f1a18055df5088106b201b6b185e85b5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Economics 4 Fajardo
Economics 4 Fajardo
 Development and Growth Development is a progressive and dynamic process. Growth is the result of the development. Therefore, growth is the product of development
Development and Growth Development is a progressive and dynamic process. Growth is the result of the development. Therefore, growth is the product of development
 For example Modern methods in planting tobacco involve a process, and this is development itself. Better harvests
For example Modern methods in planting tobacco involve a process, and this is development itself. Better harvests
 Economic growth is visible and measurable. Examples: Roads, vehicles, buildings, hospitals, banks, schools, etc. product of development
Economic growth is visible and measurable. Examples: Roads, vehicles, buildings, hospitals, banks, schools, etc. product of development
 Economic growths does not stop. It has to create more and better goods and services. In the LR, economic development embraces series of economic growths. Thus, earlier economic growths help subsequent economic development.
Economic growths does not stop. It has to create more and better goods and services. In the LR, economic development embraces series of economic growths. Thus, earlier economic growths help subsequent economic development.
 Growth without development? Whenever there is real development, there will be growth because growth is a natural consequence of development. Development without growth is inconceivable.
Growth without development? Whenever there is real development, there will be growth because growth is a natural consequence of development. Development without growth is inconceivable.
 The Objectives of Development In the past, the traditional national objective of the LDCs was to increase the GNP. Empphasis was given to material or economic progress.
The Objectives of Development In the past, the traditional national objective of the LDCs was to increase the GNP. Empphasis was given to material or economic progress.
 1982 550 billion 1983 700 billion
1982 550 billion 1983 700 billion
 However, the above example is not conclusive. And in many developing countries, despite the perceptible economic growth, social and economic conditions are deteriorating.
However, the above example is not conclusive. And in many developing countries, despite the perceptible economic growth, social and economic conditions are deteriorating.
 The reason for this has been obvious to the common people. The fruits of development have not reached to them.
The reason for this has been obvious to the common people. The fruits of development have not reached to them.
 Only the few top government officials, big landlords, and business tycoons have benefited. Government programs are in the wrong directions.
Only the few top government officials, big landlords, and business tycoons have benefited. Government programs are in the wrong directions.
 The leaders of the developing countries have realized the root causes of such depressed situations. Thus, the main focus now of development is towards the social factors.
The leaders of the developing countries have realized the root causes of such depressed situations. Thus, the main focus now of development is towards the social factors.
 Philippine Development Objectives According to Prime Minister Cesar Virata, the government has been committed to attain the 3 basic objectives which are concerned with: A. The attainment of economic stability B. The equitable distribution of the fruits of economic development C. The achievement of total human development for every Filipino.
Philippine Development Objectives According to Prime Minister Cesar Virata, the government has been committed to attain the 3 basic objectives which are concerned with: A. The attainment of economic stability B. The equitable distribution of the fruits of economic development C. The achievement of total human development for every Filipino.
 Obstacles to Development 1. Poor nations are deficient in capital 2. Another obstacle is the population explosion. 3. The greatest obstacle to econopmic development is man himself.
Obstacles to Development 1. Poor nations are deficient in capital 2. Another obstacle is the population explosion. 3. The greatest obstacle to econopmic development is man himself.
 Stages of Growth The development of nations encompasses an evolutionary process from the primitive to modern societies. However, there are societies that have until now remained primitive in their economic, social, and political insitutions.
Stages of Growth The development of nations encompasses an evolutionary process from the primitive to modern societies. However, there are societies that have until now remained primitive in their economic, social, and political insitutions.
 The industrial revolution which began in the late 1700’s in England paved the rapid economic growth of Western Europe and in the United States. Since that time, the economic historians have searched a theory that would appropriately describe the natural economic revolution that all nations will undergo through.
The industrial revolution which began in the late 1700’s in England paved the rapid economic growth of Western Europe and in the United States. Since that time, the economic historians have searched a theory that would appropriately describe the natural economic revolution that all nations will undergo through.
 One approach is the stages of economic growth based on exchange systems. That is in the form of barter economy to the money economy, and finally to a credit economy.
One approach is the stages of economic growth based on exchange systems. That is in the form of barter economy to the money economy, and finally to a credit economy.
 Another way of categorizing the stages of growth is through dominant productive sectors in the economy. According to this theory as stated by the British economist Colin Clark, these are three stages involved:
Another way of categorizing the stages of growth is through dominant productive sectors in the economy. According to this theory as stated by the British economist Colin Clark, these are three stages involved:
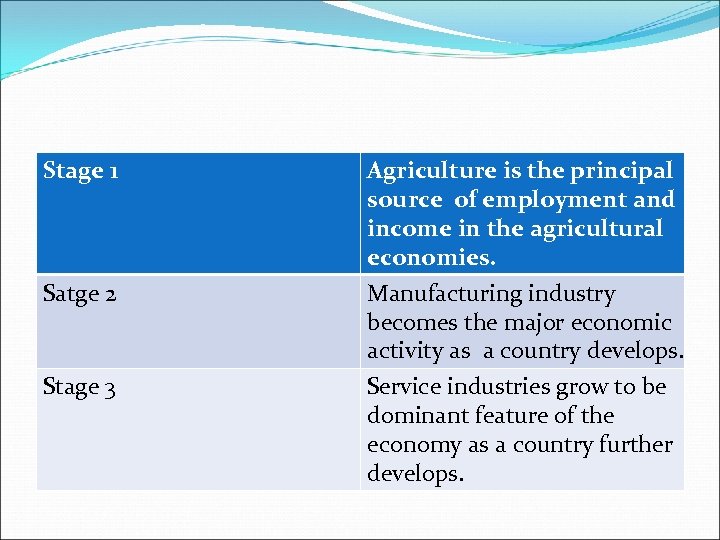 Stage 1 Satge 2 Stage 3 Agriculture is the principal source of employment and income in the agricultural economies. Manufacturing industry becomes the major economic activity as a country develops. Service industries grow to be dominant feature of the economy as a country further develops.
Stage 1 Satge 2 Stage 3 Agriculture is the principal source of employment and income in the agricultural economies. Manufacturing industry becomes the major economic activity as a country develops. Service industries grow to be dominant feature of the economy as a country further develops.
 The doctrine of Rostow Many other studies have been conducted on the stages of economic growth, However, the work of Professor Rostow, an American Economic historian appears to be the most popular.
The doctrine of Rostow Many other studies have been conducted on the stages of economic growth, However, the work of Professor Rostow, an American Economic historian appears to be the most popular.
 Base on the doctrine of Rostow, the transition of the economy of one country from underdevelopment to development passes through several stages such as: 1. Traditional Society 2. Preconditions for take-off 3. Take-Off 4. Drive to Maturity 5. Age of High Mass Consumption
Base on the doctrine of Rostow, the transition of the economy of one country from underdevelopment to development passes through several stages such as: 1. Traditional Society 2. Preconditions for take-off 3. Take-Off 4. Drive to Maturity 5. Age of High Mass Consumption
 How can a poor country take-off? They need a big push to take off.
How can a poor country take-off? They need a big push to take off.
 But: It requires huge amount of money, Domestic saving are not enough for significant investments. Public administration is not only efficient but also corrupt.
But: It requires huge amount of money, Domestic saving are not enough for significant investments. Public administration is not only efficient but also corrupt.
 And Population explosion Rich countries still continue to exploit them- their laborers, raw materials, and markets.
And Population explosion Rich countries still continue to exploit them- their laborers, raw materials, and markets.
 All over the world, 800 million individual live in extreme poverty. Most of them are found in Africa, Asia and Latin America (Central and South America)
All over the world, 800 million individual live in extreme poverty. Most of them are found in Africa, Asia and Latin America (Central and South America)
 It has been said that God did nit create poverty, Poverty is a product of defective man-made institutions.
It has been said that God did nit create poverty, Poverty is a product of defective man-made institutions.
 Social, economic and political institutions do not hamper development but are also inhuman,
Social, economic and political institutions do not hamper development but are also inhuman,
 A Good Economic System An economic system is responsible for improving economic conditions of the people.
A Good Economic System An economic system is responsible for improving economic conditions of the people.
 However economic condition does not only mean material sufficiency like money, food or houses. It also includes economic freedoms and justice.
However economic condition does not only mean material sufficiency like money, food or houses. It also includes economic freedoms and justice.
 A person who has plenty of food to eat and clothes to wear, but could not choose his job or he has no freedom to choose how and where to spend his income, is certainly not happy.
A person who has plenty of food to eat and clothes to wear, but could not choose his job or he has no freedom to choose how and where to spend his income, is certainly not happy.
 The effectiveness of an economic system is measured by the following criteria: Abundance Stability Security Growth Efficiency Justice and equity
The effectiveness of an economic system is measured by the following criteria: Abundance Stability Security Growth Efficiency Justice and equity
 The needs of the poor masses are simple. They have no love for expensive jewelries, palaces, sleek cars, and other noticeable display of wealth. All they really dream are their basic needs, the college education of their children, and some modest properties like a decent house.
The needs of the poor masses are simple. They have no love for expensive jewelries, palaces, sleek cars, and other noticeable display of wealth. All they really dream are their basic needs, the college education of their children, and some modest properties like a decent house.
 The real test of a good economic system is the welfare of the poorest of the poor. If the goods and services of the system have touched their lives, and they are contented, then it is a good economic system.
The real test of a good economic system is the welfare of the poorest of the poor. If the goods and services of the system have touched their lives, and they are contented, then it is a good economic system.




