1391c36484130b24218cf047b71b8342.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 ECE 2560 Introduction to Microcontrolllers Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The Ohio State University ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 1
ECE 2560 Introduction to Microcontrolllers Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The Ohio State University ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 1
 Today l The Course l Syllabus l Intro ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 2
Today l The Course l Syllabus l Intro ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 2
 Course Philosophy and Objective l Familiarize students the architecture, programming and use of a microcontroller. l Learn to use an actual microcontroller l Learn modern design technologies l Learn what assembler language is ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 3
Course Philosophy and Objective l Familiarize students the architecture, programming and use of a microcontroller. l Learn to use an actual microcontroller l Learn modern design technologies l Learn what assembler language is ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 3
 Embedded Systems l Chapter 1 of text l Microcontrollers are an efficient mean by which an embedded system can be implemented. l Microcontroller include (on board) Processor l Memory l Clock l I/O support and usually A-to-D conversion l ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 4
Embedded Systems l Chapter 1 of text l Microcontrollers are an efficient mean by which an embedded system can be implemented. l Microcontroller include (on board) Processor l Memory l Clock l I/O support and usually A-to-D conversion l ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 4
 An Embedded System? l What is an embedded system? l l l Features of an embedded system l l l Not a personal computer!!! A cooking timer The burner and oven controller in your stove The ABS controller in you car The landing gear control system on a plane Very focused function Usually part of a larger system Most systems today rely on digital control ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 5
An Embedded System? l What is an embedded system? l l l Features of an embedded system l l l Not a personal computer!!! A cooking timer The burner and oven controller in your stove The ABS controller in you car The landing gear control system on a plane Very focused function Usually part of a larger system Most systems today rely on digital control ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 5
 Examples l There about 100 embedded processors in each PC, not just the main processor. l A car today has about 100 embedded processors. (ABS, sound system, engine control, emissions control, …) l Electric tootbrush l Washers and Dryers ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 6
Examples l There about 100 embedded processors in each PC, not just the main processor. l A car today has about 100 embedded processors. (ABS, sound system, engine control, emissions control, …) l Electric tootbrush l Washers and Dryers ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 6
 Examples l Washer/Dryer l Others? ? ? ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 7
Examples l Washer/Dryer l Others? ? ? ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 7
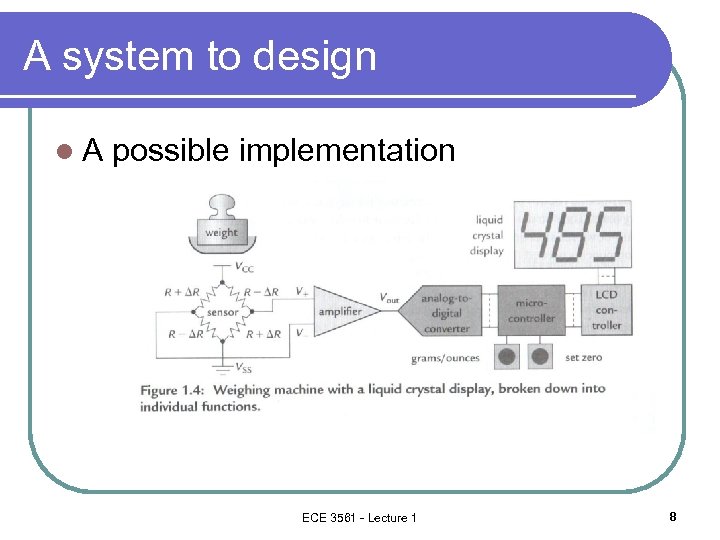 A system to design l. A possible implementation ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 8
A system to design l. A possible implementation ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 8
 Salter kitchen scale l An implementation ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 9
Salter kitchen scale l An implementation ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 9
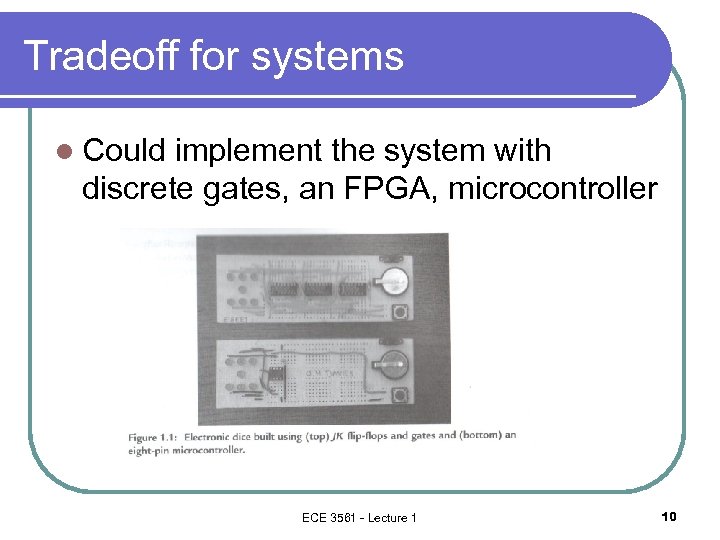 Tradeoff for systems l Could implement the system with discrete gates, an FPGA, microcontroller ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 10
Tradeoff for systems l Could implement the system with discrete gates, an FPGA, microcontroller ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 10
 Microcontrollers l History 101 l l Early device – Intel 4004 – 4 bit microprocessor – no onboard memory, timers, I/O support Over time l l On board memory, timers, A-to-D, etc microcontroller Microcontroller has little if any OS support. Many have development systems. l Microcontroller “OS” is typically a RTOS. l ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 11
Microcontrollers l History 101 l l Early device – Intel 4004 – 4 bit microprocessor – no onboard memory, timers, I/O support Over time l l On board memory, timers, A-to-D, etc microcontroller Microcontroller has little if any OS support. Many have development systems. l Microcontroller “OS” is typically a RTOS. l ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 11
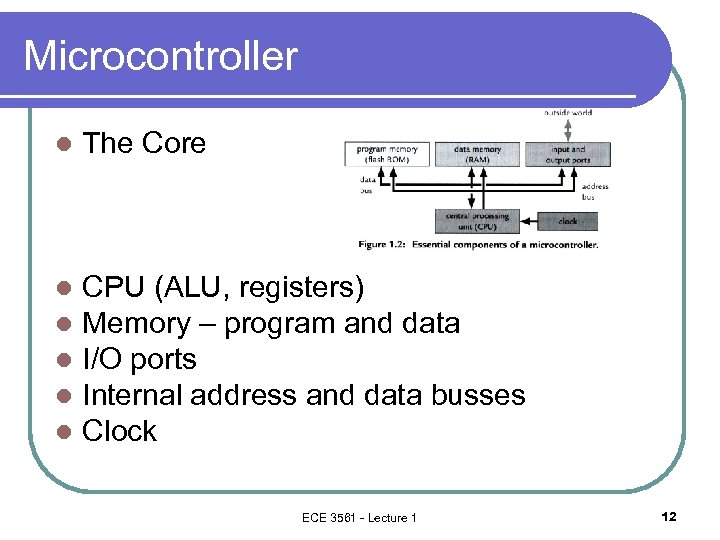 Microcontroller l The Core l l l CPU (ALU, registers) Memory – program and data I/O ports Internal address and data busses Clock ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 12
Microcontroller l The Core l l l CPU (ALU, registers) Memory – program and data I/O ports Internal address and data busses Clock ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 12
 Added to core l Watchdog timer l Communication interfaces l Nonvolatile memory for data l A-to-D converter l D-to-A converter l Real-time clock l Monitor, background debugger, embedded emulator ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 13
Added to core l Watchdog timer l Communication interfaces l Nonvolatile memory for data l A-to-D converter l D-to-A converter l Real-time clock l Monitor, background debugger, embedded emulator ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 13
 Memory l Contains the binary information and typically addressed as bytes (words) l The information stored there can be data or instructions l In many microcontrollers instruction memory is stored in one-time or flash programmable memory. l Addresses and contents typically expressed in hexadecimal ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 14
Memory l Contains the binary information and typically addressed as bytes (words) l The information stored there can be data or instructions l In many microcontrollers instruction memory is stored in one-time or flash programmable memory. l Addresses and contents typically expressed in hexadecimal ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 14
 Volatile and nonvolatile memory l Volatile – content is lost when power is removed – goes to 0’s l Nonvolatile – content is retained Masked ROM – manufactured l PROM – Programmable Read Only Memory l One time (OTP) l Programmable (UV erasable) EPROM l Flash – EEPROM – uses a higher voltage to write contents l ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 15
Volatile and nonvolatile memory l Volatile – content is lost when power is removed – goes to 0’s l Nonvolatile – content is retained Masked ROM – manufactured l PROM – Programmable Read Only Memory l One time (OTP) l Programmable (UV erasable) EPROM l Flash – EEPROM – uses a higher voltage to write contents l ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 15
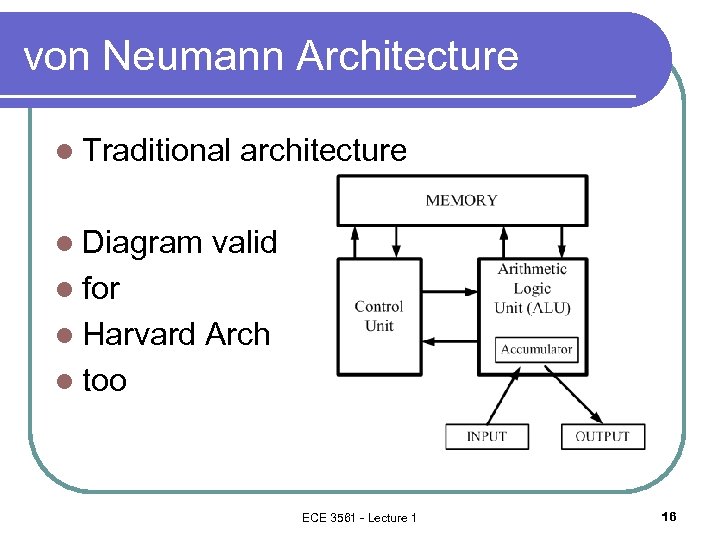 von Neumann Architecture l Traditional l Diagram architecture valid l for l Harvard Arch l too ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 16
von Neumann Architecture l Traditional l Diagram architecture valid l for l Harvard Arch l too ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 16
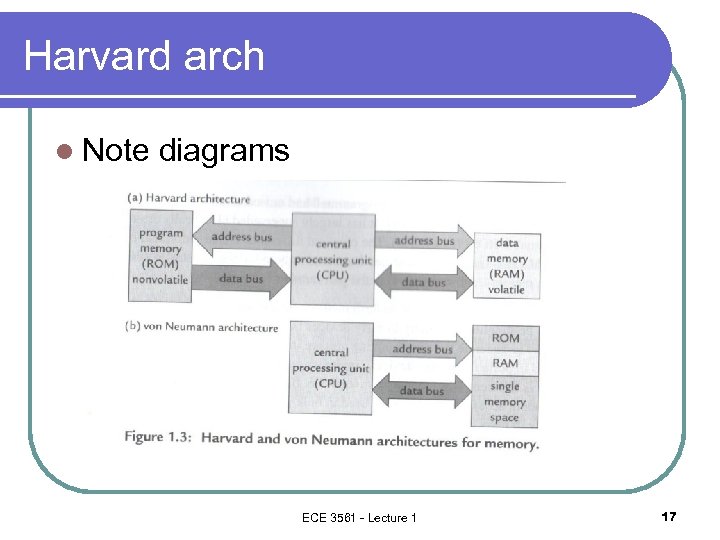 Harvard arch l Note diagrams ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 17
Harvard arch l Note diagrams ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 17
 The MSP 430 Introduced in the late 1990 s l 16 -bit von Neumann architecture – both address and data l Low power l RISC type architecture l No pages or banks in memory making it simple to use. l Can be programmed in C l Has 16 registers in CPU l ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 18
The MSP 430 Introduced in the late 1990 s l 16 -bit von Neumann architecture – both address and data l Low power l RISC type architecture l No pages or banks in memory making it simple to use. l Can be programmed in C l Has 16 registers in CPU l ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 18
 Assignment l Read Chapter 1 and 2 l Assignments will be due 2 classes after assigned to the drop box on Carmen. No paper submissions – all are electronic. l Go to ti. com and get code composer for the MSP 430 – when downloaded and installed, run the 10 minutes tutorial. l Also, buy the TI launchpad – $9. 99 ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 19
Assignment l Read Chapter 1 and 2 l Assignments will be due 2 classes after assigned to the drop box on Carmen. No paper submissions – all are electronic. l Go to ti. com and get code composer for the MSP 430 – when downloaded and installed, run the 10 minutes tutorial. l Also, buy the TI launchpad – $9. 99 ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 19
 Code composer startup l The startup Screen on Windows ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 20
Code composer startup l The startup Screen on Windows ECE 3561 - Lecture 1 20


