eaf1d17bced6fbe1c008622bb78fc714.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 114
 Ecological Sanitation high-, medium and low-tech solutions Univ. Prof. Dr. -Ing. Ralf Otterpohl Director Institute of Wastewater Management and Water Protection
Ecological Sanitation high-, medium and low-tech solutions Univ. Prof. Dr. -Ing. Ralf Otterpohl Director Institute of Wastewater Management and Water Protection
 Goals of this workshop: • solutions for the sanitation crisis in developing countries – and why WE have to work on it • understand principles of Ecological Sanitation by cases • see decentral water technologies as efficient demand side management tool • get ideas for creative CONCEPTS
Goals of this workshop: • solutions for the sanitation crisis in developing countries – and why WE have to work on it • understand principles of Ecological Sanitation by cases • see decentral water technologies as efficient demand side management tool • get ideas for creative CONCEPTS
 think about water, sanitation, hygiene technologies
think about water, sanitation, hygiene technologies

 Water misused: Brussels, 2004 raw wastewater discharge, exception in Europe, but the most common „method“ worldwide
Water misused: Brussels, 2004 raw wastewater discharge, exception in Europe, but the most common „method“ worldwide
 health in danger water misused
health in danger water misused
 Inefficient Water Usage, Loss of Soil Fertility, Pollution of Rivers, Lakes and the Seas Major problems related to Wastewater (Miss)Management: Pollution of Rivers, Lakes and the Seas Scarcity is often a consequence of inefficient Water Usage
Inefficient Water Usage, Loss of Soil Fertility, Pollution of Rivers, Lakes and the Seas Major problems related to Wastewater (Miss)Management: Pollution of Rivers, Lakes and the Seas Scarcity is often a consequence of inefficient Water Usage
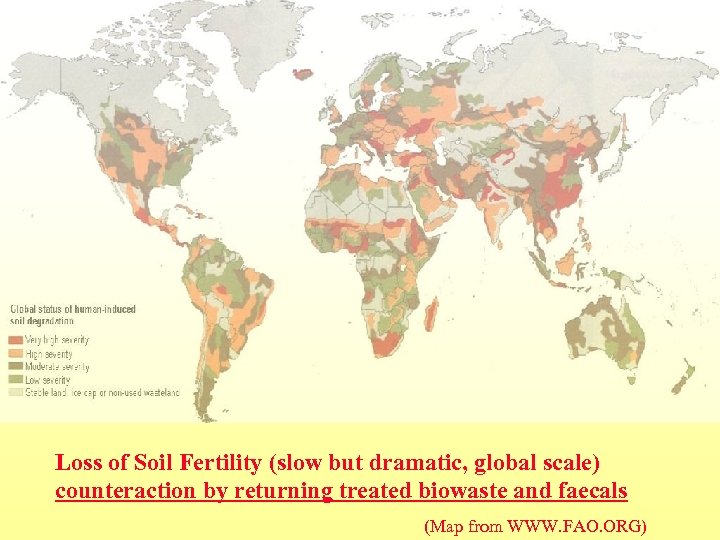 Loss of Soil Fertility (slow but dramatic, global scale) counteraction by returning treated biowaste and faecals (Map from WWW. FAO. ORG)
Loss of Soil Fertility (slow but dramatic, global scale) counteraction by returning treated biowaste and faecals (Map from WWW. FAO. ORG)
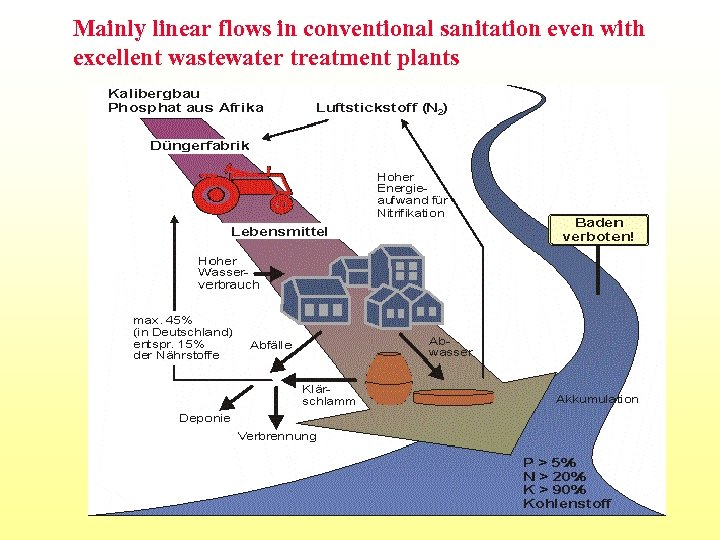 Mainly linear flows in conventional sanitation even with excellent wastewater treatment plants
Mainly linear flows in conventional sanitation even with excellent wastewater treatment plants
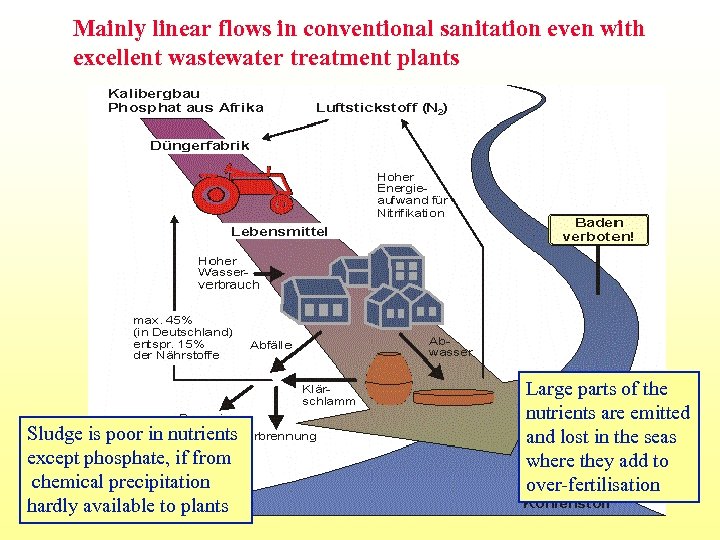 Mainly linear flows in conventional sanitation even with excellent wastewater treatment plants Sludge is poor in nutrients except phosphate, if from chemical precipitation hardly available to plants Large parts of the nutrients are emitted and lost in the seas where they add to over-fertilisation
Mainly linear flows in conventional sanitation even with excellent wastewater treatment plants Sludge is poor in nutrients except phosphate, if from chemical precipitation hardly available to plants Large parts of the nutrients are emitted and lost in the seas where they add to over-fertilisation
 Coral Reefs: endangered by global warming, excess of nutrients, industrial agriculture, wastewater, snail collectors
Coral Reefs: endangered by global warming, excess of nutrients, industrial agriculture, wastewater, snail collectors
 Monsoon: how does a flush-sewerage system perform?
Monsoon: how does a flush-sewerage system perform?
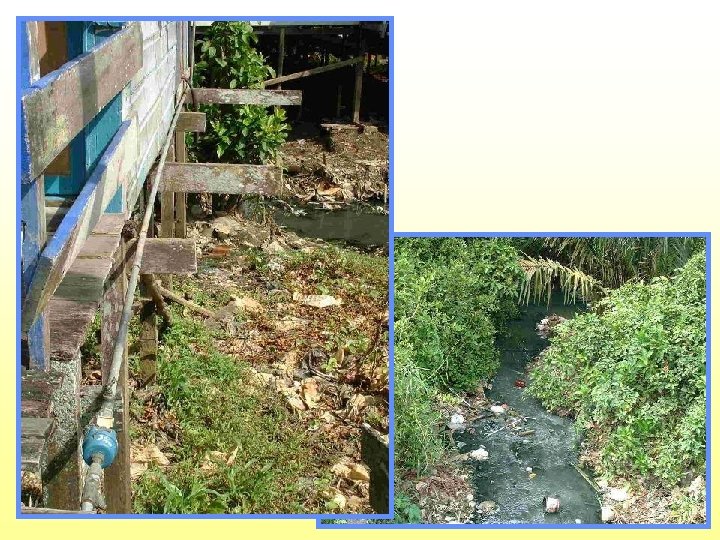
 Raw wastewater irrigation on ripe vegetables, Haroonabad, Pakistan this is NOT ecosan, sanitisation is necessary
Raw wastewater irrigation on ripe vegetables, Haroonabad, Pakistan this is NOT ecosan, sanitisation is necessary
 Millions of people die from faecal contamination of water mostly babies and children below the age of 5 years… What can be done? WE do have to act!
Millions of people die from faecal contamination of water mostly babies and children below the age of 5 years… What can be done? WE do have to act!
 Ecosan principles: Containment, sanitisation, reuse (Ecosan is not a technology but following these principles) Full REUSE ZERO Emissions…
Ecosan principles: Containment, sanitisation, reuse (Ecosan is not a technology but following these principles) Full REUSE ZERO Emissions…


 what is your solution?
what is your solution?
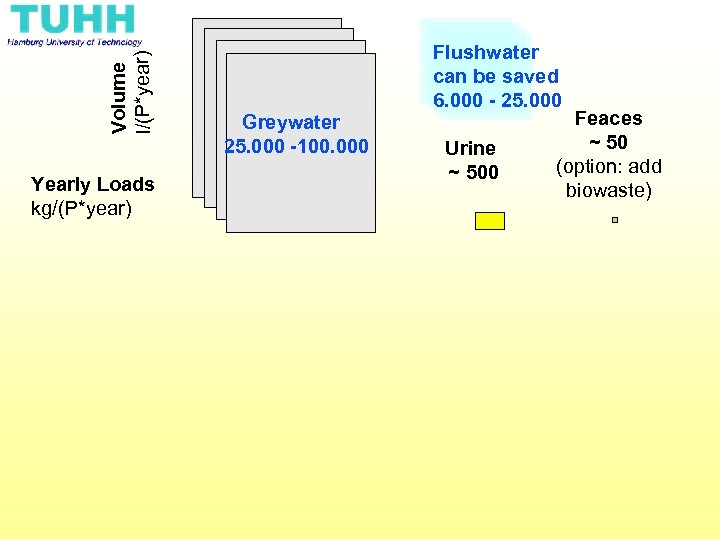 Volume l/(P*year) Yearly Loads kg/(P*year) Greywater 25. 000 -100. 000 Flushwater can be saved 6. 000 - 25. 000 Urine ~ 500 Feaces ~ 50 (option: add biowaste)
Volume l/(P*year) Yearly Loads kg/(P*year) Greywater 25. 000 -100. 000 Flushwater can be saved 6. 000 - 25. 000 Urine ~ 500 Feaces ~ 50 (option: add biowaste)
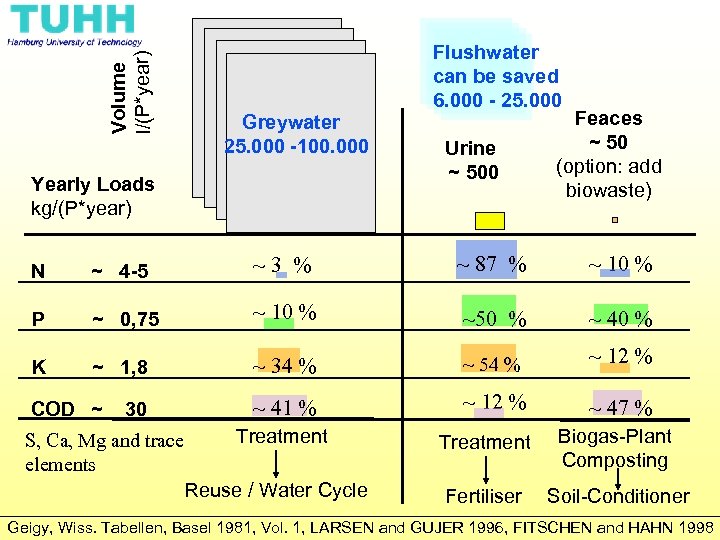 Volume l/(P*year) Greywater 25. 000 -100. 000 Yearly Loads kg/(P*year) Flushwater can be saved 6. 000 - 25. 000 Urine ~ 500 Feaces ~ 50 (option: add biowaste) N ~ 4 -5 ~3 % ~ 87 % ~ 10 % P ~ 0, 75 ~ 10 % ~50 % ~ 40 % K ~ 1, 8 ~ 34 % ~ 54 % ~ 12 % ~ 41 % ~ 12 % ~ 47 % COD ~ 30 Treatment Biogas-Plant Composting Reuse / Water Cycle S, Ca, Mg and trace elements Fertiliser Soil-Conditioner Geigy, Wiss. Tabellen, Basel 1981, Vol. 1, LARSEN and GUJER 1996, FITSCHEN and HAHN 1998
Volume l/(P*year) Greywater 25. 000 -100. 000 Yearly Loads kg/(P*year) Flushwater can be saved 6. 000 - 25. 000 Urine ~ 500 Feaces ~ 50 (option: add biowaste) N ~ 4 -5 ~3 % ~ 87 % ~ 10 % P ~ 0, 75 ~ 10 % ~50 % ~ 40 % K ~ 1, 8 ~ 34 % ~ 54 % ~ 12 % ~ 41 % ~ 12 % ~ 47 % COD ~ 30 Treatment Biogas-Plant Composting Reuse / Water Cycle S, Ca, Mg and trace elements Fertiliser Soil-Conditioner Geigy, Wiss. Tabellen, Basel 1981, Vol. 1, LARSEN and GUJER 1996, FITSCHEN and HAHN 1998
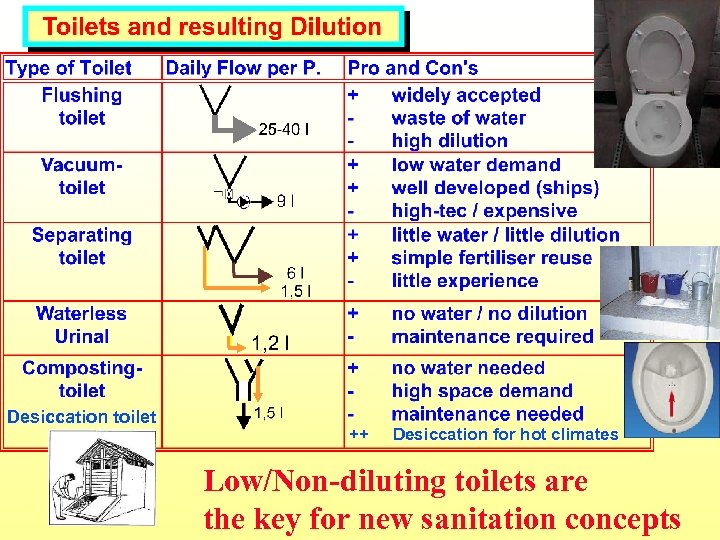 Desiccation toilet ++ Desiccation for hot climates Low/Non-diluting toilets are the key for new sanitation concepts
Desiccation toilet ++ Desiccation for hot climates Low/Non-diluting toilets are the key for new sanitation concepts
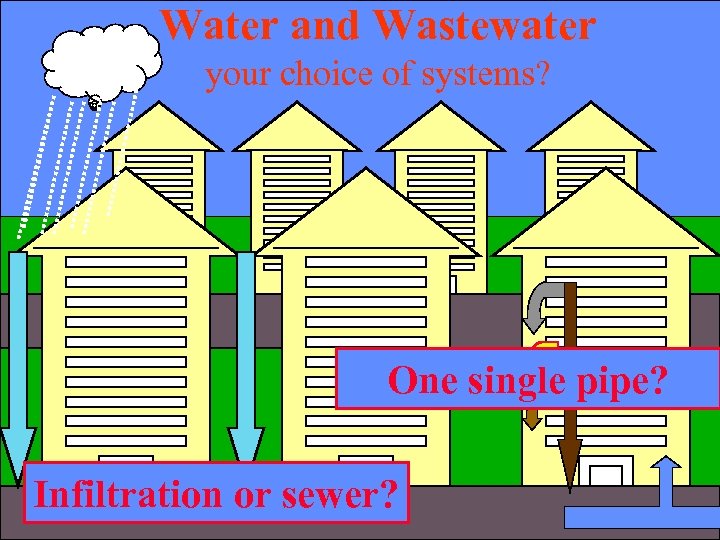 Water and Wastewater your choice of systems? One single pipe? Infiltration or sewer?
Water and Wastewater your choice of systems? One single pipe? Infiltration or sewer?
 1. Blackwater and integrated systems design 2. Dry sanitation / Low Cost solutions 3. Urine-Diversion with flush sanitation
1. Blackwater and integrated systems design 2. Dry sanitation / Low Cost solutions 3. Urine-Diversion with flush sanitation
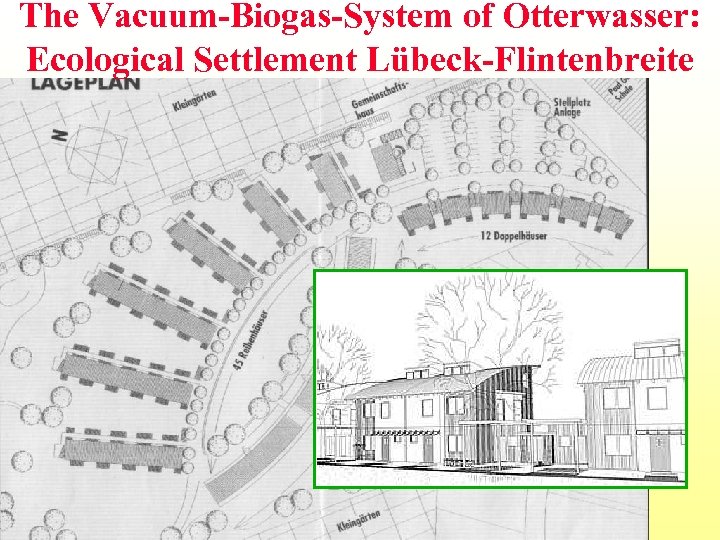 The Vacuum-Biogas-System of Otterwasser: Ecological Settlement Lübeck-Flintenbreite
The Vacuum-Biogas-System of Otterwasser: Ecological Settlement Lübeck-Flintenbreite
 Ecological Settlement Lübeck-Flintenbreite Double-Houses Terraced Houses
Ecological Settlement Lübeck-Flintenbreite Double-Houses Terraced Houses
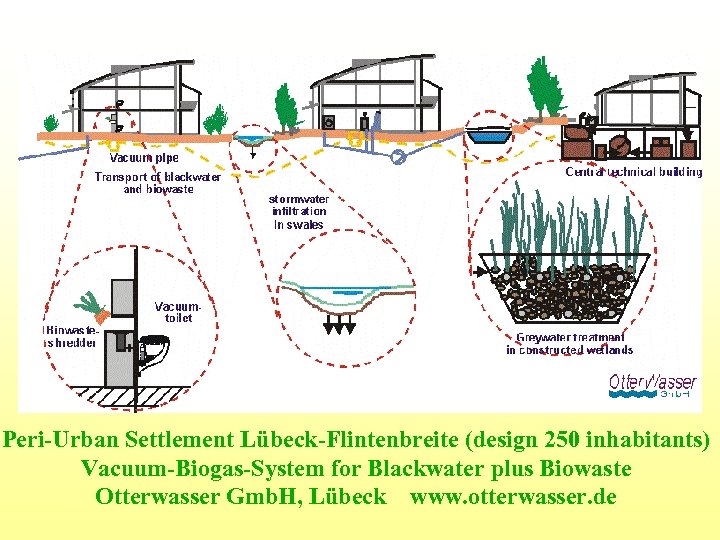 Peri-Urban Settlement Lübeck-Flintenbreite (design 250 inhabitants) Vacuum-Biogas-System for Blackwater plus Biowaste Otterwasser Gmb. H, Lübeck www. otterwasser. de
Peri-Urban Settlement Lübeck-Flintenbreite (design 250 inhabitants) Vacuum-Biogas-System for Blackwater plus Biowaste Otterwasser Gmb. H, Lübeck www. otterwasser. de
 Vacuum-Toilet 0. 7 litres/flush Vaccum-Technology: Roediger, Hanau
Vacuum-Toilet 0. 7 litres/flush Vaccum-Technology: Roediger, Hanau
 Vacuum-Toilet Vaccum-Technology: Roediger, Hanau - 0. 7 litres/flush - small diameter pipes - evacuation pump station needed - pneumatic control of the valves - can lift water up to 4. 5 meters - technically complex, maintenance needed - rather for groups of houses or hotels, office buildings - scaling in pipes: acid every 5 years - explain users functioning to avoid clogging
Vacuum-Toilet Vaccum-Technology: Roediger, Hanau - 0. 7 litres/flush - small diameter pipes - evacuation pump station needed - pneumatic control of the valves - can lift water up to 4. 5 meters - technically complex, maintenance needed - rather for groups of houses or hotels, office buildings - scaling in pipes: acid every 5 years - explain users functioning to avoid clogging
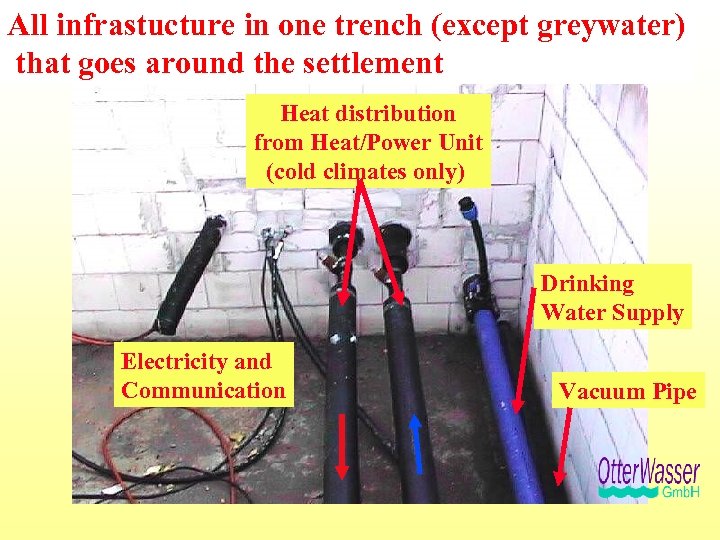 All infrastucture in one trench (except greywater) that goes around the settlement Lübeck-Flintenbreite Heat distribution from Heat/Power Unit (cold climates only) Drinking Water Supply Electricity and Communication Vacuum Pipe
All infrastucture in one trench (except greywater) that goes around the settlement Lübeck-Flintenbreite Heat distribution from Heat/Power Unit (cold climates only) Drinking Water Supply Electricity and Communication Vacuum Pipe
 Community Building with central technical Devices Lübeck-Flintenbreite Cellar: Vacuumstation, Biowaste Grinder, Hygienisation, Biogas Plant Above ground: Seminar/Party room, Office, 4 Flats and HPG (Otterwasser Gmb. H, Lübeck, Germany, 2001)
Community Building with central technical Devices Lübeck-Flintenbreite Cellar: Vacuumstation, Biowaste Grinder, Hygienisation, Biogas Plant Above ground: Seminar/Party room, Office, 4 Flats and HPG (Otterwasser Gmb. H, Lübeck, Germany, 2001)
 to Digester Vacuum Pumping Station for Blackwater Sanitisation of Blackwater and biowaste Bio-Waste Inlet and Grinder
to Digester Vacuum Pumping Station for Blackwater Sanitisation of Blackwater and biowaste Bio-Waste Inlet and Grinder
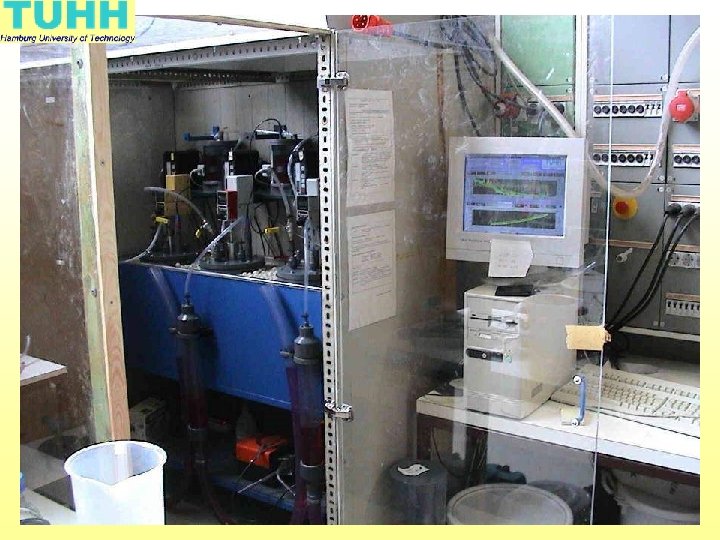
 Blackwater digestors: research at TUHH, Hamburg University of Technology
Blackwater digestors: research at TUHH, Hamburg University of Technology

 Greywater treatment: Constructed wetland / Bio-sandfilter vertical flow, subsurface, sand 0 -4 mm 2 m² per capita (cold climate, else less) Lübeck-Flintenbreite, Germany
Greywater treatment: Constructed wetland / Bio-sandfilter vertical flow, subsurface, sand 0 -4 mm 2 m² per capita (cold climate, else less) Lübeck-Flintenbreite, Germany
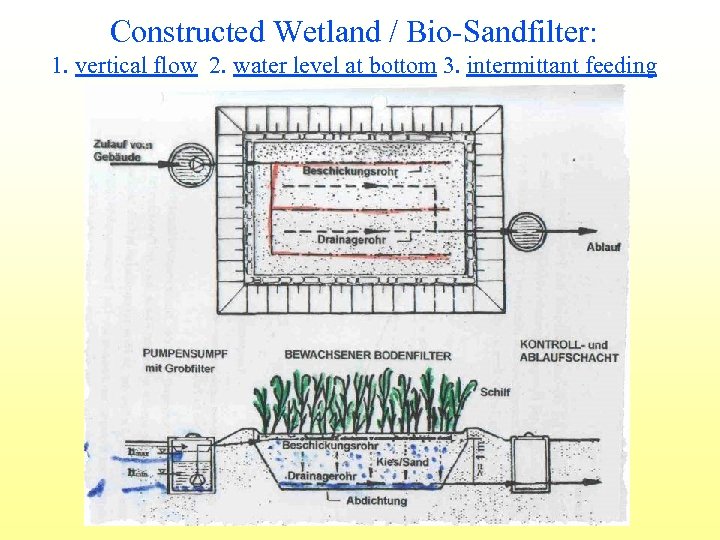 Constructed Wetland / Bio-Sandfilter: 1. vertical flow 2. water level at bottom 3. intermittant feeding
Constructed Wetland / Bio-Sandfilter: 1. vertical flow 2. water level at bottom 3. intermittant feeding
 Clean effluent, low in nutrients
Clean effluent, low in nutrients
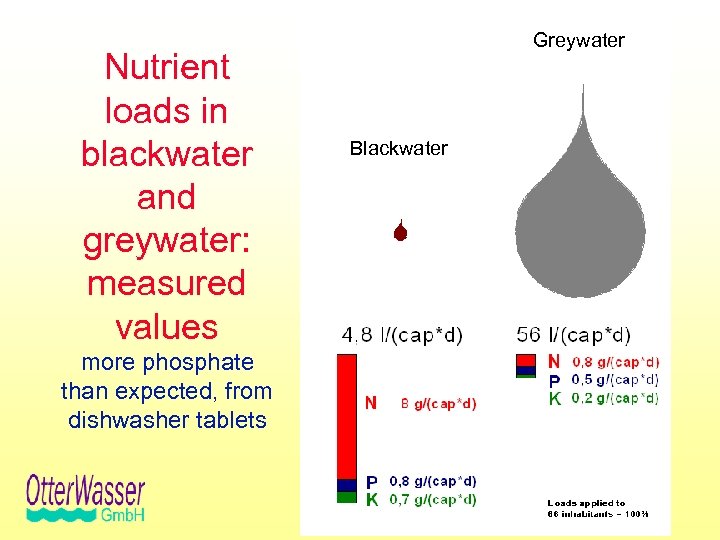 Nutrient loads in blackwater and greywater: measured values more phosphate than expected, from dishwasher tablets Greywater Blackwater
Nutrient loads in blackwater and greywater: measured values more phosphate than expected, from dishwasher tablets Greywater Blackwater
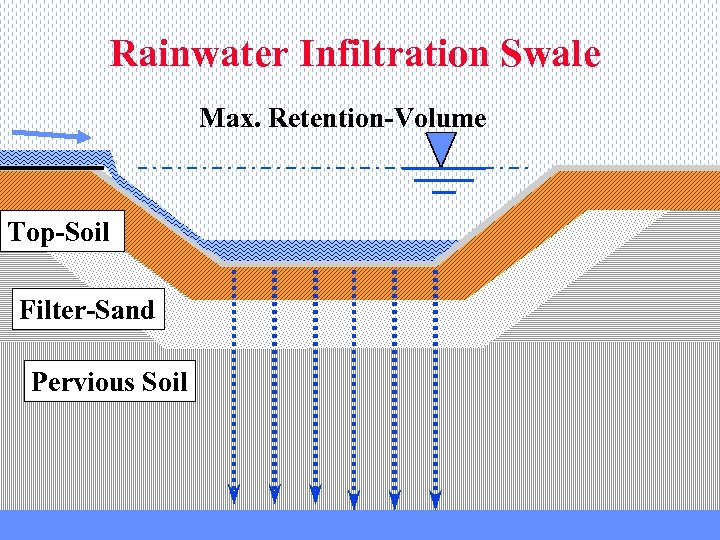 Rainwater Infiltration Swale Max. Retention-Volume Top-Soil Filter-Sand Pervious Soil
Rainwater Infiltration Swale Max. Retention-Volume Top-Soil Filter-Sand Pervious Soil
 Stormwater management is one of the major tasks of wastewater systems. Rainwater that runs off a surface is defined as wastewater. Mixing clean rainwater runoff with household and industrial wastewater is not a proper method with respect to resources efficiency and environmental protection. If ecosan solutions that mostly work without a central sewerage system are installed, other ways of rainwater management are needed. For the Flintenbreite settlement infiltration swales where made at low costs. If the ground is less pervious there is teh possibility of swale-trench systems or the open type of monsoon drains
Stormwater management is one of the major tasks of wastewater systems. Rainwater that runs off a surface is defined as wastewater. Mixing clean rainwater runoff with household and industrial wastewater is not a proper method with respect to resources efficiency and environmental protection. If ecosan solutions that mostly work without a central sewerage system are installed, other ways of rainwater management are needed. For the Flintenbreite settlement infiltration swales where made at low costs. If the ground is less pervious there is teh possibility of swale-trench systems or the open type of monsoon drains
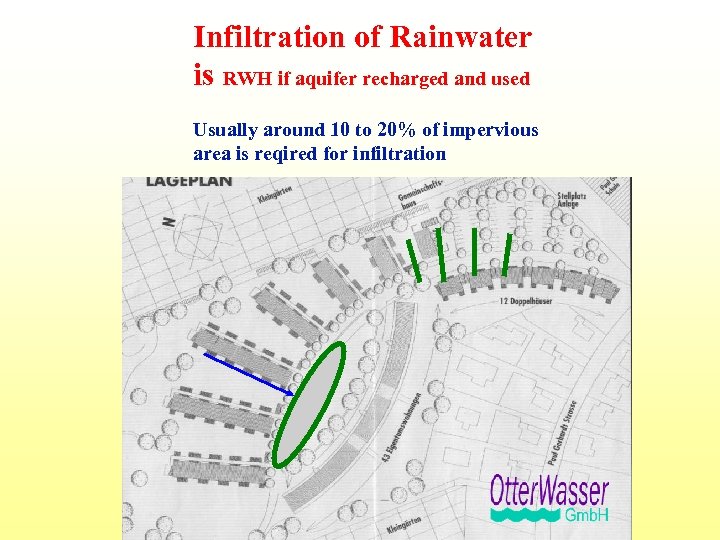 Infiltration of Rainwater is RWH if aquifer recharged and used Usually around 10 to 20% of impervious area is reqired for infiltration
Infiltration of Rainwater is RWH if aquifer recharged and used Usually around 10 to 20% of impervious area is reqired for infiltration
 Rainwater Harvesting fits well to Ecosan can diminish the freshwater demand strongly resulting in longer lasting tank reserves from CSE India see www. rainwaterharvesting. org from Lange/Otterpohl: Abwasser
Rainwater Harvesting fits well to Ecosan can diminish the freshwater demand strongly resulting in longer lasting tank reserves from CSE India see www. rainwaterharvesting. org from Lange/Otterpohl: Abwasser
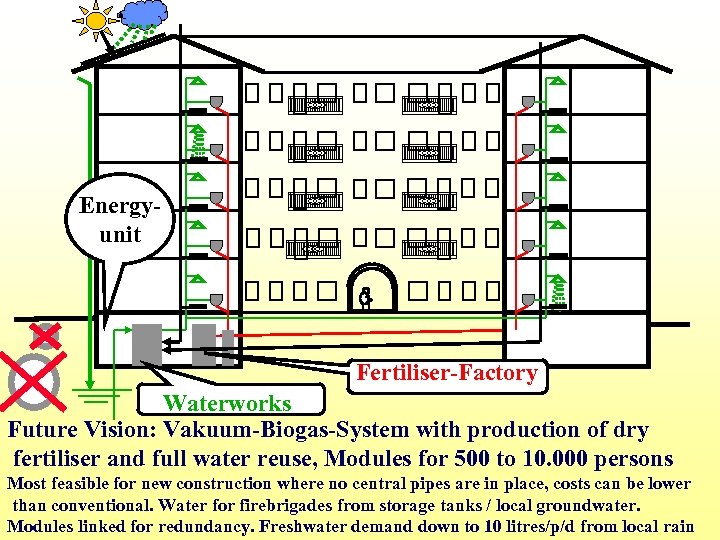 Energyunit Fertiliser-Factory Waterworks Future Vision: Vakuum-Biogas-System with production of dry fertiliser and full water reuse, Modules for 500 to 10. 000 persons Most feasible for new construction where no central pipes are in place, costs can be lower than conventional. Water for firebrigades from storage tanks / local groundwater. Modules linked for redundancy. Freshwater demand down to 10 litres/p/d from local rain
Energyunit Fertiliser-Factory Waterworks Future Vision: Vakuum-Biogas-System with production of dry fertiliser and full water reuse, Modules for 500 to 10. 000 persons Most feasible for new construction where no central pipes are in place, costs can be lower than conventional. Water for firebrigades from storage tanks / local groundwater. Modules linked for redundancy. Freshwater demand down to 10 litres/p/d from local rain
 Project Freiburg Vauban, Germany: Arbeiten & Wohnen Vacuum-Biogas-System for Blackwater/Biowaste (Passive-house: One of the most energy-efficient houses worldwide) ATURUS, Jörg Lange/Arne Panesar, Freiburg, Germany www. passivhaus-vauban. de
Project Freiburg Vauban, Germany: Arbeiten & Wohnen Vacuum-Biogas-System for Blackwater/Biowaste (Passive-house: One of the most energy-efficient houses worldwide) ATURUS, Jörg Lange/Arne Panesar, Freiburg, Germany www. passivhaus-vauban. de
 Biogas-Project of BORDA, Bremen, Germany (www. borda. de) and BEST, Indonesia, Settlement Tangerang Wastewater treatment below the building Biogas-plant for blackwater, can be low-tech in tropical climates
Biogas-Project of BORDA, Bremen, Germany (www. borda. de) and BEST, Indonesia, Settlement Tangerang Wastewater treatment below the building Biogas-plant for blackwater, can be low-tech in tropical climates
 City plan of Lanxmeer, Culemborg near Utrecht (www. eva-lanxmeer. nl; designed by Eble)
City plan of Lanxmeer, Culemborg near Utrecht (www. eva-lanxmeer. nl; designed by Eble)
 EVA Lanxmeer, Culemborg / Utrecht, The Netherlands Initiative by Marleen Kaptein and the city council of. Culemborg • Planned for 1. 000 inhabitants, small industry and conference centre • Blackwater separate, treatment in biogas plant • Greywater in constructed wetlands plus aquaculture • Solar energy usage and semicentral heat supply from earth-water heat pump
EVA Lanxmeer, Culemborg / Utrecht, The Netherlands Initiative by Marleen Kaptein and the city council of. Culemborg • Planned for 1. 000 inhabitants, small industry and conference centre • Blackwater separate, treatment in biogas plant • Greywater in constructed wetlands plus aquaculture • Solar energy usage and semicentral heat supply from earth-water heat pump
 Photos: P. D. Jenssen Greywater treatment at Klosterenga Oslo, Norway Prof. Petter Jenssen has also developed a vacuum-blackwater system www. umb. no/research/ecosan The Agricultural University of Norway
Photos: P. D. Jenssen Greywater treatment at Klosterenga Oslo, Norway Prof. Petter Jenssen has also developed a vacuum-blackwater system www. umb. no/research/ecosan The Agricultural University of Norway
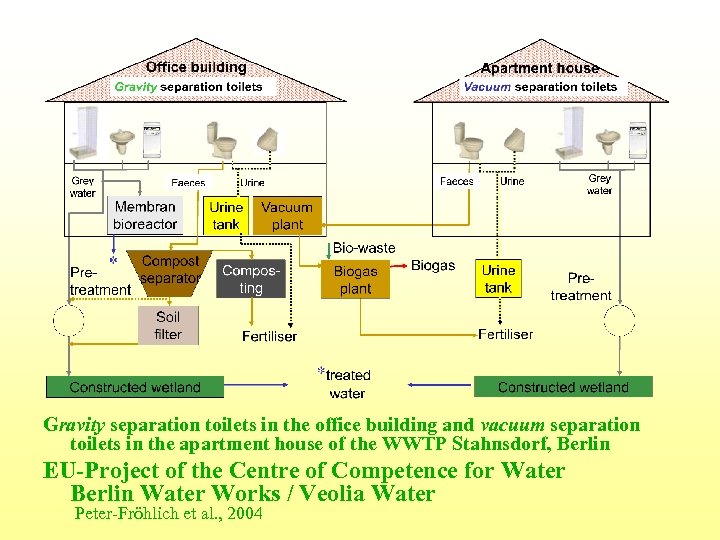 Gravity separation toilets in the office building and vacuum separation toilets in the apartment house of the WWTP Stahnsdorf, Berlin EU-Project of the Centre of Competence for Water Berlin Water Works / Veolia Water Peter-Fröhlich et al. , 2004
Gravity separation toilets in the office building and vacuum separation toilets in the apartment house of the WWTP Stahnsdorf, Berlin EU-Project of the Centre of Competence for Water Berlin Water Works / Veolia Water Peter-Fröhlich et al. , 2004
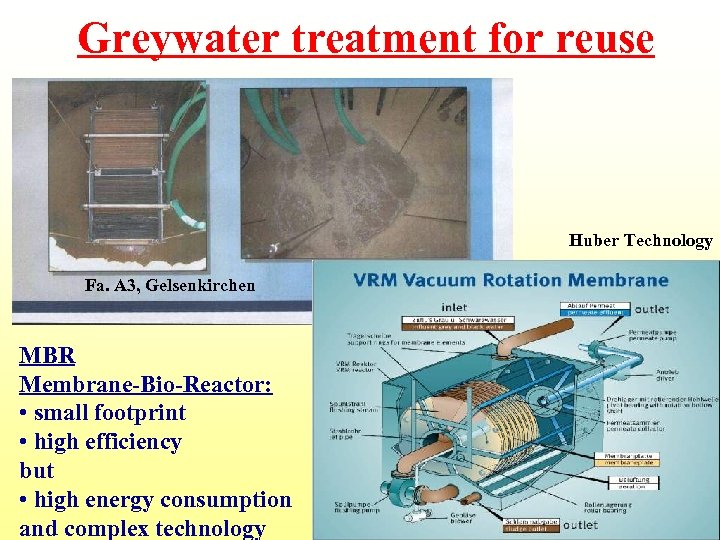 Greywater treatment for reuse Huber Technology Fa. A 3, Gelsenkirchen MBR Membrane-Bio-Reactor: • small footprint • high efficiency but • high energy consumption and complex technology
Greywater treatment for reuse Huber Technology Fa. A 3, Gelsenkirchen MBR Membrane-Bio-Reactor: • small footprint • high efficiency but • high energy consumption and complex technology
 MBR is an excellent option for water reuse, sanitisation is includes as bacteria do not pass the membrane Cost efficiency is better in case of reuse as there is a direct revenue Make sure that maintenance is assured Moduar units that can be used for greywater treatment and reuse Busse, Germany Membrane module
MBR is an excellent option for water reuse, sanitisation is includes as bacteria do not pass the membrane Cost efficiency is better in case of reuse as there is a direct revenue Make sure that maintenance is assured Moduar units that can be used for greywater treatment and reuse Busse, Germany Membrane module
 Biological Treatement Microfiltration, Reverse Osmosis Greywater to Tapwater
Biological Treatement Microfiltration, Reverse Osmosis Greywater to Tapwater
 An unique idea: The blackwater loop • Toilet wastewater is not wasted but treated for reuse as toilet flushwater • Treatment with MBR plus ozonisation including nitrification assures high quality • Pharmaceutical residues and hormones are eliminated • Closed loop producing a clear liquid with about the same volume and concentrations of nutients as put into the toilet • This system can solve the hygienic and pollution risk from hospital effluents (they usually emit to the sewerage system that is open to the environment trough stormwater overflows and inadequate treatment in conventional plants) • Sizes start from some 100 people /hotel beds, for new construction and complete reconstruction this system can be significantly cheaper than conventional ones and reduse freshwater demand to 10 litres person and day • Anaerobic treatment of faecal matter with biowaste for larger systems • Technically complex, operation and maintenance have to be organised and financed
An unique idea: The blackwater loop • Toilet wastewater is not wasted but treated for reuse as toilet flushwater • Treatment with MBR plus ozonisation including nitrification assures high quality • Pharmaceutical residues and hormones are eliminated • Closed loop producing a clear liquid with about the same volume and concentrations of nutients as put into the toilet • This system can solve the hygienic and pollution risk from hospital effluents (they usually emit to the sewerage system that is open to the environment trough stormwater overflows and inadequate treatment in conventional plants) • Sizes start from some 100 people /hotel beds, for new construction and complete reconstruction this system can be significantly cheaper than conventional ones and reduse freshwater demand to 10 litres person and day • Anaerobic treatment of faecal matter with biowaste for larger systems • Technically complex, operation and maintenance have to be organised and financed
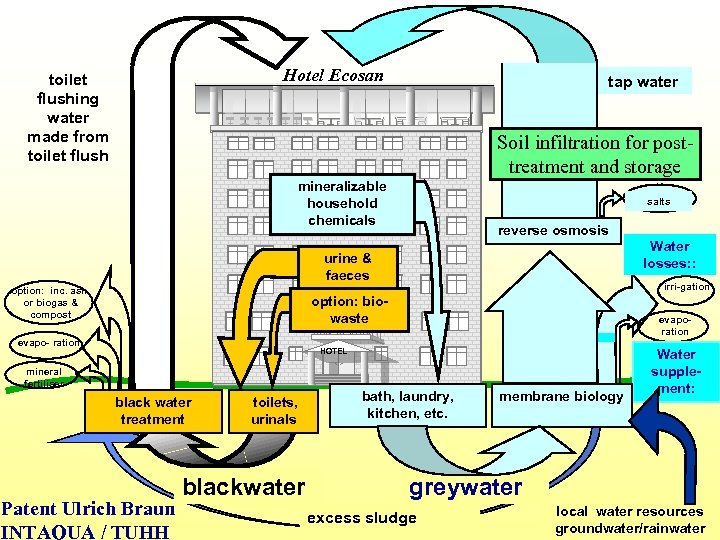 Hotel Ecosan toilet flushing water made from toilet flush tap water Soil infiltration for posttreatment and storage mineralizable household chemicals salts reverse osmosis Water losses: : urine & faeces option: inc. ash, or biogas & compost irri-gation option: biowaste evapo- ration evaporation HOTEL mineral fertiliser black water treatment Patent Ulrich Braun INTAQUA / TUHH toilets, urinals blackwater bath, laundry, kitchen, etc. membrane biology Water supplement: greywater excess sludge local water resources groundwater/rainwater
Hotel Ecosan toilet flushing water made from toilet flush tap water Soil infiltration for posttreatment and storage mineralizable household chemicals salts reverse osmosis Water losses: : urine & faeces option: inc. ash, or biogas & compost irri-gation option: biowaste evapo- ration evaporation HOTEL mineral fertiliser black water treatment Patent Ulrich Braun INTAQUA / TUHH toilets, urinals blackwater bath, laundry, kitchen, etc. membrane biology Water supplement: greywater excess sludge local water resources groundwater/rainwater
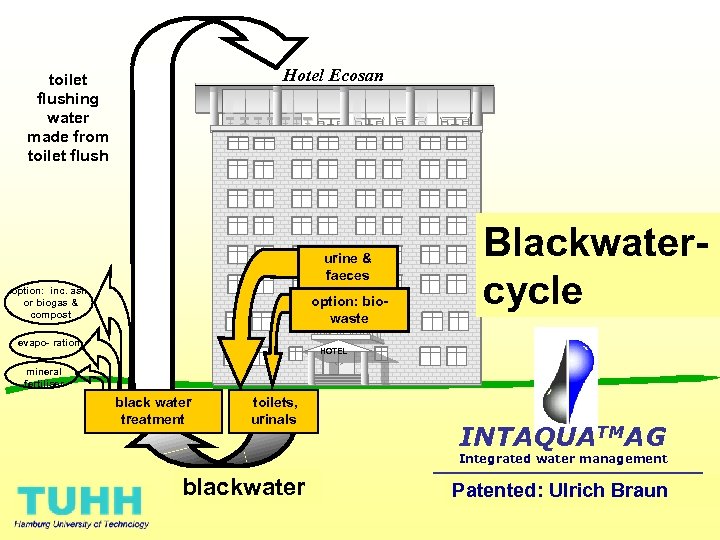 Hotel Ecosan toilet flushing water made from toilet flush urine & faeces option: inc. ash, or biogas & compost option: biowaste evapo- ration Blackwatercycle HOTEL mineral fertiliser black water treatment toilets, urinals INTAQUATMAG Integrated water management blackwater Patented: Ulrich Braun
Hotel Ecosan toilet flushing water made from toilet flush urine & faeces option: inc. ash, or biogas & compost option: biowaste evapo- ration Blackwatercycle HOTEL mineral fertiliser black water treatment toilets, urinals INTAQUATMAG Integrated water management blackwater Patented: Ulrich Braun
 Blackwater Loop Research unit at TUHH MBR INTAQUATMAG Integrated water management Solids separation
Blackwater Loop Research unit at TUHH MBR INTAQUATMAG Integrated water management Solids separation
 Breakthrough in future Water Management… • Typically 70 to 90% of investment in wastewater systems goes into transport only • Economy of scale only for WWTPs • Advances in small scale technology: Economy of scale in NUMBERS • WWTP in most situations incapable of high degree of reuse • Many micro-pollutants go through WWTPs
Breakthrough in future Water Management… • Typically 70 to 90% of investment in wastewater systems goes into transport only • Economy of scale only for WWTPs • Advances in small scale technology: Economy of scale in NUMBERS • WWTP in most situations incapable of high degree of reuse • Many micro-pollutants go through WWTPs
 Breakthrough in future Water Management… for new development and major reconstruction • Rainwater infiltration • Greywater treatment with MBR, infiltration (adapt household chemicals) • Draw raw-water from groundwater (lined underground storage if necessary) • Tapwater production through RO (drinking possible, else sourcewater) • Micro-Fertiliser factory from toilets / biowaste
Breakthrough in future Water Management… for new development and major reconstruction • Rainwater infiltration • Greywater treatment with MBR, infiltration (adapt household chemicals) • Draw raw-water from groundwater (lined underground storage if necessary) • Tapwater production through RO (drinking possible, else sourcewater) • Micro-Fertiliser factory from toilets / biowaste
 Breakthrough in future Water Management… for new development and major reconstruction • Rainwater infiltration • Greywater treatment with MBR, infiltration (adapt household chemicals) • Draw raw-water from groundwater Costs can bestorage if necessary) lower (lined underground significantly • if no central system is in place Tapwater production through RO (drinking possible, else sourcewater) • Micro-Fertiliser factory from toilets / biowaste
Breakthrough in future Water Management… for new development and major reconstruction • Rainwater infiltration • Greywater treatment with MBR, infiltration (adapt household chemicals) • Draw raw-water from groundwater Costs can bestorage if necessary) lower (lined underground significantly • if no central system is in place Tapwater production through RO (drinking possible, else sourcewater) • Micro-Fertiliser factory from toilets / biowaste
 What are the principles of blackwater systems?
What are the principles of blackwater systems?
 1. Blackwater and integrated systems design 2. Dry sanitation / Low Cost solutions 3. Urine-Diversion with flush sanitation
1. Blackwater and integrated systems design 2. Dry sanitation / Low Cost solutions 3. Urine-Diversion with flush sanitation
 Composting-toilets, Germany • maintenance cruicial for function • better with urine sorting (too many failures without) • rural and peri-urban areas Clivus Multrum company Berger Biotechnik, Hamburg
Composting-toilets, Germany • maintenance cruicial for function • better with urine sorting (too many failures without) • rural and peri-urban areas Clivus Multrum company Berger Biotechnik, Hamburg
 Eco-Settlement ‚Braamwisch‘, Hamburg, Germany • Blackwater separate, treatment in composter • Greywater in constructed wetlands • Solar energy usage
Eco-Settlement ‚Braamwisch‘, Hamburg, Germany • Blackwater separate, treatment in composter • Greywater in constructed wetlands • Solar energy usage
 One GRAM of faeces can contain • 10, 000 Viruses • 1, 000 Bacteria • 1, 000 Parasite cysts • 100 Parasite eggs. (source: UNESCO, 2001) 5 MILLION people die of polluted water every year (WHO) Sanitization easy and cheap: DO NOT MIX !!!
One GRAM of faeces can contain • 10, 000 Viruses • 1, 000 Bacteria • 1, 000 Parasite cysts • 100 Parasite eggs. (source: UNESCO, 2001) 5 MILLION people die of polluted water every year (WHO) Sanitization easy and cheap: DO NOT MIX !!!
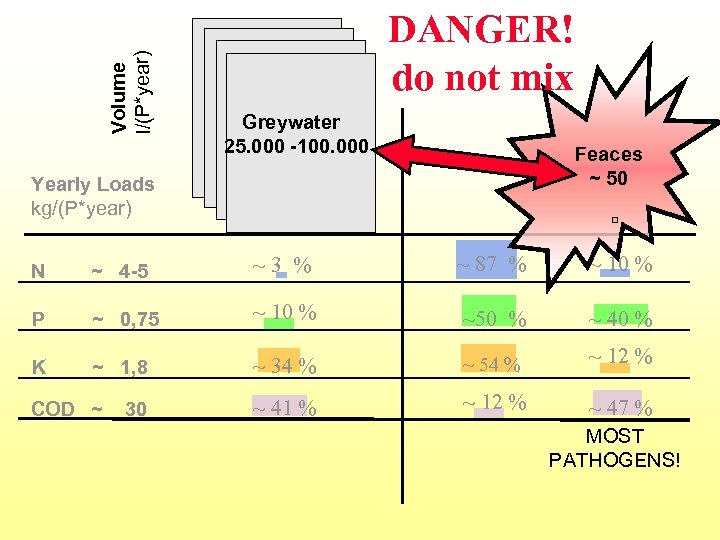 Volume l/(P*year) DANGER! do not mix Greywater 25. 000 -100. 000 Feaces ~ 50 Yearly Loads kg/(P*year) N ~ 4 -5 ~3 % ~ 87 % ~ 10 % P ~ 0, 75 ~ 10 % ~50 % ~ 40 % K ~ 1, 8 ~ 34 % ~ 54 % ~ 12 % ~ 41 % ~ 12 % ~ 47 % COD ~ 30 MOST PATHOGENS!
Volume l/(P*year) DANGER! do not mix Greywater 25. 000 -100. 000 Feaces ~ 50 Yearly Loads kg/(P*year) N ~ 4 -5 ~3 % ~ 87 % ~ 10 % P ~ 0, 75 ~ 10 % ~50 % ~ 40 % K ~ 1, 8 ~ 34 % ~ 54 % ~ 12 % ~ 41 % ~ 12 % ~ 47 % COD ~ 30 MOST PATHOGENS!
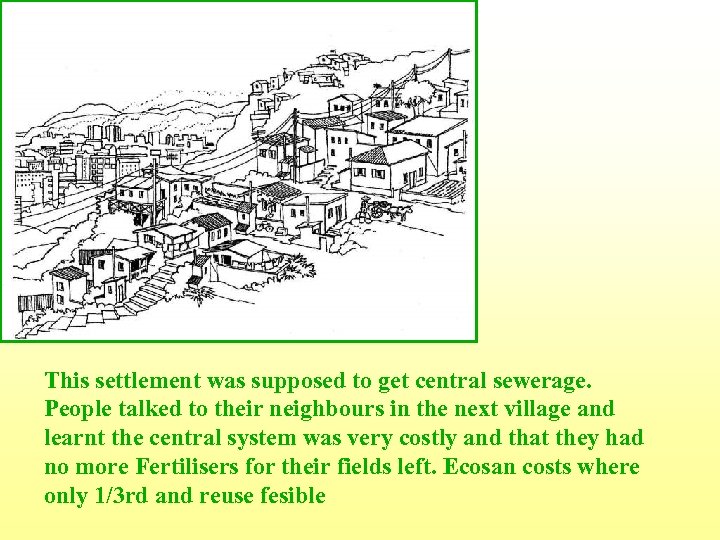 This settlement was supposed to get central sewerage. People talked to their neighbours in the next village and learnt the central system was very costly and that they had no more Fertilisers for their fields left. Ecosan costs where only 1/3 rd and reuse fesible
This settlement was supposed to get central sewerage. People talked to their neighbours in the next village and learnt the central system was very costly and that they had no more Fertilisers for their fields left. Ecosan costs where only 1/3 rd and reuse fesible
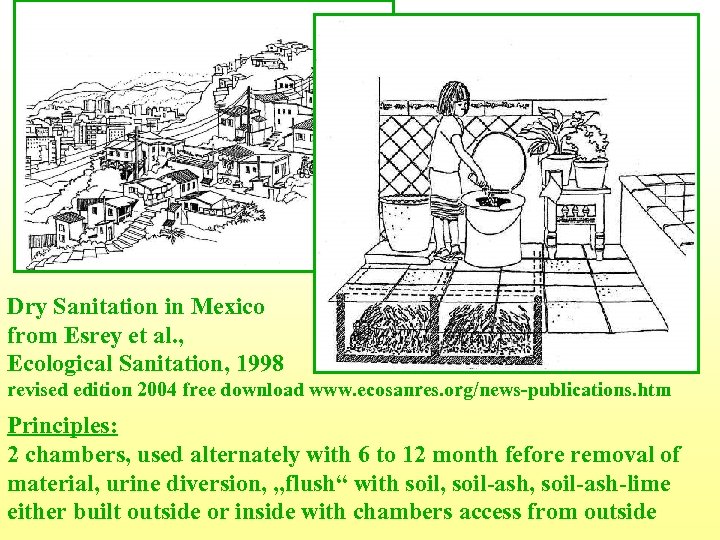 Dry Sanitation in Mexico from Esrey et al. , Ecological Sanitation, 1998 revised edition 2004 free download www. ecosanres. org/news-publications. htm Principles: 2 chambers, used alternately with 6 to 12 month fefore removal of material, urine diversion, „flush“ with soil, soil-ash-lime either built outside or inside with chambers access from outside
Dry Sanitation in Mexico from Esrey et al. , Ecological Sanitation, 1998 revised edition 2004 free download www. ecosanres. org/news-publications. htm Principles: 2 chambers, used alternately with 6 to 12 month fefore removal of material, urine diversion, „flush“ with soil, soil-ash-lime either built outside or inside with chambers access from outside
 Espacio de Salud Cuernavaca, Morelos MEXICO
Espacio de Salud Cuernavaca, Morelos MEXICO
 Can be installed in upscale homes, too Key issue: explain prospective users idea and function, operation can be organised by small local organisation Almost no water shall go into the faecals chamber (take care of washwater in cultures with wet anal cleansing) Public toilets can better be equipped with squat toilets that are available with urine diversion, too
Can be installed in upscale homes, too Key issue: explain prospective users idea and function, operation can be organised by small local organisation Almost no water shall go into the faecals chamber (take care of washwater in cultures with wet anal cleansing) Public toilets can better be equipped with squat toilets that are available with urine diversion, too
 Local production and operational services keep money inside the community. This lady will probably purchase her food in the same village. Money spent on imported goods will often go to wealthy shareholders. Ecosan has the potential to do good for the wealthy ones far away by not increasing the heavy burden of money furher. Commercial fertiliser is often imported, urine is a cost efficient alternative
Local production and operational services keep money inside the community. This lady will probably purchase her food in the same village. Money spent on imported goods will often go to wealthy shareholders. Ecosan has the potential to do good for the wealthy ones far away by not increasing the heavy burden of money furher. Commercial fertiliser is often imported, urine is a cost efficient alternative
 Two chamber dry toilet for cultures with wet anal cleansing Urine diversion and usage of urine as fertiliser, solids as soil conditioners after decomposition Community based projects are a key to success, informed choice, information about costs of alternatives, demand for mainitenance Eco. Solutions, Paul Calvert, India Ecological Sanitation, 2004 www. ecosanres. org/newspublications. htm
Two chamber dry toilet for cultures with wet anal cleansing Urine diversion and usage of urine as fertiliser, solids as soil conditioners after decomposition Community based projects are a key to success, informed choice, information about costs of alternatives, demand for mainitenance Eco. Solutions, Paul Calvert, India Ecological Sanitation, 2004 www. ecosanres. org/newspublications. htm
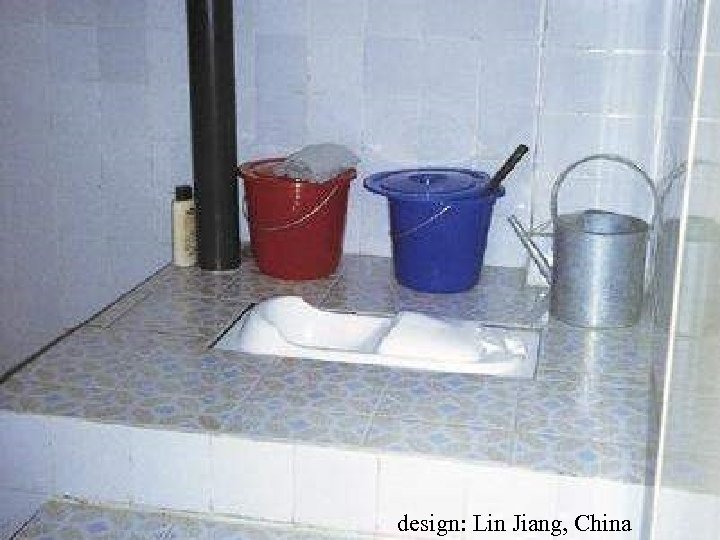 design: Lin Jiang, China
design: Lin Jiang, China
 Ecosanres has started many ecosan projects in China, including multistorey houses (Erdos, see www. ecosanres. org)
Ecosanres has started many ecosan projects in China, including multistorey houses (Erdos, see www. ecosanres. org)
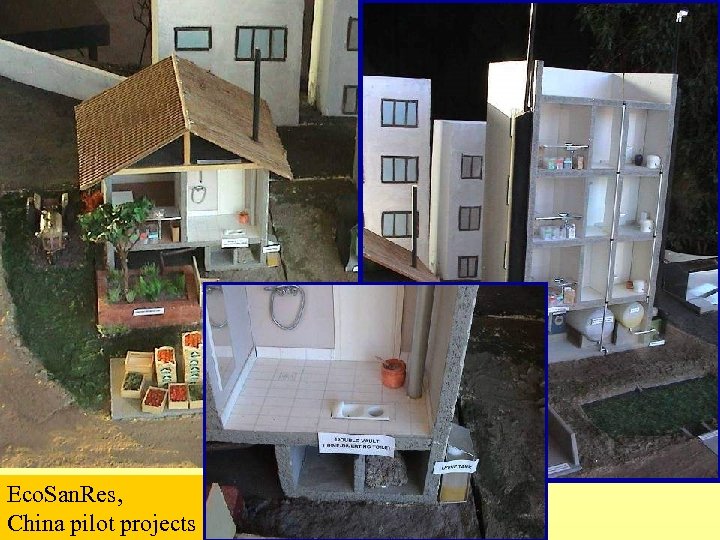 Eco. San. Res, China pilot projects
Eco. San. Res, China pilot projects
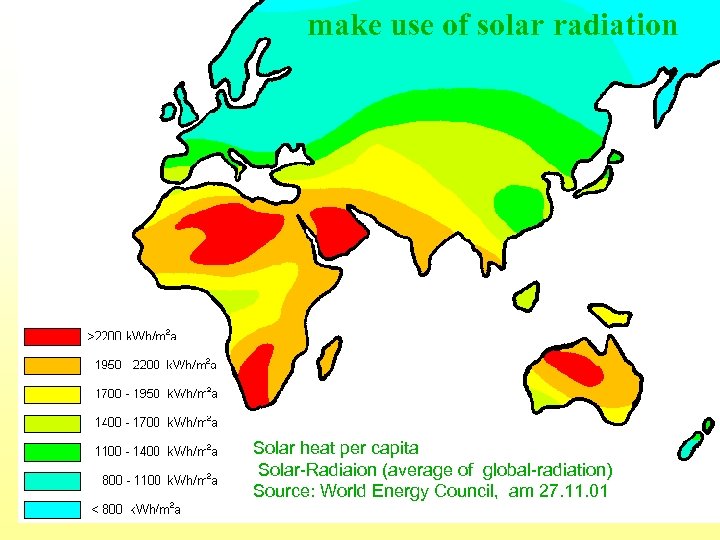 make use of solar radiation Solar heat per capita Solar-Radiaion (average of global-radiation) Source: World Energy Council, am 27. 11. 01
make use of solar radiation Solar heat per capita Solar-Radiaion (average of global-radiation) Source: World Energy Council, am 27. 11. 01
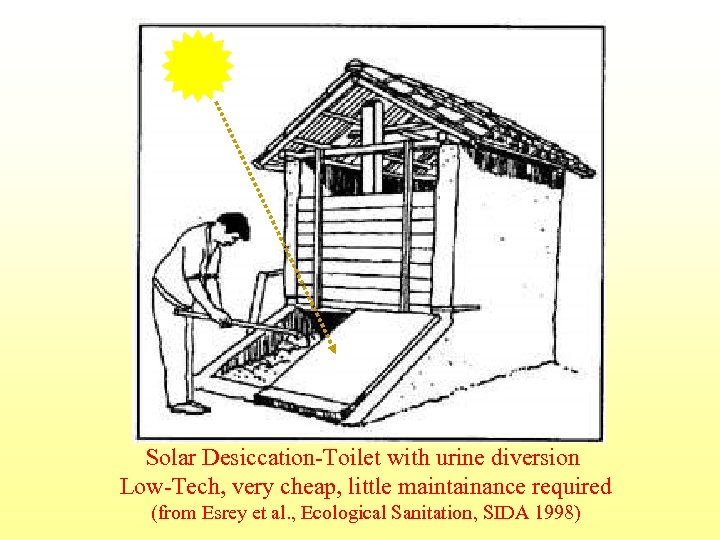 Solar Desiccation-Toilet with urine diversion Low-Tech, very cheap, little maintainance required (from Esrey et al. , Ecological Sanitation, SIDA 1998)
Solar Desiccation-Toilet with urine diversion Low-Tech, very cheap, little maintainance required (from Esrey et al. , Ecological Sanitation, SIDA 1998)
 De-siccation Toilet with solar heating of the 2 chambers Mali, West Africa GTZ / Otterwasser Gmb. H
De-siccation Toilet with solar heating of the 2 chambers Mali, West Africa GTZ / Otterwasser Gmb. H
 Solar desiccation of feaces, Mali, West Africa (GTZ / Otterwasser) black lids for solar heating Chamber 2 built ABOVE soil, no contact to groundwater, monsoons !
Solar desiccation of feaces, Mali, West Africa (GTZ / Otterwasser) black lids for solar heating Chamber 2 built ABOVE soil, no contact to groundwater, monsoons !
 Ecosan Toilets, Rumania (TUHH / WECF) Institute of Wastewater Management and Water Protection
Ecosan Toilets, Rumania (TUHH / WECF) Institute of Wastewater Management and Water Protection
 Neue Schultoilette, Ukraine (TUHH/WECF)
Neue Schultoilette, Ukraine (TUHH/WECF)
 Sawdust or ashes are used to ‚flush‘ squat-urinediversion-toilet by Lin Jiang, China WECF: Women in Europe for a Common Future (Holland) in co-operation with TUHH www. wecf. org
Sawdust or ashes are used to ‚flush‘ squat-urinediversion-toilet by Lin Jiang, China WECF: Women in Europe for a Common Future (Holland) in co-operation with TUHH www. wecf. org
 What are the principles of dry sanitation?
What are the principles of dry sanitation?
 1. Blackwater and integrated systems design 2. Dry sanitation / Low Cost solutions 3. Urine-Diversion with flush sanitation
1. Blackwater and integrated systems design 2. Dry sanitation / Low Cost solutions 3. Urine-Diversion with flush sanitation
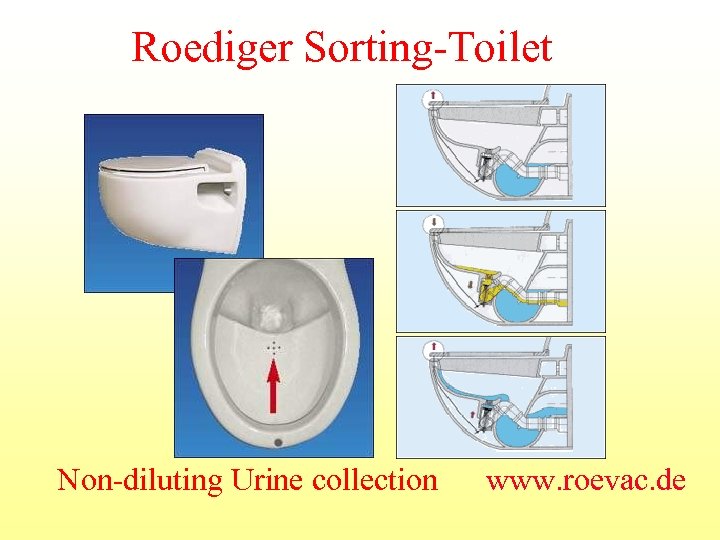 Roediger Sorting-Toilet Non-diluting Urine collection www. roevac. de
Roediger Sorting-Toilet Non-diluting Urine collection www. roevac. de
 Gustavsberg Sorting-Toilet
Gustavsberg Sorting-Toilet
 Settlement „Palsternackan“, Sweden Urine-Sorting Toilets and Yellow Water collection in urban social housing. The urine is stored and transported by vacuum-truck to agriculture
Settlement „Palsternackan“, Sweden Urine-Sorting Toilets and Yellow Water collection in urban social housing. The urine is stored and transported by vacuum-truck to agriculture
 Ecological Settlement „Understenshöjden“, Sweden Sorting Toilets and Urine collection Greywater Treatment Yellow Water Storage
Ecological Settlement „Understenshöjden“, Sweden Sorting Toilets and Urine collection Greywater Treatment Yellow Water Storage
 Pilot Project “Lambertsmühle” Initiative and Finance: • Wupperverband Verein Lambertsmühle Develpement of the Sanitation Concept • Otterwasser Gmb. H, Lübeck Scientific consultation • TUHH Inst. of Wastewater Management Elements of the Sanitation Concept: • Urine-sorting Toilets and waterless Urinals • Storage Tank for Yellow Water • Pre-Composting Tank (2 chambers, Filter Bags) • Constructed Wetland for filtered Grey- and Brownwater
Pilot Project “Lambertsmühle” Initiative and Finance: • Wupperverband Verein Lambertsmühle Develpement of the Sanitation Concept • Otterwasser Gmb. H, Lübeck Scientific consultation • TUHH Inst. of Wastewater Management Elements of the Sanitation Concept: • Urine-sorting Toilets and waterless Urinals • Storage Tank for Yellow Water • Pre-Composting Tank (2 chambers, Filter Bags) • Constructed Wetland for filtered Grey- and Brownwater
 Urine-Tank 10 Persons (Glass-Resin) Fertilizer for 200 to 400 m² in agriculture is produced person (one growth season/year) 6 month storage, then work into brown land before seeding/planting Potential problems with utilisation of urine: residues of pharmaceuticals and hormones Problem is relevant in flushsanitation, too: direct link to water supply
Urine-Tank 10 Persons (Glass-Resin) Fertilizer for 200 to 400 m² in agriculture is produced person (one growth season/year) 6 month storage, then work into brown land before seeding/planting Potential problems with utilisation of urine: residues of pharmaceuticals and hormones Problem is relevant in flushsanitation, too: direct link to water supply
 2 -Chamber Composting Tank Composting does not really work. Experiments at TUHH (nesxt slide) showed that the combination with vermicomposting can make this unit a great solids converter: 3 to 4 month from wet faecals to something like soil. . (Dissertation Moataz Shalabi, 2006, TUHH)
2 -Chamber Composting Tank Composting does not really work. Experiments at TUHH (nesxt slide) showed that the combination with vermicomposting can make this unit a great solids converter: 3 to 4 month from wet faecals to something like soil. . (Dissertation Moataz Shalabi, 2006, TUHH)
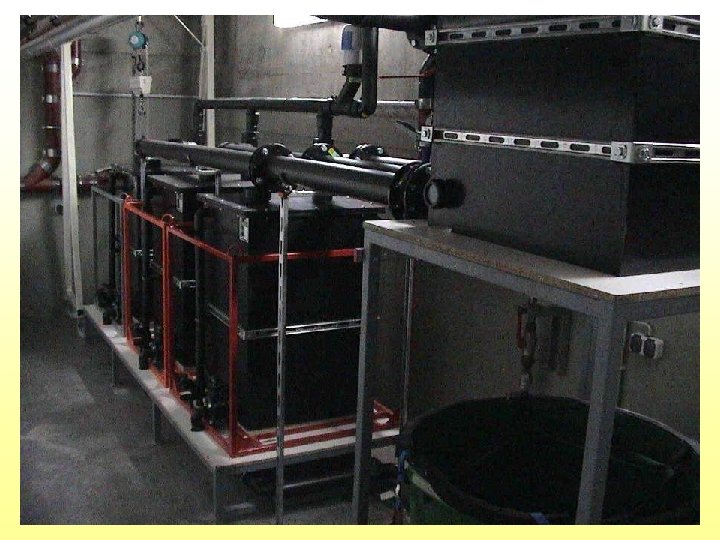

 Vertikal Sandfilter for Greywater and filtrate of Brownwater Principles of constructed wetland?
Vertikal Sandfilter for Greywater and filtrate of Brownwater Principles of constructed wetland?
 Vertical sub-surface flow constructed wetland for greywater plus filtrate from brownwater
Vertical sub-surface flow constructed wetland for greywater plus filtrate from brownwater
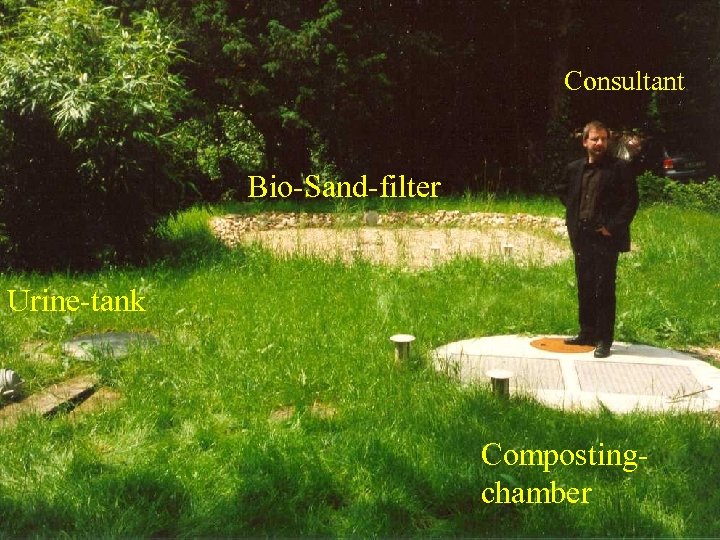 Consultant Bio-Sand-filter Urine-tank Compostingchamber
Consultant Bio-Sand-filter Urine-tank Compostingchamber
 Urine – containers and pre-composters for 106 flats and a school in Linz, Austria Reserach project of Linz AG , Water and Power Utility of the city
Urine – containers and pre-composters for 106 flats and a school in Linz, Austria Reserach project of Linz AG , Water and Power Utility of the city
 Starting the Future ® De. Sa/R – with separation Implementation in HUBER administration building that was newly built for 200 employees
Starting the Future ® De. Sa/R – with separation Implementation in HUBER administration building that was newly built for 200 employees
 Storage tanks in the construction phase Yellow Water Brownwater Greywater in use
Storage tanks in the construction phase Yellow Water Brownwater Greywater in use
 What are the principles of urine sorting flush systems?
What are the principles of urine sorting flush systems?
 Wastewater reuse from conventional WWTPs: Use as FERTILISER, not exclusive source of water to avoid heavy overfertilising
Wastewater reuse from conventional WWTPs: Use as FERTILISER, not exclusive source of water to avoid heavy overfertilising

 Fertiliser usage in China Blackwater of 900 Mio. rural Chinese people 450 Mio tons of organic Fertiliser Potential savings on commercial Fertilisers: 2, 6 Billion US$ per year! In addition soil improvement, protection of inland waters and the seas. . UNESCO, 2001
Fertiliser usage in China Blackwater of 900 Mio. rural Chinese people 450 Mio tons of organic Fertiliser Potential savings on commercial Fertilisers: 2, 6 Billion US$ per year! In addition soil improvement, protection of inland waters and the seas. . UNESCO, 2001
 Solar Water Desinfection: www. sodis. ch SANDEC/EAWAG
Solar Water Desinfection: www. sodis. ch SANDEC/EAWAG
 Rainwater Harvesting: INDIA Monsoon: short flooding, long draughts • water runs off fast • checkdams stop it and allow recharge of aquifers urban RWH in Delhi at CSE
Rainwater Harvesting: INDIA Monsoon: short flooding, long draughts • water runs off fast • checkdams stop it and allow recharge of aquifers urban RWH in Delhi at CSE
 Ecological Sanitation Options for different geographical and socio-economic conditions Dry Toilets • simple Bucket systems • Pre-Composting-Toilets • Large Chamber Composters • Solar Desiccation Toilets (2 chambers) • Earth Toilets (2 chambers) • . . Flush Toilets • Urine-Sorting in decentral and central systems • Vacuum-Toilets and Transport • Low-Flush with ‚Booster‘ • Conventional Flush Sanitation and real agricultural reuse (nutrients) comments: rural low cost more comfortable too wet or too dry hot climates, paper comfortable main step nutient recovery dense population more dilution ww not exclusive water source, HM
Ecological Sanitation Options for different geographical and socio-economic conditions Dry Toilets • simple Bucket systems • Pre-Composting-Toilets • Large Chamber Composters • Solar Desiccation Toilets (2 chambers) • Earth Toilets (2 chambers) • . . Flush Toilets • Urine-Sorting in decentral and central systems • Vacuum-Toilets and Transport • Low-Flush with ‚Booster‘ • Conventional Flush Sanitation and real agricultural reuse (nutrients) comments: rural low cost more comfortable too wet or too dry hot climates, paper comfortable main step nutient recovery dense population more dilution ww not exclusive water source, HM
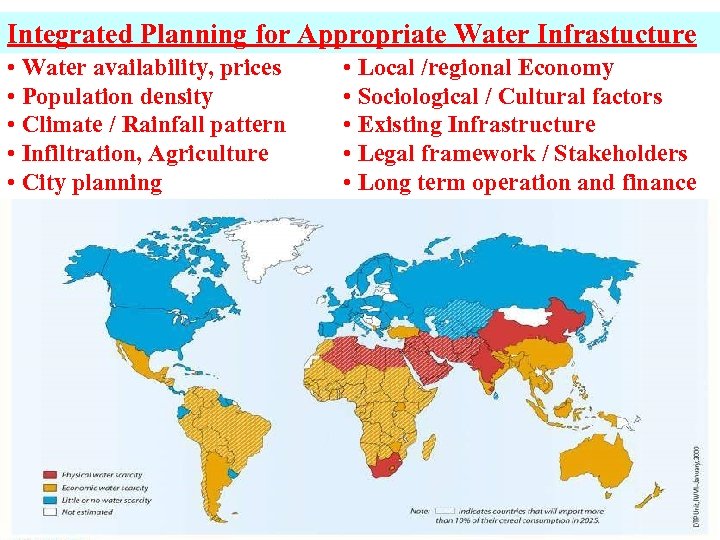 Integrated Planning for Appropriate Water Infrastucture • Water availability, prices • Population density • Climate / Rainfall pattern • Infiltration, Agriculture • City planning • Local /regional Economy • Sociological / Cultural factors • Existing Infrastructure • Legal framework / Stakeholders • Long term operation and finance
Integrated Planning for Appropriate Water Infrastucture • Water availability, prices • Population density • Climate / Rainfall pattern • Infiltration, Agriculture • City planning • Local /regional Economy • Sociological / Cultural factors • Existing Infrastructure • Legal framework / Stakeholders • Long term operation and finance
 www. ecosan. org, SIDA: www. ecosanres. org, GTZ: www. gtz. de/ecosan Thank you !
www. ecosan. org, SIDA: www. ecosanres. org, GTZ: www. gtz. de/ecosan Thank you !
 Thank you ! Goals of this class achieved? Homework: check there is a sanition crisis • see if www. ecosan. org, oriented saniation from • learn solutions of reuse examples www. ecosanres. org, • understand principles of ‘Ecological Sanitation’ www. gtz. de/ecosan • see the strength and limitations of decentral in water technologies 3 people a group of 2 or • get ideas for creative solutions adapted to the situation review the principles, make a rough ecosan design for a place you know
Thank you ! Goals of this class achieved? Homework: check there is a sanition crisis • see if www. ecosan. org, oriented saniation from • learn solutions of reuse examples www. ecosanres. org, • understand principles of ‘Ecological Sanitation’ www. gtz. de/ecosan • see the strength and limitations of decentral in water technologies 3 people a group of 2 or • get ideas for creative solutions adapted to the situation review the principles, make a rough ecosan design for a place you know
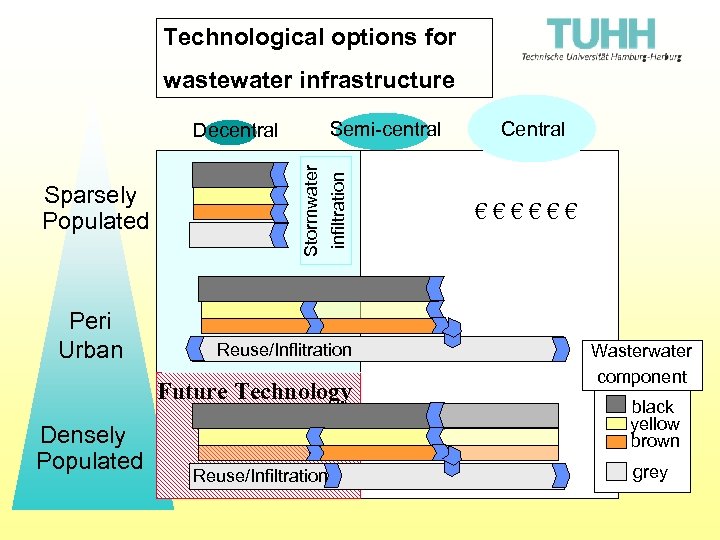 Technological options for wastewater infrastructure Semi-central Sparsely Populated Peri Urban Stormwater infiltration Decentral Reuse/Inflitration Future Technology Densely Populated Reuse/Infiltration Central €€€€€€ Wasterwater component black yellow brown grey
Technological options for wastewater infrastructure Semi-central Sparsely Populated Peri Urban Stormwater infiltration Decentral Reuse/Inflitration Future Technology Densely Populated Reuse/Infiltration Central €€€€€€ Wasterwater component black yellow brown grey
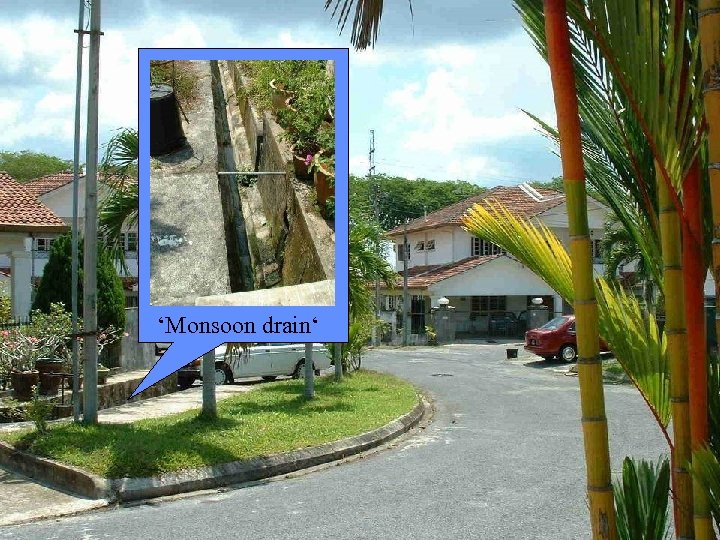
 ‘Monsoon drain‘
‘Monsoon drain‘

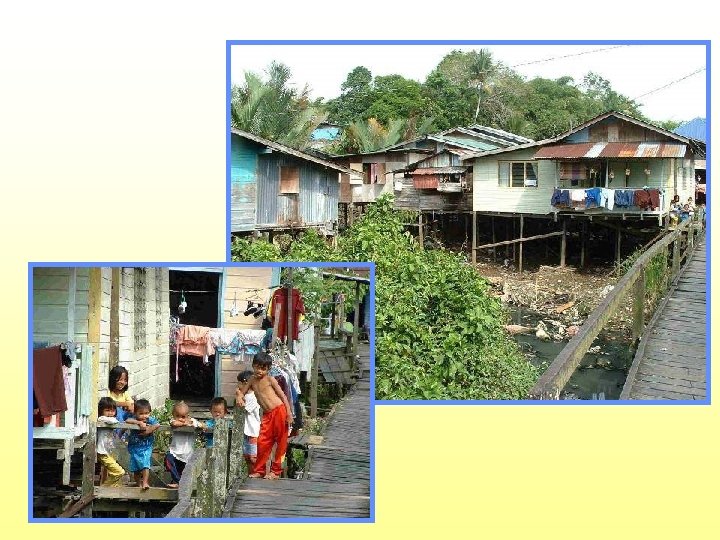
 Ecological Sanitation in new settlements
Ecological Sanitation in new settlements
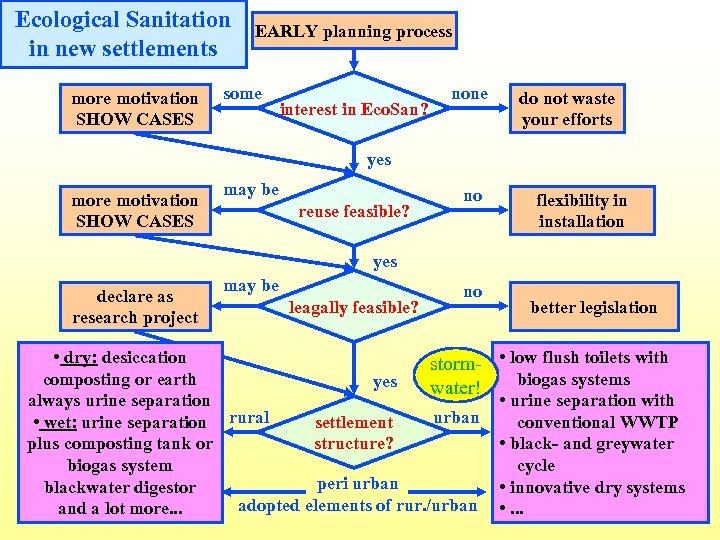 Ecological Sanitation in new settlements more motivation SHOW CASES EARLY planning process some interest in Eco. San? none do not waste your efforts yes more motivation SHOW CASES may be reuse feasible? no flexibility in installation yes declare as research project may be leagally feasible? no • dry: desiccation stormcomposting or earth yes water! always urine separation urban • wet: urine separation rural settlement plus composting tank or structure? biogas system peri urban blackwater digestor adopted elements of rur. /urban and a lot more. . . better legislation • low flush toilets with biogas systems • urine separation with conventional WWTP • black- and greywater cycle • innovative dry systems • . . .
Ecological Sanitation in new settlements more motivation SHOW CASES EARLY planning process some interest in Eco. San? none do not waste your efforts yes more motivation SHOW CASES may be reuse feasible? no flexibility in installation yes declare as research project may be leagally feasible? no • dry: desiccation stormcomposting or earth yes water! always urine separation urban • wet: urine separation rural settlement plus composting tank or structure? biogas system peri urban blackwater digestor adopted elements of rur. /urban and a lot more. . . better legislation • low flush toilets with biogas systems • urine separation with conventional WWTP • black- and greywater cycle • innovative dry systems • . . .
 ABWASSER Handbuch zu einer zukunftsfähigen Wasserwirtschaft Jörg Lange & Ralf Otterpohl 301 Seiten, 105 Abbildungen, 58 Tabellen Zweite Auflage 2000 ISBN 3 -9803502 -1 -5 Preis € 26, - incl. MWSt. MALLBETON, Donaueschingen (0771) 8005 -0 oder über den Buchhandel. . . Sorry, only in German….
ABWASSER Handbuch zu einer zukunftsfähigen Wasserwirtschaft Jörg Lange & Ralf Otterpohl 301 Seiten, 105 Abbildungen, 58 Tabellen Zweite Auflage 2000 ISBN 3 -9803502 -1 -5 Preis € 26, - incl. MWSt. MALLBETON, Donaueschingen (0771) 8005 -0 oder über den Buchhandel. . . Sorry, only in German….


