ebdab5e59e96e14fd7e6f39c02d48896.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Economic Framework
Economic Framework
 Overview • • What is Economics? What are the Factors of Production? Needs v Wants Opportunity Cost Economic Systems Economic Growth Inflation Interest Rates
Overview • • What is Economics? What are the Factors of Production? Needs v Wants Opportunity Cost Economic Systems Economic Growth Inflation Interest Rates
 Economics • Is the study of how individuals, businesses and governments with limited resources make choices.
Economics • Is the study of how individuals, businesses and governments with limited resources make choices.
 Resources • Are things such as land, machinery, workers, materials, oil, crops, money. • They are used in the production of goods and services.
Resources • Are things such as land, machinery, workers, materials, oil, crops, money. • They are used in the production of goods and services.
 The Factors of Production • Are those scarce resources which we use to produce wealth.
The Factors of Production • Are those scarce resources which we use to produce wealth.
 4 Factors of Production • Land • Labour • Capital • Enterprise
4 Factors of Production • Land • Labour • Capital • Enterprise
 Land • All things supplied by nature. • Eg. water, natural gas, oil, coal, minerals, trees……. . • The payment/reward for land is rent.
Land • All things supplied by nature. • Eg. water, natural gas, oil, coal, minerals, trees……. . • The payment/reward for land is rent.
 Labour • The human element in the production process. • Eg. employees, builders, carpenters, factory workers…. . • The reward for labour is wages.
Labour • The human element in the production process. • Eg. employees, builders, carpenters, factory workers…. . • The reward for labour is wages.
 Capital • All man-made things that help produce goods. • Buildings, machinery… • The reward for capital investment is interest.
Capital • All man-made things that help produce goods. • Buildings, machinery… • The reward for capital investment is interest.
 Enterprise • Taking the risk to sell new product/idea. . • Eg. Bill Cullen, Richard Branson… • The reward for enterprise is profit. • The risk of enterprise is loss.
Enterprise • Taking the risk to sell new product/idea. . • Eg. Bill Cullen, Richard Branson… • The reward for enterprise is profit. • The risk of enterprise is loss.
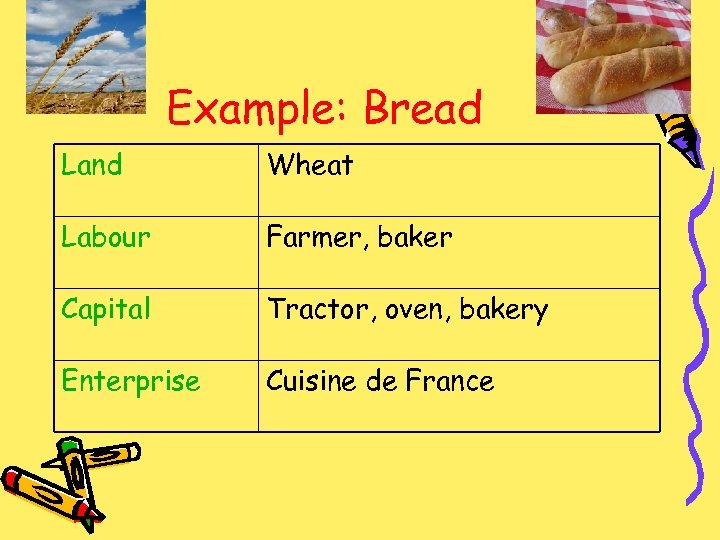 Example: Bread Land Wheat Labour Farmer, baker Capital Tractor, oven, bakery Enterprise Cuisine de France
Example: Bread Land Wheat Labour Farmer, baker Capital Tractor, oven, bakery Enterprise Cuisine de France
 Needs • Are essentials required for survival. • Basic needs. • Food, shelter, clothing.
Needs • Are essentials required for survival. • Basic needs. • Food, shelter, clothing.
 Wants • Are anything in excess of our needs. • Things we can live without. • TV, holidays, i-pod………………
Wants • Are anything in excess of our needs. • Things we can live without. • TV, holidays, i-pod………………
 Opportunity Cost • The opportunity cost is the sacrifice of the item you must do without when you have to make a choice between two items you want to produce or purchase.
Opportunity Cost • The opportunity cost is the sacrifice of the item you must do without when you have to make a choice between two items you want to produce or purchase.
 Opportunity Cost • • • Example I have € 2. 00. I can buy ice-cream or Pringles. I choose ice-cream. Financial cost = € 2. 00 Opportunity cost = Pringles.
Opportunity Cost • • • Example I have € 2. 00. I can buy ice-cream or Pringles. I choose ice-cream. Financial cost = € 2. 00 Opportunity cost = Pringles.
 Economic System Is how a country makes decisions about their factors of production. An Economic System is important to ensure the economy is controlled and run properly.
Economic System Is how a country makes decisions about their factors of production. An Economic System is important to ensure the economy is controlled and run properly.
 1. Centrally Planned Economy Communism • All industries are owned & controlled by the government. Eg China
1. Centrally Planned Economy Communism • All industries are owned & controlled by the government. Eg China
 2. Free Enterprise Economy Capitalism • All industries are owned by private entrepreneurs. Eg. USA (is the closest to free market model)
2. Free Enterprise Economy Capitalism • All industries are owned by private entrepreneurs. Eg. USA (is the closest to free market model)
 3. Mixed Economy • Some industries are controlled by the government & some are controlled by private entrepreneurs (business people). Eg. Ireland
3. Mixed Economy • Some industries are controlled by the government & some are controlled by private entrepreneurs (business people). Eg. Ireland
 Economic Growth • Occurs where there is an increase in the amount of goods and services produced in a country from one year to the next.
Economic Growth • Occurs where there is an increase in the amount of goods and services produced in a country from one year to the next.
 Advantages of economic growth • Increase in standard of living • More employment will be create • More money available for social welfare, health and education
Advantages of economic growth • Increase in standard of living • More employment will be create • More money available for social welfare, health and education
 Explain • • GNP Gross National Product GDP Gross Domestic Product • The total amount produced in a country. • + = Growth • - = Recession
Explain • • GNP Gross National Product GDP Gross Domestic Product • The total amount produced in a country. • + = Growth • - = Recession
 Formula • Change • Original X 100
Formula • Change • Original X 100
 Example 1 • 2009 100 million produced in Ireland • 2010 95 million produced in Ireland • - 5 million • 100 million X 100 = -5% Recession
Example 1 • 2009 100 million produced in Ireland • 2010 95 million produced in Ireland • - 5 million • 100 million X 100 = -5% Recession
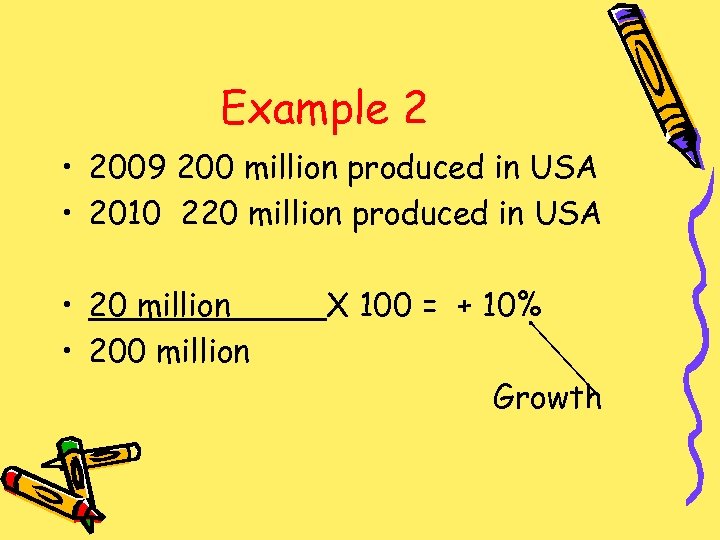 Example 2 • 2009 200 million produced in USA • 2010 220 million produced in USA • 20 million • 200 million X 100 = + 10% Growth
Example 2 • 2009 200 million produced in USA • 2010 220 million produced in USA • 20 million • 200 million X 100 = + 10% Growth
 Inflation • Is an increase in the general level of prices/cost of living from one year to the next. • It is calculated by the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Inflation • Is an increase in the general level of prices/cost of living from one year to the next. • It is calculated by the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
 Consumer Price Index • Is the measure of inflation. • The Central Statistics Office (CSO) conducts a survey of prices every few months. • This tells us if prices are rising or not.
Consumer Price Index • Is the measure of inflation. • The Central Statistics Office (CSO) conducts a survey of prices every few months. • This tells us if prices are rising or not.
 What causes inflation? • Too much money in circulation. • Interest rates too low. • Increase in oil prices.
What causes inflation? • Too much money in circulation. • Interest rates too low. • Increase in oil prices.
 ECB • The European Central Bank tries to control inflation. • See Inflation Monster DVD
ECB • The European Central Bank tries to control inflation. • See Inflation Monster DVD
 Formula for calculating rate of inflation Increase in price x 100% _______ Original Price
Formula for calculating rate of inflation Increase in price x 100% _______ Original Price
 Example • Cost of living in 2007 is € 9000 • Cost of living in 2008 is € 9600 • Rate of Inflation = € 600 x 100% ____ € 9000 • =6. 6%
Example • Cost of living in 2007 is € 9000 • Cost of living in 2008 is € 9600 • Rate of Inflation = € 600 x 100% ____ € 9000 • =6. 6%
 Benefits of low inflation • Economic growth is aided • Prices are stable • Wage demands are lower
Benefits of low inflation • Economic growth is aided • Prices are stable • Wage demands are lower
 Deflation • Is when prices are falling. • While this may seem good it is not. • Consumers will delay spending in case prices fall further. • This may lead to unemployment.
Deflation • Is when prices are falling. • While this may seem good it is not. • Consumers will delay spending in case prices fall further. • This may lead to unemployment.
 Interest Rates • Is the cost of borrowing. • Irish rates are controlled by the European Central Bank
Interest Rates • Is the cost of borrowing. • Irish rates are controlled by the European Central Bank
 Benefits of low interest rates • Mortgages and loans will be cheaper. • Encourages new investment. • Increased consumer spending.
Benefits of low interest rates • Mortgages and loans will be cheaper. • Encourages new investment. • Increased consumer spending.
 Disadvantages of high interest rates • Discourages new investment. • Reduces consumer demand. • Increases business costs.
Disadvantages of high interest rates • Discourages new investment. • Reduces consumer demand. • Increases business costs.
 Recap • • What is Economics? What are the Factors of Production? Needs v Wants Opportunity Cost Economic Systems Economic Growth Inflation Interest Rates
Recap • • What is Economics? What are the Factors of Production? Needs v Wants Opportunity Cost Economic Systems Economic Growth Inflation Interest Rates



