3b7dafec8a2bc6818609ab7f8c53bfdf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54

ECMO extracorporeal membrane oxygenation extracorporal life support 2010/9/22 Presented by Nai-Hsin Chi National Taiwan University Hospital

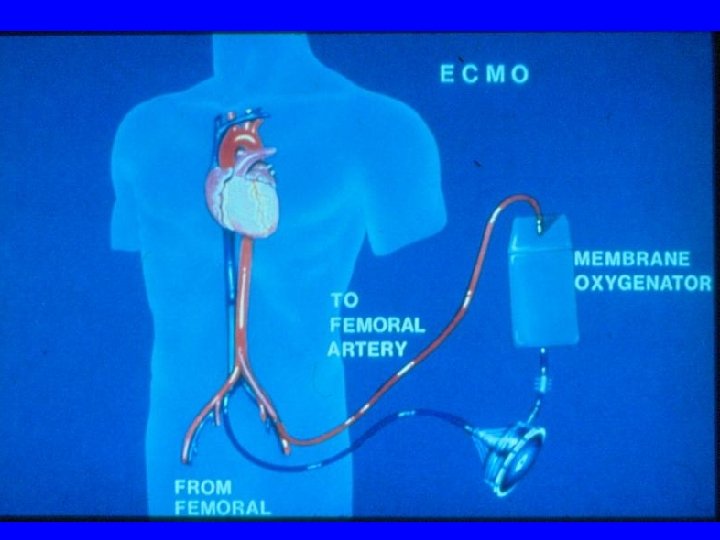
ECMO prolonged partial cardiopulmonary bypass

ECMO vs CPB • reservoir
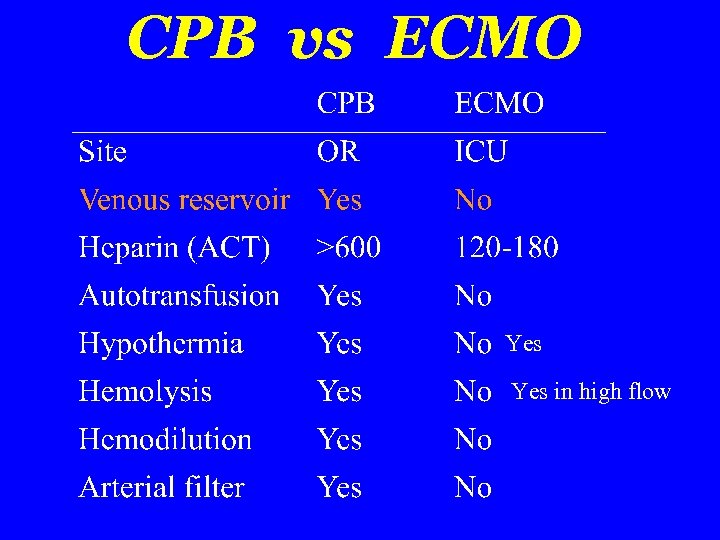
CPB vs ECMO Yes in high flow
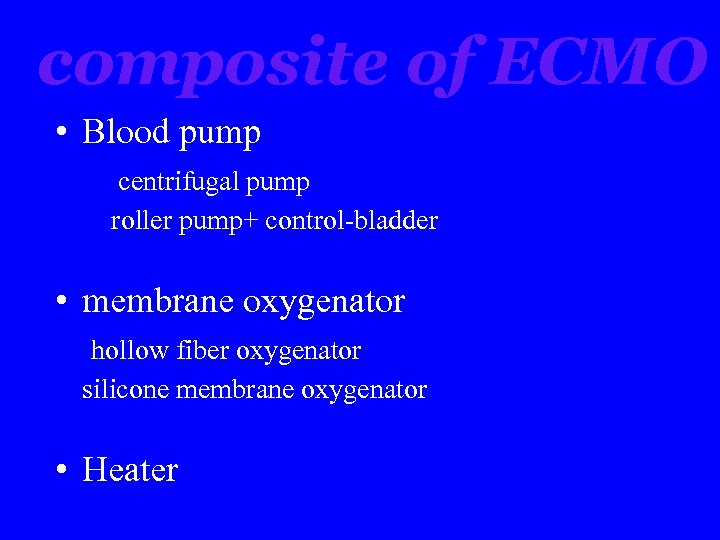
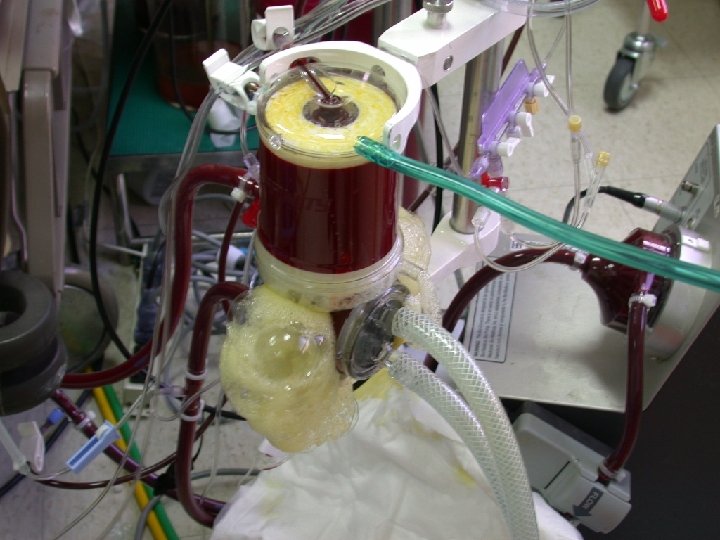
composite of ECMO • Blood pump centrifugal pump roller pump+ control-bladder • membrane oxygenator hollow fiber oxygenator silicone membrane oxygenator • Heater

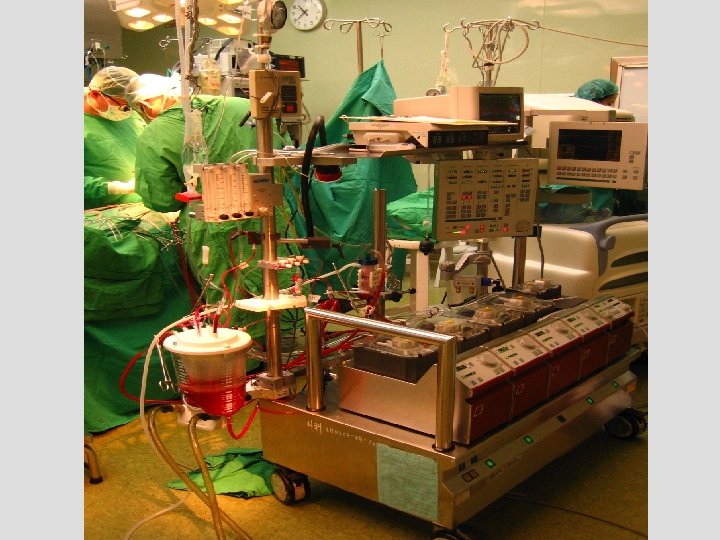
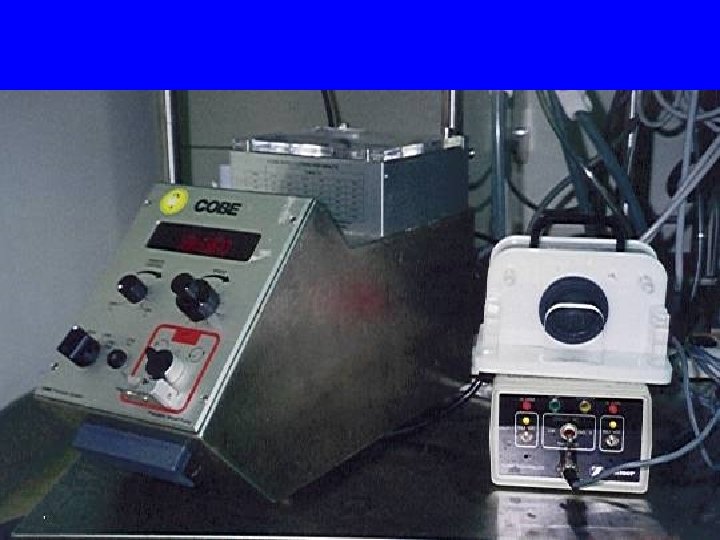
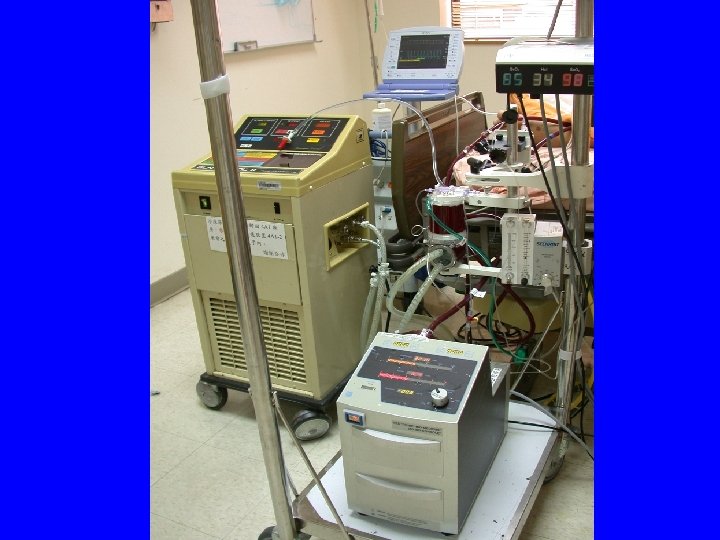
ECMO 機器

ECMO主機

Centrifugal pump

滾輪式幫浦加囊狀控制裝置
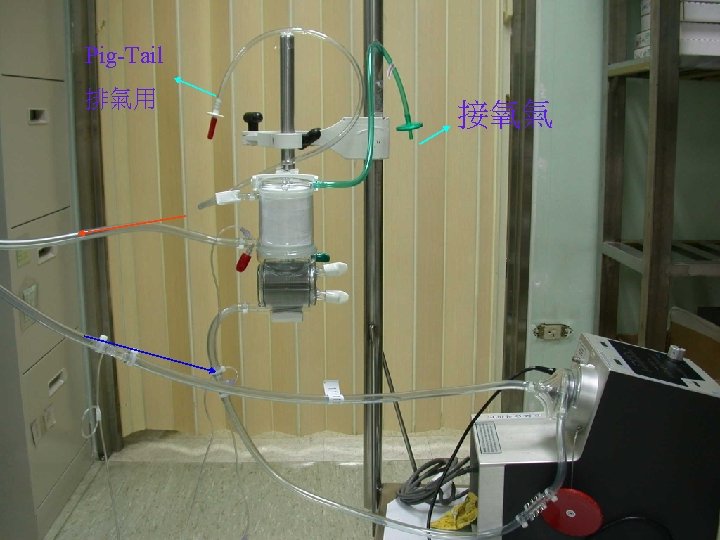


Pig-Tail 排氣用 接氧氣
Cannula
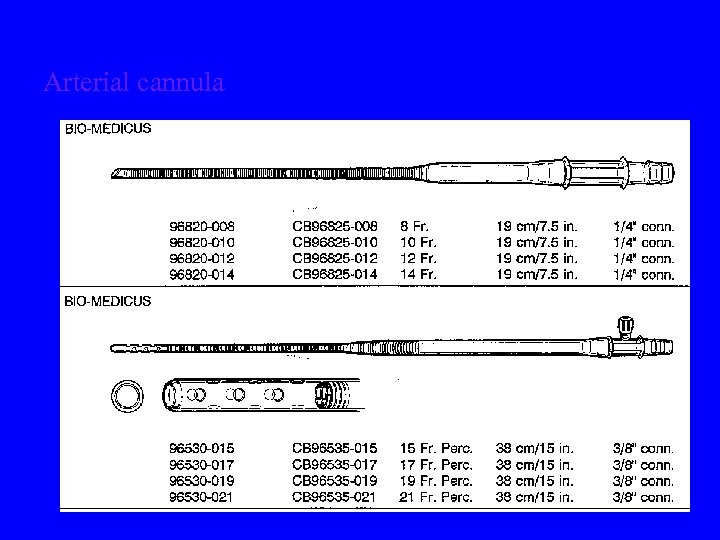
Arterial cannula
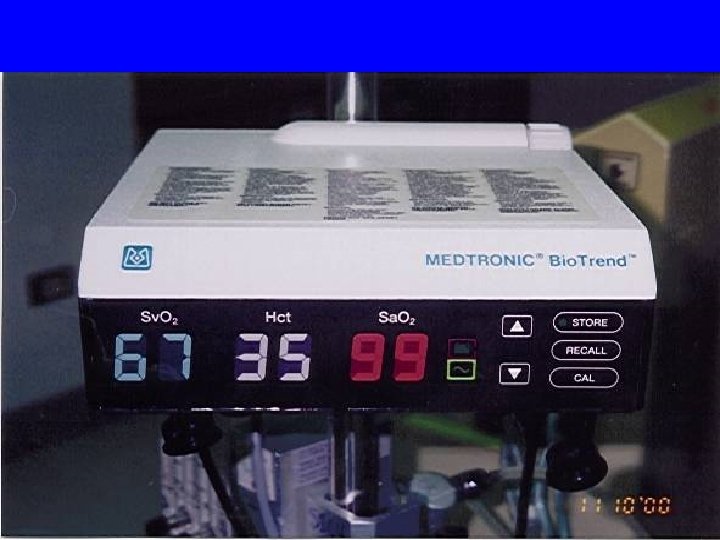

MX-2 monitor

氣體流量表

ECMO • Short-term cardiopulmonary support 1 -2 weeks • Bridge to decision Buy time to decide the next step – Recovery – Transplantation – long-term device (ventricular assist device) – Operation (CABG, pulmonary embolectomy, . . ) – Give-up

for lung 1. support : O 2 supply & CO 2 removal 2. rest : reduce ventilator induced lung injury

for heart support : improve systemic perfusion rest : ↓catecholamine ↓myocardial work decrease preload requirement and congestion

ECMO Type • VV - ECMO • VA - ECMO
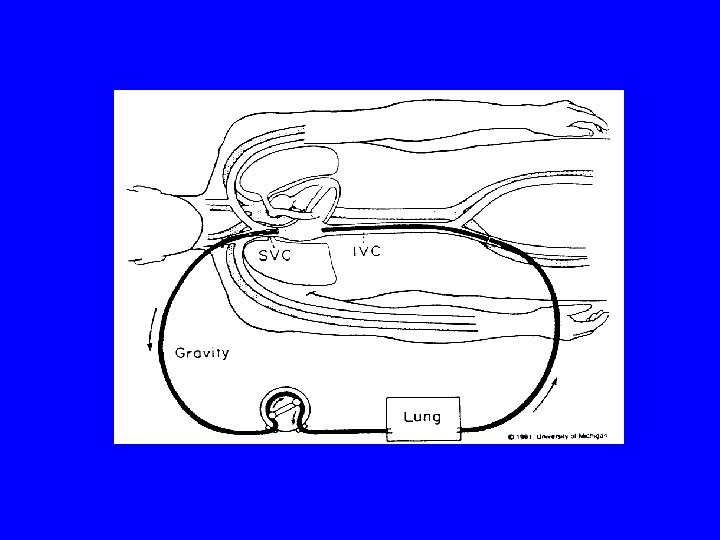

VV-ECMO indication : for lung disease only purpose : to decrease barotrauma ventilator setting : PC mode, PEEP >10 , PIP < 35 , VR --> Pa. CO 2, Fi. O 2 --> Pa. O 2
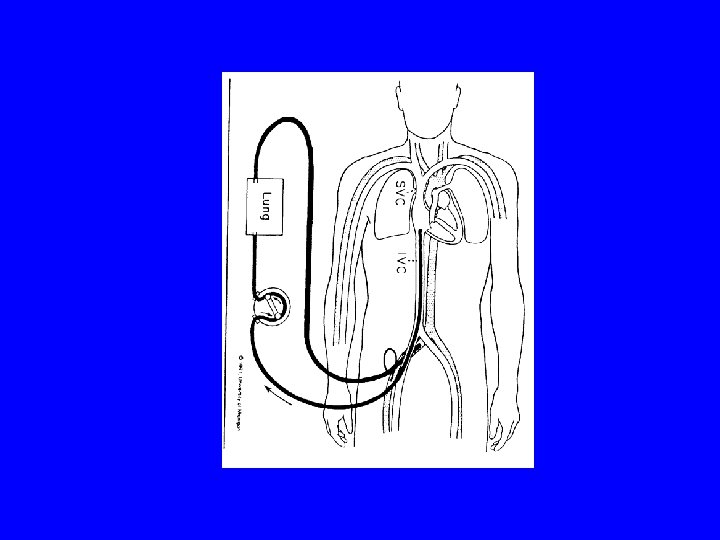

VA-ECMO advantage : 1. both lung & heart support

Application of ECMO • As a mechanical circulatory support: – – – Post-cardiotomy cardiogenic shock Double bridge (ECMO VAD HTx) Acute myocarditis AMI cardiogenic shock (ECPR) Rescue for acute pulmonary embolism • Ventilatory support – ARDS – Neonatal pulmonary diseases
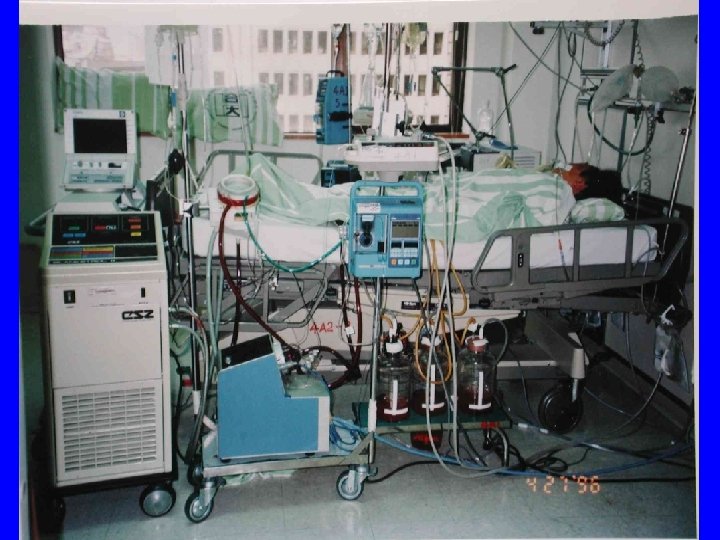
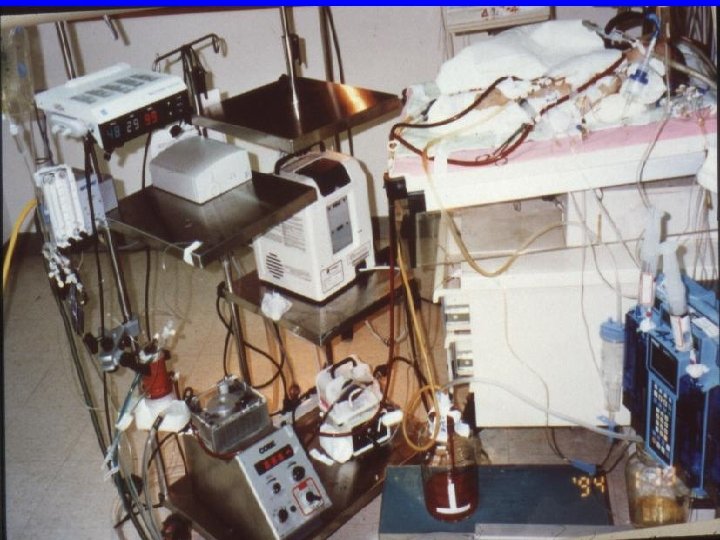
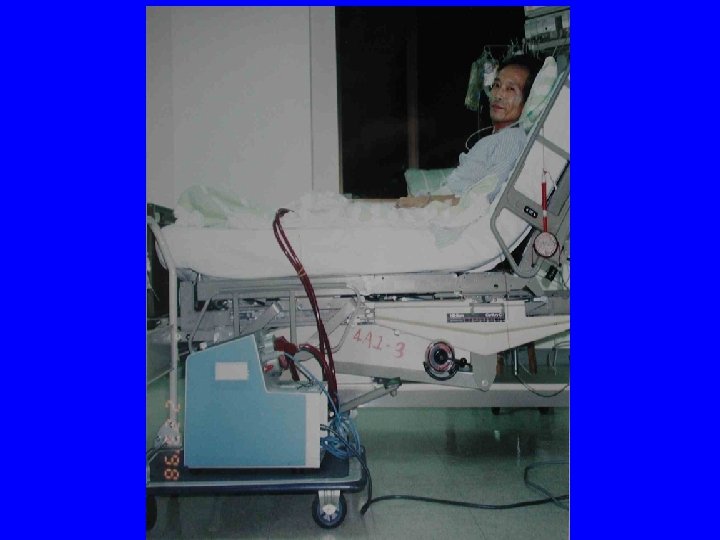
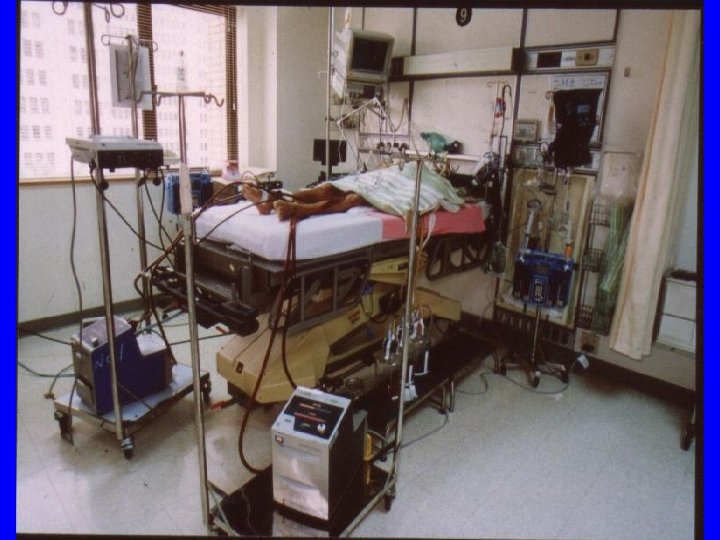

Different patients Different situation Different treatment • t
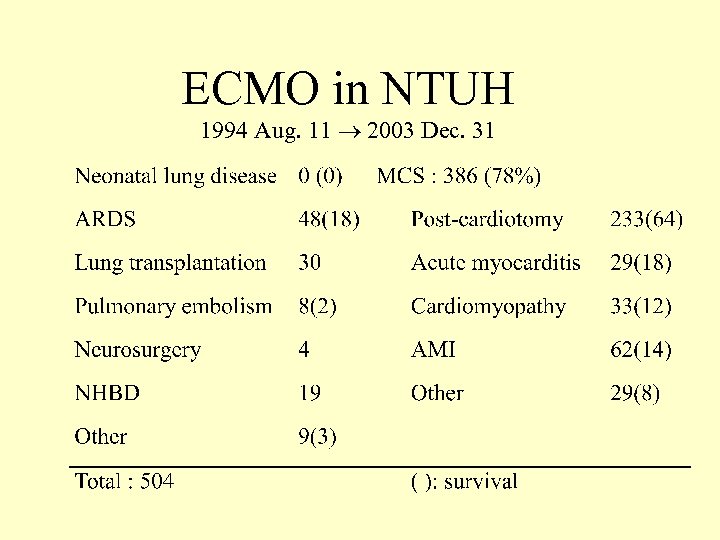
ECMO in NTUH 1994 Aug. 11 2003 Dec. 31
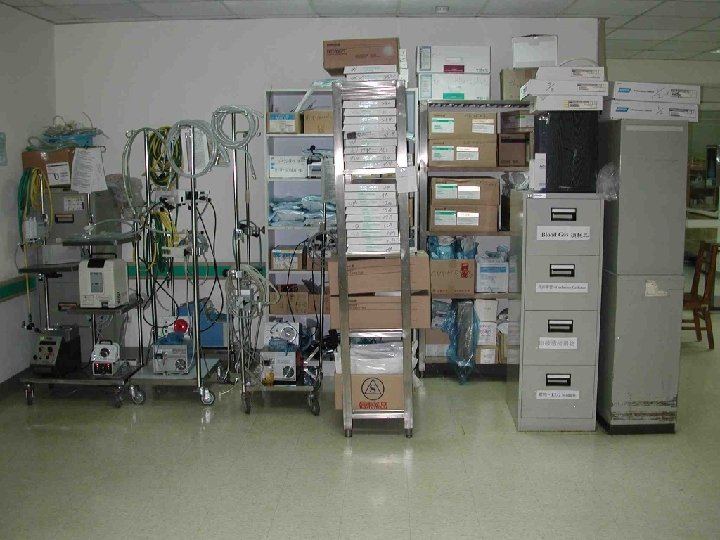
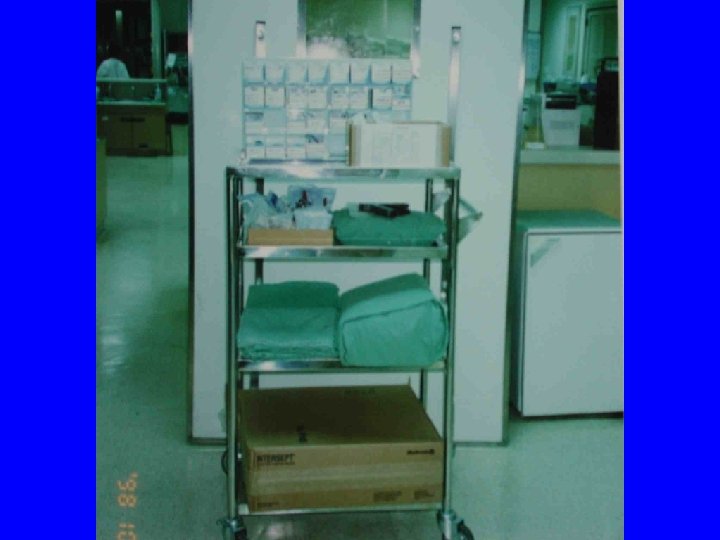
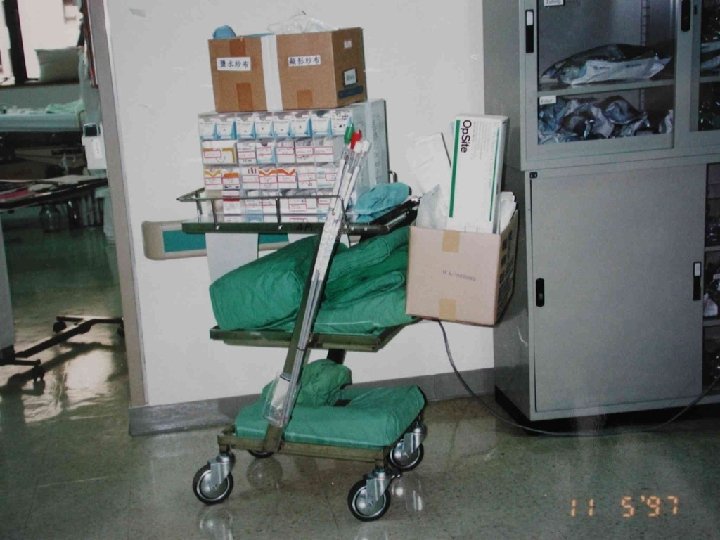
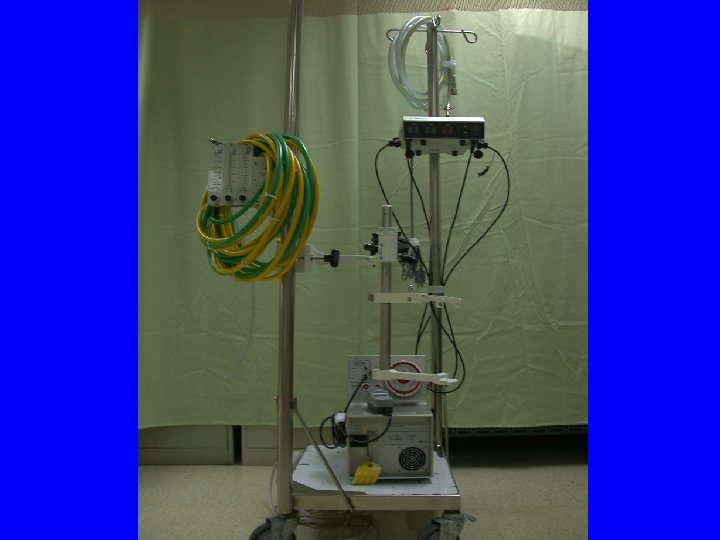


ECMO 作車 All you need to set up ECMO Put everything on the wheel Then, OR, ICU, cath room, ES, ward, etc
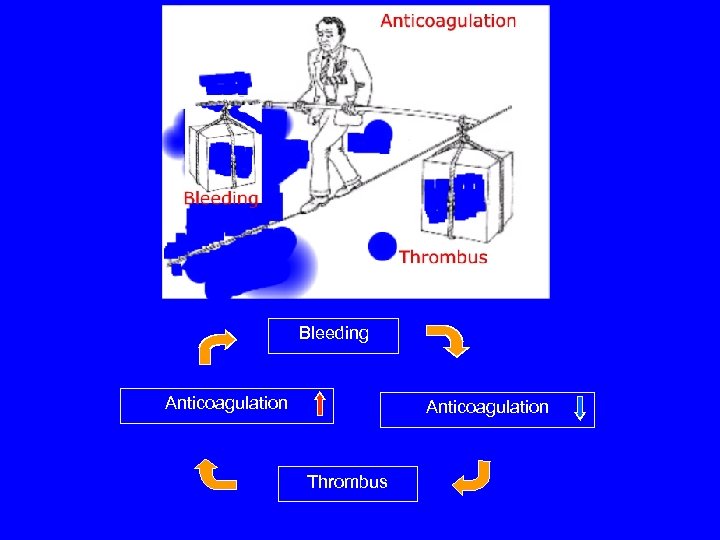
Bleeding Anticoagulation Thrombus
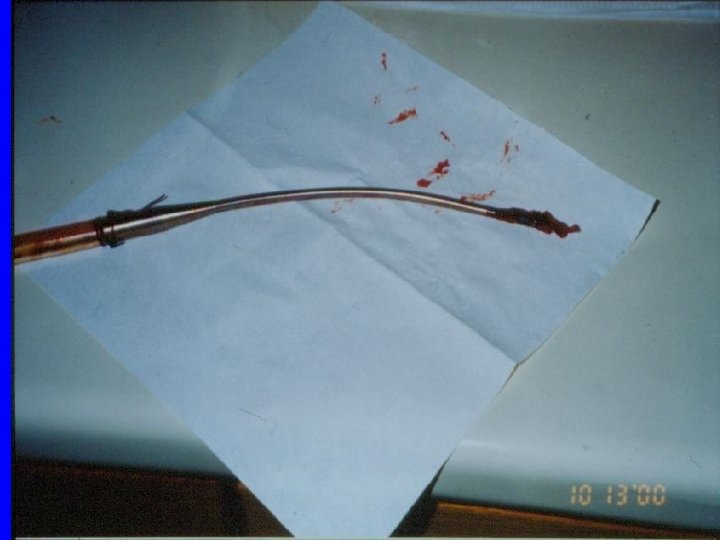
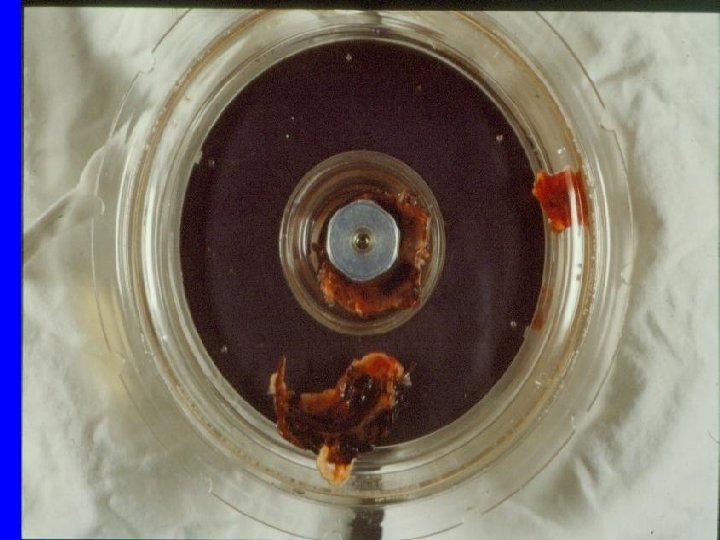
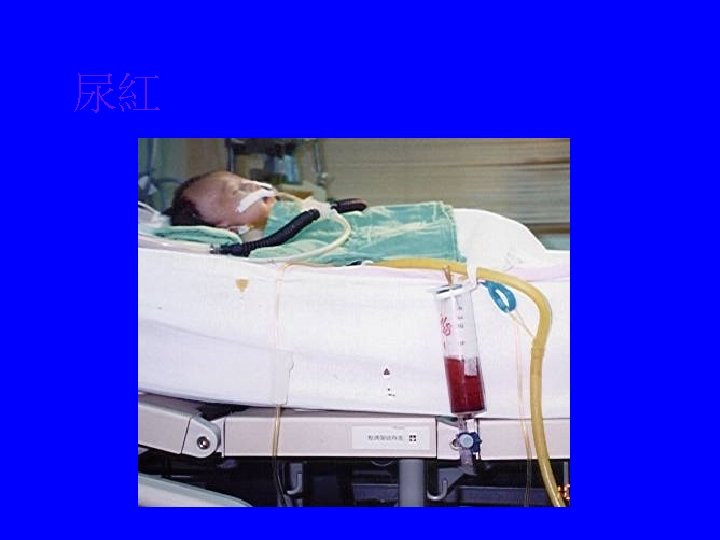
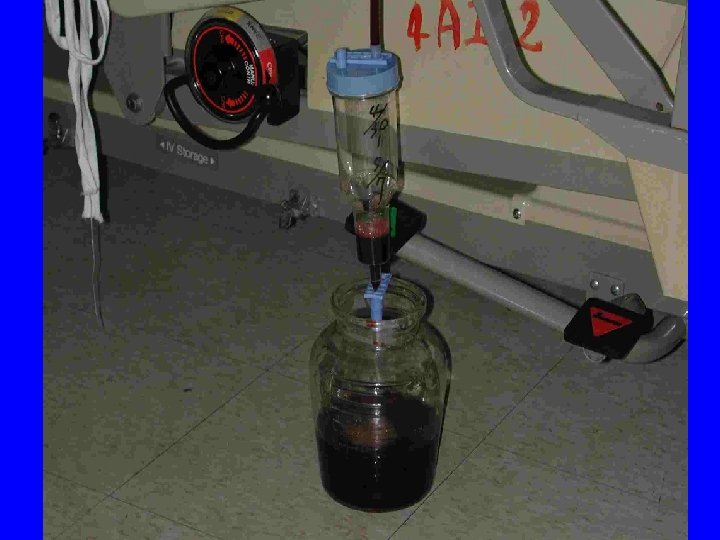
尿紅



Five-Year Results of 219 Consecutive Patients Treated With Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Refractory Postoperative Cardiogenic Shock Ann Thorac Surg 2004; 77: 151 -7
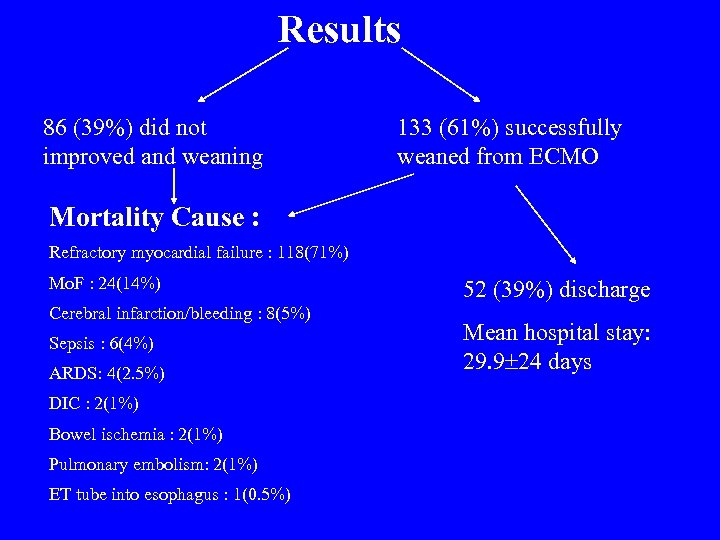
Results 86 (39%) did not improved and weaning 133 (61%) successfully weaned from ECMO Mortality Cause : Refractory myocardial failure : 118(71%) Mo. F : 24(14%) Cerebral infarction/bleeding : 8(5%) Sepsis : 6(4%) ARDS: 4(2. 5%) DIC : 2(1%) Bowel ischemia : 2(1%) Pulmonary embolism: 2(1%) ET tube into esophagus : 1(0. 5%) 52 (39%) discharge Mean hospital stay: 29. 9 24 days
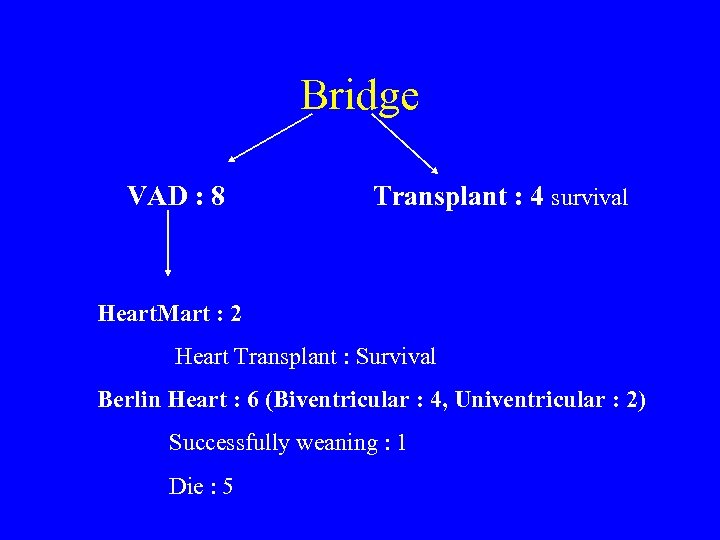
Bridge VAD : 8 Transplant : 4 survival Heart. Mart : 2 Heart Transplant : Survival Berlin Heart : 6 (Biventricular : 4, Univentricular : 2) Successfully weaning : 1 Die : 5

ECMO • Short-term cardiopulmonary support 1 -2 weeks • Bridge to decision Buy time to decide the next step – Recovery – Transplantation – long-term device (ventricular assist device) – Operation (CABG, pulmonary embolectomy, . . ) – Give-up

ECMO Advantage: 1. Both children & adult (wide range of BW) 2. Flexible cannulation site: femoral, neck, chest 3. Higher support 4. Rapid & easy set-up & remoral Disadvantage: 1. Bleeding 2. Bedridden 3. Infection 4. SIRS 5. Labor-intensive 6. Partial CP support

Thank you
3b7dafec8a2bc6818609ab7f8c53bfdf.ppt