69cc3176617f7e3db9fb07d7745e1e10.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 159



Economics and You

Chapter Objectives

Chapter Objectives

Chapter Objectives

Study Guide
Introduction
Advantages of Prices
Allocations Without Prices
The Problem of Fairness
High Administrative Cost
Diminishing Incentive
Prices as a System
Section Assessment
Section Close
Study Guide
Introduction

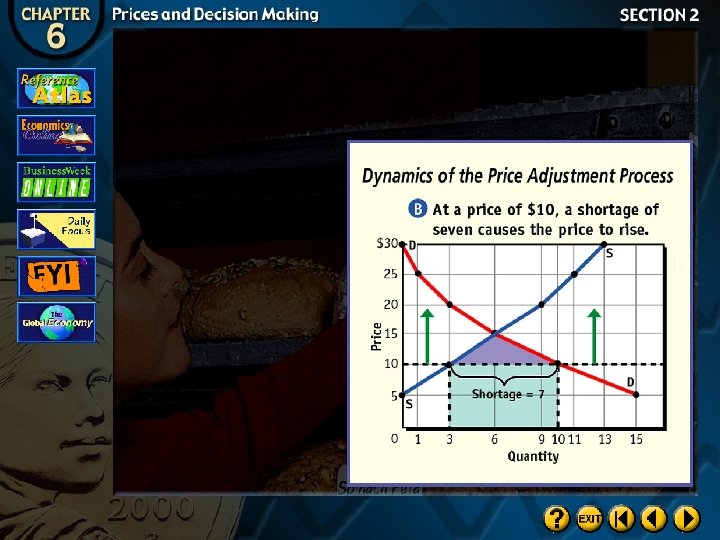
The Price Adjustment Process
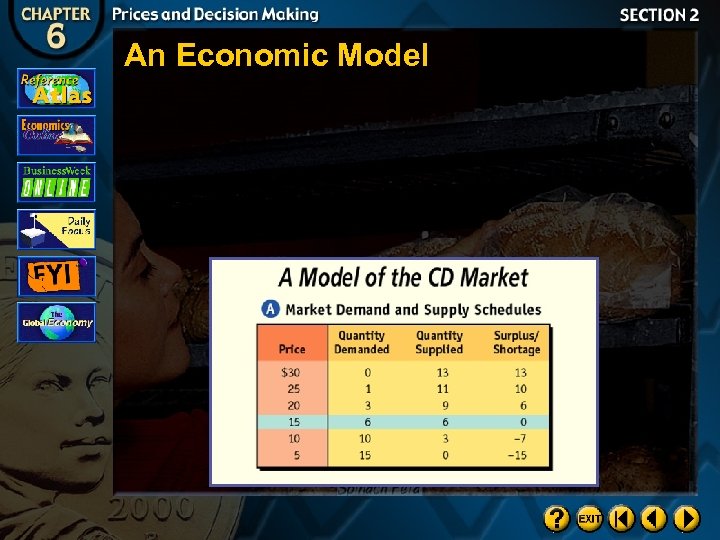
An Economic Model
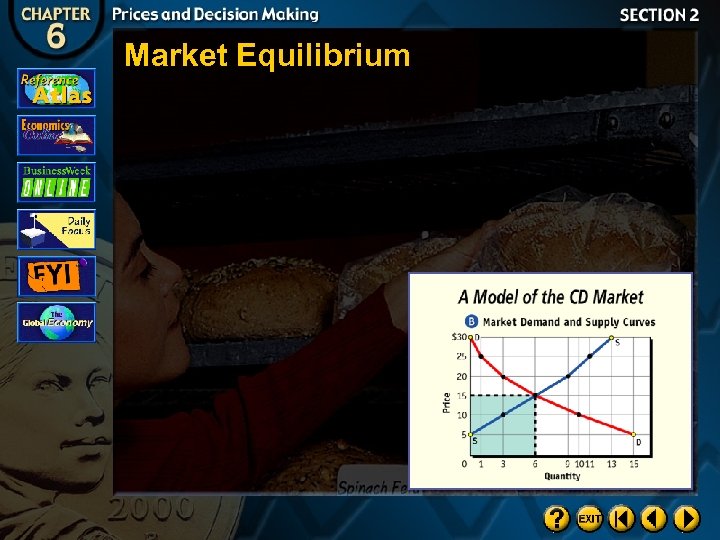
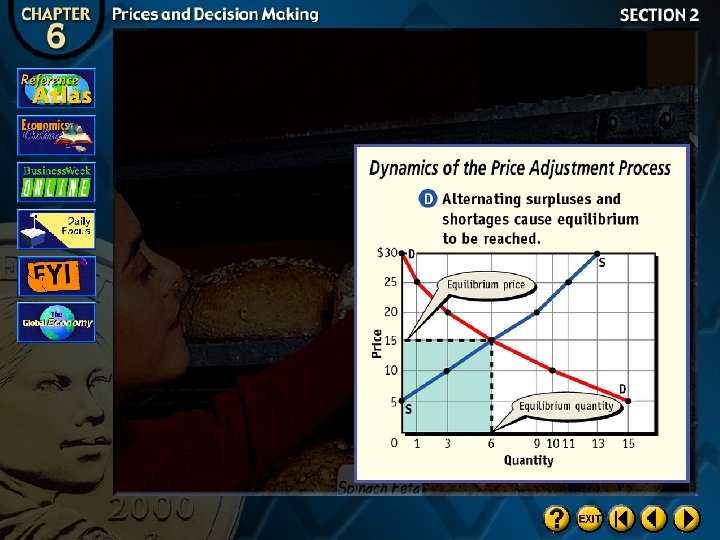
Market Equilibrium
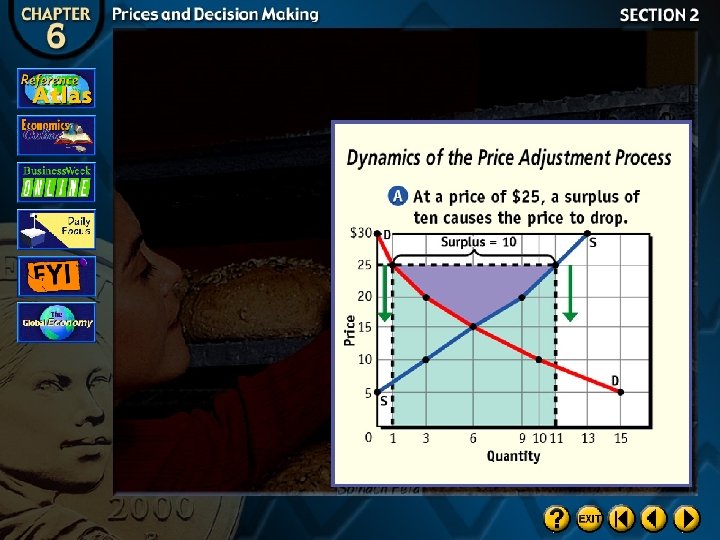
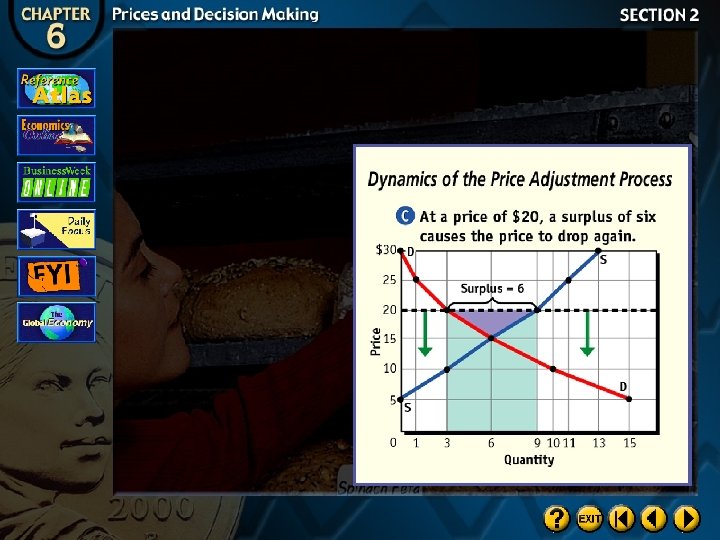
Surplus
Shortage
Equilibrium Price

Explaining and Predicting Prices
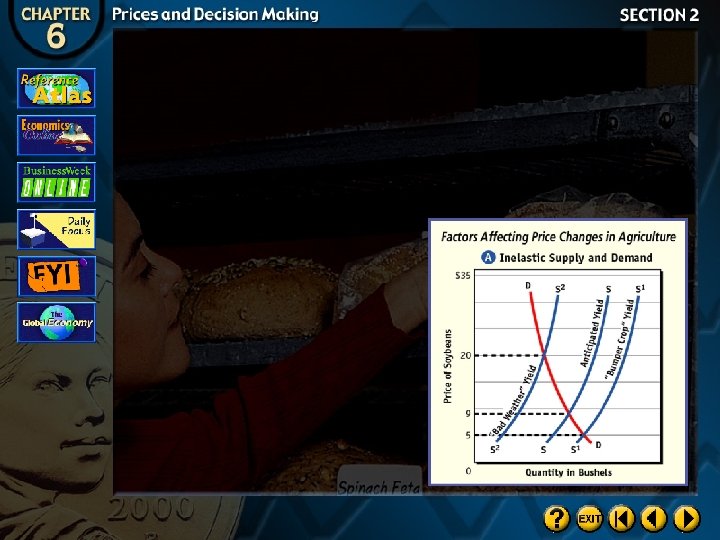
Changes in Supply
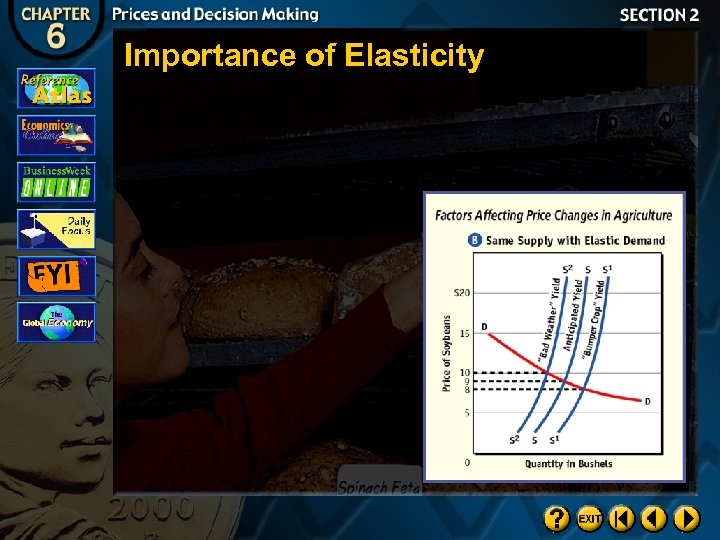
Importance of Elasticity
Changes in Demand
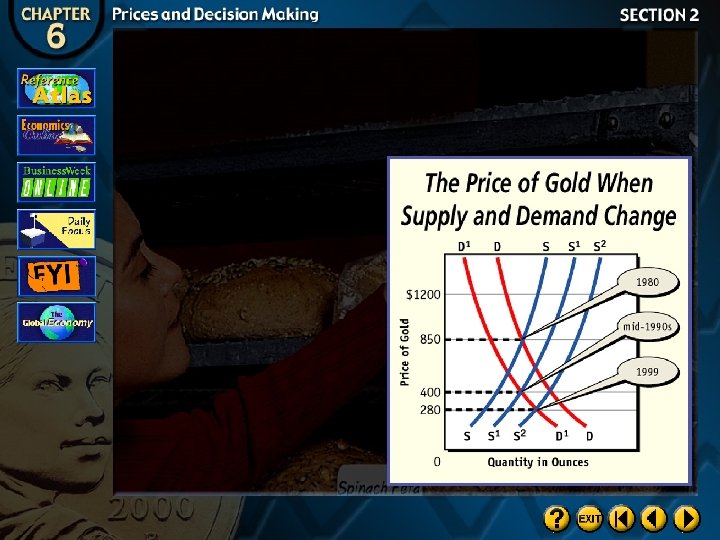
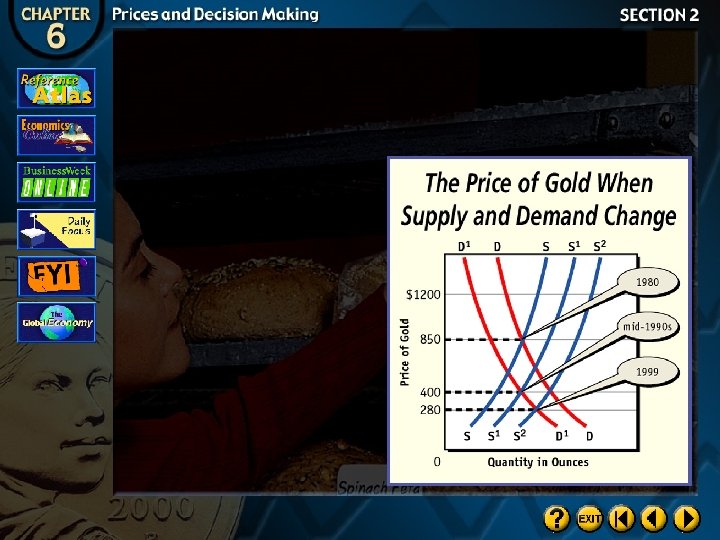
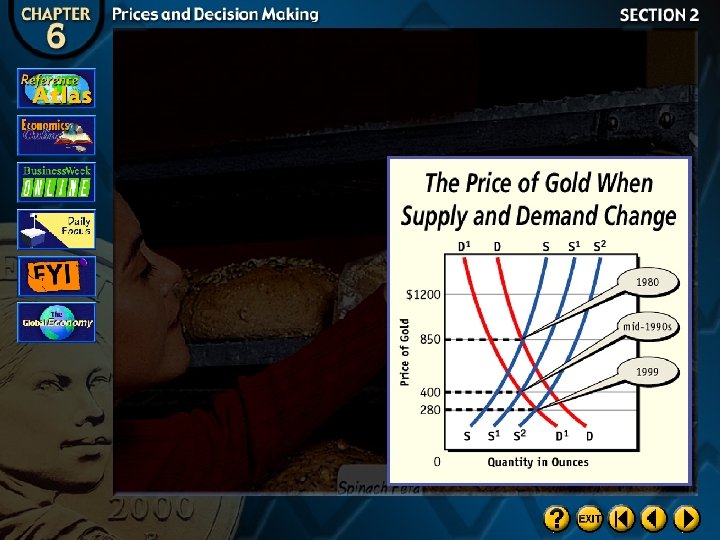
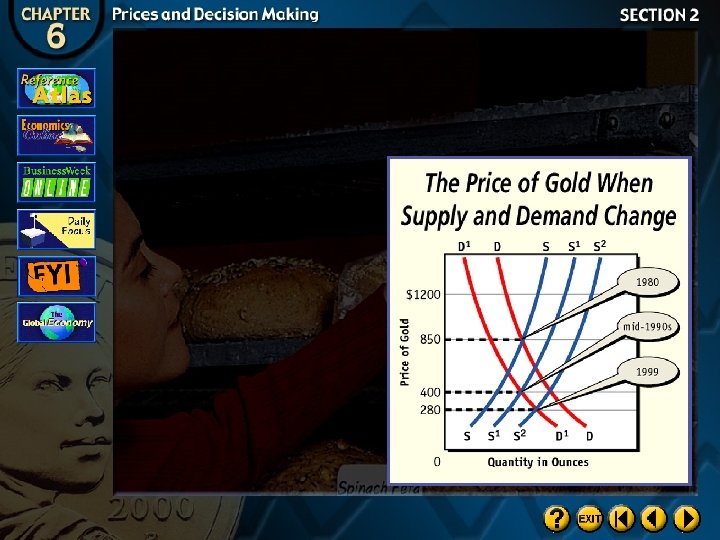

The Competitive Price Theory
Section Assessment
Section Close
Study Guide
Introduction

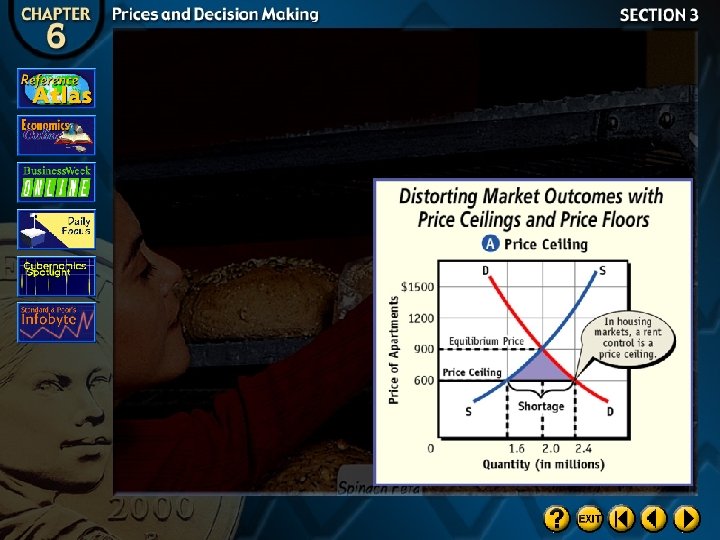
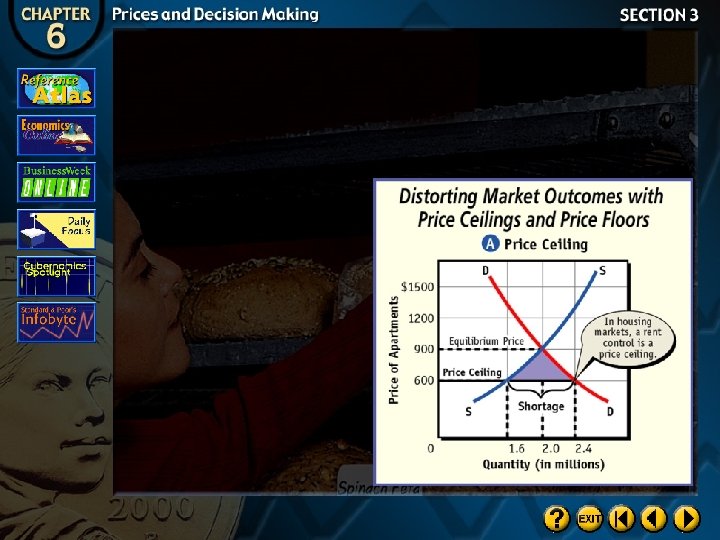
Distorting Market Outcomes
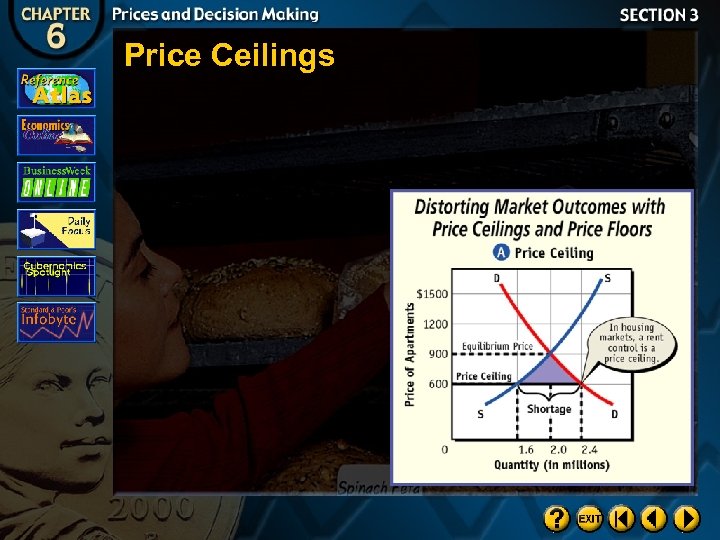
Price Ceilings
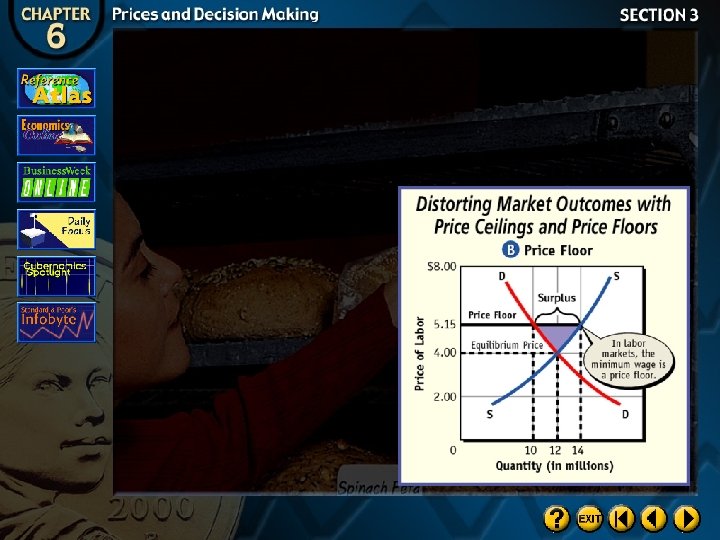
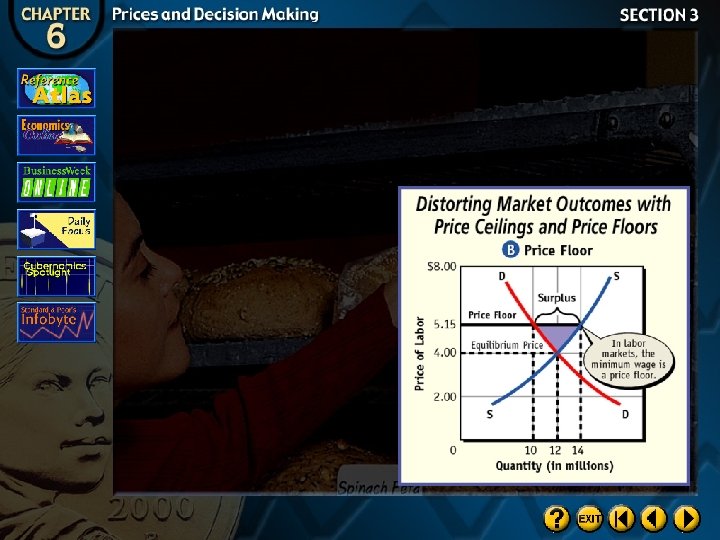
Price Floors
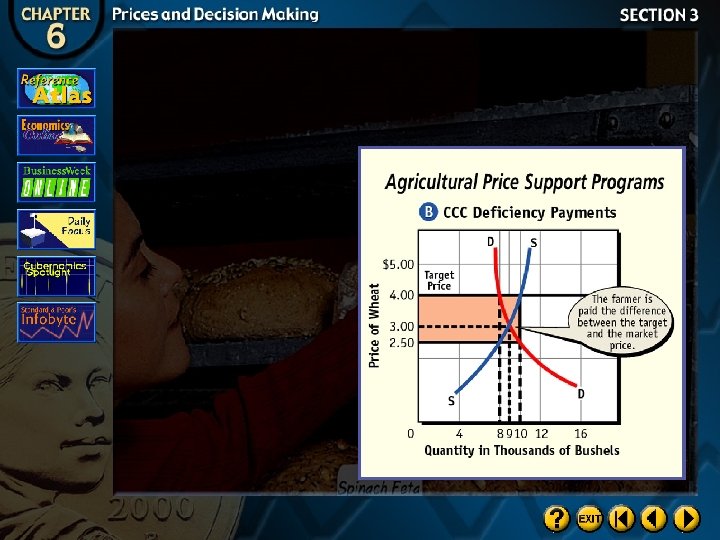
Agricultural Price Supports
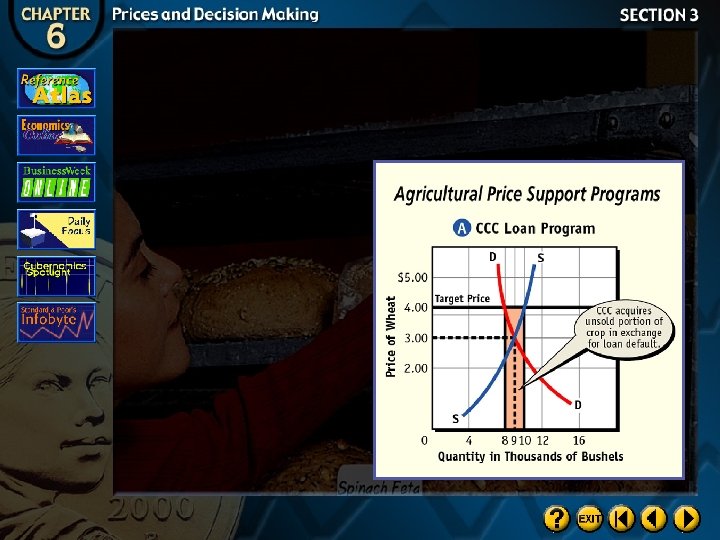
Loan Supports
Deficiency Payments
Reforming Price Supports

When Markets Talk
Section Assessment
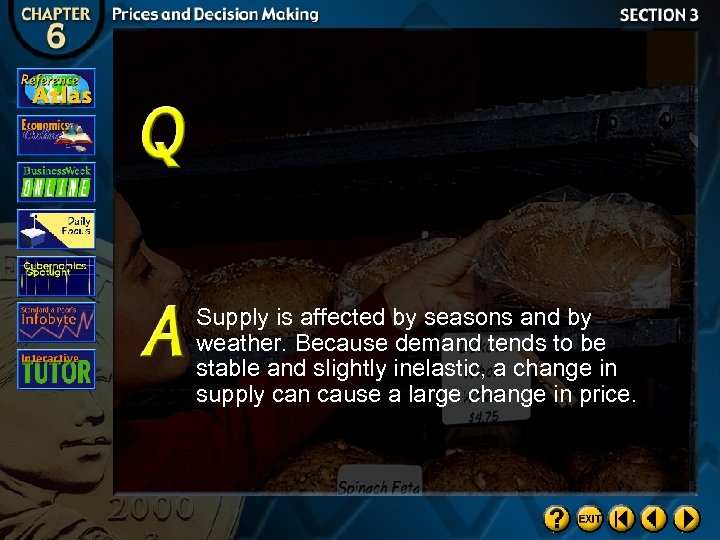
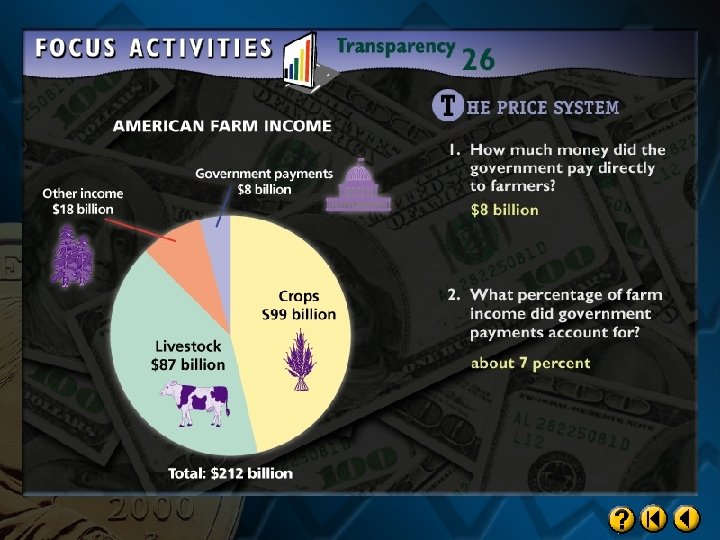
Supply is affected by seasons and by weather. Because demand tends to be stable and slightly inelastic, a change in supply can cause a large change in price.
Section Close


Section 1: Prices as Signals


Section 2: The Price System at Work


Section 3: Social Goals vs. Market Efficiency



Identifying Key Terms

Reviewing the Facts








Thinking Critically


Applying Economic Skills


















Doctors: Charting New Territory
Doctors: Charting New Territory
Doctors: Charting New Territory

Doctors: Charting New Territory



Synthesizing Information

Synthesizing Information

Synthesizing Information

Synthesizing Information

Synthesizing Information

Synthesizing Information

Synthesizing Information

Synthesizing Information

Synthesizing Information


Becker’s and Friedman’s ideas are similar in that they view economic conditions and decisions as fundamental to other aspects of life; they differ in that Becker focuses on the micro, specifically the decision-making of individuals, while Friedman focuses on the macro, specifically the importance of the supply of money or monetary policy.



69cc3176617f7e3db9fb07d7745e1e10.ppt