c560595687a792feb31d8ff325c89f57.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 86

EASYC for VEX Cortex Llano Estacado Robo. Raiders FRC Team 1817 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 1
Humans and Machines Machines are built to perform useful tasks. The way a Machine works depends entirely on the way the Human build it. Since Machines and Robots need a medium of communication, a language called “Programming Language” is used. EASYC, ROBOTC, C++, C all are programming languages. The instructions in the language are called “Programs” and the human that writes the instructions is called the “Programmer”. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 2
Task of Programmer: Understand Problem, Find a solution, Write a program to solve the problem in the required Programming language. Task of Machine: Follow the program provided. A ROBOT is a Machine. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 3

Planning and Behavior: Action the Robot has to take. Big Behavior: Solving a maze Small Behavior: Turn Left, Move Forward, etc. Big Behavior is made up of Smaller Behaviors. Plan a Solution to the problem. Break down the plan into detailed smaller steps. Each step is a behavior the robot needs to follow. Sequence of these steps in English is called “pseudocode”. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 4
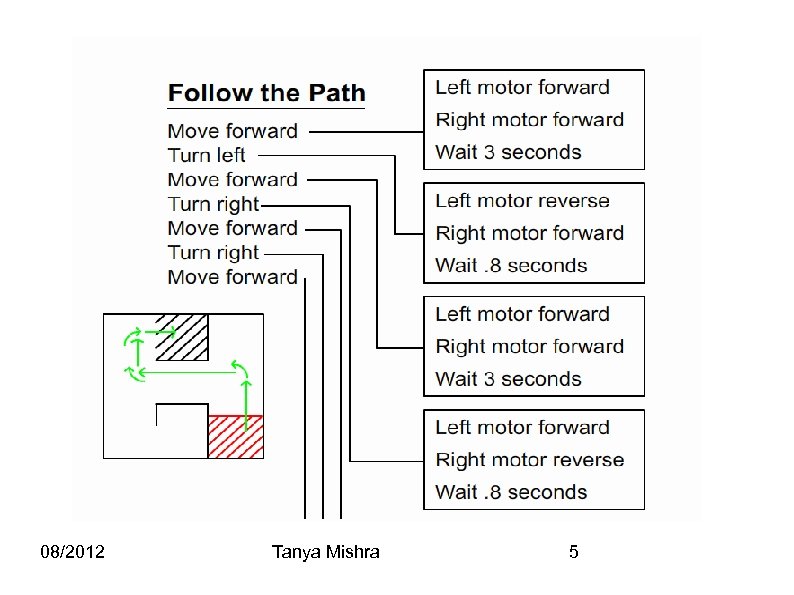
08/2012 Tanya Mishra 5
“Flow charts” are a visual representation of the program flow. Start and End: “Rounded Rectangles”. They contain the word “Start” or “End”, but can be more specific such as “Power Robot Off” or “Stop All Motors”. Actions: “Rectangles”. They act as basic commands and process steps. Decision blocks: “Diamonds”. These typically contain Yes/No questions. Based on the choice, the next step is determined. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 6
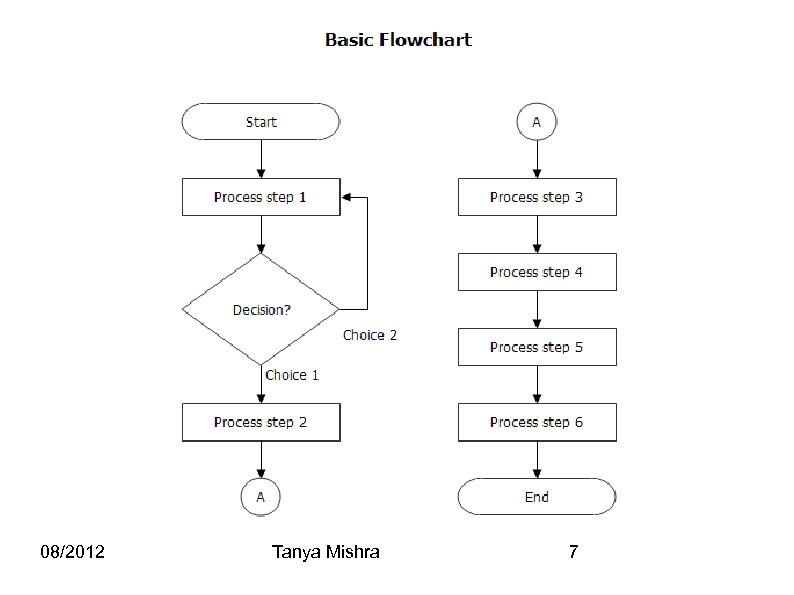
08/2012 Tanya Mishra 7

Introduction to C Programming Easy. C is based on the principles of C Programming. We will cover the following concepts: 1. Basic Components of a C Program 2. Data Types and Variables 2. Conditional operators 3. Control Structures and Loops 4. Methods and Functions 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 8

A Basic C Program #include<stdio. h> // Header File void main(void) // Main function { // Body of the main function } Header file: Includes all the required words and instructions needed to write a program Main function: Execution starts from here Body: stepwise Instructions to the Robot 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 9
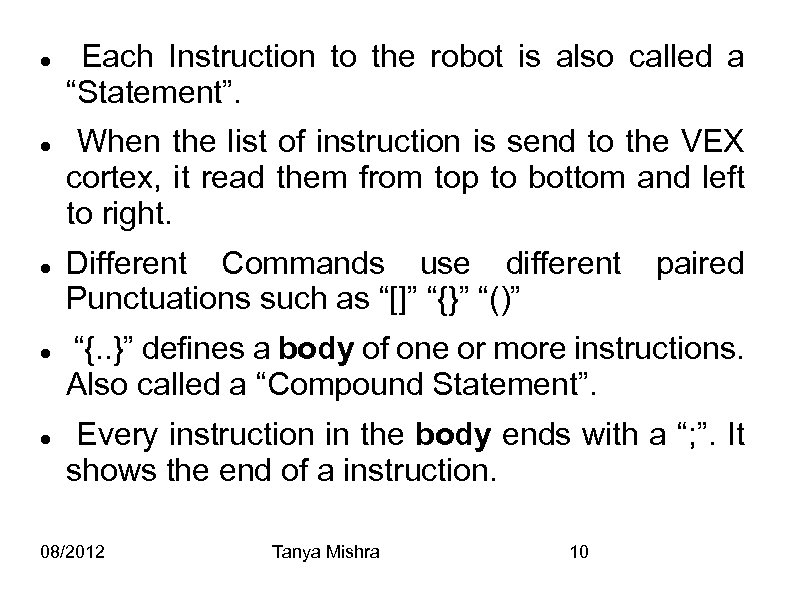
Each Instruction to the robot is also called a “Statement”. When the list of instruction is send to the VEX cortex, it read them from top to bottom and left to right. Different Commands use different Punctuations such as “[]” “{}” “()” paired “{. . }” defines a body of one or more instructions. Also called a “Compound Statement”. Every instruction in the body ends with a “; ”. It shows the end of a instruction. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 10

Comments are for the programmer to understand what a particular statement does. Two kinds of comments: 1. // This is a one line comment 2. /* This is a more than one line Comment. */ C language is case sensitive: Upper and lower cases are considered different. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 11
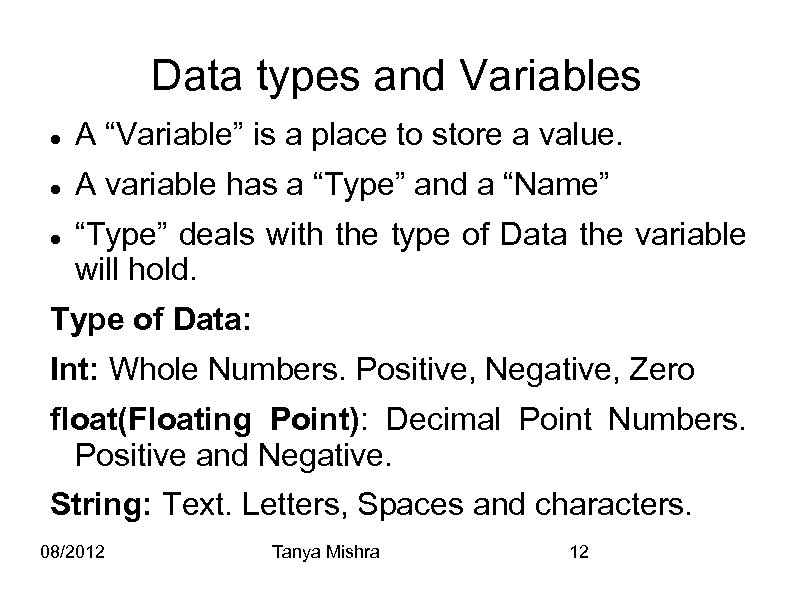
Data types and Variables A “Variable” is a place to store a value. A variable has a “Type” and a “Name” “Type” deals with the type of Data the variable will hold. Type of Data: Int: Whole Numbers. Positive, Negative, Zero float(Floating Point): Decimal Point Numbers. Positive and Negative. String: Text. Letters, Spaces and characters. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 12
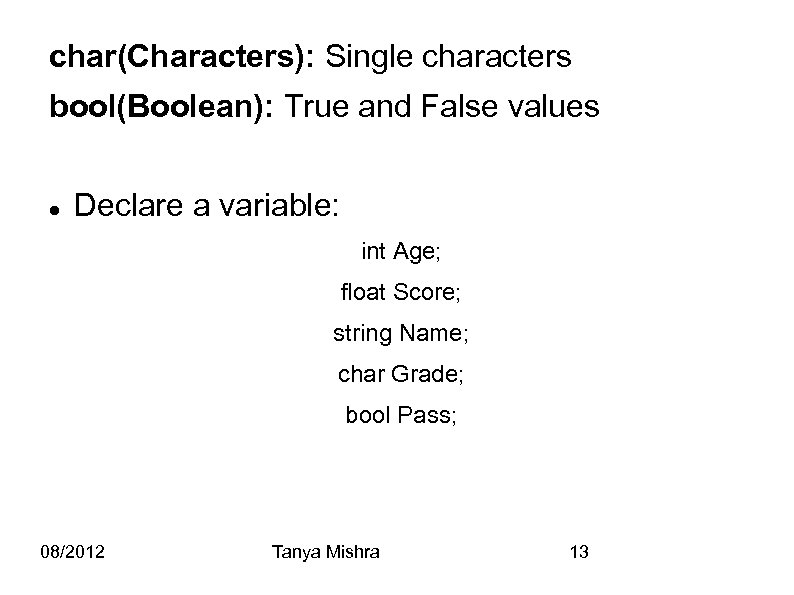
char(Characters): Single characters bool(Boolean): True and False values Declare a variable: int Age; float Score; string Name; char Grade; bool Pass; 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 13
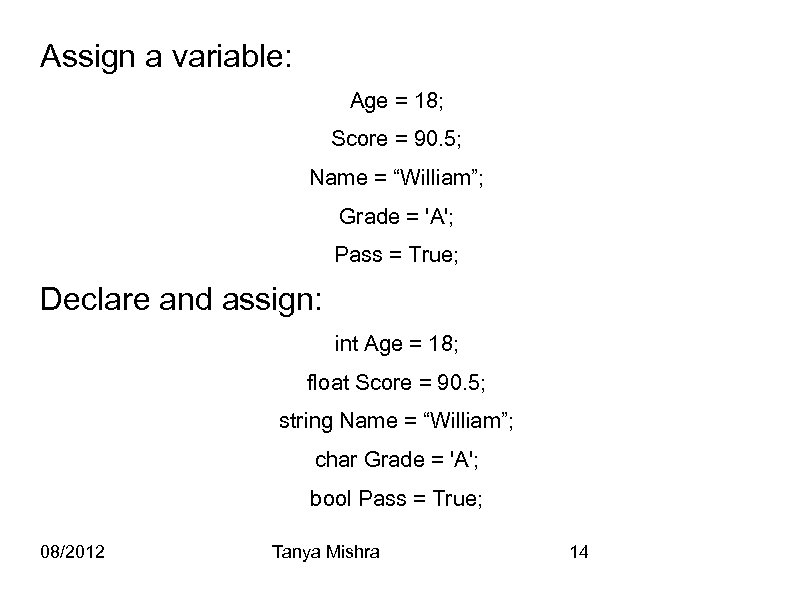
Assign a variable: Age = 18; Score = 90. 5; Name = “William”; Grade = 'A'; Pass = True; Declare and assign: int Age = 18; float Score = 90. 5; string Name = “William”; char Grade = 'A'; bool Pass = True; 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 14

Variable Naming Rules: A variable name can not have spaces in it. A variable name can not have symbols in it. A variable name can not start with a number. A variable name can not be the same as an existing reserved word. Scope of a Variable: Local variables: Within a certain block of code or function. Cannot be accessed outside. Global variables: Can be accessed anywhere in the code. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 15
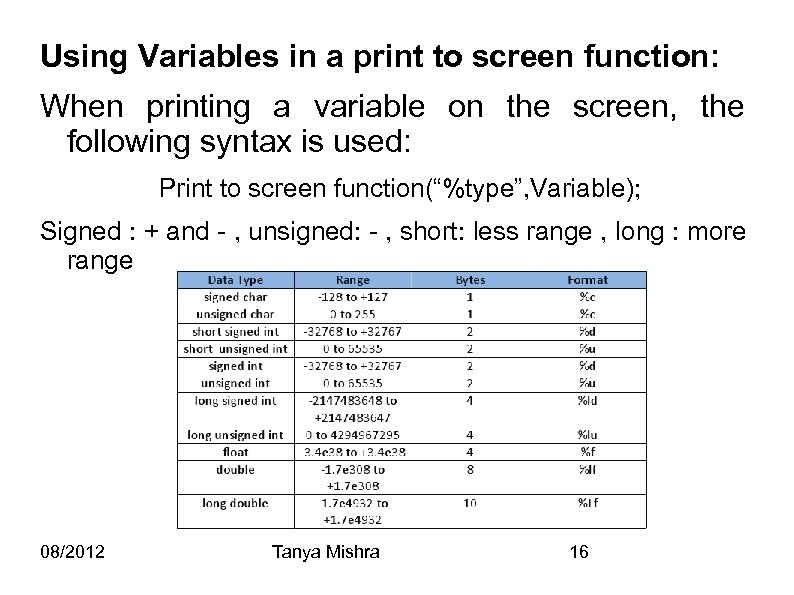
Using Variables in a print to screen function: When printing a variable on the screen, the following syntax is used: Print to screen function(“%type”, Variable); Signed : + and - , unsigned: - , short: less range , long : more range 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 16
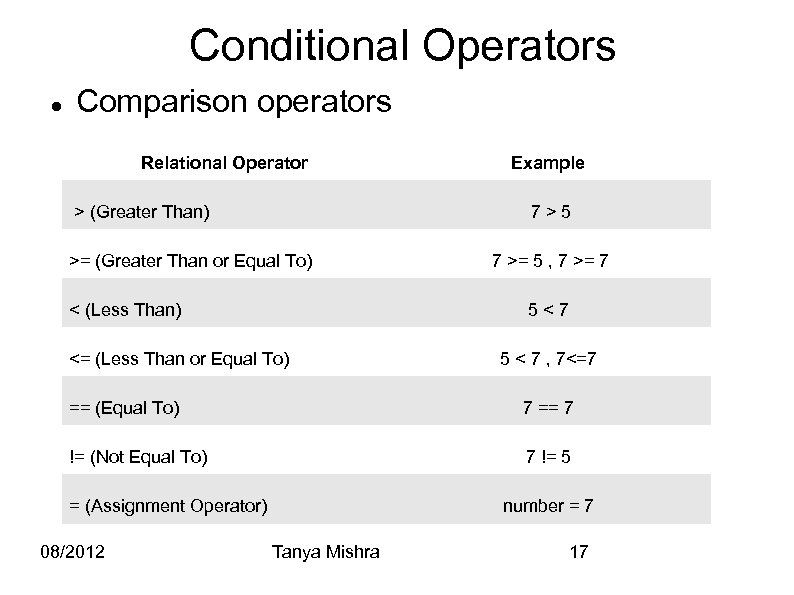
Conditional Operators Comparison operators Relational Operator > (Greater Than) Example 7>5 >= (Greater Than or Equal To) < (Less Than) 7 >= 5 , 7 >= 7 5<7 <= (Less Than or Equal To) 5 < 7 , 7<=7 == (Equal To) 7 == 7 != (Not Equal To) 7 != 5 = (Assignment Operator) 08/2012 number = 7 Tanya Mishra 17
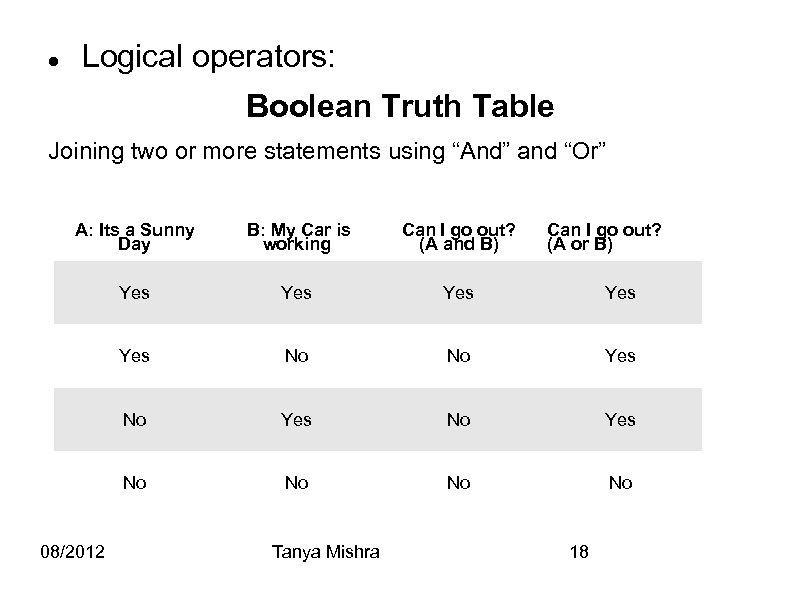
Logical operators: Boolean Truth Table Joining two or more statements using “And” and “Or” A: Its a Sunny Day B: My Car is working Can I go out? (A and B) Yes Yes Yes No No Yes No No 08/2012 Tanya Mishra Can I go out? (A or B) 18
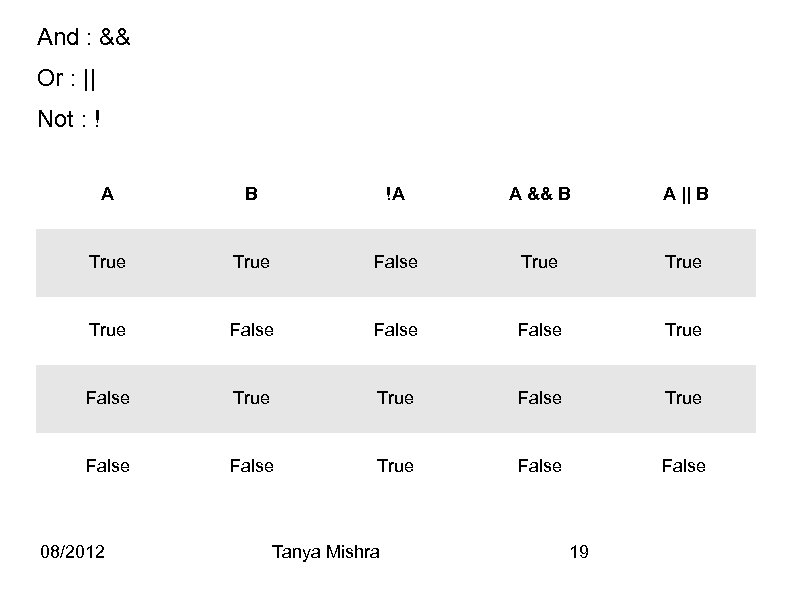
And : && Or : || Not : ! A B !A A && B A || B True False True True False False True False 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 19
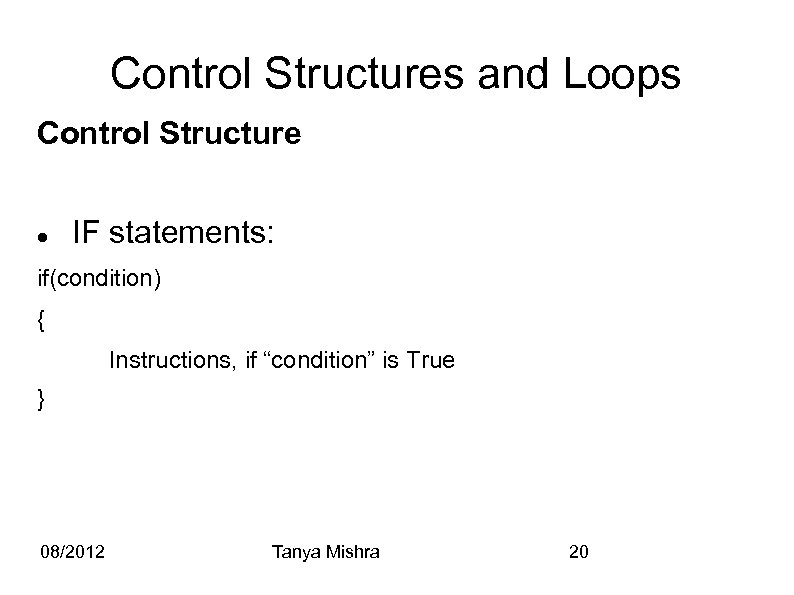
Control Structures and Loops Control Structure IF statements: if(condition) { Instructions, if “condition” is True } 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 20
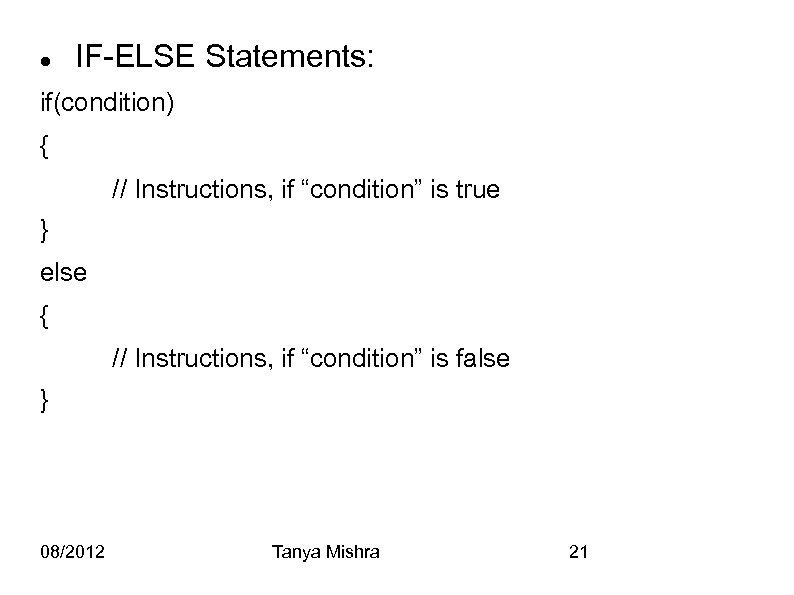
IF-ELSE Statements: if(condition) { // Instructions, if “condition” is true } else { // Instructions, if “condition” is false } 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 21

ELSE-IF Statements: if(condition 1) { // Instructions, if “condition 1” is true } else if(condition 2) { // Instructions, if “condition 2” is true } else { // Instructions, if “condition 1” and “condition 2” are false } 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 22
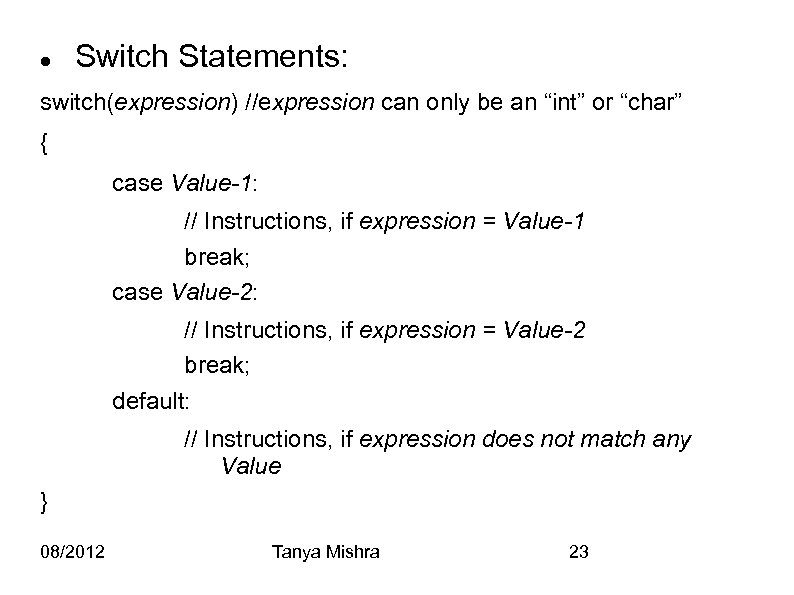
Switch Statements: switch(expression) //expression can only be an “int” or “char” { case Value-1: // Instructions, if expression = Value-1 break; case Value-2: // Instructions, if expression = Value-2 break; default: // Instructions, if expression does not match any Value } 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 23

Example: char Grade = 'A'; switch(Grade) { case A: Your Grade is A; break; case B: Your Grade is B; break; default: This is the default choice } 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 24

Loops While loops: while(condition) { // Instructions, if “condition” is true } Note: Control Structures execute only once. On the other hand, while loops execute continuously until the condition is false. If the condition in the loop is always true, the loop never ends. Such a loop is called an “Infinite Loop”. A loop will end only when the condition is false or there is a “break” statement. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 25

Example: int count = 0; //Initialization while(count <= 2) //Condition { Print. To. Screen(“ I have %d apple n”, count); count = count + 1; //Increment } Output: I have 0 apple I have 1 apple I have 2 apple 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 26
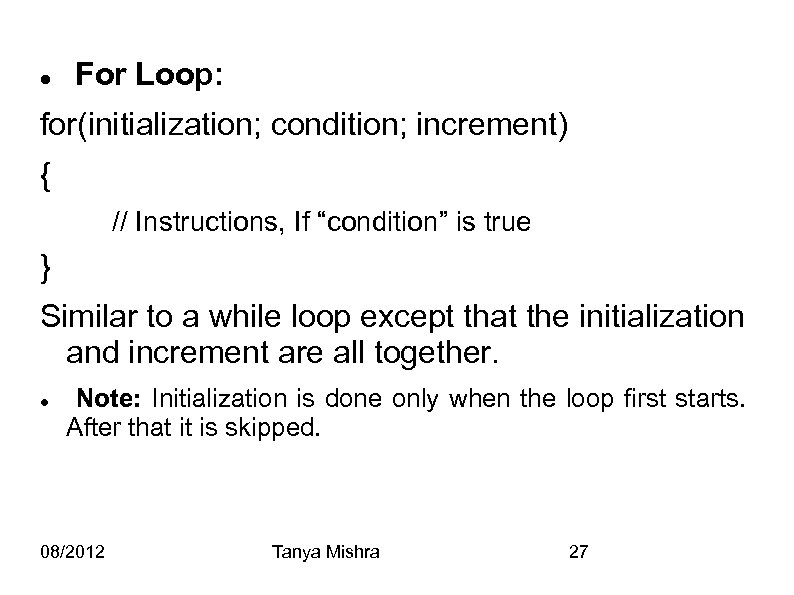
For Loop: for(initialization; condition; increment) { // Instructions, If “condition” is true } Similar to a while loop except that the initialization and increment are all together. Note: Initialization is done only when the loop first starts. After that it is skipped. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 27

Example: int count; for(count =0; count <= 2; count = count +1) { Print. To. Screen(“ I have %d apple n”, count); } Output: I have 0 apple I have 1 apple I have 2 apple Note: n is called new lines. It prints the next sentence in a new line. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 28
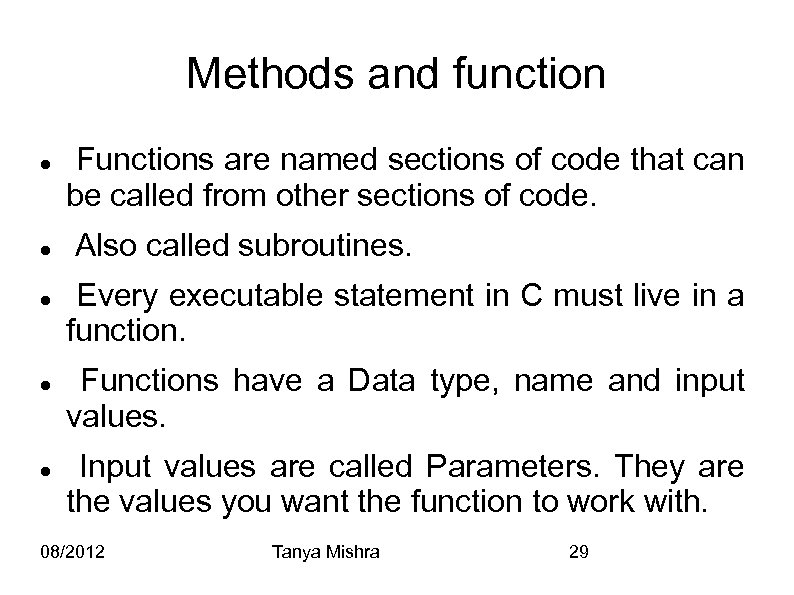
Methods and function Functions are named sections of code that can be called from other sections of code. Also called subroutines. Every executable statement in C must live in a function. Functions have a Data type, name and input values. Input values are called Parameters. They are the values you want the function to work with. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 29

The function definition specifies the “return value” and the “parameters” of the function: <data type> Function. Name(<param 1>, <param 2>, . . . ) { <function body> <return type> } Return type and Data type should be of the same kind. Return type is “void” if nothing is to be returned. Parameters is “void” if nothing is to be passed in. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 30

Example: int addition(int x, int y) { int z; z = x+ y; return z; } void main(void) { addition(2, 3); } 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 31
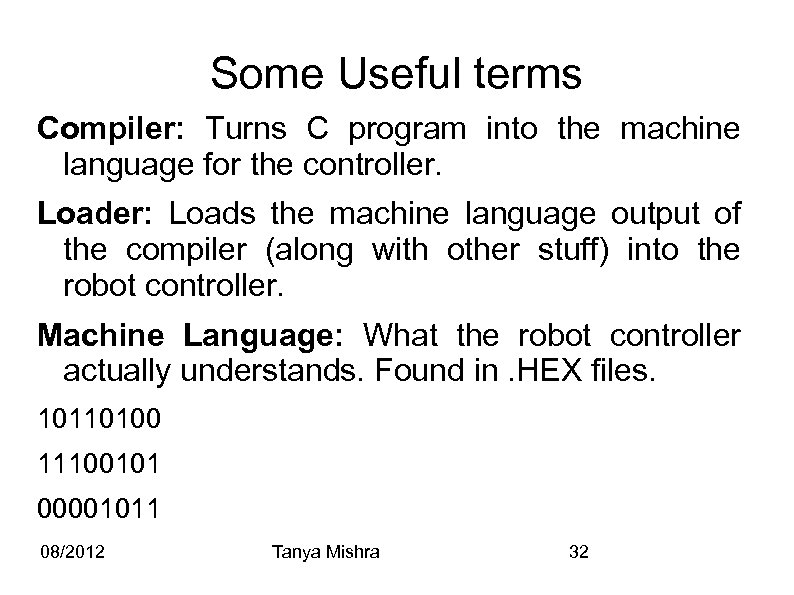
Some Useful terms Compiler: Turns C program into the machine language for the controller. Loader: Loads the machine language output of the compiler (along with other stuff) into the robot controller. Machine Language: What the robot controller actually understands. Found in. HEX files. 10110100 11100101 00001011 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 32
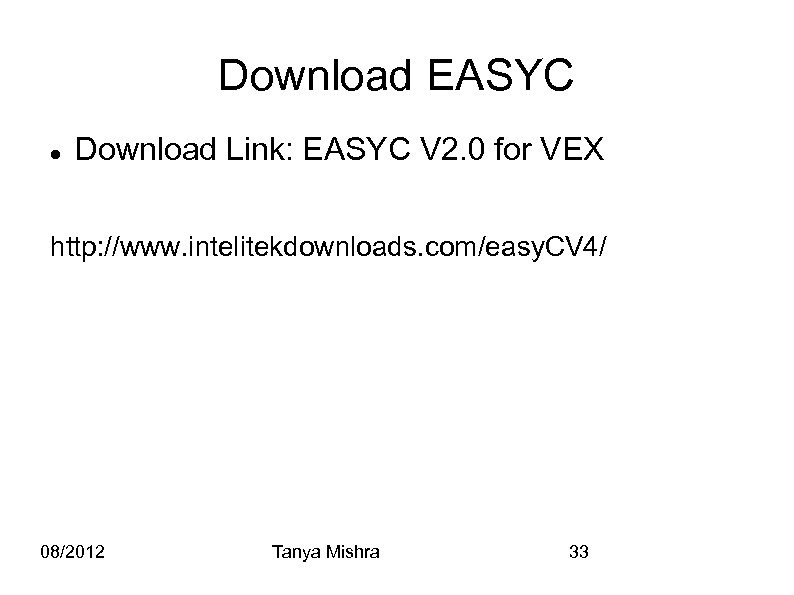
Download EASYC Download Link: EASYC V 2. 0 for VEX http: //www. intelitekdownloads. com/easy. CV 4/ 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 33

Updating EASYC If the website says you need to update Easy. C, you can do that by going to: Help->Check for updates 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 34
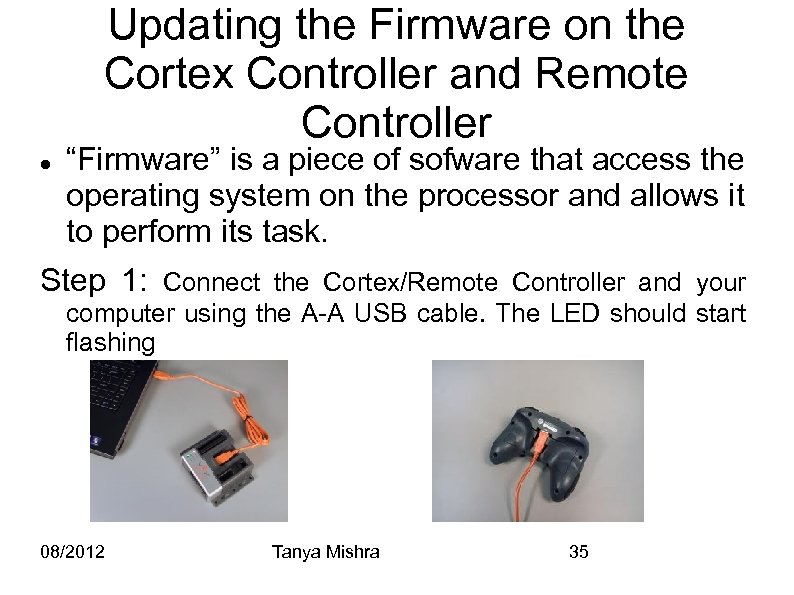
Updating the Firmware on the Cortex Controller and Remote Controller “Firmware” is a piece of sofware that access the operating system on the processor and allows it to perform its task. Step 1: Connect the Cortex/Remote Controller and your computer using the A-A USB cable. The LED should start flashing 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 35
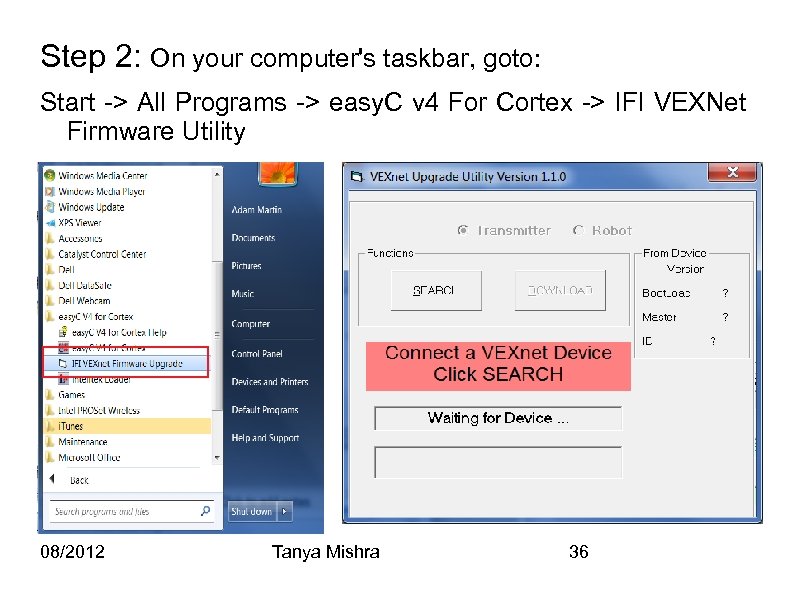
Step 2: On your computer's taskbar, goto: Start -> All Programs -> easy. C v 4 For Cortex -> IFI VEXNet Firmware Utility 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 36
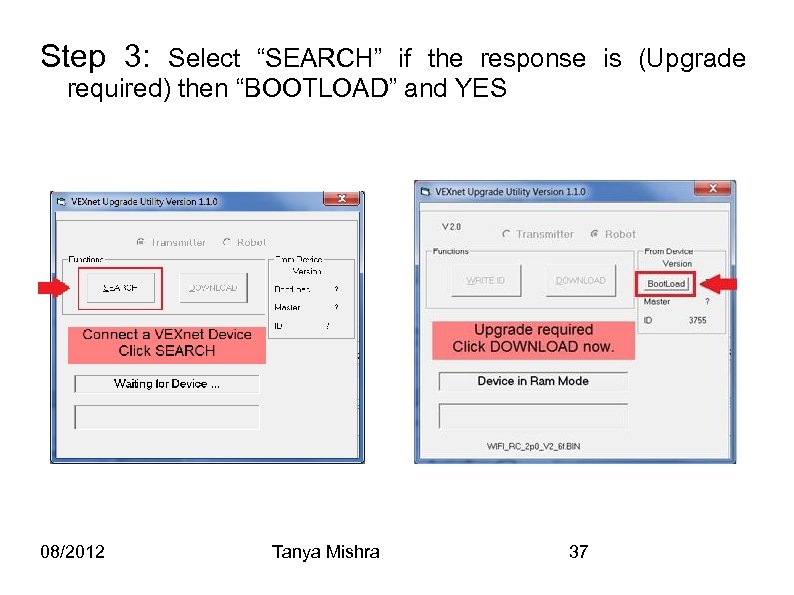
Step 3: Select “SEARCH” if the response is (Upgrade required) then “BOOTLOAD” and YES 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 37
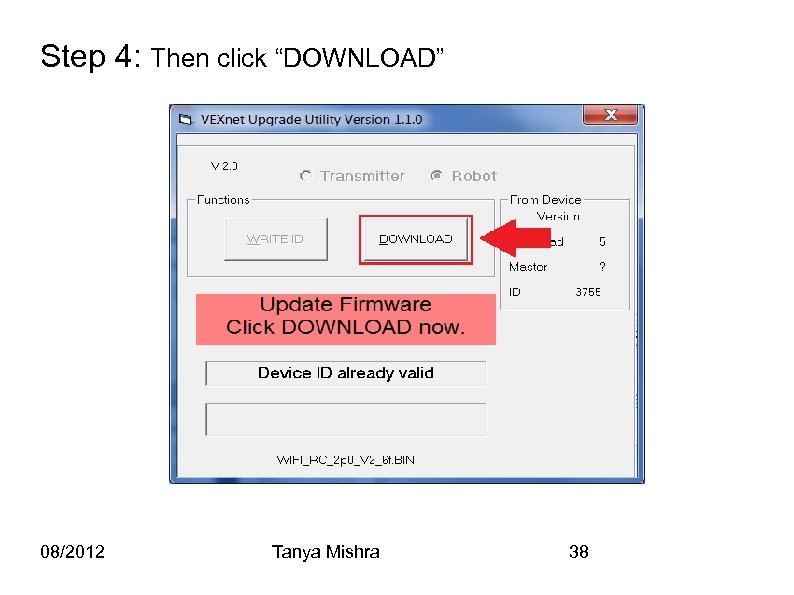
Step 4: Then click “DOWNLOAD” 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 38
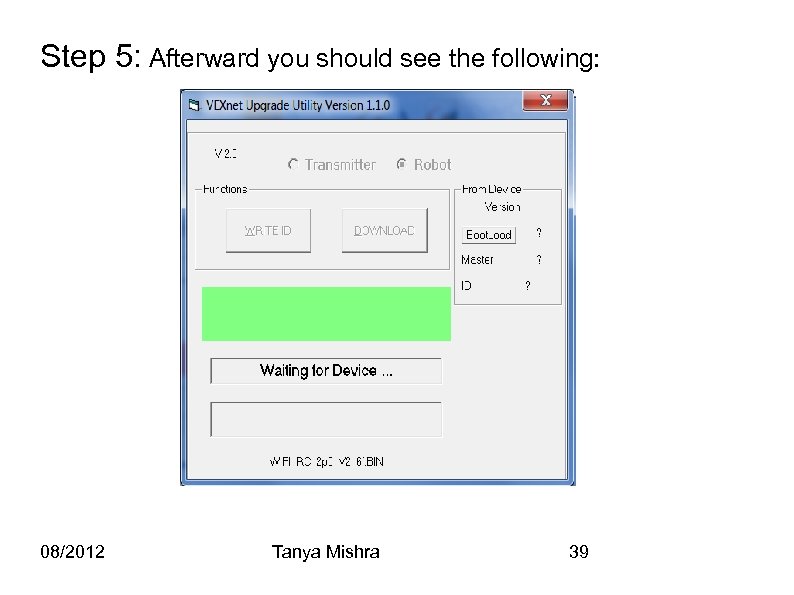
Step 5: Afterward you should see the following: 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 39
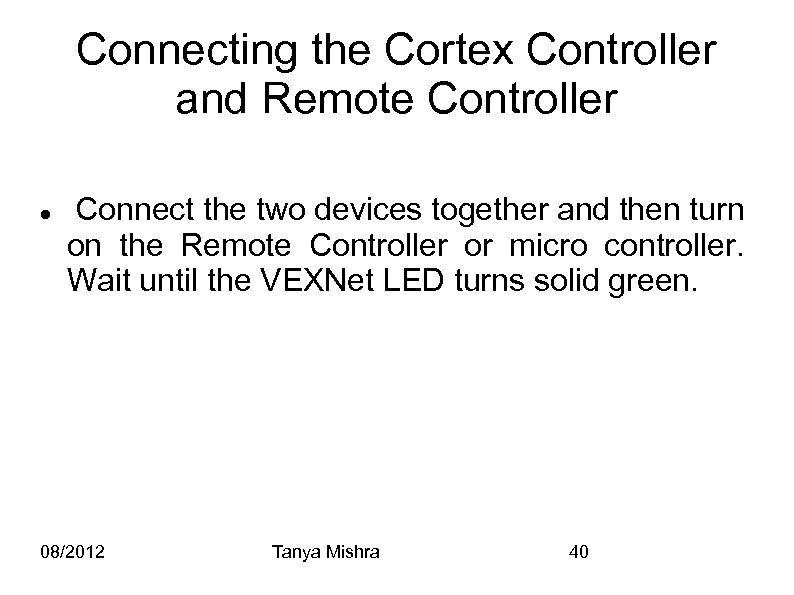
Connecting the Cortex Controller and Remote Controller Connect the two devices together and then turn on the Remote Controller or micro controller. Wait until the VEXNet LED turns solid green. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 40
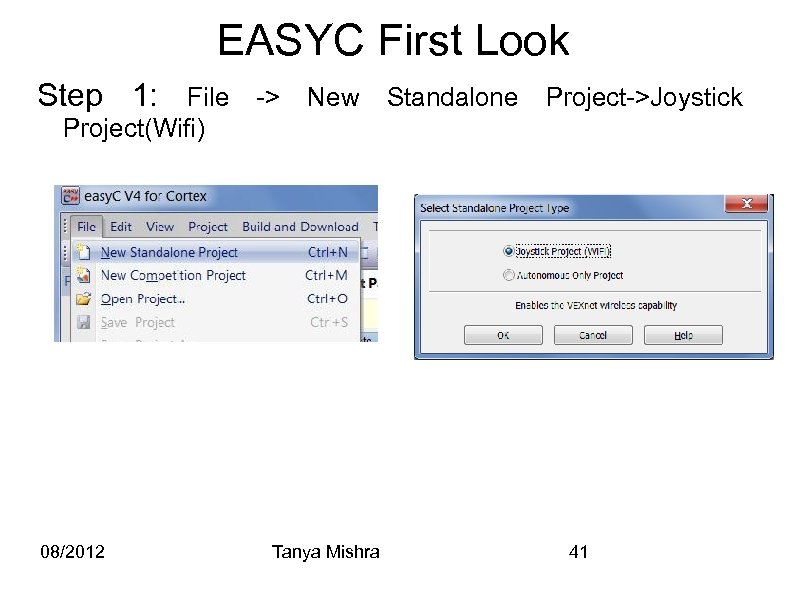
EASYC First Look Step 1: File -> New Standalone Project->Joystick Project(Wifi) 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 41
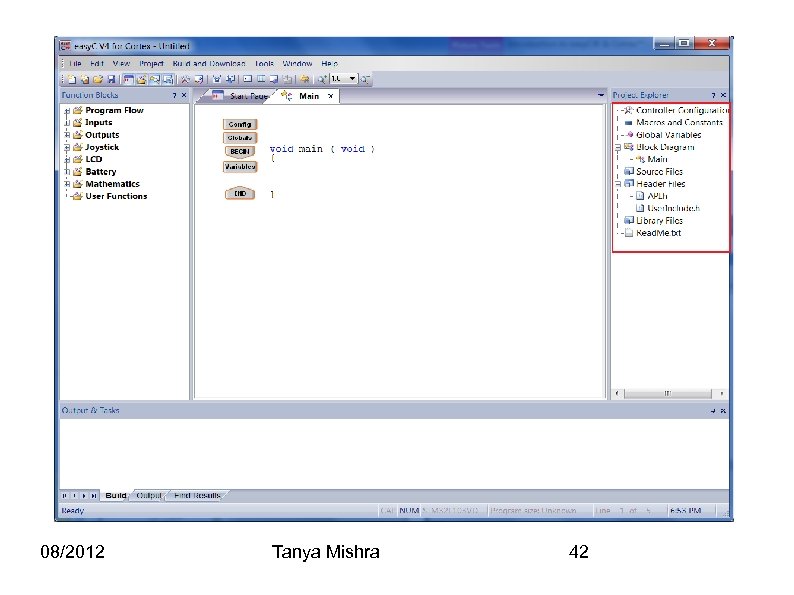
08/2012 Tanya Mishra 42

1. Function Block(Left): You can all the available functions and your project file information. 2. Main (Middle): Drag and Drop the functions here to see how they connect and get a visual look for the code. All You need to work with is the area between “Variables” and “End”. 3. Project Pane (Right) : See your project files and other files. 4. Build information (Bottom) : See any code building information here. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 43
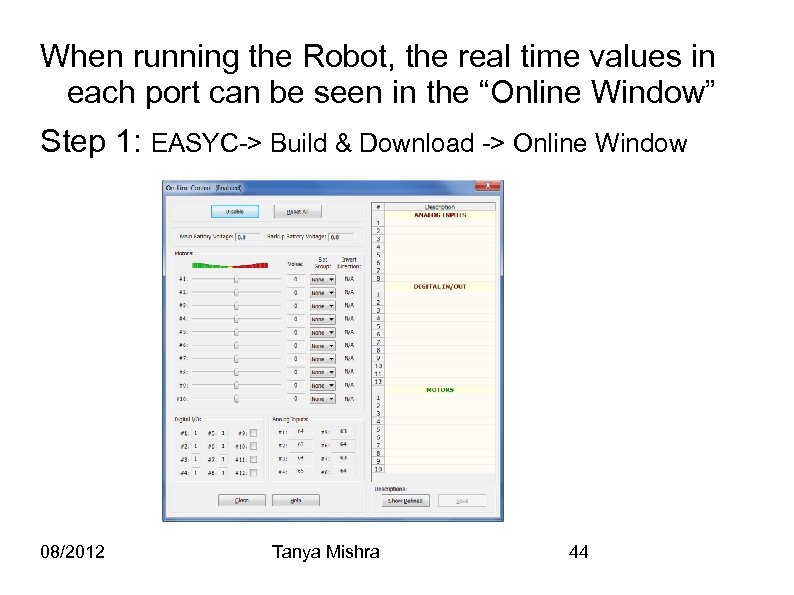
When running the Robot, the real time values in each port can be seen in the “Online Window” Step 1: EASYC-> Build & Download -> Online Window 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 44
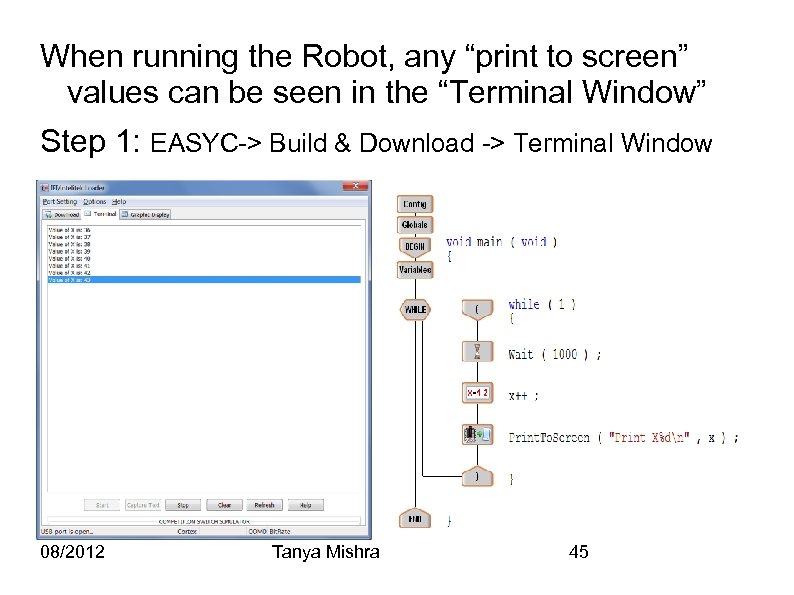
When running the Robot, any “print to screen” values can be seen in the “Terminal Window” Step 1: EASYC-> Build & Download -> Terminal Window 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 45
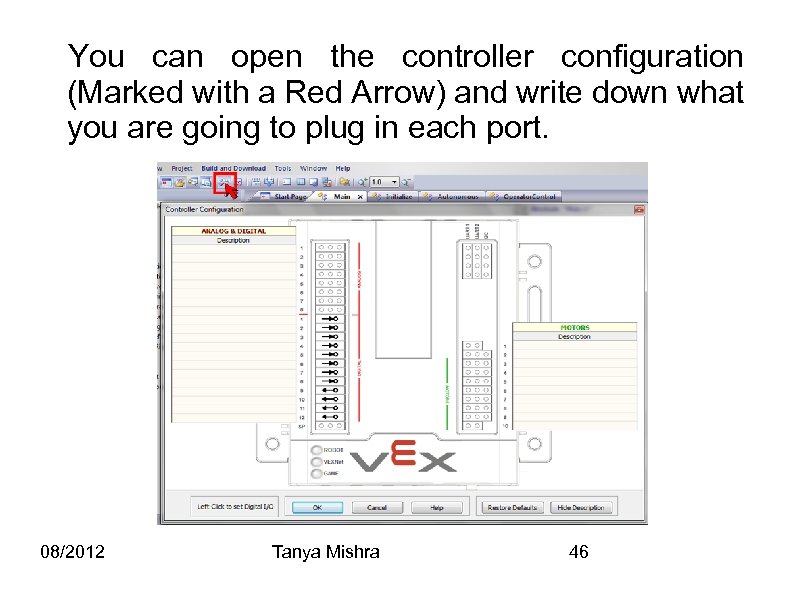
You can open the controller configuration (Marked with a Red Arrow) and write down what you are going to plug in each port. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 46

VEX Cortex Controller The VEX Cortex Micro controller has the following ports: 6 Interrupt ports Tanya Mishra 12 Digital ports 08/2012 8 Analog ports 8 Motor ports 47

VEX Remote Controller Vex Remote control provides you with two joysticks (each having a x- axis and y-axis), eight buttons on the front and four additional buttons on the top. 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 48

Each set of buttons or a pair of joystick has an assigned channel number written next to it as shown in the figure. Each of these controls are accessed using the channel number they belong to. 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 49
Incorporating C Programming baics in EASYC We start by placing the needed module between the “Variables” and “End” modules. Creating a “While” loop: Step 1: Click the “+” sign next to the Program Flow on your Function Panel (Left) Step 2: Click and drag the “While loop” on to the Main panel (Middle) and place it between the two modules you need it to. 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 50
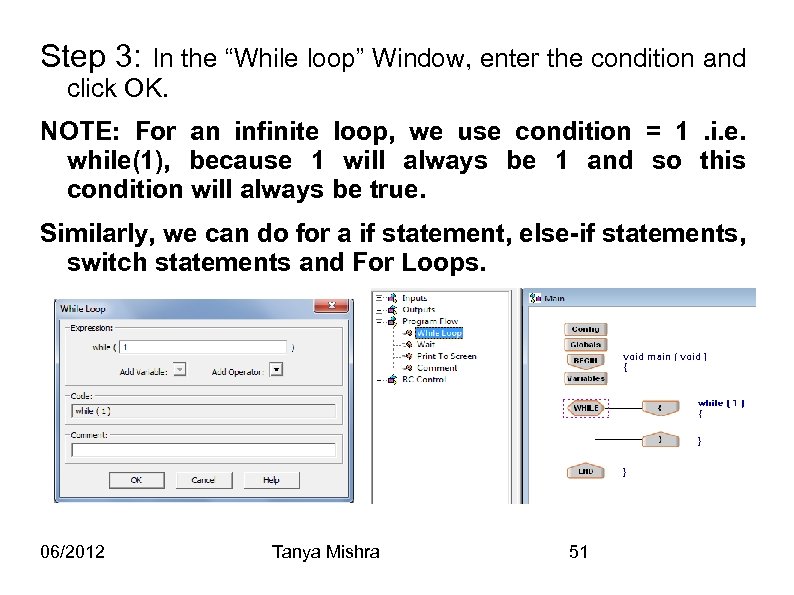
Step 3: In the “While loop” Window, enter the condition and click OK. NOTE: For an infinite loop, we use condition = 1. i. e. while(1), because 1 will always be 1 and so this condition will always be true. Similarly, we can do for a if statement, else-if statements, switch statements and For Loops. 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 51
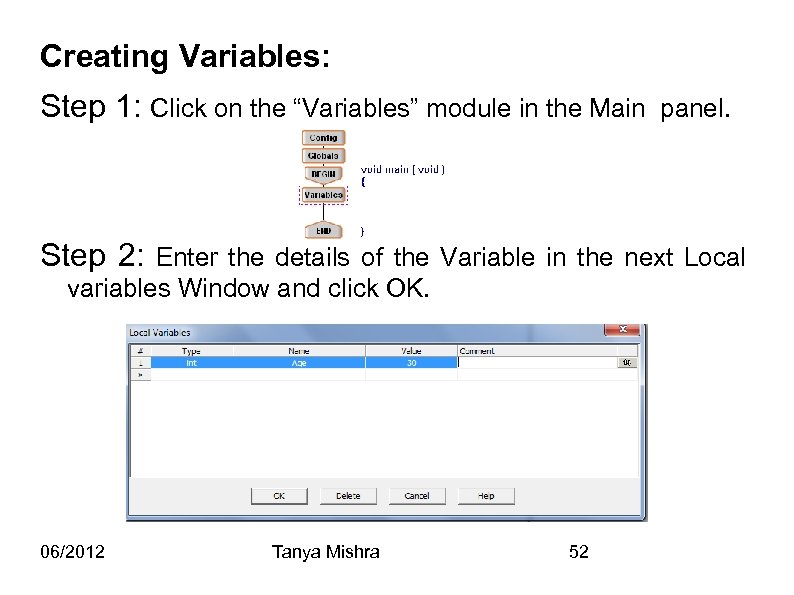
Creating Variables: Step 1: Click on the “Variables” module in the Main panel. Step 2: Enter the details of the Variable in the next Local variables Window and click OK. 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 52
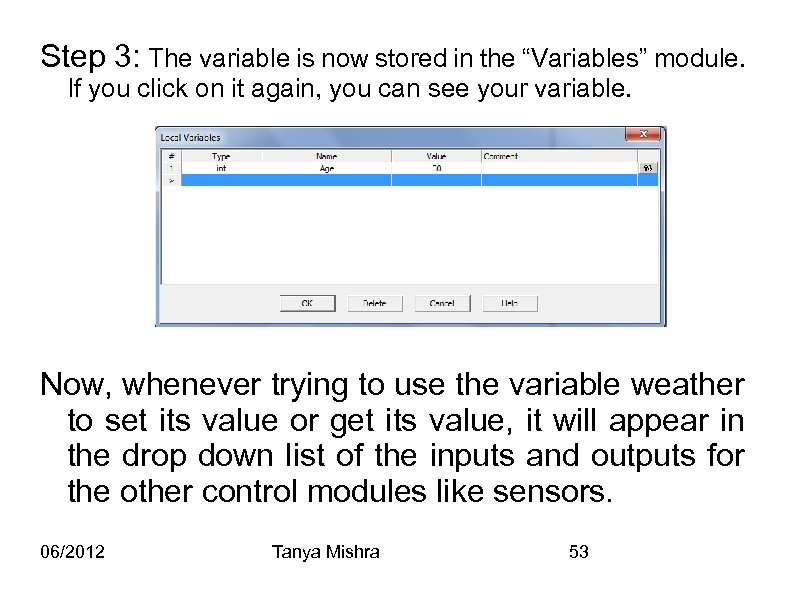
Step 3: The variable is now stored in the “Variables” module. If you click on it again, you can see your variable. Now, whenever trying to use the variable weather to set its value or get its value, it will appear in the drop down list of the inputs and outputs for the other control modules like sensors. 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 53
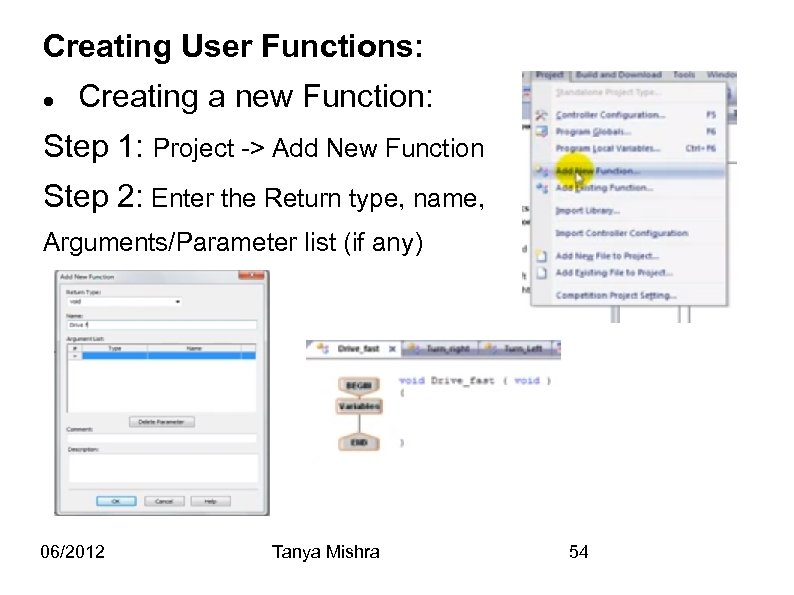
Creating User Functions: Creating a new Function: Step 1: Project -> Add New Function Step 2: Enter the Return type, name, Arguments/Parameter list (if any) 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 54
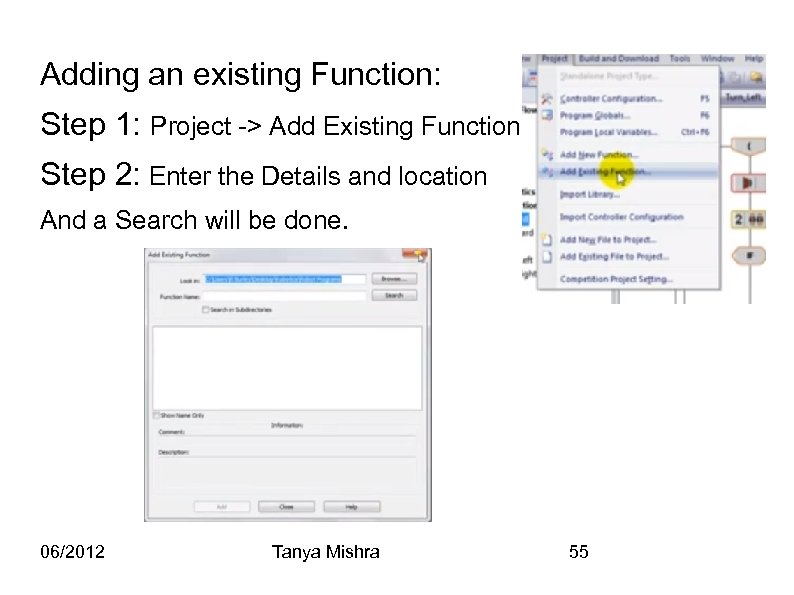
Adding an existing Function: Step 1: Project -> Add Existing Function Step 2: Enter the Details and location And a Search will be done. 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 55
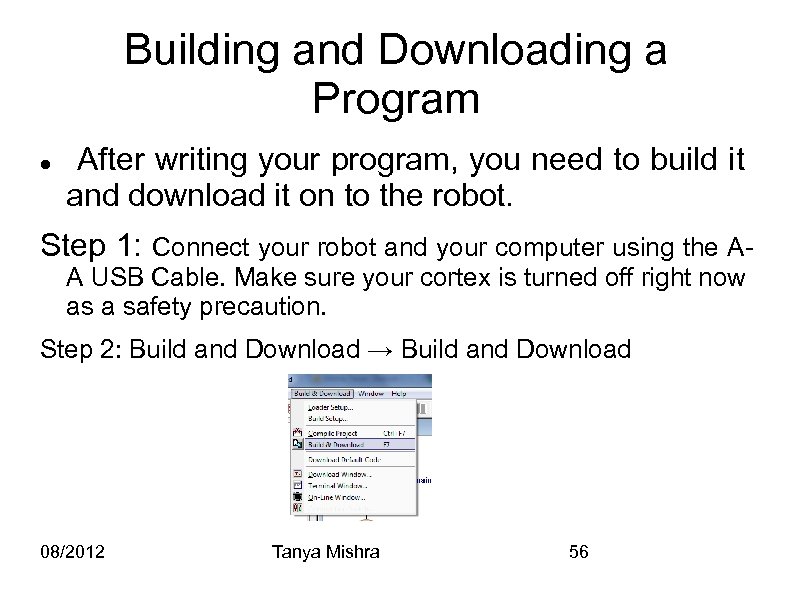
Building and Downloading a Program After writing your program, you need to build it and download it on to the robot. Step 1: Connect your robot and your computer using the AA USB Cable. Make sure your cortex is turned off right now as a safety precaution. Step 2: Build and Download → Build and Download 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 56

Step 3: Click “Yes” on the Hex file build successful message window and your code will be downloaded. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 57

Drives Simple Tank Drive involves the use of both joysticks. Step 1: Click the “+” next to the Joystick Module in the Left Pane and drop Tank- 2 Motor in the Middle Pane. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 58
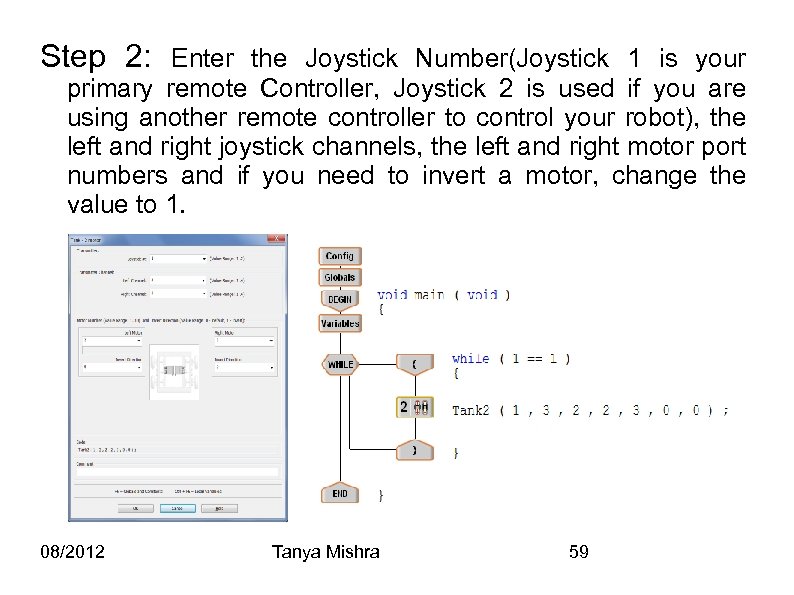
Step 2: Enter the Joystick Number(Joystick 1 is your primary remote Controller, Joystick 2 is used if you are using another remote controller to control your robot), the left and right joystick channels, the left and right motor port numbers and if you need to invert a motor, change the value to 1. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 59

Simple Arcade Drive uses one joystick to drive the robot. Step 1: Click the “+” next to the Joystick Module in the Left Pane and drop Arcade – 2 Motor in the Middle Pane. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 60
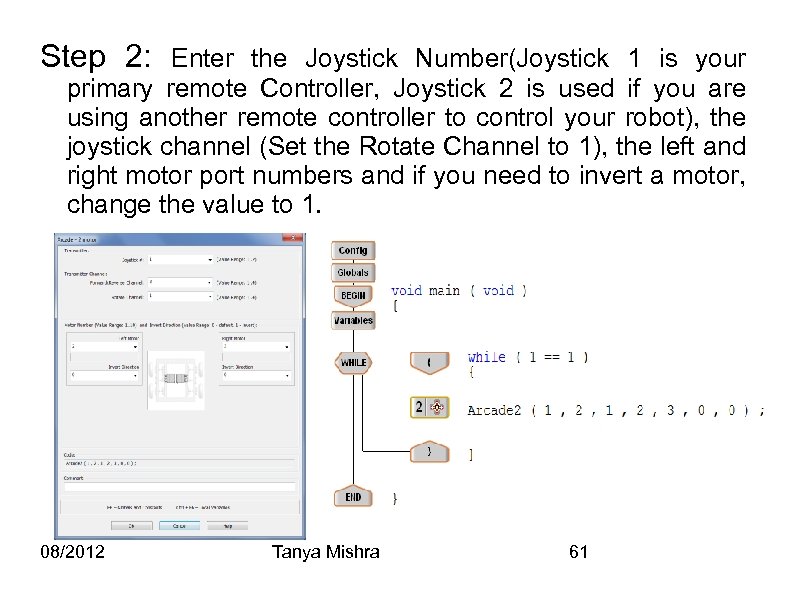
Step 2: Enter the Joystick Number(Joystick 1 is your primary remote Controller, Joystick 2 is used if you are using another remote controller to control your robot), the joystick channel (Set the Rotate Channel to 1), the left and right motor port numbers and if you need to invert a motor, change the value to 1. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 61
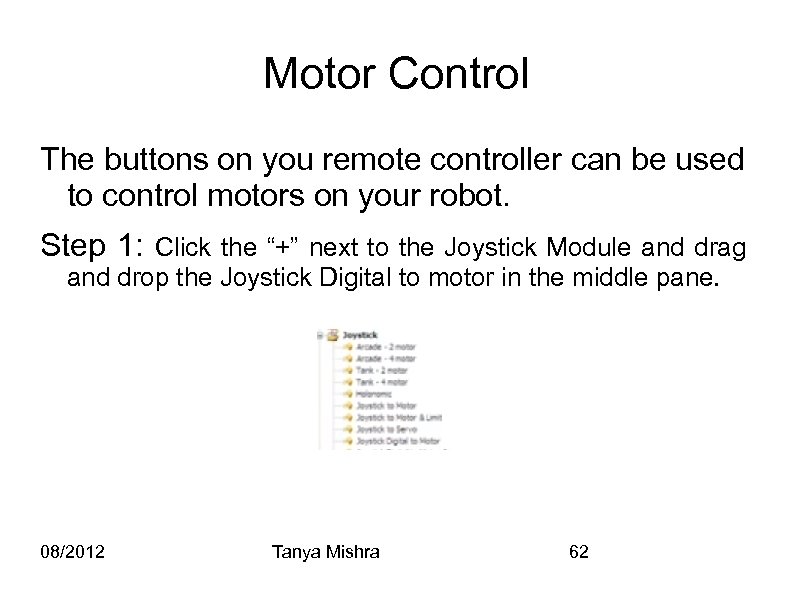
Motor Control The buttons on you remote controller can be used to control motors on your robot. Step 1: Click the “+” next to the Joystick Module and drag and drop the Joystick Digital to motor in the middle pane. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 62
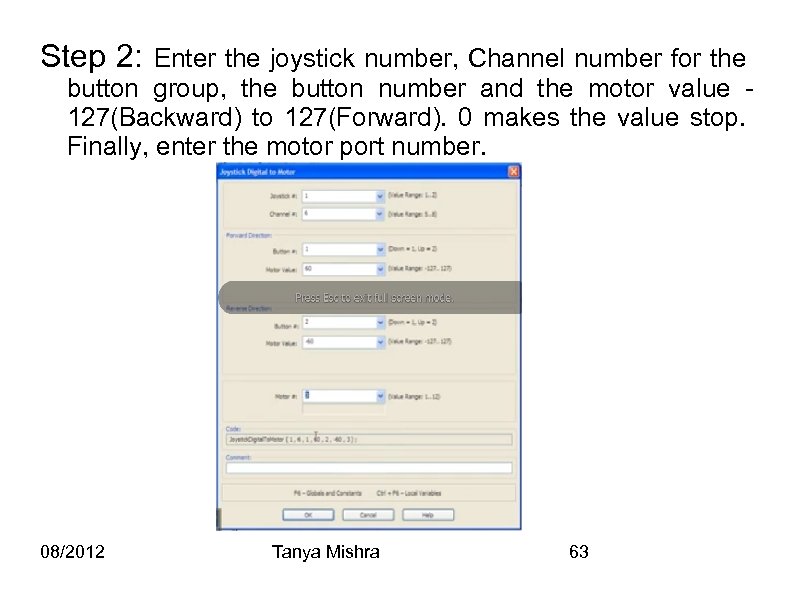
Step 2: Enter the joystick number, Channel number for the button group, the button number and the motor value 127(Backward) to 127(Forward). 0 makes the value stop. Finally, enter the motor port number. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 63
Turning of Motors Assigning Positive power Values(127) on both motors makes the robot go forward. Lower speed of robot by assigning values less than full power(127). Assigning negative power values(-127) on both motors makes the robot go reverse. Assigning zero power values(0) on both motors makes the robot stay in place. 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 64
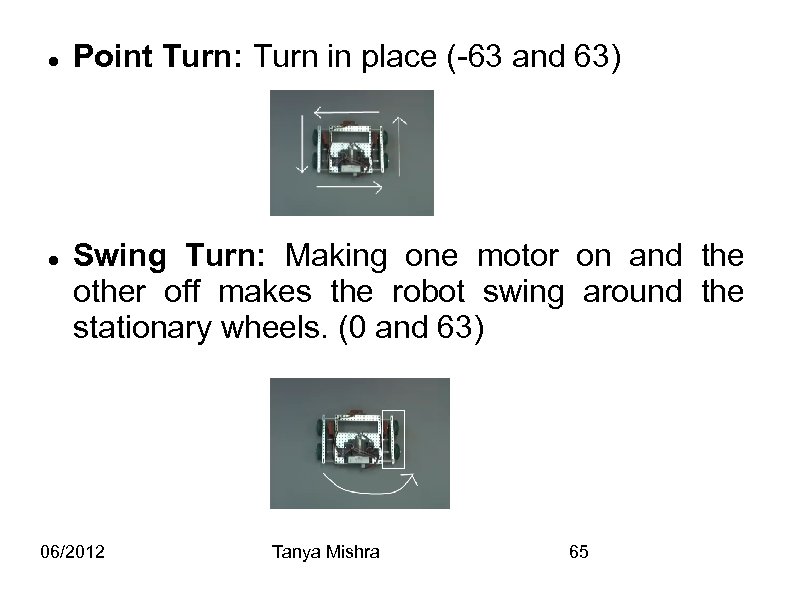
Point Turn: Turn in place (-63 and 63) Swing Turn: Making one motor on and the other off makes the robot swing around the stationary wheels. (0 and 63) 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 65
Shaft Encoders/Rotation Sensor Manual adjustments of power are not same for all robots and as the battery power drains, the robot is move shorter distances. Shaft Encoders are used to control how far the Robot Moves. Number of counts per Revolution on a axle mounted through the encoder center. Max 360 up forward movements and 360 down for reverse movements. 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 66
Encoders need to be set to zero before you use them. Clear the encoders for better consistency and precision on your robots movements. Step 1: You can find the Quadrature encoder modules by clicking the “+” next to the inputs modules in the left panel. 06/2012 Tanya Mishra 67

The corresponding text functions Quadrature modules are as follows: for the Start the Encoder: Start. Quad. Encoder(port number) It is good practice to preset the value of encoder to 0 before use. Preset. Quad. Encoder(port number, 0) Get the number of ticks passed: ticks = Get. Quad. Encoder(port number) 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 68
Limit Switch is a Digital Sensor(0 and 1) When pressed, it provides a sensor value 1, when released, it provides a sensor value 0. Step 1: The limit switch module is in the Inputs modules in the left panel. ? ? = Get. Digital. Input(port number) 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 69
Potentiometers: A potentiometer is a Analog Sensor. It measures rotation between 0 to 250 (not 360 due to internal mechanical stops) degrees and return value ranging from 0 to approximately 4095. ? ? = Get. Analog. Input(port number) 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 70
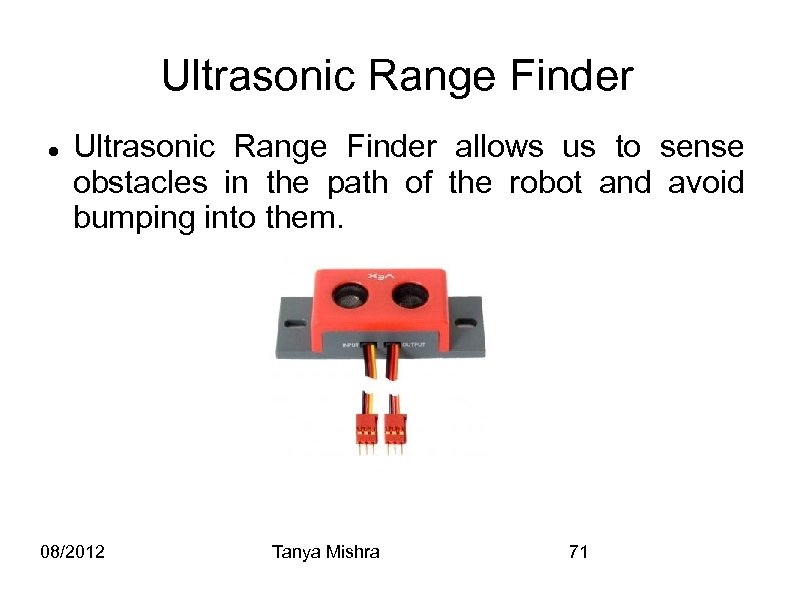
Ultrasonic Range Finder allows us to sense obstacles in the path of the robot and avoid bumping into them. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 71

It measures distance to the obstacle using sound waves. It calculates the Distance depending on how long it takes for the sound wave to bounce back. Distance = Speed * Time / 2 Step 1: Click the “+” next to the inputs and drag and drop the Ultrasonic sensor in the middle panel. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 72
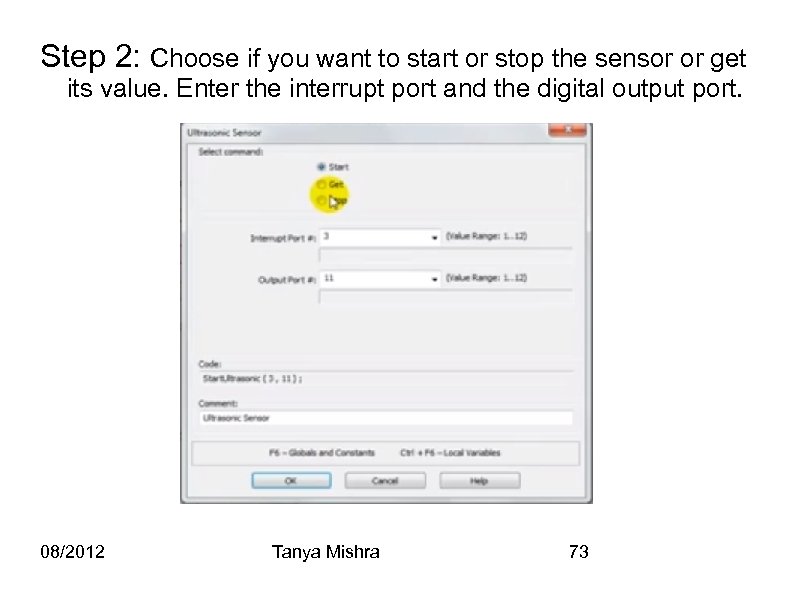
Step 2: Choose if you want to start or stop the sensor or get its value. Enter the interrupt port and the digital output port. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 73
The corressponding text functions will be as follows: Start. Ultrasonic(interrupt port numer, digital port number) ? ? = Get. Ultrasonic((interrupt port numer, digital port number) 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 74
Timers Timers are like “Stopwatches”. Used in competition to know how long the robot has been working. You have access to 6 software Timers. The time is in Microseconds (1 sec = 1000 ms) Step 1: Click the “+” next to the Program Flow module and drag and drop the Timer module. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 75

Step 2: Choose if you want to start, preset, get a value or stop the Timer. It is a good practice to Clear the Timer before use. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 76
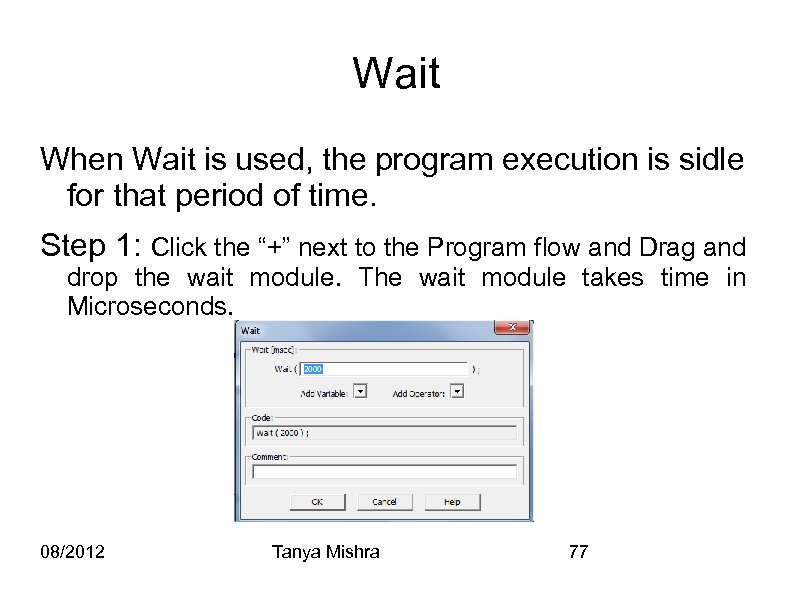
Wait When Wait is used, the program execution is sidle for that period of time. Step 1: Click the “+” next to the Program flow and Drag and drop the wait module. The wait module takes time in Microseconds. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 77
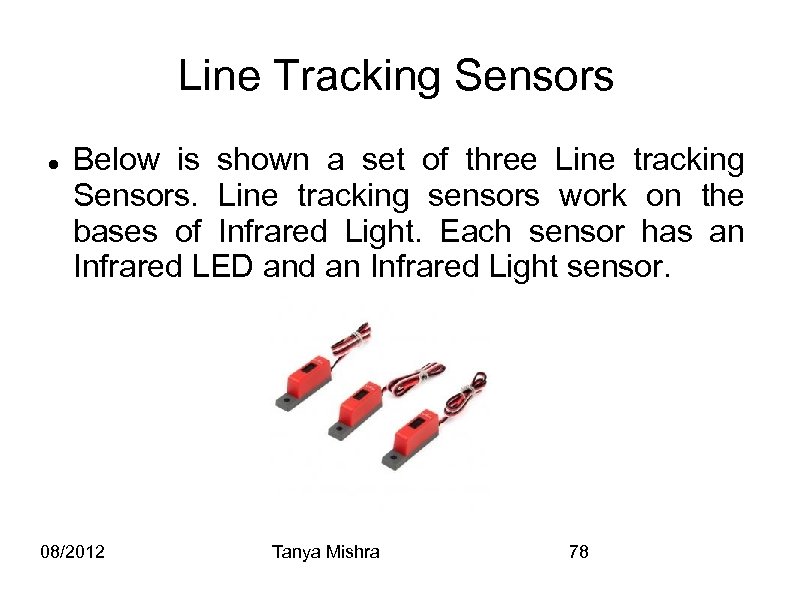
Line Tracking Sensors Below is shown a set of three Line tracking Sensors. Line tracking sensors work on the bases of Infrared Light. Each sensor has an Infrared LED and an Infrared Light sensor. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 78
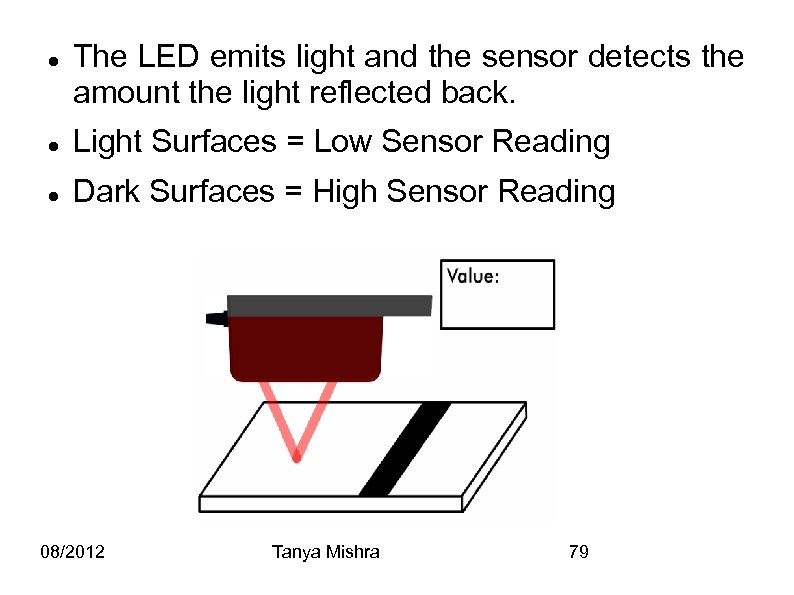
The LED emits light and the sensor detects the amount the light reflected back. Light Surfaces = Low Sensor Reading Dark Surfaces = High Sensor Reading 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 79
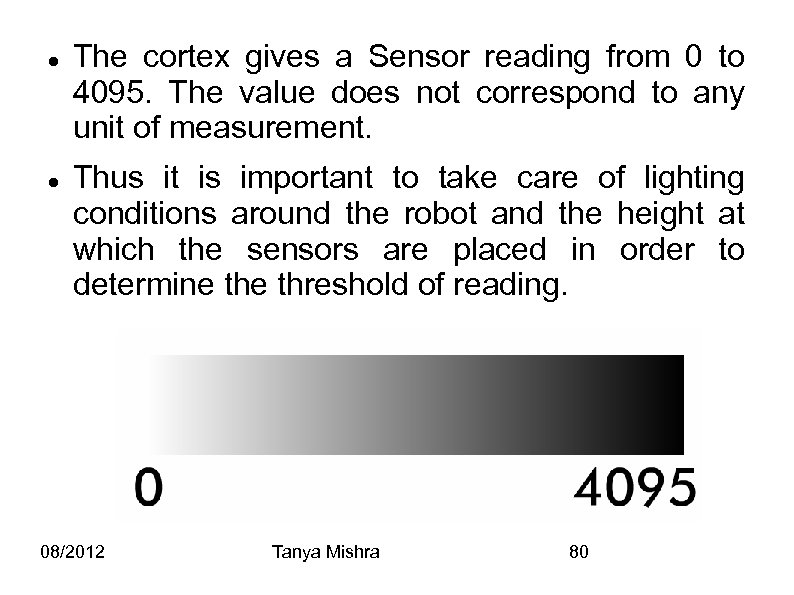
The cortex gives a Sensor reading from 0 to 4095. The value does not correspond to any unit of measurement. Thus it is important to take care of lighting conditions around the robot and the height at which the sensors are placed in order to determine threshold of reading. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 80
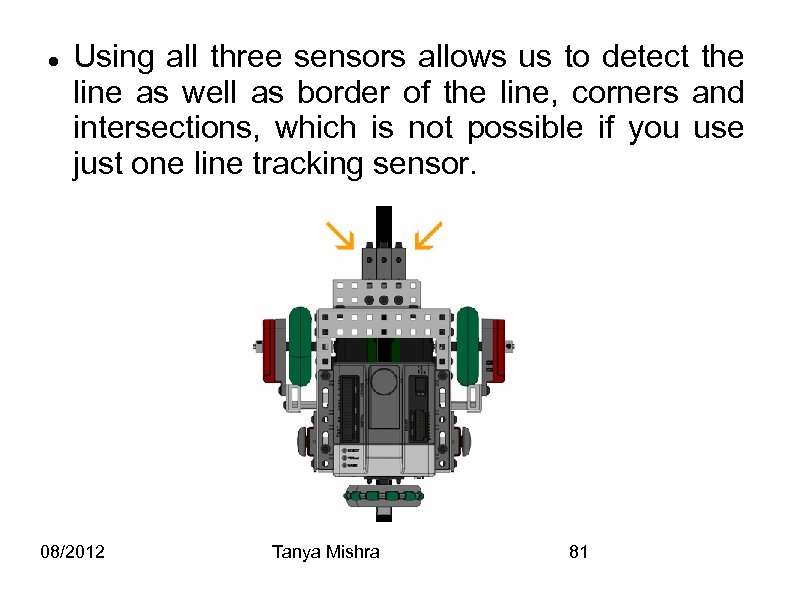
Using all three sensors allows us to detect the line as well as border of the line, corners and intersections, which is not possible if you use just one line tracking sensor. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 81

Step 1: The Line tracking Module is present in the Input modules in the Left panel. Set the Analog Input and retrieve the value returned by the Line follower. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 82

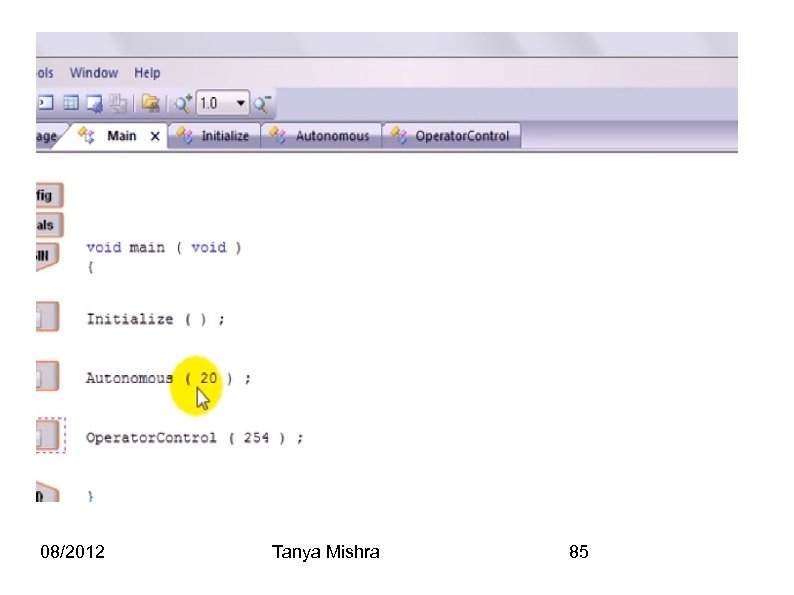
Create Competition Code Step 1: File->New Competition Project->Timed Competition Project 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 83

The Autonomous Time and operator controlled time are in seconds. Each define the number of seconds the Autonomous code and the Operator control will run for. Put down your autonomous and operator controlled code in the corresponding file modules. You can also change the running times for the autonomous and operator control mode by clicking on the modules. 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 84
08/2012 Tanya Mishra 85

That's all for Easy. C for Cortex programming. Thank you! 08/2012 Tanya Mishra 86
c560595687a792feb31d8ff325c89f57.ppt