3e2464cb1be0b4910460de2588e36e9a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 ECET-430 Advanced Digital Signal Processing 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
ECET-430 Advanced Digital Signal Processing 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
 Important Information z Your professor: John Sebeson z Phone: (630)-652 -8299 z Email: jsebeson@devry. edu or sebeson@aol. com z Web page: http: //jsebeson. webs. com z This course does not use the e. College shell z Office hours: see my faculty web page 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
Important Information z Your professor: John Sebeson z Phone: (630)-652 -8299 z Email: jsebeson@devry. edu or sebeson@aol. com z Web page: http: //jsebeson. webs. com z This course does not use the e. College shell z Office hours: see my faculty web page 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
 Course Resources Web Page z. Course syllabus z. Assignment calendar z. Lab Exercises z. Homework coversheet z. Other important information and files 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
Course Resources Web Page z. Course syllabus z. Assignment calendar z. Lab Exercises z. Homework coversheet z. Other important information and files 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
 ECET-430 Advanced Digital Signal Processing z A sequel to ECET-350. z Covers techniques used in many current applications of DSP. z Assumes concepts learned in ECET-350 (or EET 350) and familiarity with MATLAB. z Lab involves MATLAB computational exercises z Some homework assignments require MATLAB. 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
ECET-430 Advanced Digital Signal Processing z A sequel to ECET-350. z Covers techniques used in many current applications of DSP. z Assumes concepts learned in ECET-350 (or EET 350) and familiarity with MATLAB. z Lab involves MATLAB computational exercises z Some homework assignments require MATLAB. 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
 Text and other requirements z J. Kronenburger and J. Sebeson, “Analog and Digital Signal Processing: An Integrated Computational Approach with MATLAB, ” Thompson Delmar Learning (Cengage Learning), 2008. ISBN 1418041734 z Scientific graphing calculator (TI-89 recommended) z MATLAB 7. 0 or higher with Signal Processing Toolbox (available on Citrix) 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
Text and other requirements z J. Kronenburger and J. Sebeson, “Analog and Digital Signal Processing: An Integrated Computational Approach with MATLAB, ” Thompson Delmar Learning (Cengage Learning), 2008. ISBN 1418041734 z Scientific graphing calculator (TI-89 recommended) z MATLAB 7. 0 or higher with Signal Processing Toolbox (available on Citrix) 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
 Selected ECET-430 Topics • • • 3/17/2018 Review of key DSP concepts Discrete Fourier analysis of sampled signals Phase distortion and linear phase filters Impulse response of ideal filters Linear-phase FIR filter design • Windowed ideal response • Sampling method • Optimal Parks-Mc. Clellan method IIR filter design • Digital oscillators • Notch filters • Analog prototypes by the bilinear transformation Multi-rate techniques • Digital anti-aliasing • Decimation and interpolation • Noise power density and sampling • Noise-shaping, delta-sigma quantization Correlation and auto-correlation of signals Adaptive filters Image processing Wavelets Case Studies J. M. Sebeson
Selected ECET-430 Topics • • • 3/17/2018 Review of key DSP concepts Discrete Fourier analysis of sampled signals Phase distortion and linear phase filters Impulse response of ideal filters Linear-phase FIR filter design • Windowed ideal response • Sampling method • Optimal Parks-Mc. Clellan method IIR filter design • Digital oscillators • Notch filters • Analog prototypes by the bilinear transformation Multi-rate techniques • Digital anti-aliasing • Decimation and interpolation • Noise power density and sampling • Noise-shaping, delta-sigma quantization Correlation and auto-correlation of signals Adaptive filters Image processing Wavelets Case Studies J. M. Sebeson
 ECET-430 Lab z Lab consists of 8 MATLAB computational exercises emulating the problems of a typical DSP engineer. z You are expected to complete the lab exercises on your own initiative, just as a DSP engineer would. z Labs are not “cookbook. ” You may need to study lecture notes, textbook MATLAB user guides, and MATLAB help documentation to complete them. z Late labs will not receive credit. z No labs are dropped. 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
ECET-430 Lab z Lab consists of 8 MATLAB computational exercises emulating the problems of a typical DSP engineer. z You are expected to complete the lab exercises on your own initiative, just as a DSP engineer would. z Labs are not “cookbook. ” You may need to study lecture notes, textbook MATLAB user guides, and MATLAB help documentation to complete them. z Late labs will not receive credit. z No labs are dropped. 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
 Grading Weights z. Homework: 20% z. Quizzes: 20% z. Midterm Exam: 20% z. Final Exam: 20% z. Lab: 20% 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
Grading Weights z. Homework: 20% z. Quizzes: 20% z. Midterm Exam: 20% z. Final Exam: 20% z. Lab: 20% 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
 Grading Scale z. Each element (and the total grade) is based on a point system (rounded to the nearest point) where: y 90 to 100 = A (e. g. 89. 51=90. 0=A) y 80 to 89. 5 = B (e. g. 89. 49 =89. 0=B) y 70 to 79. 5 = C y 60 to 69. 5 = D y. Below 60 = F 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
Grading Scale z. Each element (and the total grade) is based on a point system (rounded to the nearest point) where: y 90 to 100 = A (e. g. 89. 51=90. 0=A) y 80 to 89. 5 = B (e. g. 89. 49 =89. 0=B) y 70 to 79. 5 = C y 60 to 69. 5 = D y. Below 60 = F 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
 Why Learn DSP With MATLAB? z Digital Signal Processing is the dominant technology today, and into the future, for small-signal electronic systems (i. e. , just about everything) z MATLAB has become one of the standard design environments for DSP engineering z Technology students need to be literate and skilled in this environment: knowledgeable in both DSP and MATLAB 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
Why Learn DSP With MATLAB? z Digital Signal Processing is the dominant technology today, and into the future, for small-signal electronic systems (i. e. , just about everything) z MATLAB has become one of the standard design environments for DSP engineering z Technology students need to be literate and skilled in this environment: knowledgeable in both DSP and MATLAB 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
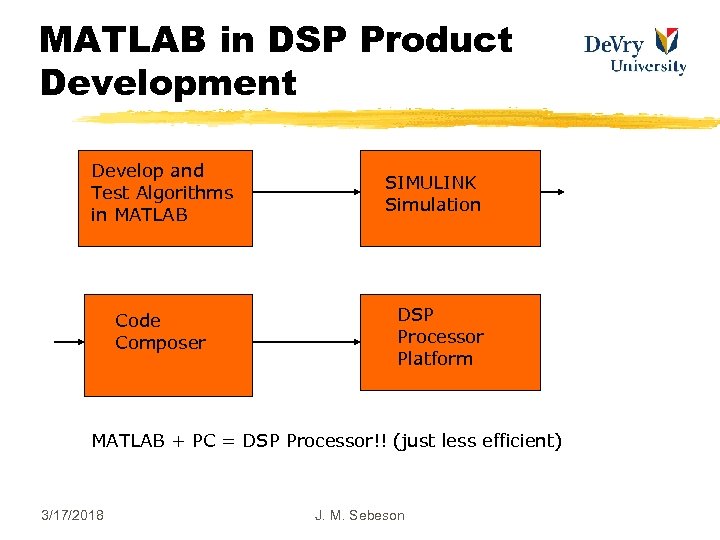 MATLAB in DSP Product Development Develop and Test Algorithms in MATLAB Code Composer SIMULINK Simulation DSP Processor Platform MATLAB + PC = DSP Processor!! (just less efficient) 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
MATLAB in DSP Product Development Develop and Test Algorithms in MATLAB Code Composer SIMULINK Simulation DSP Processor Platform MATLAB + PC = DSP Processor!! (just less efficient) 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
 My Background z Education: y B. S. Physics, 1969, Michigan State University y M. S. Electrical Engineering, 1971, Northwestern University y M. S. Materials Science and Engineering, 1973, Northwestern University y Ph. D. Candidacy (ABT) Materials Science, 1978, Northwestern University z Professional Experience: (1969 to Present) y 2000 – Present: Professor, ECET, De. Vry University y 1989 - 2000: Hardware Development Director, Switching and Access Solutions, Lucent Technologies y 1985 - 1989: Head, Computer Engineering Information Department, AT&T Data Systems Group y 1979 - 1985: Technical Manager, Data Switching Product Engineering Group, Bell Laboratories y 1969 - 1979: Member of Technical Staff, Bell Laboratories 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
My Background z Education: y B. S. Physics, 1969, Michigan State University y M. S. Electrical Engineering, 1971, Northwestern University y M. S. Materials Science and Engineering, 1973, Northwestern University y Ph. D. Candidacy (ABT) Materials Science, 1978, Northwestern University z Professional Experience: (1969 to Present) y 2000 – Present: Professor, ECET, De. Vry University y 1989 - 2000: Hardware Development Director, Switching and Access Solutions, Lucent Technologies y 1985 - 1989: Head, Computer Engineering Information Department, AT&T Data Systems Group y 1979 - 1985: Technical Manager, Data Switching Product Engineering Group, Bell Laboratories y 1969 - 1979: Member of Technical Staff, Bell Laboratories 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
 Areas of R&D z z z z No. 5 Electronic Switching Systemtm AT&T 3 Btm Computers No. 2 Signal Transfer Point Common Channel Signaling (CCIS) 1 A Processor (No. 1 A ESStm and No. 4 ESStm ) Computer Aided Design Signaling link encryption systems Hybrid integrated circuit fabrication and testing Magnetic bubble memory devices Laser holographic mass memory systems Reliability theory Solid state surface physics Molecular kinetics 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson
Areas of R&D z z z z No. 5 Electronic Switching Systemtm AT&T 3 Btm Computers No. 2 Signal Transfer Point Common Channel Signaling (CCIS) 1 A Processor (No. 1 A ESStm and No. 4 ESStm ) Computer Aided Design Signaling link encryption systems Hybrid integrated circuit fabrication and testing Magnetic bubble memory devices Laser holographic mass memory systems Reliability theory Solid state surface physics Molecular kinetics 3/17/2018 J. M. Sebeson


