cb0a272e5ff98d931842256ccd515a12.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 ECON 160 Week 13 Monopoly: Price Searcher Chapter 15
ECON 160 Week 13 Monopoly: Price Searcher Chapter 15
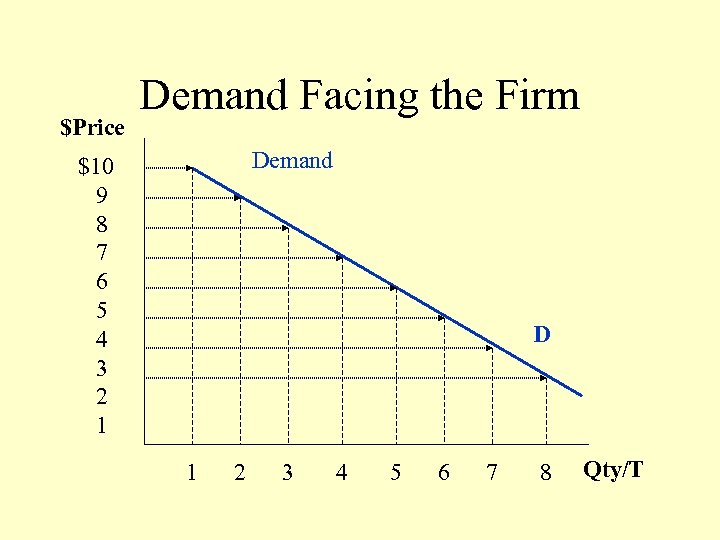 $Price Demand Facing the Firm Demand $10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 D 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Qty/T
$Price Demand Facing the Firm Demand $10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 D 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Qty/T
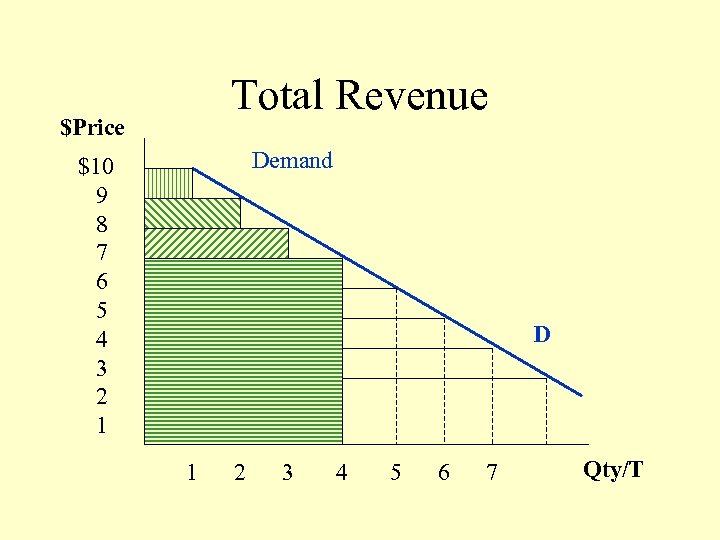 Total Revenue $Price Demand $10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 D 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Qty/T
Total Revenue $Price Demand $10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 D 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Qty/T
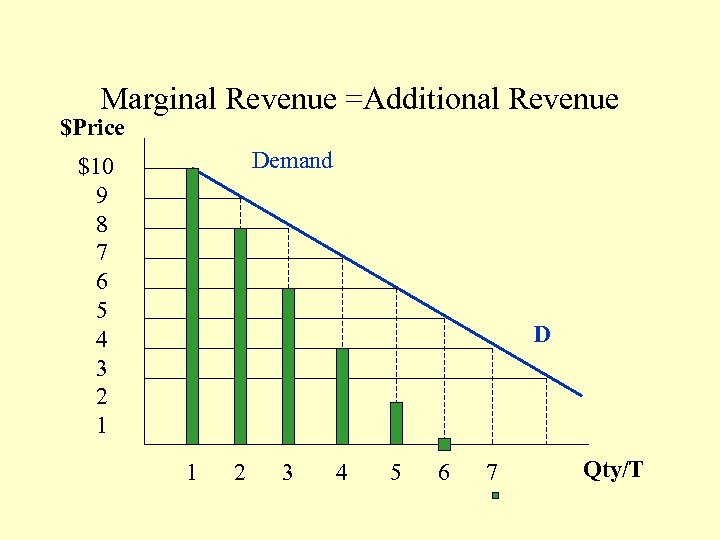 Marginal Revenue =Additional Revenue $Price Demand $10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 D 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Qty/T
Marginal Revenue =Additional Revenue $Price Demand $10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 D 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Qty/T
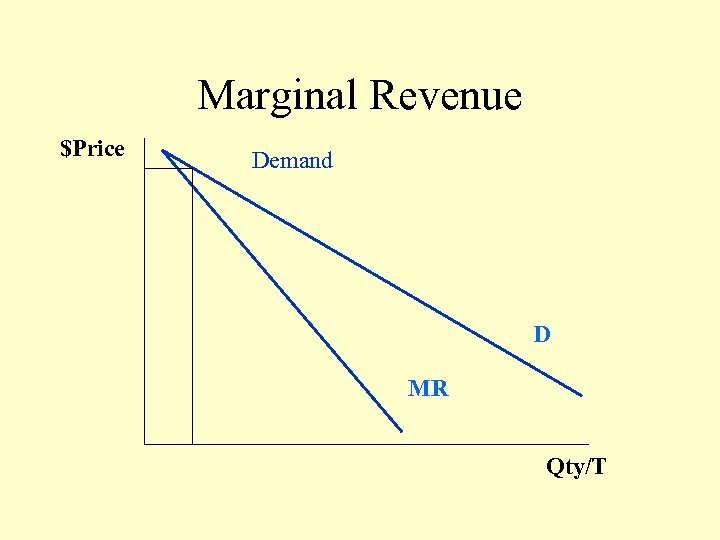 Marginal Revenue $Price Demand D MR Qty/T
Marginal Revenue $Price Demand D MR Qty/T
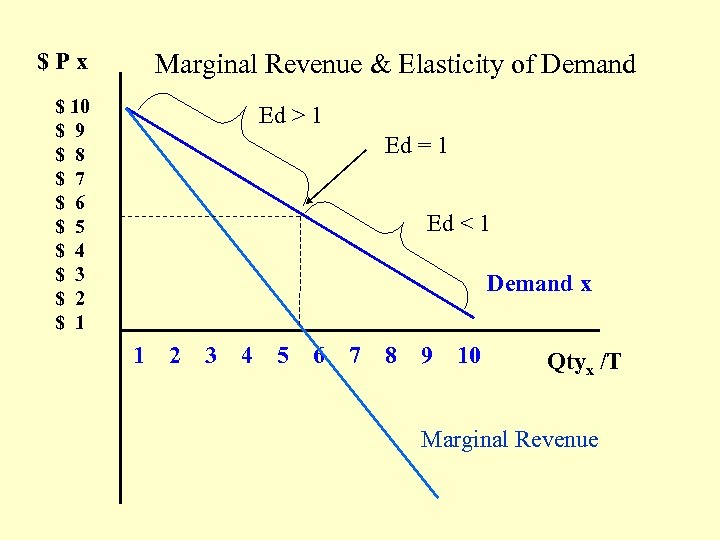 $Px Marginal Revenue & Elasticity of Demand $ 10 $ 9 $ 8 $ 7 $ 6 $ 5 $ 4 $ 3 $ 2 $ 1 Ed > 1 Ed = 1 Ed < 1 Demand x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Qtyx /T Marginal Revenue
$Px Marginal Revenue & Elasticity of Demand $ 10 $ 9 $ 8 $ 7 $ 6 $ 5 $ 4 $ 3 $ 2 $ 1 Ed > 1 Ed = 1 Ed < 1 Demand x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Qtyx /T Marginal Revenue
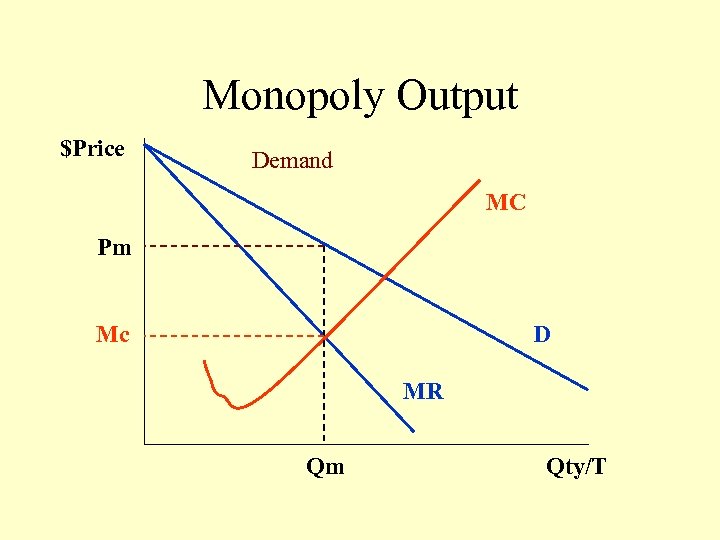 Monopoly Output $Price Demand MC Pm Mc D MR Qm Qty/T
Monopoly Output $Price Demand MC Pm Mc D MR Qm Qty/T
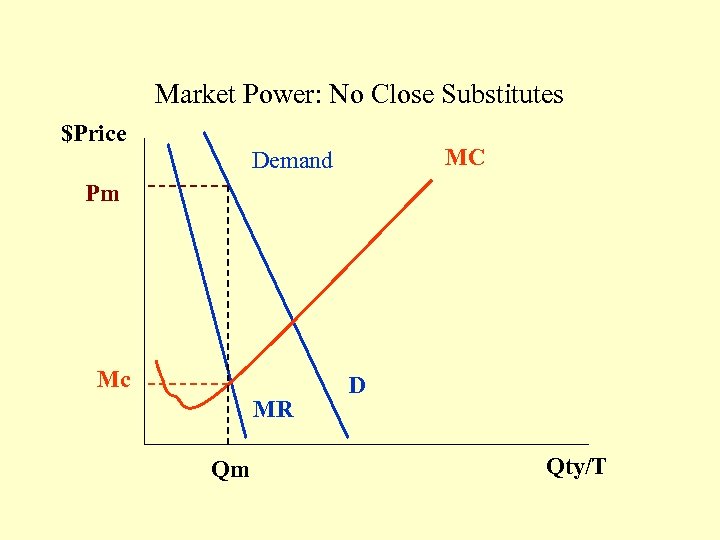 Market Power: No Close Substitutes $Price MC Demand Pm Mc MR Qm D Qty/T
Market Power: No Close Substitutes $Price MC Demand Pm Mc MR Qm D Qty/T
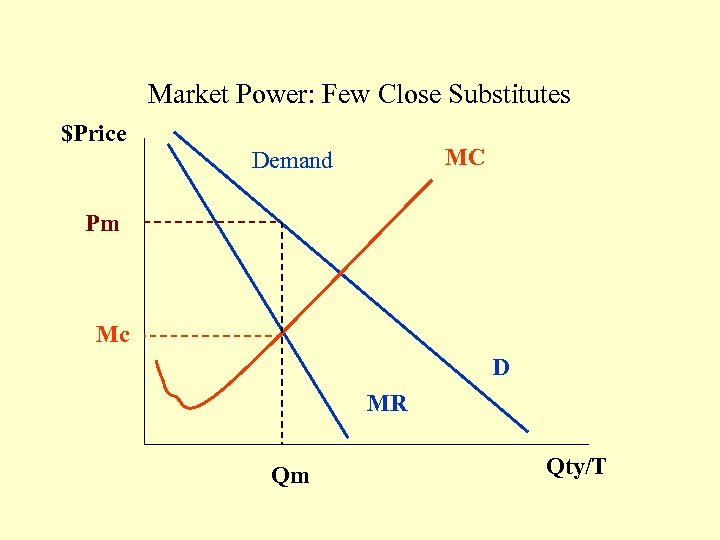 Market Power: Few Close Substitutes $Price MC Demand Pm Mc D MR Qm Qty/T
Market Power: Few Close Substitutes $Price MC Demand Pm Mc D MR Qm Qty/T
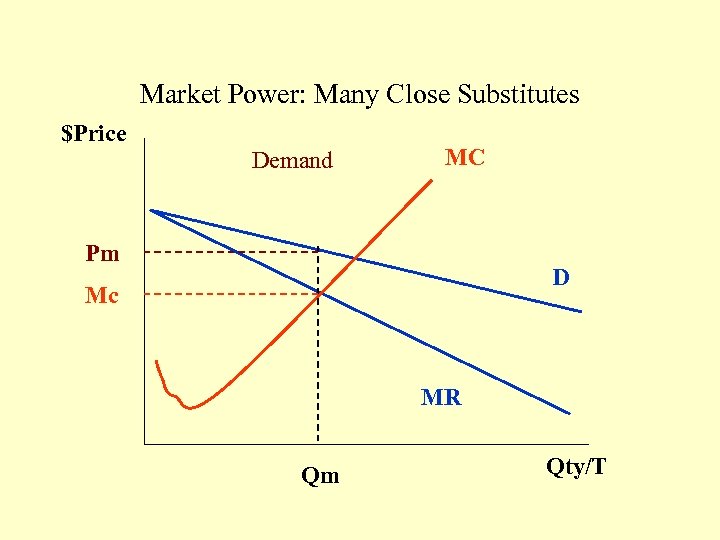 Market Power: Many Close Substitutes $Price Demand MC Pm D Mc MR Qm Qty/T
Market Power: Many Close Substitutes $Price Demand MC Pm D Mc MR Qm Qty/T
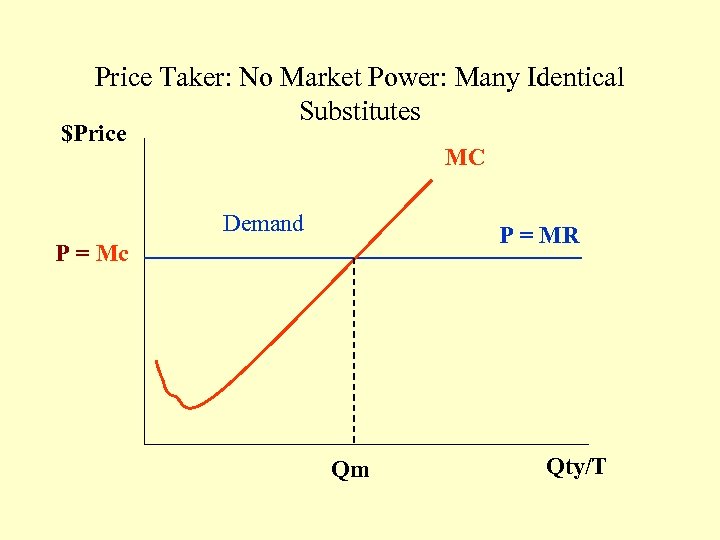 Price Taker: No Market Power: Many Identical Substitutes $Price MC Demand P = MR P = Mc Qm Qty/T
Price Taker: No Market Power: Many Identical Substitutes $Price MC Demand P = MR P = Mc Qm Qty/T
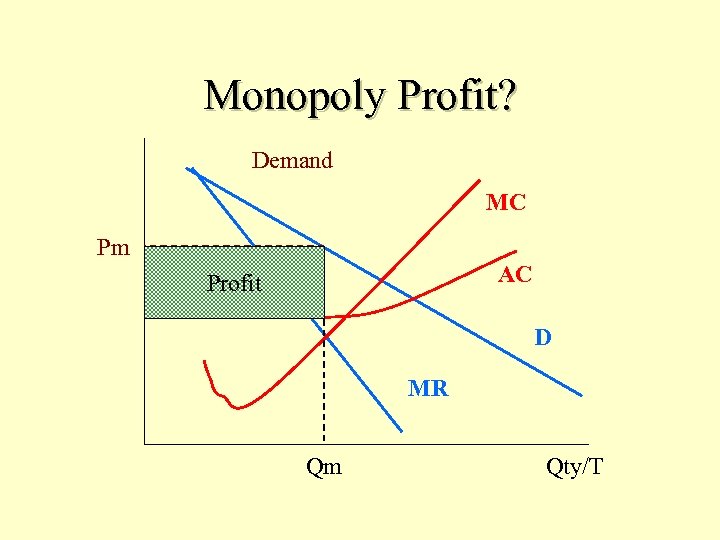 Monopoly Profit? Demand MC Pm AC Profit D MR Qm Qty/T
Monopoly Profit? Demand MC Pm AC Profit D MR Qm Qty/T
 Response to Profits • New firms enter with similar products • Demand declines and becomes more elastic • Price falls, output falls and profits decline
Response to Profits • New firms enter with similar products • Demand declines and becomes more elastic • Price falls, output falls and profits decline
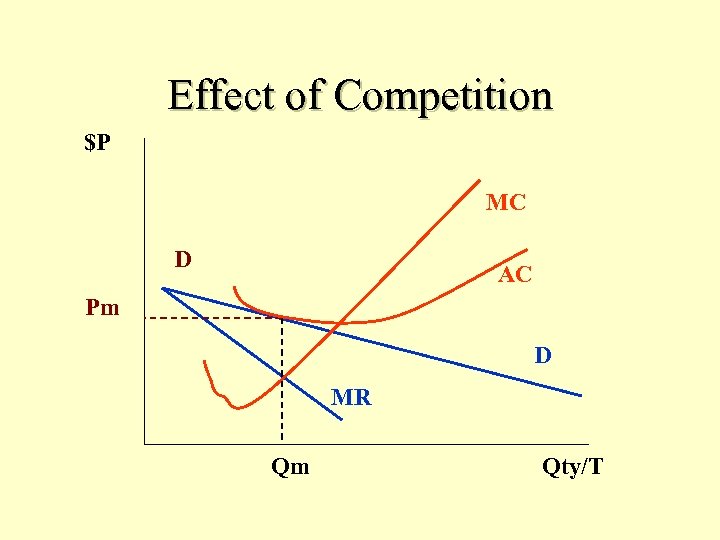 Effect of Competition $P MC D AC Pm D MR Qm Qty/T
Effect of Competition $P MC D AC Pm D MR Qm Qty/T
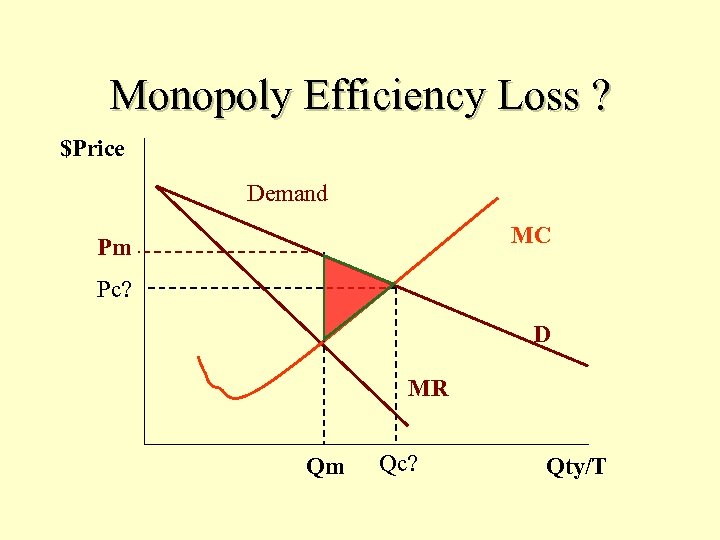 Monopoly Efficiency Loss ? $Price Demand MC Pm Pc? D MR Qm Qc? Qty/T
Monopoly Efficiency Loss ? $Price Demand MC Pm Pc? D MR Qm Qc? Qty/T
 Sources of Monopoly • Natural Monopoly • Patents • Firm actions – Legal harassment – Exclusive licensing – Bundling
Sources of Monopoly • Natural Monopoly • Patents • Firm actions – Legal harassment – Exclusive licensing – Bundling
 Solutions • Government Price regulation • Enforcement of Anti-Trust Laws • Price Discrimination
Solutions • Government Price regulation • Enforcement of Anti-Trust Laws • Price Discrimination
 Price Discrimination • Charging different prices for different units sold. • Allows firms to increase sales and capture more of consumer surplus.
Price Discrimination • Charging different prices for different units sold. • Allows firms to increase sales and capture more of consumer surplus.
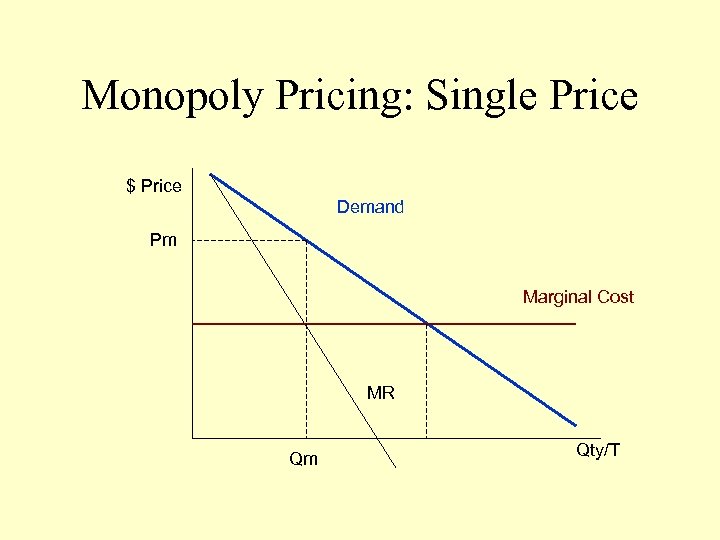 Monopoly Pricing: Single Price $ Price Demand Pm Marginal Cost MR Qm Qty/T
Monopoly Pricing: Single Price $ Price Demand Pm Marginal Cost MR Qm Qty/T
 First Degree: Charging different customers different prices. (i. e. moving down the demand curve) • Auction
First Degree: Charging different customers different prices. (i. e. moving down the demand curve) • Auction
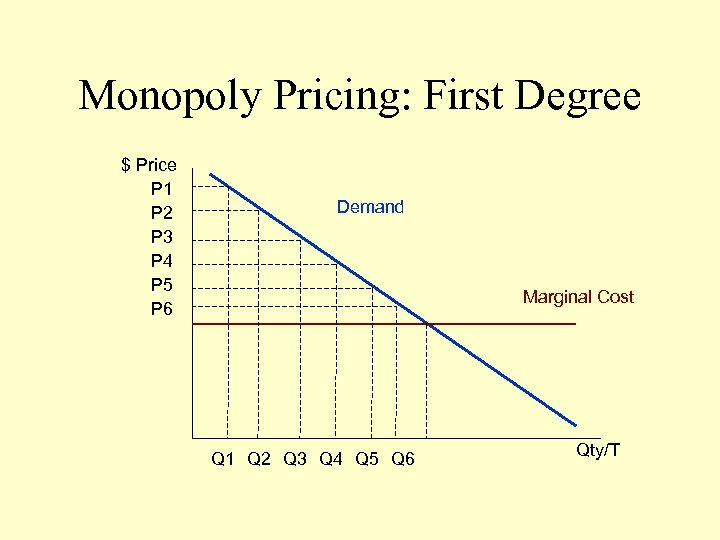 Monopoly Pricing: First Degree $ Price P 1 P 2 P 3 P 4 P 5 P 6 Demand Marginal Cost Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 Q 4 Q 5 Q 6 Qty/T
Monopoly Pricing: First Degree $ Price P 1 P 2 P 3 P 4 P 5 P 6 Demand Marginal Cost Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 Q 4 Q 5 Q 6 Qty/T
 First Degree: Charging different customers different prices. (i. e. moving down the demand curve) • Auction • College scholarships
First Degree: Charging different customers different prices. (i. e. moving down the demand curve) • Auction • College scholarships
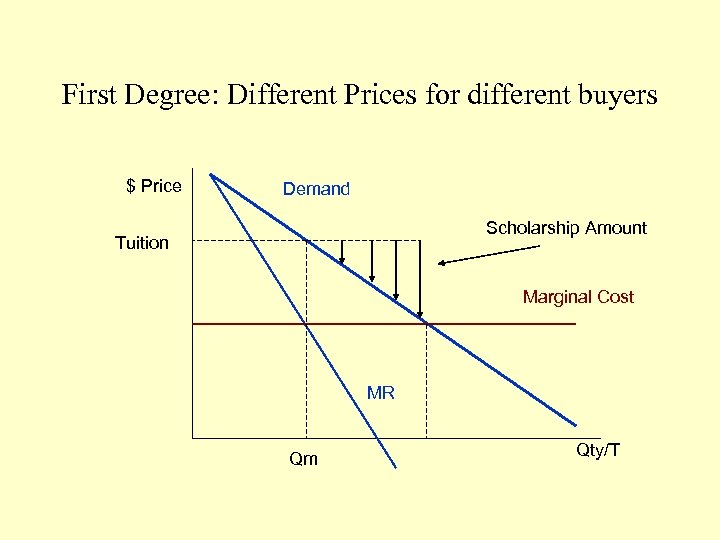 First Degree: Different Prices for different buyers $ Price Demand Scholarship Amount Tuition Marginal Cost MR Qm Qty/T
First Degree: Different Prices for different buyers $ Price Demand Scholarship Amount Tuition Marginal Cost MR Qm Qty/T
 First Degree: Charging different customers different prices. (i. e. moving down the demand curve) • • • Auction College scholarships IBM Punch Cards Polaroid Camera & Film Xerox copier & Toner Ink Jet Printers & Cartridges Razor handle & Blades Swiffer handle & Pads Glade Plugins & refills
First Degree: Charging different customers different prices. (i. e. moving down the demand curve) • • • Auction College scholarships IBM Punch Cards Polaroid Camera & Film Xerox copier & Toner Ink Jet Printers & Cartridges Razor handle & Blades Swiffer handle & Pads Glade Plugins & refills
 Second Degree: (Quantity Forcing) • Offering a schedule of prices to all buyers, which successively lowers the price for additional units, purchased (Moving down each buyers individual demand) • Tires: buy 3, get 4 th free. • Family Gym membership • Product prices, (Drinks, coffee, cereal, toothpaste) – medium 16 oz. $ 1. 09, . 07/oz. – large: 22 oz. $ 1. 19, extra 6 oz. @. 02/oz. – extra large: 32 oz. $1. 29, extra 10 oz. @. 01/ oz.
Second Degree: (Quantity Forcing) • Offering a schedule of prices to all buyers, which successively lowers the price for additional units, purchased (Moving down each buyers individual demand) • Tires: buy 3, get 4 th free. • Family Gym membership • Product prices, (Drinks, coffee, cereal, toothpaste) – medium 16 oz. $ 1. 09, . 07/oz. – large: 22 oz. $ 1. 19, extra 6 oz. @. 02/oz. – extra large: 32 oz. $1. 29, extra 10 oz. @. 01/ oz.
 Third Degree: Charging different prices to different groups according to different elasticity of Demand.
Third Degree: Charging different prices to different groups according to different elasticity of Demand.
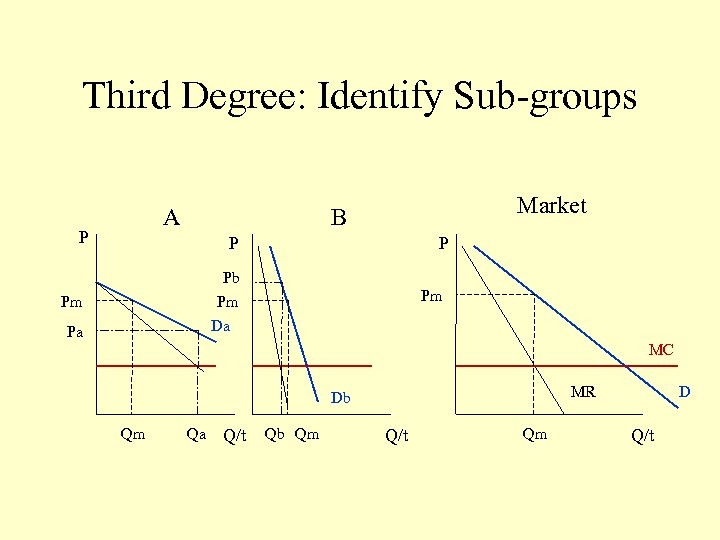 Third Degree: Identify Sub-groups A P Market B P P Pb Pm Da Pm Pa Pm MC MR Db Qm Qa Q/t Qb Qm Q/t Qm D Q/t
Third Degree: Identify Sub-groups A P Market B P P Pb Pm Da Pm Pa Pm MC MR Db Qm Qa Q/t Qb Qm Q/t Qm D Q/t
 Third Degree: Charging different prices to different groups according to different elasticity of Demand. • • • Grocery coupons Theaters Airlines & Hotels Newly released unique products (Segway) Prescription drugs in different countries. Brand name mixers (Holiday Sale) Mattresses: Match any advertised price Menu (Freeway) Menu (Chinese)
Third Degree: Charging different prices to different groups according to different elasticity of Demand. • • • Grocery coupons Theaters Airlines & Hotels Newly released unique products (Segway) Prescription drugs in different countries. Brand name mixers (Holiday Sale) Mattresses: Match any advertised price Menu (Freeway) Menu (Chinese)
 Necessary Conditions for Successful Price Discrimination • Ability to identify and separate buyers by elasticity of demand. • Collect different prices from the different buyers • Prevent Resale
Necessary Conditions for Successful Price Discrimination • Ability to identify and separate buyers by elasticity of demand. • Collect different prices from the different buyers • Prevent Resale


