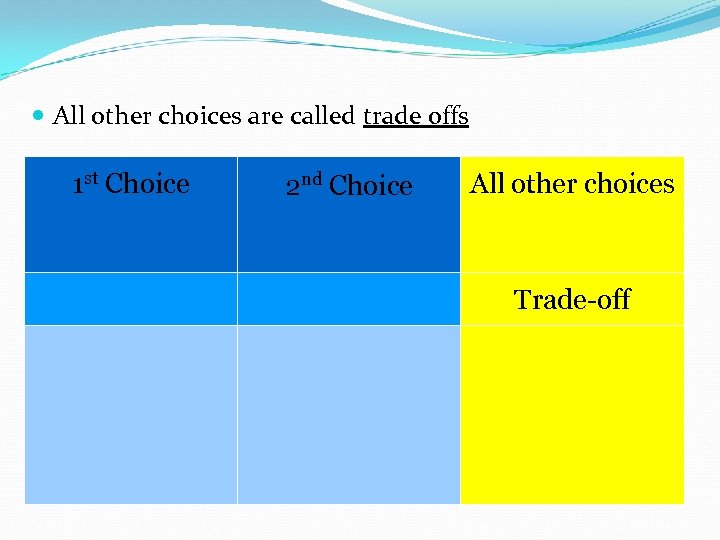 All other choices are called trade offs 1 st Choice 2 nd Choice All other choices Trade-off
All other choices are called trade offs 1 st Choice 2 nd Choice All other choices Trade-off
 H. W. Needs v. Wants & Opportunity Cost
H. W. Needs v. Wants & Opportunity Cost
 Day 2: Do Now Three choices Which one would you pick and why What is your 2 nd and 3 rd choice What is your trade off? What is your opportunity cost?
Day 2: Do Now Three choices Which one would you pick and why What is your 2 nd and 3 rd choice What is your trade off? What is your opportunity cost?
 Resources We HAVE to make choices because of scarce resources!!! The biggest problem is SCARCITY!!!! Therefore- We have to figure out how to delegate our resources according to needs and wants!!
Resources We HAVE to make choices because of scarce resources!!! The biggest problem is SCARCITY!!!! Therefore- We have to figure out how to delegate our resources according to needs and wants!!
 “Factors of Production” Something that is used to produce and distribute goods and services When all three are present, PRODUCTION can occur
“Factors of Production” Something that is used to produce and distribute goods and services When all three are present, PRODUCTION can occur
 1) Land - space/area - natural resources (wood, coal, oil) - limited supply
1) Land - space/area - natural resources (wood, coal, oil) - limited supply
 2) Labor - people to work/human resources - can vary through quantity of people and quality of workers
2) Labor - people to work/human resources - can vary through quantity of people and quality of workers
 3) Capital - something used for production Physical Capital: man-made resources used (tools, factories, machines) Human Capital: Knowledge, skills and abilities workers gain through education and experience
3) Capital - something used for production Physical Capital: man-made resources used (tools, factories, machines) Human Capital: Knowledge, skills and abilities workers gain through education and experience
 Physical Capital Human Capital
Physical Capital Human Capital
 4) Entrepreneurship • - leaders who decide how to combine Land, Labor and Capital to make new or innovative goods and services • - take risks to start new companies and develop new ideas • - Invest their time and money to help the economy grow
4) Entrepreneurship • - leaders who decide how to combine Land, Labor and Capital to make new or innovative goods and services • - take risks to start new companies and develop new ideas • - Invest their time and money to help the economy grow
 Day 3: Monsters INC Complete worksheet on Factors of Production
Day 3: Monsters INC Complete worksheet on Factors of Production
 Supply & Demand
Supply & Demand
 The most important factor you consider before you buy a good or service PRICE
The most important factor you consider before you buy a good or service PRICE
 Consumer (buyer): users of goods/services Producer (supplier, seller): create, market, and sell goods and services Market: The place where consumers and producers meet to determine the price of g/s and the amount of g/s that will be supplied
Consumer (buyer): users of goods/services Producer (supplier, seller): create, market, and sell goods and services Market: The place where consumers and producers meet to determine the price of g/s and the amount of g/s that will be supplied
 Demand The AMOUNT of a product that consumers want to BUY Consumers must be willing and able to make the purchase in order for there to be a demand
Demand The AMOUNT of a product that consumers want to BUY Consumers must be willing and able to make the purchase in order for there to be a demand
 Law of Demand Price Demand = If the cost is down, people will buy more. Price Demand = If the cost is up, people will buy less
Law of Demand Price Demand = If the cost is down, people will buy more. Price Demand = If the cost is up, people will buy less
 Human Behavior That Causes Demand 1) Substitution Effect : As the price of a good goes up it becomes more expensive than other goods, causing people to choose the less expensive product 2) The Income Effect: When the price of goods/services goes UP we feel POORER When the price of goods/services goes DOWN we feel RICHER Even though you FEEL richer/poorer you real income HAS NOT changed!
Human Behavior That Causes Demand 1) Substitution Effect : As the price of a good goes up it becomes more expensive than other goods, causing people to choose the less expensive product 2) The Income Effect: When the price of goods/services goes UP we feel POORER When the price of goods/services goes DOWN we feel RICHER Even though you FEEL richer/poorer you real income HAS NOT changed!
 The menu for school lunch reads: Cheeseburger = $1. 50 Slice of Pizza = $1. 50 (Students usually buy about 500 cheeseburgers and 500 pizzas a day) If the price of beef goes up then the price of Cheeseburgers will go up too. Then the menu will change to: Cheeseburger = $2. 50 Slice of Pizza = $1. 50 (Students will then buy about 100 cheeseburgers and 900 pizzas a day. ) This change in spending = the Substitution Effect
The menu for school lunch reads: Cheeseburger = $1. 50 Slice of Pizza = $1. 50 (Students usually buy about 500 cheeseburgers and 500 pizzas a day) If the price of beef goes up then the price of Cheeseburgers will go up too. Then the menu will change to: Cheeseburger = $2. 50 Slice of Pizza = $1. 50 (Students will then buy about 100 cheeseburgers and 900 pizzas a day. ) This change in spending = the Substitution Effect
 As the price of gas goes up it becomes more expensive to fill our cars. When gas was $1. 00 a gallon, it cost $15 to fill my tank. If gas goes to $4. 00 a gallon, it will cost $60 to fill my tank. That means I will drive fewer places in order to save my income.
As the price of gas goes up it becomes more expensive to fill our cars. When gas was $1. 00 a gallon, it cost $15 to fill my tank. If gas goes to $4. 00 a gallon, it will cost $60 to fill my tank. That means I will drive fewer places in order to save my income.
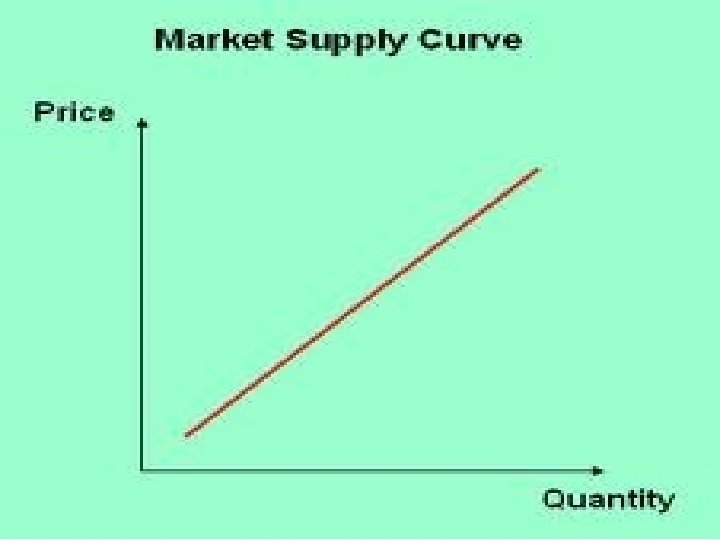
 Supply The amount of goods/services that a producer makes available to sell
Supply The amount of goods/services that a producer makes available to sell
 Law of Supply Price Supply = If the cost is up, companies will make more (because there is more money to be made) Price Supply = If the cost is down, companies will make less
Law of Supply Price Supply = If the cost is up, companies will make more (because there is more money to be made) Price Supply = If the cost is down, companies will make less
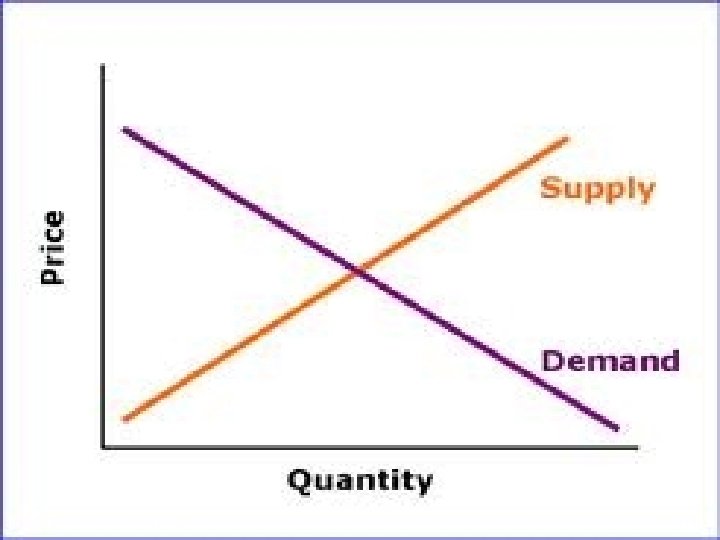
 So… Supply Demand = *When something is not scarce, there is not a high demand for it • The opposite is also true (Low supply = HIGH demand)
So… Supply Demand = *When something is not scarce, there is not a high demand for it • The opposite is also true (Low supply = HIGH demand)
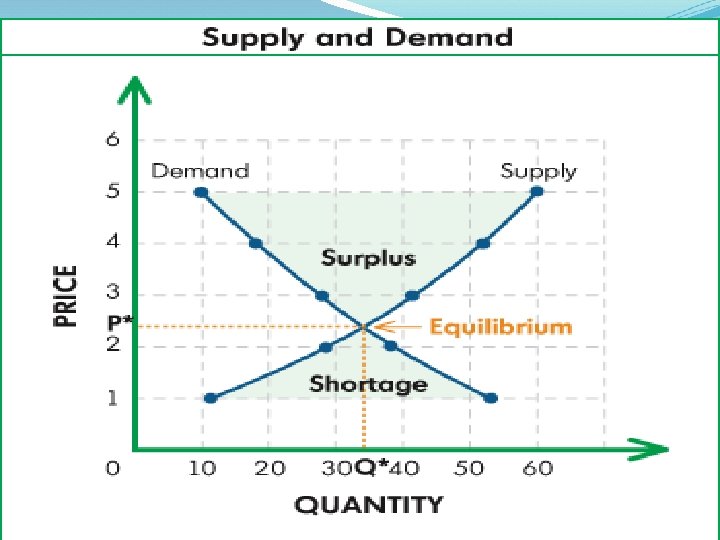
 Surplus - When you have more supply than demand Shortage – When you have less supply than demand Equilibrium – When the supply and the demand are the same (equal)
Surplus - When you have more supply than demand Shortage – When you have less supply than demand Equilibrium – When the supply and the demand are the same (equal)