47f9e11ab807a7287a8590ce8b445146.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Earth As A System Phenomena span a range of space and time scales lightning: tornadoes’ paths: major floods: weather systems: ozone holes: ocean circulation: atmospheric composition: space scale a few km’s a few 10’s of km 100’s of km ~1000 km ~2000 km 1000’s of km global time scale fractions of a second minutes days a few weeks a month years decades
Earth As A System Phenomena span a range of space and time scales lightning: tornadoes’ paths: major floods: weather systems: ozone holes: ocean circulation: atmospheric composition: space scale a few km’s a few 10’s of km 100’s of km ~1000 km ~2000 km 1000’s of km global time scale fractions of a second minutes days a few weeks a month years decades
 Earth System Connections Phenomena on all scales are connected together some volcanic eruptions alter the atmosphere globally for years El Nino in the tropical Pacific affects weather for months, even in the United States passage of a weather system can spawn tornadoes which cut a swath through a forest triggering the process of forest succession These and other connections are fundamental to the Earth system.
Earth System Connections Phenomena on all scales are connected together some volcanic eruptions alter the atmosphere globally for years El Nino in the tropical Pacific affects weather for months, even in the United States passage of a weather system can spawn tornadoes which cut a swath through a forest triggering the process of forest succession These and other connections are fundamental to the Earth system.
 Earth System Cycles The cycling of energy, water, and certain chemical elements ties the system together Energy from the Sun enters the top of the atmosphere; some is reflected back to space while the rest powers the Earth system Water evaporates from the surface, condenses or freezes, falls back to the surface, runs-off or sinks into the soil, flows to aquifers, rivers, the oceans The chemical elements C, N, P, and S cycle among living organisms, the atmosphere, sediments, soils, and water bodies
Earth System Cycles The cycling of energy, water, and certain chemical elements ties the system together Energy from the Sun enters the top of the atmosphere; some is reflected back to space while the rest powers the Earth system Water evaporates from the surface, condenses or freezes, falls back to the surface, runs-off or sinks into the soil, flows to aquifers, rivers, the oceans The chemical elements C, N, P, and S cycle among living organisms, the atmosphere, sediments, soils, and water bodies
 Earth System Measurements in GLOBE students measure components of the Earth system and its cycles Energy: temperatures of air, water, and soil; clouds; transparency Water: precipitation; soil moisture, infiltration, and bulk density; land cover Biogeochemicals: p. H of precipitation, water, and soil; soil characterization; water chemistry; land cover and biology
Earth System Measurements in GLOBE students measure components of the Earth system and its cycles Energy: temperatures of air, water, and soil; clouds; transparency Water: precipitation; soil moisture, infiltration, and bulk density; land cover Biogeochemicals: p. H of precipitation, water, and soil; soil characterization; water chemistry; land cover and biology
 Categories of Measurement Protocols Basic Advanced Optional Special
Categories of Measurement Protocols Basic Advanced Optional Special
 Basic Protocols Atmosphere Cloud Temperature Precipitation Transparency Temperature p. H Conductivity Salinity Phenology Green-Up Green-down Soil Hydrology Field Characterization Bulk Density p. H Temperature Gravimetric Moisture Land Cover MUC Qualitative Land Cover Sampling Quantitative Land Cover Sampling Manual Mapping
Basic Protocols Atmosphere Cloud Temperature Precipitation Transparency Temperature p. H Conductivity Salinity Phenology Green-Up Green-down Soil Hydrology Field Characterization Bulk Density p. H Temperature Gravimetric Moisture Land Cover MUC Qualitative Land Cover Sampling Quantitative Land Cover Sampling Manual Mapping
 Advanced Protocols Hydrology Soil Dissolved Oxygen Alkalinity Nitrate Soil Fertility Particle Size Distribution Particle Density (under development) Land Cover Computer Assisted Clustering Accuracy Assessment
Advanced Protocols Hydrology Soil Dissolved Oxygen Alkalinity Nitrate Soil Fertility Particle Size Distribution Particle Density (under development) Land Cover Computer Assisted Clustering Accuracy Assessment
 Optional Protocols Hydrology Soil Salinity Titration Marine Macroinvertebrates (under development) Freshwater Macroinvertebrates (under development) Infiltration Soil Moisture Sensor Other Automated Soil and Air Temperature Monitoring (under development)
Optional Protocols Hydrology Soil Salinity Titration Marine Macroinvertebrates (under development) Freshwater Macroinvertebrates (under development) Infiltration Soil Moisture Sensor Other Automated Soil and Air Temperature Monitoring (under development)
 Special Protocols Phenology Budburst Lilacs Snow Pack Water Equivalent Fire Ecology (under development)
Special Protocols Phenology Budburst Lilacs Snow Pack Water Equivalent Fire Ecology (under development)
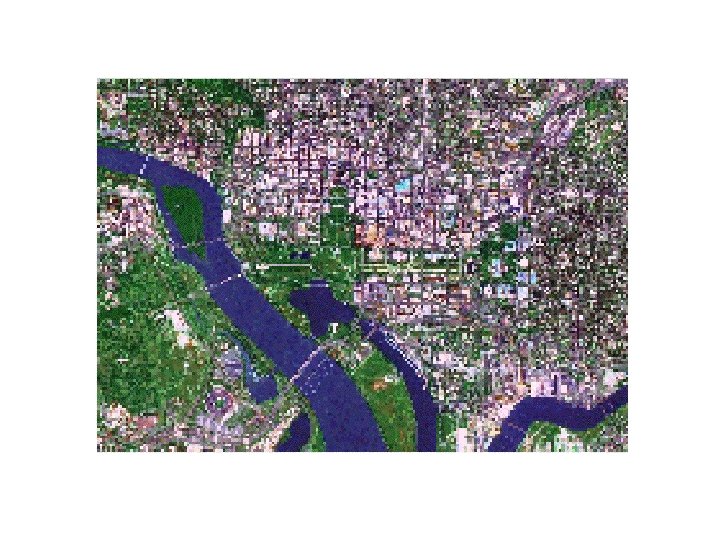


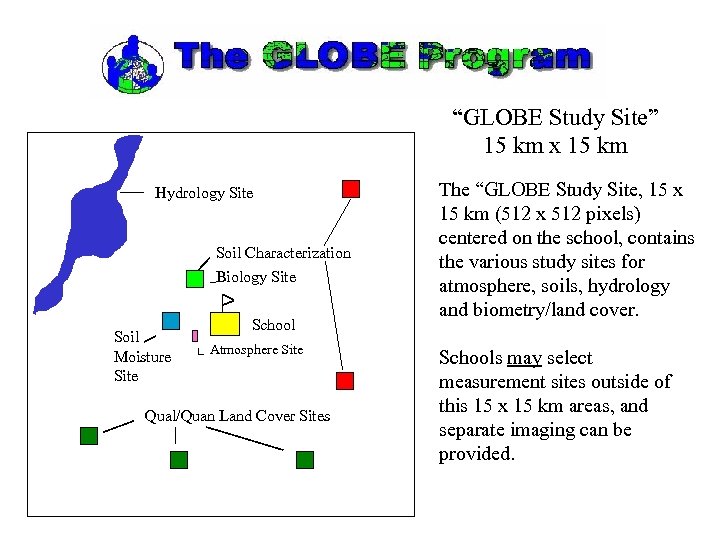 “GLOBE Study Site” 15 km x 15 km Hydrology Site Soil Characterization Biology Site Soil Moisture Site School Atmosphere Site Qual/Quan Land Cover Sites The “GLOBE Study Site, 15 x 15 km (512 x 512 pixels) centered on the school, contains the various study sites for atmosphere, soils, hydrology and biometry/land cover. Schools may select measurement sites outside of this 15 x 15 km areas, and separate imaging can be provided.
“GLOBE Study Site” 15 km x 15 km Hydrology Site Soil Characterization Biology Site Soil Moisture Site School Atmosphere Site Qual/Quan Land Cover Sites The “GLOBE Study Site, 15 x 15 km (512 x 512 pixels) centered on the school, contains the various study sites for atmosphere, soils, hydrology and biometry/land cover. Schools may select measurement sites outside of this 15 x 15 km areas, and separate imaging can be provided.

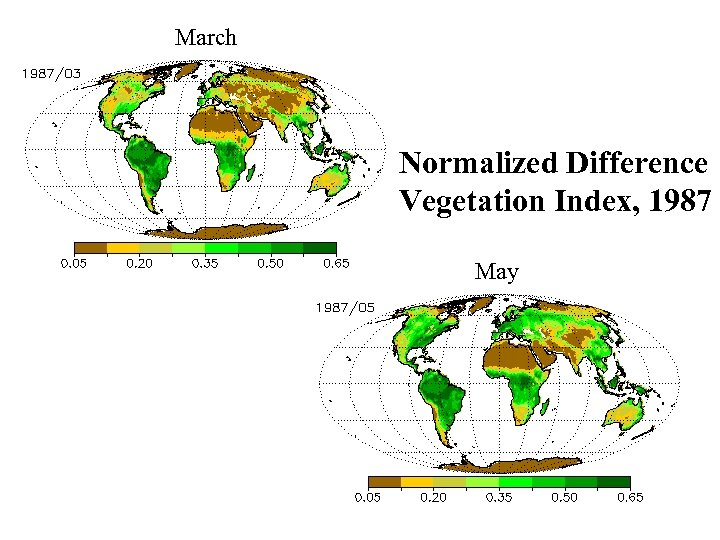 March Normalized Difference Vegetation Index, 1987 May
March Normalized Difference Vegetation Index, 1987 May
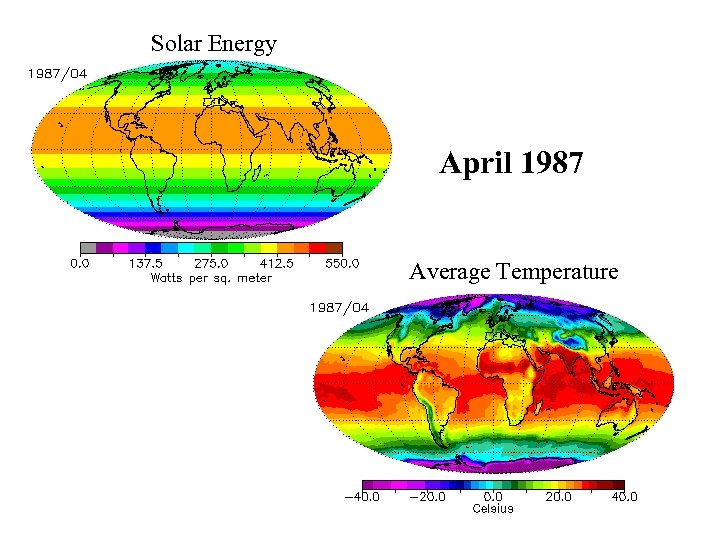 Solar Energy April 1987 Average Temperature
Solar Energy April 1987 Average Temperature
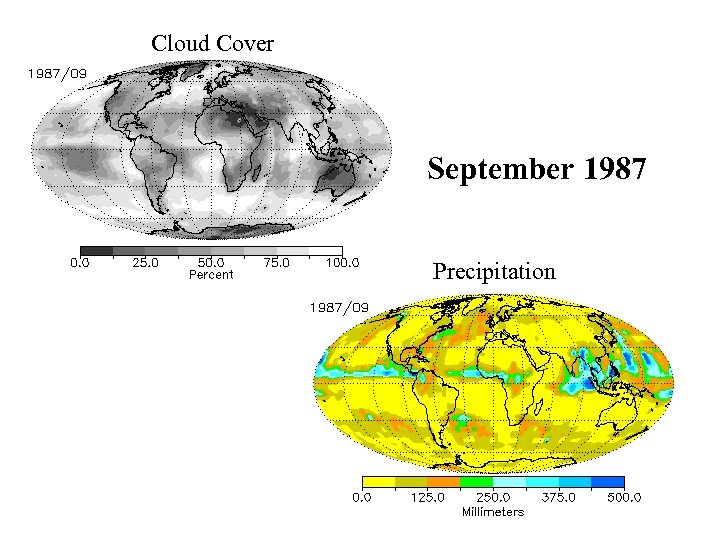 Cloud Cover September 1987 Precipitation
Cloud Cover September 1987 Precipitation


