0b64db51d9cb73e23873a205e617478a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Ecology
Ecology
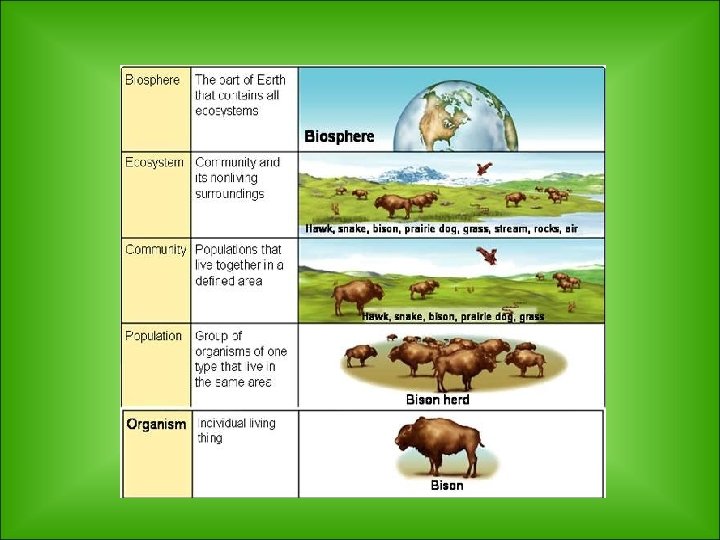
 Ecology- the study of interactions ++among living things, and between living things and their surroundings Levels of Organization • Organism- an individual living thing – EX: alligator • Population- a group of the same species that lives in one area – EX: all the alligators that living in a swamp • Community- a group of different species that live together in one area – EX: groups of alligators, turtles, birds, fish and plants that live together in the Florida Everglades • Ecosystem- all the organisms as well as the climate, soil, water, rocks and other nonliving things in a given area – EX: The grass, rocks, water, soil, turtles, birds, alligators and plants that make up a wetland ecosystem • Biosphere- all of Earth’s ecosystems
Ecology- the study of interactions ++among living things, and between living things and their surroundings Levels of Organization • Organism- an individual living thing – EX: alligator • Population- a group of the same species that lives in one area – EX: all the alligators that living in a swamp • Community- a group of different species that live together in one area – EX: groups of alligators, turtles, birds, fish and plants that live together in the Florida Everglades • Ecosystem- all the organisms as well as the climate, soil, water, rocks and other nonliving things in a given area – EX: The grass, rocks, water, soil, turtles, birds, alligators and plants that make up a wetland ecosystem • Biosphere- all of Earth’s ecosystems
 An ecosystem includes both biotic and abiotic factors. • Biotic factors- living things, such as plants, animals, fungi and bacteria • Abiotic factors- nonliving things such as moisture, temperature, wind, sunlight and soil Can you identify the biotic and abiotic factors in the pictures below?
An ecosystem includes both biotic and abiotic factors. • Biotic factors- living things, such as plants, animals, fungi and bacteria • Abiotic factors- nonliving things such as moisture, temperature, wind, sunlight and soil Can you identify the biotic and abiotic factors in the pictures below?
 • Biodiversity- the assortment or variety of living things in an ecosystem – EX: A rainforest has a high level of biodiversity because it consists of a large assortment of different species living near one another
• Biodiversity- the assortment or variety of living things in an ecosystem – EX: A rainforest has a high level of biodiversity because it consists of a large assortment of different species living near one another
 Environmental Limits on Population Size • Within any ecosystem, resources such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, nutrients, space and sunlight are finite (limited) • Competition- the struggle for resources among organisms – Competition keeps the size of that species’ population in check • Limiting Factors- factors in the environment that limit the size of populations (biotic and abiotic) – Population sizes are limited due to predator-prey relationships – Prey- organisms that are killed for food – Predators- organisms that kill and eat other organisms • Carrying Capacity- the number of organisms of any single species that an ecosystem can support – Determined by the available energy, water, oxygen, minerals, and organism interactions
Environmental Limits on Population Size • Within any ecosystem, resources such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, nutrients, space and sunlight are finite (limited) • Competition- the struggle for resources among organisms – Competition keeps the size of that species’ population in check • Limiting Factors- factors in the environment that limit the size of populations (biotic and abiotic) – Population sizes are limited due to predator-prey relationships – Prey- organisms that are killed for food – Predators- organisms that kill and eat other organisms • Carrying Capacity- the number of organisms of any single species that an ecosystem can support – Determined by the available energy, water, oxygen, minerals, and organism interactions
 • Habitat- all of the biotic and abiotic factors in the area where an organism lives • Ecological Niche- all of the physical, chemical and biologocial factors that a species needs to survive, stay healthy and reproduce – EX: type of food a species eats and how a species competes with others for food
• Habitat- all of the biotic and abiotic factors in the area where an organism lives • Ecological Niche- all of the physical, chemical and biologocial factors that a species needs to survive, stay healthy and reproduce – EX: type of food a species eats and how a species competes with others for food
 • Producers- organisms that get their energy from nonliving resources meaning they make their own food – Also called autotrophs – Provide energy for other organisms in an ecosystem • Consumers- organisms that get their energy by eating other living or once-living resources such as plants and animals – Also called heterotrophs
• Producers- organisms that get their energy from nonliving resources meaning they make their own food – Also called autotrophs – Provide energy for other organisms in an ecosystem • Consumers- organisms that get their energy by eating other living or once-living resources such as plants and animals – Also called heterotrophs
 Types of Consumers • Herbivores- organisms that eat only plants – EX: desert cottontails • Carnivores- organisms that eat only animals – EX: Harris’s hawks • Omnivores- organisms that eat both plants and animals – EX: Kangaroo rats, bears • Detritivores-organisms that eat detritus or dead, organic matter. – EX: millipede • Decomposers- detritivores that break down organic matter into simple compounds – EX: fungi, bacteria • Scavengers- consumers that eat dead organisms – EX: vulture
Types of Consumers • Herbivores- organisms that eat only plants – EX: desert cottontails • Carnivores- organisms that eat only animals – EX: Harris’s hawks • Omnivores- organisms that eat both plants and animals – EX: Kangaroo rats, bears • Detritivores-organisms that eat detritus or dead, organic matter. – EX: millipede • Decomposers- detritivores that break down organic matter into simple compounds – EX: fungi, bacteria • Scavengers- consumers that eat dead organisms – EX: vulture
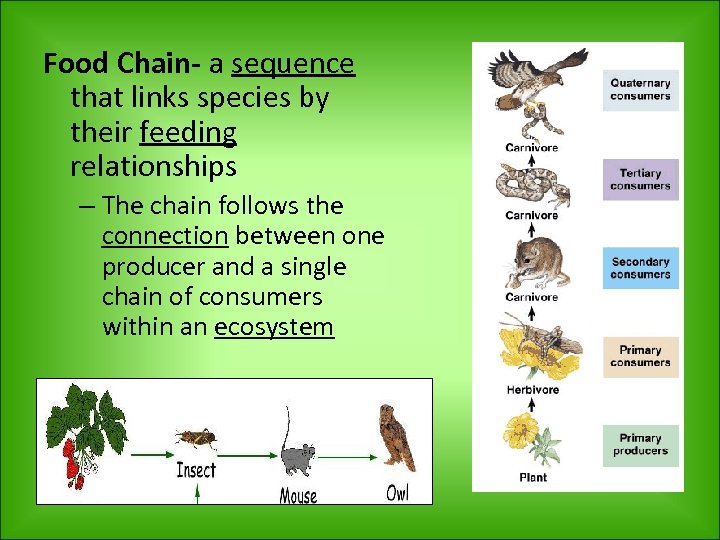 Food Chain- a sequence that links species by their feeding relationships – The chain follows the connection between one producer and a single chain of consumers within an ecosystem
Food Chain- a sequence that links species by their feeding relationships – The chain follows the connection between one producer and a single chain of consumers within an ecosystem
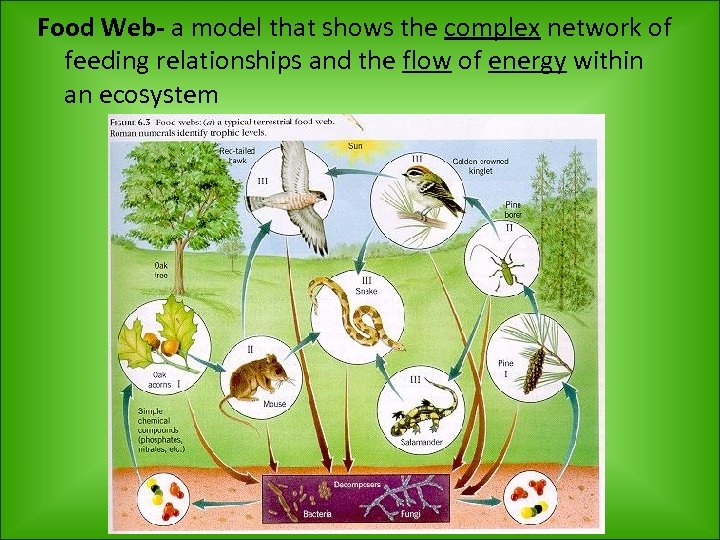 Food Web- a model that shows the complex network of feeding relationships and the flow of energy within an ecosystem
Food Web- a model that shows the complex network of feeding relationships and the flow of energy within an ecosystem
 Trophic Levels- levels of nourishment in a food chain EX: producer-herbivore-carnivore chain has 3 trophic levels – Carnivores are at the highest or top trophic level – Herbivores are at the second trophic level – Producers are at the first or bottom trophic level Primary consumer- herbivores because they are the first consumer above the producer trophic level Secondary Consumer- carnivores that eat herbivores Tertiary Consumers- carnivores that eat secondary consumers
Trophic Levels- levels of nourishment in a food chain EX: producer-herbivore-carnivore chain has 3 trophic levels – Carnivores are at the highest or top trophic level – Herbivores are at the second trophic level – Producers are at the first or bottom trophic level Primary consumer- herbivores because they are the first consumer above the producer trophic level Secondary Consumer- carnivores that eat herbivores Tertiary Consumers- carnivores that eat secondary consumers
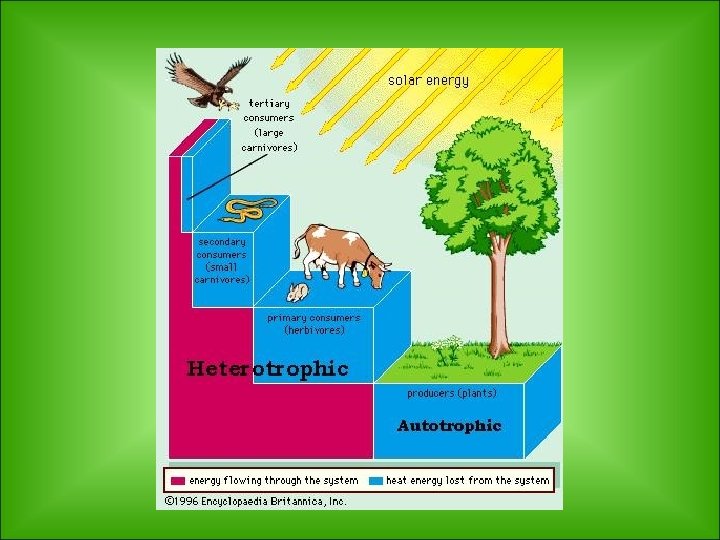
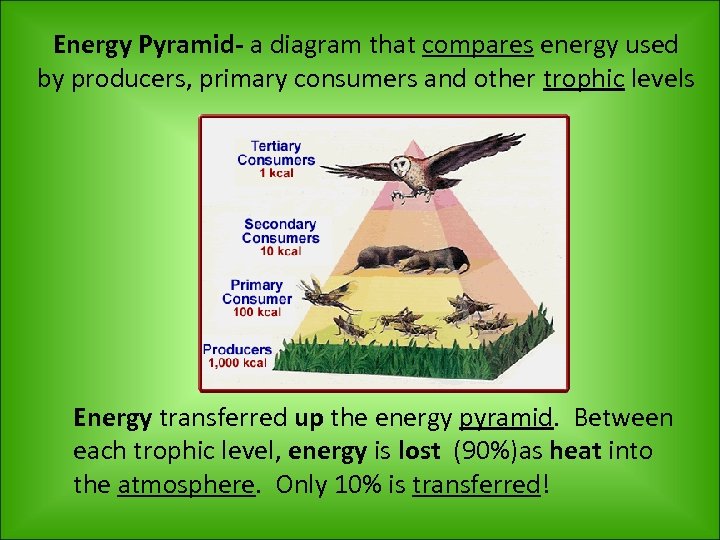 Energy Pyramid- a diagram that compares energy used by producers, primary consumers and other trophic levels Energy transferred up the energy pyramid. Between each trophic level, energy is lost (90%)as heat into the atmosphere. Only 10% is transferred!
Energy Pyramid- a diagram that compares energy used by producers, primary consumers and other trophic levels Energy transferred up the energy pyramid. Between each trophic level, energy is lost (90%)as heat into the atmosphere. Only 10% is transferred!
 Ecological Succession • Ecological Succession- series of changes by which one habitat changes into another – Environments change over long period of time to become habitats for many diverse species – Climatic changes, natural disasters and activities of animals can alter stable ecosystems – Changes can occur rapidly (forest fire or flood) or slowly (climatic changes or long-term drought)
Ecological Succession • Ecological Succession- series of changes by which one habitat changes into another – Environments change over long period of time to become habitats for many diverse species – Climatic changes, natural disasters and activities of animals can alter stable ecosystems – Changes can occur rapidly (forest fire or flood) or slowly (climatic changes or long-term drought)
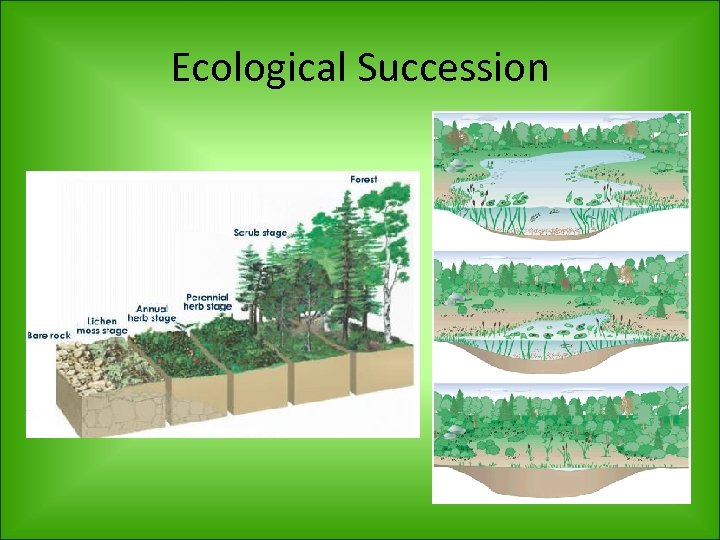 Ecological Succession
Ecological Succession
 Regents Review Questions for Ecology!
Regents Review Questions for Ecology!
 Brief Review: Ecology! • • Abiotic vs. Biotic Factors Autotroph vs. Heterotroph Food Chains and Food Webs Energy Pyramids
Brief Review: Ecology! • • Abiotic vs. Biotic Factors Autotroph vs. Heterotroph Food Chains and Food Webs Energy Pyramids
 Practice Questions Organisms that are able to manufacture organic nutrients from substances in the abiotic environment are classified as (1) heterotrophs (3) predators (2) fungi (4) autotrophs
Practice Questions Organisms that are able to manufacture organic nutrients from substances in the abiotic environment are classified as (1) heterotrophs (3) predators (2) fungi (4) autotrophs
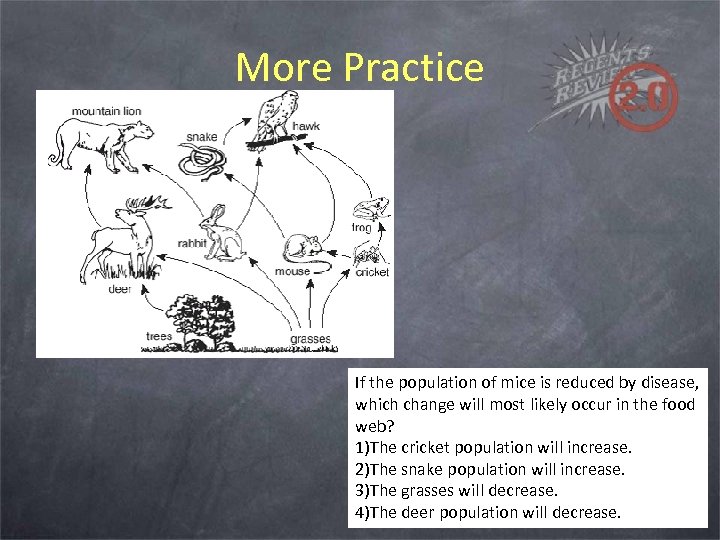 More Practice If the population of mice is reduced by disease, which change will most likely occur in the food web? 1)The cricket population will increase. 2)The snake population will increase. 3)The grasses will decrease. 4)The deer population will decrease.
More Practice If the population of mice is reduced by disease, which change will most likely occur in the food web? 1)The cricket population will increase. 2)The snake population will increase. 3)The grasses will decrease. 4)The deer population will decrease.
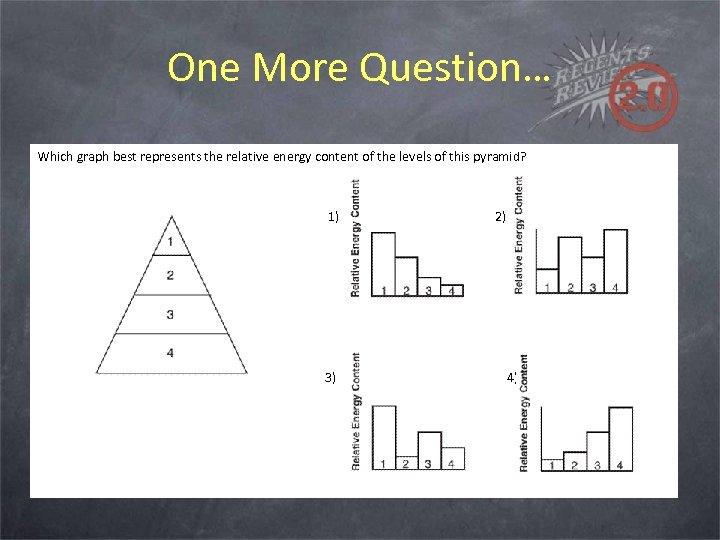 One More Question… Which graph best represents the relative energy content of the levels of this pyramid? 1) 3) 2) 4)
One More Question… Which graph best represents the relative energy content of the levels of this pyramid? 1) 3) 2) 4)
 Plant needs oxygen, carbon dioxide, water and minerals to survive. This statement shows that autotrophs depend on A) Symbiotic relationships B) Abiotic Factors C) Biotic Factors D) Food chains
Plant needs oxygen, carbon dioxide, water and minerals to survive. This statement shows that autotrophs depend on A) Symbiotic relationships B) Abiotic Factors C) Biotic Factors D) Food chains
 All plants, animals and microorganisms living in a forest ecosystem constitute a: A) Population B) Species C) Phylum D) Community
All plants, animals and microorganisms living in a forest ecosystem constitute a: A) Population B) Species C) Phylum D) Community
 Vultures, which are classified as scavengers, are an important part of an ecosystem because they a. hunt herbivores, limiting their populations in an ecosystem b. feed on dead animals, which aids in the recycling of environmental materials c. cause the decay of dead organisms, which releases usable energy to herbivores and carnivores d. are the first level in food webs and make energy available to all the other organisms in the web
Vultures, which are classified as scavengers, are an important part of an ecosystem because they a. hunt herbivores, limiting their populations in an ecosystem b. feed on dead animals, which aids in the recycling of environmental materials c. cause the decay of dead organisms, which releases usable energy to herbivores and carnivores d. are the first level in food webs and make energy available to all the other organisms in the web
 The reason that organisms can not produce populations of unlimited size is that: a. the resources of Earth are finite b. there is no carrying capacity on Earth c. species rarely compete with one another d. interactions between organisms are unchanging
The reason that organisms can not produce populations of unlimited size is that: a. the resources of Earth are finite b. there is no carrying capacity on Earth c. species rarely compete with one another d. interactions between organisms are unchanging
 Two closely related species of birds live in the same tree. Species A feeds on ants and termites, while species B feeds on caterpillars. The two species coexist successfully because a. each occupies a different niche b. they interbreed c. they use different methods of reproduction d. birds compete for food
Two closely related species of birds live in the same tree. Species A feeds on ants and termites, while species B feeds on caterpillars. The two species coexist successfully because a. each occupies a different niche b. they interbreed c. they use different methods of reproduction d. birds compete for food
 Which condition would cause an ecosystem to become unstable? A. only heterotrophic organisms remain after a change in the environment b. a slight increase in the number of heterotrophic and autotrophic organisms occurs c. a variety of nonliving factors are used by the living factors d. biotic and abiotic resources interact
Which condition would cause an ecosystem to become unstable? A. only heterotrophic organisms remain after a change in the environment b. a slight increase in the number of heterotrophic and autotrophic organisms occurs c. a variety of nonliving factors are used by the living factors d. biotic and abiotic resources interact
 Brief Review: Human Impact • Humans have a had a NEGATIVE impact on the environment. • Issues: Deforestation, Acid Rain, Loss of Biodiversity, Pollution, Global Warming, etc. • How to Correct? Make Laws or Educate
Brief Review: Human Impact • Humans have a had a NEGATIVE impact on the environment. • Issues: Deforestation, Acid Rain, Loss of Biodiversity, Pollution, Global Warming, etc. • How to Correct? Make Laws or Educate
 Question Time Which human activity would most likely deplete finite resources? (1) use of natural enemies to eliminate insect pests (2) development of wildlife refuges (3) governmental restriction of industrial pollution (4) uncontrolled population growth One possible reason for the rise in the average air temperature at Earth’s surface is that (1) decomposers are being destroyed (2) deforestation has increased the levels of oxygen in the atmosphere (3) industrialization has increased the amount of carbon dioxide in the air (4) growing crops is depleting the ozone shield
Question Time Which human activity would most likely deplete finite resources? (1) use of natural enemies to eliminate insect pests (2) development of wildlife refuges (3) governmental restriction of industrial pollution (4) uncontrolled population growth One possible reason for the rise in the average air temperature at Earth’s surface is that (1) decomposers are being destroyed (2) deforestation has increased the levels of oxygen in the atmosphere (3) industrialization has increased the amount of carbon dioxide in the air (4) growing crops is depleting the ozone shield


