acls-ECG-2010.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 116
 ECG Interpretation Advanced Cardiac Life Support William A. Shapiro, M. D. http: //anesthesia. ucsf. edu/shapiro advancing health worldwide TM Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care
ECG Interpretation Advanced Cardiac Life Support William A. Shapiro, M. D. http: //anesthesia. ucsf. edu/shapiro advancing health worldwide TM Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care
 Course Objectives & Description: • Recognize & initiate early management of periarrest conditions that may result in cardiac arrest • Manage cardiac arrest until return of spontaneous circulation, or transfer of care • Understanding of arrhythmia interpretation • Recognize the hemodynamic consequences of arrhythmias
Course Objectives & Description: • Recognize & initiate early management of periarrest conditions that may result in cardiac arrest • Manage cardiac arrest until return of spontaneous circulation, or transfer of care • Understanding of arrhythmia interpretation • Recognize the hemodynamic consequences of arrhythmias
 Normal Sinus Rhythm Normal sinus rhythm results from the initiation of an electrical signal (the cardiac impulse) by cells of the sinus node at a rate appropriate to the age and state of activity of the individual, and then the propagation of that signal in an orderly manner through the atria, AV junction, ventricular specialized conducting system and the ventricular myocardium
Normal Sinus Rhythm Normal sinus rhythm results from the initiation of an electrical signal (the cardiac impulse) by cells of the sinus node at a rate appropriate to the age and state of activity of the individual, and then the propagation of that signal in an orderly manner through the atria, AV junction, ventricular specialized conducting system and the ventricular myocardium
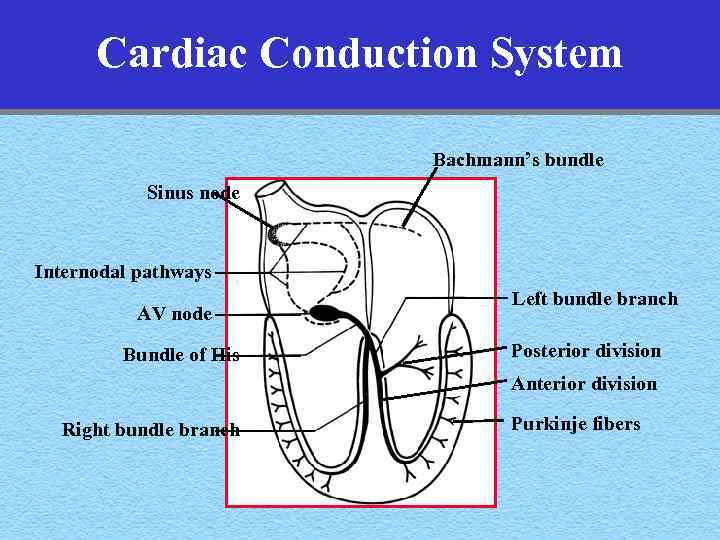 Cardiac Conduction System Bachmann’s bundle Sinus node Internodal pathways AV node Bundle of His Left bundle branch Posterior division Anterior division Right bundle branch Purkinje fibers
Cardiac Conduction System Bachmann’s bundle Sinus node Internodal pathways AV node Bundle of His Left bundle branch Posterior division Anterior division Right bundle branch Purkinje fibers
 Arrhythmia An arrhythmia reflects either abnormally rapid or slow impulse initiation by the sinus node, or interruption of the sinus rhythm by impulses originating from some other site in the heart, either for short or long periods of time
Arrhythmia An arrhythmia reflects either abnormally rapid or slow impulse initiation by the sinus node, or interruption of the sinus rhythm by impulses originating from some other site in the heart, either for short or long periods of time
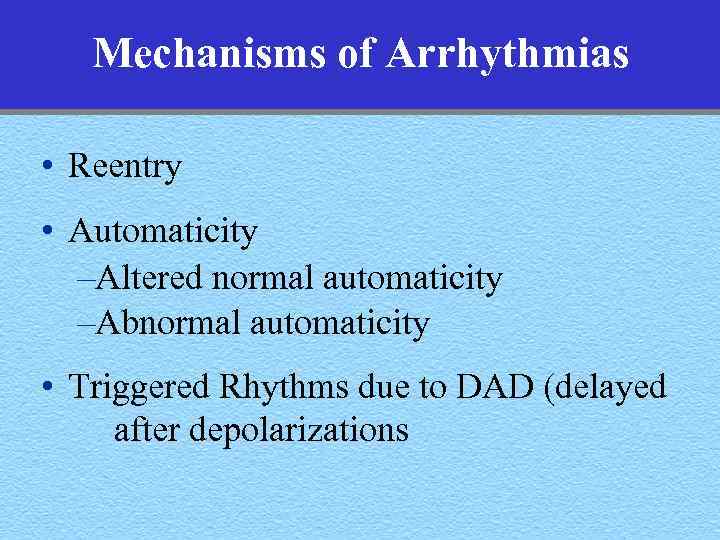 Mechanisms of Arrhythmias • Reentry • Automaticity –Altered normal automaticity –Abnormal automaticity • Triggered Rhythms due to DAD (delayed after depolarizations
Mechanisms of Arrhythmias • Reentry • Automaticity –Altered normal automaticity –Abnormal automaticity • Triggered Rhythms due to DAD (delayed after depolarizations
 Causes of Arrhythmias • Physiologic and Pathologic Processes – Vagal stimulation, Fever, Hypothermia – Electrolyte abnormalities, CNS problems – Hypovolemia, Pain, anaphylaxis, etc. • Preexisting Cardiac & Pulmonary Disease – Acute coronary syndrome, HTN, AODM – COPD, hypoxia, hypercarbia
Causes of Arrhythmias • Physiologic and Pathologic Processes – Vagal stimulation, Fever, Hypothermia – Electrolyte abnormalities, CNS problems – Hypovolemia, Pain, anaphylaxis, etc. • Preexisting Cardiac & Pulmonary Disease – Acute coronary syndrome, HTN, AODM – COPD, hypoxia, hypercarbia
 The Electrocardiogram
The Electrocardiogram
 The Electrocardiogram R T P Q PR Interval S QRS Interval U
The Electrocardiogram R T P Q PR Interval S QRS Interval U
 The Electrocardiogram PR Interval QRS Interval QT Interval
The Electrocardiogram PR Interval QRS Interval QT Interval
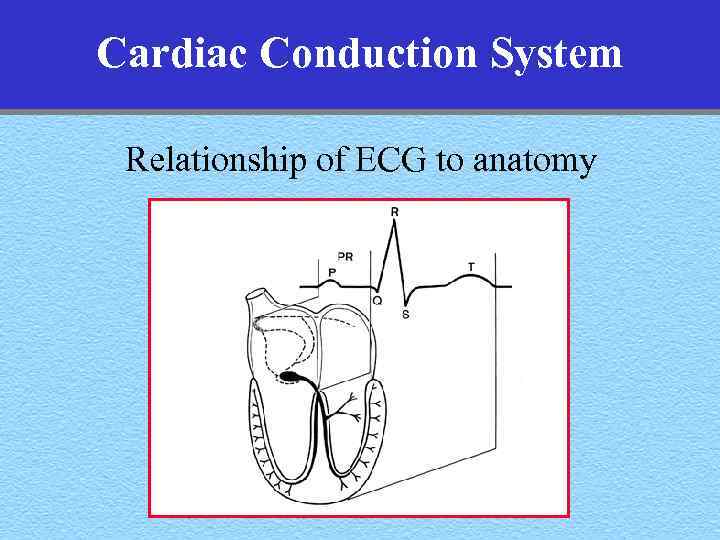 Cardiac Conduction System Relationship of ECG to anatomy
Cardiac Conduction System Relationship of ECG to anatomy
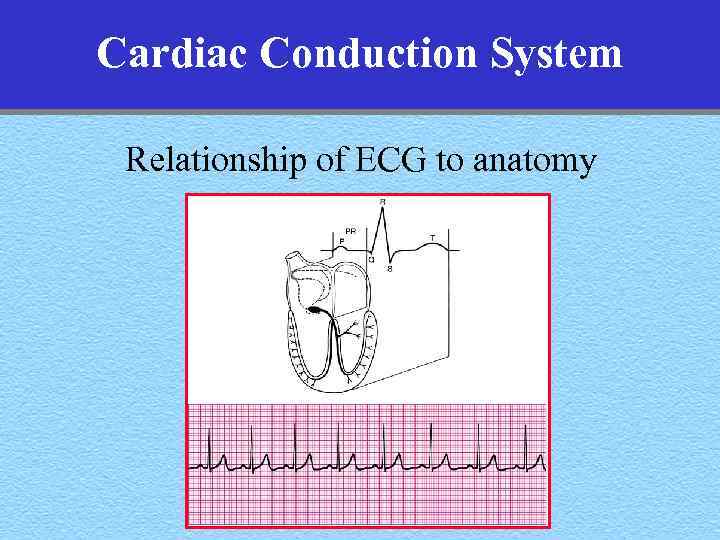 Cardiac Conduction System Relationship of ECG to anatomy
Cardiac Conduction System Relationship of ECG to anatomy
 ACLS THE ACLS PROVIDER IS: IN
ACLS THE ACLS PROVIDER IS: IN
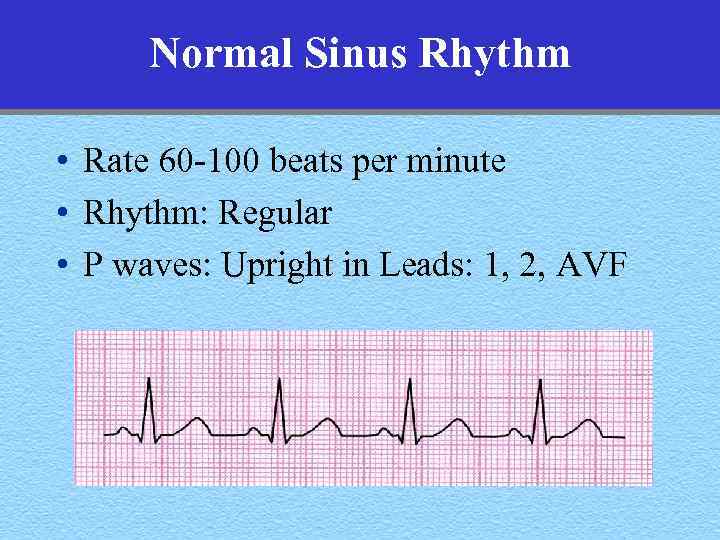 Normal Sinus Rhythm • Rate 60 -100 beats per minute • Rhythm: Regular • P waves: Upright in Leads: 1, 2, AVF
Normal Sinus Rhythm • Rate 60 -100 beats per minute • Rhythm: Regular • P waves: Upright in Leads: 1, 2, AVF
 Determining the Rate
Determining the Rate
 Determining the Rate
Determining the Rate
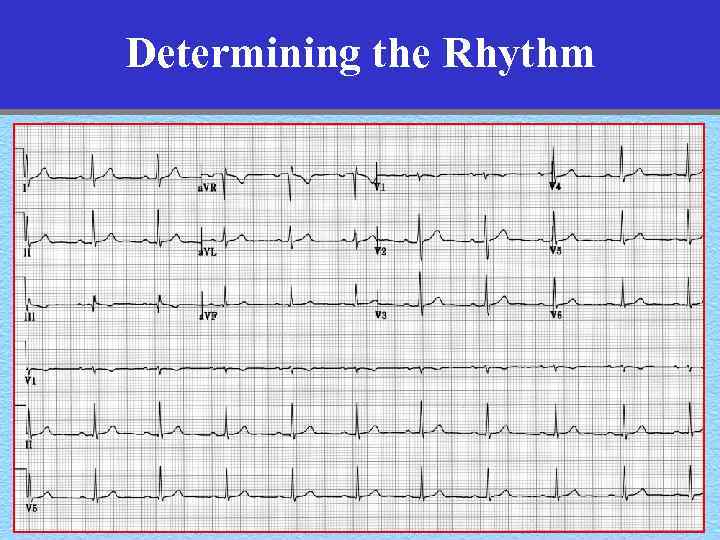 Determining the Rhythm
Determining the Rhythm
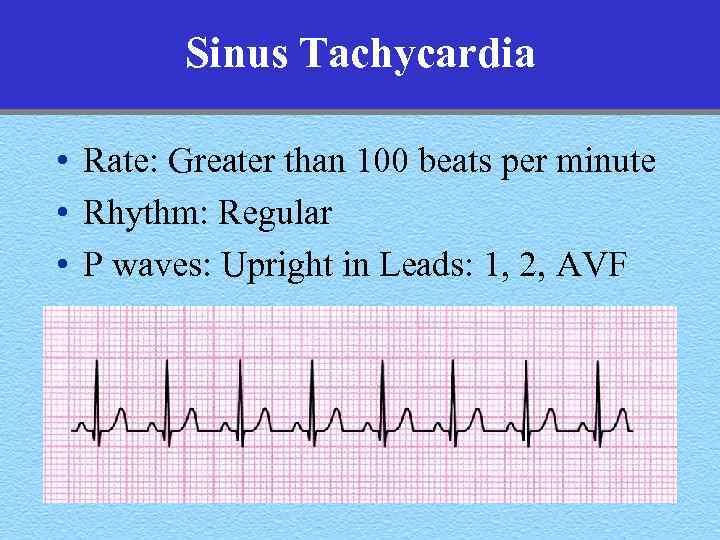 Sinus Tachycardia • Rate: Greater than 100 beats per minute • Rhythm: Regular • P waves: Upright in Leads: 1, 2, AVF
Sinus Tachycardia • Rate: Greater than 100 beats per minute • Rhythm: Regular • P waves: Upright in Leads: 1, 2, AVF
 Sinus Tachycardia • Rate: Greater than 100 beats per minute • Rhythm: Regular • P waves: Upright in Leads: 1, 2, AVF
Sinus Tachycardia • Rate: Greater than 100 beats per minute • Rhythm: Regular • P waves: Upright in Leads: 1, 2, AVF
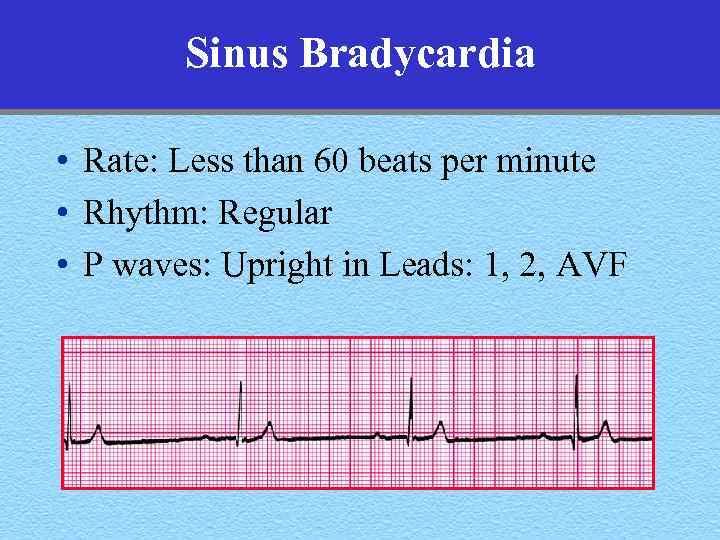 Sinus Bradycardia • Rate: Less than 60 beats per minute • Rhythm: Regular • P waves: Upright in Leads: 1, 2, AVF
Sinus Bradycardia • Rate: Less than 60 beats per minute • Rhythm: Regular • P waves: Upright in Leads: 1, 2, AVF
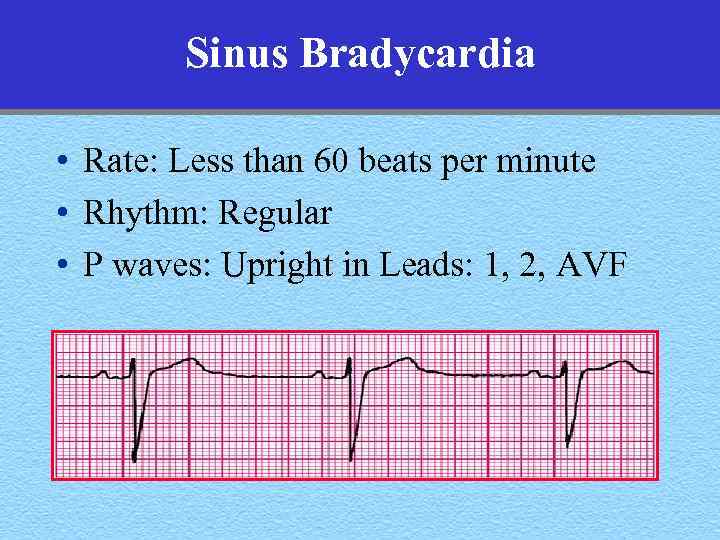 Sinus Bradycardia • Rate: Less than 60 beats per minute • Rhythm: Regular • P waves: Upright in Leads: 1, 2, AVF
Sinus Bradycardia • Rate: Less than 60 beats per minute • Rhythm: Regular • P waves: Upright in Leads: 1, 2, AVF
 Premature Atrial Complexes • P wave Rhythm: Irregular • P waves: Premature, often in the T-wave • QRS complex: Normal or widened P-wave
Premature Atrial Complexes • P wave Rhythm: Irregular • P waves: Premature, often in the T-wave • QRS complex: Normal or widened P-wave
 Premature Atrial Complexes • P wave Rhythm: Irregular • P waves: Premature, often in the T-wave • QRS complex: Normal or widened
Premature Atrial Complexes • P wave Rhythm: Irregular • P waves: Premature, often in the T-wave • QRS complex: Normal or widened
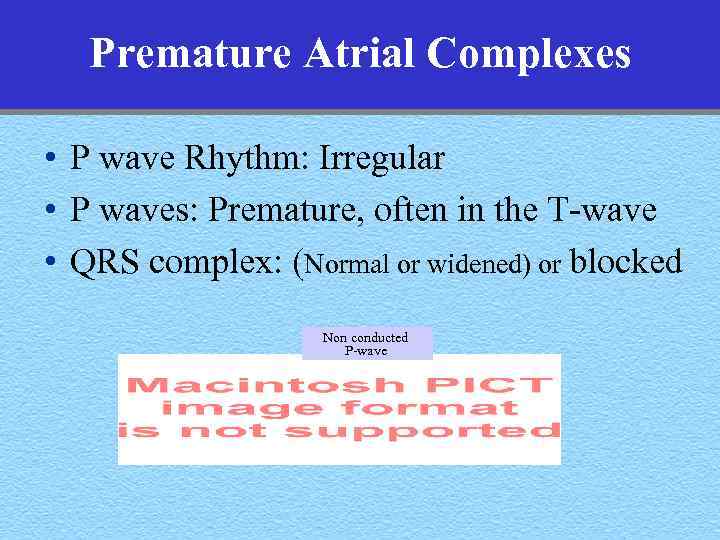 Premature Atrial Complexes • P wave Rhythm: Irregular • P waves: Premature, often in the T-wave • QRS complex: (Normal or widened) or blocked Non conducted P-wave
Premature Atrial Complexes • P wave Rhythm: Irregular • P waves: Premature, often in the T-wave • QRS complex: (Normal or widened) or blocked Non conducted P-wave
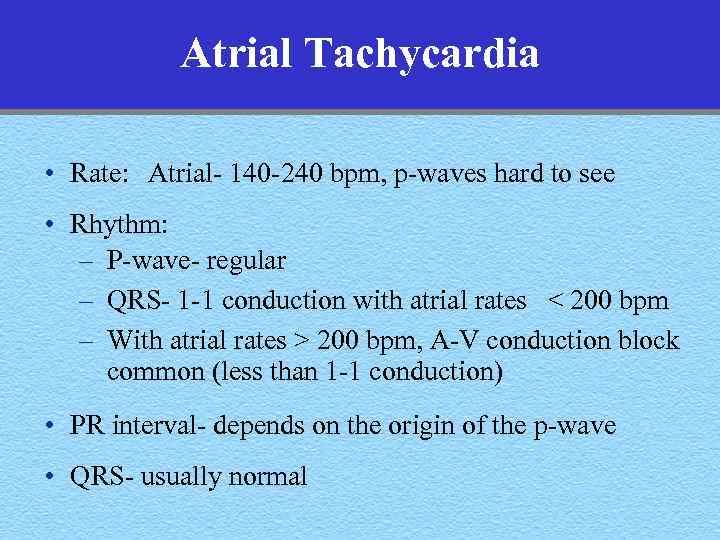 Atrial Tachycardia • Rate: Atrial- 140 -240 bpm, p-waves hard to see • Rhythm: – P-wave- regular – QRS- 1 -1 conduction with atrial rates < 200 bpm – With atrial rates > 200 bpm, A-V conduction block common (less than 1 -1 conduction) • PR interval- depends on the origin of the p-wave • QRS- usually normal
Atrial Tachycardia • Rate: Atrial- 140 -240 bpm, p-waves hard to see • Rhythm: – P-wave- regular – QRS- 1 -1 conduction with atrial rates < 200 bpm – With atrial rates > 200 bpm, A-V conduction block common (less than 1 -1 conduction) • PR interval- depends on the origin of the p-wave • QRS- usually normal
 Atrial Tachycardia P-Wave
Atrial Tachycardia P-Wave
 Atrial Tachycardia with variable block P-Waves are regular at 160 bpm
Atrial Tachycardia with variable block P-Waves are regular at 160 bpm
 Atrial Flutter • Rate: Atrial- 300 bpm (260 -320) • Rhythm: – P-waves- regular – QRS- 2 -1 conduction - 150 bpm, variable AV conduction with constant AV conduction ratio • P-waves: F-waves (Flutter), sawtooth pattern • QRS- usually normal, obviously sometimes wide
Atrial Flutter • Rate: Atrial- 300 bpm (260 -320) • Rhythm: – P-waves- regular – QRS- 2 -1 conduction - 150 bpm, variable AV conduction with constant AV conduction ratio • P-waves: F-waves (Flutter), sawtooth pattern • QRS- usually normal, obviously sometimes wide
 Atrial Flutter F-waves
Atrial Flutter F-waves
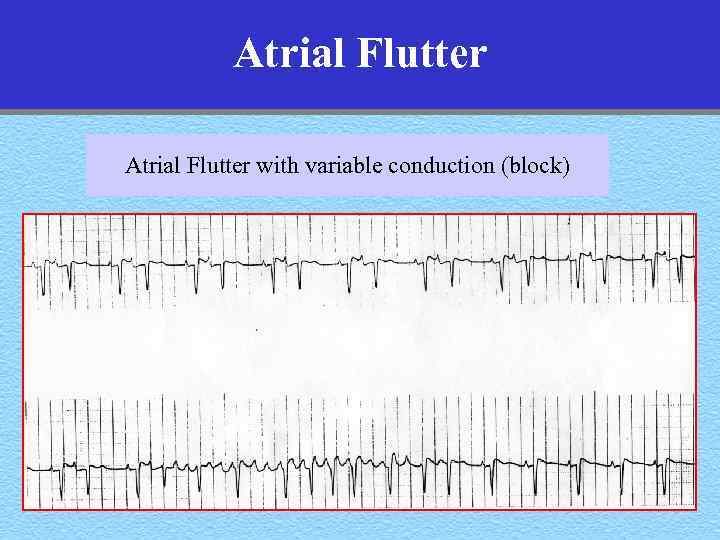 Atrial Flutter with variable conduction (block)
Atrial Flutter with variable conduction (block)
 Atrial Fibrillation • Rate: Atrial- rapid, Ventricular- Depends • Rhythm: – P-waves- irregular – QRS- beat to beat variability, Irregularly irregular • P-waves: From F-waves (Flutter) to absent • QRS duration- normal or wide
Atrial Fibrillation • Rate: Atrial- rapid, Ventricular- Depends • Rhythm: – P-waves- irregular – QRS- beat to beat variability, Irregularly irregular • P-waves: From F-waves (Flutter) to absent • QRS duration- normal or wide
 Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation
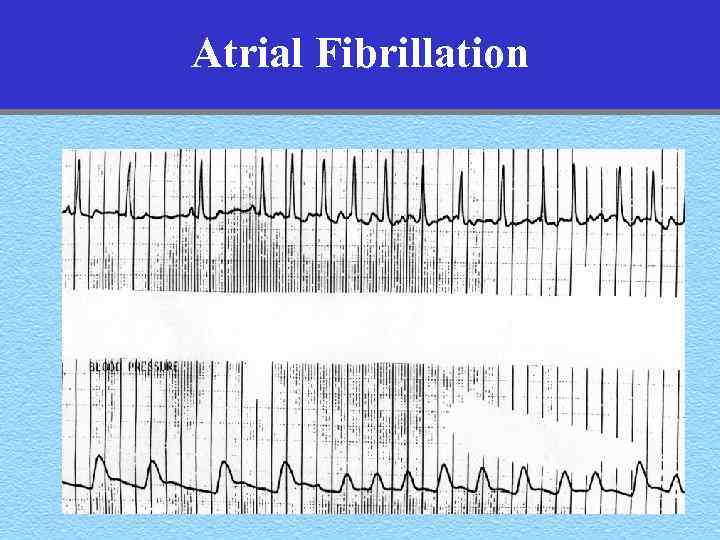 Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation
 Premature Junctional Complexes • • Rhythm: Irregular P waves: Retrograde PR interval: <. 12 sec or nonexistent QRS complex: Normal or widened
Premature Junctional Complexes • • Rhythm: Irregular P waves: Retrograde PR interval: <. 12 sec or nonexistent QRS complex: Normal or widened
 Premature Ventricular Complexes • • Rhythm: Irregular P waves: Usually not seen QRS complex: Wide >. 12 sec Compensatory pause
Premature Ventricular Complexes • • Rhythm: Irregular P waves: Usually not seen QRS complex: Wide >. 12 sec Compensatory pause
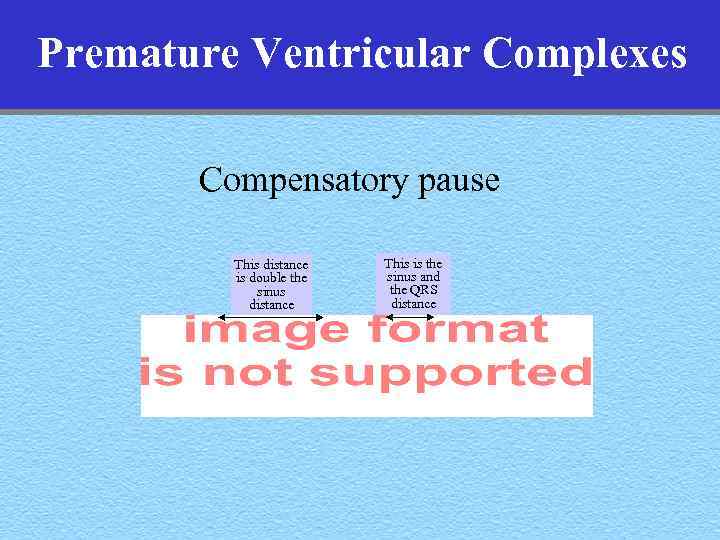 Premature Ventricular Complexes Compensatory pause This distance is double the sinus distance This is the sinus and the QRS distance
Premature Ventricular Complexes Compensatory pause This distance is double the sinus distance This is the sinus and the QRS distance
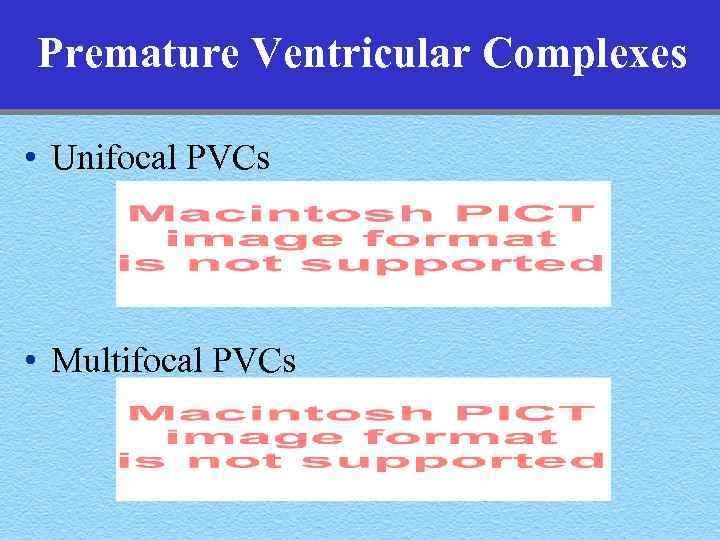 Premature Ventricular Complexes • Unifocal PVCs • Multifocal PVCs
Premature Ventricular Complexes • Unifocal PVCs • Multifocal PVCs
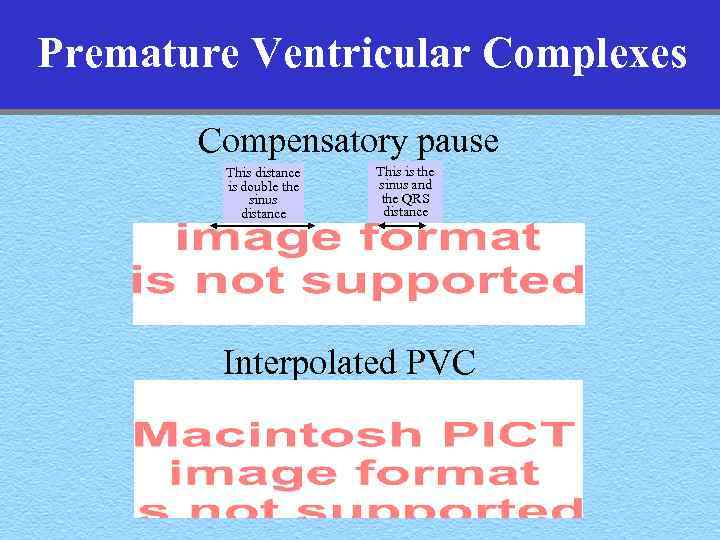 Premature Ventricular Complexes Compensatory pause This distance is double the sinus distance This is the sinus and the QRS distance Interpolated PVC
Premature Ventricular Complexes Compensatory pause This distance is double the sinus distance This is the sinus and the QRS distance Interpolated PVC
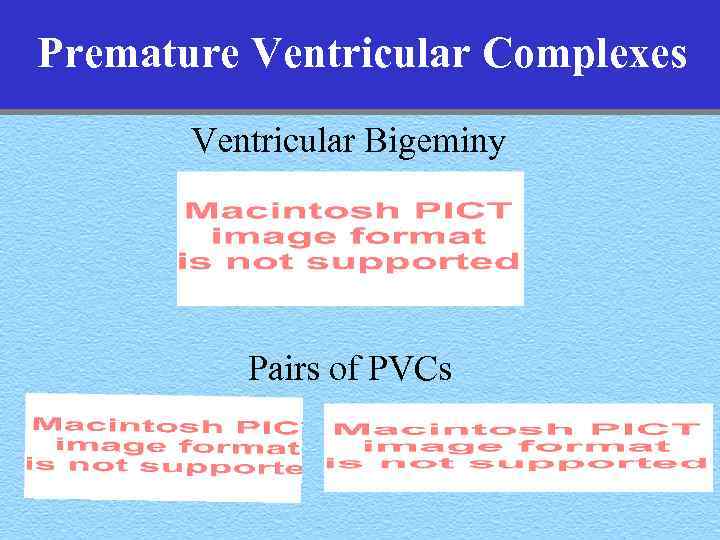 Premature Ventricular Complexes Ventricular Bigeminy Pairs of PVCs
Premature Ventricular Complexes Ventricular Bigeminy Pairs of PVCs
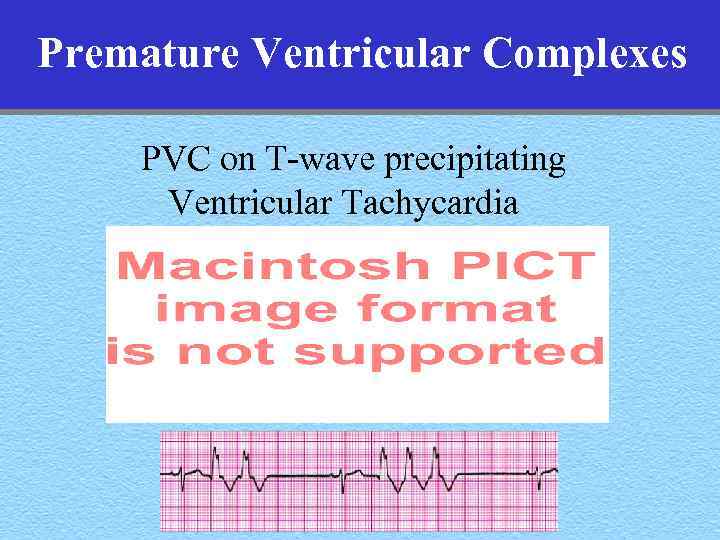 Premature Ventricular Complexes PVC on T-wave precipitating Ventricular Tachycardia
Premature Ventricular Complexes PVC on T-wave precipitating Ventricular Tachycardia
 Ventricular Tachycardia • Rate: Approx 100 -230 bpm • Rhythm: Usually regular • P waves: Usually not seen – Independent A and V activity – A-V dissociation • QRS complex: Wide >. 12 sec • Capture beats, fusion beats
Ventricular Tachycardia • Rate: Approx 100 -230 bpm • Rhythm: Usually regular • P waves: Usually not seen – Independent A and V activity – A-V dissociation • QRS complex: Wide >. 12 sec • Capture beats, fusion beats
 Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Tachycardia
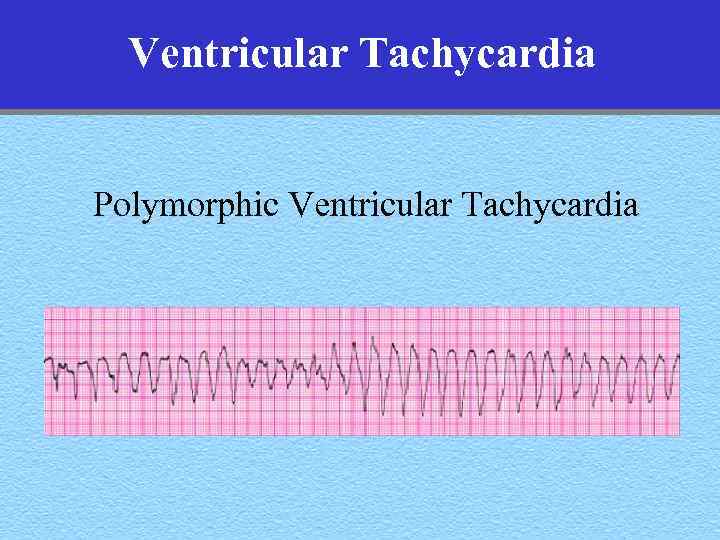 Ventricular Tachycardia Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Tachycardia Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
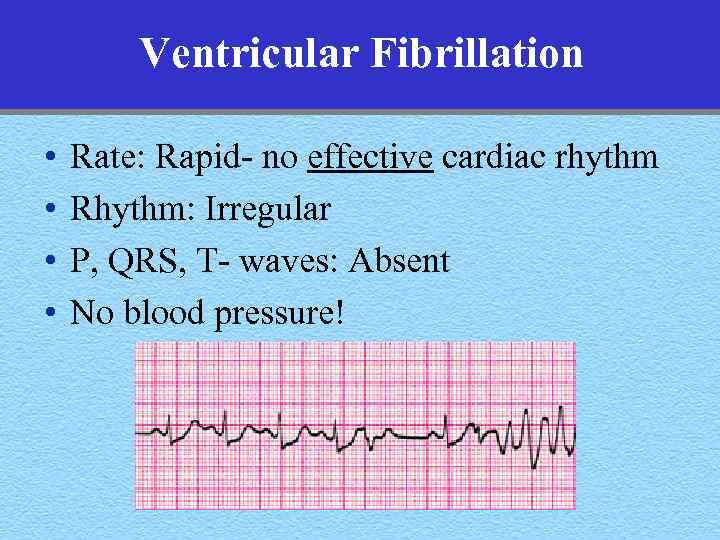 Ventricular Fibrillation • • Rate: Rapid- no effective cardiac rhythm Rhythm: Irregular P, QRS, T- waves: Absent No blood pressure!
Ventricular Fibrillation • • Rate: Rapid- no effective cardiac rhythm Rhythm: Irregular P, QRS, T- waves: Absent No blood pressure!
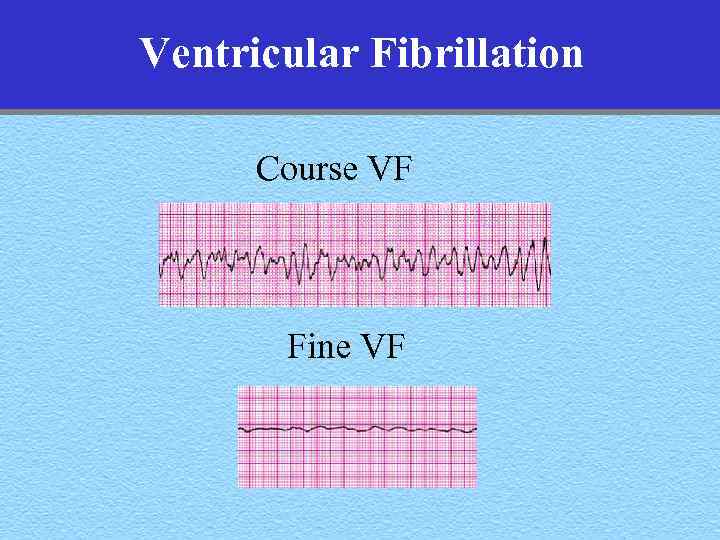 Ventricular Fibrillation Course VF Fine VF
Ventricular Fibrillation Course VF Fine VF
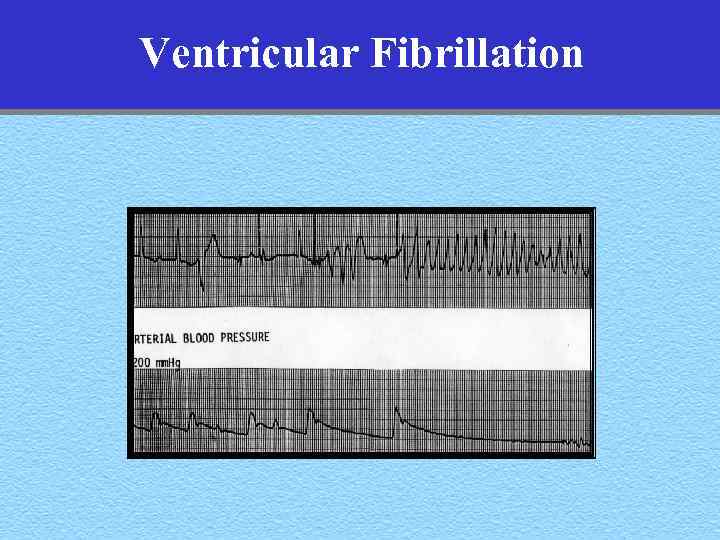 Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular Fibrillation
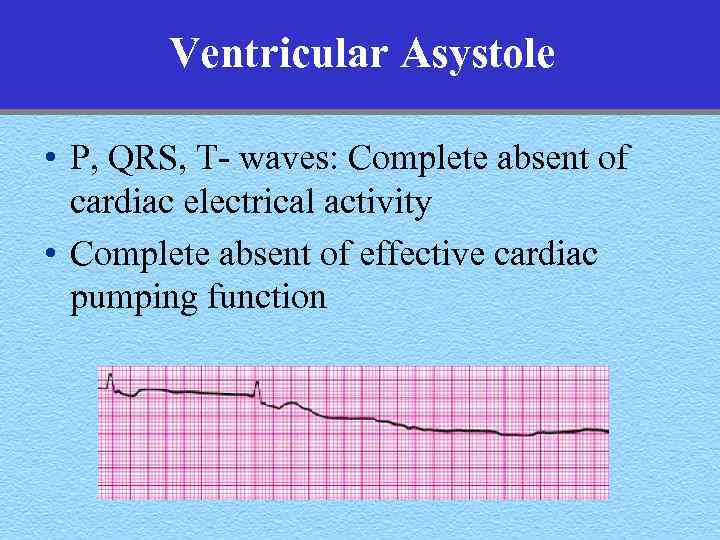 Ventricular Asystole • P, QRS, T- waves: Complete absent of cardiac electrical activity • Complete absent of effective cardiac pumping function
Ventricular Asystole • P, QRS, T- waves: Complete absent of cardiac electrical activity • Complete absent of effective cardiac pumping function
 Acute Coronary Syndromes
Acute Coronary Syndromes
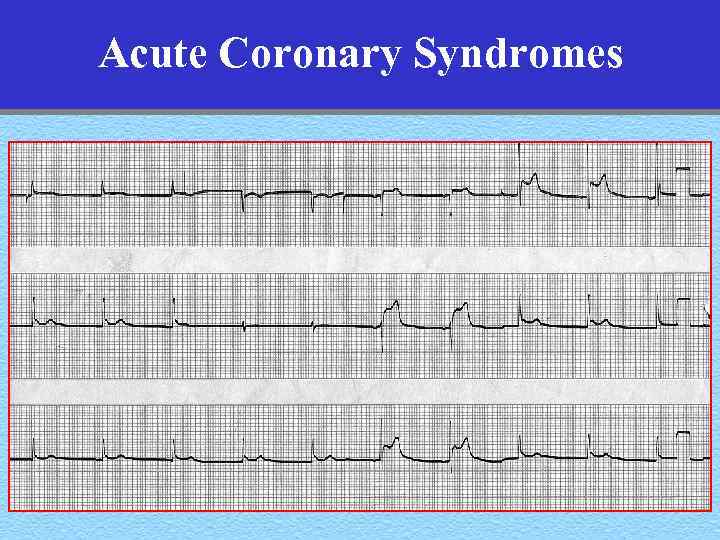 Acute Coronary Syndromes
Acute Coronary Syndromes
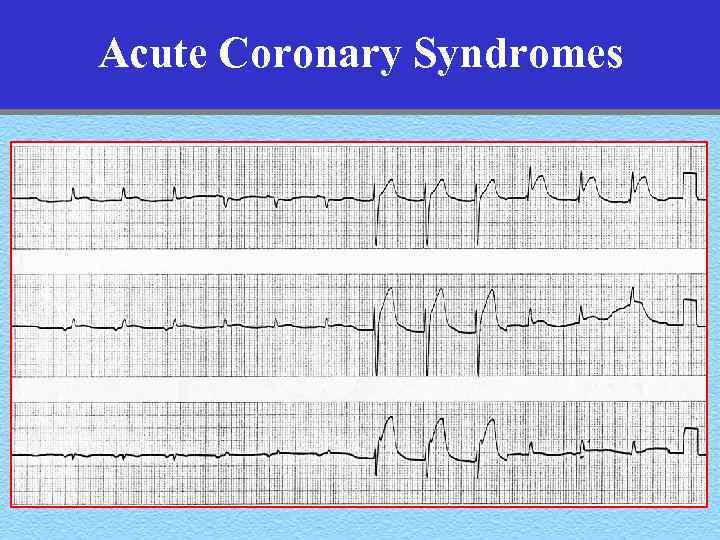 Acute Coronary Syndromes
Acute Coronary Syndromes
 Review
Review
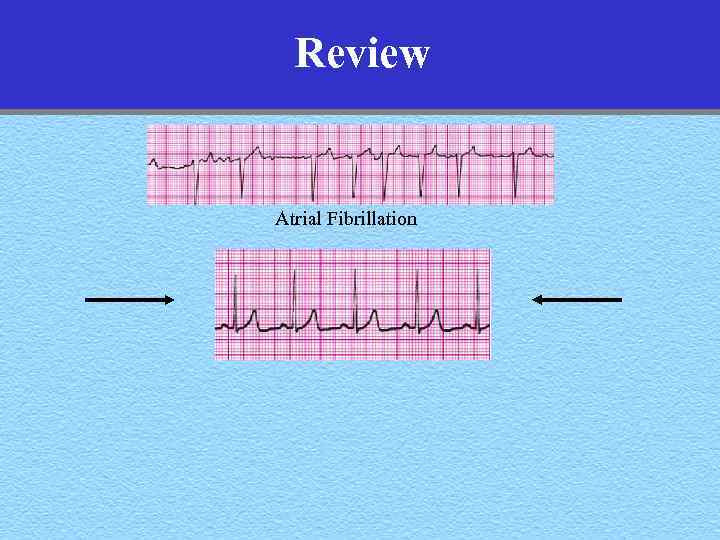 Review Atrial Fibrillation
Review Atrial Fibrillation
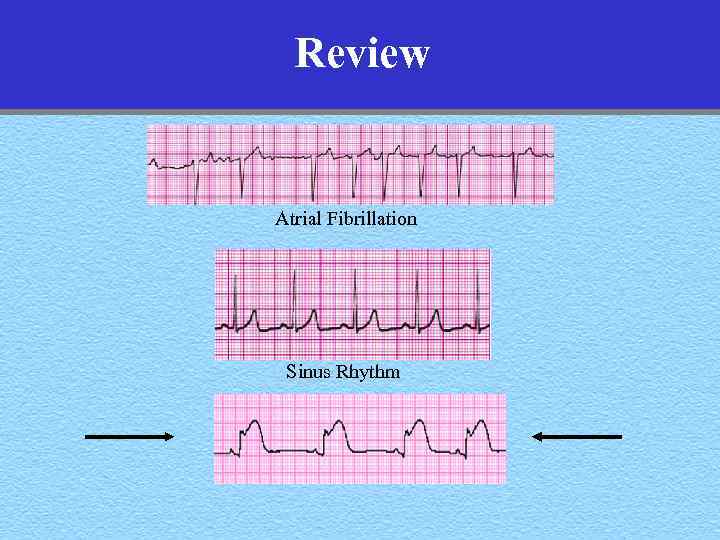 Review Atrial Fibrillation Sinus Rhythm
Review Atrial Fibrillation Sinus Rhythm
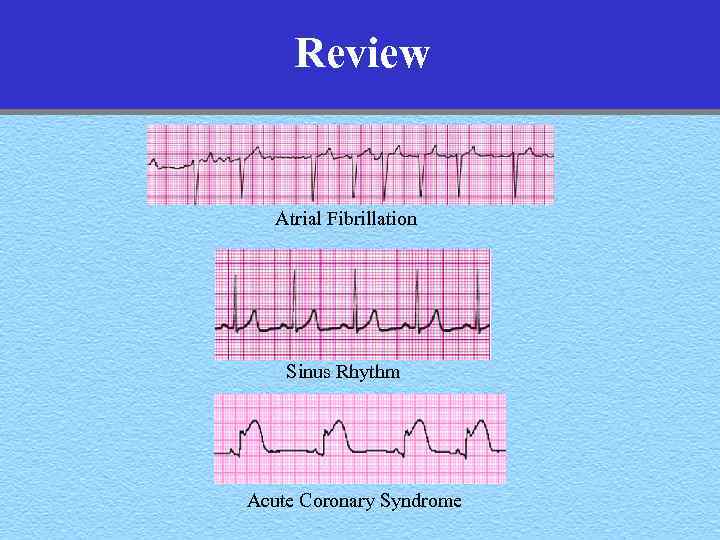 Review Atrial Fibrillation Sinus Rhythm Acute Coronary Syndrome
Review Atrial Fibrillation Sinus Rhythm Acute Coronary Syndrome
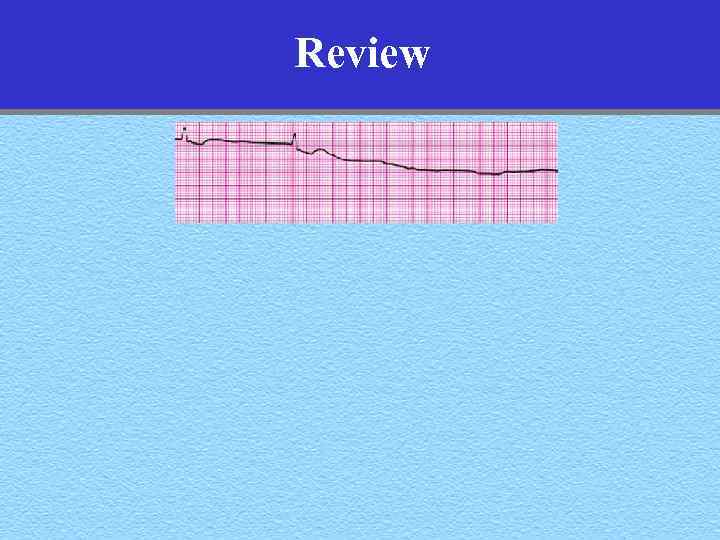 Review
Review
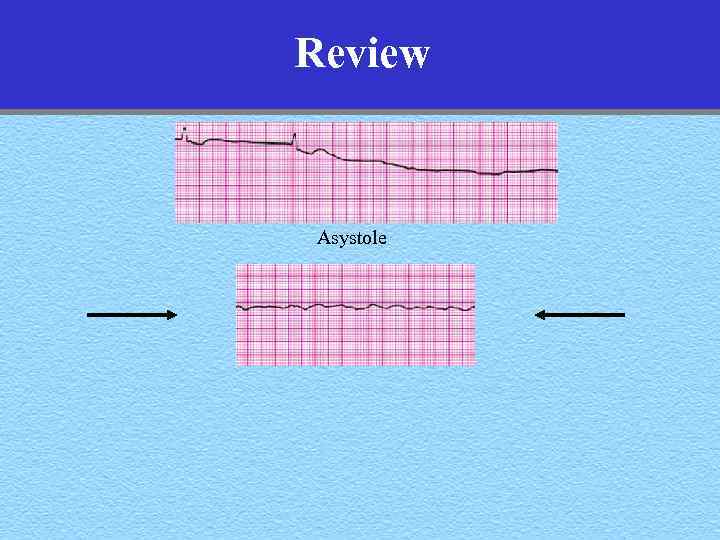 Review Asystole
Review Asystole
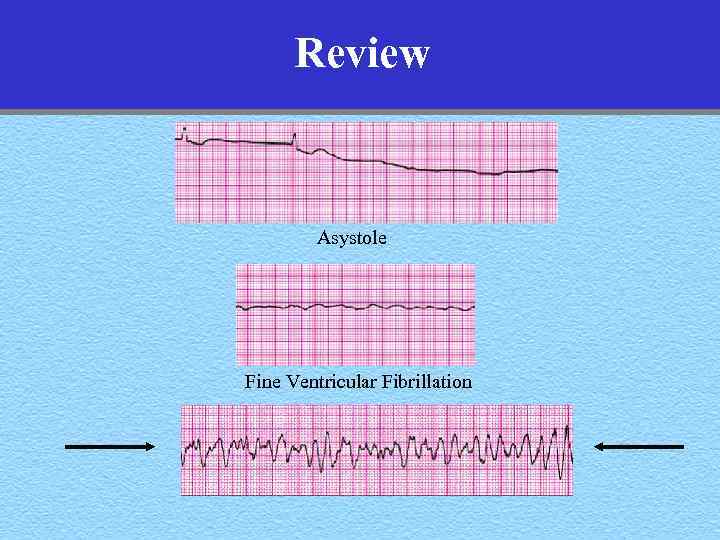 Review Asystole Fine Ventricular Fibrillation
Review Asystole Fine Ventricular Fibrillation
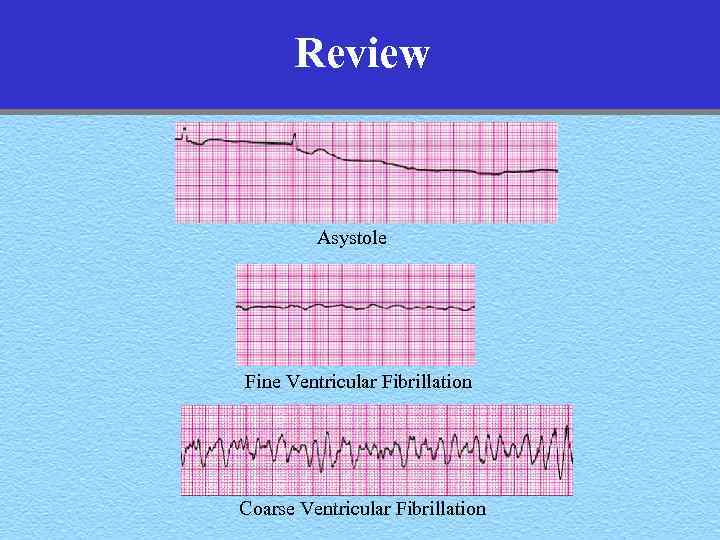 Review Asystole Fine Ventricular Fibrillation Coarse Ventricular Fibrillation
Review Asystole Fine Ventricular Fibrillation Coarse Ventricular Fibrillation
 Review
Review
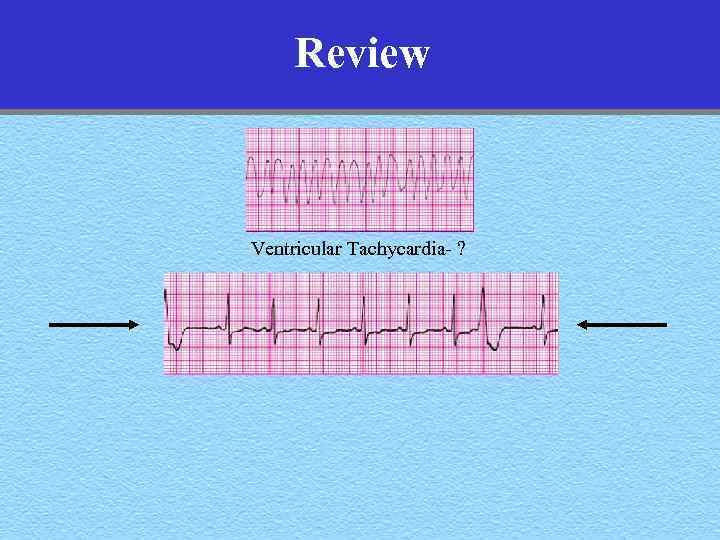 Review Ventricular Tachycardia- ?
Review Ventricular Tachycardia- ?
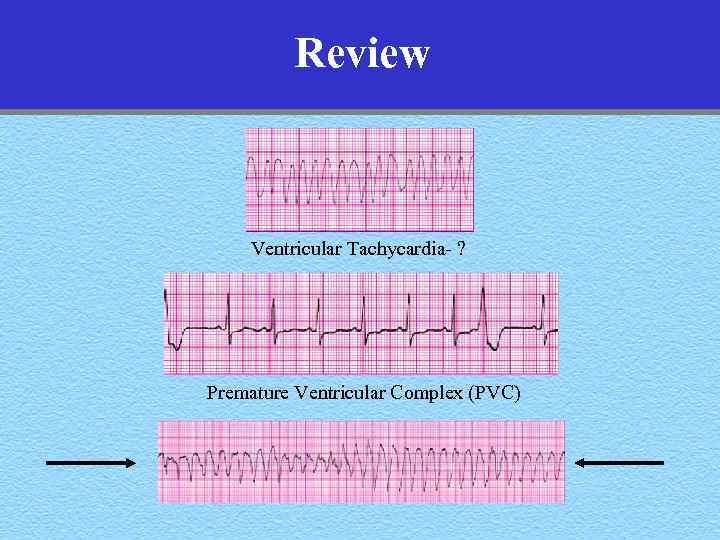 Review Ventricular Tachycardia- ? Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC)
Review Ventricular Tachycardia- ? Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC)
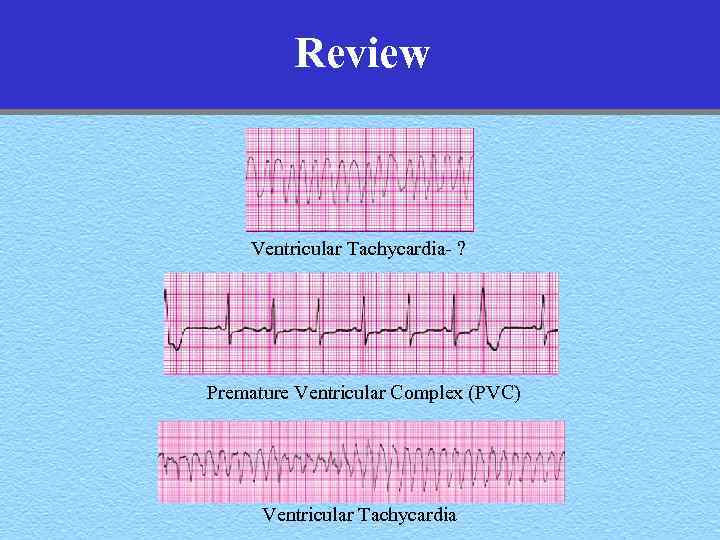 Review Ventricular Tachycardia- ? Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC) Ventricular Tachycardia
Review Ventricular Tachycardia- ? Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC) Ventricular Tachycardia
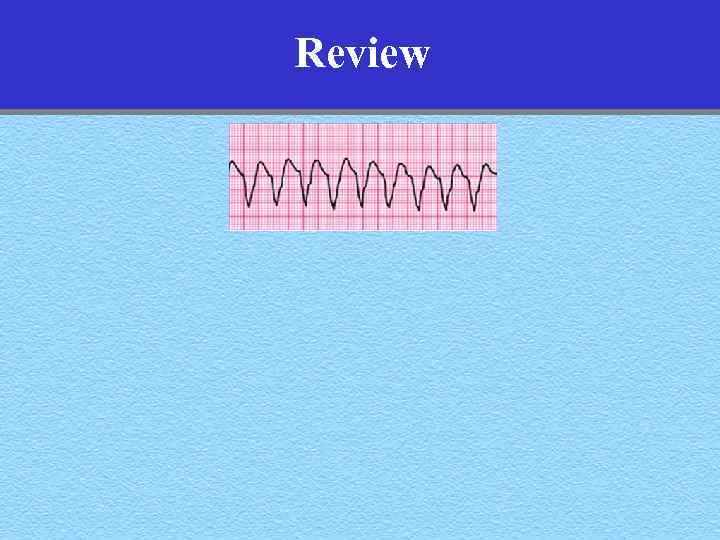 Review
Review
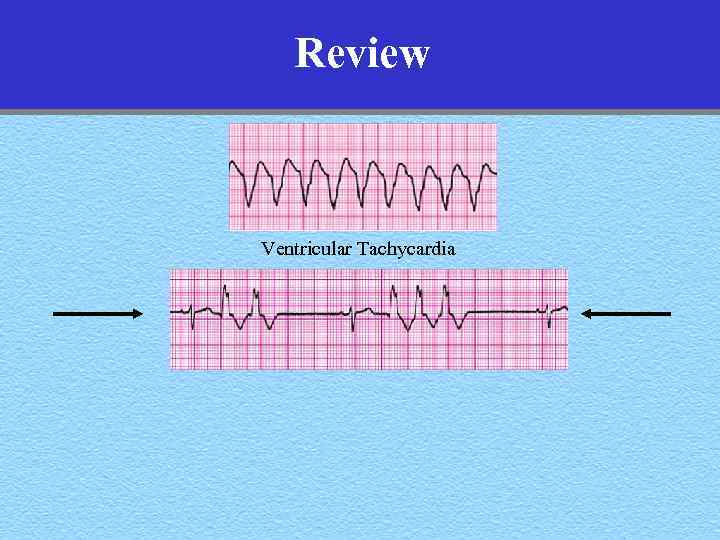 Review Ventricular Tachycardia
Review Ventricular Tachycardia
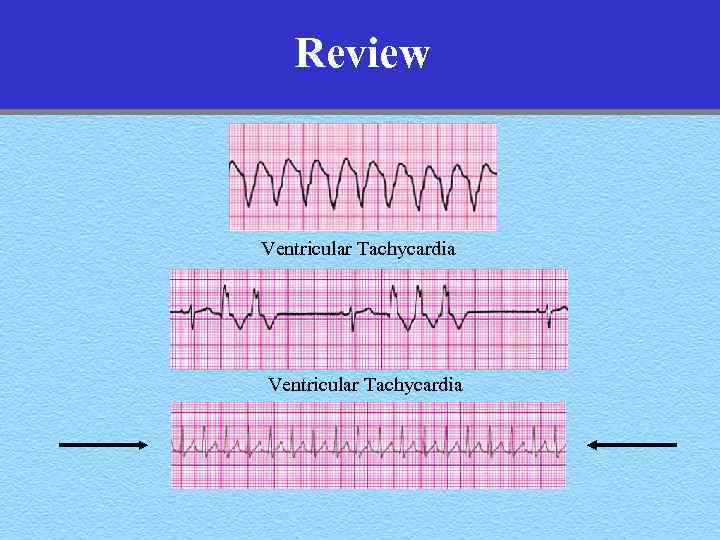 Review Ventricular Tachycardia
Review Ventricular Tachycardia
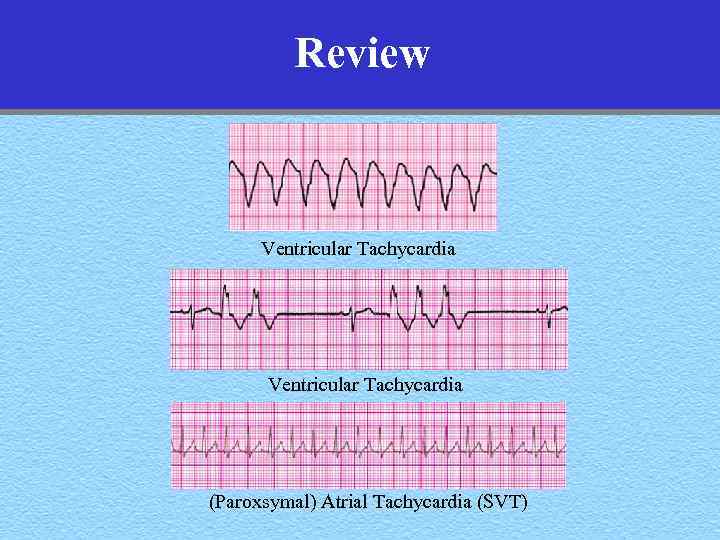 Review Ventricular Tachycardia (Paroxsymal) Atrial Tachycardia (SVT)
Review Ventricular Tachycardia (Paroxsymal) Atrial Tachycardia (SVT)
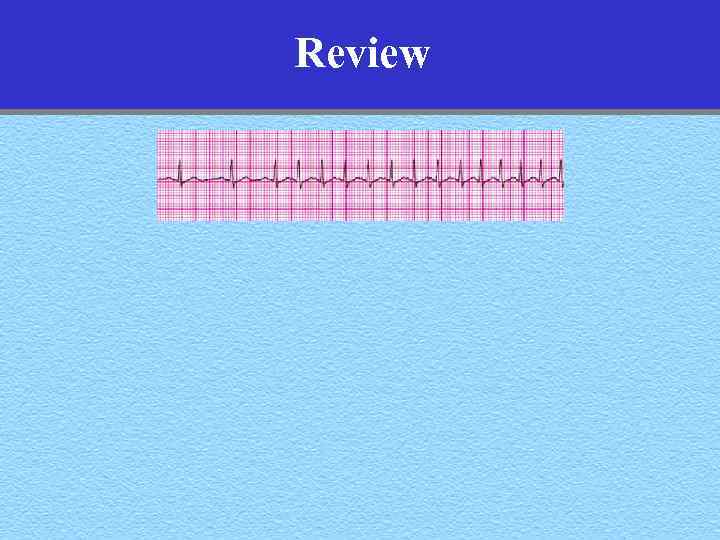 Review
Review
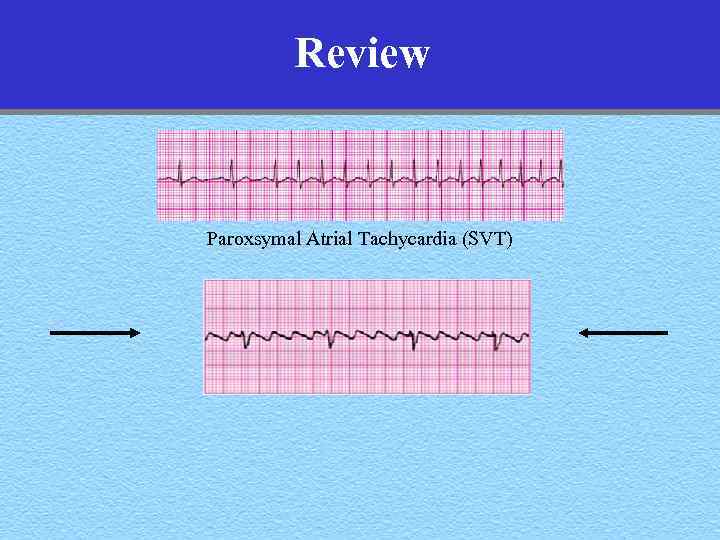 Review Paroxsymal Atrial Tachycardia (SVT)
Review Paroxsymal Atrial Tachycardia (SVT)
 Review Paroxsymal Atrial Tachycardia (SVT) Atrial Flutter
Review Paroxsymal Atrial Tachycardia (SVT) Atrial Flutter
 Treatment of All Cardiac Arrhythmias All arrhythmias that are hemodynamically significant require immediate cardioversion, defibrillation, or cardiac pacing
Treatment of All Cardiac Arrhythmias All arrhythmias that are hemodynamically significant require immediate cardioversion, defibrillation, or cardiac pacing
 Break Time
Break Time
 AV Block • Why is it important? • Where is the block? • What’s a pacemaker anyway?
AV Block • Why is it important? • Where is the block? • What’s a pacemaker anyway?
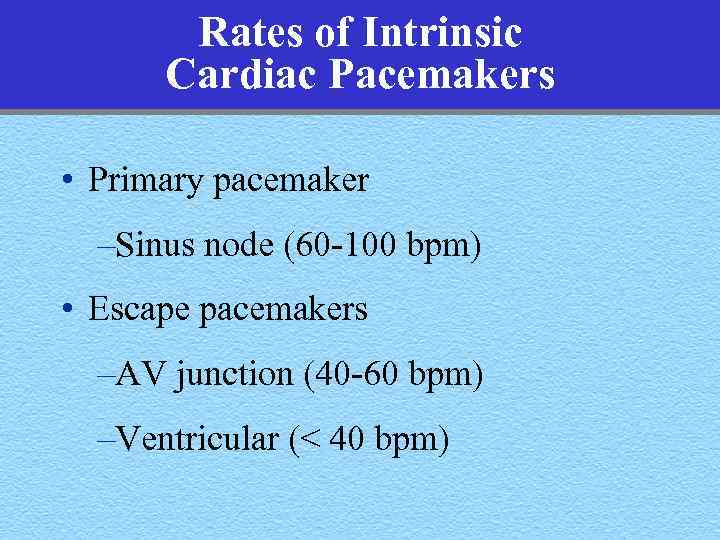 Rates of Intrinsic Cardiac Pacemakers • Primary pacemaker –Sinus node (60 -100 bpm) • Escape pacemakers –AV junction (40 -60 bpm) –Ventricular (< 40 bpm)
Rates of Intrinsic Cardiac Pacemakers • Primary pacemaker –Sinus node (60 -100 bpm) • Escape pacemakers –AV junction (40 -60 bpm) –Ventricular (< 40 bpm)
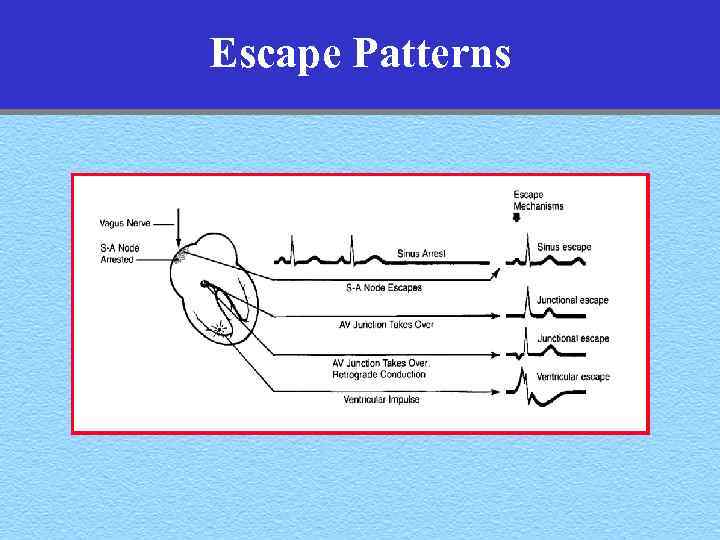 Escape Patterns
Escape Patterns
 Junctional Escape Complexes • Rate: Junctional escape rate 40 -60 bpm • Rhythm: Junctional • P-waves: Retrograde, inverted in 2, 3, avf –Before, during, or after QRS • QRS: Normal or wide
Junctional Escape Complexes • Rate: Junctional escape rate 40 -60 bpm • Rhythm: Junctional • P-waves: Retrograde, inverted in 2, 3, avf –Before, during, or after QRS • QRS: Normal or wide
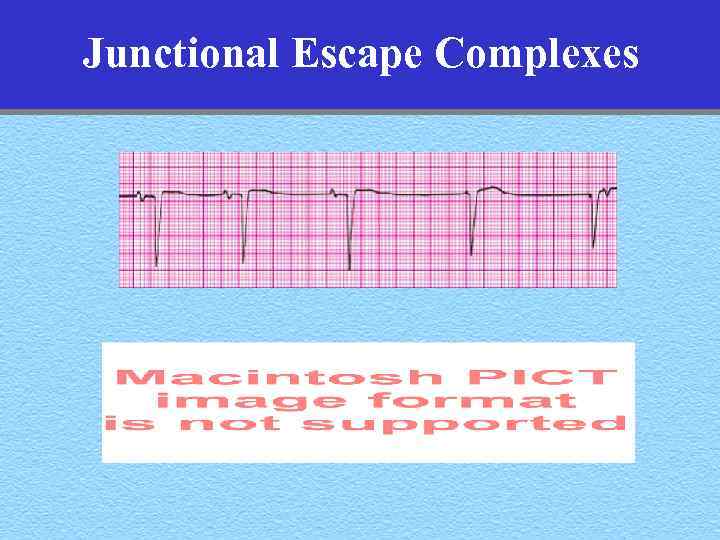 Junctional Escape Complexes
Junctional Escape Complexes
 Junctional Escape Complexes Junctional Rhythm
Junctional Escape Complexes Junctional Rhythm
 Ventricular Escape Complexes
Ventricular Escape Complexes
 Classification of AV Block • Partial – First-degree AV block – Second-degree AV block, Types I (Wenckebach) and Type II • Complete AV block – Third-degree AV Block “You should know the major AV blocks because important treatment decisions are based on the type of block present. ” Page 79
Classification of AV Block • Partial – First-degree AV block – Second-degree AV block, Types I (Wenckebach) and Type II • Complete AV block – Third-degree AV Block “You should know the major AV blocks because important treatment decisions are based on the type of block present. ” Page 79
 First-Degree AV Block • Rhythm: Regular • 1: 1 Conduction: Each P-wave is followed by a QRS complex • PR Interval: >. 20 secs • QRS Complex: Generally normal • Hemodynamic implications: None
First-Degree AV Block • Rhythm: Regular • 1: 1 Conduction: Each P-wave is followed by a QRS complex • PR Interval: >. 20 secs • QRS Complex: Generally normal • Hemodynamic implications: None
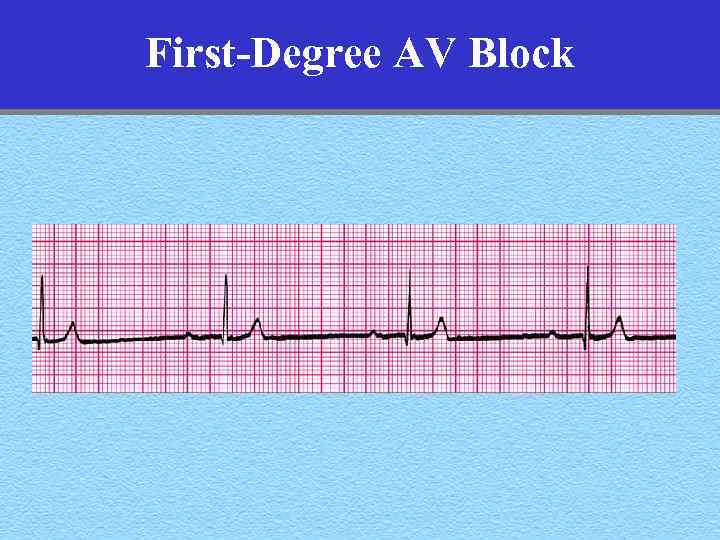 First-Degree AV Block
First-Degree AV Block
 Second-Degree AV Block, Type I • Rate: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- less than the atrial rate • Rhythm: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- progressive shortening of the R-R interval before pause • PR: progressive increase until P blocked • Why is knowing this important
Second-Degree AV Block, Type I • Rate: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- less than the atrial rate • Rhythm: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- progressive shortening of the R-R interval before pause • PR: progressive increase until P blocked • Why is knowing this important
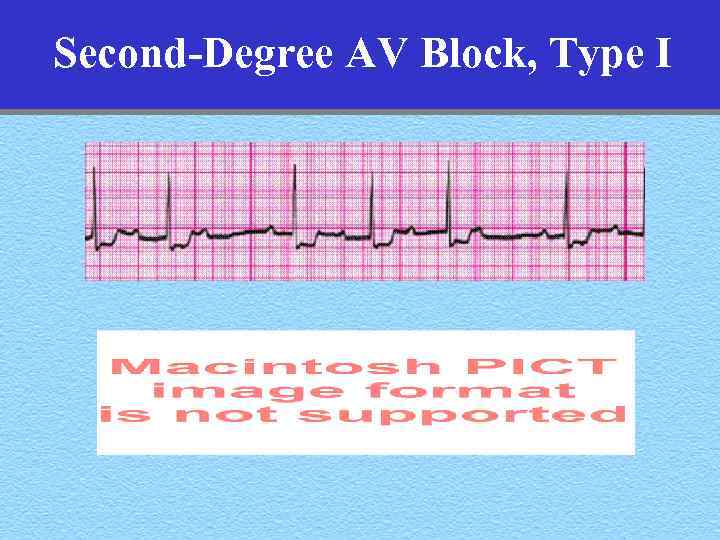 Second-Degree AV Block, Type I
Second-Degree AV Block, Type I
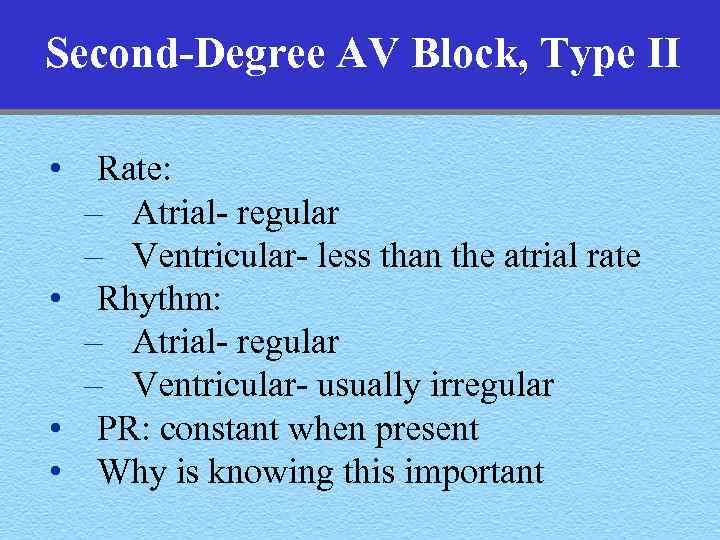 Second-Degree AV Block, Type II • Rate: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- less than the atrial rate • Rhythm: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- usually irregular • PR: constant when present • Why is knowing this important
Second-Degree AV Block, Type II • Rate: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- less than the atrial rate • Rhythm: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- usually irregular • PR: constant when present • Why is knowing this important
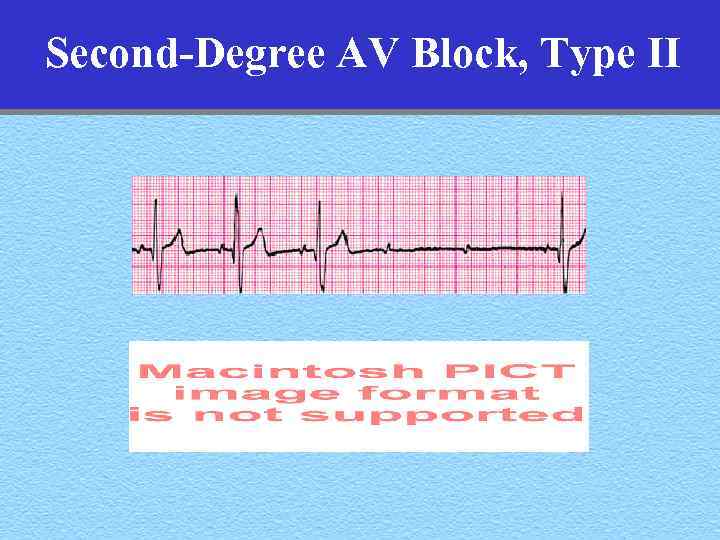 Second-Degree AV Block, Type II
Second-Degree AV Block, Type II
 Third-Degree AV Block • Rate: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- less than the atrial rate • Rhythm: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- regular • PR: varies with every beat • QRS: normal or wide • Hemodynamics: No atrial contribution
Third-Degree AV Block • Rate: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- less than the atrial rate • Rhythm: – Atrial- regular – Ventricular- regular • PR: varies with every beat • QRS: normal or wide • Hemodynamics: No atrial contribution
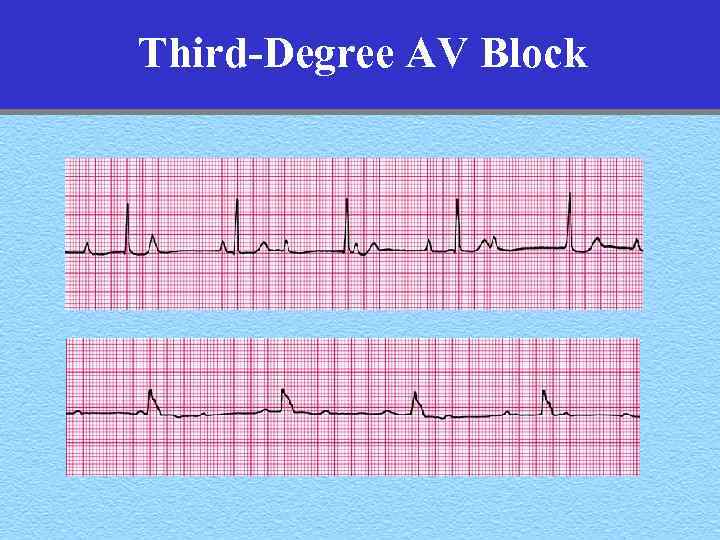 Third-Degree AV Block
Third-Degree AV Block
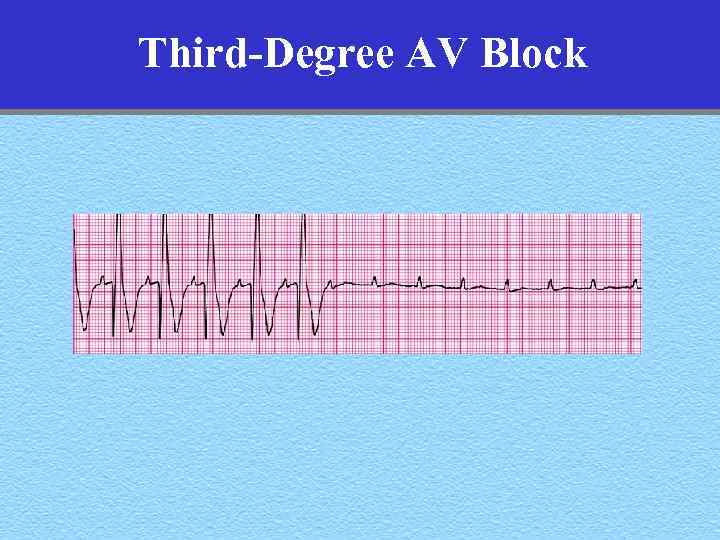 Third-Degree AV Block
Third-Degree AV Block
 Electrical Therapy All arrhythmias that are hemodynamically significant require immediate cardioversion, defibrillation, or cardiac pacing
Electrical Therapy All arrhythmias that are hemodynamically significant require immediate cardioversion, defibrillation, or cardiac pacing
 Electrical Therapy • Understand when cardioversion or defibrillation is indicated • Know the difference between unsynchronized and synchronized shocks • Energy doses for specific rhythms • Challenges of delivering shocks safely and effectively- may include iv sedation
Electrical Therapy • Understand when cardioversion or defibrillation is indicated • Know the difference between unsynchronized and synchronized shocks • Energy doses for specific rhythms • Challenges of delivering shocks safely and effectively- may include iv sedation
 Cardioversion and Defibrillation • Understand when cardioversion or defibrillation is indicated SYMPTOMS
Cardioversion and Defibrillation • Understand when cardioversion or defibrillation is indicated SYMPTOMS
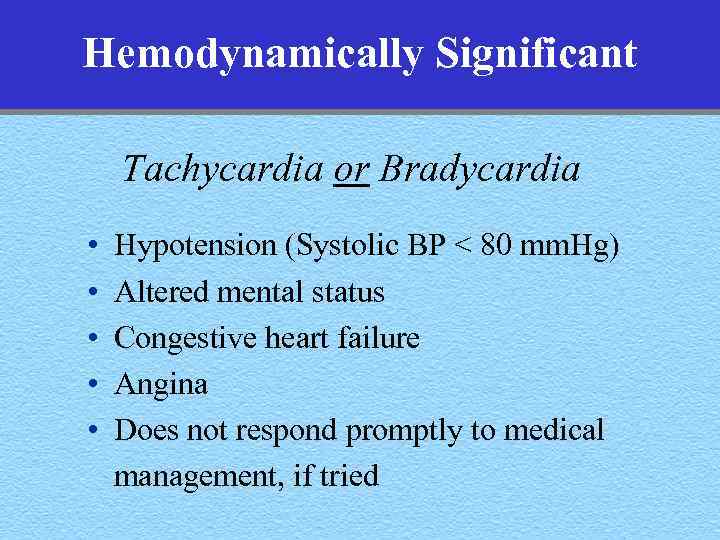 Hemodynamically Significant Tachycardia or Bradycardia • • • Hypotension (Systolic BP < 80 mm. Hg) Altered mental status Congestive heart failure Angina Does not respond promptly to medical management, if tried
Hemodynamically Significant Tachycardia or Bradycardia • • • Hypotension (Systolic BP < 80 mm. Hg) Altered mental status Congestive heart failure Angina Does not respond promptly to medical management, if tried
 Cardioversion and Defibrillation The electric shock depolarizes all excitable myocardium, interrupts reentrant circuits, discharges foci, and establishes electrical homogeneity
Cardioversion and Defibrillation The electric shock depolarizes all excitable myocardium, interrupts reentrant circuits, discharges foci, and establishes electrical homogeneity
 Cardioversion and Defibrillation • AED: Learn the one in your setting • Biphasic: 200 watt-seconds (joules) • Monophasic: 360 watt-seconds (joules) “The interval from collapse to defibrillation is one of the most important determinants of survival from cardiac arrest. ” Page 35
Cardioversion and Defibrillation • AED: Learn the one in your setting • Biphasic: 200 watt-seconds (joules) • Monophasic: 360 watt-seconds (joules) “The interval from collapse to defibrillation is one of the most important determinants of survival from cardiac arrest. ” Page 35
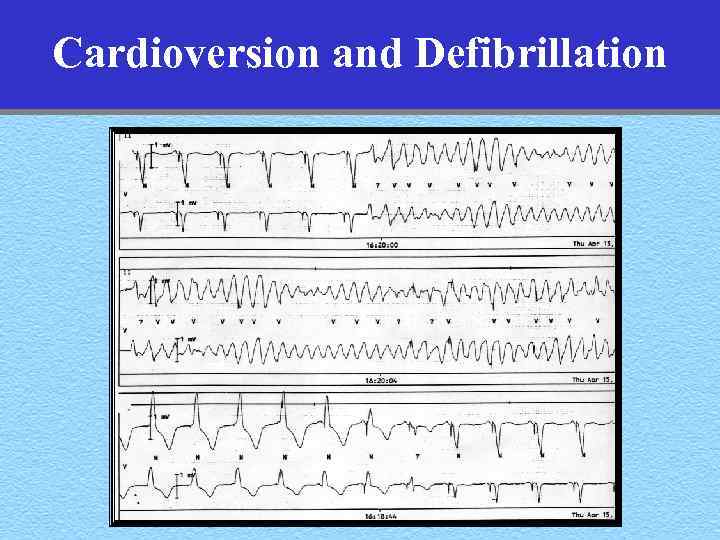 Cardioversion and Defibrillation
Cardioversion and Defibrillation
 Cardioversion and Defibrillation Procedure for Defibrillation • • • Power on Apply pads Analyze the rhythm Select the energy level Clear the area Discharge the device
Cardioversion and Defibrillation Procedure for Defibrillation • • • Power on Apply pads Analyze the rhythm Select the energy level Clear the area Discharge the device
 Cardioversion and Defibrillation Cardioversion • Know when cardioversion is indicated • Synchronized vs unsynchronized shock • What energy level for what arrhythmias • Establish iv and consider sedation
Cardioversion and Defibrillation Cardioversion • Know when cardioversion is indicated • Synchronized vs unsynchronized shock • What energy level for what arrhythmias • Establish iv and consider sedation
 Cardioversion and Defibrillation Cardioversion Anesthetic (amnestic) Agents A physician skilled in airway management (ie. , an anesthesiologist) should be in attendance, and all necessary equipment for emergency resuscitation should be immediately available
Cardioversion and Defibrillation Cardioversion Anesthetic (amnestic) Agents A physician skilled in airway management (ie. , an anesthesiologist) should be in attendance, and all necessary equipment for emergency resuscitation should be immediately available
 Cardioversion and Defibrillation Cardioversion The electric shock depolarizes all excitable myocardium, interrupts reentrant circuits, discharges foci, and establishes electrical homogeneity
Cardioversion and Defibrillation Cardioversion The electric shock depolarizes all excitable myocardium, interrupts reentrant circuits, discharges foci, and establishes electrical homogeneity
 Cardioversion and Defibrillation Synchronized cardioversion (defibrillation) uses a sensor to deliver the shock with the peak of the QRS complex. The goal is to avoid the shock on the T-wave, “R-on-T”, which is known to induce ventricular fibrillation in unstable hearts
Cardioversion and Defibrillation Synchronized cardioversion (defibrillation) uses a sensor to deliver the shock with the peak of the QRS complex. The goal is to avoid the shock on the T-wave, “R-on-T”, which is known to induce ventricular fibrillation in unstable hearts
 The Electrocardiogram PR Interval QRS Interval QT Interval
The Electrocardiogram PR Interval QRS Interval QT Interval
 Cardioversion and Defibrillation Synchronization Energy Selection • Atrial flutter & SVT: 50 -100 J (monphasic) • Atrial fibrillation: 100 -200 J (monophasic) • Ventricular tachycardia: 100 -200 J
Cardioversion and Defibrillation Synchronization Energy Selection • Atrial flutter & SVT: 50 -100 J (monphasic) • Atrial fibrillation: 100 -200 J (monophasic) • Ventricular tachycardia: 100 -200 J
 Cardioversion and Defibrillation Procedure for Cardioversion • • Power on Apply pads Turn on the SYNC control Analyze the rhythm Select the energy level Clear the area Discharge the device
Cardioversion and Defibrillation Procedure for Cardioversion • • Power on Apply pads Turn on the SYNC control Analyze the rhythm Select the energy level Clear the area Discharge the device
 Cardioversion and Defibrillation Complications of Cardioversion • Ventricular fibrillation occurs • Turn off the SYNC control • Charge to 200 J (or more) • Clear the area • Discharge the device
Cardioversion and Defibrillation Complications of Cardioversion • Ventricular fibrillation occurs • Turn off the SYNC control • Charge to 200 J (or more) • Clear the area • Discharge the device
 Review
Review
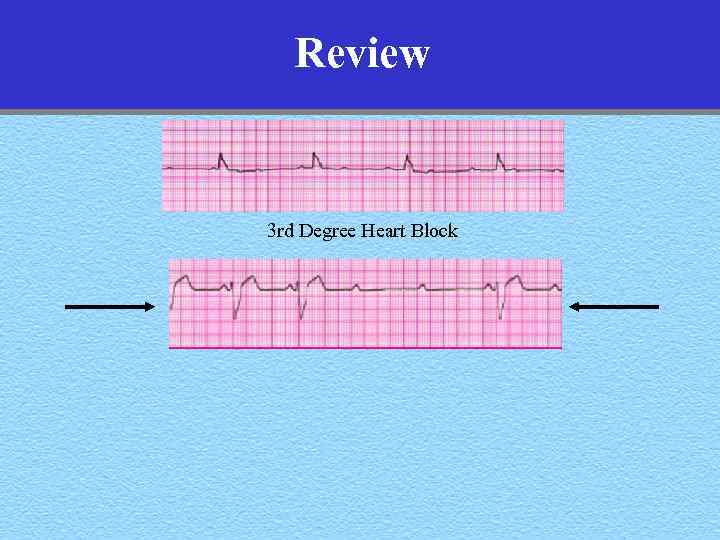 Review 3 rd Degree Heart Block
Review 3 rd Degree Heart Block
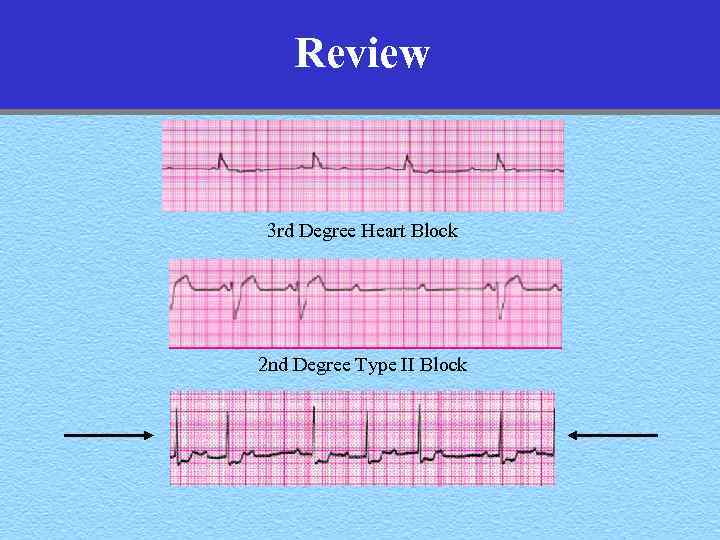 Review 3 rd Degree Heart Block 2 nd Degree Type II Block
Review 3 rd Degree Heart Block 2 nd Degree Type II Block
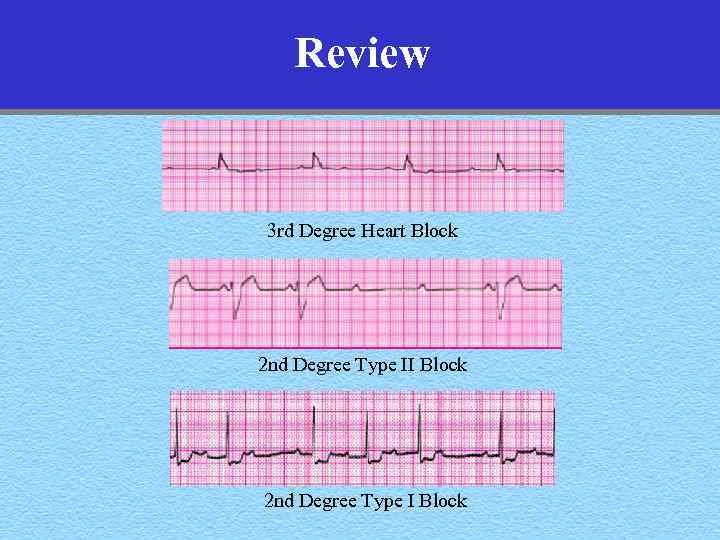 Review 3 rd Degree Heart Block 2 nd Degree Type II Block 2 nd Degree Type I Block
Review 3 rd Degree Heart Block 2 nd Degree Type II Block 2 nd Degree Type I Block
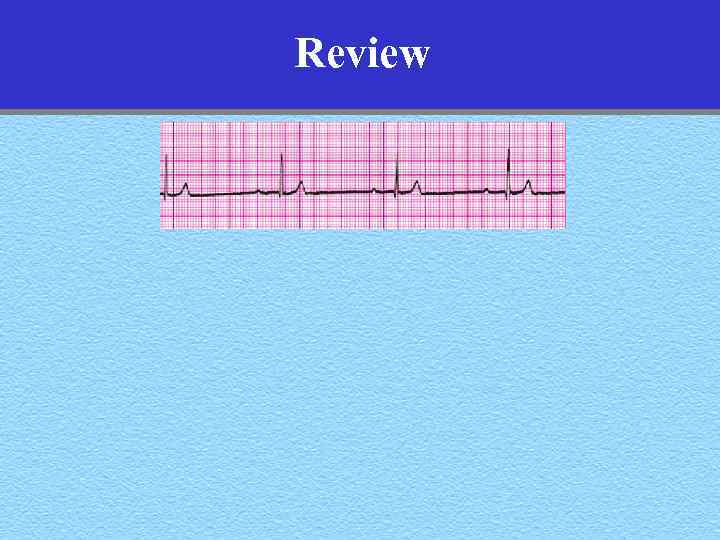 Review
Review
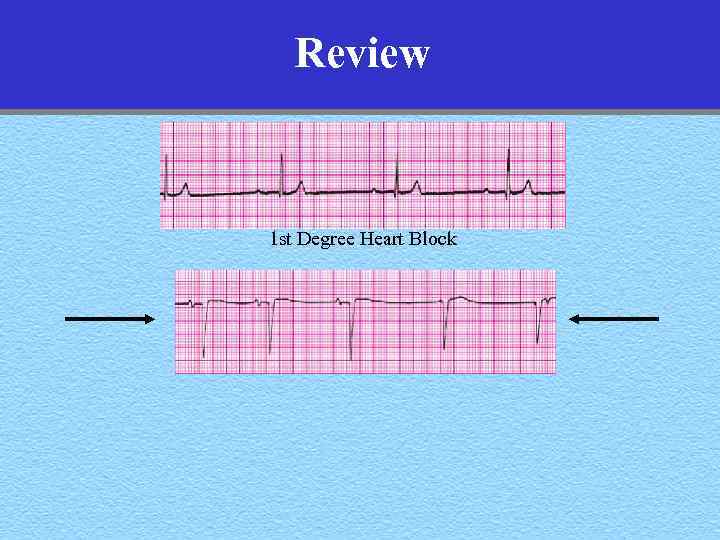 Review 1 st Degree Heart Block
Review 1 st Degree Heart Block
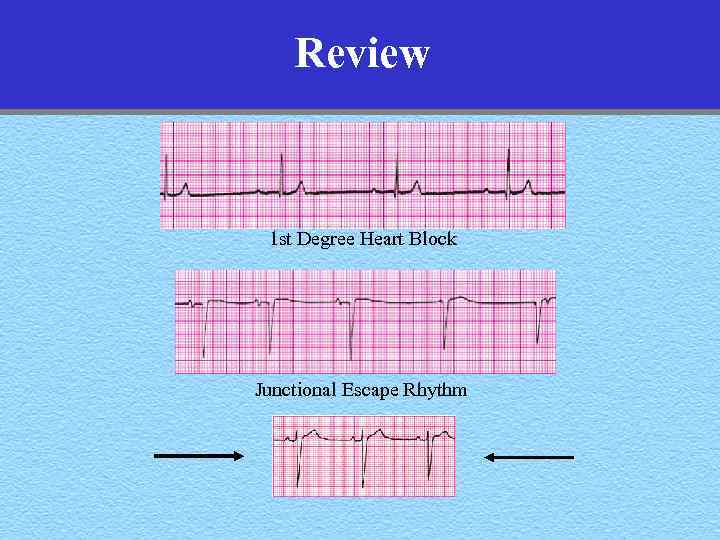 Review 1 st Degree Heart Block Junctional Escape Rhythm
Review 1 st Degree Heart Block Junctional Escape Rhythm
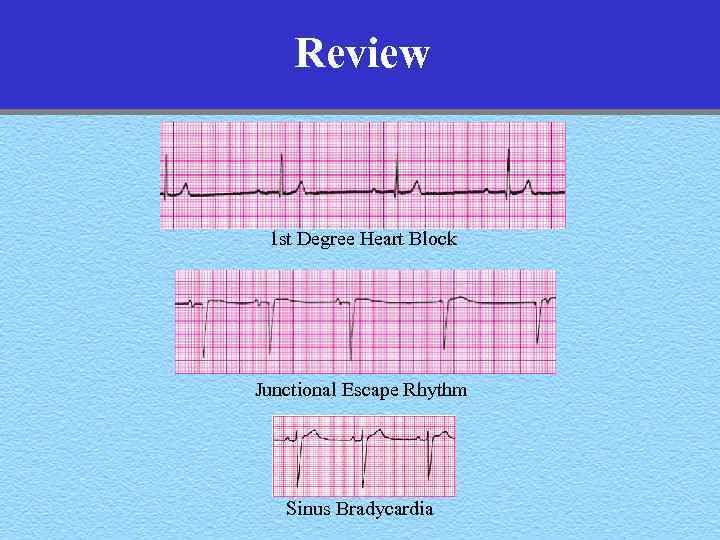 Review 1 st Degree Heart Block Junctional Escape Rhythm Sinus Bradycardia
Review 1 st Degree Heart Block Junctional Escape Rhythm Sinus Bradycardia
 Review Ventricular Tachycardia- ?
Review Ventricular Tachycardia- ?

 ECG Interpretation Advanced Cardiac Life Support That’s it- Now go forth and save lives. Make us all proud you’re from UCSF William A. Shapiro, M. D. http: //anesthesia. ucsf. edu/shapiro advancing health worldwide TM Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care
ECG Interpretation Advanced Cardiac Life Support That’s it- Now go forth and save lives. Make us all proud you’re from UCSF William A. Shapiro, M. D. http: //anesthesia. ucsf. edu/shapiro advancing health worldwide TM Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care


