1027bdc757b1ddf5f7c5aad86b8a5069.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 ECE 765 Microcomputer Structures 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 1
ECE 765 Microcomputer Structures 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 1
 Outline o o Course Overview Historical Perspective 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 2
Outline o o Course Overview Historical Perspective 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 2
 Course Overview o Syllabus Review n o Special issues this quarter n o Let’s Go Over the Syllabus From Syllabus Grading Policy n 9/22/2010 From Syllabus Lecture 1 - Introduction 3
Course Overview o Syllabus Review n o Special issues this quarter n o Let’s Go Over the Syllabus From Syllabus Grading Policy n 9/22/2010 From Syllabus Lecture 1 - Introduction 3
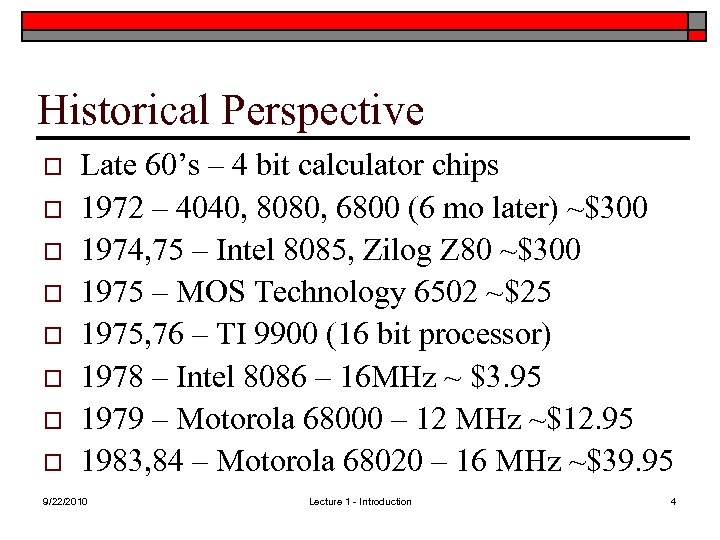 Historical Perspective o o o o Late 60’s – 4 bit calculator chips 1972 – 4040, 8080, 6800 (6 mo later) ~$300 1974, 75 – Intel 8085, Zilog Z 80 ~$300 1975 – MOS Technology 6502 ~$25 1975, 76 – TI 9900 (16 bit processor) 1978 – Intel 8086 – 16 MHz ~ $3. 95 1979 – Motorola 68000 – 12 MHz ~$12. 95 1983, 84 – Motorola 68020 – 16 MHz ~$39. 95 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 4
Historical Perspective o o o o Late 60’s – 4 bit calculator chips 1972 – 4040, 8080, 6800 (6 mo later) ~$300 1974, 75 – Intel 8085, Zilog Z 80 ~$300 1975 – MOS Technology 6502 ~$25 1975, 76 – TI 9900 (16 bit processor) 1978 – Intel 8086 – 16 MHz ~ $3. 95 1979 – Motorola 68000 – 12 MHz ~$12. 95 1983, 84 – Motorola 68020 – 16 MHz ~$39. 95 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 4
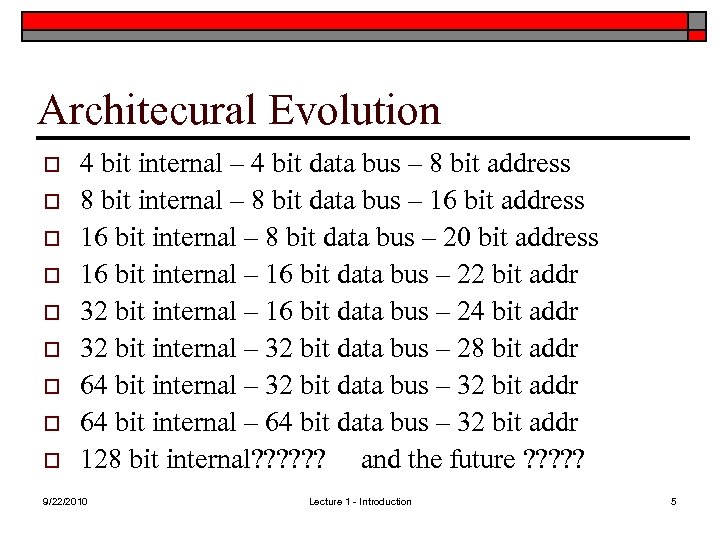 Architecural Evolution o o o o o 4 bit internal – 4 bit data bus – 8 bit address 8 bit internal – 8 bit data bus – 16 bit address 16 bit internal – 8 bit data bus – 20 bit address 16 bit internal – 16 bit data bus – 22 bit addr 32 bit internal – 16 bit data bus – 24 bit addr 32 bit internal – 32 bit data bus – 28 bit addr 64 bit internal – 32 bit data bus – 32 bit addr 64 bit internal – 64 bit data bus – 32 bit addr 128 bit internal? ? ? and the future ? ? ? 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 5
Architecural Evolution o o o o o 4 bit internal – 4 bit data bus – 8 bit address 8 bit internal – 8 bit data bus – 16 bit address 16 bit internal – 8 bit data bus – 20 bit address 16 bit internal – 16 bit data bus – 22 bit addr 32 bit internal – 16 bit data bus – 24 bit addr 32 bit internal – 32 bit data bus – 28 bit addr 64 bit internal – 32 bit data bus – 32 bit addr 64 bit internal – 64 bit data bus – 32 bit addr 128 bit internal? ? ? and the future ? ? ? 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 5
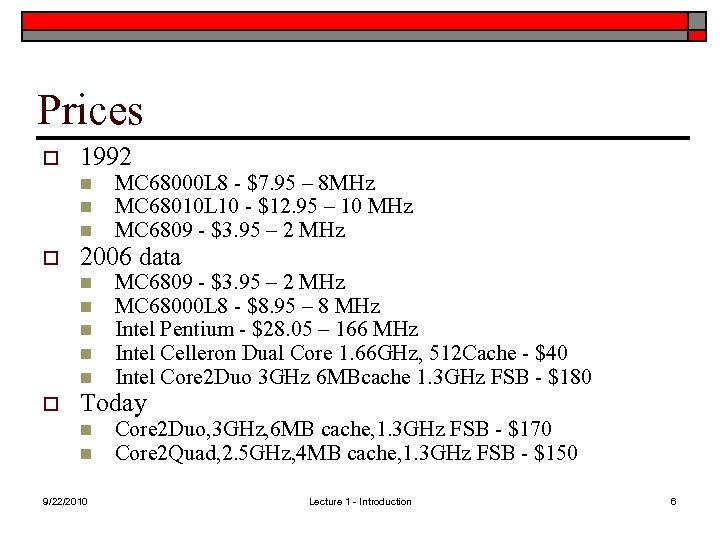 Prices o 1992 n n n o 2006 data n n n o MC 68000 L 8 - $7. 95 – 8 MHz MC 68010 L 10 - $12. 95 – 10 MHz MC 6809 - $3. 95 – 2 MHz MC 68000 L 8 - $8. 95 – 8 MHz Intel Pentium - $28. 05 – 166 MHz Intel Celleron Dual Core 1. 66 GHz, 512 Cache - $40 Intel Core 2 Duo 3 GHz 6 MBcache 1. 3 GHz FSB - $180 Today n n 9/22/2010 Core 2 Duo, 3 GHz, 6 MB cache, 1. 3 GHz FSB - $170 Core 2 Quad, 2. 5 GHz, 4 MB cache, 1. 3 GHz FSB - $150 Lecture 1 - Introduction 6
Prices o 1992 n n n o 2006 data n n n o MC 68000 L 8 - $7. 95 – 8 MHz MC 68010 L 10 - $12. 95 – 10 MHz MC 6809 - $3. 95 – 2 MHz MC 68000 L 8 - $8. 95 – 8 MHz Intel Pentium - $28. 05 – 166 MHz Intel Celleron Dual Core 1. 66 GHz, 512 Cache - $40 Intel Core 2 Duo 3 GHz 6 MBcache 1. 3 GHz FSB - $180 Today n n 9/22/2010 Core 2 Duo, 3 GHz, 6 MB cache, 1. 3 GHz FSB - $170 Core 2 Quad, 2. 5 GHz, 4 MB cache, 1. 3 GHz FSB - $150 Lecture 1 - Introduction 6
 And the price for memory o In the 1970 s n o A 16 MB memory card for a TMS 80 (max memory 64 MB) was $200. 00 Today n n n 9/22/2010 DDR 2 2 G Memory DIMM – 800 MHz - $30 DDR 3 2 G Memory DIMM– 1. 333 MHz - $50 8 G Byte MMC memory card - $20 to $30 Lecture 1 - Introduction 7
And the price for memory o In the 1970 s n o A 16 MB memory card for a TMS 80 (max memory 64 MB) was $200. 00 Today n n n 9/22/2010 DDR 2 2 G Memory DIMM – 800 MHz - $30 DDR 3 2 G Memory DIMM– 1. 333 MHz - $50 8 G Byte MMC memory card - $20 to $30 Lecture 1 - Introduction 7
 Applications and use o o o o o General Purpose PCs and Workstations Scientific/Engineering Computer Automated Manufacturing Equip Robotic Control Systems Medical Equipment Business Computers and point of sale systems Desktop Publishing Data Communications and Networking Automotive uses Microwave ovens, Stoves, dishwashers, refrigerators, 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 8
Applications and use o o o o o General Purpose PCs and Workstations Scientific/Engineering Computer Automated Manufacturing Equip Robotic Control Systems Medical Equipment Business Computers and point of sale systems Desktop Publishing Data Communications and Networking Automotive uses Microwave ovens, Stoves, dishwashers, refrigerators, 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 8
 Course Goals o o Understand more advanced micro-computer architecture concepts through the study of a representative architecture. The 68000 family is one of several microprocessor families available. It has a relatively simple instruction set and representative interfacing capabilities. It also supports multitasking. 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 9
Course Goals o o Understand more advanced micro-computer architecture concepts through the study of a representative architecture. The 68000 family is one of several microprocessor families available. It has a relatively simple instruction set and representative interfacing capabilities. It also supports multitasking. 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 9
 Some basic definitions o Microprocessor – a single CPU on a single IC chip. Contains both control and RALU n Does not have on chip memory, timers, or I/O ports o Microcomputer – u. Processor with memory, I/O, timing, control, interfaces, powersupply o RALU – Register/Arithmetic Logic Unit 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 10
Some basic definitions o Microprocessor – a single CPU on a single IC chip. Contains both control and RALU n Does not have on chip memory, timers, or I/O ports o Microcomputer – u. Processor with memory, I/O, timing, control, interfaces, powersupply o RALU – Register/Arithmetic Logic Unit 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 10
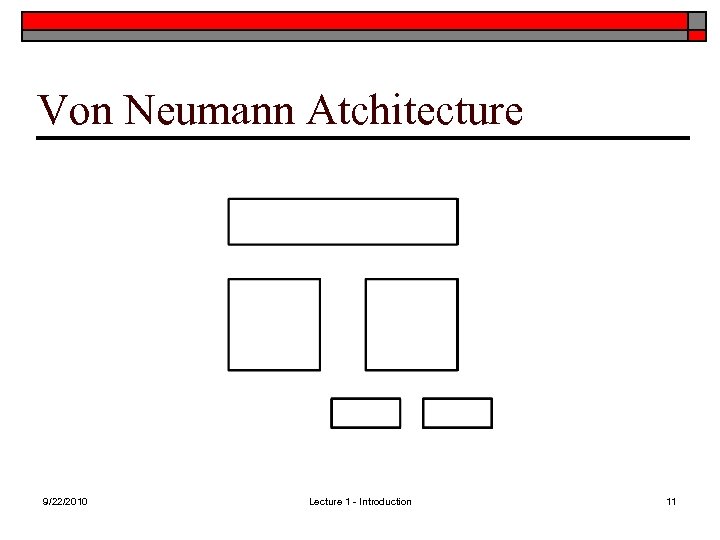 Von Neumann Atchitecture 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 11
Von Neumann Atchitecture 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 11
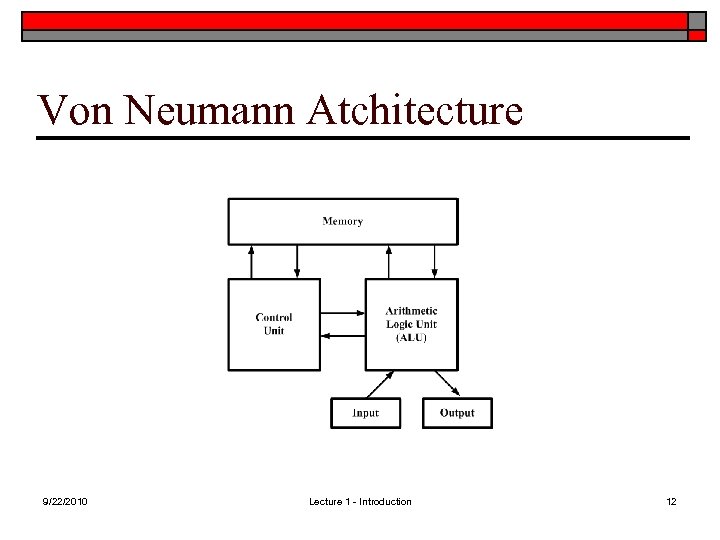 Von Neumann Atchitecture 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 12
Von Neumann Atchitecture 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 12
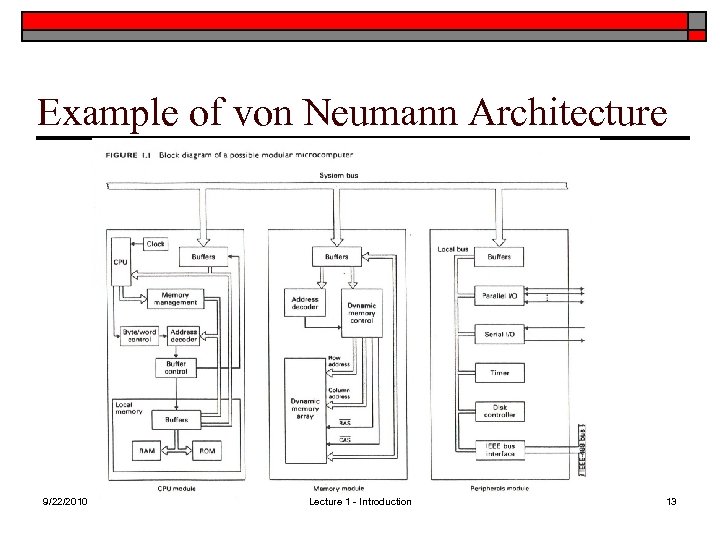 Example of von Neumann Architecture 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 13
Example of von Neumann Architecture 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 13
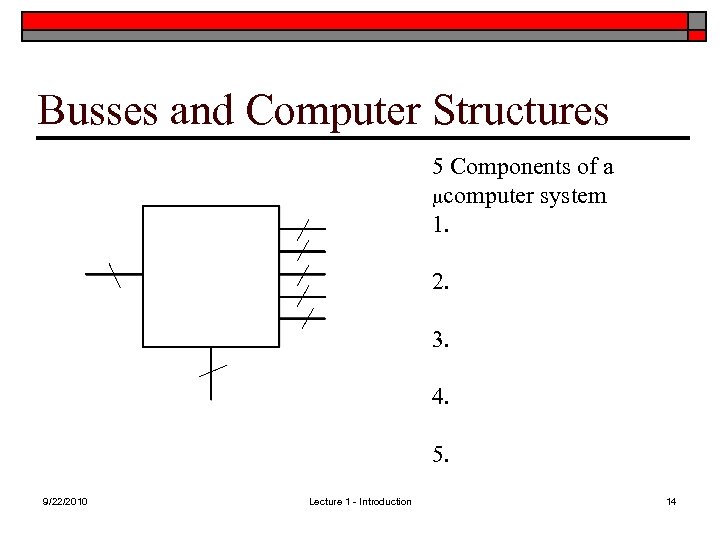 Busses and Computer Structures 5 Components of a mcomputer system 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 14
Busses and Computer Structures 5 Components of a mcomputer system 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 14
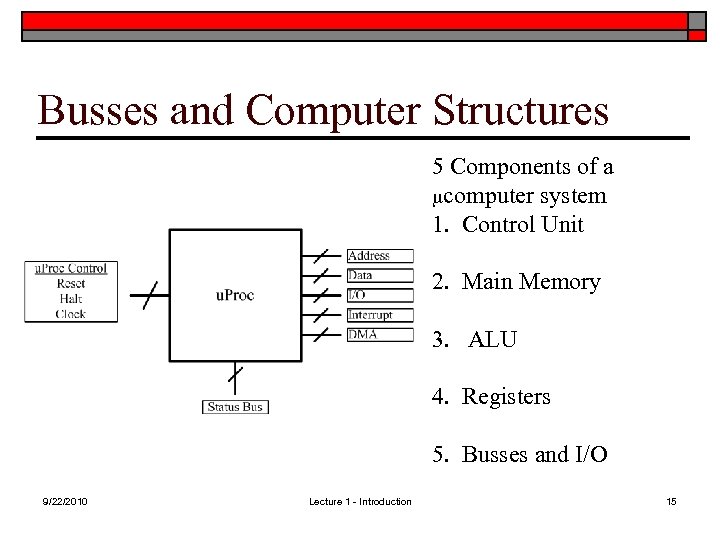 Busses and Computer Structures 5 Components of a mcomputer system 1. Control Unit 2. Main Memory 3. ALU 4. Registers 5. Busses and I/O 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 15
Busses and Computer Structures 5 Components of a mcomputer system 1. Control Unit 2. Main Memory 3. ALU 4. Registers 5. Busses and I/O 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 15
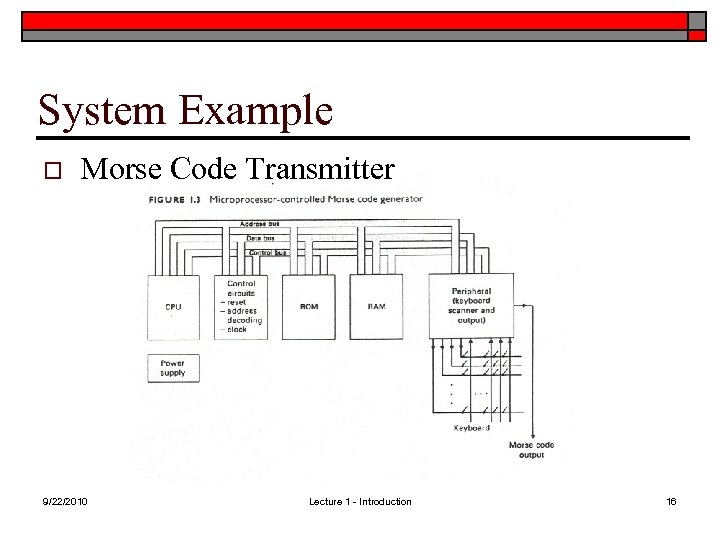 System Example o Morse Code Transmitter 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 16
System Example o Morse Code Transmitter 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 16
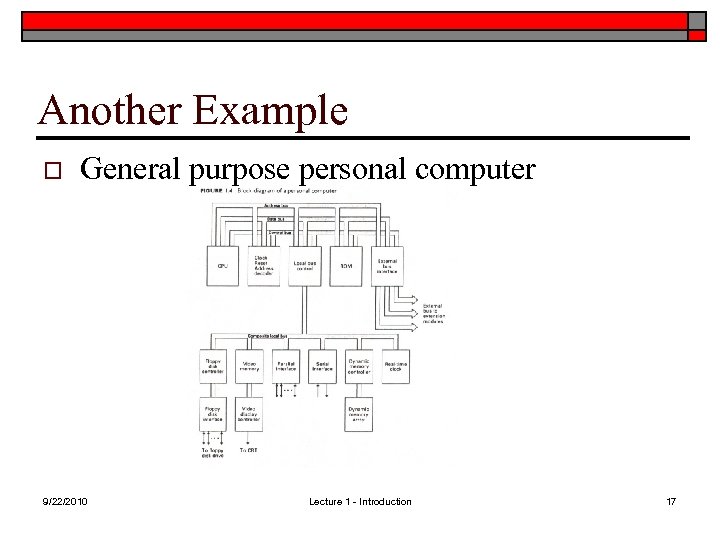 Another Example o General purpose personal computer 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 17
Another Example o General purpose personal computer 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 17
 Assignment o Read chapter 1 and chapter 2, sections 2. 1 -2. 3 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 18
Assignment o Read chapter 1 and chapter 2, sections 2. 1 -2. 3 9/22/2010 Lecture 1 - Introduction 18


