18ca12545160dc127f180ef3f5f3ee30.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Ecoinformatics in « ICT for Sustainable Growth » Prepared by: Dr. Márta Nagy-Rothengass Head of Unit ICT for Sustainable Growth, DG Information Society and Media, European Commission Talk given by P. Haastrup, European Commission, JRC Ecoinformatics 2008

Overview ICT for Sustainable Growth: • … means • Domains of activity • Community Instruments • Reasearch (FPs) • Deployment (CIP: ICT PSP) • Conclusion
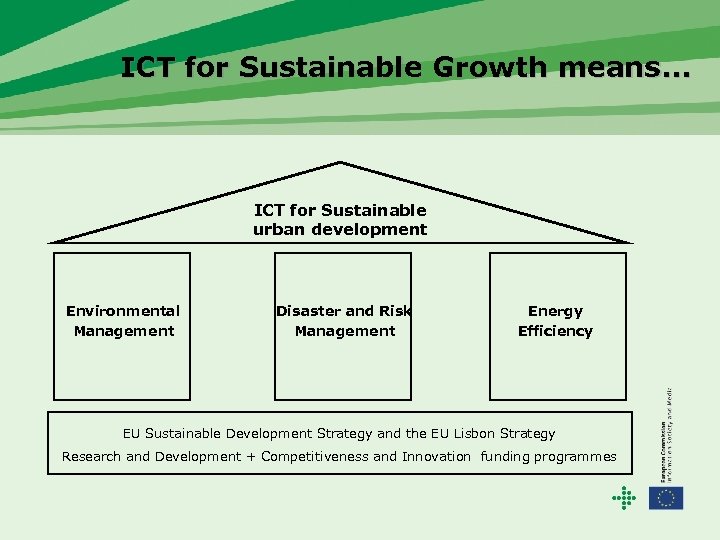
ICT for Sustainable Growth means. . . ICT for Sustainable urban development Environmental Management Disaster and Risk Management Energy Efficiency EU Sustainable Development Strategy and the EU Lisbon Strategy Research and Development + Competitiveness and Innovation funding programmes

ICT is part of the problem … … and part of the solution • ICT should not only reduce its own footprint… • ICT can also help to reduce the footprint of all other sectors/activities • Sustainable consumption and production • Better monitoring and management of the environment • Better preparedness, mitigation, adaptation to climate change, environmental threats, and disasters • Extension of independent living, improved healthcare systems, Clean mobility, • Moreover, by increasing awareness, it will be instrumental to change consumers’ behaviour

Domain of activity – 1 ICT for Energy efficiency Priority areas: • ICT in the Energy Mix and Security of Supply • ICT for better Energy Efficiency • Distributed Generation • Buildings and Homes • Industrial and Business processes • Environmental/ climate impact

Domain of activity - 2 ICT for Environmental Sustainability • Vision of ICT contributing to a cleaner, safer and healthier global environment • Focus on unsustainable trends in Europe: • Degraded environment • Exposure to diverse pollutants • Exposure to ever more frequent disasters • Targets a consolidated European capacity of mastering, predicting and managing the environment and its resources, making use of ICT that interoperate in a Single Information Space for the Environment in Europe (SISE) • Urban environment earmarked as a possible priority test bed

Contributing technical interoperability to ongoing policy initiatives • INSPIRE EC Directive establishing an infrastructure for spatial information in the Community • GMES EC-ESA initiative for the Global Monitoring of the Environment and Security • GEO Recent intergovernmental partnership of 70 Nations to build GEOSS, the Global Earth Observation System of Systems
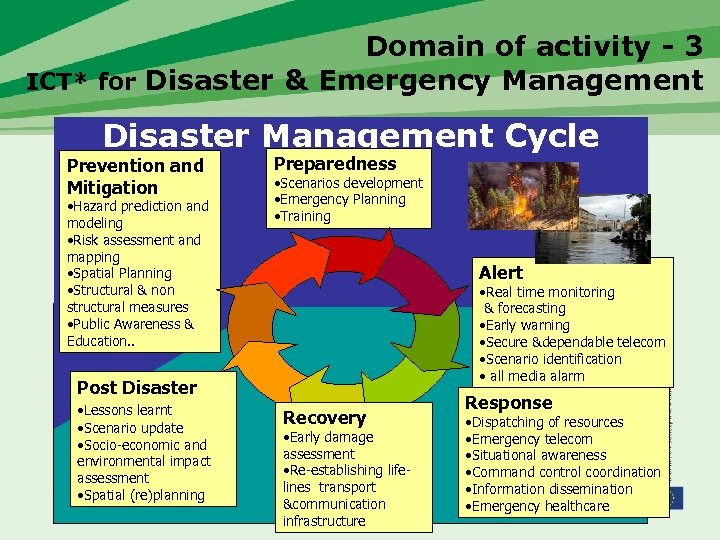
Domain of activity - 3 ICT* for Disaster & Emergency Management Disaster Management Cycle Prevention and Mitigation • Hazard prediction and modeling • Risk assessment and mapping • Spatial Planning • Structural & non structural measures • Public Awareness & Education. . Preparedness • Scenarios development • Emergency Planning • Training Alert • Real time monitoring & forecasting • Early warning • Secure &dependable telecom • Scenario identification • all media alarm Post Disaster • Lessons learnt • Scenario update • Socio-economic and environmental impact assessment • Spatial (re)planning Recovery • Early damage assessment • Re-establishing lifelines transport &communication infrastructure Response • Dispatching of resources • Emergency telecom • Situational awareness • Command control coordination • Information dissemination • Emergency healthcare

Sustainable growth A panoply of converging instruments AN OVERALL STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK FOR COMMUNITY ACTION • To devise and implement adequate European policies • To support RTD on next generation of ICTs contributing to sustainable growth • To raise awareness and deploy ICT-based solutions for environmental sustainability

Building upon FP 6 research in ICT for Disaster Management Three calls in 2003, 2005 and 2006 • • • In-situ monitoring and smart sensor networks Risk information infrastructure and generic services Public safety communication, alert systems and rapidly deployable emergency telecommunications systems Emergency management and rescue operations Distributed tsunami early warning and alert system (Europe & Indian Ocean) Humanitarian demining Projects will deliver in 2007 -2010
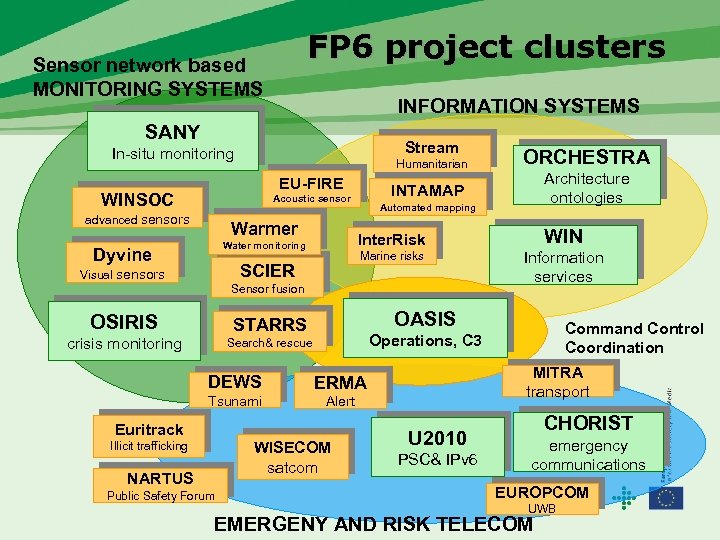
FP 6 project clusters Sensor network based MONITORING SYSTEMS INFORMATION SYSTEMS SANY Stream In-situ monitoring Humanitarian EU-FIRE WINSOC Warmer WIN Marine risks SCIER Visual sensors Automated mapping Inter. Risk Water monitoring Dyvine Information services Sensor fusion OSIRIS OASIS STARRS crisis monitoring DEWS Tsunami MITRA transport ERMA Alert Euritrack WISECOM satcom NARTUS Public Safety Forum Command Control Coordination Operations, C 3 Search& rescue Illicit trafficking Architecture ontologies INTAMAP Acoustic sensor advanced sensors ORCHESTRA U 2010 PSC& IPv 6 CHORIST emergency communications EUROPCOM UWB EMERGENY AND RISK TELECOM

E MM RA OG 8 PR 0 RK 7 -20 O W 200 ICT for Environmental Management Expected Outcome I a) Collaborative systems for environmental management • • From monitoring to reporting, management, alert and response Enhanced capacity to assess population exposure and health risk Generic solutions with typical validation focus on water and air Visionary concepts, as well as evolutionary integrated systems Funding schemes: IP and STREPS

ME AM GR RO 8 K P -200 R WO 2007 ICT for Environmental Management Expected Outcome II b) Coordination and Support Actions • • • Adoption of common open architectures (INSPIRE, GMES, GEOSS) ICT research for risk reduction and disaster and emergency management Building the European Research Area in the field of ICT for environmental sustainability Funding scheme: CSA e) Specific International Cooperation Action • • ICT for environmental disaster reduction and management Development and interoperability of rapidly deployable ICT-based solutions Assessment of natural hazards and communities vulnerability For public warnings and emergency management Funding schemes: STREP/SICA, CSA

Towards future research needs Flexible chaining of distributed environmental services • • • Methods and protocols for service discovery and chaining Automatic data and services quality control Semantics and ontology services Chaining of models, predictive tools On-demand distributed geo-processing Interactive, Web-based 3 D analysis and visualisation tools Smart wireless monitoring networks • • • . . . Sensor Web Portable sensors Massive deployment of low cost miniaturised sensors

Conclusion Cooperation in Eco-informatics • Very ambitious goals and challenges • Need to ensure interoperability worldwide • Common research topics • Exchange of best practices • Supporting links between “project clusters” • Standardisation, SDI • …. WG Eco-informatics

Further Information & Contact • DG INFSO Unit “ICT for Sustainable Growth” Email: INFSO–ICTfor. SG@ec. europa. eu http: //ec. europa. eu/information-society/activities/sustainable-growth • Home page of the i 2010 initiative: http: //ec. europa. eu/information-society/eeurope/i 2010/index-en. htm • FP 7 ICT • home page on CORDIS (including the Work Programme 2007 -2008) http: //cordis. europa. eu/fp 7/ict/ • Registration as an expert: https: //cordis. europa. eu/emmfp 7/index. cfm? fuseaction=wel. welcome • CIP - Competitveness and Innovation Programme http: //intra. infso. cec. eu. int/index. htm? url=/ictc/

18ca12545160dc127f180ef3f5f3ee30.ppt