4dcda8280f8c728b32f214996618c53b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Econ 201 Winter 2010 Demand Suppy Ceteris Paribus 1 -12 -2010

Overview • Individual and Market Demand Curves • Factors that Shift Demand Curves • More useful websites
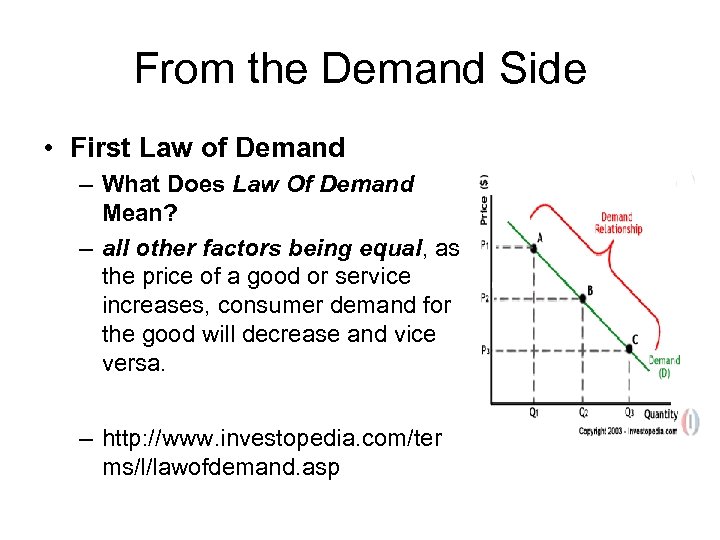
From the Demand Side • First Law of Demand – What Does Law Of Demand Mean? – all other factors being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, consumer demand for the good will decrease and vice versa. – http: //www. investopedia. com/ter ms/l/lawofdemand. asp
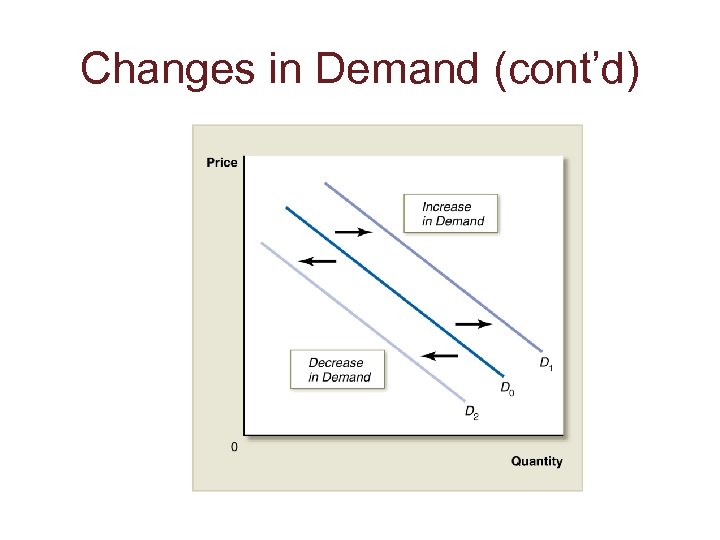
Changes in Demand (cont’d)

Factors That Can Shift Demand • Individual and Market Demand Curves – Income – Price of Substitutes – Price of Compliments – Product Quality – Future Prices – Taste and Preferences • Market Demand Curves – Population (market)
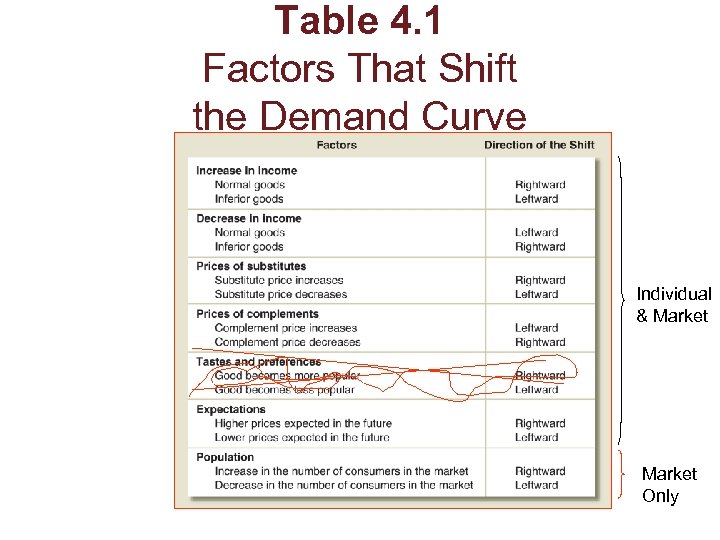
Table 4. 1 Factors That Shift the Demand Curve Individual & Market Only
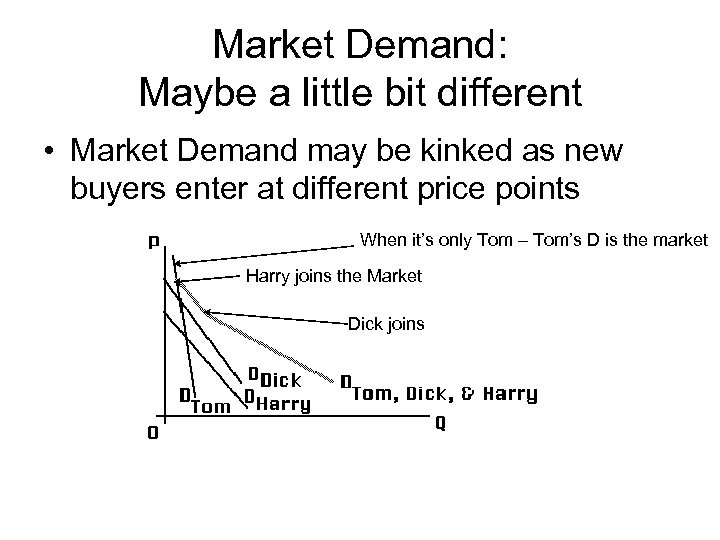
Market Demand: Maybe a little bit different • Market Demand may be kinked as new buyers enter at different price points When it’s only Tom – Tom’s D is the market Harry joins the Market Dick joins

What We’ve Learned • Sell rule for firms (Qs: P=MC) – Firms will supply y units up to the point where the MC of producing the next/last unit (yth) is just equal to the price it receives for the good – First law of supply: supply curves will be upward sloping • Buy rule for consumers (Qd: P=MV) – Consumers will buy x units up to the point that price equals MV for the last (xth) unit • First law of demand: demand curves are downward sloping • Negative slope diminishing marginal value of consuming next unit

Homework Assignment #1 Problem # 1 Due Friday 1/15 Seattle Times Oct 3, 2007 Olympic National Park officials are suggesting raising the price of an entrance pass for motorists — good for seven days — from $15 to $25 starting in 2009, with the fee for individuals such as cyclists climbing from $5 to $12. Season passes would increase from $30 to $50 But public response, particularly from tourist-dependent local businesses has been generally negative said a spokeswoman for Olympic National Park. 1. Illustrate the effect of the increase of the price for park passes on the demand for trips to the park 2. Illustrate how the park fee increase would affect the demand for other tourist-related businesses, e. g. , hotels, restaurants.
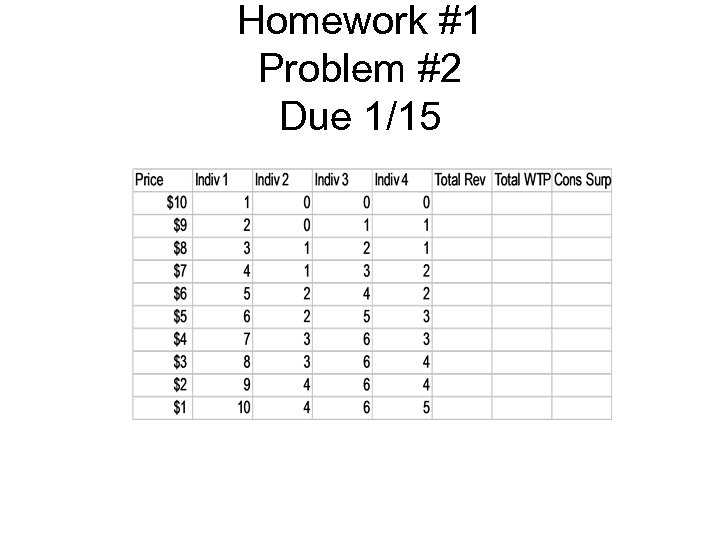
Homework #1 Problem #2 Due 1/15
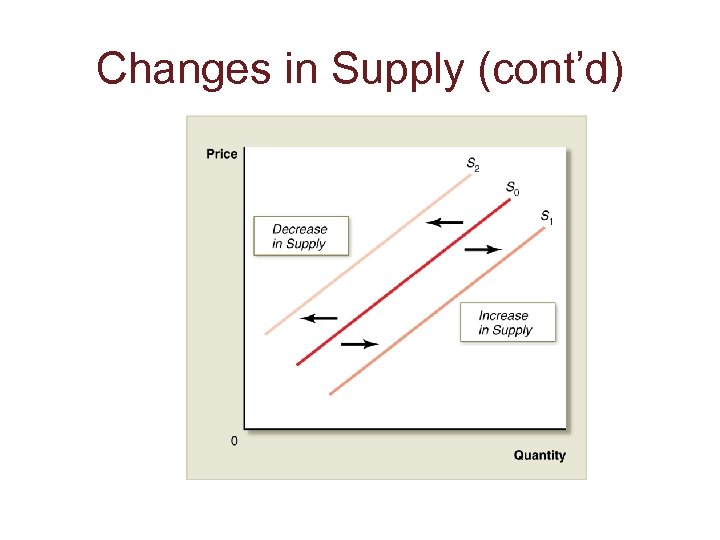
Changes in Supply (cont’d)

Changes in Supply • Factors that affect the supply of a good: – Prices of inputs (such as wages) – Technology – Natural disruptions (such as bad weather) – The number of firms in the market – Expectations – Government policies
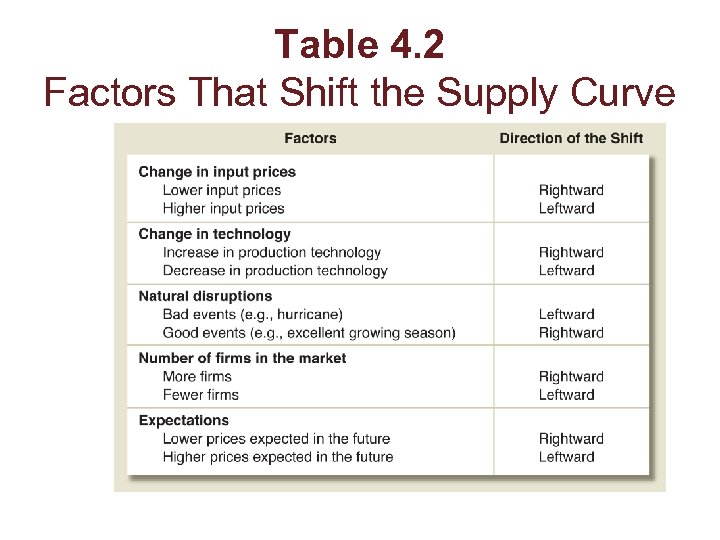
Table 4. 2 Factors That Shift the Supply Curve

Equilibrium • The combined forces of supply and demand in a market determine: – The quantity of a product bought and sold, and – The price per unit of the product. • The equilibrium price is the price at which: – The quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied and the market “clears. ”

Equilibrium (cont’d) • When a market is in equilibrium, there will be no tendency for price or quantity to change.
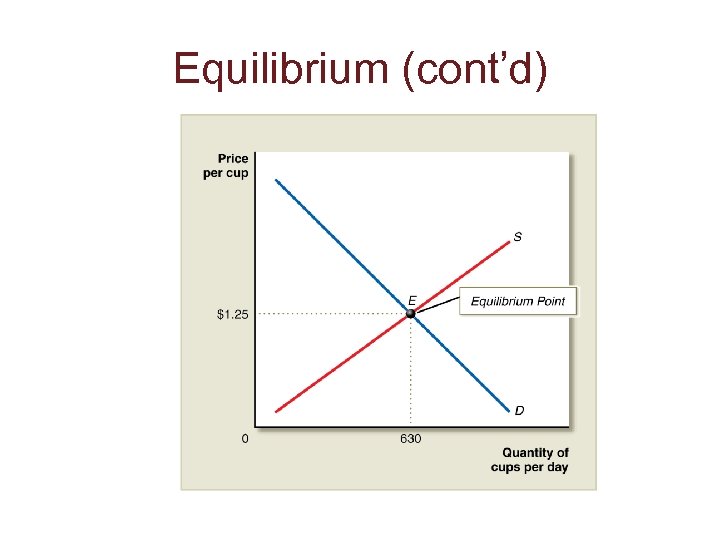
Equilibrium (cont’d)
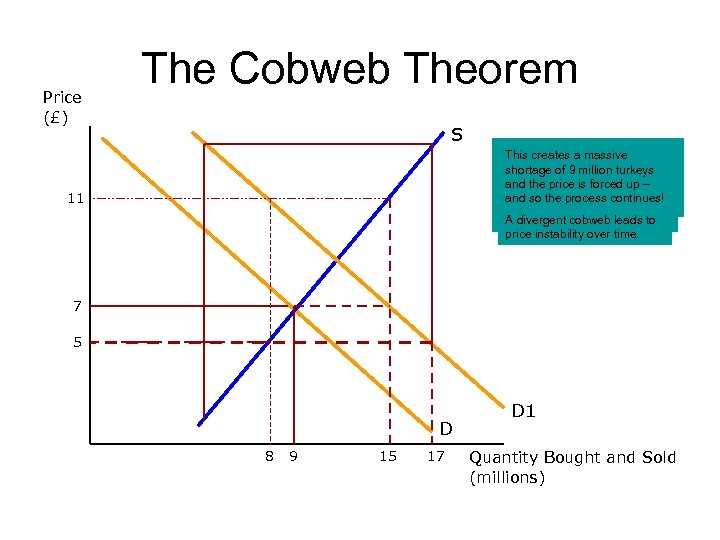
Price (£) The Cobweb Theorem S 11 The price falls to £ 5 and farmers Farmers respond by planning to Assume the initial equilibrium This creates a massive In a ‘divergent cobweb’ react by cutting plans for turkey increase supply, ten months price is £ 7 and the quantity 9. If shortage of 9 million turkeys also termed an unstable production. Ten months later, the supply of turkeys is 15 demand rises, the shortage and the price is forced up – cobweb - the price tends to supply on the market will be 8 million. At this level, there will be pushes the price up to £ 11 per and so the process continues! move away from equilibrium. million. a surplus of turkeys and the turkey. A divergent cobweb leads to price drops. price instability over time. 7 5 D 8 9 15 17 D 1 Quantity Bought and Sold (millions)

Cobweb Theorem • http: //www. bized. co. uk/current/mind/2004_5/251004. ppt • Hungarian-born economist Nicholas Kaldor (1908 -1986) • Simple dynamic model of cyclical demand with time lags between the response of production and a change in price (most often seen in agricultural sectors). • Cobweb theory is the process of adjustment in markets • Traces the path of prices and outputs in different equilibrium situations. Path resembles a cobweb with the equilibrium point at the center of the cobweb. • Sometimes referred to as the hog-cycle (after the phenomenon observed in American pig prices during the 1930 s).

Useful Websites – Basics of demand supply • http: //www. investopedia. com/university/economics/ economics 3. asp Understanding differences between factors that cause shifts in demand or supply • http: //hspm. sph. sc. edu/COURSES/ECON/SD/SD. h tml – Cobweb theorem • http: //www. bized. co. uk/current/mind/2004_5/25100 4. ppt
4dcda8280f8c728b32f214996618c53b.ppt