b6cfc99c0986c1d27e105a4a80f6d659.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 Econ 338 c Review 4/26/07
Econ 338 c Review 4/26/07


 Time needed to complete Corn Planings • U. S. About 24 days with perfect weather – Likely completion date: around May 30 – Days beyond optimum: about 21 days – Yield impact: about 0. 4% decrease/day after 5/10? • Iowa About 18 days with perfect weather – Likely completion date: around May 22 – Potential % of crop planted after May 10: • 60% • Yield impact?
Time needed to complete Corn Planings • U. S. About 24 days with perfect weather – Likely completion date: around May 30 – Days beyond optimum: about 21 days – Yield impact: about 0. 4% decrease/day after 5/10? • Iowa About 18 days with perfect weather – Likely completion date: around May 22 – Potential % of crop planted after May 10: • 60% • Yield impact?



 First & nd 4 th 2 Sessions • Big picture of global marketing system --Participants --Merchandising & arbitrage --5 Main economic- marketing functions --Sources of global competition --Some major trends—especially bio-energy --Price discovery mechanisms: futures mkts. • Marketing from a farmer perspective --Price-sensitive govt. payments --Importance of knowing farm finances --Basis: determining geographical price variations, analyzing marketing opportunities
First & nd 4 th 2 Sessions • Big picture of global marketing system --Participants --Merchandising & arbitrage --5 Main economic- marketing functions --Sources of global competition --Some major trends—especially bio-energy --Price discovery mechanisms: futures mkts. • Marketing from a farmer perspective --Price-sensitive govt. payments --Importance of knowing farm finances --Basis: determining geographical price variations, analyzing marketing opportunities
 Major Marketing Functions • Providing time utility • Providing form utility • Providing space utility • Financing • Price/value discovery
Major Marketing Functions • Providing time utility • Providing form utility • Providing space utility • Financing • Price/value discovery
 Key work area for Grain Merchandisers
Key work area for Grain Merchandisers




 Sources of information and rust location map: http: //www. sbrusa. net/ http: //www. plantpath. iasta te. edu/soybeanrust/
Sources of information and rust location map: http: //www. sbrusa. net/ http: //www. plantpath. iasta te. edu/soybeanrust/
 Overview of Grain Marketing • World futures markets (Price Discovery) – Chicago: corn, soft red wheat, soybeans, oats – Kansas City: hard red winter wheat – Minneapolis: hard spring and hard white wheat, Corn & Soybean cash index markets – Tokyo: GMO & non-GMO soybeans, corn – Various other futures markets: Brazil, Argentina, China, Europe – Foreign exchange futures
Overview of Grain Marketing • World futures markets (Price Discovery) – Chicago: corn, soft red wheat, soybeans, oats – Kansas City: hard red winter wheat – Minneapolis: hard spring and hard white wheat, Corn & Soybean cash index markets – Tokyo: GMO & non-GMO soybeans, corn – Various other futures markets: Brazil, Argentina, China, Europe – Foreign exchange futures
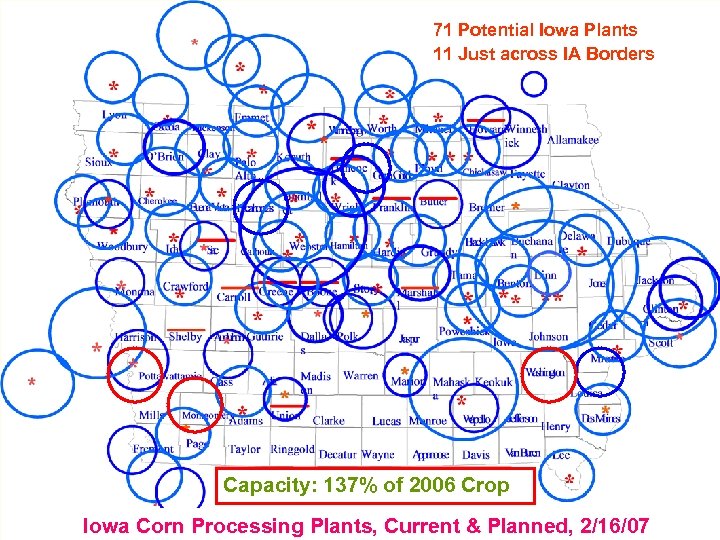 71 Potential Iowa Plants 11 Just across IA Borders Capacity: 137% of 2006 Crop Iowa Corn Processing Plants, Current & Planned, 2/16/07
71 Potential Iowa Plants 11 Just across IA Borders Capacity: 137% of 2006 Crop Iowa Corn Processing Plants, Current & Planned, 2/16/07
 Cost, Price & Yield
Cost, Price & Yield
 Major elements in producer grain marketing • External: world & govt. (need outlook info) • Historical record of price & farm yields • Farm financial needs • Pricing tools: new & old contracts • Production risk-control tools • Trigger pulling mechanism: Exit Plan • Evaluation: relative to market, producer costs & goals
Major elements in producer grain marketing • External: world & govt. (need outlook info) • Historical record of price & farm yields • Farm financial needs • Pricing tools: new & old contracts • Production risk-control tools • Trigger pulling mechanism: Exit Plan • Evaluation: relative to market, producer costs & goals
 Cash-Flow Risk Ratio: Percent of the crop required to be sold to cover cash-flow costs • Formula for computation: • Cash-flow break-even price divided by selling price
Cash-Flow Risk Ratio: Percent of the crop required to be sold to cover cash-flow costs • Formula for computation: • Cash-flow break-even price divided by selling price
 Net-Worth Risk Ratio • The maximum dollars per acre which can be lost in any one year before a predetermined percentage of the equity is lost.
Net-Worth Risk Ratio • The maximum dollars per acre which can be lost in any one year before a predetermined percentage of the equity is lost.
 Calculating Net-Worth Risk Ratio • Max. dollars of net worth to be placed at risk divided by number of acres = Max. $ that can be risked per acre • To compute max. loss per bu. : divide $/A. by normal yld. = $/bu. that can be risked for predetermined loss of equity
Calculating Net-Worth Risk Ratio • Max. dollars of net worth to be placed at risk divided by number of acres = Max. $ that can be risked per acre • To compute max. loss per bu. : divide $/A. by normal yld. = $/bu. that can be risked for predetermined loss of equity
 Govt. Payments • Loan Deficiency Pmts: Market Sensitive LDP is Positive if Posted County Price is Below Loan Rate: LDP = LR-PCP • Counter Cyclical Pmts: Market Sensitive CCP Paid if higher of $2. 35 -LR or $2. 35 U. S. Mktg. Year Avg. Price if positive • Direct Payment: Not Market Sensitive
Govt. Payments • Loan Deficiency Pmts: Market Sensitive LDP is Positive if Posted County Price is Below Loan Rate: LDP = LR-PCP • Counter Cyclical Pmts: Market Sensitive CCP Paid if higher of $2. 35 -LR or $2. 35 U. S. Mktg. Year Avg. Price if positive • Direct Payment: Not Market Sensitive
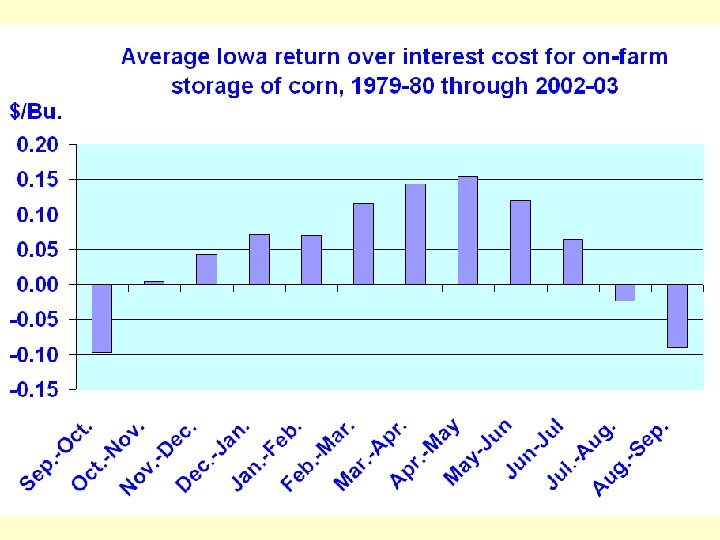
 Storage Economics • Costs to store on & off farm • Seasonality of prices • Harvest basis & carrying charge • Timing and amount of cash-flow needs
Storage Economics • Costs to store on & off farm • Seasonality of prices • Harvest basis & carrying charge • Timing and amount of cash-flow needs
 8 -Month. Storage Costs @ $2. 90 Corn On-farm • • • Shrinkage below 15% Extra drying Extra handling Interest (8%) Storage charge Quality deterioration & storage shrink • Total costs Off-farm $0. 073 (to 13%) 0. 047 0. 03 0. 152 (Fixed cost) $0. 039 0. 0425 0. 00 0. 152 0. 191 0. 029 $0. 331 0. 00 $0. 425
8 -Month. Storage Costs @ $2. 90 Corn On-farm • • • Shrinkage below 15% Extra drying Extra handling Interest (8%) Storage charge Quality deterioration & storage shrink • Total costs Off-farm $0. 073 (to 13%) 0. 047 0. 03 0. 152 (Fixed cost) $0. 039 0. 0425 0. 00 0. 152 0. 191 0. 029 $0. 331 0. 00 $0. 425
 8 -Month. Storage Costs @ $7. 00 Soybeans On-farm Off-farm • • Extra handling Interest (8%) Storage charge Quality deterioration & storage shrink Total costs 0. 03 0. 373 (Fixed cost) 0. 00 0. 373 0. 191 0. 029 $0. 425 0. 00 $0. 564
8 -Month. Storage Costs @ $7. 00 Soybeans On-farm Off-farm • • Extra handling Interest (8%) Storage charge Quality deterioration & storage shrink Total costs 0. 03 0. 373 (Fixed cost) 0. 00 0. 373 0. 191 0. 029 $0. 425 0. 00 $0. 564




 Traditional Grain Contracts • Forward Contract • Hedge to Arrive • Minimum Price • Basis contract • Delayed Payment contract • Price later contract • Premium offer contract
Traditional Grain Contracts • Forward Contract • Hedge to Arrive • Minimum Price • Basis contract • Delayed Payment contract • Price later contract • Premium offer contract


 If harvest Basis is strong • Market says sell now • If weak: Signals to store & hedge or use hta contract
If harvest Basis is strong • Market says sell now • If weak: Signals to store & hedge or use hta contract
 Traditional Grain Contracts • Forward contract: locks in price level, basis, spreads • Hedge to Arrive: does not lock in Basis • Basis Contract: locks in basis but not price • Price Later contract: doesn’t lock in either one (You lose ownership— cash out LDP first)
Traditional Grain Contracts • Forward contract: locks in price level, basis, spreads • Hedge to Arrive: does not lock in Basis • Basis Contract: locks in basis but not price • Price Later contract: doesn’t lock in either one (You lose ownership— cash out LDP first)
 Traditional Grain Contracts • Premium offer contract • Typically involves sale of options & farmer potential sale commitment in next season
Traditional Grain Contracts • Premium offer contract • Typically involves sale of options & farmer potential sale commitment in next season
 Credit-Sale Contracts • Ownership is transferred to elevator • Protection of warehouse receipts is not available • In case of elevator bankruptcy, farmer becomes just another creditor • Warehouse receipts give 1 st claim on assets in bankruptcy
Credit-Sale Contracts • Ownership is transferred to elevator • Protection of warehouse receipts is not available • In case of elevator bankruptcy, farmer becomes just another creditor • Warehouse receipts give 1 st claim on assets in bankruptcy
 Credit-Sale Contracts • Delayed Price or Price Later contracts • Basis Contracts (often less risk exposure) • Delayed Payment contracts
Credit-Sale Contracts • Delayed Price or Price Later contracts • Basis Contracts (often less risk exposure) • Delayed Payment contracts
 Grain Contracts: Areas of Risk Exposure • • Price Level Basis Spreads (Intra-and Inter-Year) Options volatility risk Production risk Counter-party or business risk Control risk Tax risk
Grain Contracts: Areas of Risk Exposure • • Price Level Basis Spreads (Intra-and Inter-Year) Options volatility risk Production risk Counter-party or business risk Control risk Tax risk
 Refresher on Options Markets • Two Types: Puts & Calls (CBOT) • Buying Puts: Insure against lower prices • Buying Calls: lets you follow market higher after a cash sale • No further market expense after buying • Cost: premium plus brokerage charge • Selling puts: you have an obligation to buy grain at strike price if market goes lower • Maximum gain = initial premium (loss no limit)
Refresher on Options Markets • Two Types: Puts & Calls (CBOT) • Buying Puts: Insure against lower prices • Buying Calls: lets you follow market higher after a cash sale • No further market expense after buying • Cost: premium plus brokerage charge • Selling puts: you have an obligation to buy grain at strike price if market goes lower • Maximum gain = initial premium (loss no limit)
 Options Definitions: Put: Buying the right but not the obligation to sell underlying futures contract at a specific price Call: Buying the right but not the obligation to buy underlying futures contract at a specific price
Options Definitions: Put: Buying the right but not the obligation to sell underlying futures contract at a specific price Call: Buying the right but not the obligation to buy underlying futures contract at a specific price
 Options: factors affecting PREMIUM LEVELS A. STRIKE PRICE vs. FUTURES B. TIME REMAINING before expiration C. VOLATILITY OF FUTURES D. INTEREST RATES
Options: factors affecting PREMIUM LEVELS A. STRIKE PRICE vs. FUTURES B. TIME REMAINING before expiration C. VOLATILITY OF FUTURES D. INTEREST RATES
 Options Summary A. Buy Puts to set floor price --No further financial exposure after initial purchase B. Buy Calls to retain ownership after sale -- No further financial exposure after initial purchase C. Caution: options can expire worthless. Plan exit strategy.
Options Summary A. Buy Puts to set floor price --No further financial exposure after initial purchase B. Buy Calls to retain ownership after sale -- No further financial exposure after initial purchase C. Caution: options can expire worthless. Plan exit strategy.
 Storage Returns Study • Storing corn without pricing on average lost money, esp. off-farm • Corn storage & hedging made small profits, with less year-to-year variability • Soybean storage: you would have to work hard to make bean storage pay— on average. • Iowa exit strategy: Typically in May on farm, Jan-Feb. off farm
Storage Returns Study • Storing corn without pricing on average lost money, esp. off-farm • Corn storage & hedging made small profits, with less year-to-year variability • Soybean storage: you would have to work hard to make bean storage pay— on average. • Iowa exit strategy: Typically in May on farm, Jan-Feb. off farm


 New Generation Grain-Marketing Contracts (NGC) Pg. 3 1. Automated pricing (averaging) Cargill Pro. Pricing (A+) 2. Managed hedging Cargill Pro. Pricing Market Pros 3. Combination contracts Decision Commodities (Rally) – Cargill Pro. Pricing (Target Range)
New Generation Grain-Marketing Contracts (NGC) Pg. 3 1. Automated pricing (averaging) Cargill Pro. Pricing (A+) 2. Managed hedging Cargill Pro. Pricing Market Pros 3. Combination contracts Decision Commodities (Rally) – Cargill Pro. Pricing (Target Range)

 Advisory Service Performance • 7 -year study period, 15 -16 services for entire period • Many services didn’t last entire period • For many, performance varied widely from year to year
Advisory Service Performance • 7 -year study period, 15 -16 services for entire period • Many services didn’t last entire period • For many, performance varied widely from year to year
 Crop insurance • Importance depends some on location • Depends on how much grain you price before harvest • Harvest-price revenue insurance: an important companion tool for use with pre-harvest pricing
Crop insurance • Importance depends some on location • Depends on how much grain you price before harvest • Harvest-price revenue insurance: an important companion tool for use with pre-harvest pricing
 10 Traits of a Successful Grain Marketer 1. Starts Early (before planting) 2. Knows production, storage costs & risk bearing ability 3. Understands basis & mkt. carry 4. Follows several relevant markets daily 5. Manages yield risk with revenue insurance 6. Has discipline to price when goals are reached 7. Knows various contracts & when to use them 8. Relies on good sources of market information 9. Has an exit plan 10. Keeps marketing records & evaluates results
10 Traits of a Successful Grain Marketer 1. Starts Early (before planting) 2. Knows production, storage costs & risk bearing ability 3. Understands basis & mkt. carry 4. Follows several relevant markets daily 5. Manages yield risk with revenue insurance 6. Has discipline to price when goals are reached 7. Knows various contracts & when to use them 8. Relies on good sources of market information 9. Has an exit plan 10. Keeps marketing records & evaluates results
 Key Points • Starting point in a mktg plan: financial needs of the business • Know your break-even price • Know your risk-bearing ability • Plan marketing with a goal of at least covering cash-flow needs • Look for mktg. & insurance tools to minimize risk of losing the business Start Early
Key Points • Starting point in a mktg plan: financial needs of the business • Know your break-even price • Know your risk-bearing ability • Plan marketing with a goal of at least covering cash-flow needs • Look for mktg. & insurance tools to minimize risk of losing the business Start Early


