585833913dfed41865b8a2cf1eed73da.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Economics Circular Flow & GDP How the U. S. Economy works
Economics Circular Flow & GDP How the U. S. Economy works
 What is an Economy? • The way goods, services & money flow through an economic system The Circular Flow describes how goods, services & money flow through a market economy
What is an Economy? • The way goods, services & money flow through an economic system The Circular Flow describes how goods, services & money flow through a market economy
 2 Sides of a Market Economy • Consumers decide what to BUY! – Demand side of economy • Producers decide what to SELL (MAKE) – Supply side of economy
2 Sides of a Market Economy • Consumers decide what to BUY! – Demand side of economy • Producers decide what to SELL (MAKE) – Supply side of economy
 4 Factors of Production • Resources used to make goods & services 1) Land 2) Labor 3) Physical Capital 4) Human Capital To open a coffee shop: all basic natural resources human work/labor previously produced goods education, skills, etc… Labor = worker Physical Capital = Coffee Machine Land = Beans & Rent store Human Capital = Skills of workers & owner of store
4 Factors of Production • Resources used to make goods & services 1) Land 2) Labor 3) Physical Capital 4) Human Capital To open a coffee shop: all basic natural resources human work/labor previously produced goods education, skills, etc… Labor = worker Physical Capital = Coffee Machine Land = Beans & Rent store Human Capital = Skills of workers & owner of store
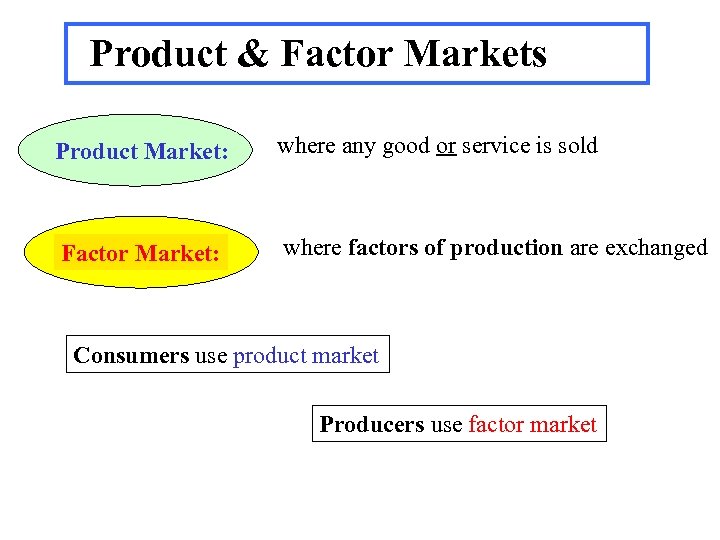 Product & Factor Markets Product Market: where any good or service is sold Factor Market: where factors of production are exchanged Consumers use product market Producers use factor market
Product & Factor Markets Product Market: where any good or service is sold Factor Market: where factors of production are exchanged Consumers use product market Producers use factor market
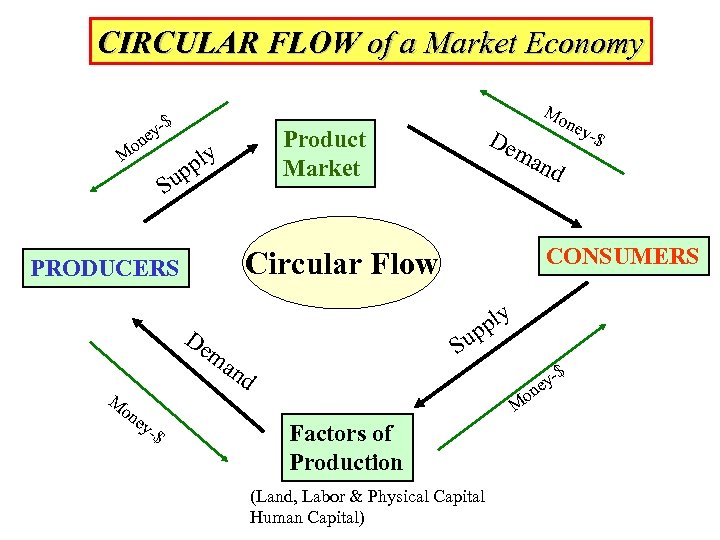 CIRCULAR FLOW of a Market Economy -$ ey on M up S De m an on ma -$ -$ nd CONSUMERS ply up S d $ ey on M ey ney Circular Flow PRODUCERS M De Product Market ply Mo Factors of Production (Land, Labor & Physical Capital Human Capital)
CIRCULAR FLOW of a Market Economy -$ ey on M up S De m an on ma -$ -$ nd CONSUMERS ply up S d $ ey on M ey ney Circular Flow PRODUCERS M De Product Market ply Mo Factors of Production (Land, Labor & Physical Capital Human Capital)
 Circular Flow Worksheet
Circular Flow Worksheet
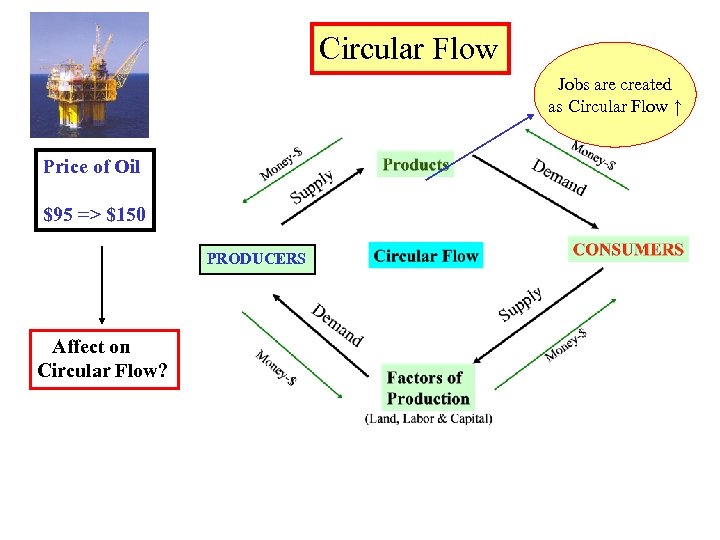 Circular Flow Jobs are created as Circular Flow ↑ Price of Oil $95 => $150 PRODUCERS Affect on Circular Flow?
Circular Flow Jobs are created as Circular Flow ↑ Price of Oil $95 => $150 PRODUCERS Affect on Circular Flow?
 Gross Domestic Product Measuring Economic Growth
Gross Domestic Product Measuring Economic Growth
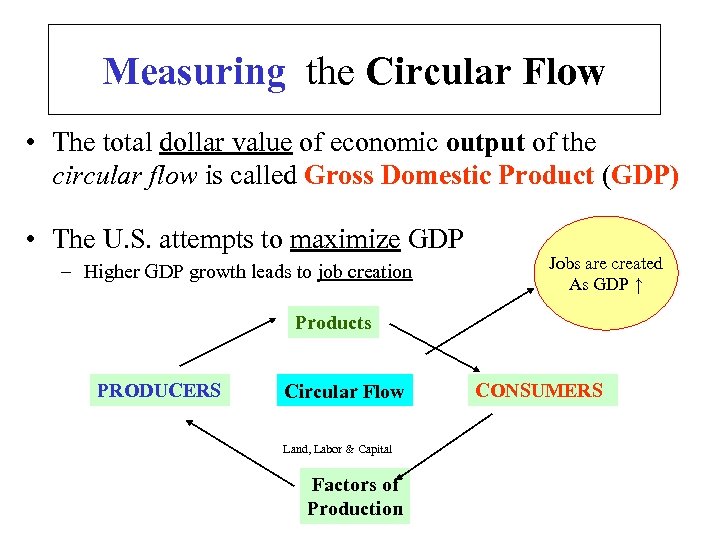 Measuring the Circular Flow • The total dollar value of economic output of the circular flow is called Gross Domestic Product (GDP) • The U. S. attempts to maximize GDP – Higher GDP growth leads to job creation Jobs are created As GDP ↑ Products PRODUCERS Circular Flow Land, Labor & Capital Factors of Production CONSUMERS
Measuring the Circular Flow • The total dollar value of economic output of the circular flow is called Gross Domestic Product (GDP) • The U. S. attempts to maximize GDP – Higher GDP growth leads to job creation Jobs are created As GDP ↑ Products PRODUCERS Circular Flow Land, Labor & Capital Factors of Production CONSUMERS
 GDP growth: what is too high? • The economy has an upper and lower “speed limit” of growth • Too fast: If GDP grows above 5. 0% per year, the economy may experience inflation – Prices rise • Too slow: If GDP grows below 2%, not enough jobs are created – Unemployment rate increases
GDP growth: what is too high? • The economy has an upper and lower “speed limit” of growth • Too fast: If GDP grows above 5. 0% per year, the economy may experience inflation – Prices rise • Too slow: If GDP grows below 2%, not enough jobs are created – Unemployment rate increases
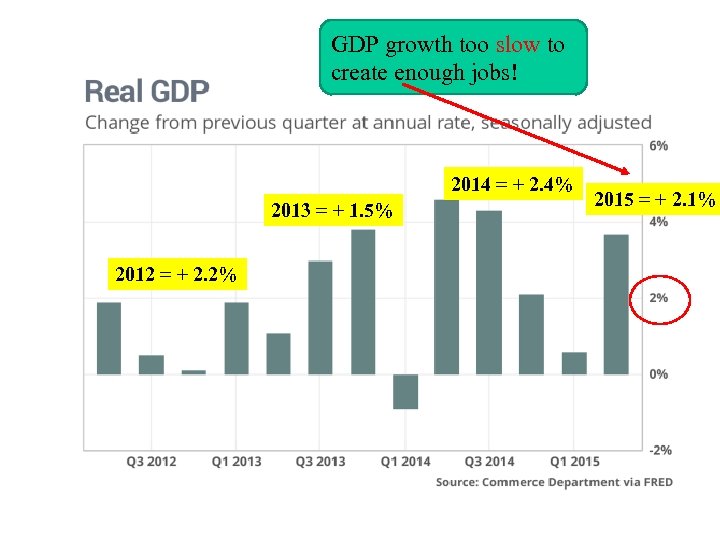 GDP growth too slow to create enough jobs! 2014 = + 2. 4% 2013 = + 1. 5% 2012 = + 2. 2% 2015 = + 2. 1%
GDP growth too slow to create enough jobs! 2014 = + 2. 4% 2013 = + 1. 5% 2012 = + 2. 2% 2015 = + 2. 1%
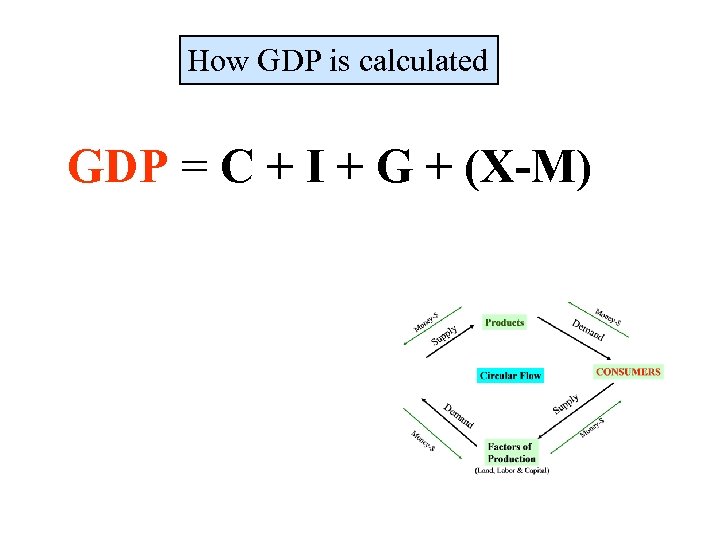 How GDP is calculated GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
How GDP is calculated GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
 What goods count in GDP? • Dollar Value of all FINAL new goods & services produced in USA over one year – Imports do not count – Used goods do not count • Must avoid “double counting” in GDP Example: Steel used in automobiles Count value of the entire car (final good)—not the parts
What goods count in GDP? • Dollar Value of all FINAL new goods & services produced in USA over one year – Imports do not count – Used goods do not count • Must avoid “double counting” in GDP Example: Steel used in automobiles Count value of the entire car (final good)—not the parts
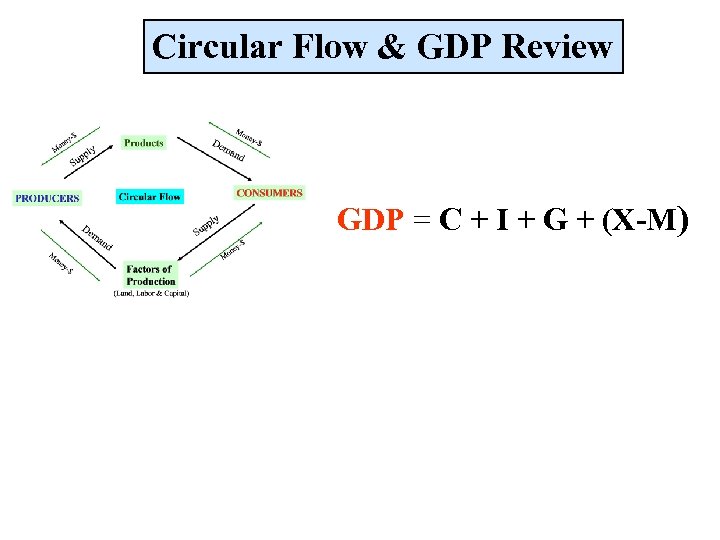 Circular Flow & GDP Review GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
Circular Flow & GDP Review GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
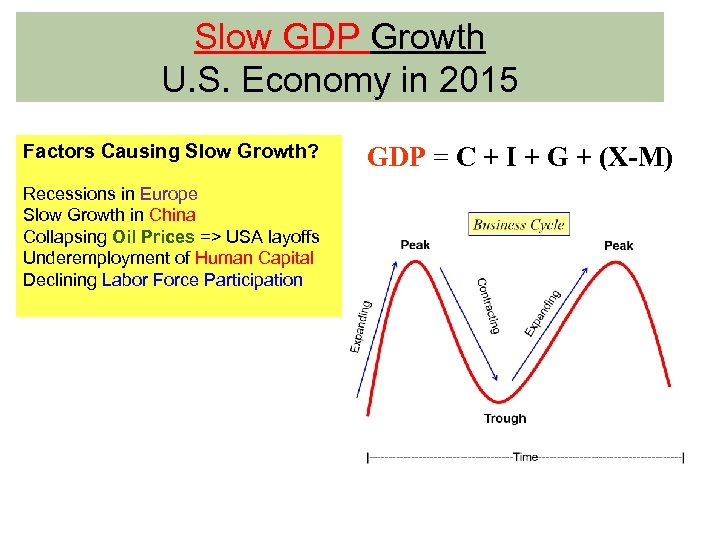 Slow GDP Growth U. S. Economy in 2015 Factors Causing Slow Growth? Recessions in Europe Slow Growth in China Collapsing Oil Prices => USA layoffs Underemployment of Human Capital Declining Labor Force Participation GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
Slow GDP Growth U. S. Economy in 2015 Factors Causing Slow Growth? Recessions in Europe Slow Growth in China Collapsing Oil Prices => USA layoffs Underemployment of Human Capital Declining Labor Force Participation GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
 GDP Worksheet • Circular Flow
GDP Worksheet • Circular Flow
 GDP does NOT Measure: • Leisure time – Vacation Days: Europe get many more than U. S. workers • Hours Worked: – Work 80 hours vs. 40 hrs per week => GDP goes up • What you produce – Guns vs. butter: all products count the same!
GDP does NOT Measure: • Leisure time – Vacation Days: Europe get many more than U. S. workers • Hours Worked: – Work 80 hours vs. 40 hrs per week => GDP goes up • What you produce – Guns vs. butter: all products count the same!
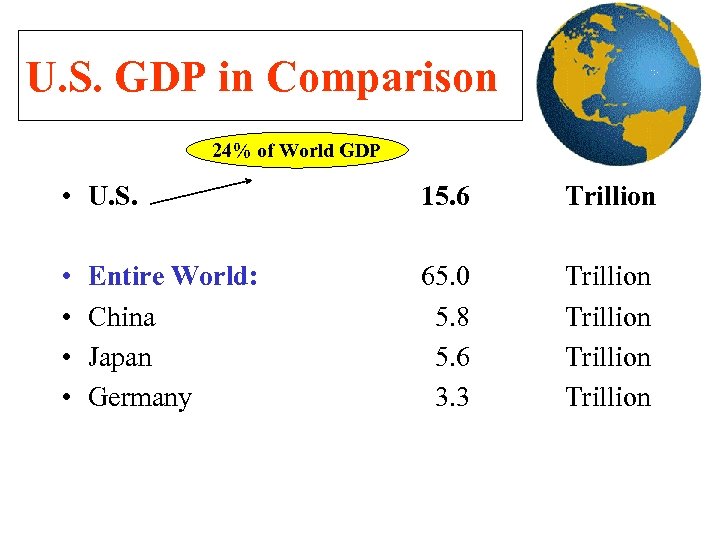 U. S. GDP in Comparison 24% of World GDP • U. S. 15. 6 Trillion • • 65. 0 5. 8 5. 6 3. 3 Trillion Entire World: China Japan Germany
U. S. GDP in Comparison 24% of World GDP • U. S. 15. 6 Trillion • • 65. 0 5. 8 5. 6 3. 3 Trillion Entire World: China Japan Germany


