8f17ad49920f323741514266830687b0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

eb. XML Overview Cory Casanave Data Access Technologies www. enterprise-component. com cory-c@enterprise-component. com (305) 234 -7077
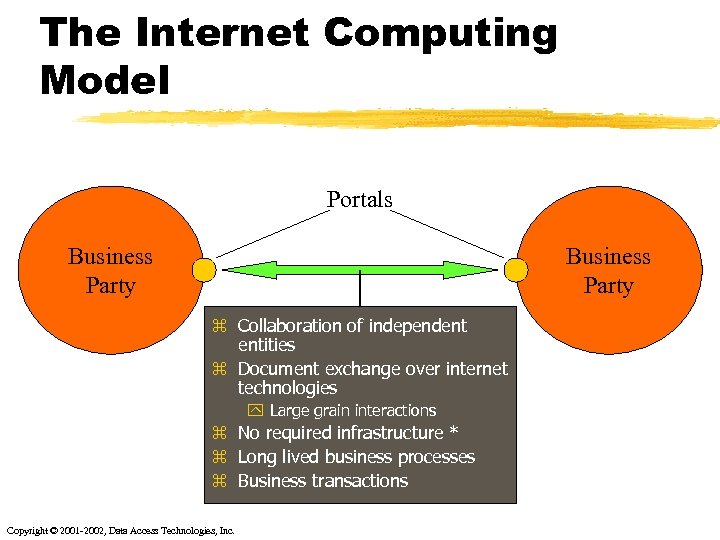
The Internet Computing Model Portals Business Party z Collaboration of independent entities z Document exchange over internet technologies y Large grain interactions z No required infrastructure * z Long lived business processes z Business transactions Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
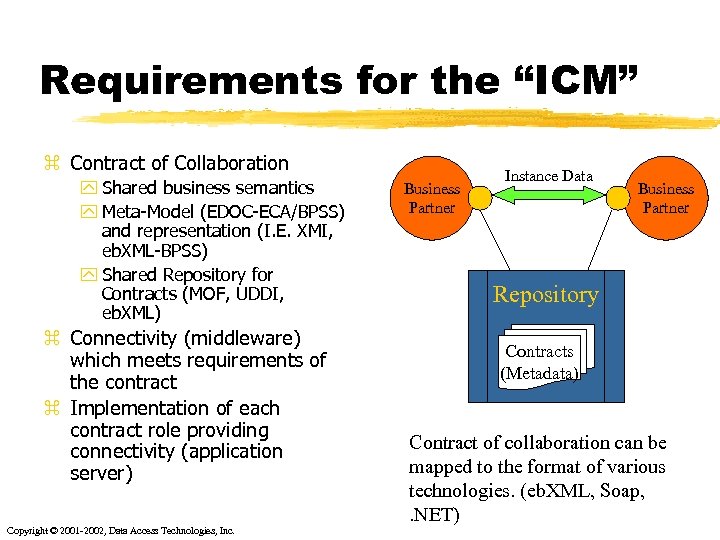
Requirements for the “ICM” z Contract of Collaboration y Shared business semantics y Meta-Model (EDOC-ECA/BPSS) and representation (I. E. XMI, eb. XML-BPSS) y Shared Repository for Contracts (MOF, UDDI, eb. XML) z Connectivity (middleware) which meets requirements of the contract z Implementation of each contract role providing connectivity (application server) Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc. Business Partner Instance Data Business Partner Repository Contracts (Metadata) Contract of collaboration can be mapped to the format of various technologies. (eb. XML, Soap, . NET)
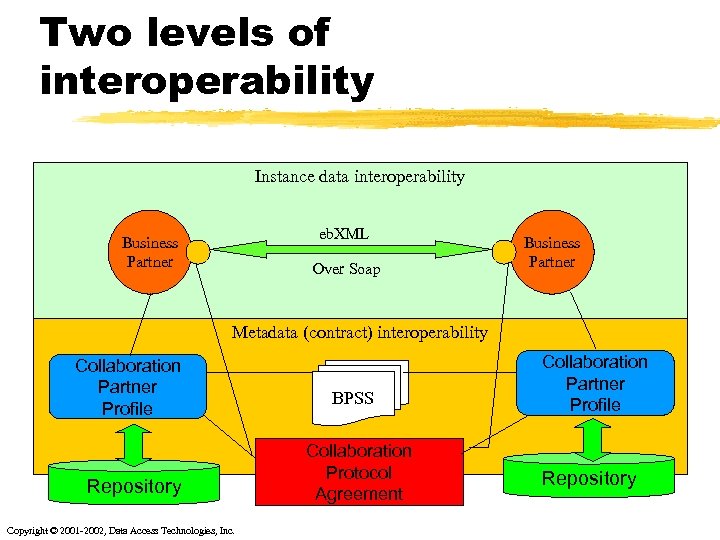
Two levels of interoperability Instance data interoperability eb. XML Business Partner Over Soap Business Partner Metadata (contract) interoperability Collaboration Partner Profile Repository Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc. BPSS Collaboration Protocol Agreement Collaboration Partner Profile Repository
Parts of eb. XML Specification z Requirements (RE) z Technical Architecture (TA) z Business Process Specification Schema (BPSS) z Collaboration protocol profile & agreement (CCP) z Message Service (MS) z Registry Information Model (RI) z Glossasry (Gloss) Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
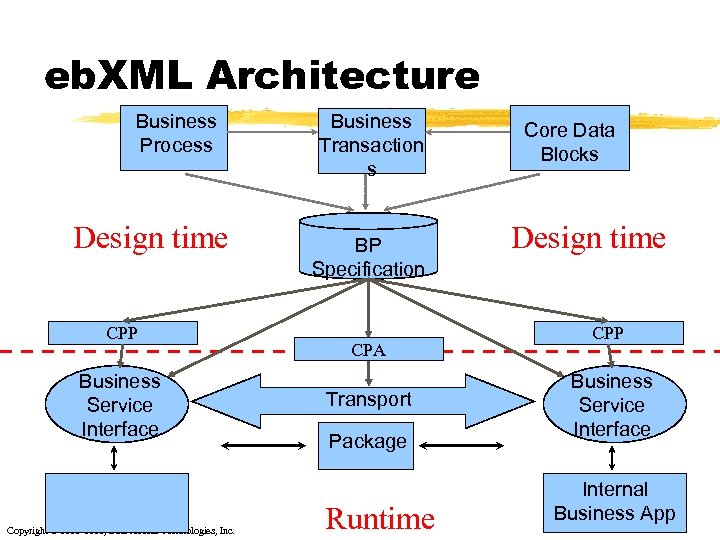
eb. XML Architecture Business Process Business Context For Transaction s Built With Core Data Blocks Register Implement time Design one Partner Role CPP Business Service Interface Internal Business App Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc. BP Specification CPA Transport Package Runtime Design time Implement other Partner Roles CPP Business Service Interface Internal Business App
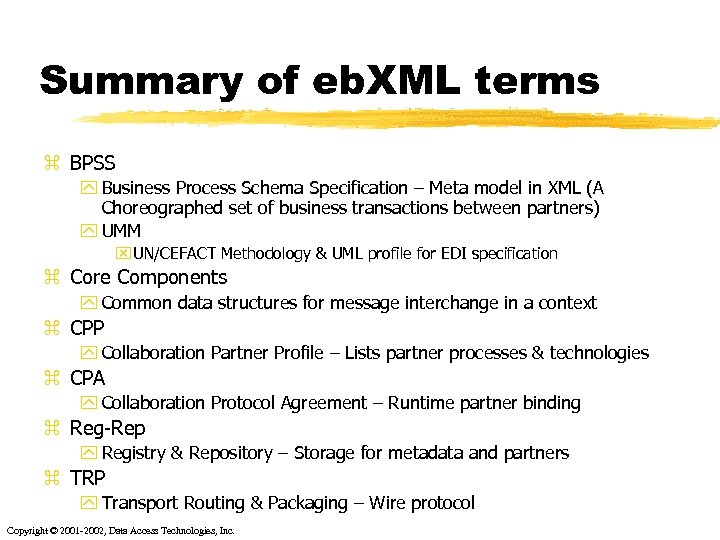
Summary of eb. XML terms z BPSS y Business Process Schema Specification – Meta model in XML (A Choreographed set of business transactions between partners) y UMM x UN/CEFACT Methodology & UML profile for EDI specification z Core Components y Common data structures for message interchange in a context z CPP y Collaboration Partner Profile – Lists partner processes & technologies z CPA y Collaboration Protocol Agreement – Runtime partner binding z Reg-Rep y Registry & Repository – Storage for metadata and partners z TRP y Transport Routing & Packaging – Wire protocol Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
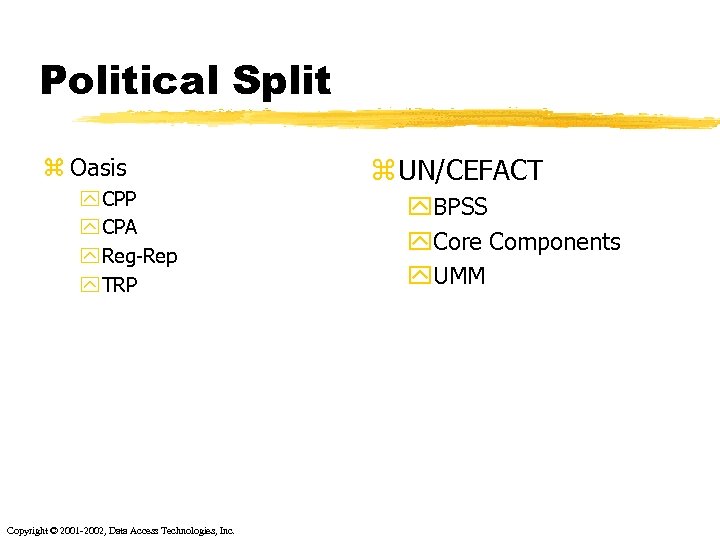
Political Split z Oasis y CPP y CPA y Reg-Rep y TRP Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc. z UN/CEFACT y. BPSS y. Core Components y. UMM
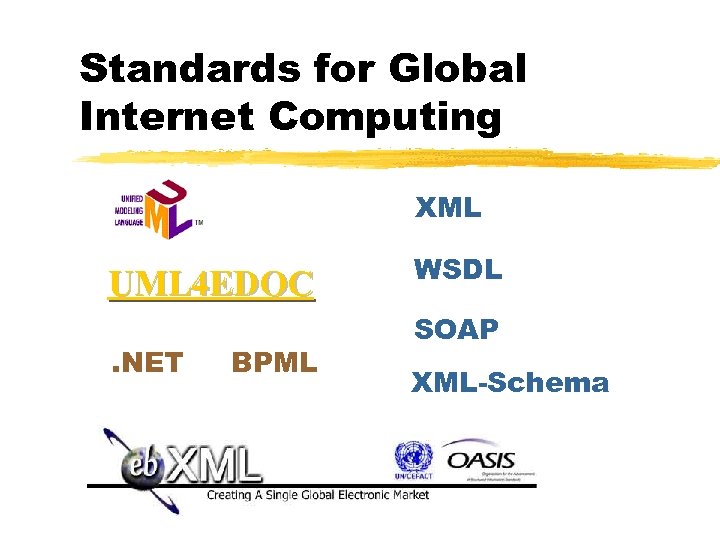
Standards for Global Internet Computing XML UML 4 EDOC. NET BPML WSDL SOAP XML-Schema

XML Standards z. XML Schema & DTD y. Description and packaging of data z. Soap y. Basic messaging and packaging y. Extensions for Soap-RPC with WSDL y. May be extended to support collaborative messaging Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
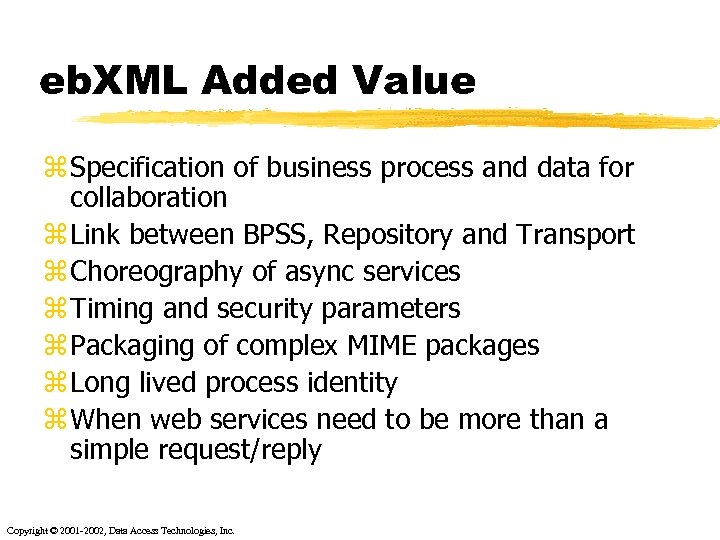
eb. XML Added Value z Specification of business process and data for collaboration z Link between BPSS, Repository and Transport z Choreography of async services z Timing and security parameters z Packaging of complex MIME packages z Long lived process identity z When web services need to be more than a simple request/reply Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
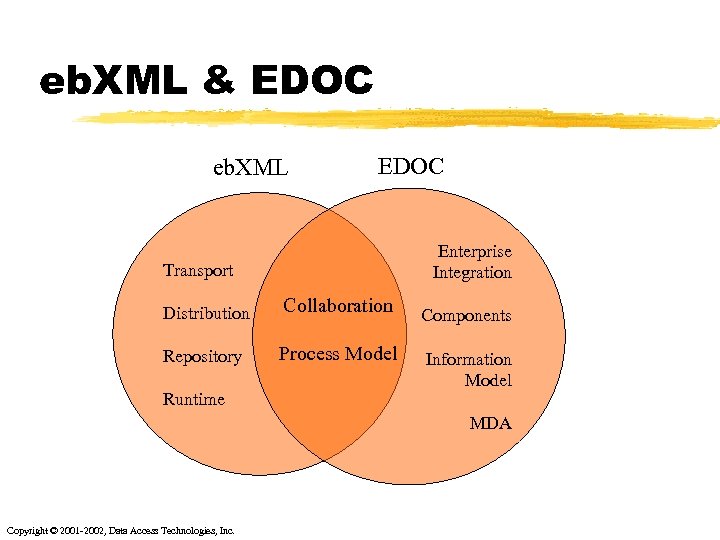
eb. XML & EDOC eb. XML EDOC Enterprise Integration Transport Distribution Collaboration Repository Process Model Runtime Components Information Model MDA Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
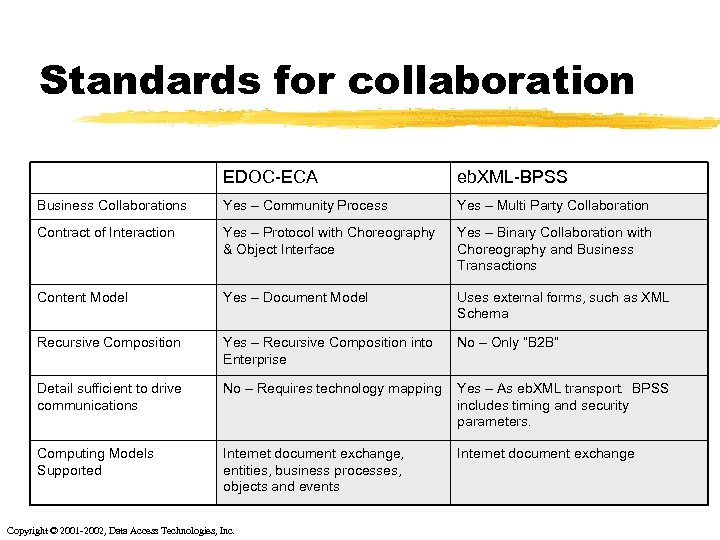
Standards for collaboration EDOC-ECA eb. XML-BPSS Business Collaborations Yes – Community Process Yes – Multi Party Collaboration Contract of Interaction Yes – Protocol with Choreography & Object Interface Yes – Binary Collaboration with Choreography and Business Transactions Content Model Yes – Document Model Uses external forms, such as XML Schema Recursive Composition Yes – Recursive Composition into Enterprise No – Only “B 2 B” Detail sufficient to drive communications No – Requires technology mapping Yes – As eb. XML transport. BPSS includes timing and security parameters. Computing Models Supported Internet document exchange, entities, business processes, objects and events Internet document exchange Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.

The model driven architecture for web services and collaborative internet computing
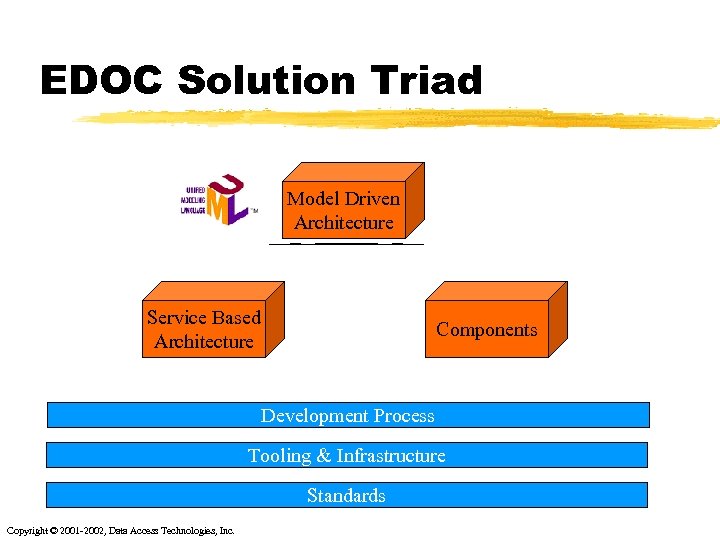
EDOC Solution Triad Model Driven Architecture Service Based Architecture Components Development Process Tooling & Infrastructure Standards Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
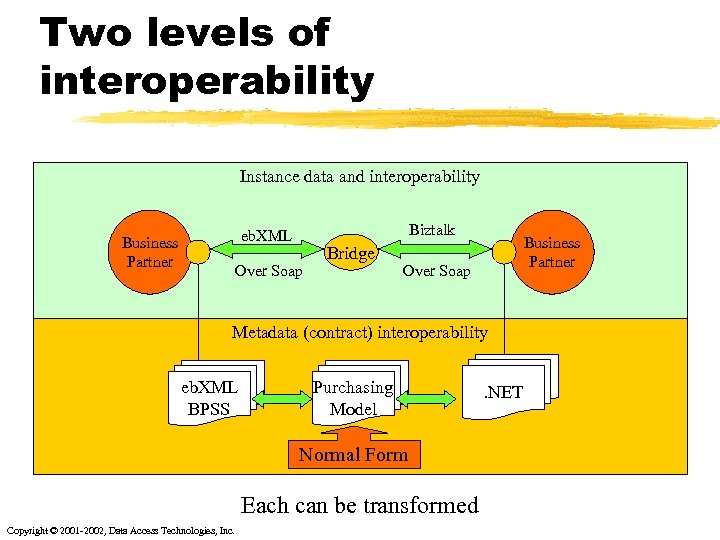
Two levels of interoperability Instance data and interoperability Biztalk eb. XML Business Partner Over Soap Bridge Business Partner Over Soap Metadata (contract) interoperability eb. XML BPSS Purchasing Model Normal Form Each can be transformed Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc. . NET
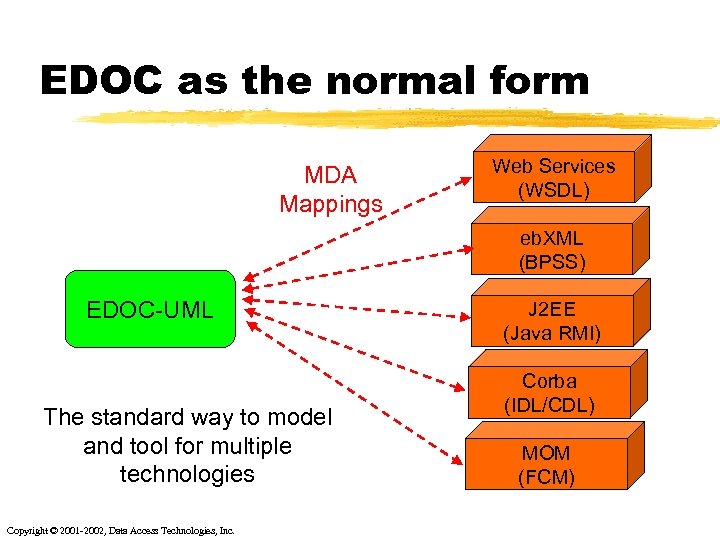
EDOC as the normal form MDA Mappings Web Services (WSDL) eb. XML (BPSS) EDOC-UML The standard way to model and tool for multiple technologies Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc. J 2 EE (Java RMI) Corba (IDL/CDL) MOM (FCM)
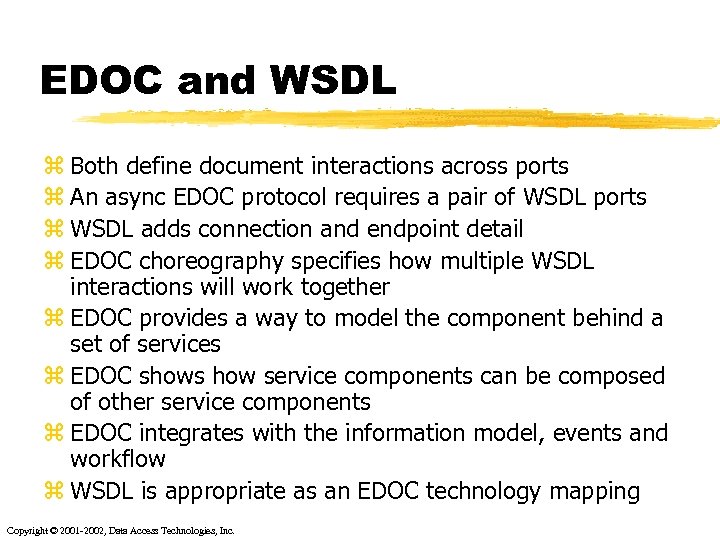
EDOC and WSDL z Both define document interactions across ports z An async EDOC protocol requires a pair of WSDL ports z WSDL adds connection and endpoint detail z EDOC choreography specifies how multiple WSDL interactions will work together z EDOC provides a way to model the component behind a set of services z EDOC shows how service components can be composed of other service components z EDOC integrates with the information model, events and workflow z WSDL is appropriate as an EDOC technology mapping Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
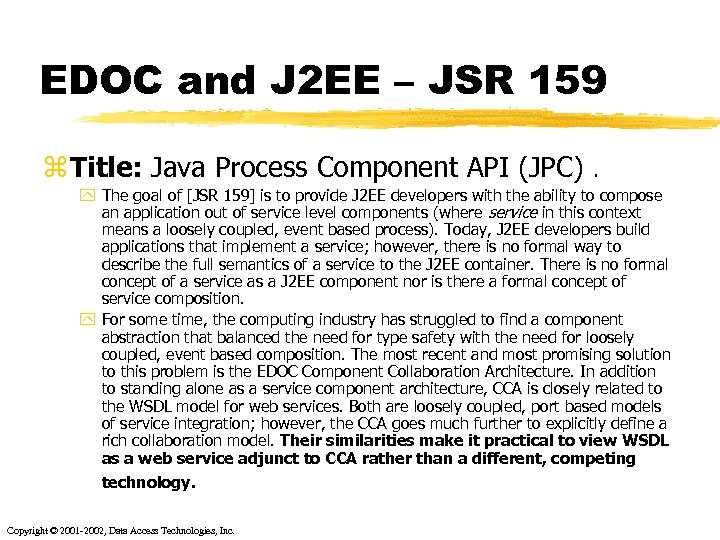
EDOC and J 2 EE – JSR 159 z Title: Java Process Component API (JPC) . y The goal of [JSR 159] is to provide J 2 EE developers with the ability to compose an application out of service level components (where service in this context means a loosely coupled, event based process). Today, J 2 EE developers build applications that implement a service; however, there is no formal way to describe the full semantics of a service to the J 2 EE container. There is no formal concept of a service as a J 2 EE component nor is there a formal concept of service composition. y For some time, the computing industry has struggled to find a component abstraction that balanced the need for type safety with the need for loosely coupled, event based composition. The most recent and most promising solution to this problem is the EDOC Component Collaboration Architecture. In addition to standing alone as a service component architecture, CCA is closely related to the WSDL model for web services. Both are loosely coupled, port based models of service integration; however, the CCA goes much further to explicitly define a rich collaboration model. Their similarities make it practical to view WSDL as a web service adjunct to CCA rather than a different, competing technology. Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.

From the enterprise to technology viewpoints EDOC collaborations as the basis of multiple viewpoints
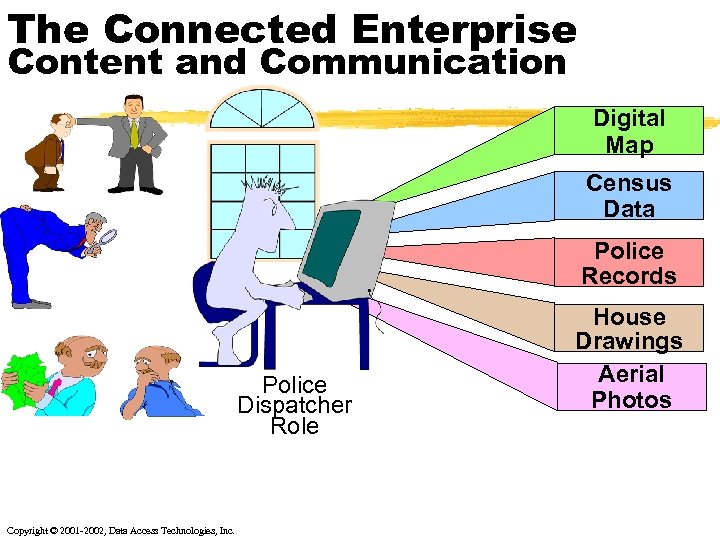
The Connected Enterprise Content and Communication Digital Map Census Data Police Records Police Dispatcher Role Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc. House Drawings Aerial Photos
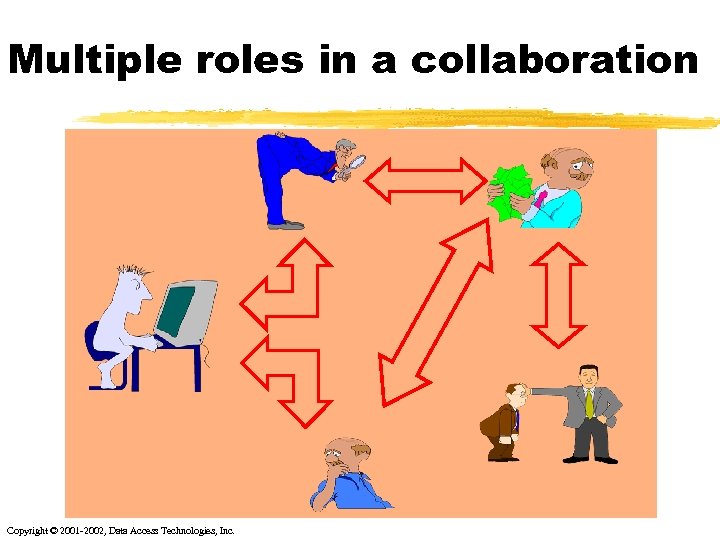
Multiple roles in a collaboration Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
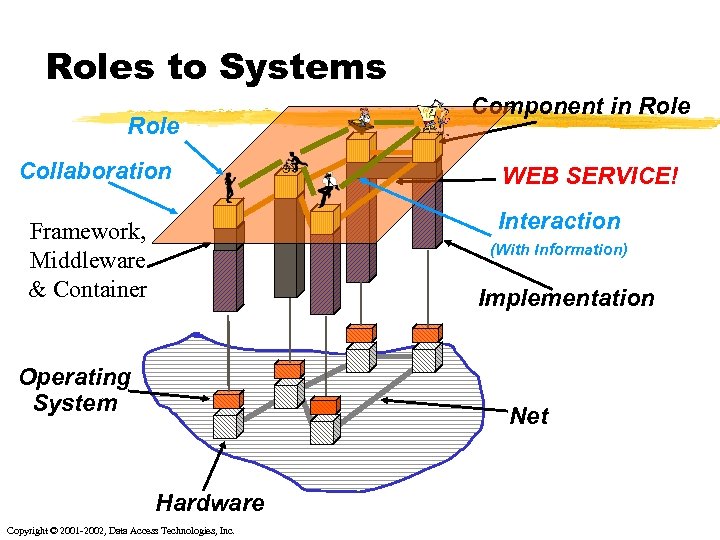
Roles to Systems Role Collaboration Component in Role WEB SERVICE! Interaction Framework, Middleware & Container (With Information) Implementation Operating System Net Hardware Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.

Vision Building and adapting systems for collaboration, reuse and change
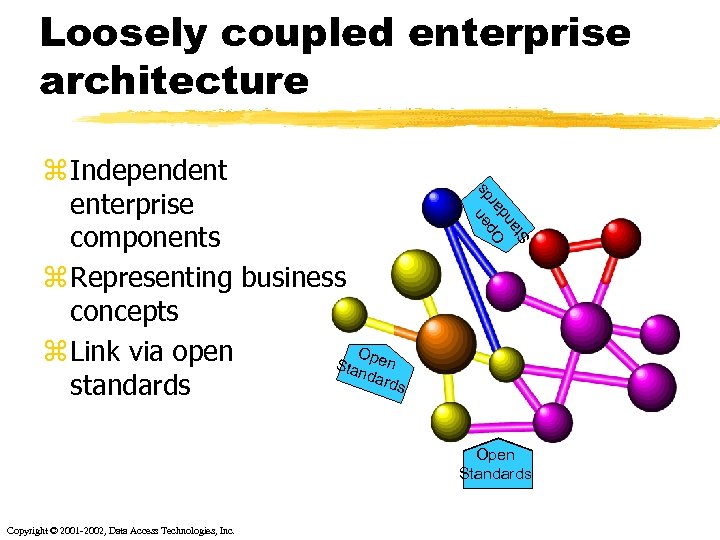
z Independent enterprise components z Representing business concepts Op z Link via open Sta en nda rds standards n s pe ard O d n ta S Loosely coupled enterprise architecture Open Standards Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
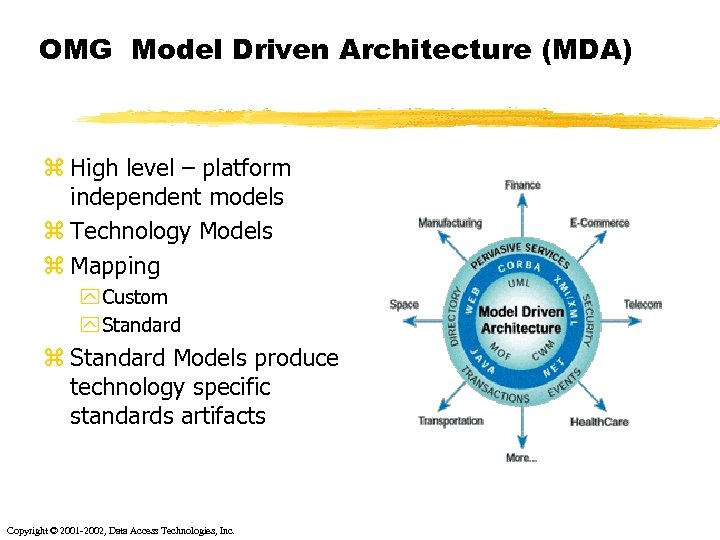
OMG Model Driven Architecture (MDA) z High level – platform independent models z Technology Models z Mapping y Custom y Standard z Standard Models produce technology specific standards artifacts Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
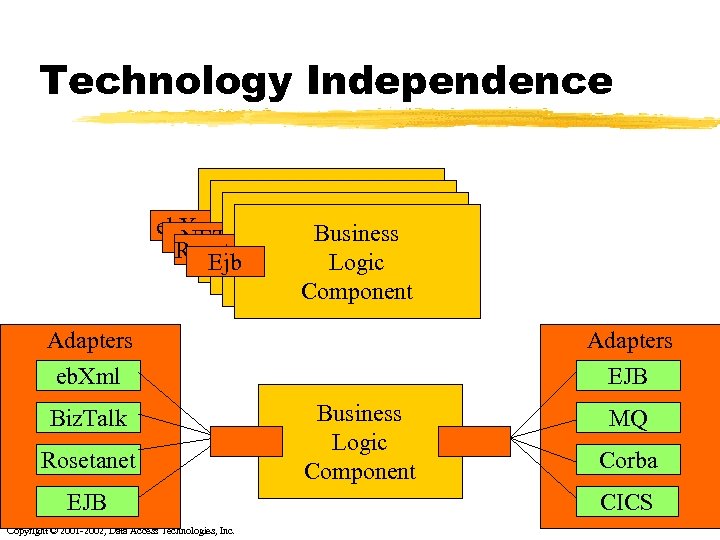
Technology Independence What some infrastructure Business Logic eb. Xml vendors would Business Logic. NET Roseta. Net have Logic you do Ejb Component Logic Component Adapters eb. Xml Biz. Talk Rosetanet EJB Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc. Adapters EJB Business Logic Component MQ Corba CICS
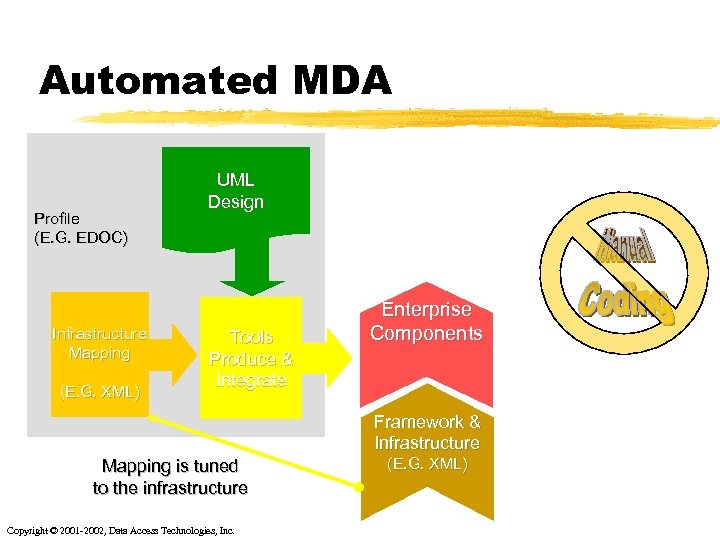
Automated MDA Profile (E. G. EDOC) Infrastructure Mapping (E. G. XML) UML Design Tools Produce & Integrate Enterprise Components Framework & Infrastructure Mapping is tuned to the infrastructure Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc. (E. G. XML)
High level tooling & infrastructure z MUST BE SIMPLE! y. We must be able to create better applications faster y. We must separate the technology and business concerns, enable the user z Tooling + Infrastructure y. Executable models are source code y. Tooling must be technology aware y. Infrastructure must support tooling, not manual techniques z Model based component architectures Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
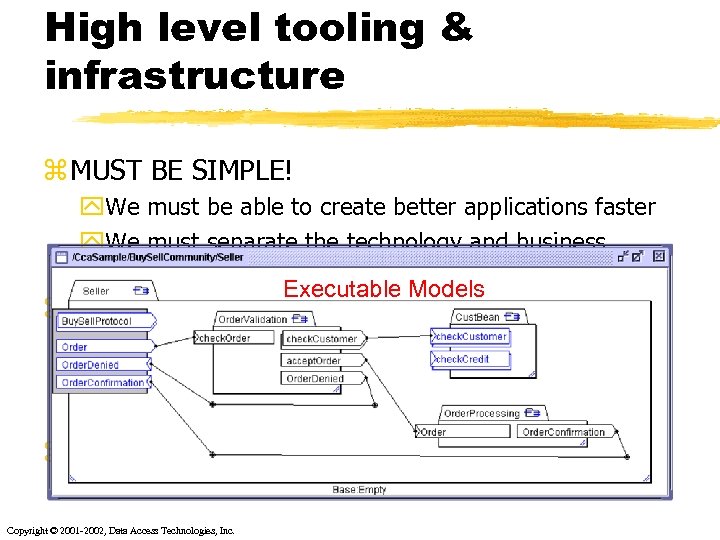
High level tooling & infrastructure z MUST BE SIMPLE! y. We must be able to create better applications faster y. We must separate the technology and business concerns, enable the user Executable Models z Tooling + Infrastructure y. Executable models are source code ya. Tooling must be technology aware y. Infrastructure must support tooling z Model based component architectures Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
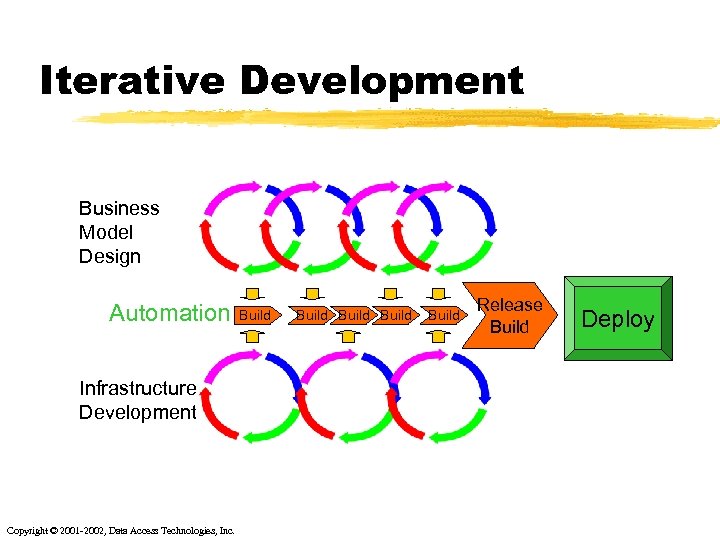
Iterative Development Business Model Design Automation Infrastructure Development Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc. Build Build Release Build Deploy

Business Component Marketplace z The business component marketplace is projected to be a 10 b market in 5 years z Consider the value of XML components that wrap popular legacy z New application functionality built from components z Components for integration and transformation z XML and web services makes an excellent basis for such components z Technology components, such as for repositories and DBMS z Marketplace my be inside the enterprise or commercial Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
Net effect z Using these open standards and automated techniques we can; y. Achieve the strategic advantage of an open and flexible enterprise y. Produce and/or integrate these systems FASTER and CHEAPER than could be done with legacy techniques y. Provide a lasting asset that will outlive the technology of the day Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.

Role of the OMG z While web services have huge potential but the enterprise needs to see how to bring these technologies together to solve business problems z The OMG can bring business focus and unification to web services by applying Model Driven Architecture (MDA); y Bridging technologies y Unifying tools y Automating the development process z We have just adopted EDOC for this vary purpose Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.

Discussion Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.

Contact Cory Casanave Data Access Technologies www. enterprise-component. com cory-c@enterprise-component. com (305) 234 -7077 Copyright © 2001 -2002, Data Access Technologies, Inc.
8f17ad49920f323741514266830687b0.ppt