cbe9991c4635e1c584136d86dbc84a8e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 ECEN 4533 Data Communications Lecture #33 1 April 2013 Dr. George Scheets Read Vo. IP Tutorial n Web 25 & 26 n Exam #2, 8 April n Corrected Quizzes due 10 April n
ECEN 4533 Data Communications Lecture #33 1 April 2013 Dr. George Scheets Read Vo. IP Tutorial n Web 25 & 26 n Exam #2, 8 April n Corrected Quizzes due 10 April n
 ECEN 4533 Data Communications Lecture #34 3 April 2013 Dr. George Scheets Problems: Exam #2 2010 & (1 st Half) 2011 n Exam #2, 8 April n u Probability & Queuing (including) up to RF (excluding) n Corrected Designs due u 5 April (Live) u 1 Week after return (DL) n Corrected Quizzes due 10 April? ?
ECEN 4533 Data Communications Lecture #34 3 April 2013 Dr. George Scheets Problems: Exam #2 2010 & (1 st Half) 2011 n Exam #2, 8 April n u Probability & Queuing (including) up to RF (excluding) n Corrected Designs due u 5 April (Live) u 1 Week after return (DL) n Corrected Quizzes due 10 April? ?
 ECEN 4533 Data Communications Lecture #35 5 April 2013 Dr. George Scheets n n Problems: Exam #2 2012 & 2011 (2 nd Half) Exam #2: 8 April (Live), < 15 April (DL) u Probability & Queuing (including) up to RF (excluding) Corrected Designs due u Today (Live) u 1 week after return (DL) Corrected Quizzes due u 10 April (Live) u 1 week after return (DL)
ECEN 4533 Data Communications Lecture #35 5 April 2013 Dr. George Scheets n n Problems: Exam #2 2012 & 2011 (2 nd Half) Exam #2: 8 April (Live), < 15 April (DL) u Probability & Queuing (including) up to RF (excluding) Corrected Designs due u Today (Live) u 1 week after return (DL) Corrected Quizzes due u 10 April (Live) u 1 week after return (DL)
 2013 OSU ECE Spring Banquet n n n n n Hosted by Student Branch of IEEE Wednesday, 17 April, at Meditations Doors open at 5: 30 pm, meal at 6: 00 pm Cash Bar Sign up in ES 202 to reserve your seat(s) $5 a head (for a $16 meal!) u if pay in advance and resume submitted to OSUIEEEresume@gmail. com < 5: 00 pm, 15 April. Otherwise $8. Speaker: Dr. Matt Perry Director, Si. Arch Dress is Business Casual Many door prizes available! +10 points extra credit All are invited! Sponsored in part by:
2013 OSU ECE Spring Banquet n n n n n Hosted by Student Branch of IEEE Wednesday, 17 April, at Meditations Doors open at 5: 30 pm, meal at 6: 00 pm Cash Bar Sign up in ES 202 to reserve your seat(s) $5 a head (for a $16 meal!) u if pay in advance and resume submitted to OSUIEEEresume@gmail. com < 5: 00 pm, 15 April. Otherwise $8. Speaker: Dr. Matt Perry Director, Si. Arch Dress is Business Casual Many door prizes available! +10 points extra credit All are invited! Sponsored in part by:
 Tsega Debele $17, 057. 31 Qo. S Internet
Tsega Debele $17, 057. 31 Qo. S Internet
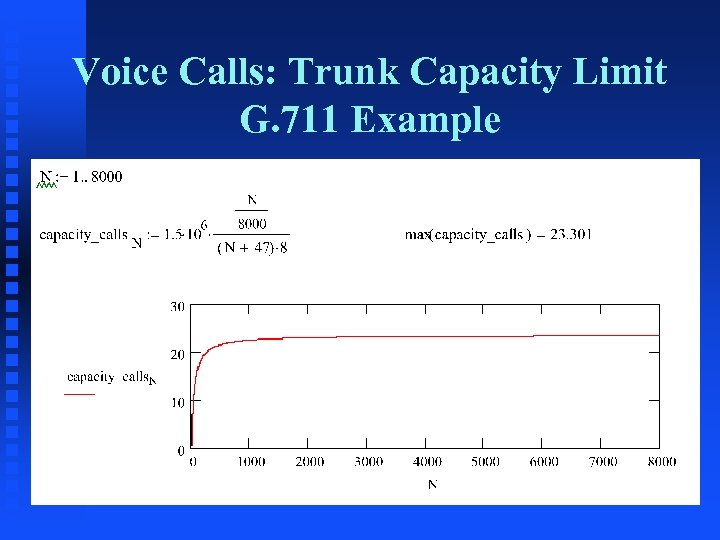 Voice Calls: Trunk Capacity Limit G. 711 Example
Voice Calls: Trunk Capacity Limit G. 711 Example
 Voice Calls: M 2 E Delay Limit G. 711 Example
Voice Calls: M 2 E Delay Limit G. 711 Example
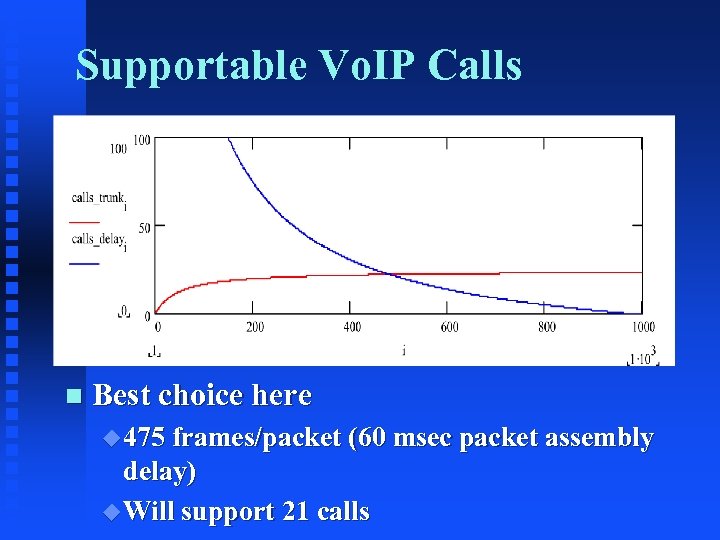 Supportable Vo. IP Calls n Best choice here u 475 frames/packet (60 msec packet assembly delay) u Will support 21 calls
Supportable Vo. IP Calls n Best choice here u 475 frames/packet (60 msec packet assembly delay) u Will support 21 calls
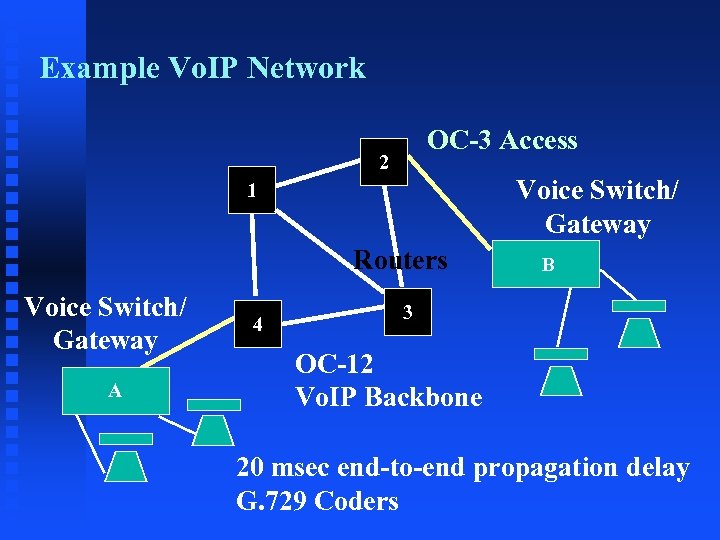 Example Vo. IP Network OC-3 Access 2 Voice Switch/ Gateway 1 Routers Voice Switch/ Gateway A 4 B 3 OC-12 Vo. IP Backbone 20 msec end-to-end propagation delay G. 729 Coders
Example Vo. IP Network OC-3 Access 2 Voice Switch/ Gateway 1 Routers Voice Switch/ Gateway A 4 B 3 OC-12 Vo. IP Backbone 20 msec end-to-end propagation delay G. 729 Coders
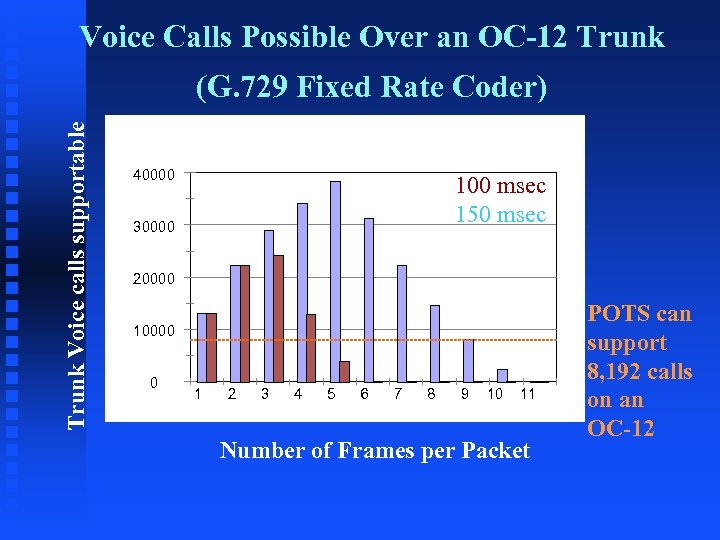 Voice Calls Possible Over an OC-12 Trunk Voice calls supportable (G. 729 Fixed Rate Coder) 40000 100 msec 150 msec 30000 20000 10000 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Number of Frames per Packet POTS can support 8, 192 calls on an OC-12
Voice Calls Possible Over an OC-12 Trunk Voice calls supportable (G. 729 Fixed Rate Coder) 40000 100 msec 150 msec 30000 20000 10000 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Number of Frames per Packet POTS can support 8, 192 calls on an OC-12
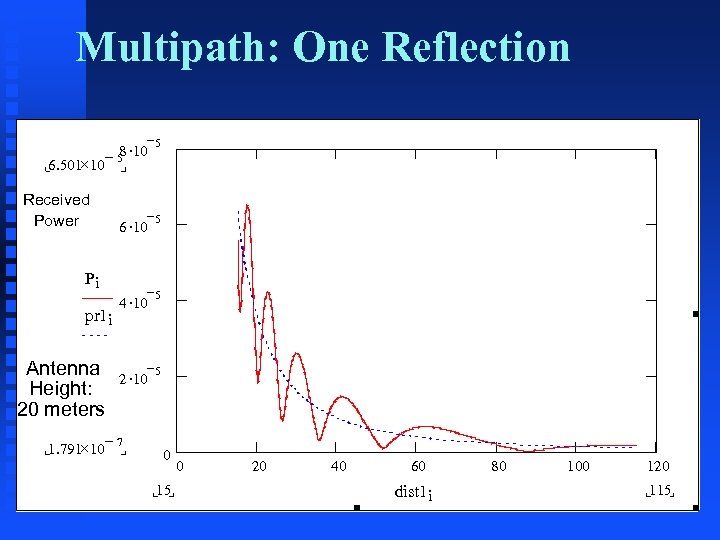 Multipath: One Reflection 8. - 5 10 6. 501´ 10 Received Power Pi pr 1 i Antenna Height: 20 meters 1. 791´ 10 - 5 6. 10 5 4. 10 5 2. 10 5 7 0 15 0 20 40 60 dist 1 i 80 100 120 115
Multipath: One Reflection 8. - 5 10 6. 501´ 10 Received Power Pi pr 1 i Antenna Height: 20 meters 1. 791´ 10 - 5 6. 10 5 4. 10 5 2. 10 5 7 0 15 0 20 40 60 dist 1 i 80 100 120 115
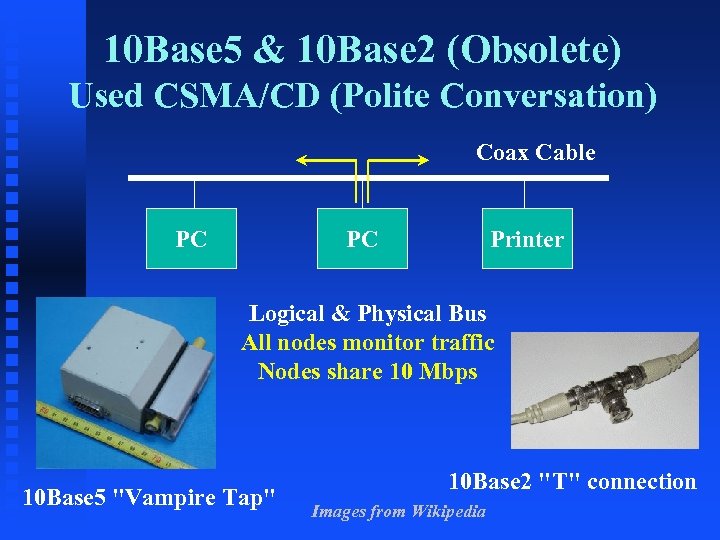 10 Base 5 & 10 Base 2 (Obsolete) Used CSMA/CD (Polite Conversation) Coax Cable PC PC Printer Logical & Physical Bus All nodes monitor traffic Nodes share 10 Mbps 10 Base 5 "Vampire Tap" 10 Base 2 "T" connection Images from Wikipedia
10 Base 5 & 10 Base 2 (Obsolete) Used CSMA/CD (Polite Conversation) Coax Cable PC PC Printer Logical & Physical Bus All nodes monitor traffic Nodes share 10 Mbps 10 Base 5 "Vampire Tap" 10 Base 2 "T" connection Images from Wikipedia
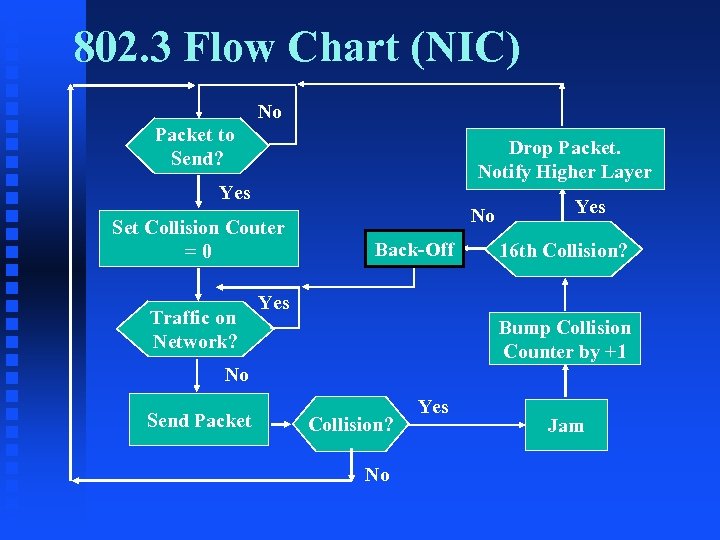 802. 3 Flow Chart (NIC) No Packet to Send? Drop Packet. Notify Higher Layer Yes Set Collision Couter =0 Traffic on Network? No Back-Off Yes 16 th Collision? Yes Bump Collision Counter by +1 No Send Packet Collision? No Yes Jam
802. 3 Flow Chart (NIC) No Packet to Send? Drop Packet. Notify Higher Layer Yes Set Collision Couter =0 Traffic on Network? No Back-Off Yes 16 th Collision? Yes Bump Collision Counter by +1 No Send Packet Collision? No Yes Jam
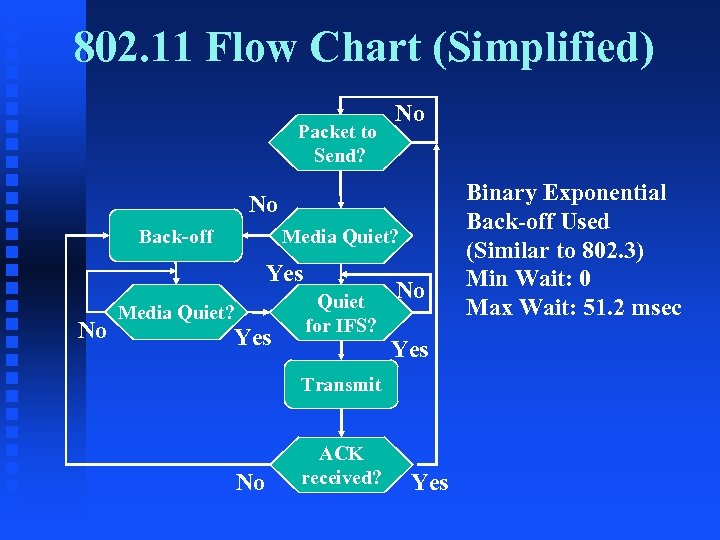 802. 11 Flow Chart (Simplified) Packet to Send? No No Back-off Media Quiet? Yes No Media Quiet? Yes Quiet for IFS? No Yes Transmit No ACK received? Yes Binary Exponential Back-off Used (Similar to 802. 3) Min Wait: 0 Max Wait: 51. 2 msec
802. 11 Flow Chart (Simplified) Packet to Send? No No Back-off Media Quiet? Yes No Media Quiet? Yes Quiet for IFS? No Yes Transmit No ACK received? Yes Binary Exponential Back-off Used (Similar to 802. 3) Min Wait: 0 Max Wait: 51. 2 msec
 Fall 2002 Final n 'Average' based on 1 test chosen at random 126. 00 out of 150 u One point average X 1 n 'Average' based on 10 tests chosen randomly 109. 44 out of 150 u Ten point average X 10 n Actual Midterm Average 106. 85 out of 150
Fall 2002 Final n 'Average' based on 1 test chosen at random 126. 00 out of 150 u One point average X 1 n 'Average' based on 10 tests chosen randomly 109. 44 out of 150 u Ten point average X 10 n Actual Midterm Average 106. 85 out of 150
 Wireless Design Options Adjust Transmitter Power Out n Reduce System Noise n u Signal off antenna very small u Thermal Noise off antenna ≈ 80*10 -15 watts F 20 MHz Bandwidth F Stuck with this u Electronic Noise can be >> F Can n be reduced with $$ Slow down XMTR symbol rate (= 1/T) u Allows more accurate average in T seconds
Wireless Design Options Adjust Transmitter Power Out n Reduce System Noise n u Signal off antenna very small u Thermal Noise off antenna ≈ 80*10 -15 watts F 20 MHz Bandwidth F Stuck with this u Electronic Noise can be >> F Can n be reduced with $$ Slow down XMTR symbol rate (= 1/T) u Allows more accurate average in T seconds
 Averages n N point average? S. I. points? σ2 average = σ2 points/N n N point average? Self-Similar points? σ2 average = σ2 points/N 2(1 -H) u If Statistically Independent, H = 1/2
Averages n N point average? S. I. points? σ2 average = σ2 points/N n N point average? Self-Similar points? σ2 average = σ2 points/N 2(1 -H) u If Statistically Independent, H = 1/2
 Very Large Array Parabolics Directional antennas. Larger size → narrower beam. Narrower beam → energy more focused (XMTR) Narrower beam → better at picking up weak signal (RCVR) image source: Wikipedia
Very Large Array Parabolics Directional antennas. Larger size → narrower beam. Narrower beam → energy more focused (XMTR) Narrower beam → better at picking up weak signal (RCVR) image source: Wikipedia
 Satcom & Flat Panel Antenna Arrays USS Lake Champlain: Aegis Guided Missile Cruiser image source: wikipedia
Satcom & Flat Panel Antenna Arrays USS Lake Champlain: Aegis Guided Missile Cruiser image source: wikipedia
 Omni-Directional Antenna Array Belkin Wireless Pre-N Router F 5 D 8230 -4 Steerable beams. source: http: //www. pcmag. com/article 2/0, 1759, 1822020, 00. asp
Omni-Directional Antenna Array Belkin Wireless Pre-N Router F 5 D 8230 -4 Steerable beams. source: http: //www. pcmag. com/article 2/0, 1759, 1822020, 00. asp
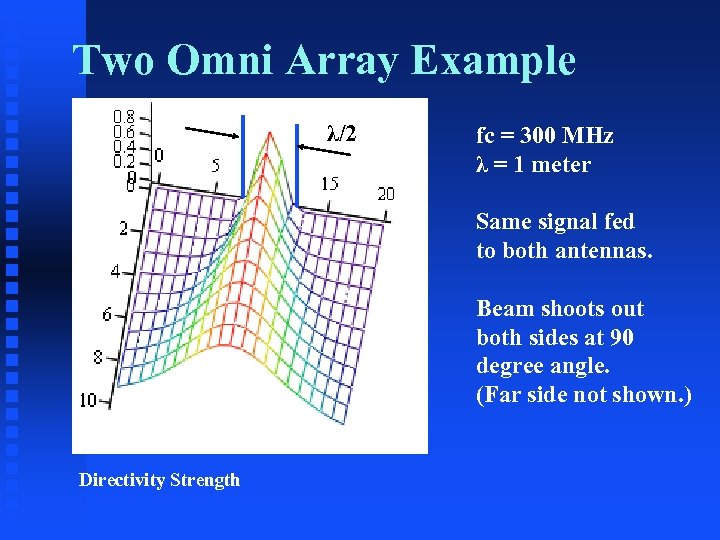 Two Omni Array Example λ/2 fc = 300 MHz λ = 1 meter Same signal fed to both antennas. Beam shoots out both sides at 90 degree angle. (Far side not shown. ) Directivity Strength
Two Omni Array Example λ/2 fc = 300 MHz λ = 1 meter Same signal fed to both antennas. Beam shoots out both sides at 90 degree angle. (Far side not shown. ) Directivity Strength
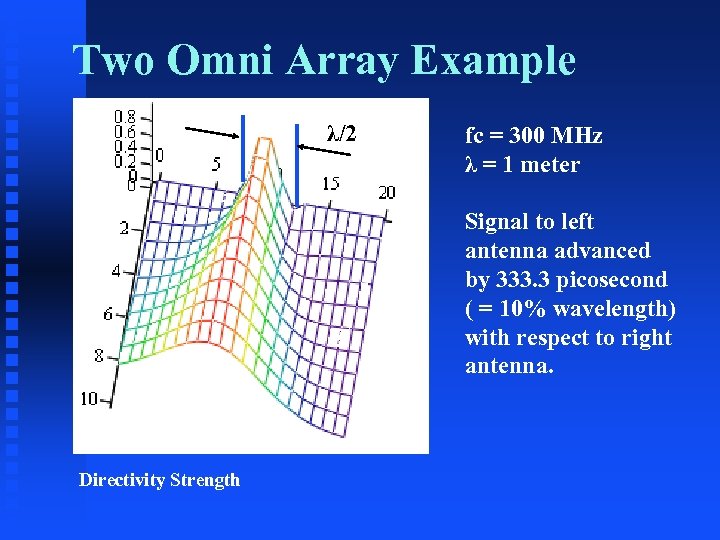 Two Omni Array Example λ/2 fc = 300 MHz λ = 1 meter Signal to left antenna advanced by 333. 3 picosecond ( = 10% wavelength) with respect to right antenna. Directivity Strength
Two Omni Array Example λ/2 fc = 300 MHz λ = 1 meter Signal to left antenna advanced by 333. 3 picosecond ( = 10% wavelength) with respect to right antenna. Directivity Strength
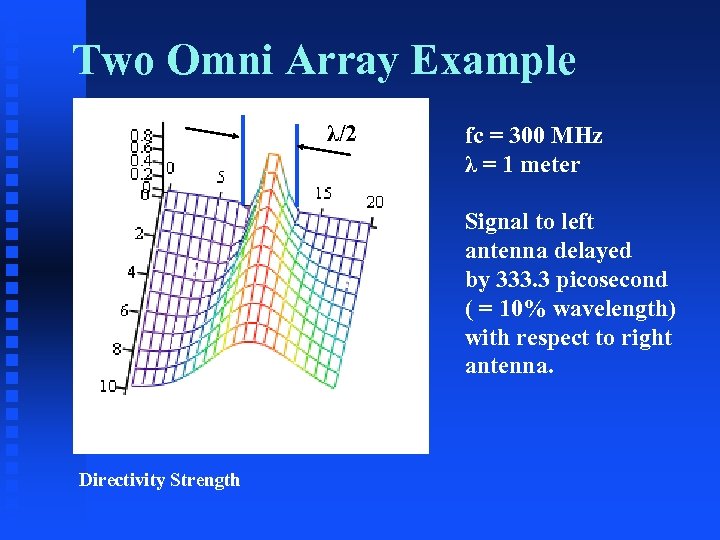 Two Omni Array Example λ/2 fc = 300 MHz λ = 1 meter Signal to left antenna delayed by 333. 3 picosecond ( = 10% wavelength) with respect to right antenna. Directivity Strength
Two Omni Array Example λ/2 fc = 300 MHz λ = 1 meter Signal to left antenna delayed by 333. 3 picosecond ( = 10% wavelength) with respect to right antenna. Directivity Strength
 Two Omni Array Example λ/2 fc = 300 MHz λ = 1 meter Signal to left antenna delayed by 833. 3 picosecond ( = 25% wavelength) with respect to right antenna. Directivity Strength
Two Omni Array Example λ/2 fc = 300 MHz λ = 1 meter Signal to left antenna delayed by 833. 3 picosecond ( = 25% wavelength) with respect to right antenna. Directivity Strength
 Two Omni Array Example λ/2 fc = 300 MHz λ = 1 meter Signal to left antenna delayed by 1 2/3 nanosecond ( = 50% wavelength) with respect to right antenna. Directivity Strength
Two Omni Array Example λ/2 fc = 300 MHz λ = 1 meter Signal to left antenna delayed by 1 2/3 nanosecond ( = 50% wavelength) with respect to right antenna. Directivity Strength
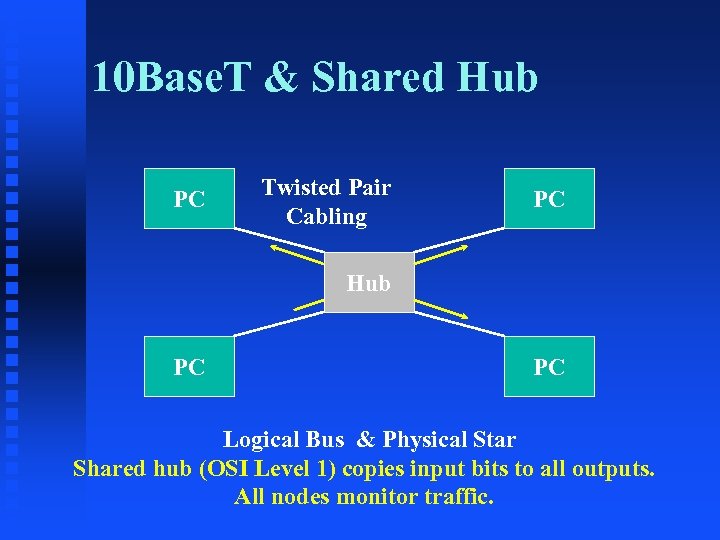 10 Base. T & Shared Hub PC Twisted Pair Cabling PC Hub PC PC Logical Bus & Physical Star Shared hub (OSI Level 1) copies input bits to all outputs. All nodes monitor traffic.
10 Base. T & Shared Hub PC Twisted Pair Cabling PC Hub PC PC Logical Bus & Physical Star Shared hub (OSI Level 1) copies input bits to all outputs. All nodes monitor traffic.
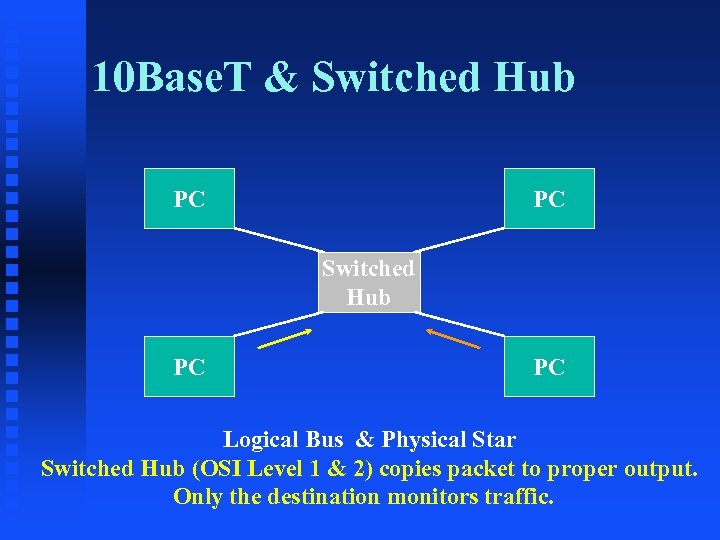 10 Base. T & Switched Hub PC PC Logical Bus & Physical Star Switched Hub (OSI Level 1 & 2) copies packet to proper output. Only the destination monitors traffic.
10 Base. T & Switched Hub PC PC Logical Bus & Physical Star Switched Hub (OSI Level 1 & 2) copies packet to proper output. Only the destination monitors traffic.
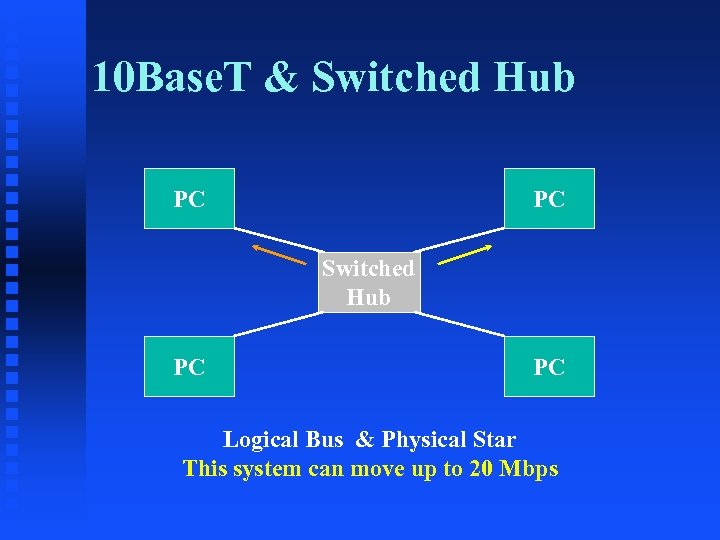 10 Base. T & Switched Hub PC PC Logical Bus & Physical Star This system can move up to 20 Mbps
10 Base. T & Switched Hub PC PC Logical Bus & Physical Star This system can move up to 20 Mbps
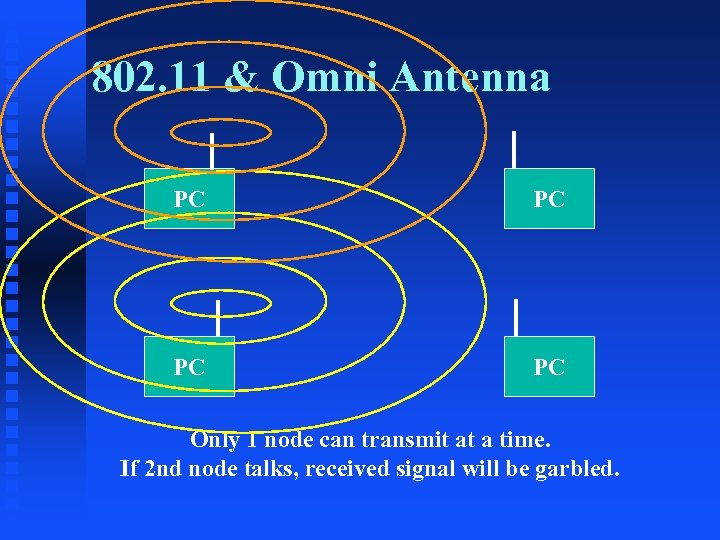 802. 11 & Omni Antenna PC PC Only 1 node can transmit at a time. If 2 nd node talks, received signal will be garbled.
802. 11 & Omni Antenna PC PC Only 1 node can transmit at a time. If 2 nd node talks, received signal will be garbled.
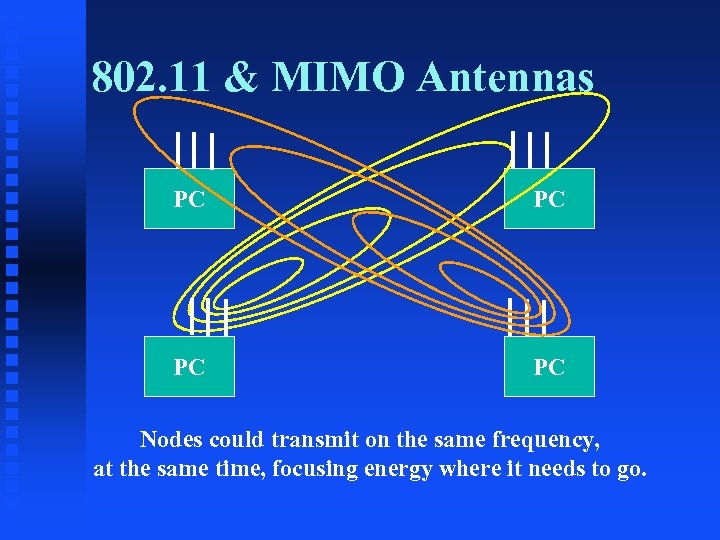 802. 11 & MIMO Antennas PC PC Nodes could transmit on the same frequency, at the same time, focusing energy where it needs to go.
802. 11 & MIMO Antennas PC PC Nodes could transmit on the same frequency, at the same time, focusing energy where it needs to go.
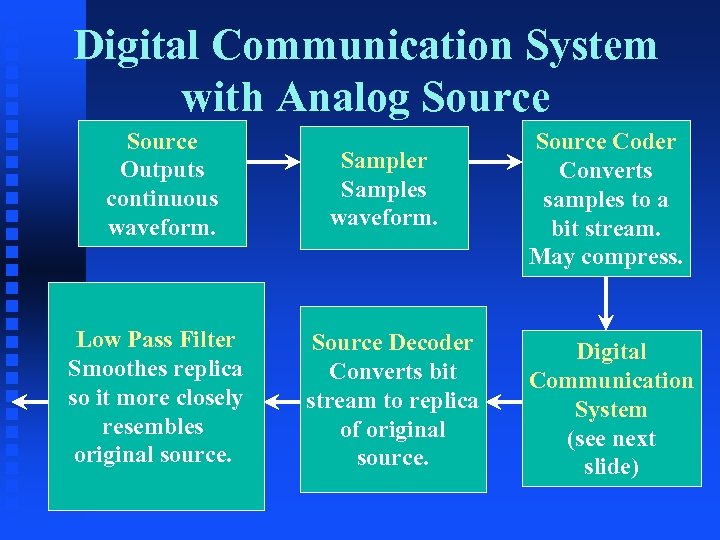 Digital Communication System with Analog Source Outputs continuous waveform. Low Pass Filter Smoothes replica so it more closely resembles original source. Sampler Samples waveform. Source Decoder Converts bit stream to replica of original source. Source Coder Converts samples to a bit stream. May compress. Digital Communication System (see next slide)
Digital Communication System with Analog Source Outputs continuous waveform. Low Pass Filter Smoothes replica so it more closely resembles original source. Sampler Samples waveform. Source Decoder Converts bit stream to replica of original source. Source Coder Converts samples to a bit stream. May compress. Digital Communication System (see next slide)
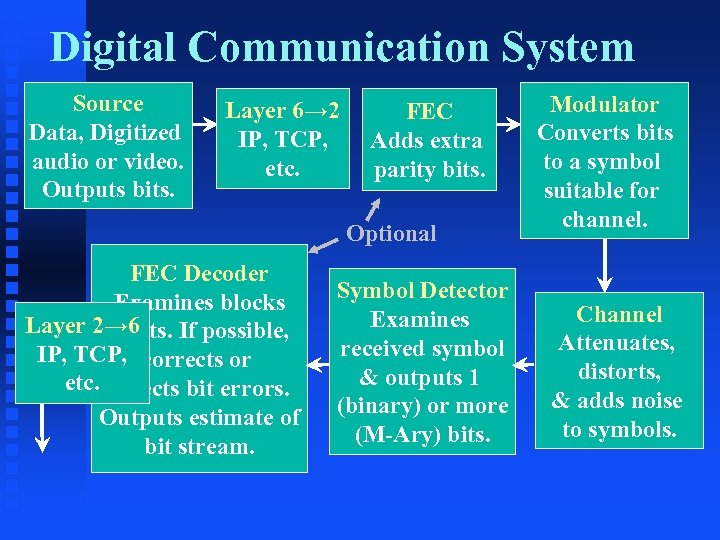 Digital Communication System Source Data, Digitized audio or video. Outputs bits. Layer 6→ 2 IP, TCP, etc. FEC Adds extra parity bits. Optional FEC Decoder Examines blocks Layer 2→ 6 of bits. If possible, IP, TCP, corrects or etc. detects bit errors. Outputs estimate of bit stream. Symbol Detector Examines received symbol & outputs 1 (binary) or more (M-Ary) bits. Modulator Converts bits to a symbol suitable for channel. Channel Attenuates, distorts, & adds noise to symbols.
Digital Communication System Source Data, Digitized audio or video. Outputs bits. Layer 6→ 2 IP, TCP, etc. FEC Adds extra parity bits. Optional FEC Decoder Examines blocks Layer 2→ 6 of bits. If possible, IP, TCP, corrects or etc. detects bit errors. Outputs estimate of bit stream. Symbol Detector Examines received symbol & outputs 1 (binary) or more (M-Ary) bits. Modulator Converts bits to a symbol suitable for channel. Channel Attenuates, distorts, & adds noise to symbols.



