5ecd430bf3d7e00b2753e874ec52d914.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 77

Economics Bell Ringer Tuesday, 9/4/2012 Please answer these questions in the box for Tuesday’s Bell Ringer. Update your table of contents for today’s handouts: Why did you sign up for this class? What do you think you know about Economics? What do you think you will learn in this class? Today’s Handouts: #0 – Table of Contents #1 – 9/4 – Bell Ringer (9/4 -9/7)

I Know What You Did Last Summer! • • Split a sheet of looseleaf paper with a neighbor and number 1 -10 You must find a different person and write their name next to the answer for each question 1. I worked a job doing ____________ 2. I went downtown to the ___________ 3. I went on a road trip to _____________ 4. I went to sports/band/activity camp for ___________ 5. I volunteered/service learning at ____________ 6. I got on a plane and went to ______________ 7. I met some new people from _______________ 8. I saved money for _________because __________ 9. I bought a new __________ because __________ 10. My top priority this year is __________________

Economics Bell Ringer Wednesday, 9/5/2012 Opening Unit Essential Question: Is Competition Good/Bad for Public Schools? Use complete sentences to write an answer to these questions. Explain your reasoning: a) Is competition always good? Always bad? b) When making a decision (purchase, college, etc. ), how does competition impact your decision? Today’s Handouts: #2 – 9/5 - Syllabus #3 – 9/5 – KWL Chart

Economics Bell Ringer Thursday, 9/6/2012 Opening Unit Essential Question: Is Competition Good/Bad for Public Schools? Use complete sentences to write an answer to the questions. Explain your reasoning: Think about something that you spent money on. a) What were the benefits and the costs of this purchase decision? b) How do these benefits/costs affect your decision? Today’s Handouts: #4 – 9/6 – NPR Audio Transcript #5 – 9/6 – NPR Audio Notes

Economics Bell Ringer Friday, 9/7/2012 Opening Unit Essential Question: Is Competition Good/Bad for Public Schools? Use complete sentences to write an answer to the questions. Explain your reasoning. Then complete the self- reflection. a) What are two things you learned about: competition in schools, school choice, or vouchers? b) What is one question you still have about competition in schools? Today’s Handouts: #6 – 9/7 – School Voucher Questions

Economics Bell Ringer Wednesday, September 19, 2012 What is Economics? Ch 1. 1: How can we make the best economic choices? BELL RINGER: a) What are some examples of needs and wants b) What is the difference between the two? c) Why do we have needs and wants? d) Why can’t we get everything we need or want? Today’s Handouts: #7 – 9/19 – Bell Ringer (9/19 -9/21) #8 – 9/19 – Notes Ch 1. 1 (on loose leaf)

Economics Wednesday, September 19, 2012 Ch 1. 1 How can we make the best economic choices? Get out looseleaf, Handout #8, Title: “Notes Ch 1. 1 – Scarcity” NEEDS WANTS - Draw this spectrum on your notes. Place our list of needs/wants on the spectrum. Be ready to explain your reasoning.

Economics Wednesday, September 19, 2012 Ch 1. 1 How can we make the best economic choices? Get out looseleaf, Handout #8, Title: “Notes Ch 1. 1 – Scarcity” DISCUSSION NOTES: -Why do we have Needs/Wants? -What’s the difference between Needs/Wants? -Can something be a Need and a Want? Will these ever change? -Are Needs/Wants unlimited? -Why can’t we satisfy all Needs/Wants?

Economics Wednesday, September 19, 2012 Ch 1. 1 How can we make the best economic choices? WORD SPLASH Based on your prior knowledge and this discussion, write a brief paragraph connecting the following key terms: • Scarcity • Needs/Wants • Goods/Services • Factors of Production • Resources • Limited • Happiness/Satisfaction • Utility When done, check out your book for the year (always bring to class) Setup Cornell Notes outline and take notes on Section 1. 1 until the bell (Due Thursday)

Economics Bell Ringer Thursday, September 20, 2012 What is Economics? Ch 1. 1: How can we make the best economic choices? BELL RINGER: a) Why can’t you satisfy unlimited needs and wants?

Economics Thursday, September 20, 2012 Ch 1. 1 How can we make the best economic choices? WORD SPLASH Based on your prior knowledge, yesterday’s discussion and the reading, write a paragraph connecting the following key terms: • Scarcity • Needs/Wants • Goods/Services • Factors of Production • Resources • Limited • Happiness/Satisfaction • Utility

Economics Bell Ringer Thursday, September 20, 2012 What is Economics? Ch 1. 1: How can we make the best economic choices? Ch 1. 1 SECTION QUESTIONS: P. 7 #2 -7 a) You may write your answers on Handout #8 (your looseleaf notes) b)Answer in complete sentences c)Ch 1. 1 Cornell Notes and Section ? s Due END OF CLASS

Economics Bell Ringer Friday, September 21, 2012 What is Economics? Ch 1. 1: How can we make the best economic choices? BELL RINGER: a) Explain how scarcity affects the factors of production Today’s Handouts: #9 – 9/21 – PPT Notes Ch 1. 1 #10 – 9/21 – Business Idea Brainstorm

Economics Bell Ringer Monday, September 24, 2012 What is Economics? Ch 1. 2: How does opportunity cost affect our choices? BELL RINGER: a) Write down 10 decisions you made recently involving limited resources (time, money, factors of production) Today’s Handouts: #11 – 9/24 – Bell Ringer (9/24 -9/28) #12 – 9/24 – Ch 1. 2 Notes and ? s (looseleaf paper)
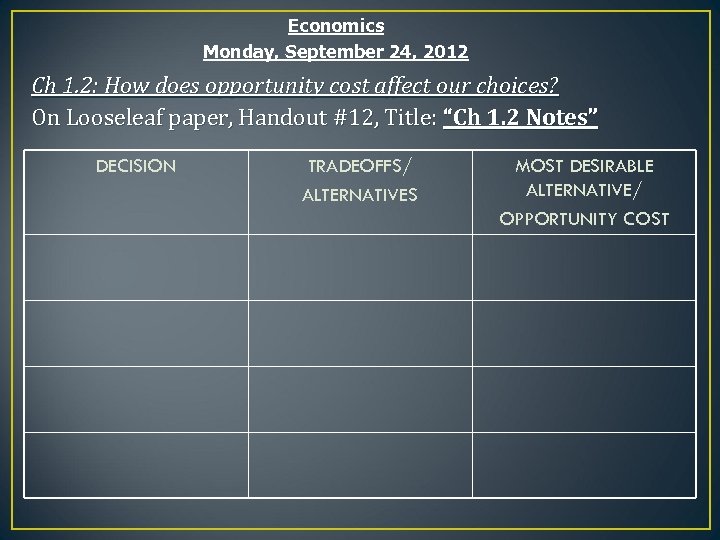
Economics Monday, September 24, 2012 Ch 1. 2: How does opportunity cost affect our choices? On Looseleaf paper, Handout #12, Title: “Ch 1. 2 Notes” DECISION TRADEOFFS/ ALTERNATIVES MOST DESIRABLE ALTERNATIVE/ OPPORTUNITY COST

Economics Monday, September 24, 2012 Ch 1. 2: How does opportunity cost affect our choices? On Looseleaf paper, Handout #12, Title: “Ch 1. 2 Notes” DUE END OF CLASS 1. Read Ch 1. 2 (p 8 -12) and complete your Concept Web (p 8) or Cornell Notes. You should add ovals. 2. Section ? s P. 12 1 -8 3. Notes on Key Terms Ch 1. 2

Economics Bell Ringer Tuesday, September 25, 2012 What is Economics? Ch 1. 2: How does opportunity cost affect our choices? BELL RINGER: a) Think of a decision you recently made (or we discussed yesterday). Explain how needs, wants, scarcity and tradeoffs are related to this decision. Today’s Handouts: #13 – 9/25 – PPT Notes Ch 1. 2 #14 – 9/25 – Ch 1. 2 Reading Review

Economics Bell Ringer Wednesday, September 26, 2012 BELL RINGER: a) CLEAR DESKS FOR ECONOMICS ASSESSMENT b)When done with assessment, quietly organize binders, finish work due today

Economics Bell Ringer Thursday, September 27, 2012 BELL RINGER: a) Which decision would you make? Remember thinking at the margin as you explain your reason. Decision Benefit Opportunity Cost Spend $0 on food, $5 on Get 3 Gatorades, not drinks thirsty Very hungry Spend $2. 50 on food, $2. 50 on drinks Get 1 Gatorade, chips and fruit, not thirsty Still pretty hungry Spend $3. 50 on food, $1. 50 on drink Get 1 Gatorade, chips, Still a bit thirsty small sandwich, pretty full Spend $5 on food, $0 on Get $5 sandwich, very drink full You are very thirsty Today’s Handouts: #15 – 9/27 – Decision Making Wksht

Economics Thursday, October 4, 2012 KITCHEN CHALLENGE: a) You will weigh alternatives to determine most efficient use of scarce resources b) Groups decide how to use their physical and human capital and how the labor will be accomplished given the size of their group and the time limits c) You must design a menu with the limited number of people in your group and time allowed d) Work through Day 1 Questions (finish for HW); we finish Day 2 tomorrow

Economics Thursday, September 27, 2012 1. Identify the Key Term a) The principle that limited amounts of goods and services are available to meet unlimited needs and wants Scarcity b) The resources that are used to make goods and services (and what are the different types? ) c) The study of how people seek to satisfy their needs and wants by making choices Economics d) e) f) g) Factors of production: Land, Labor, Physical Capital, Human Capital 1. Economics The process of deciding how much more or less to do 2. Tradeoffs for the extra/next unit of production 3. Utility Thinking at the margin The most desirable alternative given up as a result of 4. Opportunity Cost a decision 5. Marginal Benefit the alternatives that we give up when we choose one 6. Scarcity course of action over another 7. Marginal Cost Tradeoffs the total satisfaction gained from getting needs and 8. Factors of Production 9. Needs/Wants Utility wants

Economics Bell Ringer Friday, September 28, 2012 What is Economics? Ch 1. 2: How does opportunity cost affect our choices? BELL RINGER: a) Complete the self-reflection, update Table of Contents and turn-in Bell Ringers b) Clear your desk of everything for Quiz #1 Today’s Handouts: #17 – 9/28 – Quiz #1 #18 – 9/28 – Opportunity Cost: GMO

Economics Bell Ringer Monday, October 1, 2012 What is Economics? Ch 1. 3: How does a business decide what and how much to produce? BELL RINGER: a) Imagine you and two friends are planning the Homecoming dance. Plan who will do what to prepare for the dance. b)Get out your book. Label a looseleaf #19 and title “Notes Ch 1. 3” Today’s Handouts: #18 – 10/1 – Bell Ringer (10/1 -10/5) #19 – 10/1 – Ch 1. 3 Notes and ? s

Economics Monday, October 1, 2012 Ch 1. 3: How does a business decide what and how much to produce? Label Looseleaf paper #19 and title, “Ch 1. 3 Notes”. Use for all of today and tonight’s work. CASE STUDY: CAR INDUSTRY OUTSOURCING TO ASIA Read case study on P 16 and answer these questions: • Why are the auto-makers moving high-skilled jobs into low-cost countries? • How might production and quality control be compromised if Nissan designs cars in Vietnam?

Economics Monday, October 1, 2012 Ch 1. 3: How does a business decide what and how much to produce? Label Looseleaf paper #18 and title, “Ch 1. 3 Notes”. Use for all of today and tonight’s work. BOOK WORK (DUE THURSDAY BEG. OF CLASS) Read Ch 1. 3 (p 13 -18) • • Review Key Terms (Notes and Flash Cards) Answer CHECKPOINT Questions P. 14 Graph Skills #1, 2 P. 18 #2 -10

Economics Bell Ringer Tuesday, October 2, 2012 What is Economics? Ch 1. 3: How does a business decide what and how much to produce? BELL RINGER: 1. Think about yesterday’s case study about Nissan moving production to Viet Nam a) What were the scarce factors of production? b) What was the marginal benefit of moving production? c) What was the opportunity cost of moving production? d) Use cost/benefit analysis to explain how Nissan made their decision Today’s Handouts: #20 – 10/2 – PPT Notes Ch 1. 3
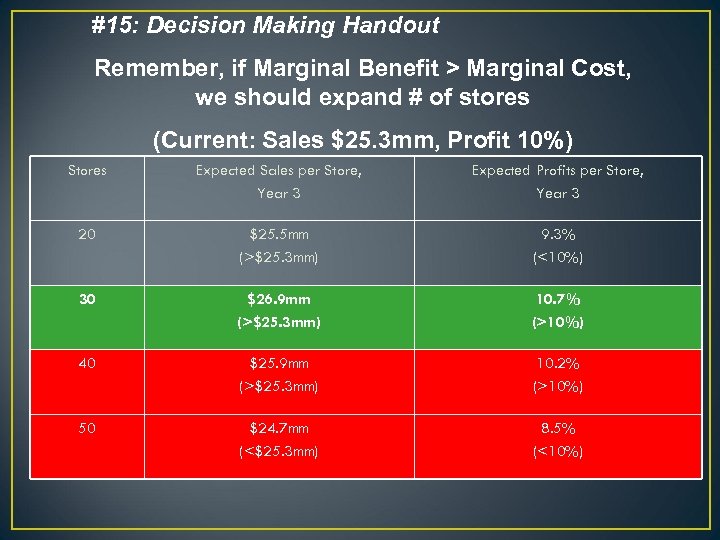
#15: Decision Making Handout Remember, if Marginal Benefit > Marginal Cost, we should expand # of stores (Current: Sales $25. 3 mm, Profit 10%) Stores Expected Sales per Store, Year 3 Expected Profits per Store, Year 3 20 $25. 5 mm (>$25. 3 mm) 9. 3% (<10%) 30 $26. 9 mm (>$25. 3 mm) 10. 7% (>10%) 40 $25. 9 mm (>$25. 3 mm) 10. 2% (>10%) 50 $24. 7 mm (<$25. 3 mm) 8. 5% (<10%)
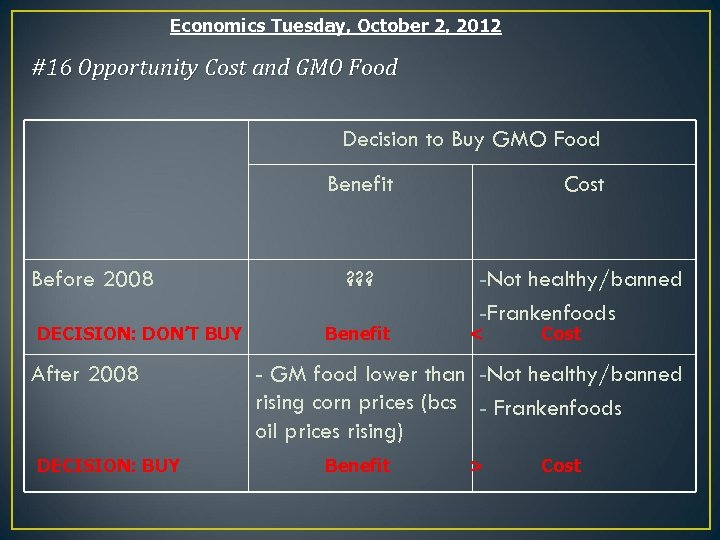
Economics Tuesday, October 2, 2012 #16 Opportunity Cost and GMO Food Decision to Buy GMO Food Benefit Before 2008 DECISION: DON’T BUY After 2008 DECISION: BUY Cost ? ? ? -Not healthy/banned -Frankenfoods Benefit < Cost - GM food lower than -Not healthy/banned rising corn prices (bcs - Frankenfoods oil prices rising) Benefit > Cost
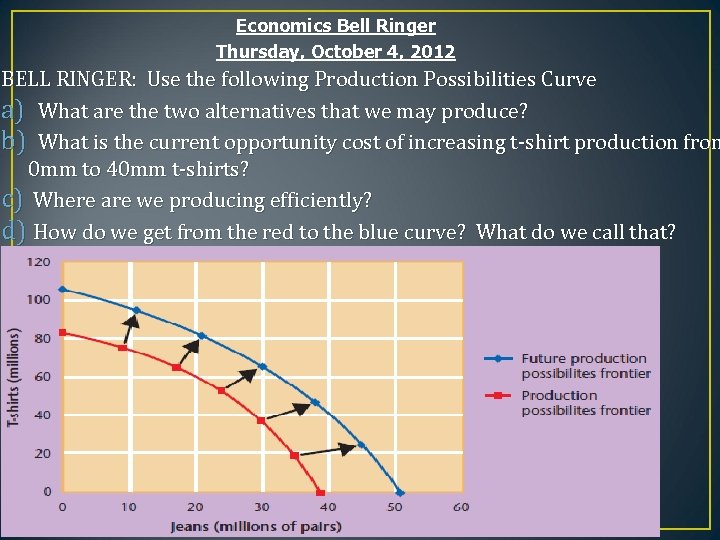
Economics Bell Ringer Thursday, October 4, 2012 BELL RINGER: Use the following Production Possibilities Curve a) What are the two alternatives that we may produce? b) What is the current opportunity cost of increasing t-shirt production from 0 mm to 40 mm t-shirts? c) Where are we producing efficiently? d) How do we get from the red to the blue curve? What do we call that?

Economics Thursday, October 4, 2012 To receive text reminders from Mr. Vasu for Economics: Text the message @vasuecon to (720)-924 -4156. Standard messaging rates apply.

Economics Bell Ringer Friday, October 5, 2012 1. Identify the Key Term a) the use of resources in such a way as to maximize the Efficiency (on PPF) output of goods and services b) a line on a production possibilities curve that shows the maximum possible output an economy can Production Possibilities Frontier produce c) the extra cost of adding a unit Marginal Cost d) e) f) 1. Prod. Possibilities Curve 2. Prod. Possibilities Frontier The most desirable alternative given up as a result of 3. Opportunity Cost a decision Opportunity Cost 4. Marginal Benefit the use of fewer resources than an economy is 5. Efficiency capable of using Underutilization (inside/under PPF) 6. Marginal Cost The process of deciding how much more or less 7. Underutilization to do for the extra/next unit of production 8. Needs/Wants Thinking on the Margin 9. Thinking on the Margin

Economics Bell Ringer Friday, October 5, 2012 1. Describe a good or service you consumed recently a) What was the opportunity cost? b) What factors of production were used to make the good or service? • Be specific what factor of production it is Today’s Handouts: #21 – 10/5 – Kitchen Challenge

Economics Bell Ringer Monday, October 8, 2012 1. Make a production possibilities frontier on this production possibilities curve. Label your axes. 2. What is the opportunity cost of producing more than 70 mm i. Pads? 3. What would be a point of underutilization? 4. What might cause you to be to the right of your PPF? i. Pads (millions) i. Phones (millions) 0 100 25 80 50 55 70 25 100 0 0 Today’s Handouts: #22 – 10/8 – Bell Ringer (10/8 -10/12)
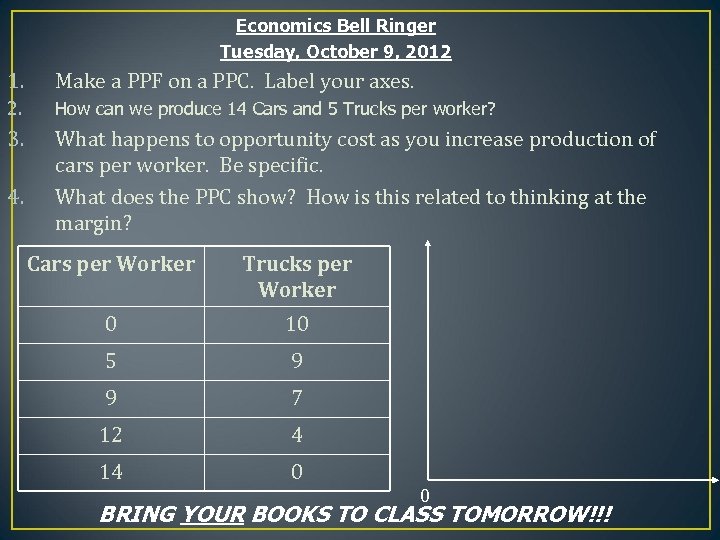
Economics Bell Ringer Tuesday, October 9, 2012 1. Make a PPF on a PPC. Label your axes. 2. How can we produce 14 Cars and 5 Trucks per worker? 3. What happens to opportunity cost as you increase production of cars per worker. Be specific. What does the PPC show? How is this related to thinking at the margin? 4. Cars per Worker Trucks per Worker 0 10 5 9 9 7 12 4 14 0 0 BRING YOUR BOOKS TO CLASS TOMORROW!!!

Economics Bell Ringer Wednesday, October 10, 2012 Use at least 4 key terms in your answers: scarcity, needs/wants, goods/services, efficiency, cost/benefit analysis, thinking at the margin 1. Why does every decision involve tradeoffs and opportunity cost? 2. How does a PPC show opportunity cost?

Economics Wednesday, October 10, 2012 1. Finish the Kitchen Challenge. It is due on Thursday 2. Review for the Ch 1 Test (Thursday in class) • You are allowed one side of 3 x 5 index card I give you as aid for the test • Resources: • Handouts #8, 9, 12, 13, 19, 20 • P. 19 Key Terms • P. 20 #1 -9
Economics Friday, October 5, 2012 KITCHEN CHALLENGE: RESULTS Group Total Money Raised Total Time Taken

Economics Monday, October 15, 2012 • Think of a business idea and answer the following three questions. Explain your reasoning. Use Tuesday’s BR space if you need more room. 1. What goods/services are you going to produce? 2. How are you going to produce these goods/services? (specific factors of production) 3. Who is going to consume the goods and services? Today’s Handouts: #24 – 10/15 – Bell Ringer (10/15 -10/19) #25 – 10/15 – Ch 2. 1 Book Work

Economics Tuesday, October 16, 2012 • One of everyone’s basic needs is for food. To satisfy this need, how should the 3 economic questions be answered? 1. What goods/services should be produced? 2. How should these goods/services be produced? 3. Who is going to consume the goods and services? Today’s Handouts: #26 – 10/16 – PPT Notes Ch 2. 1

Economics Bell Ringer Thursday, October 18, 2012 • What are three key economic questions? • List the five economic goals • Describe two of the goals

Economics Thursday, October 18, 2012 • Any questions on p 28? • Finish Book Work • Review Key Terms to study for Quiz • Organize Binder to be checked tomorrow

Economics Bell Ringer Monday, October 29, 2012 1. What are three key economic questions? 2. What are the five economic goals? Today’s Handouts: #28 – 10/22 – Bell Ringer (10/29 -11/03) #29 – Ch 2 Notes

Economics Classwork Monday, October 29, 2012 1. Take out a sheet of a paper and number it #29 with the title, Chapter 2 Notes: Economic Systems 2. Quickwrite your thoughts for Why do markets exist? 3. Tear another sheet of paper into 8 equal pieces. Think of a need/want. Identify a business idea. Write down a good/service your business provides on each of the pieces

Economics Classwork Monday, October 29, 2012 1. Create markets to exchange for your other needs/wants. The market is only open for 10 minutes. 2. Why do markets exist?

Economics Classwork Monday, October 29, 2012 1. We need markets because most people are not selfsufficient • We are households/consumers • Firms/producers are organizations that produce goods/services • Households need to trade/exchange for goods/services to satisfy our needs/wants • This is the product market • We also need to work and sell our scarce resources to get money to buy goods/services. This income is a factor payment • This is the factor market 2. This is the circular flow of income and output

Economics Classwork Monday, October 29, 2012 This week’s book work (#29 Ch 2 Notes) • Key Terms • Checkpoint Questions • Read Ch 2. 2 p 29 -34 • P 35 -36 • P 39 -40 • P. 34 #2 -5, 10 • DUE FRIDAY

Economics Bell Ringer Tuesday, October 30, 2012 1. Why do markets exist? 2. What do these words mean: 1. Households/consumers 2. Product market 3. Factor market 4. Firms/producers Today’s Handouts: #30 – 10/30 – PPT Notes Ch 2. 2

Economics Bell Ringer Wednesday, October 31, 2012 1. Why do households/entrepreneurs specialize? How can specialization benefit both buyers and sellers in a free market economy? 2. Explain what you remember about the Circular Flow of Income and Output? Today’s Handouts: #31 – 10/31 – Activity of Firms

Economics Exit Ticket Wednesday, October 31, 2012 1. How do incentives influence the decisions we make? Provides reward or punishment; motivation to do certain things 2. How are incentives and self-interest related to the free market? Self-interest provides the incentive for households to look for lowest prices and firms to look for highest prices, so they get the highest profits. 3. How are free market economic systems selfregulated? Self-interest means no one will pay more than they are willing. Competition means firms cannot charge unfairly high prices, earning unfair profits, since others will enter the business.

Economics Bell Ringer Thursday, November 1, 2012 • How does the government help provide for economic equity? • How does the government pay for its programs? Today’s Handouts: #33 – 11/01 – Quiz Ch 2. 2

#29 – Ch 2 Notes (continued) Economic Systems and the 5 Goals • Free Market Economy • No government; markets control all (Hong Kong, Dubai, markets for illegal goods) • Private property – households own factors of production • Values: Growth, Efficiency, Freedom, Security • Doesn’t Value: Equity

#29 – Ch 2 Notes (continued) Economic Systems and the 5 Goals • We need government to provide for equity • Centrally Planned Economy • Only government answers all 3 economic questions • No individual choice: opposite of Free Market (China 1950 s, Cuba, North Korea) • Values: Equity, Security • Doesn’t Value: Freedom, Efficiency, Growth

#29 – Ch 2 Notes (continued) Economic Systems and the 5 Goals • Mixed Economy • Individuals mostly answer the 3 economic questions; Markets very important • Some government to provide safety nets and other services (US, Europe, India, MOST OF THE WORLD) • Values vary from country to country • US is more free mkt: efficiency, freedom, growth • India is more centrally planned: equity, growth

Economics Bell Ringer Friday, November 2, 2012 • • List the 5 economic values or goals Choose one economic system and explain how they value or don’t value the 5 goals: 1. Free Market Economic System 2. Centrally Planned Economic System Today’s Handouts: #34 – 11/02 – Econ Systems and Goals Chart

#34: Economic Systems and the 5 Goals Economic System Free Market Economy Mixed Economy Centrally Planned Who Answers 3 ? s Individuals and Government Role of Government None Small to Large Controls ALL the Economy Goals Valued Freedom Efficiency Growth Security All 5 Equity Security Goals Not Valued Equity Examples Hong Kong Different in Difft countries Freedom Efficiency, Growth US, Germany, India, Brazil North Korea, Cuba
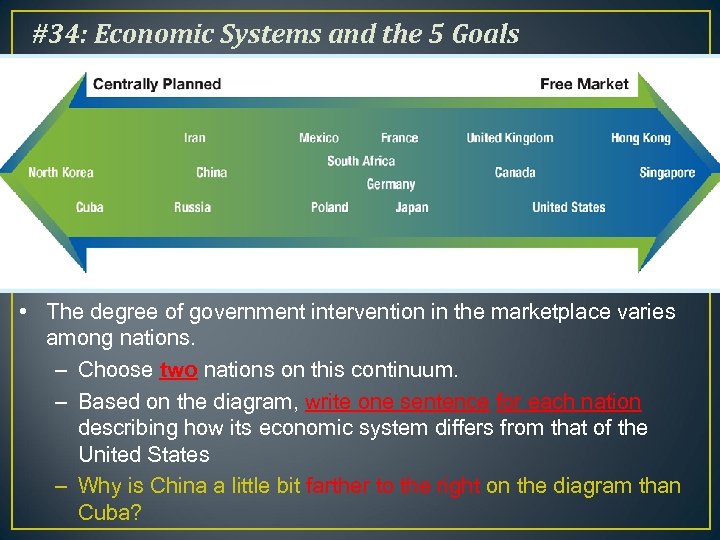
#34: Economic Systems and the 5 Goals • The degree of government intervention in the marketplace varies among nations. – Choose two nations on this continuum. – Based on the diagram, write one sentence for each nation describing how its economic system differs from that of the United States – Why is China a little bit farther to the right on the diagram than Cuba?

Economics Bell Ringer 9/7/2011 – Per 3 What might cause an increased demand for food stamps? -Teens dropping out -Price food rises -Increased population rates -Lower incomes -Unemployed/Lack of Jobs -Easier accessibility

Economics Bell Ringer 9/7/2011 – Per 6 What might cause an increased demand for food stamps? -Supply and Demand of food -Losing your job/Increased unemployment -Upcoming recession -Bigger families/households (more mouths to feed)/less birth control -Greater obesity -Inflation (prices rise) -Other costs rise (rents, etc. )
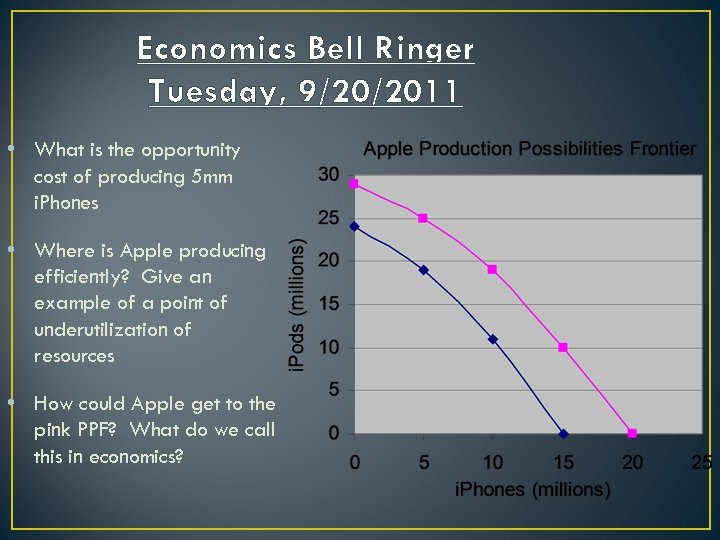
Economics Bell Ringer Tuesday, 9/20/2011 • What is the opportunity cost of producing 5 mm i. Phones • Where is Apple producing efficiently? Give an example of a point of underutilization of resources • How could Apple get to the pink PPF? What do we call this in economics?

Economics Bell Ringer Monday, 10/3/2011 1. Why aren’t all workers paid the same amount in factor payments for the resources they provide 2. What types of investment on the part of manufacturers result in growth? 3. How does this improve a nation’s standard of living?

Economics Bell Ringer Wednesday, 10/05/2011 • What is at least one thing you learned during yesterday’s simulation? • What was the biggest problem in the economic system we had during yesterday’s simulation? • Quietly finish your reflection questions from yesterday if not completed

Economics Bell Ringer Wednesday, 10/12/2011 • List three examples of ways the US or Illinois government provides or regulates how goods and services are provided? • List the 5 economic values or goals • Choose one and explain how they value or devalue the 5 goals: • Free Market Economic System • Centrally Planned Economic System

Economics Bell Ringer Thursday, 10/13/2011 • Sweden has a mixed economy that blends a free market with socialism. Swedes pay twice the amount of taxes as Americans. As a result, Swedes pay very little for medical care and everyone gets at least 30 days vacation every year. • Compare and contrast the US and Swedish economic systems. Which is more beneficial for workers? (Use Key Terms and think of 3 Questions and Economic Goals) • Log on to computers and Ed. Modo and download today’s assignment (HANDOUT #30)

Economics Bell Ringer Friday, 10/14/2011 • The degree of government intervention in the marketplace varies among nations. – Choose two nations on this continuum. Based on the diagram, write one sentence for each nation describing how its economic system differs from that of the United States – Why is China a little bit farther to the right on the diagram than Cuba?

Economics Bell Ringer Monday, 10/17/2011 1. How do Households and Firms interact in the Factor Market? In the Product Market? 2. Suppose you are the owner of a beauty salon. Give two specific ways your business might interact with households? 3. How might the introduction of government into the Circular Flow model affect your business?

Economics Bell Ringer Tuesday, 10/18/2011 • Clear your desk of all materials except for scratch paper and pen/pencil • Quietly wait for instructions from Mr. Vasu

Economics Bell Ringer Wednesday, 10/19/2011 • Reflect on how you prepared for yesterday’s test: • Write one thing you did that prepared you well for the test • Write two things you should do to be better prepared for future Econ tests • Put your post-it notes on the Economic System Continuum • Go get your textbook from your locker if you don’t have it

Economics Bell Ringer Thursday, 10/20/2011 • Complete the Warm-Up in your Chapter 3 Packet (handout for today)

Economics Bell Ringer Friday, 10/21/2011 • Write two characteristics of public goods • Complete Bell Ringer Reflection for this week

Economics Bell Ringer Friday, 10/21/2011 Public School Construction • Proposal: A new high school for half the 5, 000 students in the existing overcrowded high school • Funding: A federal government loan, paid back by increasing local taxes 10 percent annually for 12 years • What are the benefits to the community? • What are the costs to the community? • Complete Bell Ringer Reflection for this week

Economics Bell Ringer Monday, 10/24/2011 1. What am I? (Identify the key term; try not to use notes) a) a situation in which the free market, operating on its own, does not Market failure distribute resources efficiently b) a shared good or service for which it would be inefficient or impractical to make consumers pay individually and to exclude those who did not pay c) someone who would not be willing to pay for a certain good or service but who would get the benefits of it anyway if it were provided as a public good d) Free Rider an economic side effect of a good or service that generates benefits or costs to someone other than the person deciding how much to produce or consume e) Public good Externality (Positive/Negative) – a good or service that can be used by fromnumber and private goods any public of consumers without reducing the benefits to any single consumer Non-Rival Good

Economics Bell Ringer Tuesday, 10/25/2011 • • Have HW (Public Goods Handout) Ready to be Stamped Pick 2 of these infrastructure projects and identify how they are an example of a market failure (think why they are public goods, may suffer from the free-rider problem or have any positive/negative externalities and who’s going to pay for/build it if the government doesn’t? ) • • More train service is needed on the south side as the CTA Red Line ends at 95 th street Uplift needs a better field in the back with a real track Chicago has way too many potholes and they need to be fixed! Kids need more basketball courts and baseball fields to play on and keep them off the streets

Economics Bell Ringer Wednesday, 10/26/2011 • If there were no “sin” taxes (prices were lower), how and why would consumption of cigarettes or gas change? • Would the change in consumption have any costs to society? • Give an example of a cost to society? • What do we call a benefit/cost to someone who did not produce or consume a good?

Economics Bell Ringer Thursday, 10/27/2011 • Write any questions related to this week’s material (Public Goods) • Quietly work on something from another class or related to your college/scholarship apps

Economics Bell Ringer Tuesday, 11/01/2011 1. What am I? (Identify the key term; try not to use notes) These are Chapter 1 Terms a) The principle that limited amounts of goods and services are available to Scarcity meet unlimited needs and wants b) The resources that are used to make goods and services (and what are the Factors of production: Land, Labor, different types? ) Physical Capital, Human Capital c) The use of resources in such a way as to maximize the output of goods and Efficiency services d) The process of deciding how much more or less to do for the extra/next unit of production Thinking at the margin e) The most desirable alternative given up as a result of a decision f) A graph that shows alternative (two) ways to use an economy’s productive resources Production Possibilities Curve Opportunity Cost

Economics Bell Ringer Wednesday, 11/02/2011 1. What am I? (Identify the key term; try not to use notes) These are Chapter 2 Terms a) The amount of money a business receives in excess of its expenses b) The process of bringing new methods, products or ideas into use c) Any arrangement that allows buyers and sellers to exchange things d) An organization that uses resources to produce a product or service, which it Firm then sells e) The area of exchange in which firms purchase the factors of production Factor Market from households f) The hope of reward or fear of penalty that encourages a person to behave in a certain way Incentive g) What are the 5 main economic goals? Profit Innovation Market Growth, Efficiency, Security, Freedom, Equity

Economics Bell Ringer Friday, 11/04/2011 1. What am I? (Identify the key term; try not to use notes) a) The study of how people seek to satisfy their needs and wants by making Economics choices b) A person or group of people who provide the factors of production c) The arena of exchange in which households purchase goods and services Product Market from firms d) The struggle amongst producers for the dollars of consumers e) An economic system where the government makes all decisions on the three Centrally Planned or Command key economic questions. Households/Consumers Competition Economy f) The process of selling businesses or services operated by the government to individual investors, and then allowing them to compete in the marketplace g) What are the 3 key economic questions? Privatization (a form of economic transition) What are we going to produce? How are we going to produce? Who is going to consume?
5ecd430bf3d7e00b2753e874ec52d914.ppt