 ECON 308 Week 6 Chapter 6: Market Structure
ECON 308 Week 6 Chapter 6: Market Structure
 Market structure: Objectives • Students should be able to • Differentiate among the four archetypal market structures • Distinguish between price takers and price searchers
Market structure: Objectives • Students should be able to • Differentiate among the four archetypal market structures • Distinguish between price takers and price searchers
 Market structure • What is a market? • All firms and individuals willing and able to buy or sell a particular product • What is market structure? • Defined by attributes of the market environment
Market structure • What is a market? • All firms and individuals willing and able to buy or sell a particular product • What is market structure? • Defined by attributes of the market environment
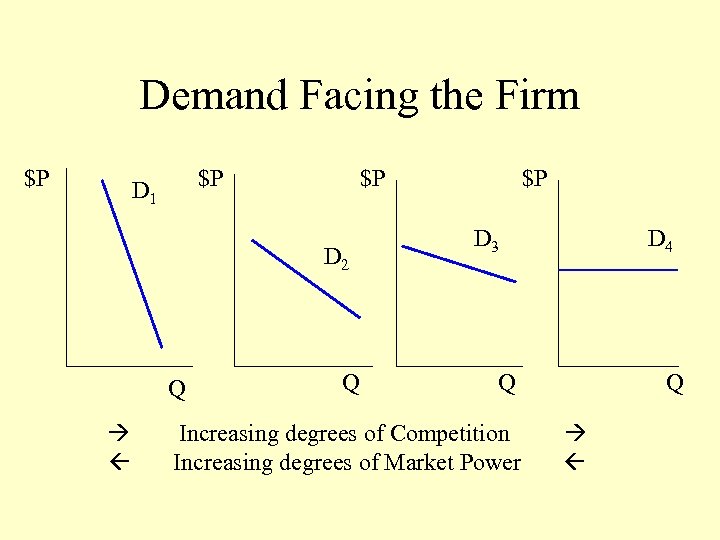 Demand Facing the Firm $P $P D 1 $P D 2 Q Q $P D 3 D 4 Q Increasing degrees of Competition Increasing degrees of Market Power Q
Demand Facing the Firm $P $P D 1 $P D 2 Q Q $P D 3 D 4 Q Increasing degrees of Competition Increasing degrees of Market Power Q
 Market structure the archetypes • • Monopoly Oligopoly Monopolistic competition Perfect competition
Market structure the archetypes • • Monopoly Oligopoly Monopolistic competition Perfect competition
 Alternative Market Structures The Most Competitive Case: The Price Taker Firm
Alternative Market Structures The Most Competitive Case: The Price Taker Firm
 Perfect competition = Price Taker Characteristics • • Many buyers and sellers Product homogeneity Low cost and accurate information Free entry and exit • Best regarded as a benchmark
Perfect competition = Price Taker Characteristics • • Many buyers and sellers Product homogeneity Low cost and accurate information Free entry and exit • Best regarded as a benchmark
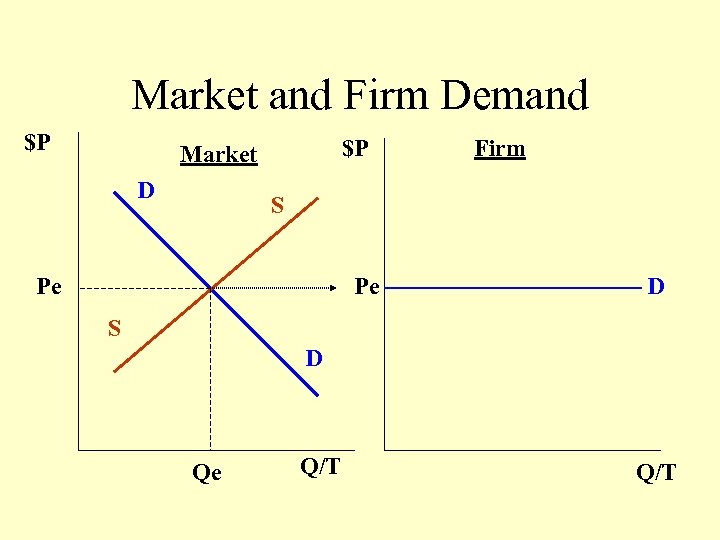 Market and Firm Demand $P $P Market D Firm S Pe Pe D S D Qe Q/T
Market and Firm Demand $P $P Market D Firm S Pe Pe D S D Qe Q/T
 Firm supply • Short run – Marginal cost curve above average variable cost – P* = SRMC • Long run – Long-run marginal cost curve above long-run average cost
Firm supply • Short run – Marginal cost curve above average variable cost – P* = SRMC • Long run – Long-run marginal cost curve above long-run average cost
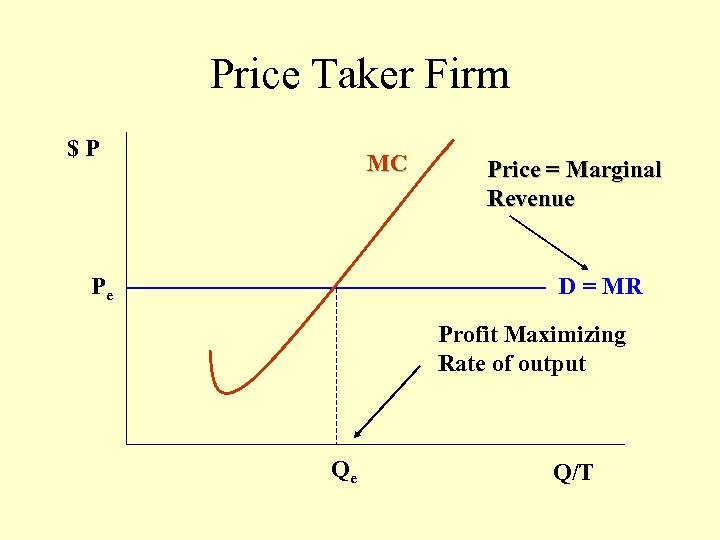 Price Taker Firm $P MC Pe Price = Marginal Revenue D = MR Profit Maximizing Rate of output Qe Q/T
Price Taker Firm $P MC Pe Price = Marginal Revenue D = MR Profit Maximizing Rate of output Qe Q/T
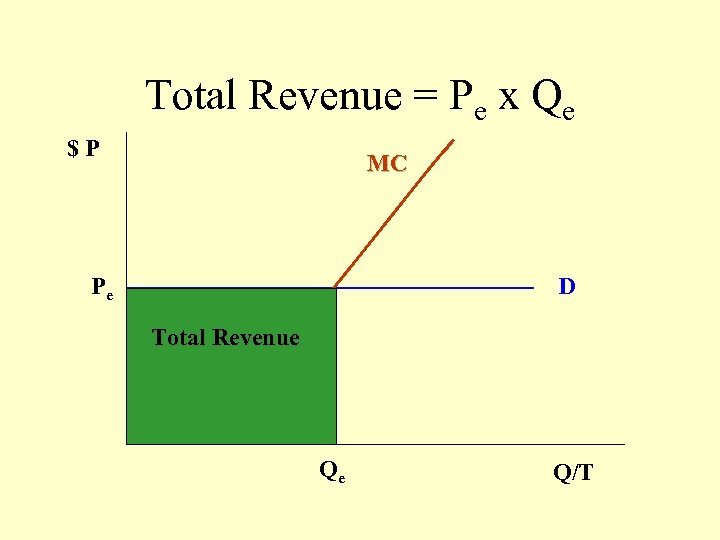 Total Revenue = Pe x Qe $P MC Pe D Total Revenue Qe Q/T
Total Revenue = Pe x Qe $P MC Pe D Total Revenue Qe Q/T
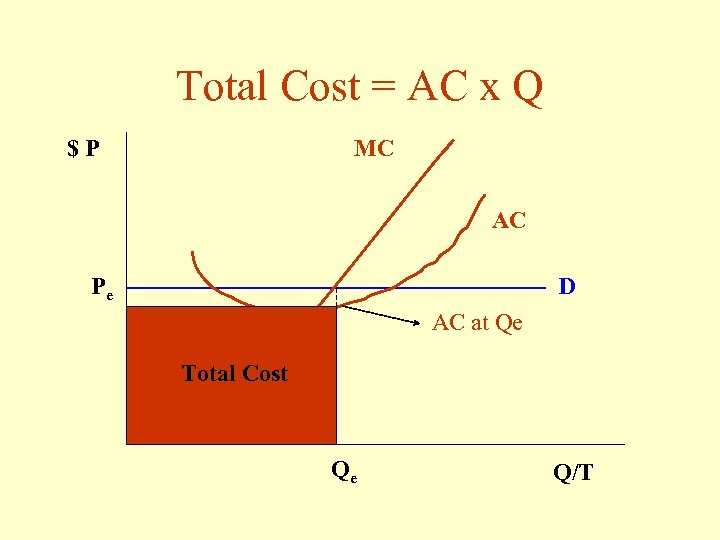 Total Cost = AC x Q $P MC AC Pe D AC at Qe Total Cost Qe Q/T
Total Cost = AC x Q $P MC AC Pe D AC at Qe Total Cost Qe Q/T
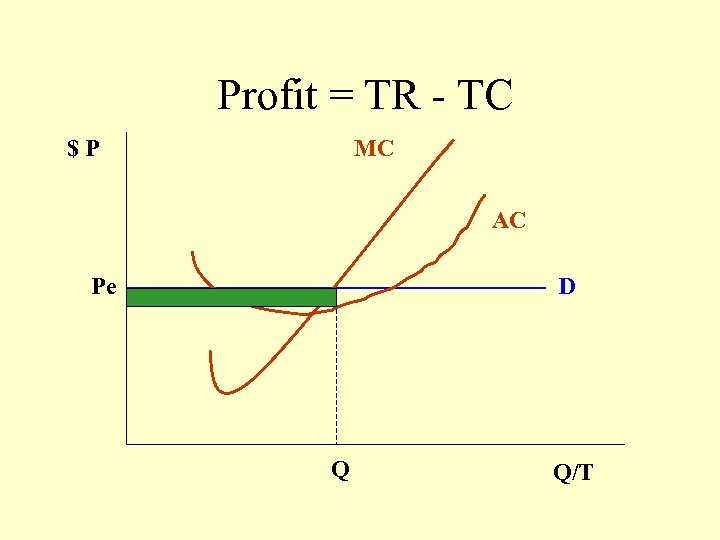 Profit = TR - TC $P MC AC Pe D Q Q/T
Profit = TR - TC $P MC AC Pe D Q Q/T
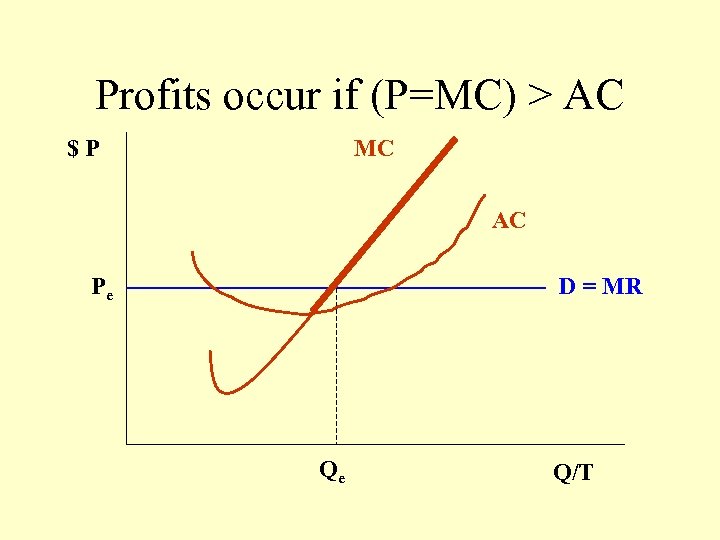 Profits occur if (P=MC) > AC $P MC AC Pe D = MR Qe Q/T
Profits occur if (P=MC) > AC $P MC AC Pe D = MR Qe Q/T
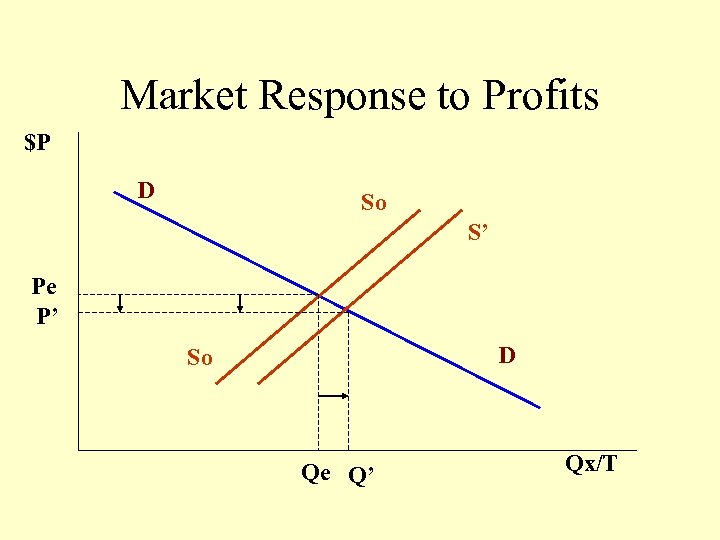 Market Response to Profits $P D So S’ Pe P’ D So Qe Q’ Qx/T
Market Response to Profits $P D So S’ Pe P’ D So Qe Q’ Qx/T
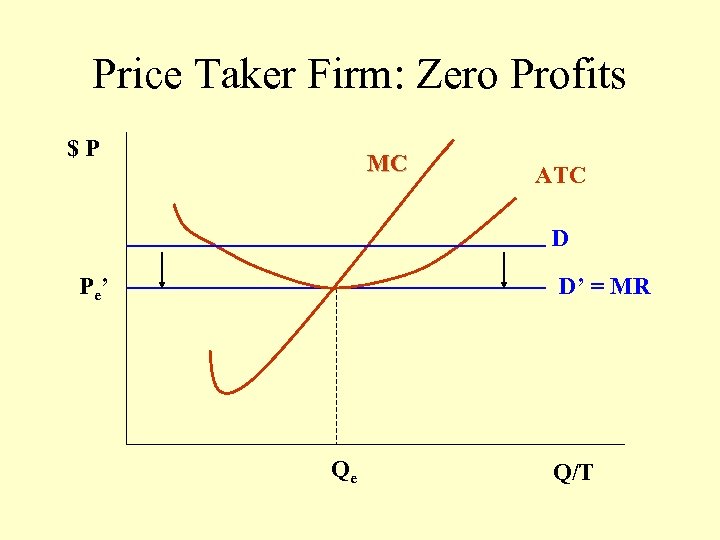 Price Taker Firm: Zero Profits $P MC ATC D P e’ D’ = MR Qe Q/T
Price Taker Firm: Zero Profits $P MC ATC D P e’ D’ = MR Qe Q/T
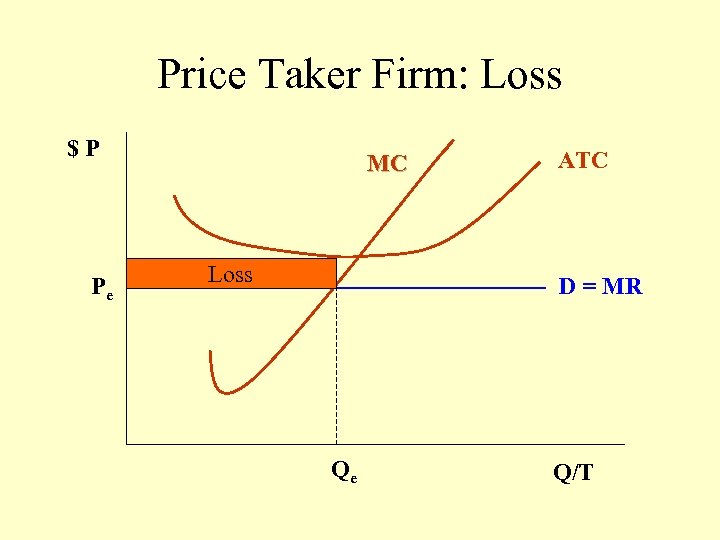 Price Taker Firm: Loss $P Pe MC Loss ATC D = MR Qe Q/T
Price Taker Firm: Loss $P Pe MC Loss ATC D = MR Qe Q/T
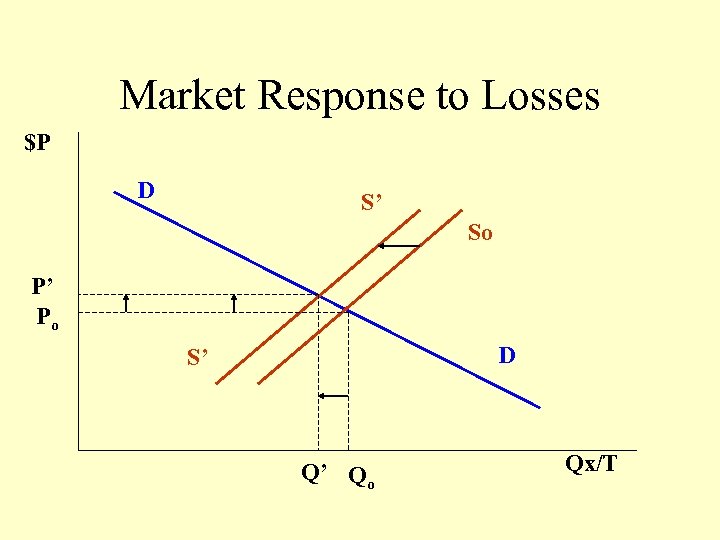 Market Response to Losses $P D S’ So P’ Po D S’ Q’ Qo Qx/T
Market Response to Losses $P D S’ So P’ Po D S’ Q’ Qo Qx/T
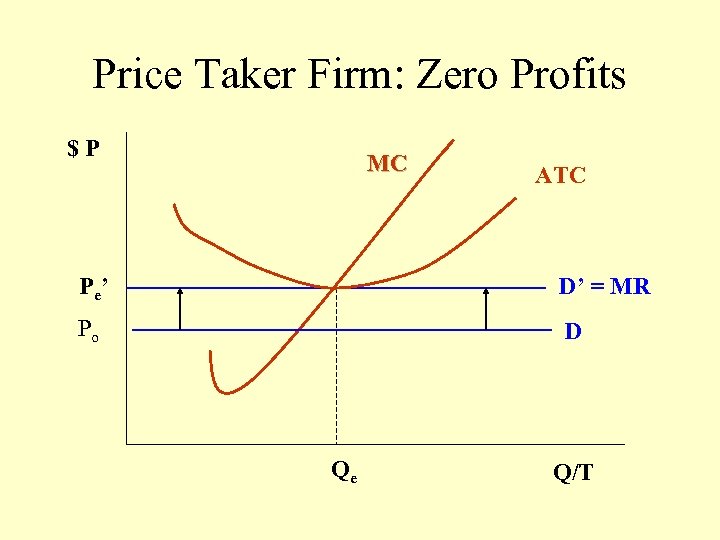 Price Taker Firm: Zero Profits $P MC ATC P e’ D’ = MR Po D Qe Q/T
Price Taker Firm: Zero Profits $P MC ATC P e’ D’ = MR Po D Qe Q/T
 Implications of Price-Taker Industry • Demand for the firm is horizontal at the market price • Efficiency: Price equals marginal cost of production • Competition drives price to equal Average cost • Economic profits only exist in the short-run.
Implications of Price-Taker Industry • Demand for the firm is horizontal at the market price • Efficiency: Price equals marginal cost of production • Competition drives price to equal Average cost • Economic profits only exist in the short-run.
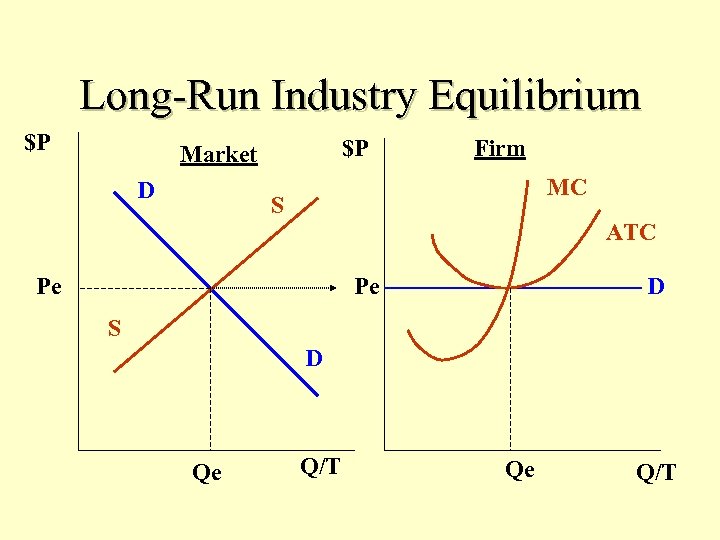 Long-Run Industry Equilibrium $P $P Market D Firm MC S ATC Pe Pe D S D Qe Q/T
Long-Run Industry Equilibrium $P $P Market D Firm MC S ATC Pe Pe D S D Qe Q/T
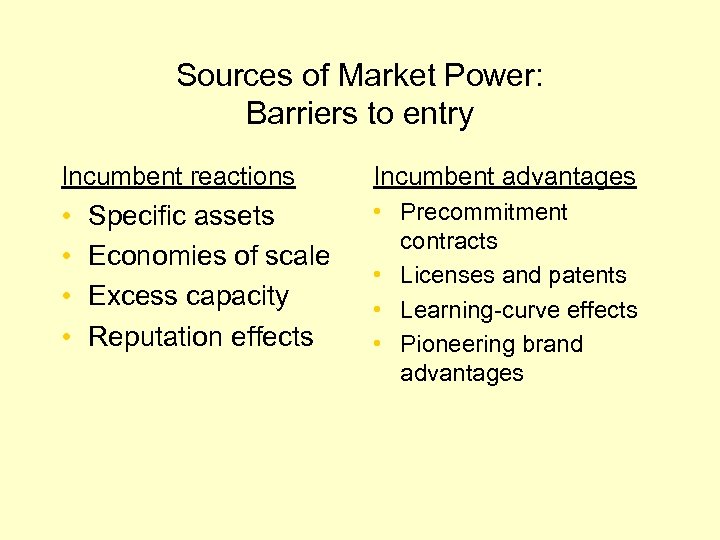 Sources of Market Power: Barriers to entry Incumbent reactions Incumbent advantages • • • Precommitment contracts • Licenses and patents • Learning-curve effects • Pioneering brand advantages Specific assets Economies of scale Excess capacity Reputation effects
Sources of Market Power: Barriers to entry Incumbent reactions Incumbent advantages • • • Precommitment contracts • Licenses and patents • Learning-curve effects • Pioneering brand advantages Specific assets Economies of scale Excess capacity Reputation effects
 Monopoly • Strong barriers to entry single supplier • Profit maximization – faces market demand sets MR=MC • Unexploited gains from trade
Monopoly • Strong barriers to entry single supplier • Profit maximization – faces market demand sets MR=MC • Unexploited gains from trade
 Oligopoly • A few firms produce most market output • Products may or may not be differentiated • Effective entry barriers protect firm profitability • Firm interdependence requires strategic thinking
Oligopoly • A few firms produce most market output • Products may or may not be differentiated • Effective entry barriers protect firm profitability • Firm interdependence requires strategic thinking
 Monopolistic competition • • Multiple firms produce similar products Firms face downsloping demand curves Profit maximization occurs where MC=MR In the limit, firms compete away economic profits
Monopolistic competition • • Multiple firms produce similar products Firms face downsloping demand curves Profit maximization occurs where MC=MR In the limit, firms compete away economic profits