0444bc7760d219dba8360f81bebfd563.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

ECE 480 Fall 2011 Team 5 Jordan Bennett Kyle Schultz Min Jae Lee Kevin Yeh

Introduction • Project Objectives: • Design a sensor module, compatible to TI’s wireless sensing system (µMAVRK), for the immersion of concrete • Specifically: • Relay temperature and humidity metrics from the sensor module, wirelessly, to a centralized unit (MAVRK) for further analysis • Implement code for communication from the µMAVRK to the MAVRK

Modular And Versatile Reference Kit. • Purpose – Used for rapid prototyping – Modules to encapsulate functionality • Advantage LESS Component Level Interaction FOR MORE System Level Design
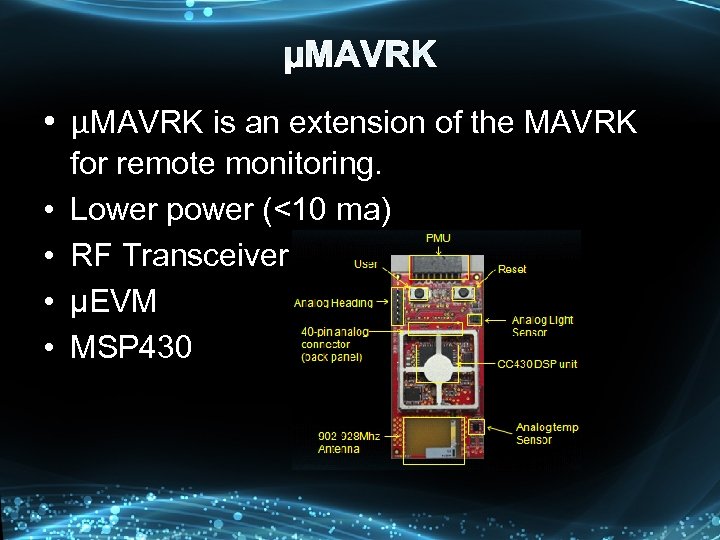
• µMAVRK is an extension of the MAVRK • • for remote monitoring. Lower power (<10 ma) RF Transceiver µEVM MSP 430

• • • Dc to Dc boost converter Temperature Circuit Amplification Circuit What if TI had modules for all three? Program firmware to handle interaction between all three.

Design Requirements - kyle • Functionality • Sense Temperature/Humidity of • Concrete • Communicate with u. MAVRK • Send Signal to MAVRK • calibrate data received • Accuracy • +-1 degree tolerance on temperature • 1~3% RH Humidity error • multiple data point for comparison • Compatibility • Small enough to be embedded in concrete • Power source lasting at least 3 weeks • • end product that can be shown on public demonstration
Design Approach - kyle

Design Approach House of Quality
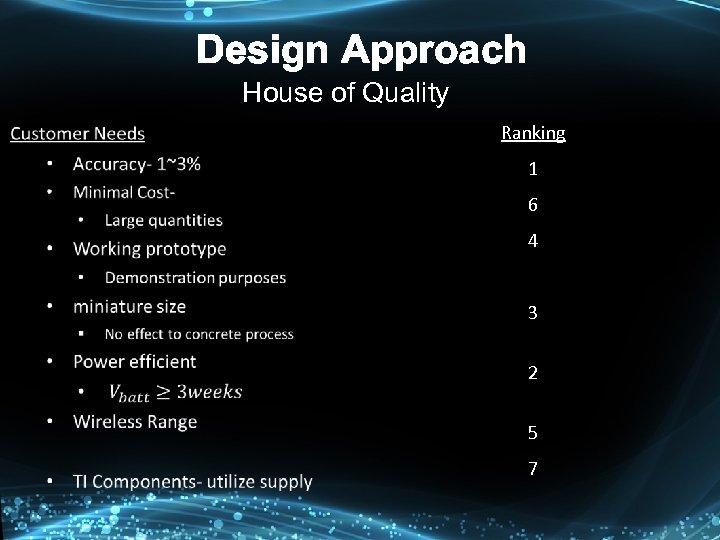
Design Approach House of Quality Ranking 1 6 4 3 2 5 7
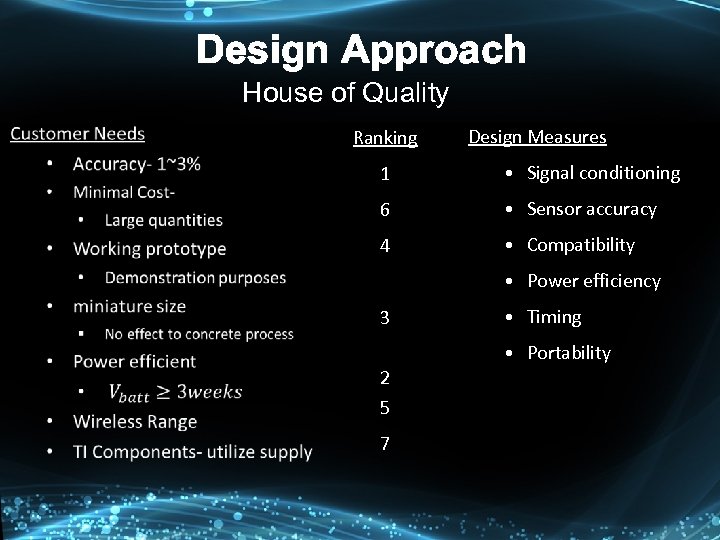
Design Approach House of Quality Ranking Design Measures 1 • Signal conditioning 6 • Sensor accuracy 4 • Compatibility • Power efficiency 3 • Timing • Portability 2 5 7

Proposed Solution • Temperature Sensor - Wheatstone Bridge Circuitry - Voltage Amplification - ADC optimization • Humidity Sensor - Built-in signal conditioning Circuitry - Voltage Amplification - ADC optimization
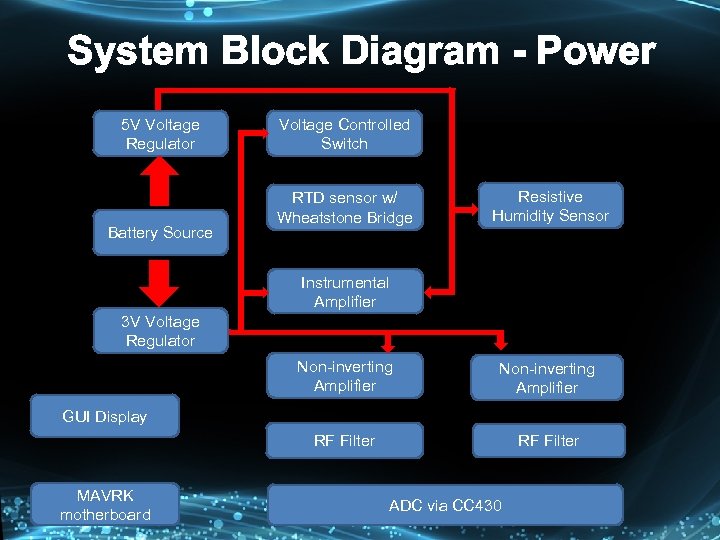
System Block Diagram - Power 5 V Voltage Regulator Battery Source Voltage Controlled Switch RTD sensor w/ Wheatstone Bridge Resistive Humidity Sensor Instrumental Amplifier 3 V Voltage Regulator Non-inverting Amplifier RF Filter GUI Display MAVRK motherboard ADC via CC 430
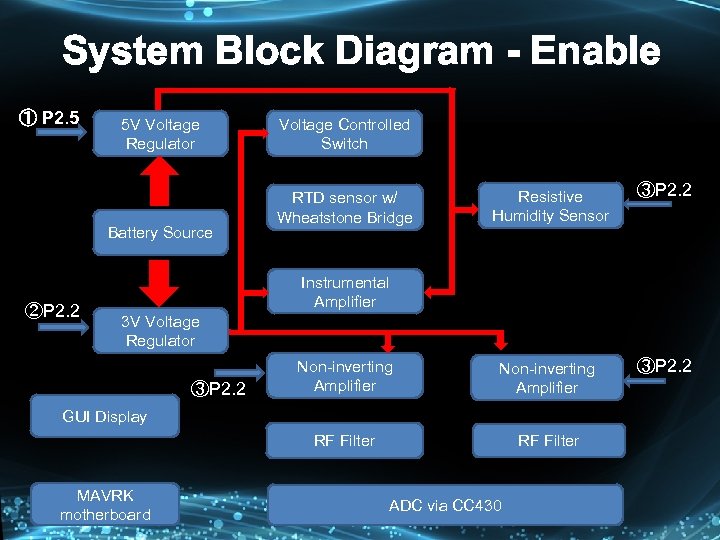
System Block Diagram - Enable ① P 2. 5 5 V Voltage Regulator Voltage Controlled Switch ②P 2. 2 ③P 2. 2 Non-inverting Amplifier ③P 2. 2 RF Filter Battery Source Resistive Humidity Sensor RF Filter RTD sensor w/ Wheatstone Bridge Instrumental Amplifier 3 V Voltage Regulator ③P 2. 2 GUI Display MAVRK motherboard ADC via CC 430
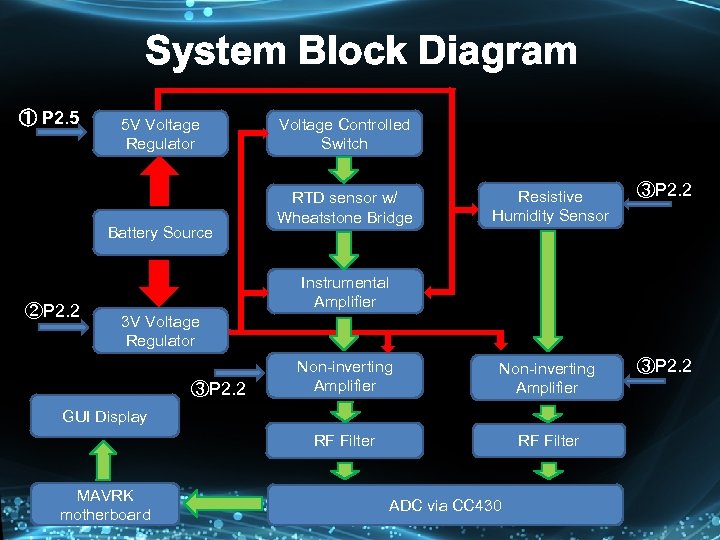
System Block Diagram ① P 2. 5 5 V Voltage Regulator Voltage Controlled Switch ②P 2. 2 ③P 2. 2 Non-inverting Amplifier ③P 2. 2 RF Filter Battery Source Resistive Humidity Sensor RF Filter RTD sensor w/ Wheatstone Bridge Instrumental Amplifier 3 V Voltage Regulator ③P 2. 2 GUI Display MAVRK motherboard ADC via CC 430
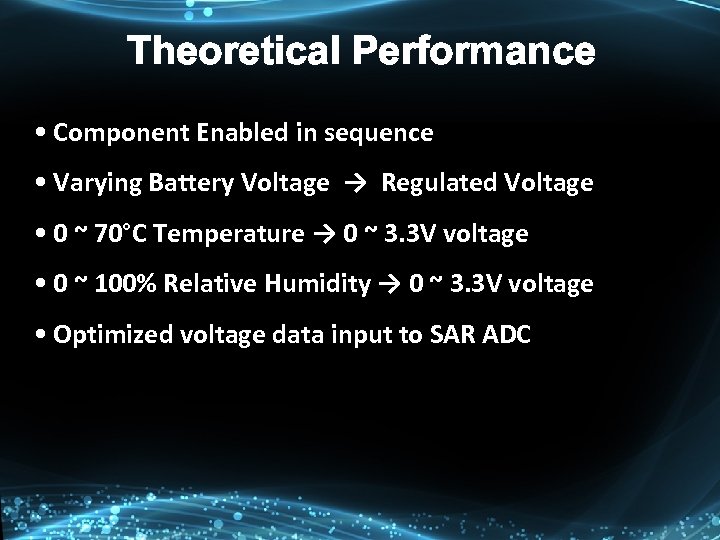
Theoretical Performance • Component Enabled in sequence • Varying Battery Voltage → Regulated Voltage • 0 ~ 70°C Temperature → 0 ~ 3. 3 V voltage • 0 ~ 100% Relative Humidity → 0 ~ 3. 3 V voltage • Optimized voltage data input to SAR ADC
Testing & Simulation • TINA Simulation Wheatstone Bridge Instrumentation Amplifier Buffer Amplifier • Proto board Testing Temperature Sensor Humidity Sensor 5 V Voltage Regulator
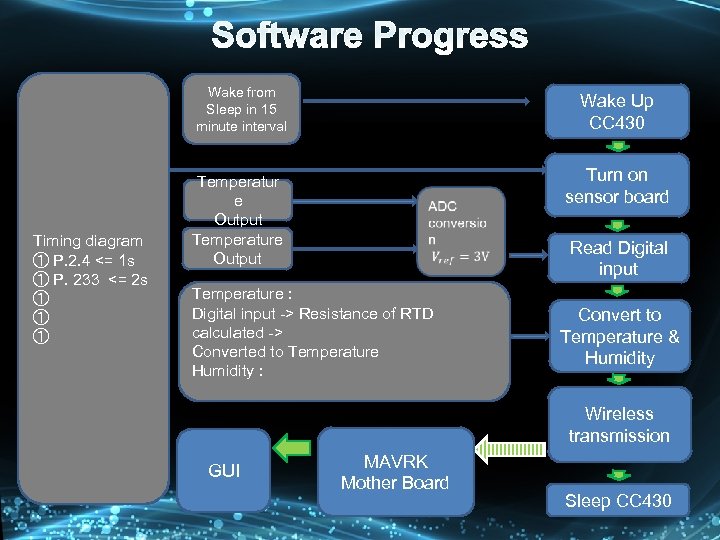
Wake from Sleep in 15 minute interval Wake Up CC 430 3. 3 V output from GPIO Timing diagram ① P. 2. 4 <= 1 s ① P. 233 <= 2 s ① ① ① Temperatur e Output Temperature Output P 2. 4 : 0 ~ 3 V P 2. 2 : 0 ~ 3 V Temperature : Digital input -> Resistance of RTD calculated -> Converted to Temperature Humidity : Turn on sensor board Read Digital input Convert to Temperature & Humidity Wireless transmission GUI MAVRK Mother Board Sleep CC 430

Results • Hardware • Temperature reading with ± 2°C error • Ambient Humidity Reading with 5% RH error • PCB fabrication & population • Software • GUI improvement(Database storage, Graph display

Result • Voltage VS RTD resistance Graph • ambient humidity test result
Future implementation • Hardware • Enclosure Design • Sensing humidity from within enclosure. • Software • Database on PC for packet store. • Accept inputs from several sensor module • Implementation of averaging algorithm • completion of curing Indication. • Algorithm to compensate for any differences
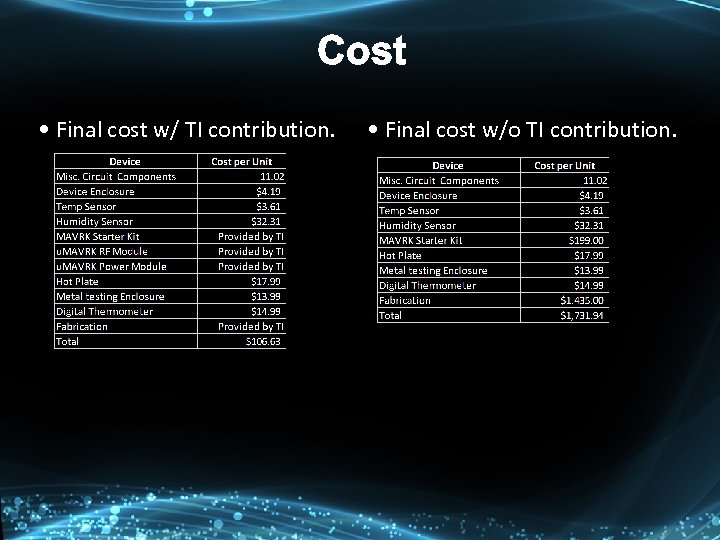
Cost • Final cost w/ TI contribution. • Final cost w/o TI contribution.

Demonstration • Video of analog circuitry test goes here

Questions
0444bc7760d219dba8360f81bebfd563.ppt