Small Business.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Economics and Finance Companies Presentation: Kushniruk S. R.
Economics and Finance Companies Presentation: Kushniruk S. R.
 Small business • Small businesses are privately owned corporations, partnerships, or solo proprietorships that have fewer employees and/or less annual revenue than a regularsized business or corporation.
Small business • Small businesses are privately owned corporations, partnerships, or solo proprietorships that have fewer employees and/or less annual revenue than a regularsized business or corporation.
 Іntroduction • While small businesses may not generate as much money as large corporations, they are a critical component of and major contributor to the strength of local economies. Small businesses present new employment opportunities and serve as the building blocks of the United States' largest corporations. • Small businesses play an important role in any society. When they are first established, they represent ways that business owners test their business ideas in a market. Those companies that survive over time provide economic stability for owners and their families. Small businesses that create jobs for workers in addition to the owner offer even more economic stability. Providing a steady source of income to business owners and employees is just one reason they are important.
Іntroduction • While small businesses may not generate as much money as large corporations, they are a critical component of and major contributor to the strength of local economies. Small businesses present new employment opportunities and serve as the building blocks of the United States' largest corporations. • Small businesses play an important role in any society. When they are first established, they represent ways that business owners test their business ideas in a market. Those companies that survive over time provide economic stability for owners and their families. Small businesses that create jobs for workers in addition to the owner offer even more economic stability. Providing a steady source of income to business owners and employees is just one reason they are important.
 Benefits Low overheads Inventiveness and innovation Developing personal relationships Responding flexibly to problems and challenges Catering for limited or niche markets
Benefits Low overheads Inventiveness and innovation Developing personal relationships Responding flexibly to problems and challenges Catering for limited or niche markets
 Importance (general): • Importance: • 1. Taxpayer. • 2. Create jobs. • 3. High profitability. • 4. Infrastructure for large firms. • 5. Implementation of projects, novelty.
Importance (general): • Importance: • 1. Taxpayer. • 2. Create jobs. • 3. High profitability. • 4. Infrastructure for large firms. • 5. Implementation of projects, novelty.
 Importance (components): Economic Growth Adaptability to Changing Climates Schools and Local Government Offices Future Growth Science and Engineering Productivity Innovation
Importance (components): Economic Growth Adaptability to Changing Climates Schools and Local Government Offices Future Growth Science and Engineering Productivity Innovation
 Economic Growth • Small businesses contribute to local economies by bringing growth and innovation to the community in which the business is established. Small businesses also help stimulate economic growth by providing employment opportunities to people who may not be employable by larger corporations. Small businesses tend to attract talent who invent new products or implement new solutions for existing ideas. Larger businesses also often benefit from small businesses within the same local community, as many large corporations depend on small businesses for the completion of various business functions through outsourcing. Adaptability to Changing Climates • Many small businesses also possess the ability to respond adapt quickly to changing economic climates. This is due to the fact that small businesses are often very customer-oriented. Many local customers will remain loyal to their favorite small businesses in the midst of an economic crisis. This loyalty means that small businesses are often able to stay afloat during tough times, which can further strengthen local economies. Small businesses also accumulate less revenue than larger corporations, meaning they may have less to lose in times of economic crisis.
Economic Growth • Small businesses contribute to local economies by bringing growth and innovation to the community in which the business is established. Small businesses also help stimulate economic growth by providing employment opportunities to people who may not be employable by larger corporations. Small businesses tend to attract talent who invent new products or implement new solutions for existing ideas. Larger businesses also often benefit from small businesses within the same local community, as many large corporations depend on small businesses for the completion of various business functions through outsourcing. Adaptability to Changing Climates • Many small businesses also possess the ability to respond adapt quickly to changing economic climates. This is due to the fact that small businesses are often very customer-oriented. Many local customers will remain loyal to their favorite small businesses in the midst of an economic crisis. This loyalty means that small businesses are often able to stay afloat during tough times, which can further strengthen local economies. Small businesses also accumulate less revenue than larger corporations, meaning they may have less to lose in times of economic crisis.
 Schools and Local Government Offices • When consumers patronize local small businesses, they are essentially giving money back to their local community. A thriving local business will generate high levels of revenue, which means that the business will pay higher taxes, including local taxes. This money is then used for local police and fire departments as well as schools. Future Growth • Small businesses do not always stay small. Large corporations, such as Nike and Ben and Jerry’s, started off as small businesses that grew to become major players in the national and international marketplace. Many computer-industry leaders began as “tinkerers, ” working on hand-assembled machines out of their garages. Microsoft is a prime example of how a small business idea can change the world. Small businesses that grow into large businesses often remain in the community in which the business was first established. Having a large corporation headquartered in a community can further help provide employment and stimulate the local economy.
Schools and Local Government Offices • When consumers patronize local small businesses, they are essentially giving money back to their local community. A thriving local business will generate high levels of revenue, which means that the business will pay higher taxes, including local taxes. This money is then used for local police and fire departments as well as schools. Future Growth • Small businesses do not always stay small. Large corporations, such as Nike and Ben and Jerry’s, started off as small businesses that grew to become major players in the national and international marketplace. Many computer-industry leaders began as “tinkerers, ” working on hand-assembled machines out of their garages. Microsoft is a prime example of how a small business idea can change the world. Small businesses that grow into large businesses often remain in the community in which the business was first established. Having a large corporation headquartered in a community can further help provide employment and stimulate the local economy.
 Science and Engineering Productivity • Businesses of a smaller nature can be more productive than larger companies. The U. S. Small Business Technology Council reports that smaller firms employ 32 percent of scientists and engineers, whereas larger firms employ 27 percent. These professionals in small businesses produce more patents than their counterparts in large companies and universities. It is important for science and engineering talent to enjoy this choice of the kind of organization to work for as they research new ways to solve society's technical and scientific problems. Innovation • Innovation is very possible in small businesses. In these tiny enterprises, employees usually work in close proximity to consumers and learn firsthand about their needs. Also, these small businesses typically have few ranks of managers separating line workers from the business owner. Employees can help their organizations grow by sharing ideas that will benefit consumers. In turn, business owners must go through less bureaucracy to put employees' new ideas into action. This reality accounts for why some innovative workers prefer to work in smaller businesses.
Science and Engineering Productivity • Businesses of a smaller nature can be more productive than larger companies. The U. S. Small Business Technology Council reports that smaller firms employ 32 percent of scientists and engineers, whereas larger firms employ 27 percent. These professionals in small businesses produce more patents than their counterparts in large companies and universities. It is important for science and engineering talent to enjoy this choice of the kind of organization to work for as they research new ways to solve society's technical and scientific problems. Innovation • Innovation is very possible in small businesses. In these tiny enterprises, employees usually work in close proximity to consumers and learn firsthand about their needs. Also, these small businesses typically have few ranks of managers separating line workers from the business owner. Employees can help their organizations grow by sharing ideas that will benefit consumers. In turn, business owners must go through less bureaucracy to put employees' new ideas into action. This reality accounts for why some innovative workers prefer to work in smaller businesses.
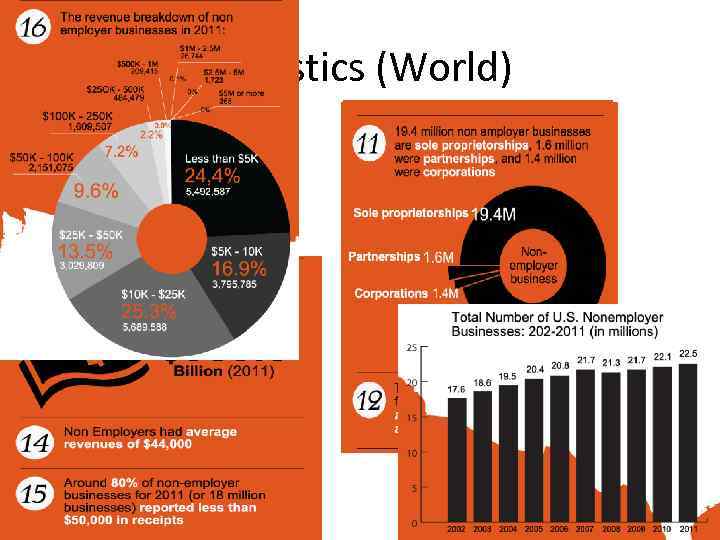 Statistics (World)
Statistics (World)
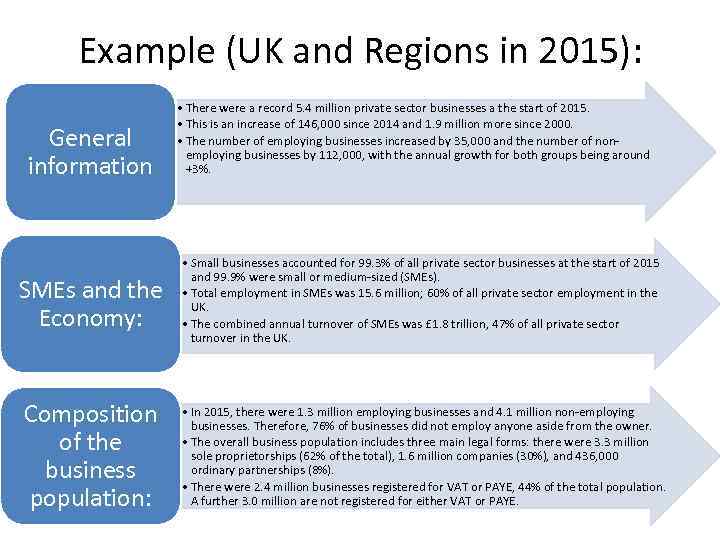 Example (UK and Regions in 2015): General information • There were a record 5. 4 million private sector businesses a the start of 2015. • This is an increase of 146, 000 since 2014 and 1. 9 million more since 2000. • The number of employing businesses increased by 35, 000 and the number of nonemploying businesses by 112, 000, with the annual growth for both groups being around +3%. SMEs and the Economy: • Small businesses accounted for 99. 3% of all private sector businesses at the start of 2015 and 99. 9% were small or medium-sized (SMEs). • Total employment in SMEs was 15. 6 million; 60% of all private sector employment in the UK. • The combined annual turnover of SMEs was £ 1. 8 trillion, 47% of all private sector turnover in the UK. Composition of the business population: • In 2015, there were 1. 3 million employing businesses and 4. 1 million non-employing businesses. Therefore, 76% of businesses did not employ anyone aside from the owner. • The overall business population includes three main legal forms: there were 3. 3 million sole proprietorships (62% of the total), 1. 6 million companies (30%), and 436, 000 ordinary partnerships (8%). • There were 2. 4 million businesses registered for VAT or PAYE, 44% of the total population. A further 3. 0 million are not registered for either VAT or PAYE.
Example (UK and Regions in 2015): General information • There were a record 5. 4 million private sector businesses a the start of 2015. • This is an increase of 146, 000 since 2014 and 1. 9 million more since 2000. • The number of employing businesses increased by 35, 000 and the number of nonemploying businesses by 112, 000, with the annual growth for both groups being around +3%. SMEs and the Economy: • Small businesses accounted for 99. 3% of all private sector businesses at the start of 2015 and 99. 9% were small or medium-sized (SMEs). • Total employment in SMEs was 15. 6 million; 60% of all private sector employment in the UK. • The combined annual turnover of SMEs was £ 1. 8 trillion, 47% of all private sector turnover in the UK. Composition of the business population: • In 2015, there were 1. 3 million employing businesses and 4. 1 million non-employing businesses. Therefore, 76% of businesses did not employ anyone aside from the owner. • The overall business population includes three main legal forms: there were 3. 3 million sole proprietorships (62% of the total), 1. 6 million companies (30%), and 436, 000 ordinary partnerships (8%). • There were 2. 4 million businesses registered for VAT or PAYE, 44% of the total population. A further 3. 0 million are not registered for either VAT or PAYE.
 Example (UK and Regions in 2015): Trends in the business population: Locations and industries: • There has been sustained growth in the total business population, with increases of +55% since 2000 and +3% since 2014. • The majority of population growth since 2000 has been due to non-employing businesses, which accounted for 90% of the 1. 9 m increase. • The growth in numbers of businesses last year reflected the composition of the business population in 2014, with non-employing businesses accounting for three quarters of the overall 146, 000 increase. • The number of companies has increased in recent years and increased again in the last year by 117, 000 (+8%). In contrast, the number of ordinary partnerships continued to fall, with a 21, 000 (-5%) reduction from 2014. The number of sole proprietorships increased by 50, 000 (+2%). • The business population in southern England is larger relative to resident population than elsewhere in the UK. • SMEs account for at least 99% of the businesses in every main industry sector. • Just under a fifth of all SMEs operate in Construction, compared to just 1% in the Mining, Quarrying and Utilities sector.
Example (UK and Regions in 2015): Trends in the business population: Locations and industries: • There has been sustained growth in the total business population, with increases of +55% since 2000 and +3% since 2014. • The majority of population growth since 2000 has been due to non-employing businesses, which accounted for 90% of the 1. 9 m increase. • The growth in numbers of businesses last year reflected the composition of the business population in 2014, with non-employing businesses accounting for three quarters of the overall 146, 000 increase. • The number of companies has increased in recent years and increased again in the last year by 117, 000 (+8%). In contrast, the number of ordinary partnerships continued to fall, with a 21, 000 (-5%) reduction from 2014. The number of sole proprietorships increased by 50, 000 (+2%). • The business population in southern England is larger relative to resident population than elsewhere in the UK. • SMEs account for at least 99% of the businesses in every main industry sector. • Just under a fifth of all SMEs operate in Construction, compared to just 1% in the Mining, Quarrying and Utilities sector.
 Statistics (Ukraine) comparison In developed European countries 50% of the population is employed in small business, in Japan - 80%, in Ukraine - 17%. (!) In the European Union, the share of small business in GDP is about 65%. For those of neighboring countries with Ukraine, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Hungary, the figure is 30 -40%. We - 5 -6% (!) Loans for Small Business in Germany - 4 -5% per annum for a period of 10 years. Credits for the development of small business in Ukraine - 26 -28% per year for 1 -5 years. (!) The maximum amount of micro-credit for small businesses in developed countries, 25 thousand. Euros (about 620 thousand. UAH. ) At 4 -6%. The maximum loan amount for small business in Ukraine - 100 thousand UAH. . by 26 -28%. Thus, a small business in Ukraine occupies a very modest position in the creation of GDP, while according to rough statistics, there are now (including the shadow economy) is involved about 30% of the population. However, for the government small business it is just a sphere of malicious defaulters of taxes and social contributions. Therefore, the state represented by state officials does not support small business. And as long as this situation persists, Ukraine will remain corrupt and economically backward country with the poor and disenfranchised populations.
Statistics (Ukraine) comparison In developed European countries 50% of the population is employed in small business, in Japan - 80%, in Ukraine - 17%. (!) In the European Union, the share of small business in GDP is about 65%. For those of neighboring countries with Ukraine, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Hungary, the figure is 30 -40%. We - 5 -6% (!) Loans for Small Business in Germany - 4 -5% per annum for a period of 10 years. Credits for the development of small business in Ukraine - 26 -28% per year for 1 -5 years. (!) The maximum amount of micro-credit for small businesses in developed countries, 25 thousand. Euros (about 620 thousand. UAH. ) At 4 -6%. The maximum loan amount for small business in Ukraine - 100 thousand UAH. . by 26 -28%. Thus, a small business in Ukraine occupies a very modest position in the creation of GDP, while according to rough statistics, there are now (including the shadow economy) is involved about 30% of the population. However, for the government small business it is just a sphere of malicious defaulters of taxes and social contributions. Therefore, the state represented by state officials does not support small business. And as long as this situation persists, Ukraine will remain corrupt and economically backward country with the poor and disenfranchised populations.
 10 facts about the small and medium business in Ukraine 1. Small companies - the main taxpayers 5. Over the past 15 years dynamics of registration of new companies is deteriorating. 2. Small and medium business leads in the number of jobs created 3. Smaller companies are more profitable than large enterprises 4. Small and medium enterprises are not satisfied with the work of public services 6. At the same time fewer and fewer small companies cease to exist 7. The number of business entities in Ukraine is comparable with indicators of European countries 8. Small companies - the most vulnerable link in the export 9. Small companies have to pay dearly for bureaucracy 10. Deregulation brings investments to the Ukrainian economy
10 facts about the small and medium business in Ukraine 1. Small companies - the main taxpayers 5. Over the past 15 years dynamics of registration of new companies is deteriorating. 2. Small and medium business leads in the number of jobs created 3. Smaller companies are more profitable than large enterprises 4. Small and medium enterprises are not satisfied with the work of public services 6. At the same time fewer and fewer small companies cease to exist 7. The number of business entities in Ukraine is comparable with indicators of European countries 8. Small companies - the most vulnerable link in the export 9. Small companies have to pay dearly for bureaucracy 10. Deregulation brings investments to the Ukrainian economy
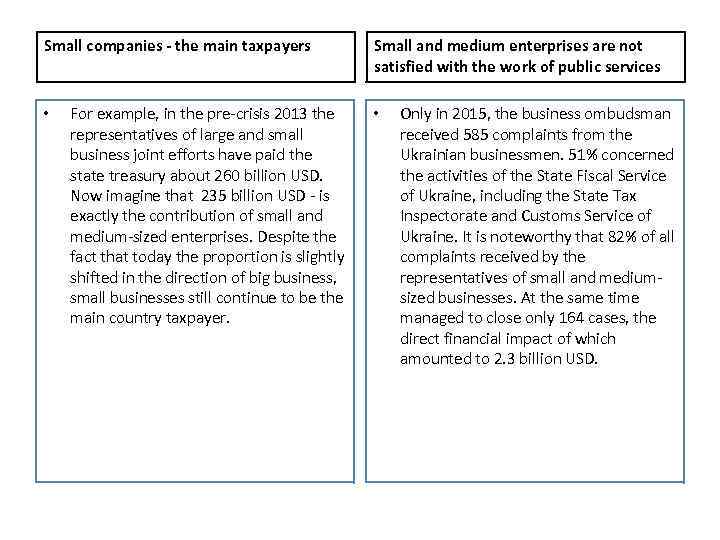 Small companies - the main taxpayers • For example, in the pre-crisis 2013 the representatives of large and small business joint efforts have paid the state treasury about 260 billion USD. Now imagine that 235 billion USD - is exactly the contribution of small and medium-sized enterprises. Despite the fact that today the proportion is slightly shifted in the direction of big business, small businesses still continue to be the main country taxpayer. Small and medium enterprises are not satisfied with the work of public services • Only in 2015, the business ombudsman received 585 complaints from the Ukrainian businessmen. 51% concerned the activities of the State Fiscal Service of Ukraine, including the State Tax Inspectorate and Customs Service of Ukraine. It is noteworthy that 82% of all complaints received by the representatives of small and mediumsized businesses. At the same time managed to close only 164 cases, the direct financial impact of which amounted to 2. 3 billion USD.
Small companies - the main taxpayers • For example, in the pre-crisis 2013 the representatives of large and small business joint efforts have paid the state treasury about 260 billion USD. Now imagine that 235 billion USD - is exactly the contribution of small and medium-sized enterprises. Despite the fact that today the proportion is slightly shifted in the direction of big business, small businesses still continue to be the main country taxpayer. Small and medium enterprises are not satisfied with the work of public services • Only in 2015, the business ombudsman received 585 complaints from the Ukrainian businessmen. 51% concerned the activities of the State Fiscal Service of Ukraine, including the State Tax Inspectorate and Customs Service of Ukraine. It is noteworthy that 82% of all complaints received by the representatives of small and mediumsized businesses. At the same time managed to close only 164 cases, the direct financial impact of which amounted to 2. 3 billion USD.
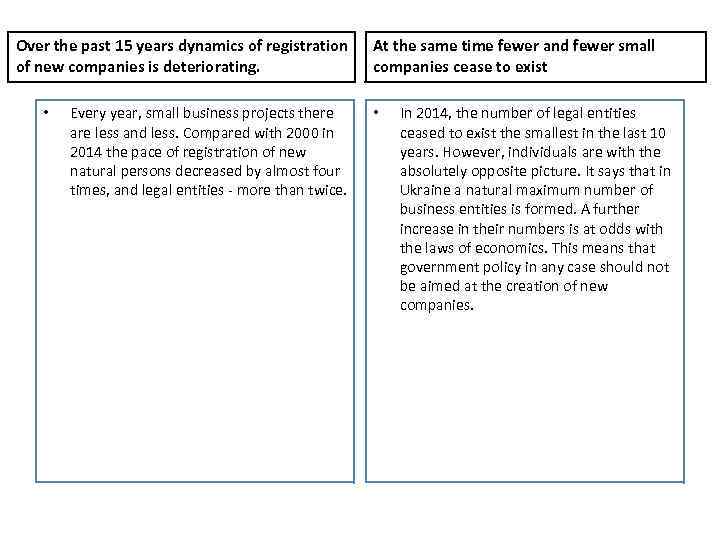 Over the past 15 years dynamics of registration of new companies is deteriorating. • Every year, small business projects there are less and less. Compared with 2000 in 2014 the pace of registration of new natural persons decreased by almost four times, and legal entities - more than twice. At the same time fewer and fewer small companies cease to exist • In 2014, the number of legal entities ceased to exist the smallest in the last 10 years. However, individuals are with the absolutely opposite picture. It says that in Ukraine a natural maximum number of business entities is formed. A further increase in their numbers is at odds with the laws of economics. This means that government policy in any case should not be aimed at the creation of new companies.
Over the past 15 years dynamics of registration of new companies is deteriorating. • Every year, small business projects there are less and less. Compared with 2000 in 2014 the pace of registration of new natural persons decreased by almost four times, and legal entities - more than twice. At the same time fewer and fewer small companies cease to exist • In 2014, the number of legal entities ceased to exist the smallest in the last 10 years. However, individuals are with the absolutely opposite picture. It says that in Ukraine a natural maximum number of business entities is formed. A further increase in their numbers is at odds with the laws of economics. This means that government policy in any case should not be aimed at the creation of new companies.
 The number of business entities in Ukraine is comparable with indicators of European countries • For example, in 1000 people in Ukraine there are for 40 business entities. In Hungary the figure is 53 subject, and in France - 44 subject. Small companies - the most vulnerable link in the export • The structure of the ratio of small, medium and large businesses in Ukraine is different from that of the EU. For small companies to take its rightful position in the building trade with the EU, it is necessary to spend a lot of reforms. In particular, the state has to provide free services through non-governmental agencies and state support (including financial).
The number of business entities in Ukraine is comparable with indicators of European countries • For example, in 1000 people in Ukraine there are for 40 business entities. In Hungary the figure is 53 subject, and in France - 44 subject. Small companies - the most vulnerable link in the export • The structure of the ratio of small, medium and large businesses in Ukraine is different from that of the EU. For small companies to take its rightful position in the building trade with the EU, it is necessary to spend a lot of reforms. In particular, the state has to provide free services through non-governmental agencies and state support (including financial).
 Small companies have to pay dearly for bureaucracy • • • Since the increase in the number of companies will not bring the desired effect, it is necessary to do everything for the development of existing ones. State policy should create the optimum conditions for doing business and encourage entrepreneurship. The main problem for small and mediumsized businesses in our country - poor business climate. To improve it, you need to apply the policy of deregulation, of which there is much talk in recent years. So you can get rid of the bureaucracy in the business environment and to simplify governance. Deregulation will be a breath of fresh air for small businesses, which are now a heavy burden the cost of compliance with tax rules and regulations. Deregulation brings investments to the Ukrainian economy • • The Ministry of Economic Development and Trade has responsibility of the deregulation of business. In 2015, the ministry has canceled 41% of permitting documents, removed more than 100 regulatory barriers and reduced business registration up to two days. Also, the Ministry has canceled about 13 thousand Soviet state standards. This has allowed Ukraine to rise in the ranking of Doing Business with 87 places on the 83. Advancement even one step in this rating can count on the billions of dollars of investment. State Regulatory Service of Ukraine in the past year has taken care of the problem with cash registers. Now they are obliged to use only enterprises with a turnover of more than 1 million USD.
Small companies have to pay dearly for bureaucracy • • • Since the increase in the number of companies will not bring the desired effect, it is necessary to do everything for the development of existing ones. State policy should create the optimum conditions for doing business and encourage entrepreneurship. The main problem for small and mediumsized businesses in our country - poor business climate. To improve it, you need to apply the policy of deregulation, of which there is much talk in recent years. So you can get rid of the bureaucracy in the business environment and to simplify governance. Deregulation will be a breath of fresh air for small businesses, which are now a heavy burden the cost of compliance with tax rules and regulations. Deregulation brings investments to the Ukrainian economy • • The Ministry of Economic Development and Trade has responsibility of the deregulation of business. In 2015, the ministry has canceled 41% of permitting documents, removed more than 100 regulatory barriers and reduced business registration up to two days. Also, the Ministry has canceled about 13 thousand Soviet state standards. This has allowed Ukraine to rise in the ranking of Doing Business with 87 places on the 83. Advancement even one step in this rating can count on the billions of dollars of investment. State Regulatory Service of Ukraine in the past year has taken care of the problem with cash registers. Now they are obliged to use only enterprises with a turnover of more than 1 million USD.
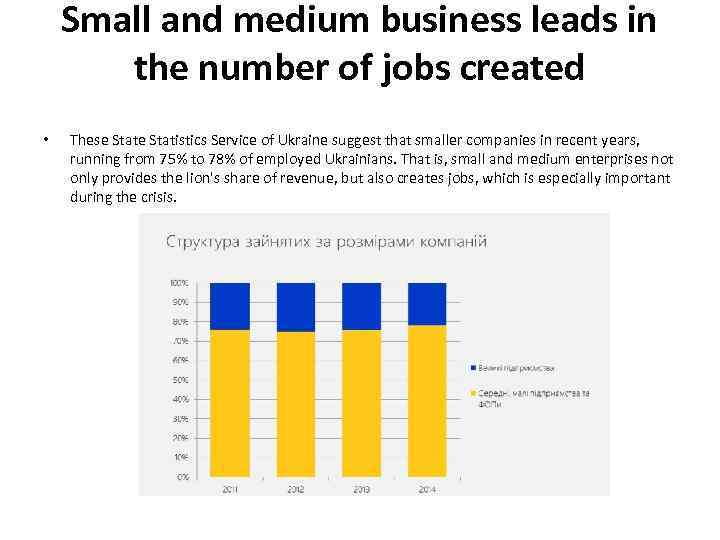 Small and medium business leads in the number of jobs created • These Statistics Service of Ukraine suggest that smaller companies in recent years, running from 75% to 78% of employed Ukrainians. That is, small and medium enterprises not only provides the lion's share of revenue, but also creates jobs, which is especially important during the crisis.
Small and medium business leads in the number of jobs created • These Statistics Service of Ukraine suggest that smaller companies in recent years, running from 75% to 78% of employed Ukrainians. That is, small and medium enterprises not only provides the lion's share of revenue, but also creates jobs, which is especially important during the crisis.
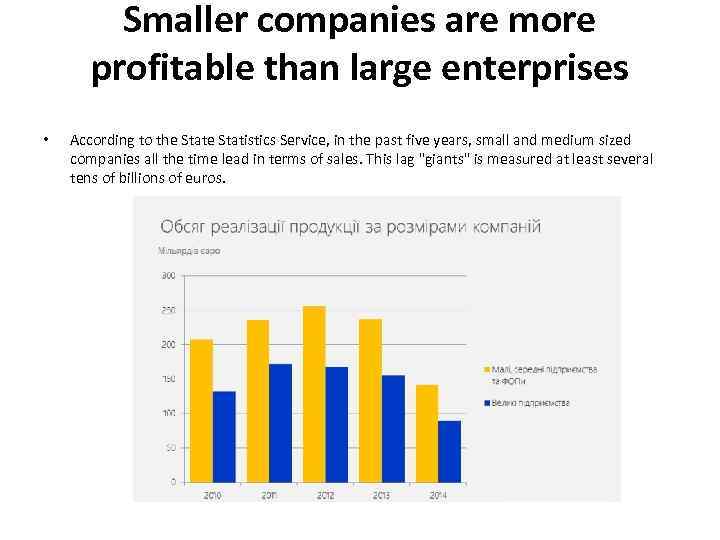 Smaller companies are more profitable than large enterprises • According to the Statistics Service, in the past five years, small and medium sized companies all the time lead in terms of sales. This lag "giants" is measured at least several tens of billions of euros.
Smaller companies are more profitable than large enterprises • According to the Statistics Service, in the past five years, small and medium sized companies all the time lead in terms of sales. This lag "giants" is measured at least several tens of billions of euros.


