ECDIS KMA Part 1.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 55
 ECDIS Electronic Chart Display and Information System KMA Deck Officers Year 1 2012 – 2013 Part 1
ECDIS Electronic Chart Display and Information System KMA Deck Officers Year 1 2012 – 2013 Part 1
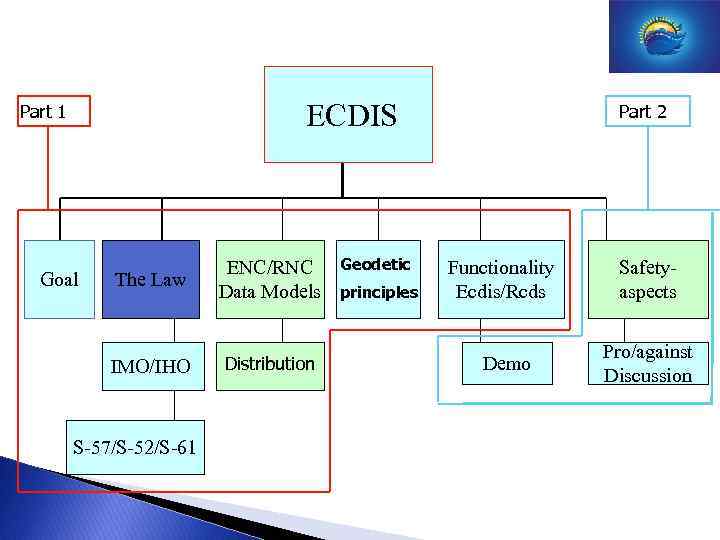
 ECDIS Part 1 Intro and Goal The Law ENC/RNC Data Models IMO/IHO Distribution S-57/S-52/S-61 Geodetic principles Part 2 Functionality Ecdis/Rcds Demo Safetyaspects Pro/against Discussion
ECDIS Part 1 Intro and Goal The Law ENC/RNC Data Models IMO/IHO Distribution S-57/S-52/S-61 Geodetic principles Part 2 Functionality Ecdis/Rcds Demo Safetyaspects Pro/against Discussion
 What is ECDIS? ELECTRONIC CHART DISPLAY AND INFORMATION SYSTEM
What is ECDIS? ELECTRONIC CHART DISPLAY AND INFORMATION SYSTEM
 Definition and purpose of a nav. chart: Def: A chart is an abstract reproduction of the physical characteristics of the earth surface on a flat paper map. Purpose: The purpose of a chart is to give the navigator information of his surroundings which are necessary for safe and efficient navigation.
Definition and purpose of a nav. chart: Def: A chart is an abstract reproduction of the physical characteristics of the earth surface on a flat paper map. Purpose: The purpose of a chart is to give the navigator information of his surroundings which are necessary for safe and efficient navigation.
 Ecdis: More than a Chart Navigation Information System
Ecdis: More than a Chart Navigation Information System
 ECDIS Part 1 The Law IMO/IHO Goal ENC/RNC Data Models Distribution S-57/S-52/S-61 Geodetic principles Part 2 Functionality Ecdis/Rcds Demo Safetyaspects Pro/against Discussion
ECDIS Part 1 The Law IMO/IHO Goal ENC/RNC Data Models Distribution S-57/S-52/S-61 Geodetic principles Part 2 Functionality Ecdis/Rcds Demo Safetyaspects Pro/against Discussion
 Law IMO New SOLAS Chapter V knows 4 rules that refer (in)direct to ECDIS. 1. Regulation 2. 2 Definitions: what is a chart or publication? 2. Regulation 18 Approval, surveys and performance standards of navigational systems and equipment: which requirements the system must meet! 3. Regulation 19 Carriage requirements for shipborne nav. systems and equipment: who must carry a chart or publication ! 4. Regulation 27 Nautical charts and nautical publications: Adequate and up to date.
Law IMO New SOLAS Chapter V knows 4 rules that refer (in)direct to ECDIS. 1. Regulation 2. 2 Definitions: what is a chart or publication? 2. Regulation 18 Approval, surveys and performance standards of navigational systems and equipment: which requirements the system must meet! 3. Regulation 19 Carriage requirements for shipborne nav. systems and equipment: who must carry a chart or publication ! 4. Regulation 27 Nautical charts and nautical publications: Adequate and up to date.
 Law, IMO SOLAS Charter V Important: SOLAS requires that Nautical Charts and Publications: 1. Are issued by official governmental bodies. 2. nautical Charts and Publications can, instead of paper, also be a relevant database.
Law, IMO SOLAS Charter V Important: SOLAS requires that Nautical Charts and Publications: 1. Are issued by official governmental bodies. 2. nautical Charts and Publications can, instead of paper, also be a relevant database.
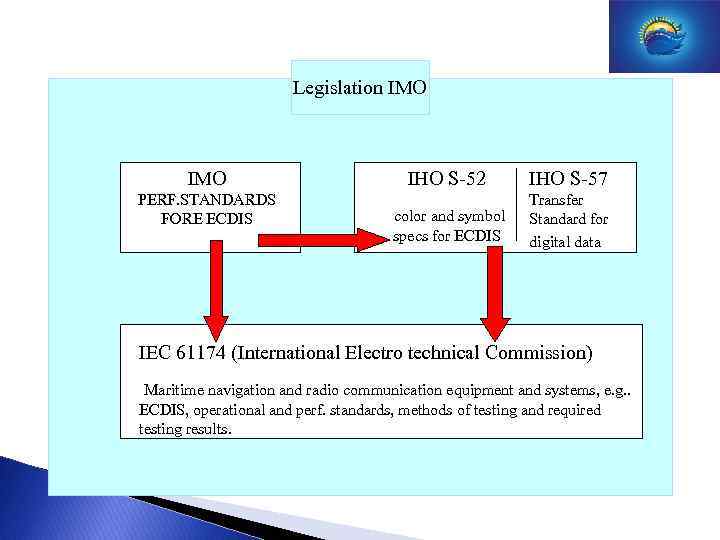 Legislation IMO PERF. STANDARDS FORE ECDIS IHO S-52 color and symbol specs for ECDIS IHO S-57 Transfer Standard for digital data IEC 61174 (International Electro technical Commission) Maritime navigation and radio communication equipment and systems, e. g. . ECDIS, operational and perf. standards, methods of testing and required testing results.
Legislation IMO PERF. STANDARDS FORE ECDIS IHO S-52 color and symbol specs for ECDIS IHO S-57 Transfer Standard for digital data IEC 61174 (International Electro technical Commission) Maritime navigation and radio communication equipment and systems, e. g. . ECDIS, operational and perf. standards, methods of testing and required testing results.
 ISM-CODE: Section 5, 6, 7, 8, … (development of procedures and checklists) STCW : IMO Model Course 1. 27
ISM-CODE: Section 5, 6, 7, 8, … (development of procedures and checklists) STCW : IMO Model Course 1. 27
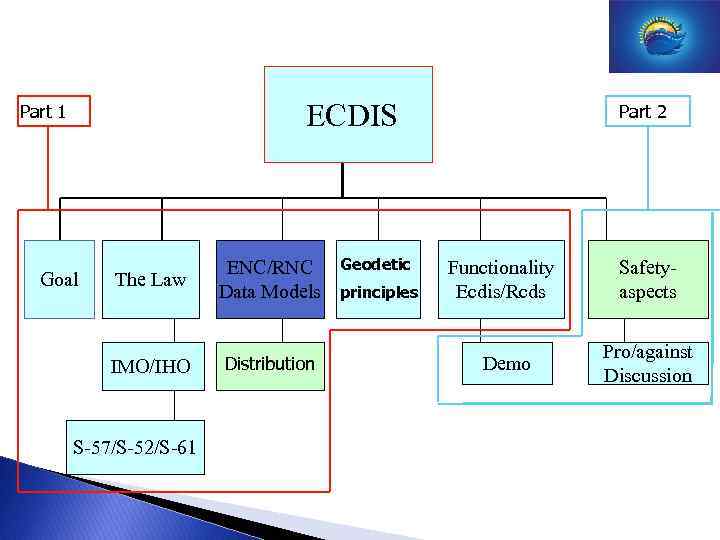 ECDIS Part 1 The Law IMO/IHO Goal ENC/RNC Data Models Distribution S-57/S-52/S-61 Geodetic principles Part 2 Functionality Ecdis/Rcds Demo Safetyaspects Pro/against Discussion
ECDIS Part 1 The Law IMO/IHO Goal ENC/RNC Data Models Distribution S-57/S-52/S-61 Geodetic principles Part 2 Functionality Ecdis/Rcds Demo Safetyaspects Pro/against Discussion
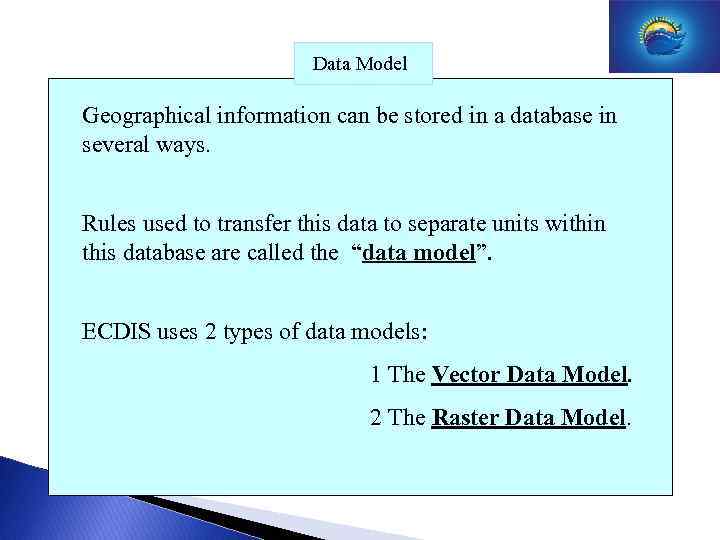 Data Model Geographical information can be stored in a database in several ways. Rules used to transfer this data to separate units within this database are called the “data model”. ECDIS uses 2 types of data models: 1 The Vector Data Model. 2 The Raster Data Model.
Data Model Geographical information can be stored in a database in several ways. Rules used to transfer this data to separate units within this database are called the “data model”. ECDIS uses 2 types of data models: 1 The Vector Data Model. 2 The Raster Data Model.
 Data Model Vector Data Model: Smallest element is a point. By connecting 2 points one creates a line or vector. By connecting different lines we create areas or figures. Useful points (wrecks, depth figures etc), lines (pipelines , depth contours etc) or areas (anchor areas , TSS, etc) are stored as objects in a data base. Every object is marked with attributes (this is extra info about that point, line or area of interest. Beside this every point has a position coordinate.
Data Model Vector Data Model: Smallest element is a point. By connecting 2 points one creates a line or vector. By connecting different lines we create areas or figures. Useful points (wrecks, depth figures etc), lines (pipelines , depth contours etc) or areas (anchor areas , TSS, etc) are stored as objects in a data base. Every object is marked with attributes (this is extra info about that point, line or area of interest. Beside this every point has a position coordinate.
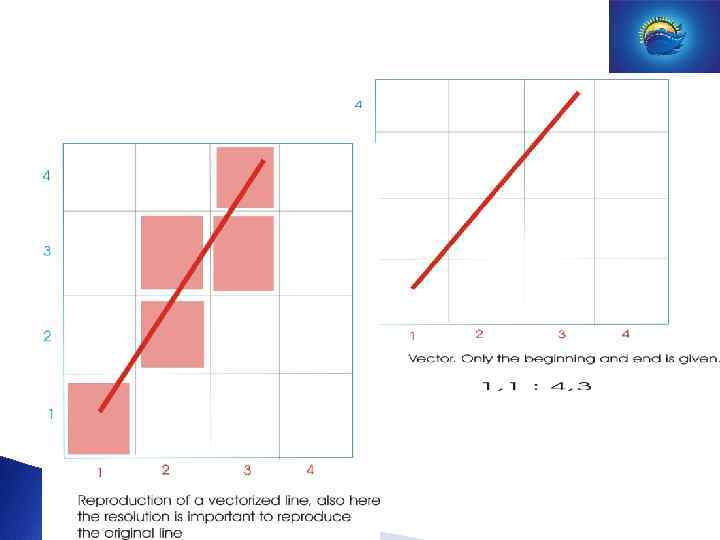
 Example ENC:
Example ENC:
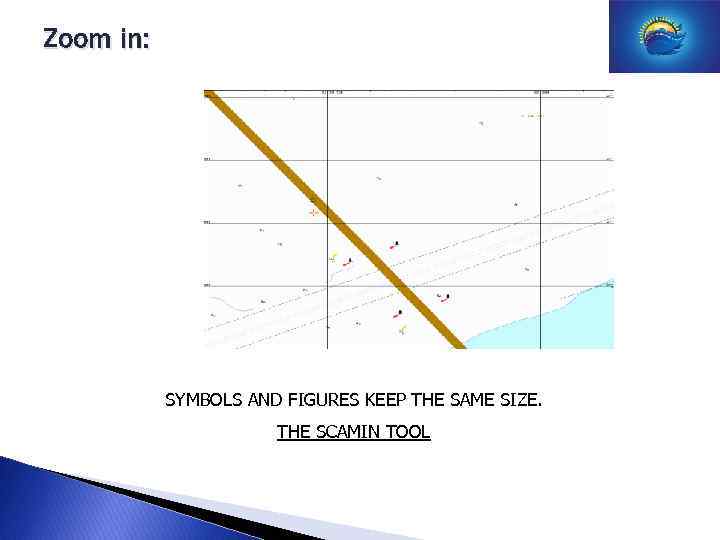 Zoom in: SYMBOLS AND FIGURES KEEP THE SAME SIZE. THE SCAMIN TOOL
Zoom in: SYMBOLS AND FIGURES KEEP THE SAME SIZE. THE SCAMIN TOOL
 Data Modellen ENC Electronic Navigational Chart (Vector Data Model) S-57 : I. H. O. TRANSFER STANDARD FOR DIGITAL HYDROGRAFIC DATA. S-52 : SPECIFICATIONS FOR CHART CONTENT AND DISPLAY ASPECTS FOR ECDIS.
Data Modellen ENC Electronic Navigational Chart (Vector Data Model) S-57 : I. H. O. TRANSFER STANDARD FOR DIGITAL HYDROGRAFIC DATA. S-52 : SPECIFICATIONS FOR CHART CONTENT AND DISPLAY ASPECTS FOR ECDIS.
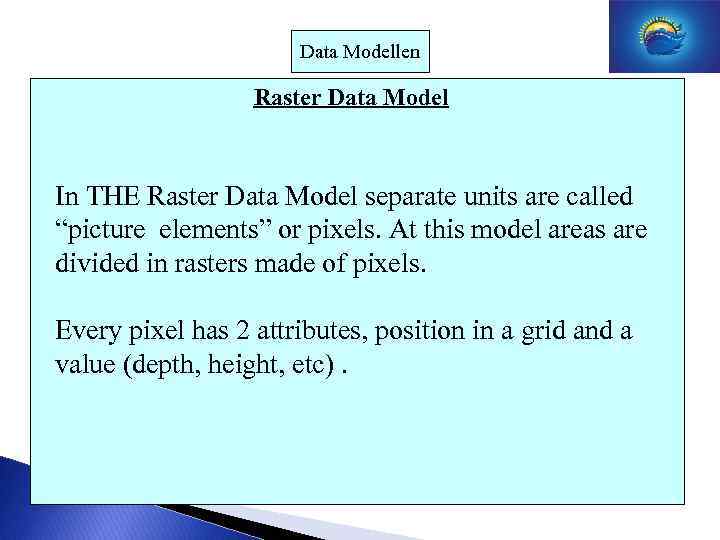 Data Modellen Raster Data Model In THE Raster Data Model separate units are called “picture elements” or pixels. At this model areas are divided in rasters made of pixels. Every pixel has 2 attributes, position in a grid and a value (depth, height, etc).
Data Modellen Raster Data Model In THE Raster Data Model separate units are called “picture elements” or pixels. At this model areas are divided in rasters made of pixels. Every pixel has 2 attributes, position in a grid and a value (depth, height, etc).
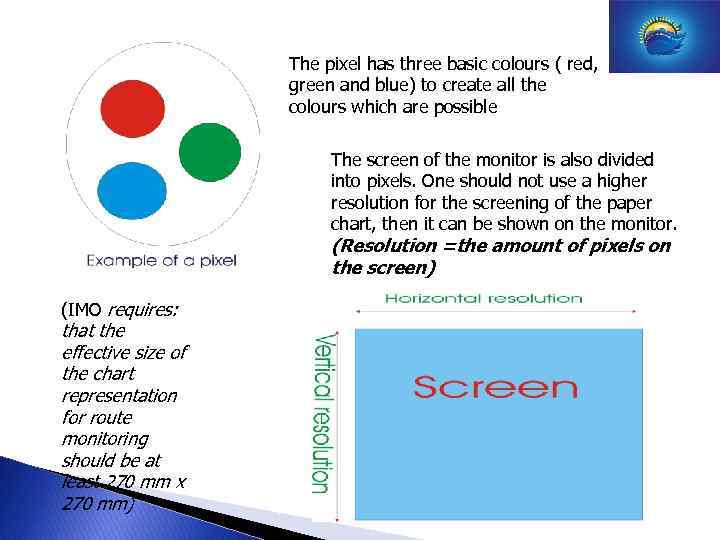 The pixel has three basic colours ( red, green and blue) to create all the colours which are possible The screen of the monitor is also divided into pixels. One should not use a higher resolution for the screening of the paper chart, then it can be shown on the monitor. (Resolution =the amount of pixels on the screen) (IMO requires: that the effective size of the chart representation for route monitoring should be at least 270 mm x 270 mm)
The pixel has three basic colours ( red, green and blue) to create all the colours which are possible The screen of the monitor is also divided into pixels. One should not use a higher resolution for the screening of the paper chart, then it can be shown on the monitor. (Resolution =the amount of pixels on the screen) (IMO requires: that the effective size of the chart representation for route monitoring should be at least 270 mm x 270 mm)
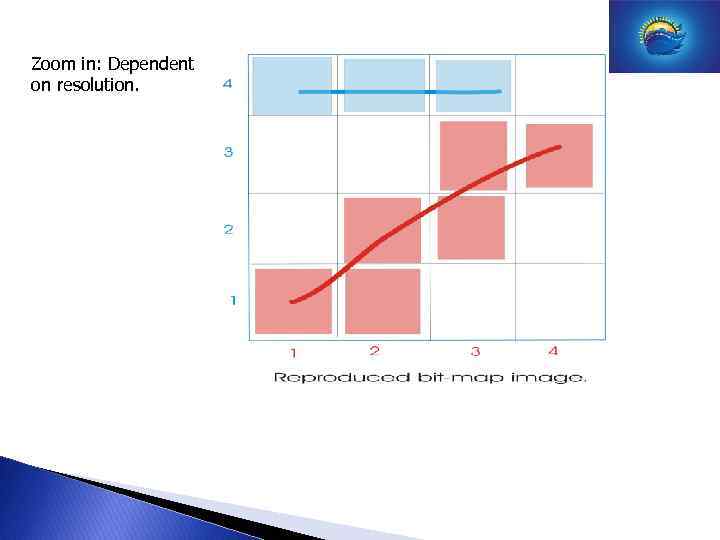 Zoom in: Dependent on resolution.
Zoom in: Dependent on resolution.
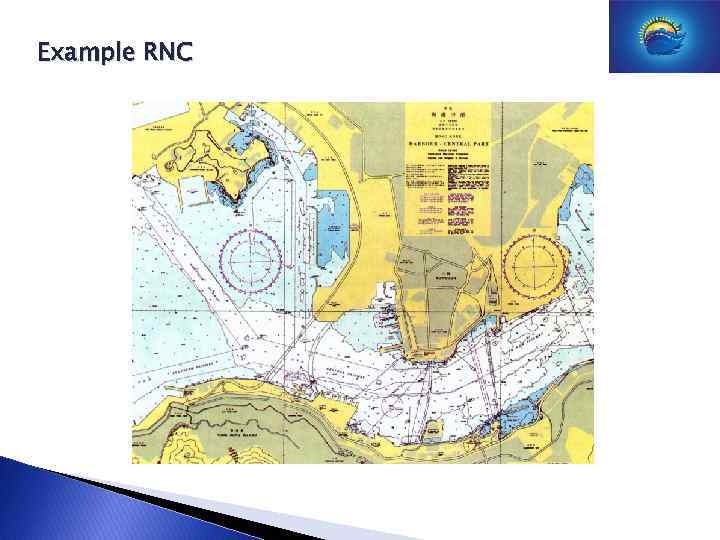 Example RNC
Example RNC
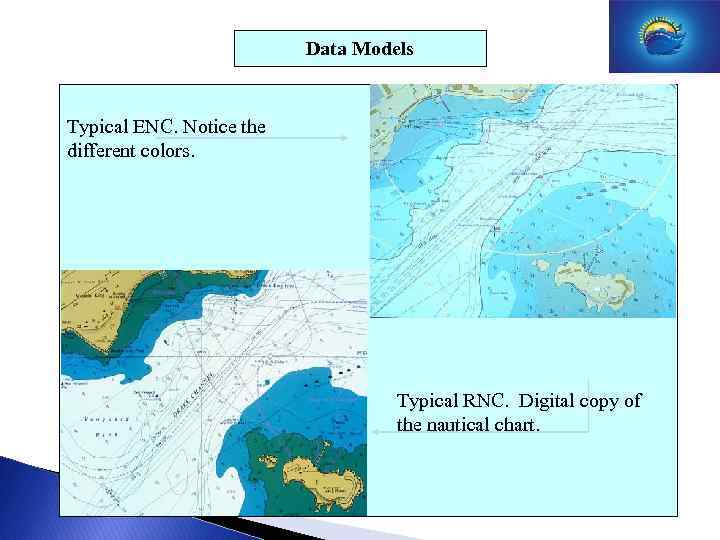 Data Models Typical ENC. Notice the different colors. Typical RNC. Digital copy of the nautical chart.
Data Models Typical ENC. Notice the different colors. Typical RNC. Digital copy of the nautical chart.
 Data Models RNC Raster Navigational Chart (Raster Data Model) S-61 : PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS FOR RASTER NAVIGATIONAL CHARTS.
Data Models RNC Raster Navigational Chart (Raster Data Model) S-61 : PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS FOR RASTER NAVIGATIONAL CHARTS.
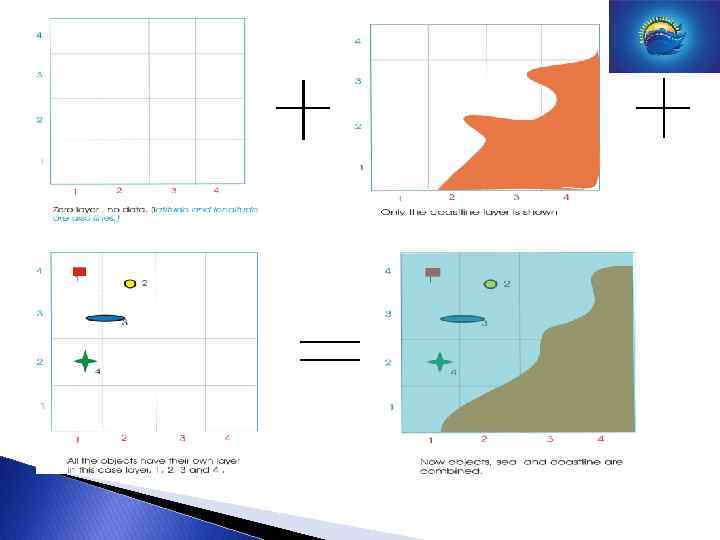
 Data Models Layers Raster as well as vector charts can be stored in different layers (some charts consist of 400 layers).
Data Models Layers Raster as well as vector charts can be stored in different layers (some charts consist of 400 layers).
 ENC/RNC & Distribution ECDIS VECTOR ENC RCDS RASTER RNC If one combines ECDIS and RCDS we talk about DUAL- FUEL use. This is done when there are no ENC ‘s available for the whole route.
ENC/RNC & Distribution ECDIS VECTOR ENC RCDS RASTER RNC If one combines ECDIS and RCDS we talk about DUAL- FUEL use. This is done when there are no ENC ‘s available for the whole route.
 ENC/RNC & Distribution Pro - ENC: • “ intelligent” use (info on request). • scale in dependant. • compact Data-type (uses little space). Pro RNC: • exact copy of the paper map (familiar for the mariner). • simple data structure. • cheap, easy to produce
ENC/RNC & Distribution Pro - ENC: • “ intelligent” use (info on request). • scale in dependant. • compact Data-type (uses little space). Pro RNC: • exact copy of the paper map (familiar for the mariner). • simple data structure. • cheap, easy to produce
 ENC/RNC & Distribution Against ENC: • Complex data-structure. • Expensive to produce and maintain. • Different colors and symbols. Against RNC: • limited info on request (often only 1 layer). • Limited ‘zooming’. • It is becoming ‘crowded’ more easily.
ENC/RNC & Distribution Against ENC: • Complex data-structure. • Expensive to produce and maintain. • Different colors and symbols. Against RNC: • limited info on request (often only 1 layer). • Limited ‘zooming’. • It is becoming ‘crowded’ more easily.
 ENC/RNC & Distribution WEND: Worldwide ENC Database concept. Within this concept HO’s maintain a so-called : ECDB: Electronic Chart Data Base. Contains chart info and other nautical hydrographical info in the S 57 vector data model. Fed and used by national HO’s. The hydrographic services deliver data from a certain area from the ECDB to the so called RENC: Regional ENC Coordinating Centre. The RENC is the Issuing Authority and is responsible for the issuing of official ENC’s and updates.
ENC/RNC & Distribution WEND: Worldwide ENC Database concept. Within this concept HO’s maintain a so-called : ECDB: Electronic Chart Data Base. Contains chart info and other nautical hydrographical info in the S 57 vector data model. Fed and used by national HO’s. The hydrographic services deliver data from a certain area from the ECDB to the so called RENC: Regional ENC Coordinating Centre. The RENC is the Issuing Authority and is responsible for the issuing of official ENC’s and updates.
 ENC/RNC & Distribution Official dealers by ENC ‘s from regional RENC. (Primar/ICENC/BA). Certified manufacturers issue ENC’s as well nowadays. Well known dealers in Holland are DATEMA and Observator. ENC’s and updates are delivered on CD-ROM. Updates and license codes CAN ALSO BE SEND VIA Inmarsat or E-mail.
ENC/RNC & Distribution Official dealers by ENC ‘s from regional RENC. (Primar/ICENC/BA). Certified manufacturers issue ENC’s as well nowadays. Well known dealers in Holland are DATEMA and Observator. ENC’s and updates are delivered on CD-ROM. Updates and license codes CAN ALSO BE SEND VIA Inmarsat or E-mail.
 ENC/RNC & Distribution ECS: ELECTRONIC CHART SYSTEM. Def. : All systems which do not comply with the ECDIS performance standard are called ECS. This can be soft- or hardware related (RCDS is also a form of ECS). Well known producers of ECS are C-MAP, Chart Works and Win. GPS/pro.
ENC/RNC & Distribution ECS: ELECTRONIC CHART SYSTEM. Def. : All systems which do not comply with the ECDIS performance standard are called ECS. This can be soft- or hardware related (RCDS is also a form of ECS). Well known producers of ECS are C-MAP, Chart Works and Win. GPS/pro.
 ECDIS Part 1 The Law IMO/IHO Goal ENC/RNC Data Models Distribution S-57/S-52/S-61 Geodetic principles Part 2 Functionality Ecdis/Rcds Demo Safetyaspects Pro/against Discussion
ECDIS Part 1 The Law IMO/IHO Goal ENC/RNC Data Models Distribution S-57/S-52/S-61 Geodetic principles Part 2 Functionality Ecdis/Rcds Demo Safetyaspects Pro/against Discussion
 Datum: Horizontal en Vertical
Datum: Horizontal en Vertical
 The sixties and space.
The sixties and space.
 standard globe: radius a=6366707. 019 m.
standard globe: radius a=6366707. 019 m.
 Why? 6366707. 019 m. The nautical mile 2 x x. R/(360 x 60) =1852 m R = 6366707. 019 m
Why? 6366707. 019 m. The nautical mile 2 x x. R/(360 x 60) =1852 m R = 6366707. 019 m
 Ellipsoid, revolutions figure ellipse a=radius equator, b=half earth axis c=half focal distance = (a 2 -b 2) e=c/a (eccentricity) f=(a-b)/a (flattening) = e 2/2+e 4/8
Ellipsoid, revolutions figure ellipse a=radius equator, b=half earth axis c=half focal distance = (a 2 -b 2) e=c/a (eccentricity) f=(a-b)/a (flattening) = e 2/2+e 4/8
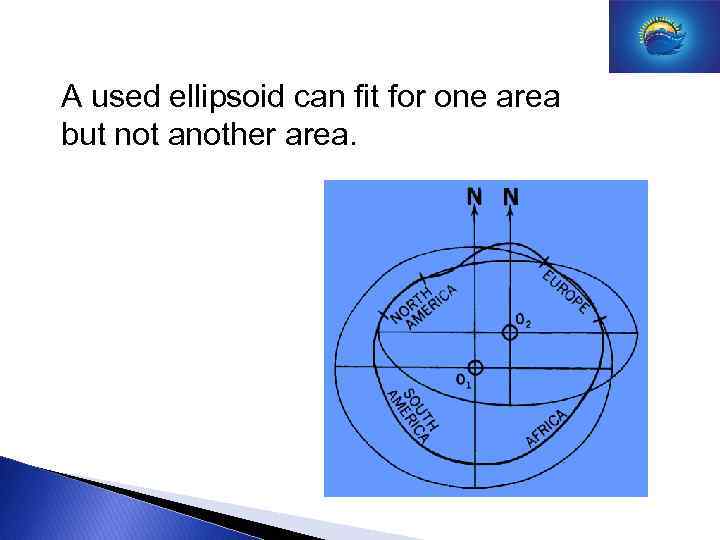 A used ellipsoid can fit for one area but not another area.
A used ellipsoid can fit for one area but not another area.
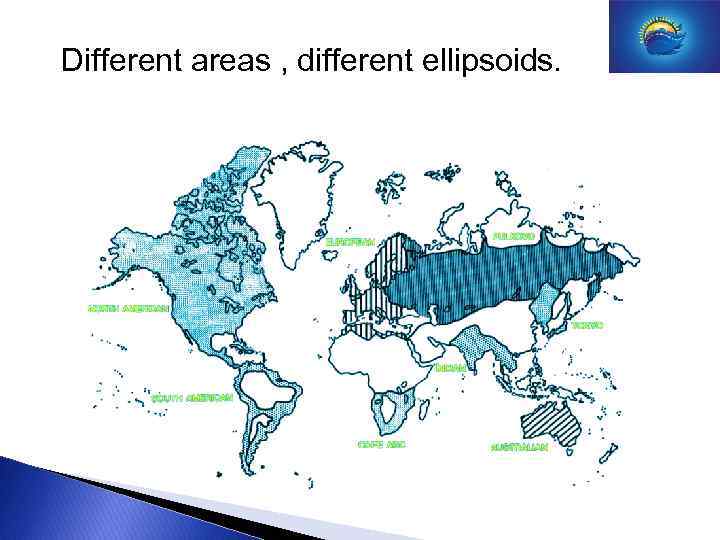 Different areas , different ellipsoids.
Different areas , different ellipsoids.
 This moment the most used ellipsoid for charting is WGS 84 GPS
This moment the most used ellipsoid for charting is WGS 84 GPS
 Geoid Close to earth surface, pending on gravity.
Geoid Close to earth surface, pending on gravity.
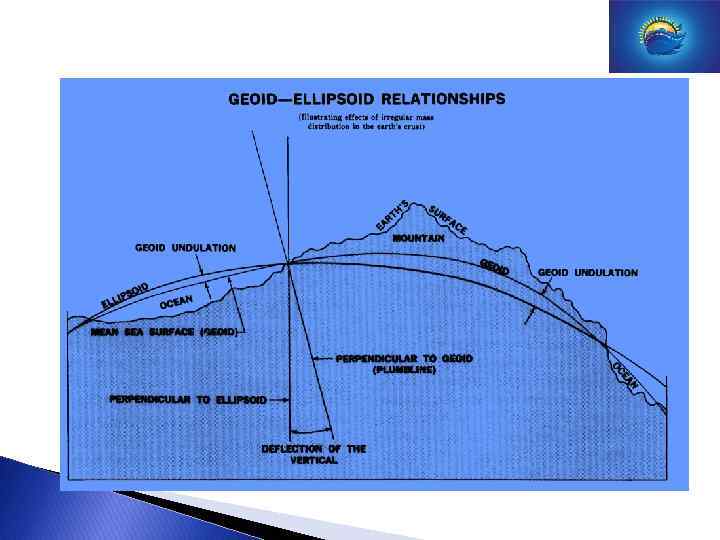
 The vertical distance between the geoid and the ellipsoid is called the geoid-height.
The vertical distance between the geoid and the ellipsoid is called the geoid-height.
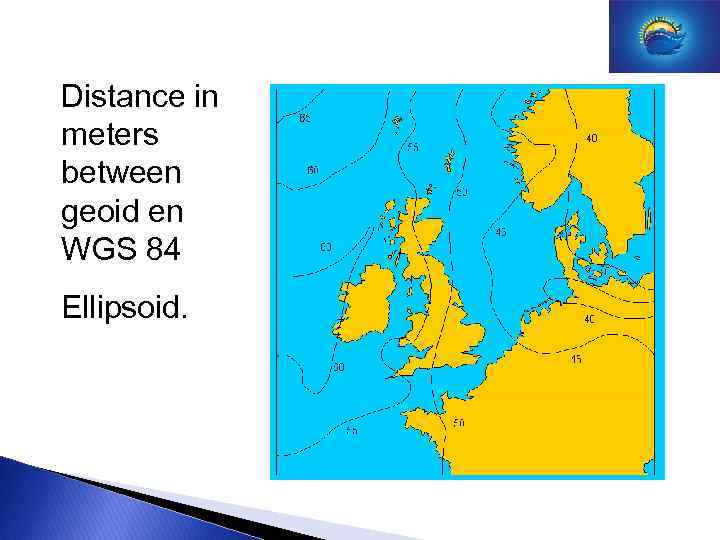 Distance in meters between geoid en WGS 84 Ellipsoid.
Distance in meters between geoid en WGS 84 Ellipsoid.
 Note: Minimum Water depth. Wind effect Air pressure. IHO vs. LAT Important: datum shift with every transition to a different reference plane.
Note: Minimum Water depth. Wind effect Air pressure. IHO vs. LAT Important: datum shift with every transition to a different reference plane.
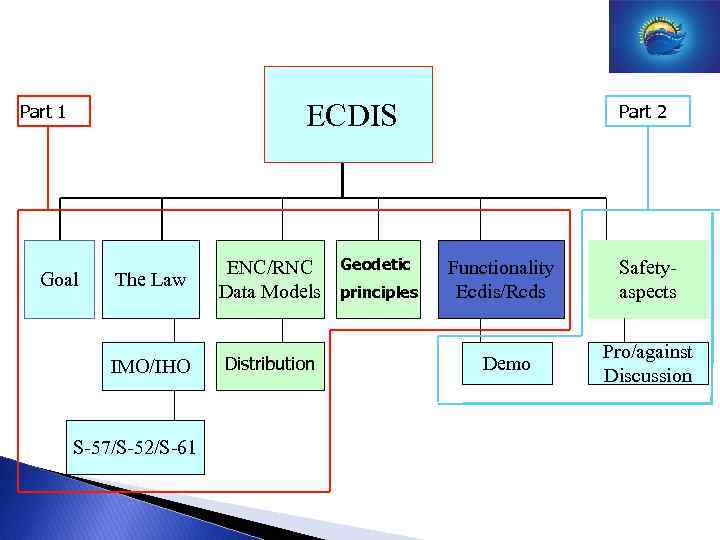 ECDIS Part 1 The Law IMO/IHO Goal ENC/RNC Data Models Distribution S-57/S-52/S-61 Geodetic principles Part 2 Functionality Ecdis/Rcds Demo Safetyaspects Pro/against Discussion
ECDIS Part 1 The Law IMO/IHO Goal ENC/RNC Data Models Distribution S-57/S-52/S-61 Geodetic principles Part 2 Functionality Ecdis/Rcds Demo Safetyaspects Pro/against Discussion
 Functionalities Normally the menu consists of 3 submenu’s : 1. CHART 2. PLANNING 3. MONITORING 1: Chart Works, Chart settings, Chart Color, Chart Handling 2: Planning: Route, Construction. 3: Monitoring: Voyage, Frame, Prediction. DEMO TRY ECDIS
Functionalities Normally the menu consists of 3 submenu’s : 1. CHART 2. PLANNING 3. MONITORING 1: Chart Works, Chart settings, Chart Color, Chart Handling 2: Planning: Route, Construction. 3: Monitoring: Voyage, Frame, Prediction. DEMO TRY ECDIS
 Functionalities Display Basis - Standard Display – All other info. • Display Basis : minimum info, always visible, insufficient for safe navigation. • Standard Display: determines which SENC data is displayed. Adjusted and manipulated by user. • All other info: shown on request.
Functionalities Display Basis - Standard Display – All other info. • Display Basis : minimum info, always visible, insufficient for safe navigation. • Standard Display: determines which SENC data is displayed. Adjusted and manipulated by user. • All other info: shown on request.
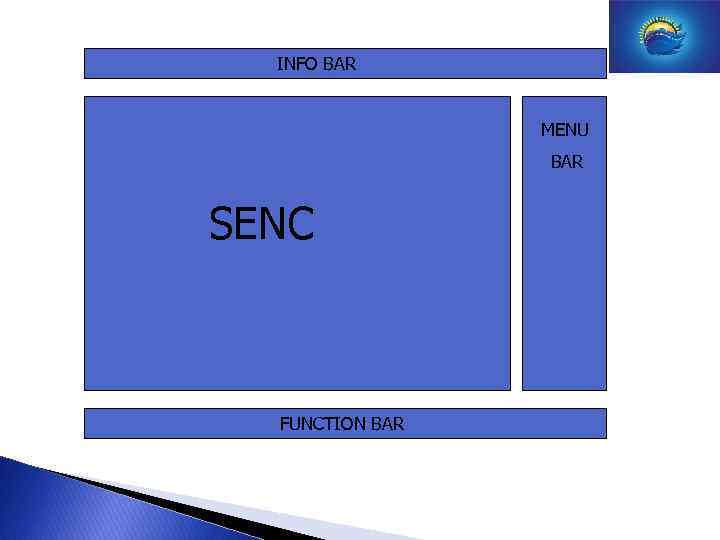 INFO BAR MENU BAR SENC FUNCTION BAR
INFO BAR MENU BAR SENC FUNCTION BAR
 What do we want to see? BASIC STANDARD OR EVERYTHING
What do we want to see? BASIC STANDARD OR EVERYTHING
 Chart content depending on use. The “SCAMIN-SCAMAX” tool.
Chart content depending on use. The “SCAMIN-SCAMAX” tool.
 Special functions (integration dynamic data) Sailing directions. Tide info (real time). Current info. Weather info. Ice info. Rules and regulations Advice. Conning-Docking
Special functions (integration dynamic data) Sailing directions. Tide info (real time). Current info. Weather info. Ice info. Rules and regulations Advice. Conning-Docking
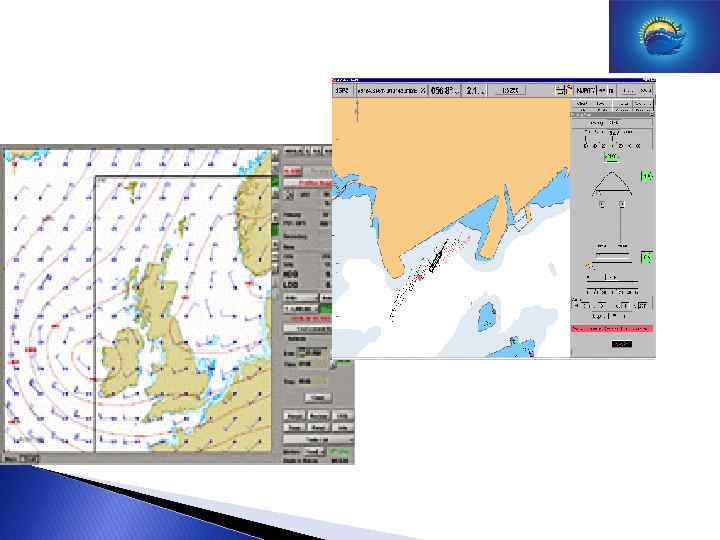
 Special Monitoring functions Radar overlay AIS Data Conning Display Docking Display
Special Monitoring functions Radar overlay AIS Data Conning Display Docking Display
 END Questions?
END Questions?


