0f7f44d2d12d8fd7c7a50c2dfb575843.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Earth Sciences Division European Contribution to the Global Precipitation Mission (EGPM) A new ESA Earth Explorer Opportunity Mission Paul Ingmann and Pedro Baptista Earth Sciences Division ESA/ESTEC Noordwijk/NL 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002

The Elements of ESA’s EO Programme • Earth Sciences Division Individual Optional Missions Ø METEOSAT and METEOSAT Second Generation (MSG) - with EUMETSAT Ø ERS-2 Ø ENVISAT Ø METOP - with EUMETSAT • Covered by the Earth Observation Envelope Programme Ø Earth Explorer and Earth Watch Missions 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
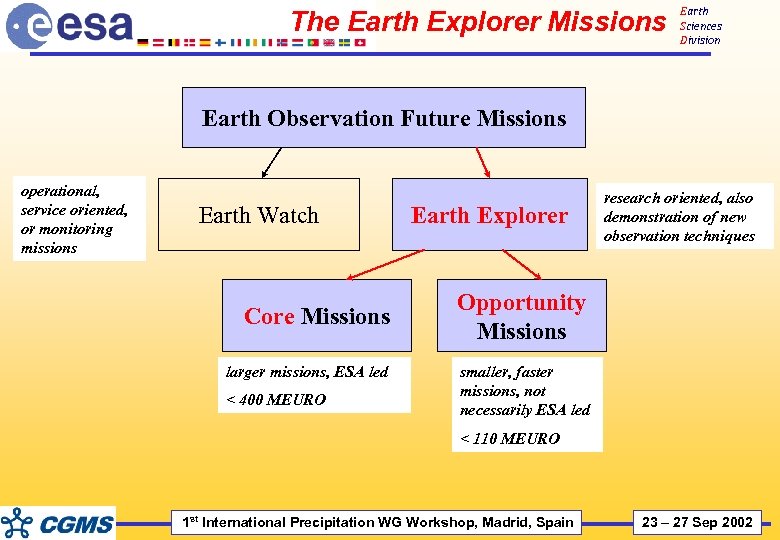
The Earth Explorer Missions Earth Sciences Division Earth Observation Future Missions operational, service oriented, or monitoring missions Earth Watch Core Missions larger missions, ESA led < 400 MEURO Earth Explorer research oriented, also demonstration of new observation techniques Opportunity Missions smaller, faster missions, not necessarily ESA led < 110 MEURO 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002

Current Situation of the Earth Explorer Missions. Earth Sciences Division GOCE CRYOSAT ADM/Aeolus SMOS Phases C/D/E 1 started Launch 2006 Phases C/D/E 1 started Launch 2004 Lidar pre-development on-going Phase B started in July 2002 Launch 2007 Extended Phase A ongoing Launch 2005 Opportunity-1 Core-2 Opportunity-2 Core-1 Ø Homepage: http: //www. esa. int/livingplanet 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002

Earth Sciences Division The Earth Explorer Core Missions: 2 nd Cycle è Three Earth Explorer Core Mission Concepts selected for Phase A study: • Earth. CARE – Earth clouds aerosol and radiation explorer • SPECTRA – surface processes and ecosystems changes through response analysis • WALES - water vapour lidar experiment in space 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002

The Earth Explorer Core Missions Earth Sciences Division Earth. CARE Science Objectives Earth. CARE has been specifically defined with the scientific objectives of determining for the first time, in a radiatively consistent manner, the global distribution of vertical profiles of cloud and aerosol field characteristics to provide basic essential input data for numerical modelling and global studies of: • divergence of radiative energy, • aerosol-cloud-radiation interaction, • vertical distribution of water and ice and their transport by clouds, • the vertical cloud field overlap and cloud-precipitation interactions. Core elements: cloud radar, backscatter lidar plus MSI, BBR, FTS 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
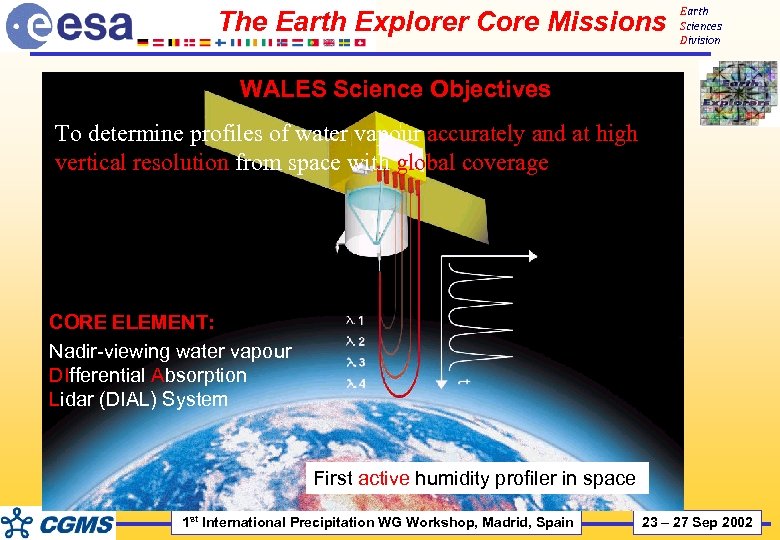
The Earth Explorer Core Missions Earth Sciences Division WALES Science Objectives To determine profiles of water vapour accurately and at high vertical resolution from space with global coverage CORE ELEMENT: Nadir-viewing water vapour DIfferential Absorption Lidar (DIAL) System First active humidity profiler in space 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
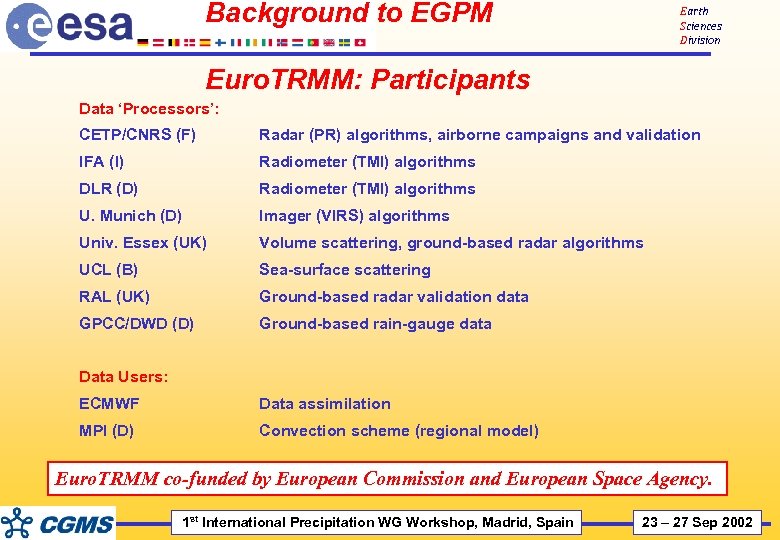
Background to EGPM Earth Sciences Division Euro. TRMM: Participants Data ‘Processors’: CETP/CNRS (F) Radar (PR) algorithms, airborne campaigns and validation IFA (I) Radiometer (TMI) algorithms DLR (D) Radiometer (TMI) algorithms U. Munich (D) Imager (VIRS) algorithms Univ. Essex (UK) Volume scattering, ground-based radar algorithms UCL (B) Sea-surface scattering RAL (UK) Ground-based radar validation data GPCC/DWD (D) Ground-based rain-gauge data Data Users: ECMWF Data assimilation MPI (D) Convection scheme (regional model) Euro. TRMM co-funded by European Commission and European Space Agency. 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
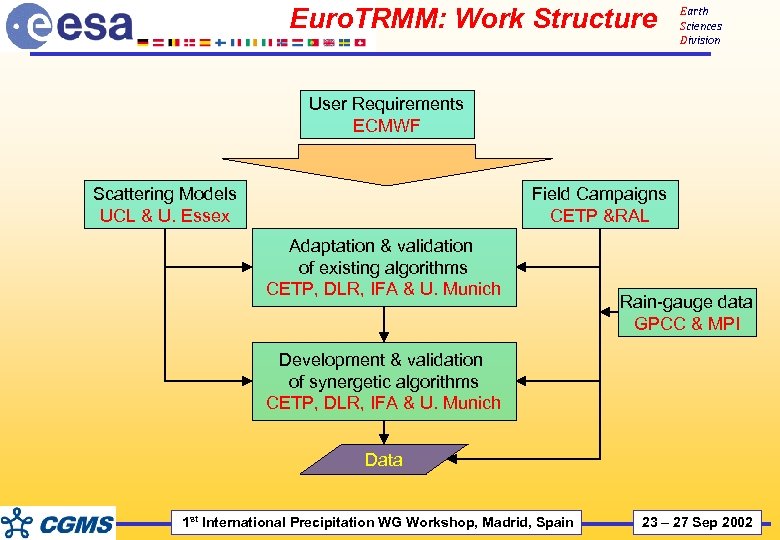
Euro. TRMM: Work Structure Earth Sciences Division User Requirements ECMWF Scattering Models UCL & U. Essex Field Campaigns CETP &RAL Adaptation & validation of existing algorithms CETP, DLR, IFA & U. Munich Rain-gauge data GPCC & MPI Development & validation of synergetic algorithms CETP, DLR, IFA & U. Munich Data 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
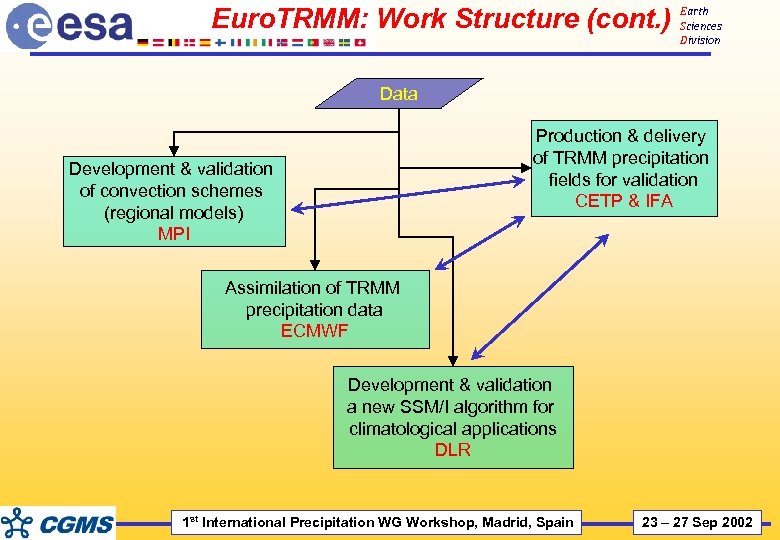
Euro. TRMM: Work Structure (cont. ) Earth Sciences Division Data Production & delivery of TRMM precipitation fields for validation CETP & IFA Development & validation of convection schemes (regional models) MPI Assimilation of TRMM precipitation data ECMWF Development & validation a new SSM/I algorithm for climatological applications DLR 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
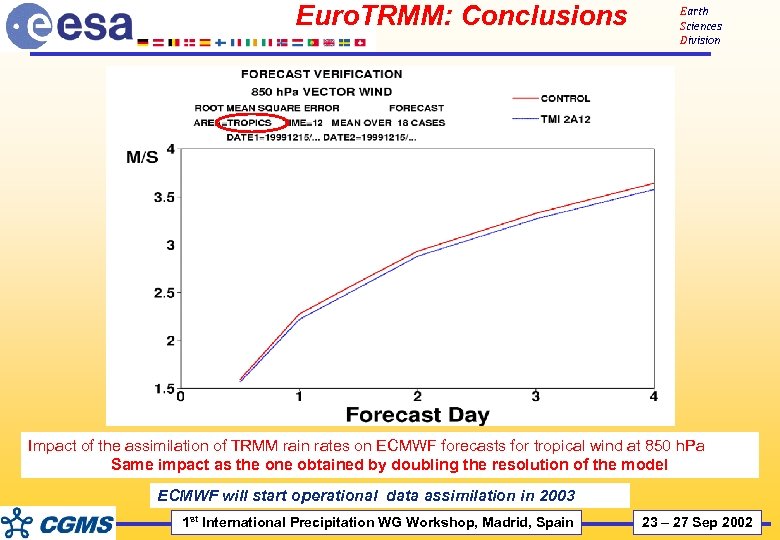
Euro. TRMM: Conclusions Earth Sciences Division Impact of the assimilation of TRMM rain rates on ECMWF forecasts for tropical wind at 850 h. Pa Same impact as the one obtained by doubling the resolution of the model ECMWF will start operational data assimilation in 2003 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002

Earth Sciences Division EGPM and Euro. TRMM • Euro. TRMM has proven very useful for the exploitation of TRMM data • Euro. TRMM has been an essential building block in preparation of EGPM • Members of Euro. TRMM team proposed EGPM to ESA • Key members of Euro. TRMM are also members of the EGPM-MAG èEnsures continuity 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002

The Earth Explorer Opportunity Missions Earth Sciences Division Earth Explorer Opportunity Missions: 2 nd Cycle è 25 Earth Explorer Opportunity Mission Concepts submitted (by early 2002) Addressing all Earth science disciplines including atmospheric chemistry, physics, land, ocean/ice. Evaluation on-going – final scientific recommendation by the ESAC. 3 missions recommended for Phase A study: 1. 2. 3. ACE+ - radio occultation constellation mission EGPM – European contribution to GPM SWARM – magnetosphere mission 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002

The Earth Explorer Opportunity Missions Earth Sciences Division EEOM - Assessment of EGPM • Availability of fresh water is so dominant for human development. • Mission is a major European contribution to the Global Precipitation Mission (GPM). • EGPM features additional deliverables that are needed at high latitudes (such as Europe and Canada); achieved by extending the microwave radiometer measurements to higher frequencies ensuring the capability to measure snowfall. • As an option, a 36 GHz radar to improve the accuracy of the precipitation retrieved from the microwave radiometer is considered. 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002

The Earth Explorer Opportunity Missions Earth Sciences Division The EGPM-MAG - Members • • EOEP – user driven programme Missions supported by mission advisory groups (MAGs) 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
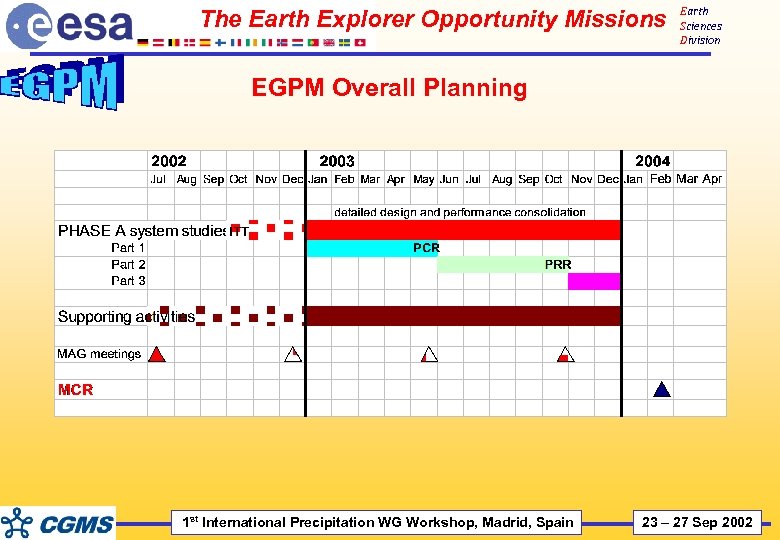
The Earth Explorer Opportunity Missions Earth Sciences Division EGPM Overall Planning 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
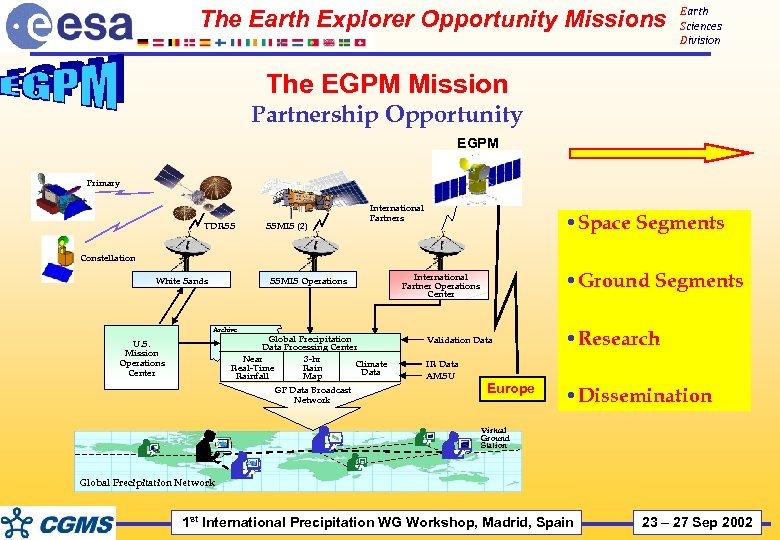
The Earth Explorer Opportunity Missions Earth Sciences Division The EGPM Mission Partnership Opportunity EGPM Primary TDRSS SSMIS (2) International Partners • Space Segments Constellation White Sands SSMIS Operations • Ground Segments International Partner Operations Center Archive Global Precipitation Data Processing Center Near 3 -hr Climate Real-Time Rain Data Rainfall Map U. S. Mission Operations Center GP Data Broadcast Network Validation Data IR Data AMSU Europe • Research • Dissemination Virtual Ground Station Global Precipitation Network 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
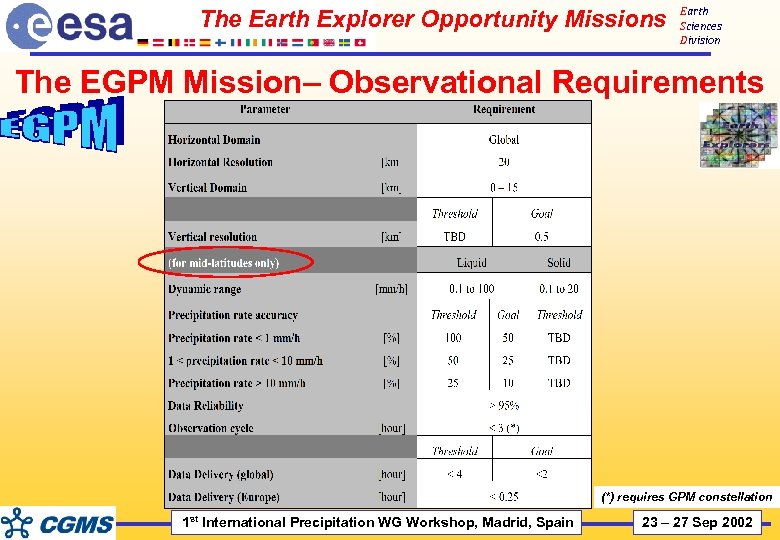
The Earth Explorer Opportunity Missions Earth Sciences Division The EGPM Mission– Observational Requirements (*) requires GPM constellation 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002

The Earth Explorer Opportunity Missions Earth Sciences Division The EGPM Mission - Data Users Three different classes of users can be identified: Ø Near-real-time users (‘nowcasting’) Ø Operational meteorology users Ø Research oriented users • The first group requires delivery within 15 minutes for issuing e. g. warnings (raw data dumps, Level 0) • The second group for operational applications require the Level 1 b data product in near real-time (< 4 hrs after the observation) throughout the mission • For research applications, any processing level may be required, from level 0 data to Level 2 – strong link to other GPM partners. Level 0 and Level 1 b data products should be archived for 10 years (or more) to allow re-analysis. Data should be available to the international scientific user community on request. 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002

The Earth Explorer Opportunity Missions Earth Sciences Division EGPM System – Observation Requirements • Sun-synchronous orbit Equator crossing time 14: 30 LST (TBC) • Global coverage (tropical to polar while focus on mid-latitudes) • Altitude 635 km (passive only) or 510 km (passive and active) (TBC) • Coverage to be optimised for Europe (in space and time) • Instrument foot prints and allowed horizontal integration length are assumed to satisfy the mission requirements (coverage, spatial and temporal resolution) • Only a posteriori geo-location, horizontal location error better than 2 km (TBC) • 3 years mission duration; satellite designed for a lifetime of 5 yrs • Launch date 2008 -2012 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
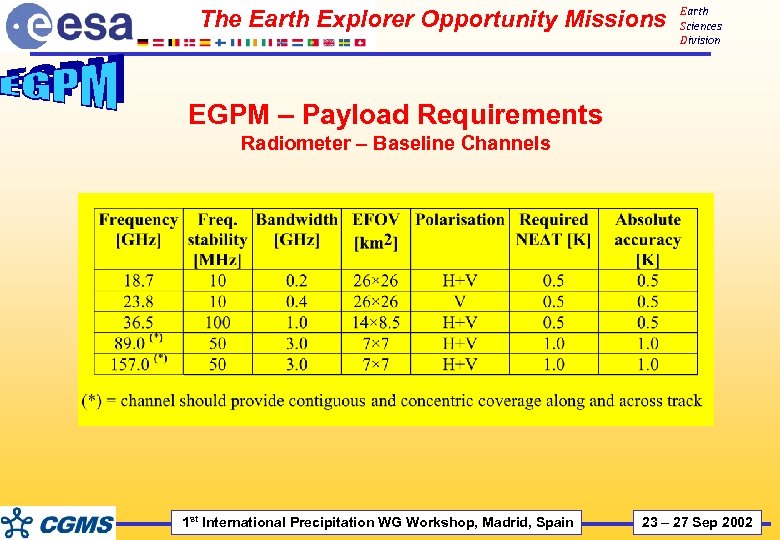
The Earth Explorer Opportunity Missions Earth Sciences Division EGPM – Payload Requirements Radiometer – Baseline Channels 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
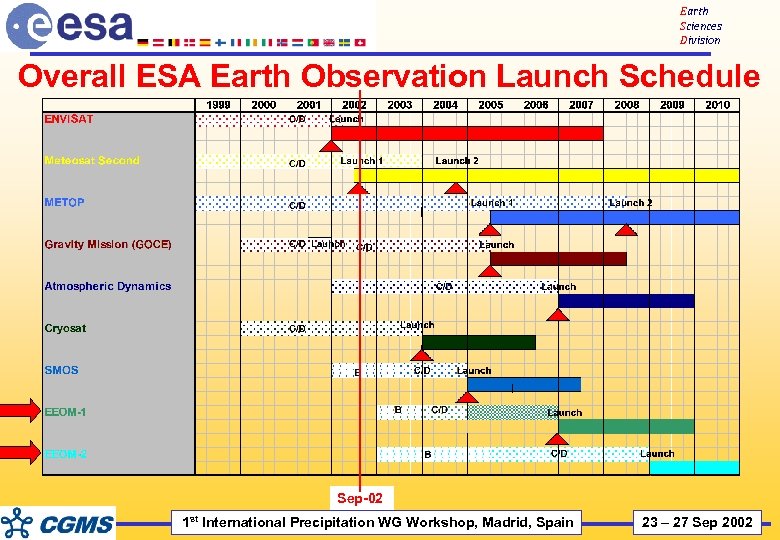
Earth Sciences Division Overall ESA Earth Observation Launch Schedule Sep-02 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
Earth Sciences Division Conclusions • • Major contribution to ‘precipitation’ from EGPM, one of the forthcoming Earth Explorer missions Other missions in preparation by ESA in the context of the Earth Explorers providing relevant observations also getting implemented: è The Atmospheric Dynamics Mission (for transports) - Core mission è CRYOSAT (polar ice thickness) - Opportunity mission è SMOS (soil moisture and ocean salinity) - Opportunity mission Plus two of the three candidate Earth Explorer Core missions, Earth. CARE and WALES. (ESA Earth Observation WEB Portal - http: //www. esa. int/livingplanet) 1 st International Precipitation WG Workshop, Madrid, Spain 23 – 27 Sep 2002
0f7f44d2d12d8fd7c7a50c2dfb575843.ppt