10751817c6922aa8462aaa3f3bc36c65.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 EARTH SCIENCE Introduction Unit
EARTH SCIENCE Introduction Unit
 Day 1 • OBJECTIVE I can describe how Earth and Environmental Science is organized.
Day 1 • OBJECTIVE I can describe how Earth and Environmental Science is organized.
 WHAT IS SCIENCE? • System of knowledge • Methods used to find that Knowledge • Begins with curiosity • Ends with Discovery
WHAT IS SCIENCE? • System of knowledge • Methods used to find that Knowledge • Begins with curiosity • Ends with Discovery
 What is EARTH SCIENCE? • Name for the group of sciences that deals with the Earth and its neighbors in space
What is EARTH SCIENCE? • Name for the group of sciences that deals with the Earth and its neighbors in space
 Earth Science Areas of Study A. Astronomy B. Meteorology Study of objects past the atmosphere Ex: Stars, moon, comets Study of the atmosphere Processes of weather and climate Ex: clouds, rain, hurricanes C. Geology D. Oceanography Study of materials that make-up the Earth Processes that form and change those materials Ex: rocks, minerals, earthquakes, volcanoes Study of the oceans Ex: trenches, marine animals
Earth Science Areas of Study A. Astronomy B. Meteorology Study of objects past the atmosphere Ex: Stars, moon, comets Study of the atmosphere Processes of weather and climate Ex: clouds, rain, hurricanes C. Geology D. Oceanography Study of materials that make-up the Earth Processes that form and change those materials Ex: rocks, minerals, earthquakes, volcanoes Study of the oceans Ex: trenches, marine animals
 Earth’s Major Spheres/Systems A. Hydrosphere v All water on Earth v Oceans, rivers, streams, lakes & seas v 97% of the water is salt water v 3% of water is freshwater B. Atmosphere v Gaseous layers above the surface of Earth v Weather and Climate on Earth v Makes life possible on Earth
Earth’s Major Spheres/Systems A. Hydrosphere v All water on Earth v Oceans, rivers, streams, lakes & seas v 97% of the water is salt water v 3% of water is freshwater B. Atmosphere v Gaseous layers above the surface of Earth v Weather and Climate on Earth v Makes life possible on Earth
 C. Geosphere/Lithosphere v Beneath both the Hydrosphere and Atmosphere v Three Parts § Core § Mantle § Crust D. Biosphere v All organisms on Earth v Environments where organisms live
C. Geosphere/Lithosphere v Beneath both the Hydrosphere and Atmosphere v Three Parts § Core § Mantle § Crust D. Biosphere v All organisms on Earth v Environments where organisms live
 What is Environmental Science? • The study of how humans use resources and the affect it has on the Earth
What is Environmental Science? • The study of how humans use resources and the affect it has on the Earth
 What Environmental Science deals with? • Renewable Resources – Plants, animals, water, wind • Nonrenewable Resources – Coal, oil, natural gas • Population Growth • Environmental Problems – Pollution, global warming • Natural Hazards – Flooding, droughts, earthquakes
What Environmental Science deals with? • Renewable Resources – Plants, animals, water, wind • Nonrenewable Resources – Coal, oil, natural gas • Population Growth • Environmental Problems – Pollution, global warming • Natural Hazards – Flooding, droughts, earthquakes
 Day 2 • Objective – I can explain why scientists do experiments – I can explain how to perform experiments
Day 2 • Objective – I can explain why scientists do experiments – I can explain how to perform experiments
 Scientific Method • An organized plan for gathering, organizing and communication of information • GOAL – Solve a problem – Better understand something
Scientific Method • An organized plan for gathering, organizing and communication of information • GOAL – Solve a problem – Better understand something
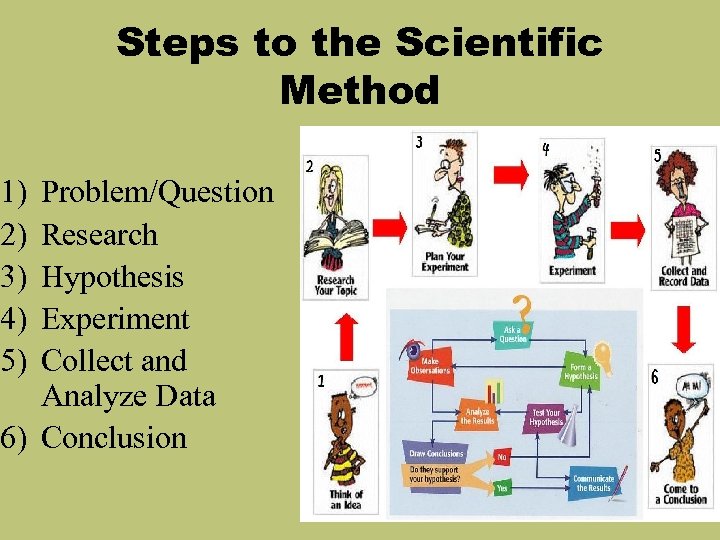 Steps to the Scientific Method 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Problem/Question Research Hypothesis Experiment Collect and Analyze Data 6) Conclusion
Steps to the Scientific Method 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Problem/Question Research Hypothesis Experiment Collect and Analyze Data 6) Conclusion
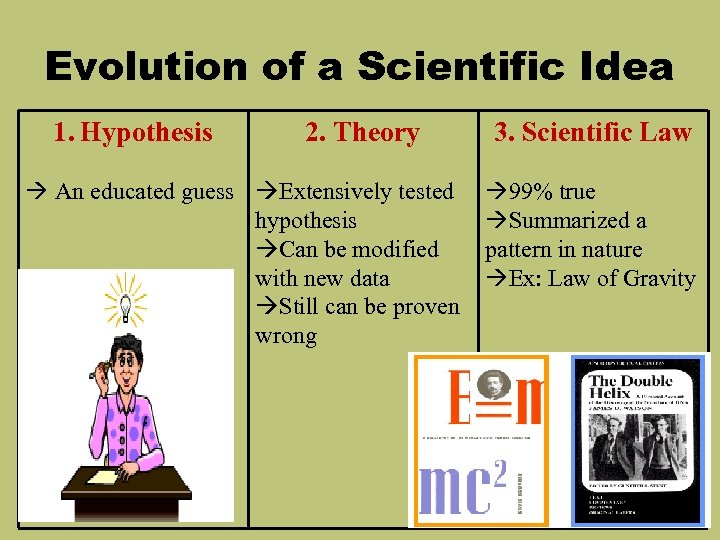 Evolution of a Scientific Idea 1. Hypothesis 2. Theory An educated guess Extensively tested hypothesis Can be modified with new data Still can be proven wrong 3. Scientific Law 99% true Summarized a pattern in nature Ex: Law of Gravity
Evolution of a Scientific Idea 1. Hypothesis 2. Theory An educated guess Extensively tested hypothesis Can be modified with new data Still can be proven wrong 3. Scientific Law 99% true Summarized a pattern in nature Ex: Law of Gravity
 Parts of an Experiment • Variable – Factor that changes – Two types • Independent variable • Dependent variable • Independent Variable – Fact YOU change – AKA: Manipulated Variable • Dependent Variable – Factor that changes BECAUSE you changed something – AKA: Responding Variable
Parts of an Experiment • Variable – Factor that changes – Two types • Independent variable • Dependent variable • Independent Variable – Fact YOU change – AKA: Manipulated Variable • Dependent Variable – Factor that changes BECAUSE you changed something – AKA: Responding Variable
 • Constant – Factors that never are changed from test to test • Trial – Repeating the experiment – 3 times for best result
• Constant – Factors that never are changed from test to test • Trial – Repeating the experiment – 3 times for best result
 Data • Information gathered from an experiment • Two types – Qualitative – Quantitative • Qua. Litative Data – Data in the form of words – Mainly observations – Ex: Mike has a blue shirt • Qua. Ntitative Data – Data in the form of numbers – Observations & measurements – Ex: There are 14 tables in the house
Data • Information gathered from an experiment • Two types – Qualitative – Quantitative • Qua. Litative Data – Data in the form of words – Mainly observations – Ex: Mike has a blue shirt • Qua. Ntitative Data – Data in the form of numbers – Observations & measurements – Ex: There are 14 tables in the house
 DAY 3 • Objective – I can describe how data is collected – I can perform measurements in a scientific background
DAY 3 • Objective – I can describe how data is collected – I can perform measurements in a scientific background
 Measurements • Data collected in sometimes in this forms • SI Units – Means Standard International – By adhering to one system of units, scientists can readily interpret one another’s data
Measurements • Data collected in sometimes in this forms • SI Units – Means Standard International – By adhering to one system of units, scientists can readily interpret one another’s data
 Measurement Types A. LENGTH v Straight line distance between two points v How long something is v SI unit = meters (m) v Tools for finding Ø Meter stick or ruler
Measurement Types A. LENGTH v Straight line distance between two points v How long something is v SI unit = meters (m) v Tools for finding Ø Meter stick or ruler
 B. TEMPERATURE v Amount of heat given off by an object v How hot or cold something is v SI unit = Kelvin (K) v Tools for finding Ø Thermometer
B. TEMPERATURE v Amount of heat given off by an object v How hot or cold something is v SI unit = Kelvin (K) v Tools for finding Ø Thermometer
 C. MASS v How much Matter is in an object v SI unit: kilogram (kg) v Tools for Finding v Balances or scales Note: § Mass and Weight are two different things § Mass never changes from place to place
C. MASS v How much Matter is in an object v SI unit: kilogram (kg) v Tools for Finding v Balances or scales Note: § Mass and Weight are two different things § Mass never changes from place to place
 D. VOLUME v Amount of Space an object takes up v Units: L, m. L, cm 3 v Tools: graduated cylinder or ruler v Three Different Methods for finding Volume q Regular object q Irregular object q Liquid
D. VOLUME v Amount of Space an object takes up v Units: L, m. L, cm 3 v Tools: graduated cylinder or ruler v Three Different Methods for finding Volume q Regular object q Irregular object q Liquid
 Finding Volume 1. Liquids (water) § Place the liquid in a graduated cylinder and read the level 2. Regular Object (block) o L* W*H 3. Irregular Object (rock) Ø Do Water Displacement Ø Subtract water level without object from water level with object
Finding Volume 1. Liquids (water) § Place the liquid in a graduated cylinder and read the level 2. Regular Object (block) o L* W*H 3. Irregular Object (rock) Ø Do Water Displacement Ø Subtract water level without object from water level with object
 Last Measurement Type E. DENSITY v Mass per unit Volume v Unit: g/m. L or g/cm 3 v Formula v Density = mass ÷ volume v Density of water is 1 g/m. L v Less means float v More means sink
Last Measurement Type E. DENSITY v Mass per unit Volume v Unit: g/m. L or g/cm 3 v Formula v Density = mass ÷ volume v Density of water is 1 g/m. L v Less means float v More means sink
 Day 4 • Objective –I can explain how data is represented –I can use and read maps and graphs
Day 4 • Objective –I can explain how data is represented –I can use and read maps and graphs
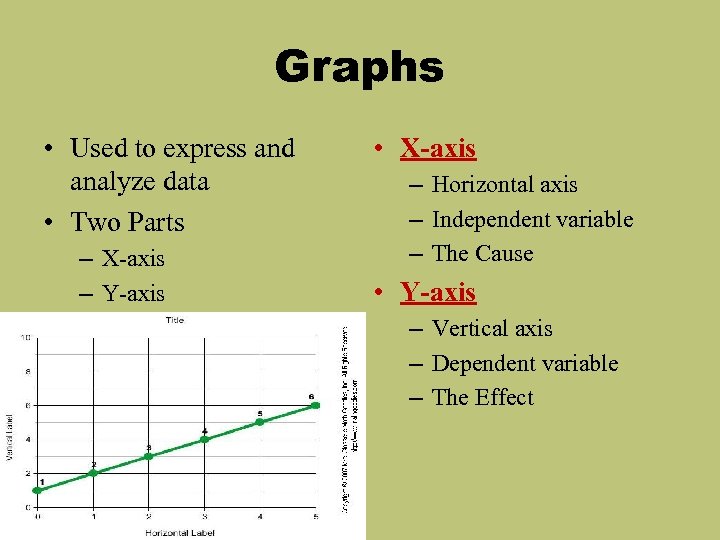 Graphs • Used to express and analyze data • Two Parts – X-axis – Y-axis • X-axis – Horizontal axis – Independent variable – The Cause • Y-axis – Vertical axis – Dependent variable – The Effect
Graphs • Used to express and analyze data • Two Parts – X-axis – Y-axis • X-axis – Horizontal axis – Independent variable – The Cause • Y-axis – Vertical axis – Dependent variable – The Effect
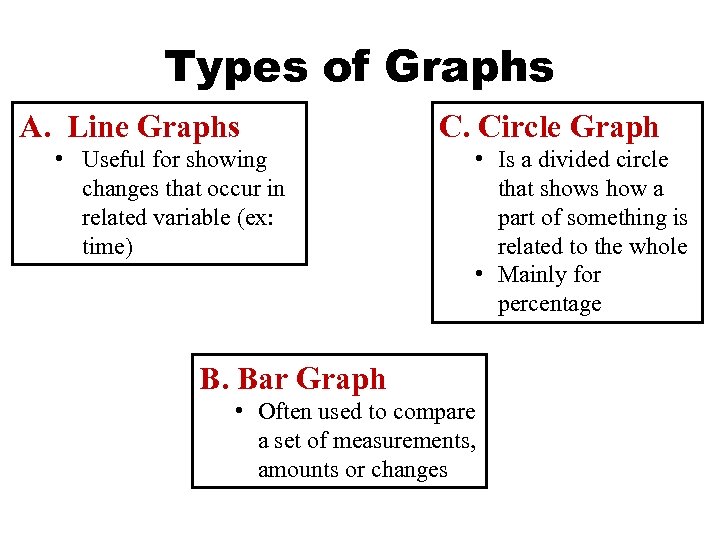 Types of Graphs A. Line Graphs • Useful for showing changes that occur in related variable (ex: time) C. Circle Graph • Is a divided circle that shows how a part of something is related to the whole • Mainly for percentage B. Bar Graph • Often used to compare a set of measurements, amounts or changes
Types of Graphs A. Line Graphs • Useful for showing changes that occur in related variable (ex: time) C. Circle Graph • Is a divided circle that shows how a part of something is related to the whole • Mainly for percentage B. Bar Graph • Often used to compare a set of measurements, amounts or changes
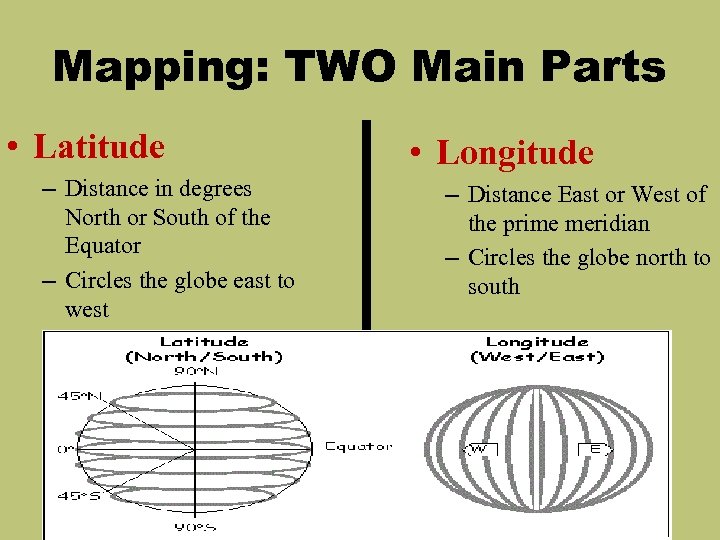 Mapping: TWO Main Parts • Latitude – Distance in degrees North or South of the Equator – Circles the globe east to west • Longitude – Distance East or West of the prime meridian – Circles the globe north to south
Mapping: TWO Main Parts • Latitude – Distance in degrees North or South of the Equator – Circles the globe east to west • Longitude – Distance East or West of the prime meridian – Circles the globe north to south
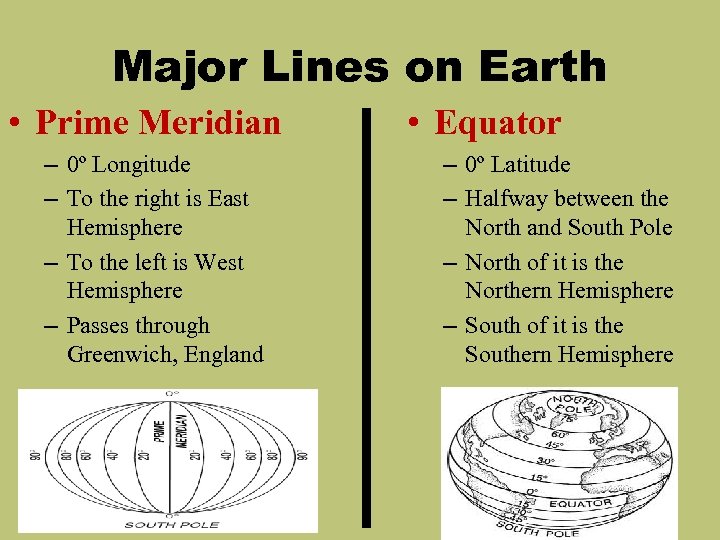 Major Lines on Earth • Prime Meridian – 0º Longitude – To the right is East Hemisphere – To the left is West Hemisphere – Passes through Greenwich, England • Equator – 0º Latitude – Halfway between the North and South Pole – North of it is the Northern Hemisphere – South of it is the Southern Hemisphere
Major Lines on Earth • Prime Meridian – 0º Longitude – To the right is East Hemisphere – To the left is West Hemisphere – Passes through Greenwich, England • Equator – 0º Latitude – Halfway between the North and South Pole – North of it is the Northern Hemisphere – South of it is the Southern Hemisphere
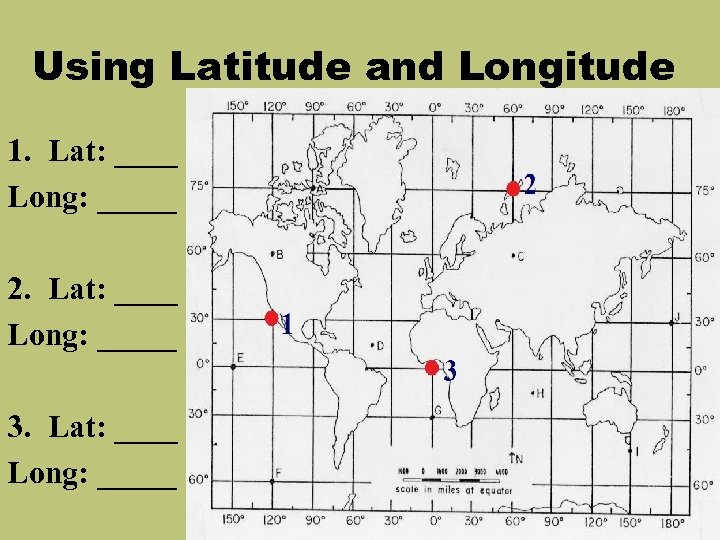 Using Latitude and Longitude 1. Lat: ____ Long: _____ 2. Lat: ____ Long: _____ 3. Lat: ____ Long: _____
Using Latitude and Longitude 1. Lat: ____ Long: _____ 2. Lat: ____ Long: _____ 3. Lat: ____ Long: _____


