b825d64ff5c42dc84aea61bf42de015d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Economics Chapter 4 Demand
Economics Chapter 4 Demand
 Demand is the desire, ability and willingness of a consumer to buy a product. A WANT n Microeconomics is the study of the behavior of one consumer or one business n Macroeconomics is the study of the economy of the whole country. n
Demand is the desire, ability and willingness of a consumer to buy a product. A WANT n Microeconomics is the study of the behavior of one consumer or one business n Macroeconomics is the study of the economy of the whole country. n
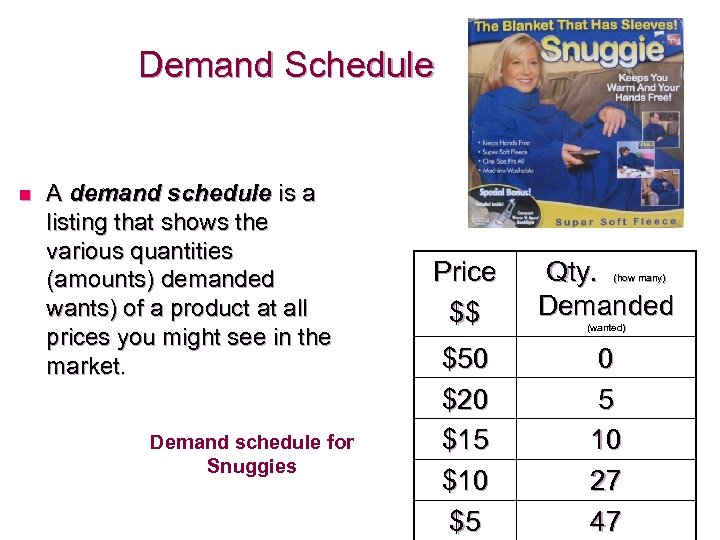 Demand Schedule n A demand schedule is a listing that shows the various quantities (amounts) demanded wants) of a product at all prices you might see in the market. Demand schedule for Snuggies Price $$ Qty. Demanded $50 $20 $15 $10 $5 0 5 10 27 47 (how many) (wanted)
Demand Schedule n A demand schedule is a listing that shows the various quantities (amounts) demanded wants) of a product at all prices you might see in the market. Demand schedule for Snuggies Price $$ Qty. Demanded $50 $20 $15 $10 $5 0 5 10 27 47 (how many) (wanted)
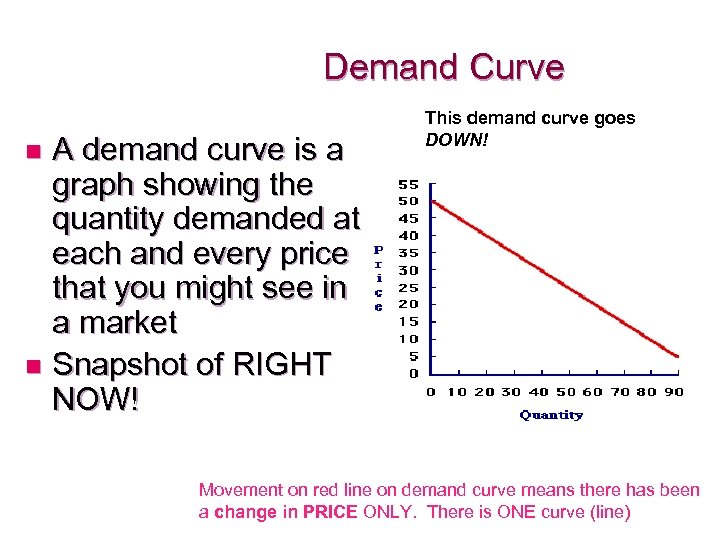 Demand Curve A demand curve is a graph showing the quantity demanded at each and every price that you might see in a market n Snapshot of RIGHT NOW! n This demand curve goes DOWN! Movement on red line on demand curve means there has been a change in PRICE ONLY. There is ONE curve (line)
Demand Curve A demand curve is a graph showing the quantity demanded at each and every price that you might see in a market n Snapshot of RIGHT NOW! n This demand curve goes DOWN! Movement on red line on demand curve means there has been a change in PRICE ONLY. There is ONE curve (line)
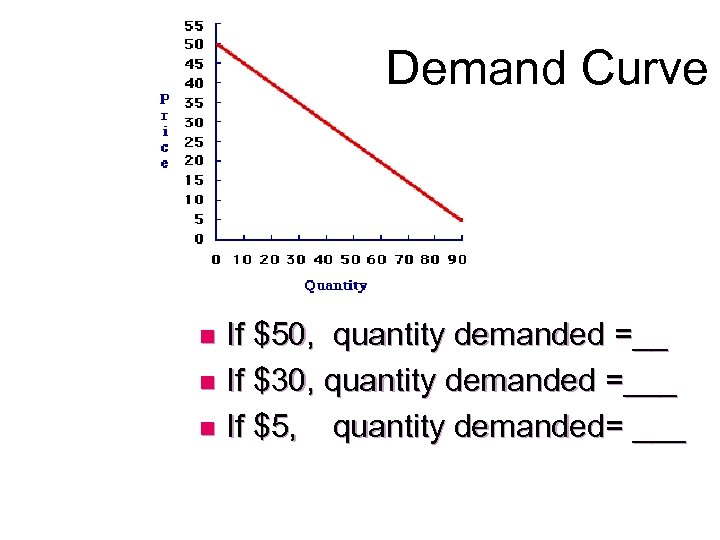 Demand Curve If $50, quantity demanded =__ n If $30, quantity demanded =___ n If $5, quantity demanded= ___ n
Demand Curve If $50, quantity demanded =__ n If $30, quantity demanded =___ n If $5, quantity demanded= ___ n
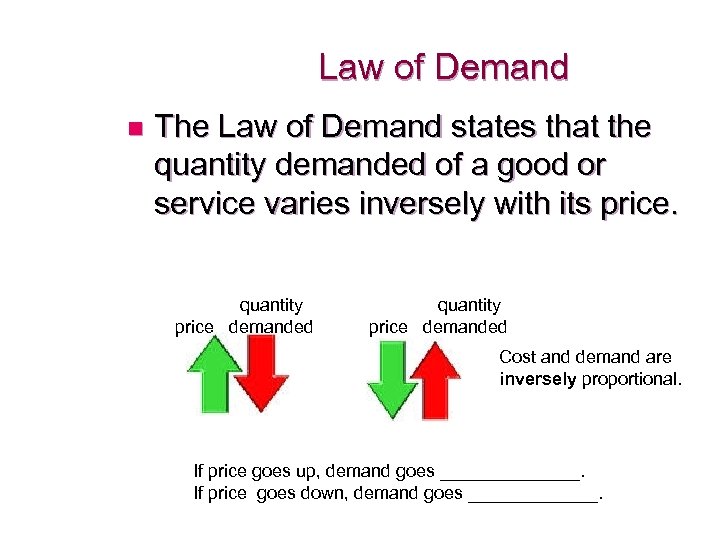 Law of Demand n The Law of Demand states that the quantity demanded of a good or service varies inversely with its price. quantity price demanded Cost and demand are inversely proportional. If price goes up, demand goes _______. If price goes down, demand goes _______.
Law of Demand n The Law of Demand states that the quantity demanded of a good or service varies inversely with its price. quantity price demanded Cost and demand are inversely proportional. If price goes up, demand goes _______. If price goes down, demand goes _______.
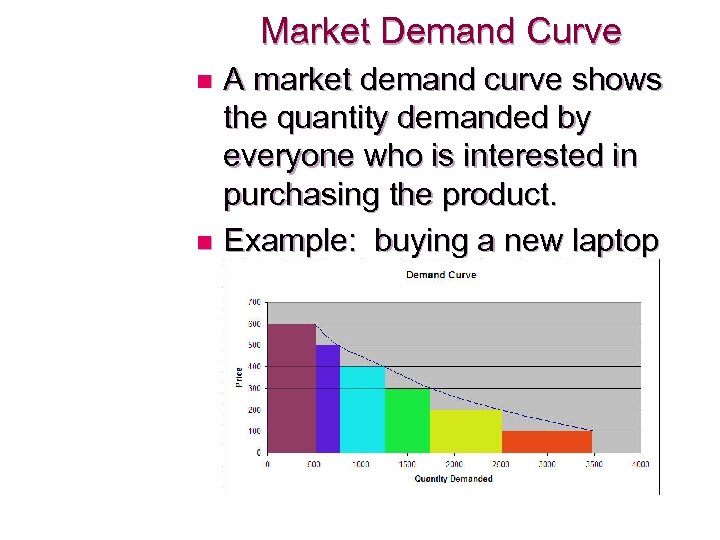 Market Demand Curve A market demand curve shows the quantity demanded by everyone who is interested in purchasing the product. n Example: buying a new laptop n
Market Demand Curve A market demand curve shows the quantity demanded by everyone who is interested in purchasing the product. n Example: buying a new laptop n
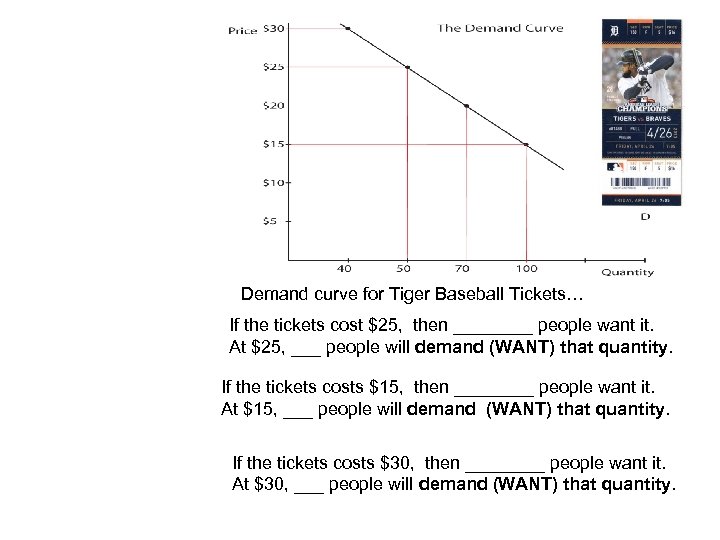 Demand curve for Tiger Baseball Tickets… If the tickets cost $25, then ____ people want it. At $25, ___ people will demand (WANT) that quantity. If the tickets costs $15, then ____ people want it. At $15, ___ people will demand (WANT) that quantity. If the tickets costs $30, then ____ people want it. At $30, ___ people will demand (WANT) that quantity.
Demand curve for Tiger Baseball Tickets… If the tickets cost $25, then ____ people want it. At $25, ___ people will demand (WANT) that quantity. If the tickets costs $15, then ____ people want it. At $15, ___ people will demand (WANT) that quantity. If the tickets costs $30, then ____ people want it. At $30, ___ people will demand (WANT) that quantity.
 Marginal Utility Marginal utility is the extra enjoyment that a person gets from getting one more! YES! One more sucker!!! n Extra lollipops bring Erick extra utility!
Marginal Utility Marginal utility is the extra enjoyment that a person gets from getting one more! YES! One more sucker!!! n Extra lollipops bring Erick extra utility!
 Diminishing Marginal Utility The principle of diminishing marginal utility means that the enjoyment we get from more decreases. n NOT ANOTHER HOT DOG!!! n Think of eating contests or block days at KHS!
Diminishing Marginal Utility The principle of diminishing marginal utility means that the enjoyment we get from more decreases. n NOT ANOTHER HOT DOG!!! n Think of eating contests or block days at KHS!
 Section 2 Factors Affecting Demand When there is a change in a people’s willingness and ability to buy, it is because of 2 reasons: 1. Change in QUANTITY DEMANDED OR 2. CHANGE IN DEMAND n
Section 2 Factors Affecting Demand When there is a change in a people’s willingness and ability to buy, it is because of 2 reasons: 1. Change in QUANTITY DEMANDED OR 2. CHANGE IN DEMAND n
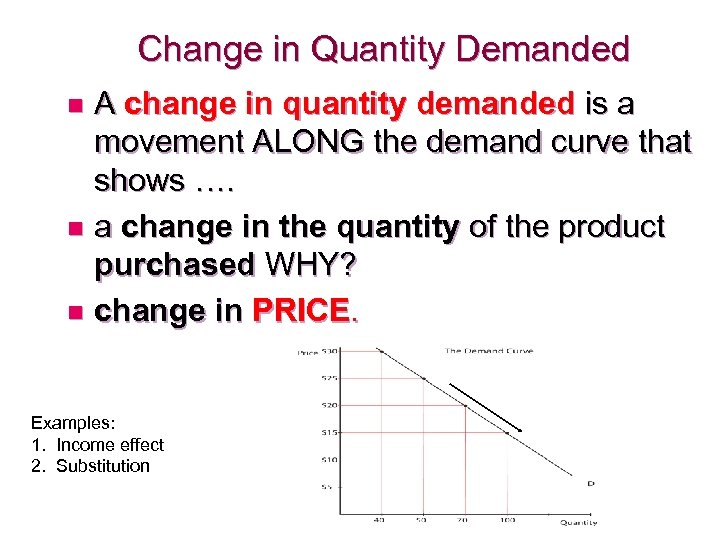 Change in Quantity Demanded A change in quantity demanded is a movement ALONG the demand curve that shows …. n a change in the quantity of the product purchased WHY? n change in PRICE. n Examples: 1. Income effect 2. Substitution
Change in Quantity Demanded A change in quantity demanded is a movement ALONG the demand curve that shows …. n a change in the quantity of the product purchased WHY? n change in PRICE. n Examples: 1. Income effect 2. Substitution
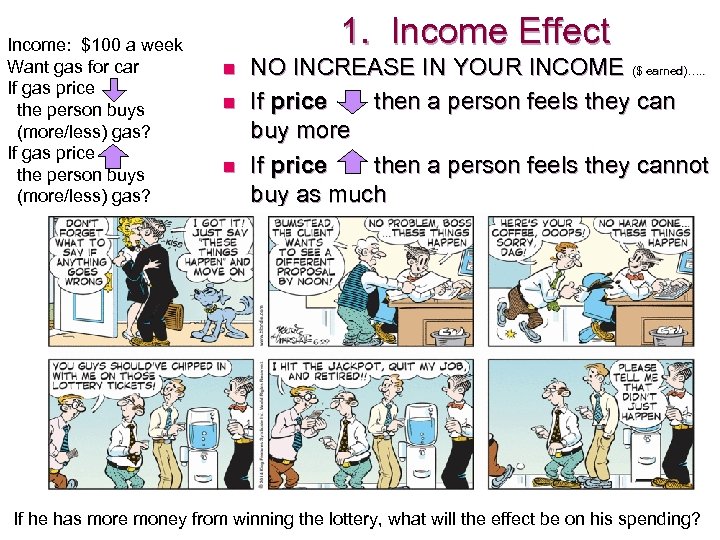 Income: $100 a week Want gas for car If gas price the person buys (more/less) gas? 1. Income Effect n n n NO INCREASE IN YOUR INCOME ($ earned)…. . If price then a person feels they can buy more If price then a person feels they cannot buy as much If he has more money from winning the lottery, what will the effect be on his spending?
Income: $100 a week Want gas for car If gas price the person buys (more/less) gas? 1. Income Effect n n n NO INCREASE IN YOUR INCOME ($ earned)…. . If price then a person feels they can buy more If price then a person feels they cannot buy as much If he has more money from winning the lottery, what will the effect be on his spending?
 2. Substitution Effect n n n CD The substitution effect is the change in quantity demanded because of a change in the price of an item. Example – Substituting a concert ticket for a CD Will a person buy more CDs or concert tickets? $12. 99 Concert Ticket $34. 75 Mississippi mud pie $3 Severn sludge souffle $5
2. Substitution Effect n n n CD The substitution effect is the change in quantity demanded because of a change in the price of an item. Example – Substituting a concert ticket for a CD Will a person buy more CDs or concert tickets? $12. 99 Concert Ticket $34. 75 Mississippi mud pie $3 Severn sludge souffle $5
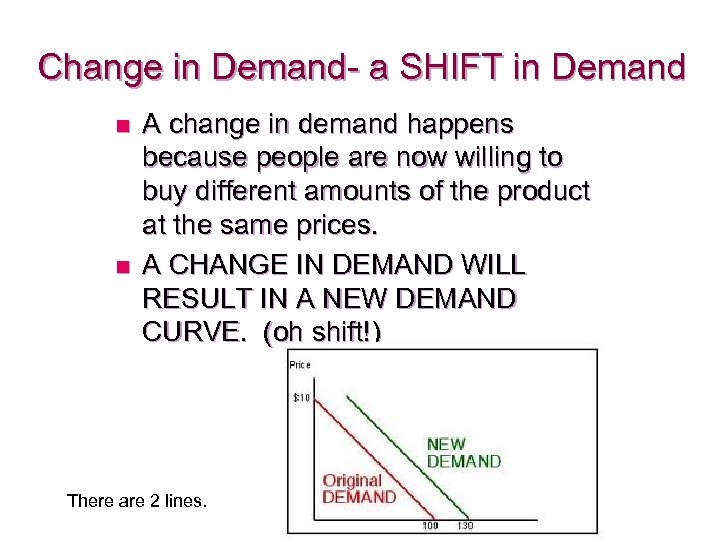 Change in Demand- a SHIFT in Demand n n A change in demand happens because people are now willing to buy different amounts of the product at the same prices. A CHANGE IN DEMAND WILL RESULT IN A NEW DEMAND CURVE. (oh shift!) There are 2 lines.
Change in Demand- a SHIFT in Demand n n A change in demand happens because people are now willing to buy different amounts of the product at the same prices. A CHANGE IN DEMAND WILL RESULT IN A NEW DEMAND CURVE. (oh shift!) There are 2 lines.
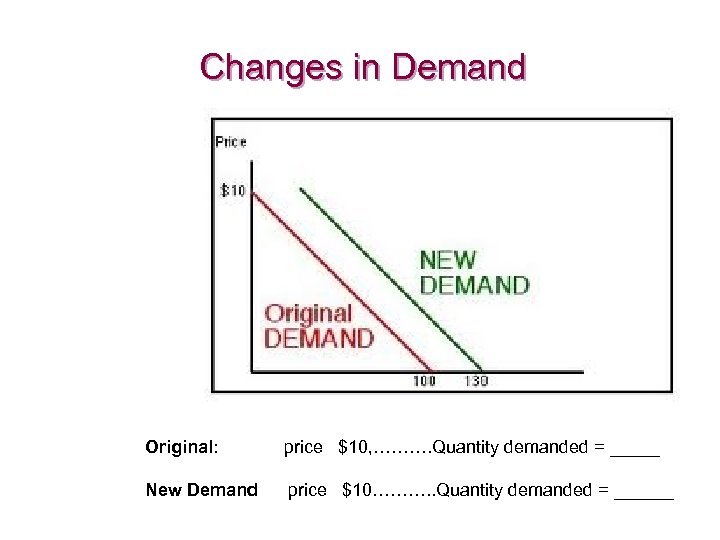 Changes in Demand Original: price $10, ………. Quantity demanded = _____ New Demand price $10………. . Quantity demanded = ______
Changes in Demand Original: price $10, ………. Quantity demanded = _____ New Demand price $10………. . Quantity demanded = ______
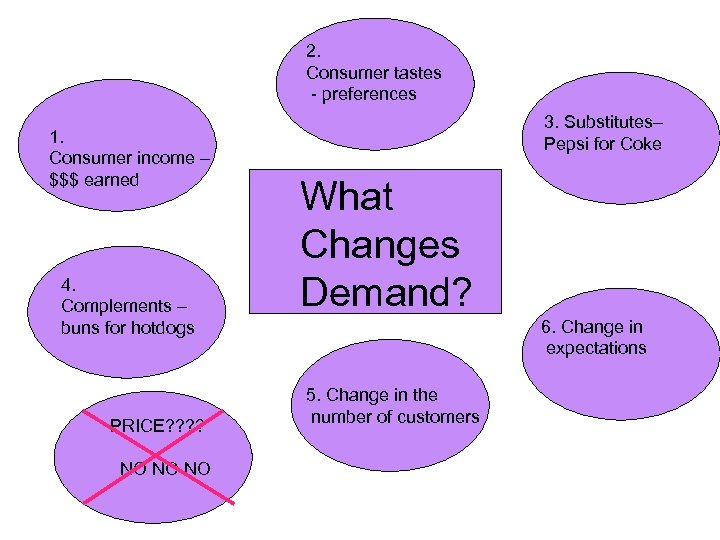 2. Consumer tastes - preferences 1. Consumer income – $$$ earned 4. Complements – buns for hotdogs PRICE? ? NO NO NO 3. Substitutes– Pepsi for Coke What Changes Demand? 6. Change in expectations 5. Change in the number of customers
2. Consumer tastes - preferences 1. Consumer income – $$$ earned 4. Complements – buns for hotdogs PRICE? ? NO NO NO 3. Substitutes– Pepsi for Coke What Changes Demand? 6. Change in expectations 5. Change in the number of customers
 Consumer Income Changes in consumer income can cause a change in demand. n Example – you get a raise or you lose your job n I can buy (more/less) I can by (more/less)
Consumer Income Changes in consumer income can cause a change in demand. n Example – you get a raise or you lose your job n I can buy (more/less) I can by (more/less)
 Consumer Tastes n n Consumers do not always want the same thing. Example – change in fashion, style, the development of new products
Consumer Tastes n n Consumers do not always want the same thing. Example – change in fashion, style, the development of new products
 More on Changing Tastes… n Changing tastes shift demand curves (and can actually be quite amusing after a few years!).
More on Changing Tastes… n Changing tastes shift demand curves (and can actually be quite amusing after a few years!).
 Substitutes $2. 75 n n $2. 00 A change in the price of related products can cause a change in demand. Substitutes can be used in place of other products.
Substitutes $2. 75 n n $2. 00 A change in the price of related products can cause a change in demand. Substitutes can be used in place of other products.
 Complements n Related goods are known as complements because the use of one increases the use of the other. With cereal, you must buy _______. n Example – peanut butter and jelly, hotdogs and hotdog buns With a hot dog, you must buy _____ and ______.
Complements n Related goods are known as complements because the use of one increases the use of the other. With cereal, you must buy _______. n Example – peanut butter and jelly, hotdogs and hotdog buns With a hot dog, you must buy _____ and ______.
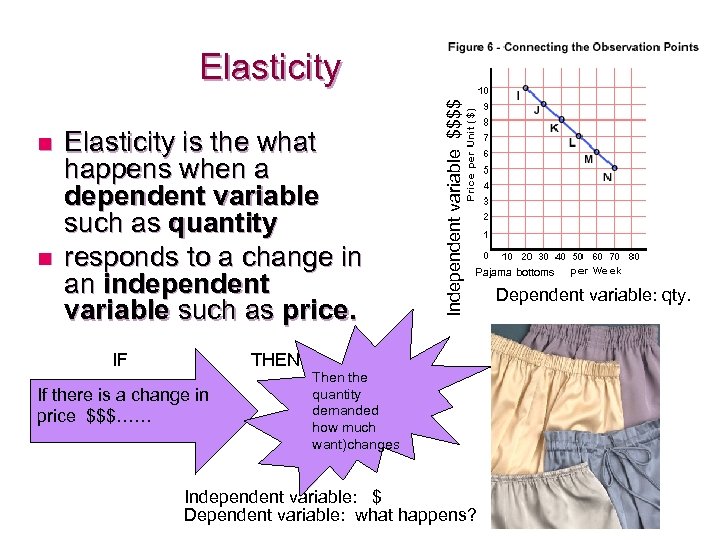 n n Elasticity is the what happens when a dependent variable such as quantity responds to a change in an independent variable such as price. IF THEN If there is a change in price $$$…… Independent variable $$$$ Elasticity Pajama bottoms Then the quantity demanded how much want)changes Independent variable: $ Dependent variable: what happens? Dependent variable: qty.
n n Elasticity is the what happens when a dependent variable such as quantity responds to a change in an independent variable such as price. IF THEN If there is a change in price $$$…… Independent variable $$$$ Elasticity Pajama bottoms Then the quantity demanded how much want)changes Independent variable: $ Dependent variable: what happens? Dependent variable: qty.
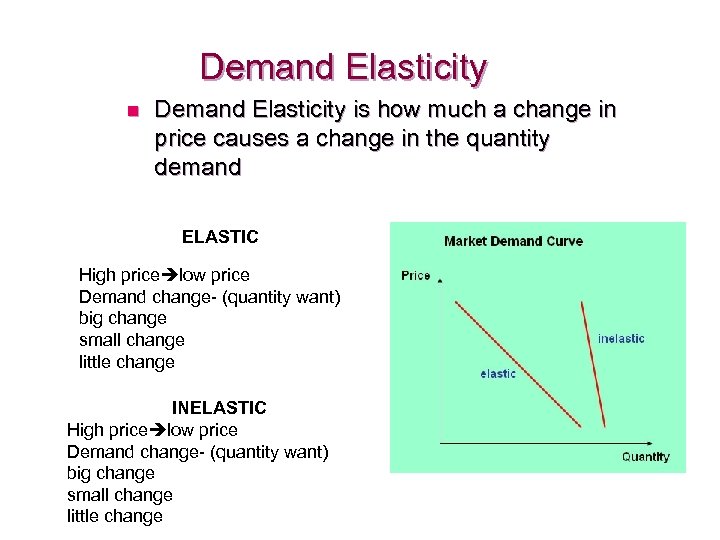 Demand Elasticity n Demand Elasticity is how much a change in price causes a change in the quantity demand ELASTIC High price low price Demand change- (quantity want) big change small change little change INELASTIC High price low price Demand change- (quantity want) big change small change little change
Demand Elasticity n Demand Elasticity is how much a change in price causes a change in the quantity demand ELASTIC High price low price Demand change- (quantity want) big change small change little change INELASTIC High price low price Demand change- (quantity want) big change small change little change
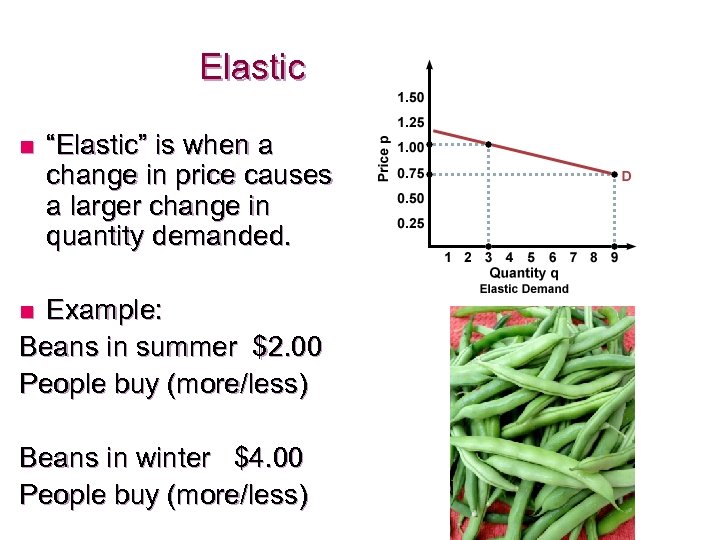 Elastic n “Elastic” is when a change in price causes a larger change in quantity demanded. Example: Beans in summer $2. 00 People buy (more/less) n Beans in winter $4. 00 People buy (more/less)
Elastic n “Elastic” is when a change in price causes a larger change in quantity demanded. Example: Beans in summer $2. 00 People buy (more/less) n Beans in winter $4. 00 People buy (more/less)
 Inelastic Demand n Inelastic means that a change in price causes a smaller change in the quantity demanded. People need medicine. Will continue buy if price is low. Will continue to buy if price is high.
Inelastic Demand n Inelastic means that a change in price causes a smaller change in the quantity demanded. People need medicine. Will continue buy if price is low. Will continue to buy if price is high.
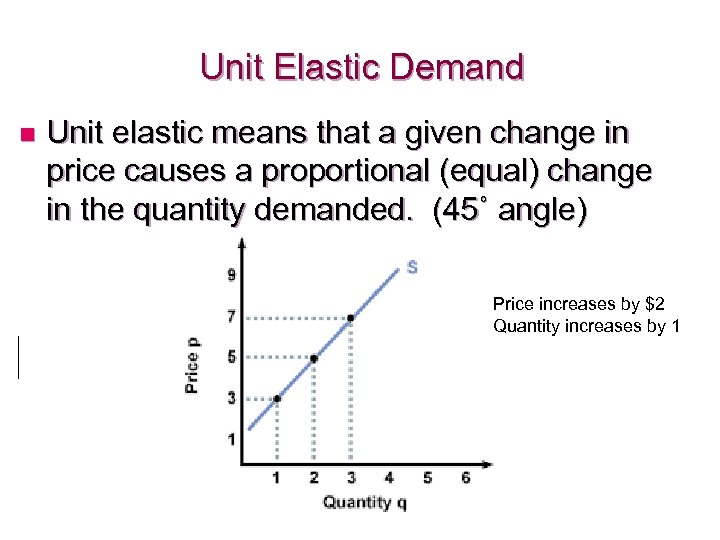 Unit Elastic Demand n Unit elastic means that a given change in price causes a proportional (equal) change in the quantity demanded. (45˚ angle) Price increases by $2 Quantity increases by 1
Unit Elastic Demand n Unit elastic means that a given change in price causes a proportional (equal) change in the quantity demanded. (45˚ angle) Price increases by $2 Quantity increases by 1
 What determines demand elasticity? n Can the purchase be delayed? (can I buy it later? ) n Are adequate substitutes available? (Snickers candy instead of Milky Way? ) n Does the purchase use a large portion of income? ( I have been saving for a new phone for a long time. Do I want to use all of my savings for the phone and have nothing left? )
What determines demand elasticity? n Can the purchase be delayed? (can I buy it later? ) n Are adequate substitutes available? (Snickers candy instead of Milky Way? ) n Does the purchase use a large portion of income? ( I have been saving for a new phone for a long time. Do I want to use all of my savings for the phone and have nothing left? )


