f6fe762a1ebf2ee88b917974c37c1469.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Ecology and Ecological Health • • • Ecology Defined Biochemical Cycles: The Carbon Cycle Energy Flow Through a Community or Ecosystem Symbiotic Relationships Ecological Succession Environmental Problems and Issues – – – Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems • Acid Rain • Ozone Depletion • Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming – Renewable Energy Sources – Biodiversity Loss – Human Population Density • What We Can Do
Ecology and Ecological Health • • • Ecology Defined Biochemical Cycles: The Carbon Cycle Energy Flow Through a Community or Ecosystem Symbiotic Relationships Ecological Succession Environmental Problems and Issues – – – Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems • Acid Rain • Ozone Depletion • Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming – Renewable Energy Sources – Biodiversity Loss – Human Population Density • What We Can Do
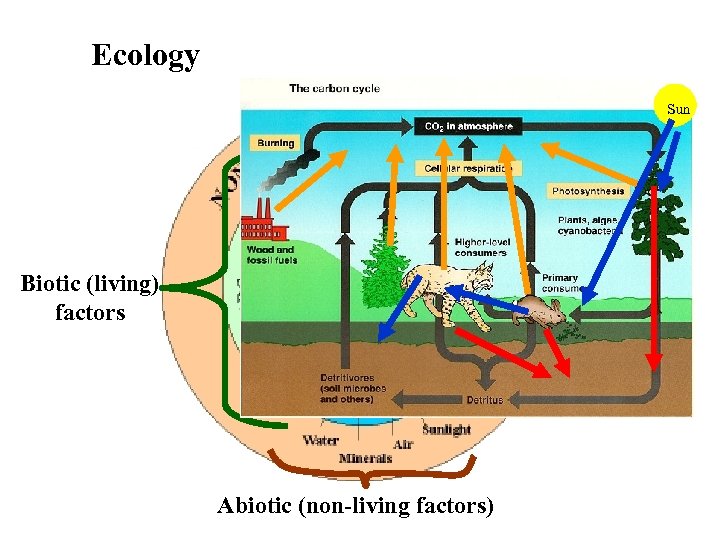 Ecology = Study of the interaction of living and nonliving things Sun Biotic (living) factors Abiotic (non-living factors)
Ecology = Study of the interaction of living and nonliving things Sun Biotic (living) factors Abiotic (non-living factors)
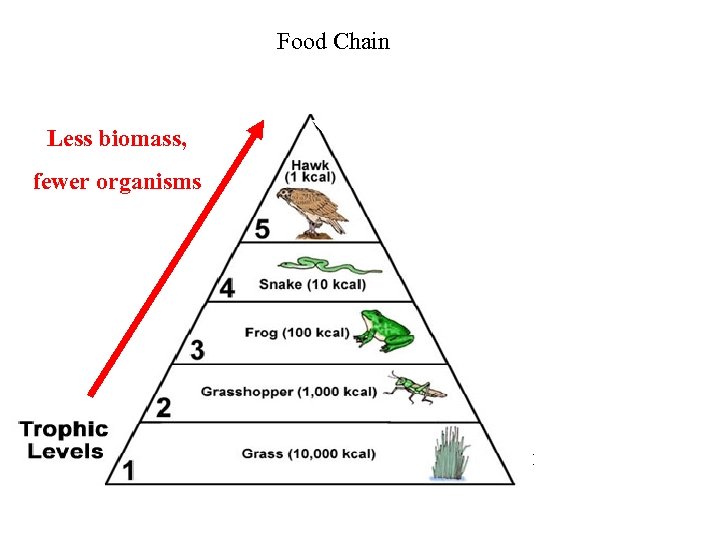 Food Chain Less biomass, fewer organisms Quaternary consumer- carnivore Tertiary consumer –carnivore Secondary consumer-carnivore Primary consumer-herbivore Primary producer Pyramid of energy (autotroph)
Food Chain Less biomass, fewer organisms Quaternary consumer- carnivore Tertiary consumer –carnivore Secondary consumer-carnivore Primary consumer-herbivore Primary producer Pyramid of energy (autotroph)
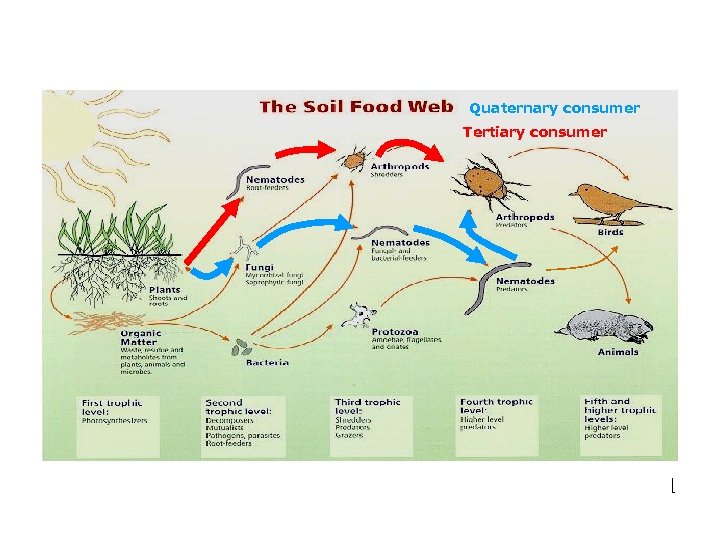 Quaternary consumer Tertiary consumer The more biodiversity, the more complex the food web and the more stable the community is.
Quaternary consumer Tertiary consumer The more biodiversity, the more complex the food web and the more stable the community is.
 Symbiotic Relationships Flea sucking blood from a dog Barnacles on a whale Mycorrhizal fungi on pine seedling roots Lamprey eels attached to fish Clown fish among sea anemone tentacles Ants living on an acacia tree Parasitism Commensalism Mutualism One party benefits One party is harmed One party benefits One party is unaffected Both parties benefit
Symbiotic Relationships Flea sucking blood from a dog Barnacles on a whale Mycorrhizal fungi on pine seedling roots Lamprey eels attached to fish Clown fish among sea anemone tentacles Ants living on an acacia tree Parasitism Commensalism Mutualism One party benefits One party is harmed One party benefits One party is unaffected Both parties benefit
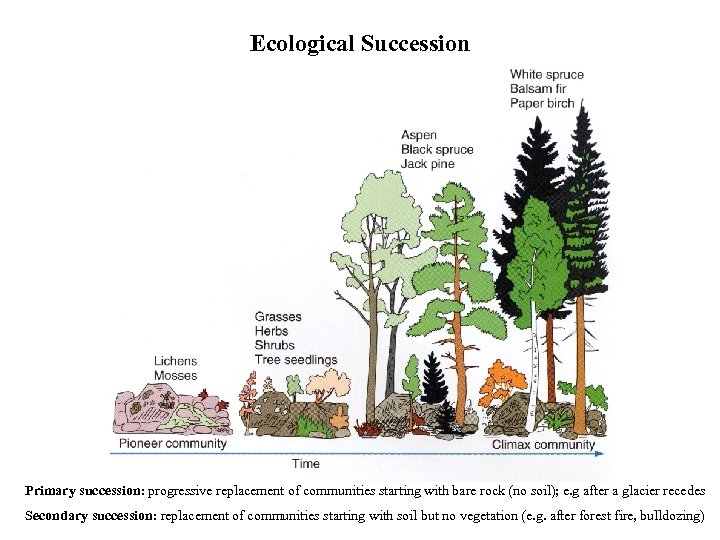 Ecological Succession Primary succession: progressive replacement of communities starting with bare rock (no soil); e. g after a glacier recedes Secondary succession: replacement of communities starting with soil but no vegetation (e. g. after forest fire, bulldozing)
Ecological Succession Primary succession: progressive replacement of communities starting with bare rock (no soil); e. g after a glacier recedes Secondary succession: replacement of communities starting with soil but no vegetation (e. g. after forest fire, bulldozing)
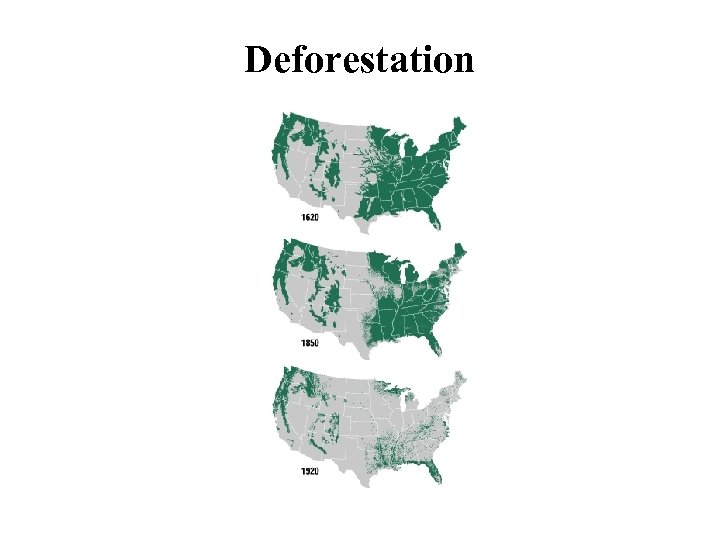 Deforestation
Deforestation
 Human Impact and Global Concerns • • Flow of Energy; Food Chains Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution: Controlling Human Waste Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems – Acid Rain – Ozone Depletion – Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming • • Renewable Energy Sources Biodiversity Loss Human Population Density What We Can Do
Human Impact and Global Concerns • • Flow of Energy; Food Chains Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution: Controlling Human Waste Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems – Acid Rain – Ozone Depletion – Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming • • Renewable Energy Sources Biodiversity Loss Human Population Density What We Can Do
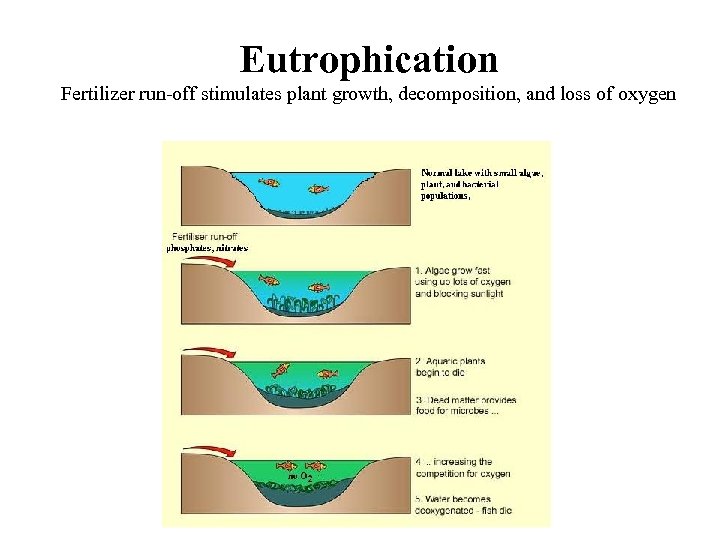 Eutrophication Fertilizer run-off stimulates plant growth, decomposition, and loss of oxygen
Eutrophication Fertilizer run-off stimulates plant growth, decomposition, and loss of oxygen
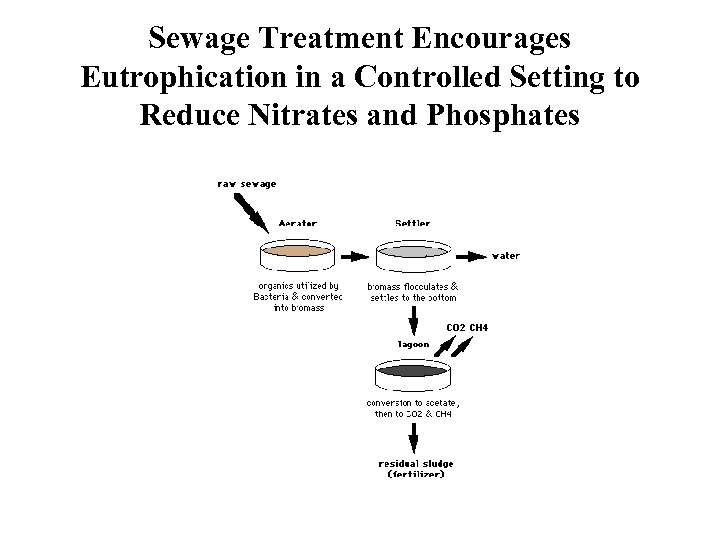 Sewage Treatment Encourages Eutrophication in a Controlled Setting to Reduce Nitrates and Phosphates
Sewage Treatment Encourages Eutrophication in a Controlled Setting to Reduce Nitrates and Phosphates
 Human Impact and Global Concerns • • Flow of Energy; Food Chains Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution: Controlling Human Waste Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems – Acid Rain – Ozone Depletion – Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming • • Renewable Energy Sources Biodiversity Loss Human Population Density What We Can Do
Human Impact and Global Concerns • • Flow of Energy; Food Chains Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution: Controlling Human Waste Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems – Acid Rain – Ozone Depletion – Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming • • Renewable Energy Sources Biodiversity Loss Human Population Density What We Can Do
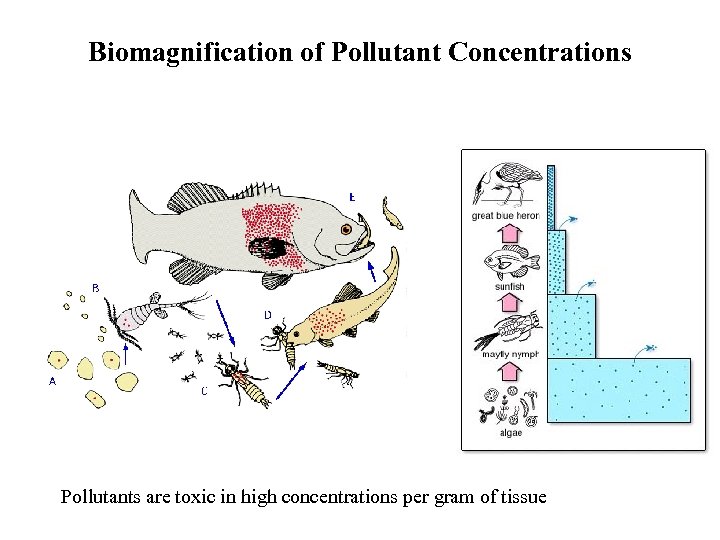 Biomagnification of Pollutant Concentrations Pollutants are toxic in high concentrations per gram of tissue
Biomagnification of Pollutant Concentrations Pollutants are toxic in high concentrations per gram of tissue
 Human Impact and Global Concerns • • Flow of Energy; Food Chains Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution: Controlling Human Waste Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems – Acid Rain – Ozone Depletion – Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming • • Renewable Energy Sources Biodiversity Loss Human Population Density What We Can Do
Human Impact and Global Concerns • • Flow of Energy; Food Chains Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution: Controlling Human Waste Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems – Acid Rain – Ozone Depletion – Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming • • Renewable Energy Sources Biodiversity Loss Human Population Density What We Can Do
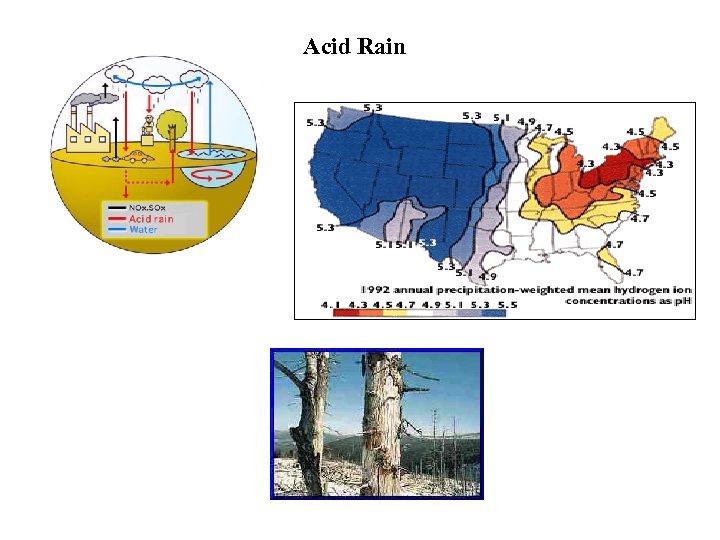 Acid Rain
Acid Rain
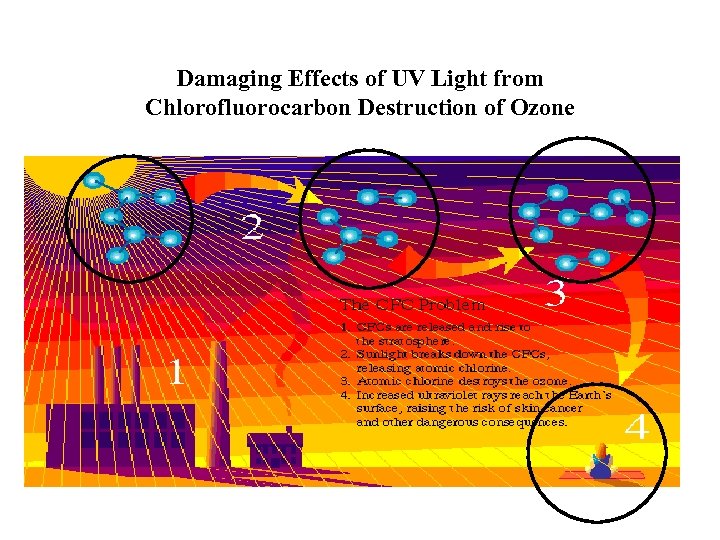 Damaging Effects of UV Light from Chlorofluorocarbon Destruction of Ozone
Damaging Effects of UV Light from Chlorofluorocarbon Destruction of Ozone
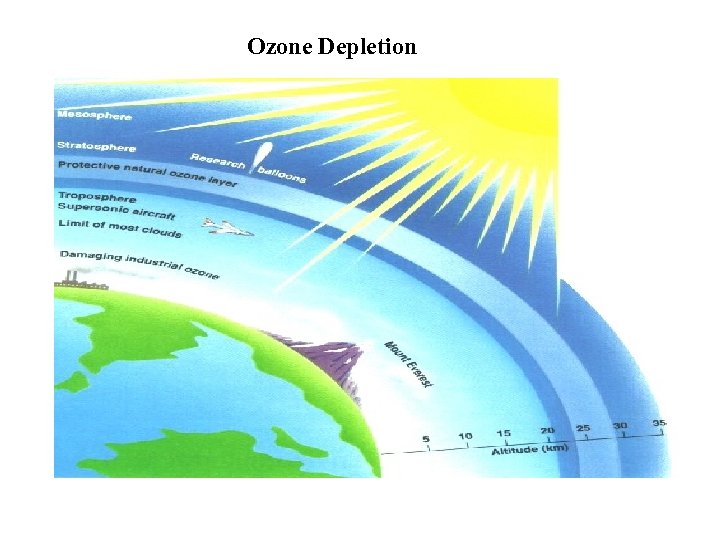 Ozone Depletion
Ozone Depletion
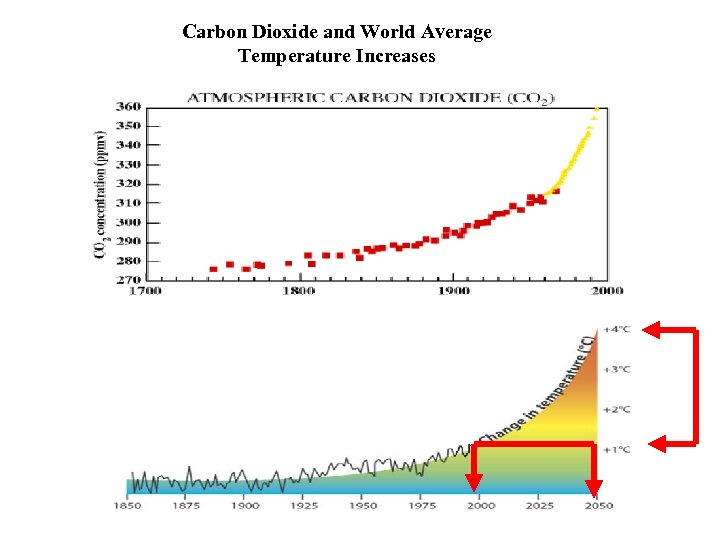 Carbon Dioxide and World Average Temperature Increases
Carbon Dioxide and World Average Temperature Increases
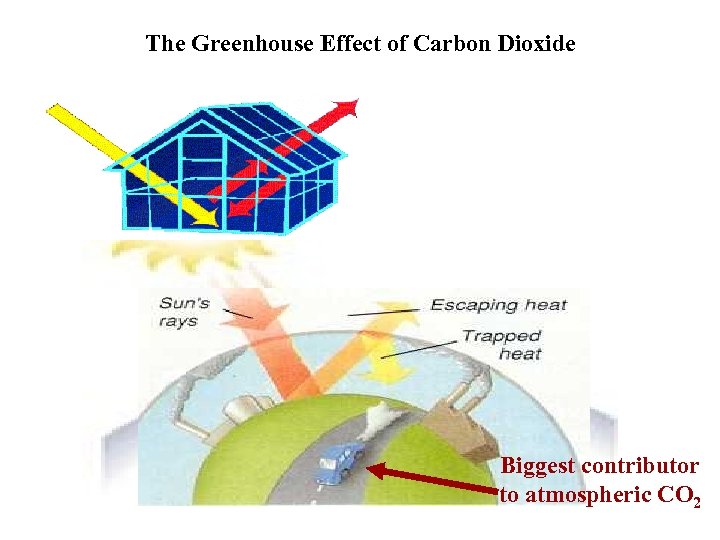 The Greenhouse Effect of Carbon Dioxide Biggest contributor to atmospheric CO 2
The Greenhouse Effect of Carbon Dioxide Biggest contributor to atmospheric CO 2
 Human Impact and Global Concerns • • Flow of Energy; Food Chains Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution: Controlling Human Waste Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems – Acid Rain – Ozone Depletion – Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming • • Renewable Energy Sources Biodiversity Loss Human Population Density What We Can Do
Human Impact and Global Concerns • • Flow of Energy; Food Chains Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution: Controlling Human Waste Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems – Acid Rain – Ozone Depletion – Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming • • Renewable Energy Sources Biodiversity Loss Human Population Density What We Can Do
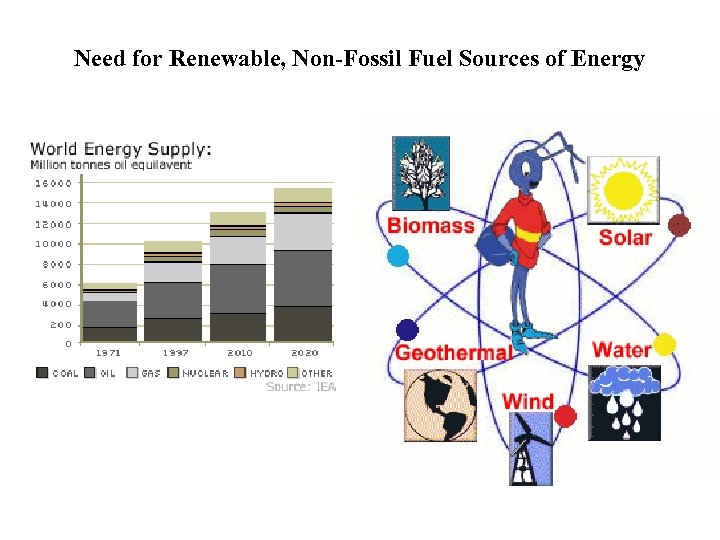 Need for Renewable, Non-Fossil Fuel Sources of Energy
Need for Renewable, Non-Fossil Fuel Sources of Energy
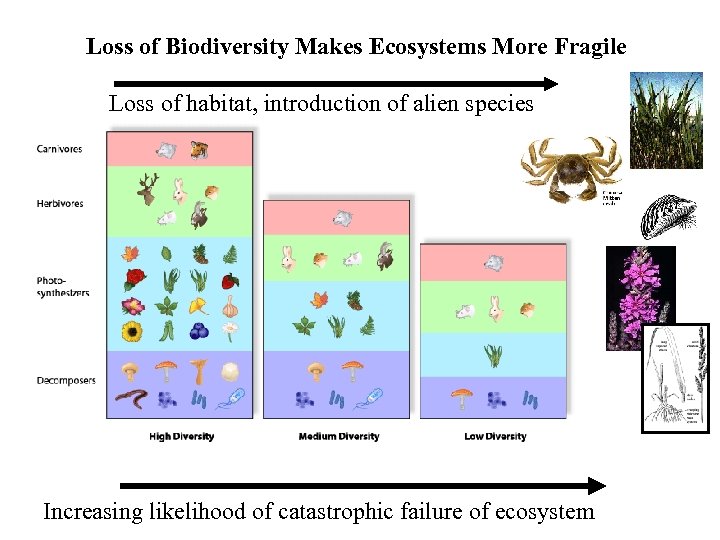 Loss of Biodiversity Makes Ecosystems More Fragile Loss of habitat, introduction of alien species Increasing likelihood of catastrophic failure of ecosystem
Loss of Biodiversity Makes Ecosystems More Fragile Loss of habitat, introduction of alien species Increasing likelihood of catastrophic failure of ecosystem
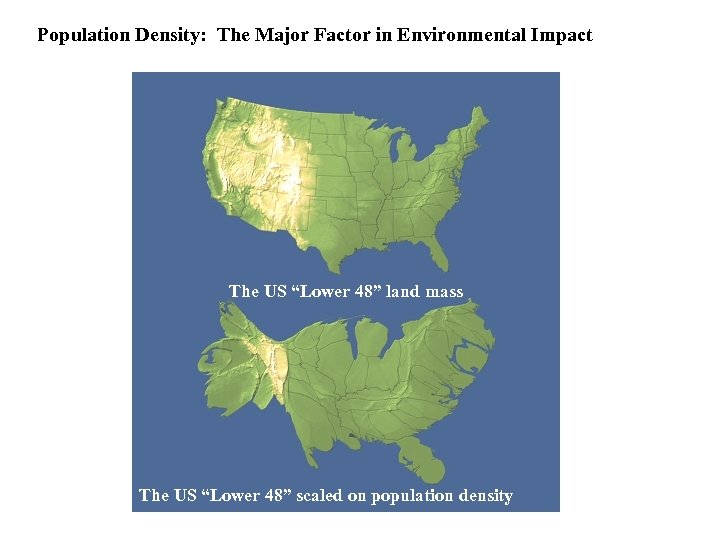 Population Density: The Major Factor in Environmental Impact The US “Lower 48” land mass The US “Lower 48” scaled on population density
Population Density: The Major Factor in Environmental Impact The US “Lower 48” land mass The US “Lower 48” scaled on population density
 Human Impact and Global Concerns • • Flow of Energy; Food Chains Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution: Controlling Human Waste Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems – Acid Rain – Ozone Depletion – Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming • • Renewable Energy Sources Biodiversity Loss Human Population Density What We Can Do
Human Impact and Global Concerns • • Flow of Energy; Food Chains Deforestation Eutrophication Water pollution: Controlling Human Waste Biomagnification Air pollution Atmospheric Problems – Acid Rain – Ozone Depletion – Greenhouse Effect/Global Warming • • Renewable Energy Sources Biodiversity Loss Human Population Density What We Can Do
 Managing Solid Waste 1. 2 3. Precycling Limiting what and how much you buy based on packaging
Managing Solid Waste 1. 2 3. Precycling Limiting what and how much you buy based on packaging
 Basic Steps Towards Environmental Stewardship 1. Reduce, reuse, recycle 2. Precycle, exercise product choice 3. Use ecologically sensitive transportation (reduce CO 2, oil, antifreeze releases) 4. Reduce chemical use (solvents, paints, pesticides, herbicides) 5. Eat lower on the food chain 6. Advocate sustainable and renewable practices 7. Get involved in community habitat restoration (e. g. www. hylebos. org)
Basic Steps Towards Environmental Stewardship 1. Reduce, reuse, recycle 2. Precycle, exercise product choice 3. Use ecologically sensitive transportation (reduce CO 2, oil, antifreeze releases) 4. Reduce chemical use (solvents, paints, pesticides, herbicides) 5. Eat lower on the food chain 6. Advocate sustainable and renewable practices 7. Get involved in community habitat restoration (e. g. www. hylebos. org)
 Environmental Stewardship: Getting Involved
Environmental Stewardship: Getting Involved


