e26c25e84c43960a5eb558435521d2f6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 105
 Early Stage NSCLC: Imprimatur of Adjuvant Therapy Overview of Recent Data Corey J Langer MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Director of Thoracic Oncology Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA 19104
Early Stage NSCLC: Imprimatur of Adjuvant Therapy Overview of Recent Data Corey J Langer MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Director of Thoracic Oncology Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA 19104
 Disclosures: Past 10 yrs • Grant/Research Support: – Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Imclone, Lilly, Schering. Plough Research Institute, Sanofi-Aventis, Amgen, Cell Therapeutics, Ortho. Biotech, Celgene, Vertex, Genentech, OSI, Astra. Zeneca, Pfizer, Medimmune, GSK • Scientific Advisor: – Bristol Myers Squibb, Imclone, Sanofi-Aventis, Pfizer, Glaxo. Smith. Kline, Pharmacyclics, Amgen, Astra. Zeneca, Novartis, Genentech, OSI, Savient, Bayer/Onyx, Abraxis, Clarient, Morphotek, Biodesix, AVEO, Synta • Speakers Bureau: curtailed as of 12/10 – Bristol Myers Squibb, Imclone, Sanofi-Aventis, Lilly, Genentech, OSI
Disclosures: Past 10 yrs • Grant/Research Support: – Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Imclone, Lilly, Schering. Plough Research Institute, Sanofi-Aventis, Amgen, Cell Therapeutics, Ortho. Biotech, Celgene, Vertex, Genentech, OSI, Astra. Zeneca, Pfizer, Medimmune, GSK • Scientific Advisor: – Bristol Myers Squibb, Imclone, Sanofi-Aventis, Pfizer, Glaxo. Smith. Kline, Pharmacyclics, Amgen, Astra. Zeneca, Novartis, Genentech, OSI, Savient, Bayer/Onyx, Abraxis, Clarient, Morphotek, Biodesix, AVEO, Synta • Speakers Bureau: curtailed as of 12/10 – Bristol Myers Squibb, Imclone, Sanofi-Aventis, Lilly, Genentech, OSI
 Welcome to Winter in NJ 2 -14 3
Welcome to Winter in NJ 2 -14 3
 Stage is Destiny!
Stage is Destiny!
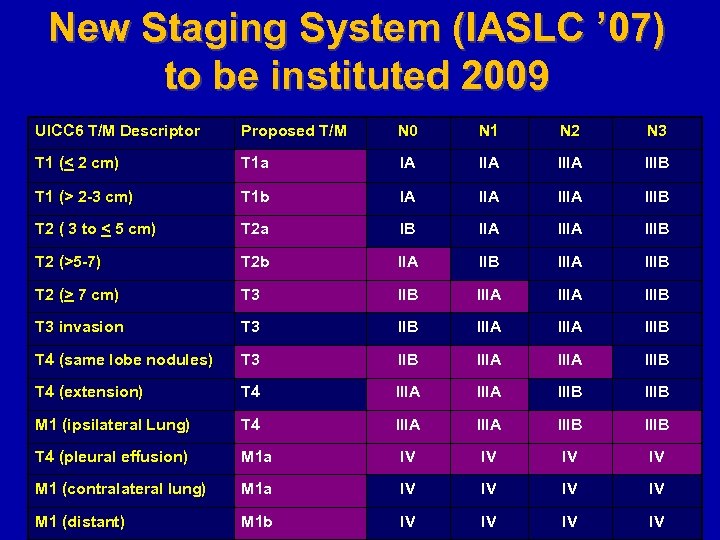 New Staging System (IASLC ’ 07) to be instituted 2009 UICC 6 T/M Descriptor Proposed T/M N 0 N 1 N 2 N 3 T 1 (< 2 cm) T 1 a IA IIIA IIIB T 1 (> 2 -3 cm) T 1 b IA IIIA IIIB T 2 ( 3 to < 5 cm) T 2 a IB IIA IIIB T 2 (>5 -7) T 2 b IIA IIB IIIA IIIB T 2 (> 7 cm) T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 3 invasion T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 4 (same lobe nodules) T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 4 (extension) T 4 IIIA IIIB M 1 (ipsilateral Lung) T 4 IIIA IIIB T 4 (pleural effusion) M 1 a IV IV M 1 (contralateral lung) M 1 a IV IV M 1 (distant) M 1 b IV IV
New Staging System (IASLC ’ 07) to be instituted 2009 UICC 6 T/M Descriptor Proposed T/M N 0 N 1 N 2 N 3 T 1 (< 2 cm) T 1 a IA IIIA IIIB T 1 (> 2 -3 cm) T 1 b IA IIIA IIIB T 2 ( 3 to < 5 cm) T 2 a IB IIA IIIB T 2 (>5 -7) T 2 b IIA IIB IIIA IIIB T 2 (> 7 cm) T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 3 invasion T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 4 (same lobe nodules) T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 4 (extension) T 4 IIIA IIIB M 1 (ipsilateral Lung) T 4 IIIA IIIB T 4 (pleural effusion) M 1 a IV IV M 1 (contralateral lung) M 1 a IV IV M 1 (distant) M 1 b IV IV
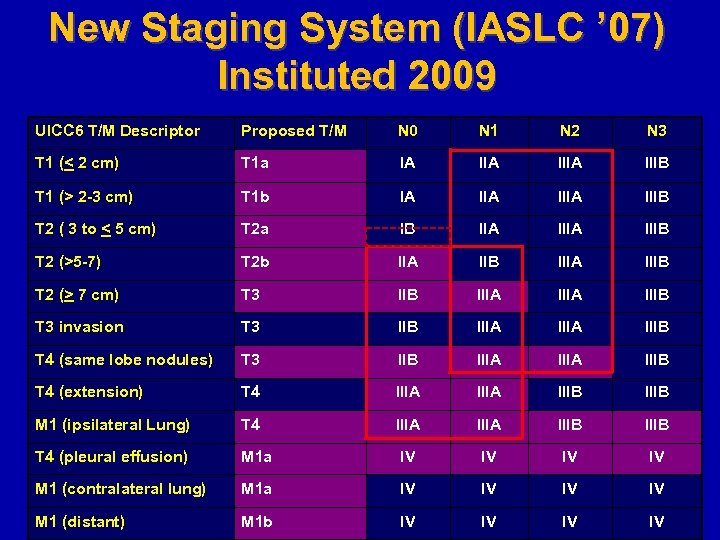 New Staging System (IASLC ’ 07) Instituted 2009 UICC 6 T/M Descriptor Proposed T/M N 0 N 1 N 2 N 3 T 1 (< 2 cm) T 1 a IA IIIA IIIB T 1 (> 2 -3 cm) T 1 b IA IIIA IIIB T 2 ( 3 to < 5 cm) T 2 a IB IIA IIIB T 2 (>5 -7) T 2 b IIA IIB IIIA IIIB T 2 (> 7 cm) T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 3 invasion T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 4 (same lobe nodules) T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 4 (extension) T 4 IIIA IIIB M 1 (ipsilateral Lung) T 4 IIIA IIIB T 4 (pleural effusion) M 1 a IV IV M 1 (contralateral lung) M 1 a IV IV M 1 (distant) M 1 b IV IV
New Staging System (IASLC ’ 07) Instituted 2009 UICC 6 T/M Descriptor Proposed T/M N 0 N 1 N 2 N 3 T 1 (< 2 cm) T 1 a IA IIIA IIIB T 1 (> 2 -3 cm) T 1 b IA IIIA IIIB T 2 ( 3 to < 5 cm) T 2 a IB IIA IIIB T 2 (>5 -7) T 2 b IIA IIB IIIA IIIB T 2 (> 7 cm) T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 3 invasion T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 4 (same lobe nodules) T 3 IIB IIIA IIIB T 4 (extension) T 4 IIIA IIIB M 1 (ipsilateral Lung) T 4 IIIA IIIB T 4 (pleural effusion) M 1 a IV IV M 1 (contralateral lung) M 1 a IV IV M 1 (distant) M 1 b IV IV
 Limitations of Earlier Adjuvant Trials • Use of regimens with marginal activity in advanced NSCLC • Inclusion of patients with compromised PS and multiple co-morbidities • Difficulty administering systemic therapy in the post-op setting • Inadequate power or overly ambitious survival endpoints
Limitations of Earlier Adjuvant Trials • Use of regimens with marginal activity in advanced NSCLC • Inclusion of patients with compromised PS and multiple co-morbidities • Difficulty administering systemic therapy in the post-op setting • Inadequate power or overly ambitious survival endpoints
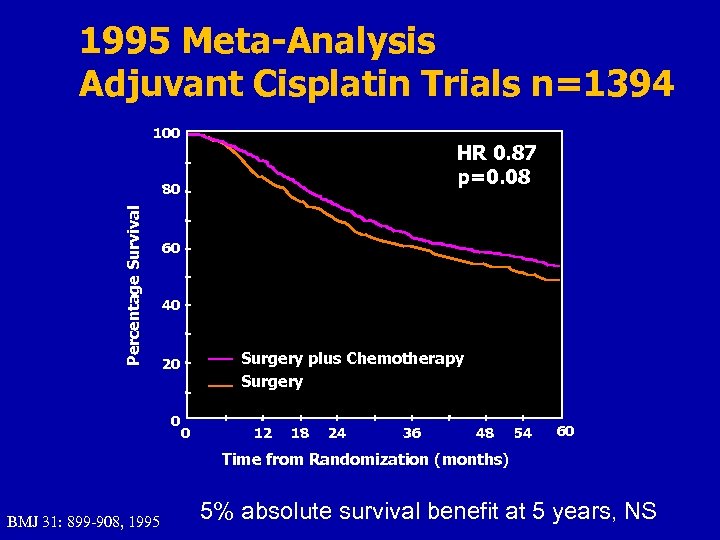 1995 Meta-Analysis Adjuvant Cisplatin Trials n=1394 100 HR 0. 87 p=0. 08 Percentage Survival 80 60 40 Surgery plus Chemotherapy Surgery 20 0 0 12 18 24 36 48 54 60 Time from Randomization (months) BMJ 31: 899 -908, 1995 5% absolute survival benefit at 5 years, NS
1995 Meta-Analysis Adjuvant Cisplatin Trials n=1394 100 HR 0. 87 p=0. 08 Percentage Survival 80 60 40 Surgery plus Chemotherapy Surgery 20 0 0 12 18 24 36 48 54 60 Time from Randomization (months) BMJ 31: 899 -908, 1995 5% absolute survival benefit at 5 years, NS
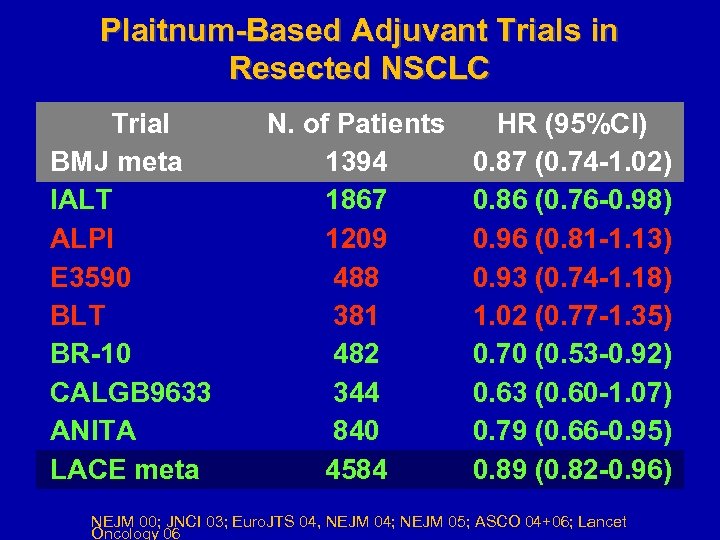 Plaitnum-Based Adjuvant Trials in Resected NSCLC Trial BMJ meta IALT ALPI E 3590 BLT BR-10 CALGB 9633 ANITA LACE meta N. of Patients 1394 1867 1209 488 381 482 344 840 4584 HR (95%CI) 0. 87 (0. 74 -1. 02) 0. 86 (0. 76 -0. 98) 0. 96 (0. 81 -1. 13) 0. 93 (0. 74 -1. 18) 1. 02 (0. 77 -1. 35) 0. 70 (0. 53 -0. 92) 0. 63 (0. 60 -1. 07) 0. 79 (0. 66 -0. 95) 0. 89 (0. 82 -0. 96) NEJM 00; JNCI 03; Euro. JTS 04, NEJM 04; NEJM 05; ASCO 04+06; Lancet Oncology 06
Plaitnum-Based Adjuvant Trials in Resected NSCLC Trial BMJ meta IALT ALPI E 3590 BLT BR-10 CALGB 9633 ANITA LACE meta N. of Patients 1394 1867 1209 488 381 482 344 840 4584 HR (95%CI) 0. 87 (0. 74 -1. 02) 0. 86 (0. 76 -0. 98) 0. 96 (0. 81 -1. 13) 0. 93 (0. 74 -1. 18) 1. 02 (0. 77 -1. 35) 0. 70 (0. 53 -0. 92) 0. 63 (0. 60 -1. 07) 0. 79 (0. 66 -0. 95) 0. 89 (0. 82 -0. 96) NEJM 00; JNCI 03; Euro. JTS 04, NEJM 04; NEJM 05; ASCO 04+06; Lancet Oncology 06
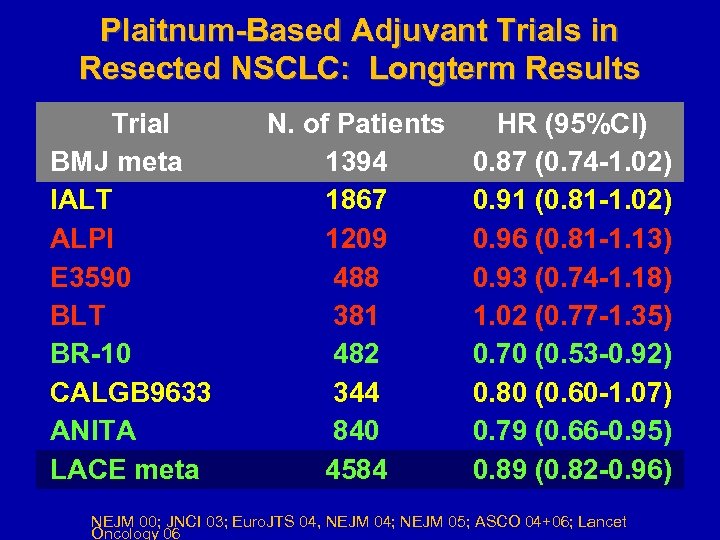 Plaitnum-Based Adjuvant Trials in Resected NSCLC: Longterm Results Trial BMJ meta IALT ALPI E 3590 BLT BR-10 CALGB 9633 ANITA LACE meta N. of Patients 1394 1867 1209 488 381 482 344 840 4584 HR (95%CI) 0. 87 (0. 74 -1. 02) 0. 91 (0. 81 -1. 02) 0. 96 (0. 81 -1. 13) 0. 93 (0. 74 -1. 18) 1. 02 (0. 77 -1. 35) 0. 70 (0. 53 -0. 92) 0. 80 (0. 60 -1. 07) 0. 79 (0. 66 -0. 95) 0. 89 (0. 82 -0. 96) NEJM 00; JNCI 03; Euro. JTS 04, NEJM 04; NEJM 05; ASCO 04+06; Lancet Oncology 06
Plaitnum-Based Adjuvant Trials in Resected NSCLC: Longterm Results Trial BMJ meta IALT ALPI E 3590 BLT BR-10 CALGB 9633 ANITA LACE meta N. of Patients 1394 1867 1209 488 381 482 344 840 4584 HR (95%CI) 0. 87 (0. 74 -1. 02) 0. 91 (0. 81 -1. 02) 0. 96 (0. 81 -1. 13) 0. 93 (0. 74 -1. 18) 1. 02 (0. 77 -1. 35) 0. 70 (0. 53 -0. 92) 0. 80 (0. 60 -1. 07) 0. 79 (0. 66 -0. 95) 0. 89 (0. 82 -0. 96) NEJM 00; JNCI 03; Euro. JTS 04, NEJM 04; NEJM 05; ASCO 04+06; Lancet Oncology 06
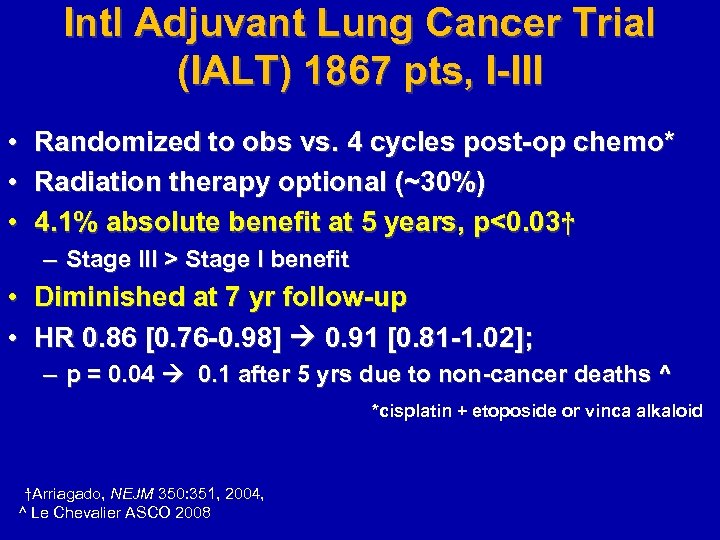 Intl Adjuvant Lung Cancer Trial (IALT) 1867 pts, I-III • • • Randomized to obs vs. 4 cycles post-op chemo* Radiation therapy optional (~30%) 4. 1% absolute benefit at 5 years, p<0. 03† – Stage III > Stage I benefit • Diminished at 7 yr follow-up • HR 0. 86 [0. 76 -0. 98] 0. 91 [0. 81 -1. 02]; – p = 0. 04 0. 1 after 5 yrs due to non-cancer deaths ^ *cisplatin + etoposide or vinca alkaloid †Arriagado, NEJM 350: 351, 2004, ^ Le Chevalier ASCO 2008
Intl Adjuvant Lung Cancer Trial (IALT) 1867 pts, I-III • • • Randomized to obs vs. 4 cycles post-op chemo* Radiation therapy optional (~30%) 4. 1% absolute benefit at 5 years, p<0. 03† – Stage III > Stage I benefit • Diminished at 7 yr follow-up • HR 0. 86 [0. 76 -0. 98] 0. 91 [0. 81 -1. 02]; – p = 0. 04 0. 1 after 5 yrs due to non-cancer deaths ^ *cisplatin + etoposide or vinca alkaloid †Arriagado, NEJM 350: 351, 2004, ^ Le Chevalier ASCO 2008
 Randomized International Adjuvant Lung Cancer Trial (IALT): Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy vs No Chemotherapy for Resected NSCLC Stage I-III NSCLC Complete surgical resection within 60 days N=1867 R A N D O M IZ E Arm A* Cisplatin 80 mg/m 2 4 cycles OR Cisplatin 100 mg/m 2 3 -4 cycles OR Cisplatin 120 mg/m 2 3 cycles PLUS Etoposide 100 mg/m 2 3 days/cycle OR Vinorelbine 30 mg/m 2 weekly OR Vinblastine 4 mg/m 2 weekly OR Vindesine 3 mg/m 2 weekly n=935 Arm B Observation ± thoracic radiotherapy 60 Gy† n=932 *Each center selected which chemotherapy it would use. †Optional, but predefined by N stage at each center. Le Chevalier et al. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2003; 22: 2. Abstract and oral presentation; Arriagada et al. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350: 351.
Randomized International Adjuvant Lung Cancer Trial (IALT): Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy vs No Chemotherapy for Resected NSCLC Stage I-III NSCLC Complete surgical resection within 60 days N=1867 R A N D O M IZ E Arm A* Cisplatin 80 mg/m 2 4 cycles OR Cisplatin 100 mg/m 2 3 -4 cycles OR Cisplatin 120 mg/m 2 3 cycles PLUS Etoposide 100 mg/m 2 3 days/cycle OR Vinorelbine 30 mg/m 2 weekly OR Vinblastine 4 mg/m 2 weekly OR Vindesine 3 mg/m 2 weekly n=935 Arm B Observation ± thoracic radiotherapy 60 Gy† n=932 *Each center selected which chemotherapy it would use. †Optional, but predefined by N stage at each center. Le Chevalier et al. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2003; 22: 2. Abstract and oral presentation; Arriagada et al. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350: 351.
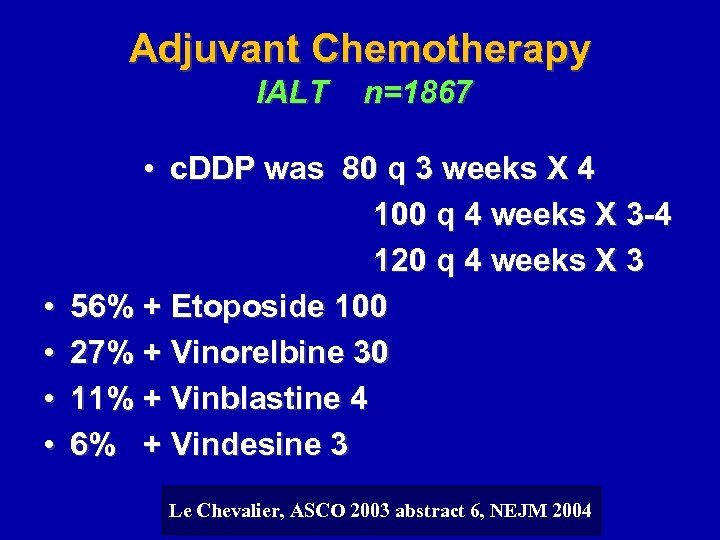 Adjuvant Chemotherapy IALT • • n=1867 • c. DDP was 80 q 3 weeks X 4 100 q 4 weeks X 3 -4 120 q 4 weeks X 3 56% + Etoposide 100 27% + Vinorelbine 30 11% + Vinblastine 4 6% + Vindesine 3 Le Chevalier, ASCO 2003 abstract 6, NEJM 2004
Adjuvant Chemotherapy IALT • • n=1867 • c. DDP was 80 q 3 weeks X 4 100 q 4 weeks X 3 -4 120 q 4 weeks X 3 56% + Etoposide 100 27% + Vinorelbine 30 11% + Vinblastine 4 6% + Vindesine 3 Le Chevalier, ASCO 2003 abstract 6, NEJM 2004
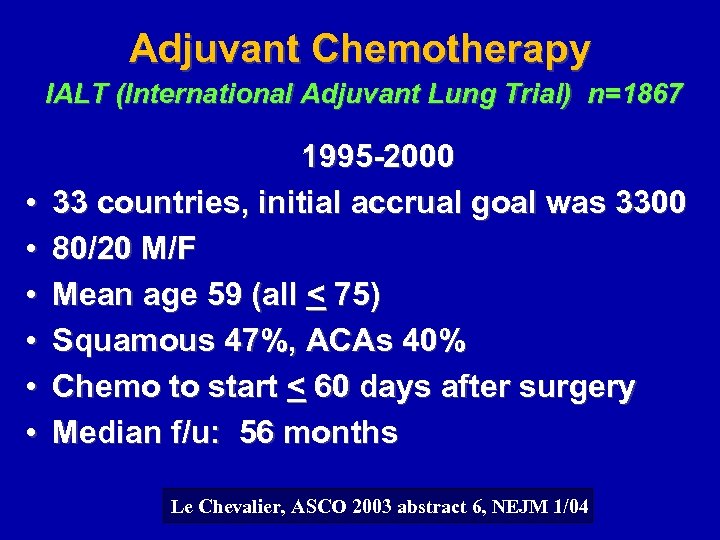 Adjuvant Chemotherapy IALT (International Adjuvant Lung Trial) n=1867 • • • 1995 -2000 33 countries, initial accrual goal was 3300 80/20 M/F Mean age 59 (all < 75) Squamous 47%, ACAs 40% Chemo to start < 60 days after surgery Median f/u: 56 months Le Chevalier, ASCO 2003 abstract 6, NEJM 1/04
Adjuvant Chemotherapy IALT (International Adjuvant Lung Trial) n=1867 • • • 1995 -2000 33 countries, initial accrual goal was 3300 80/20 M/F Mean age 59 (all < 75) Squamous 47%, ACAs 40% Chemo to start < 60 days after surgery Median f/u: 56 months Le Chevalier, ASCO 2003 abstract 6, NEJM 1/04
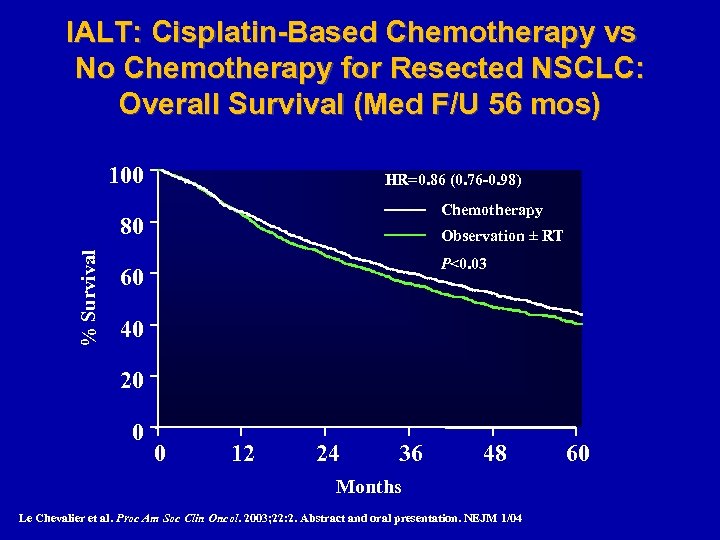 IALT: Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy vs No Chemotherapy for Resected NSCLC: Overall Survival (Med F/U 56 mos) 100 HR=0. 86 (0. 76 -0. 98) Chemotherapy % Survival 80 Observation ± RT P<0. 03 60 40 20 0 0 12 24 36 48 Months Le Chevalier et al. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2003; 22: 2. Abstract and oral presentation. NEJM 1/04 60
IALT: Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy vs No Chemotherapy for Resected NSCLC: Overall Survival (Med F/U 56 mos) 100 HR=0. 86 (0. 76 -0. 98) Chemotherapy % Survival 80 Observation ± RT P<0. 03 60 40 20 0 0 12 24 36 48 Months Le Chevalier et al. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2003; 22: 2. Abstract and oral presentation. NEJM 1/04 60
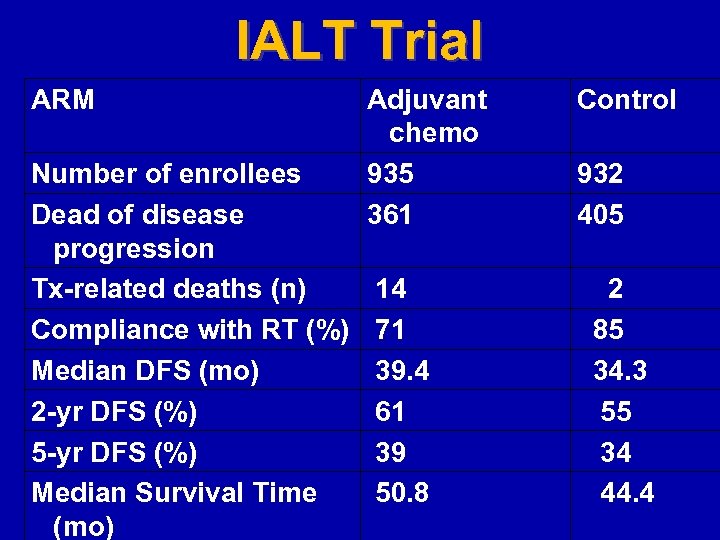 IALT Trial ARM Number of enrollees Dead of disease progression Tx-related deaths (n) Compliance with RT (%) Median DFS (mo) 2 -yr DFS (%) 5 -yr DFS (%) Median Survival Time (mo) Adjuvant chemo 935 361 Control 14 71 39. 4 61 39 50. 8 2 85 34. 3 55 34 44. 4 932 405
IALT Trial ARM Number of enrollees Dead of disease progression Tx-related deaths (n) Compliance with RT (%) Median DFS (mo) 2 -yr DFS (%) 5 -yr DFS (%) Median Survival Time (mo) Adjuvant chemo 935 361 Control 14 71 39. 4 61 39 50. 8 2 85 34. 3 55 34 44. 4 932 405
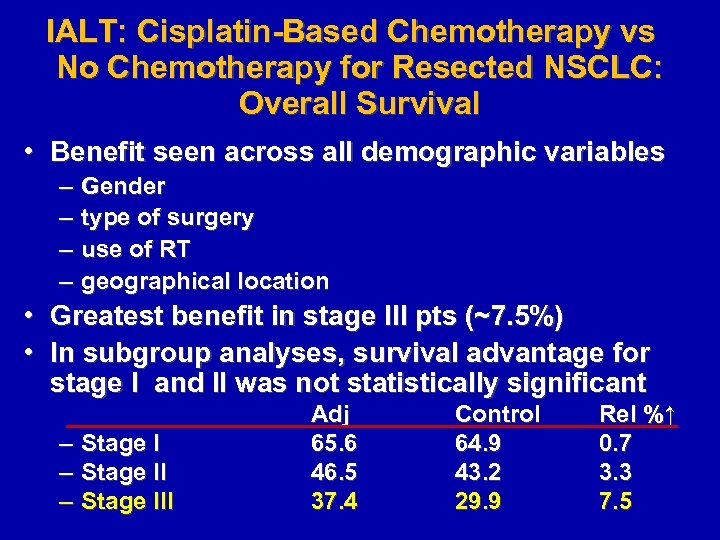 IALT: Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy vs No Chemotherapy for Resected NSCLC: Overall Survival • Benefit seen across all demographic variables – – Gender type of surgery use of RT geographical location • Greatest benefit in stage III pts (~7. 5%) • In subgroup analyses, survival advantage for stage I and II was not statistically significant – – – Stage III Adj 65. 6 46. 5 37. 4 Control 64. 9 43. 2 29. 9 Rel %↑ 0. 7 3. 3 7. 5
IALT: Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy vs No Chemotherapy for Resected NSCLC: Overall Survival • Benefit seen across all demographic variables – – Gender type of surgery use of RT geographical location • Greatest benefit in stage III pts (~7. 5%) • In subgroup analyses, survival advantage for stage I and II was not statistically significant – – – Stage III Adj 65. 6 46. 5 37. 4 Control 64. 9 43. 2 29. 9 Rel %↑ 0. 7 3. 3 7. 5
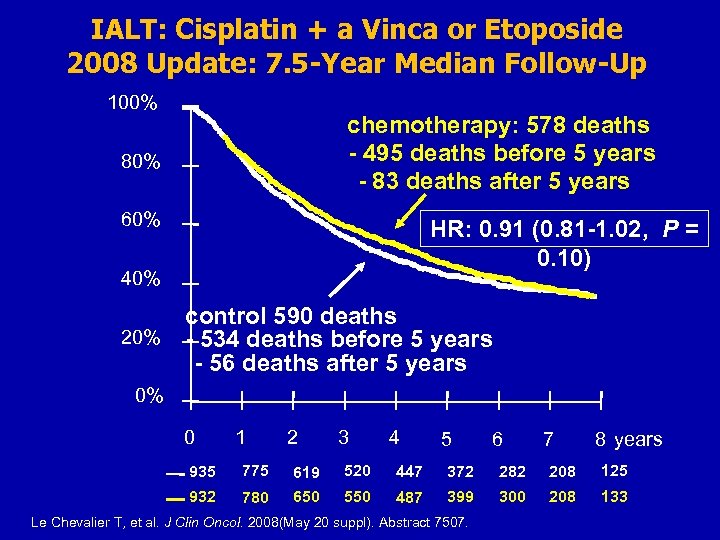 IALT: Cisplatin + a Vinca or Etoposide 2008 Update: 7. 5 -Year Median Follow-Up 100% chemotherapy: 578 deaths - 495 deaths before 5 years - 83 deaths after 5 years 80% 60% HR: 0. 91 (0. 81 -1. 02, P = 0. 10) 40% control 590 deaths 20% - 534 deaths before 5 years - 56 deaths after 5 years 0% 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 years 935 775 619 520 447 372 282 208 125 932 780 650 550 487 399 300 208 133 Le Chevalier T, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2008(May 20 suppl). Abstract 7507.
IALT: Cisplatin + a Vinca or Etoposide 2008 Update: 7. 5 -Year Median Follow-Up 100% chemotherapy: 578 deaths - 495 deaths before 5 years - 83 deaths after 5 years 80% 60% HR: 0. 91 (0. 81 -1. 02, P = 0. 10) 40% control 590 deaths 20% - 534 deaths before 5 years - 56 deaths after 5 years 0% 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 years 935 775 619 520 447 372 282 208 125 932 780 650 550 487 399 300 208 133 Le Chevalier T, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2008(May 20 suppl). Abstract 7507.
 Criticisms of IALT • Heterogenous staging, chemo and application of RT (HR favored stage III, not stage I or II) • Study actually closed earlier than planned because of emerging interest in neoadjuvant Tx • Potential Molecular Imbalances: Results of ERCC 1 suggest that one can select a group more likely to benefit; other bio-correlatives still pending • Elderly (> 75) excluded; how do we address this expanding cohort? • Dissipation of survival benefit after 5 years • Why was this trial positive when so many similar trials proved negative?
Criticisms of IALT • Heterogenous staging, chemo and application of RT (HR favored stage III, not stage I or II) • Study actually closed earlier than planned because of emerging interest in neoadjuvant Tx • Potential Molecular Imbalances: Results of ERCC 1 suggest that one can select a group more likely to benefit; other bio-correlatives still pending • Elderly (> 75) excluded; how do we address this expanding cohort? • Dissipation of survival benefit after 5 years • Why was this trial positive when so many similar trials proved negative?
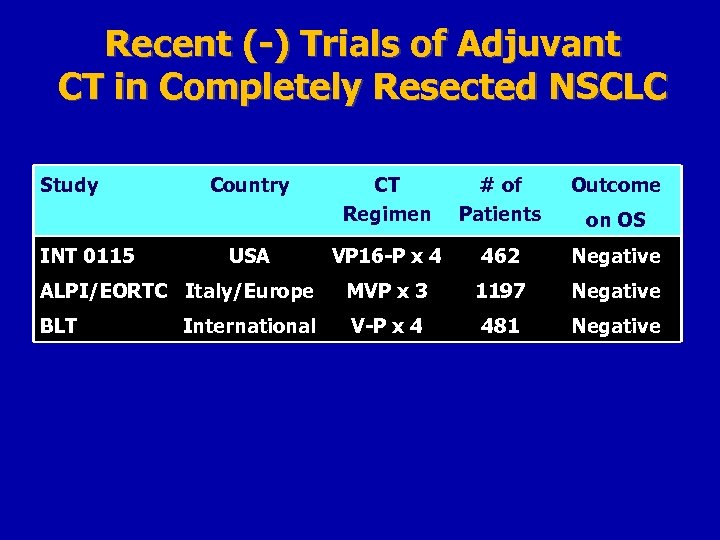 Recent (-) Trials of Adjuvant CT in Completely Resected NSCLC Study CT Regimen # of Patients Outcome VP 16 -P x 4 462 Negative ALPI/EORTC Italy/Europe MVP x 3 1197 Negative BLT V-P x 4 481 Negative INT 0115 Country USA International on OS
Recent (-) Trials of Adjuvant CT in Completely Resected NSCLC Study CT Regimen # of Patients Outcome VP 16 -P x 4 462 Negative ALPI/EORTC Italy/Europe MVP x 3 1197 Negative BLT V-P x 4 481 Negative INT 0115 Country USA International on OS
 2004: Paradigm Shift
2004: Paradigm Shift
 2004: Paradigm Shift Recently Completed (+) Randomized Adjuvant Trials in Early Stage NSCLC Stage No. Intervention CALGB 9633 IB 500 Carboplatin/Paclitaxel NCI-C* IB-II 480 Cisplatin/Vinorelbine
2004: Paradigm Shift Recently Completed (+) Randomized Adjuvant Trials in Early Stage NSCLC Stage No. Intervention CALGB 9633 IB 500 Carboplatin/Paclitaxel NCI-C* IB-II 480 Cisplatin/Vinorelbine
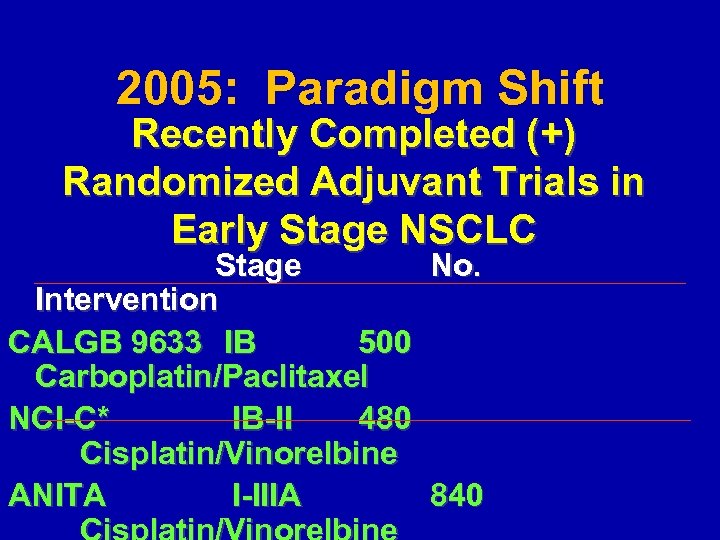 2005: Paradigm Shift Recently Completed (+) Randomized Adjuvant Trials in Early Stage NSCLC Stage No. Intervention CALGB 9633 IB 500 Carboplatin/Paclitaxel NCI-C* IB-II 480 Cisplatin/Vinorelbine ANITA I-IIIA 840
2005: Paradigm Shift Recently Completed (+) Randomized Adjuvant Trials in Early Stage NSCLC Stage No. Intervention CALGB 9633 IB 500 Carboplatin/Paclitaxel NCI-C* IB-II 480 Cisplatin/Vinorelbine ANITA I-IIIA 840
 CALGB 9633 - 344 pts, stage IB • 4 cycles carboplatin/paclitaxel vs. observation • Radiation therapy not allowed • 2004 - HR 0. 62; p = 0. 028 • 2006 - HR 0. 80; p = 0. 10 Strauss Proc ASCO 2004 abs 7019, 2006 abs 7007, JCO 2009
CALGB 9633 - 344 pts, stage IB • 4 cycles carboplatin/paclitaxel vs. observation • Radiation therapy not allowed • 2004 - HR 0. 62; p = 0. 028 • 2006 - HR 0. 80; p = 0. 10 Strauss Proc ASCO 2004 abs 7019, 2006 abs 7007, JCO 2009
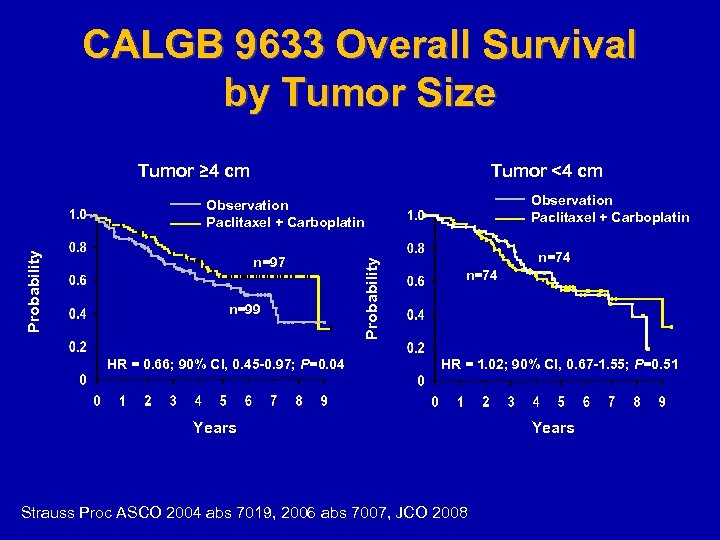 CALGB 9633 Overall Survival by Tumor Size Tumor ≥ 4 cm Tumor <4 cm Observation Paclitaxel + Carboplatin n=97 n=99 HR = 0. 66; 90% CI, 0. 45 -0. 97; P=0. 04 Probability Observation Paclitaxel + Carboplatin n=74 HR = 1. 02; 90% CI, 0. 67 -1. 55; P=0. 51 Years Strauss Proc ASCO 2004 abs 7019, 2006 abs 7007, JCO 2008 Years
CALGB 9633 Overall Survival by Tumor Size Tumor ≥ 4 cm Tumor <4 cm Observation Paclitaxel + Carboplatin n=97 n=99 HR = 0. 66; 90% CI, 0. 45 -0. 97; P=0. 04 Probability Observation Paclitaxel + Carboplatin n=74 HR = 1. 02; 90% CI, 0. 67 -1. 55; P=0. 51 Years Strauss Proc ASCO 2004 abs 7019, 2006 abs 7007, JCO 2008 Years
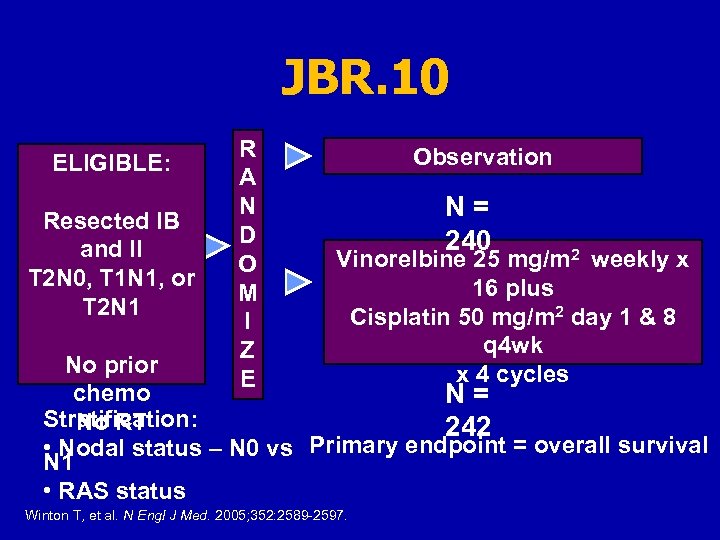 JBR. 10 ELIGIBLE: Resected IB and II T 2 N 0, T 1 N 1, or T 2 N 1 R A N D O M I Z E Observation N = 240 Vinorelbine 25 mg/m 2 weekly x 16 plus Cisplatin 50 mg/m 2 day 1 & 8 q 4 wk x 4 cycles No prior chemo N = Stratification: No RT 242 • Nodal status – N 0 vs Primary endpoint = overall survival N 1 • RAS status Winton T, et al. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352: 2589 -2597.
JBR. 10 ELIGIBLE: Resected IB and II T 2 N 0, T 1 N 1, or T 2 N 1 R A N D O M I Z E Observation N = 240 Vinorelbine 25 mg/m 2 weekly x 16 plus Cisplatin 50 mg/m 2 day 1 & 8 q 4 wk x 4 cycles No prior chemo N = Stratification: No RT 242 • Nodal status – N 0 vs Primary endpoint = overall survival N 1 • RAS status Winton T, et al. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352: 2589 -2597.
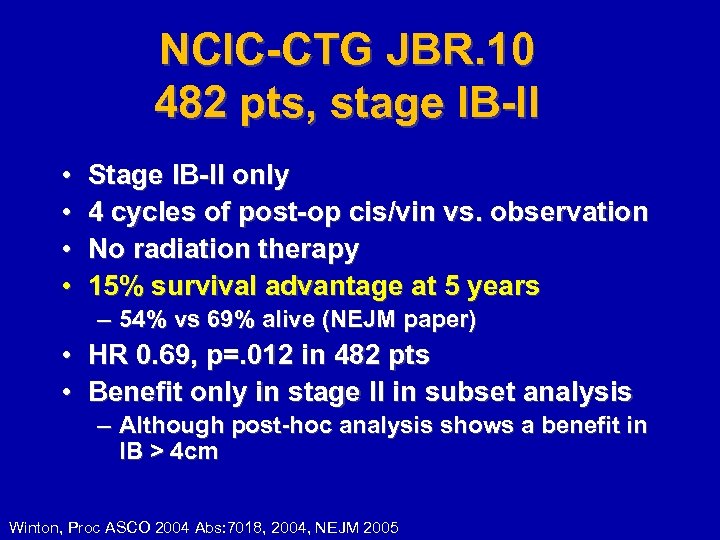 NCIC-CTG JBR. 10 482 pts, stage IB-II • • Stage IB-II only 4 cycles of post-op cis/vin vs. observation No radiation therapy 15% survival advantage at 5 years – 54% vs 69% alive (NEJM paper) • HR 0. 69, p=. 012 in 482 pts • Benefit only in stage II in subset analysis – Although post-hoc analysis shows a benefit in IB > 4 cm Winton, Proc ASCO 2004 Abs: 7018, 2004, NEJM 2005
NCIC-CTG JBR. 10 482 pts, stage IB-II • • Stage IB-II only 4 cycles of post-op cis/vin vs. observation No radiation therapy 15% survival advantage at 5 years – 54% vs 69% alive (NEJM paper) • HR 0. 69, p=. 012 in 482 pts • Benefit only in stage II in subset analysis – Although post-hoc analysis shows a benefit in IB > 4 cm Winton, Proc ASCO 2004 Abs: 7018, 2004, NEJM 2005
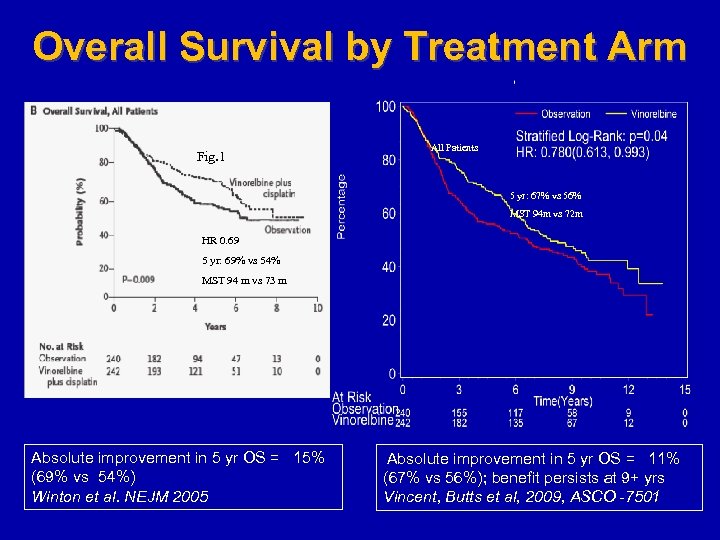 Overall Survival by Treatment Arm Fig. 1 All Patients 5 yr: 67% vs 56% MST 94 m vs 72 m HR 0. 69 5 yr: 69% vs 54% MST 94 m vs 73 m Absolute improvement in 5 yr OS = 15% (69% vs 54%) Winton et al. NEJM 2005 Absolute improvement in 5 yr OS = 11% (67% vs 56%); benefit persists at 9+ yrs Vincent, Butts et al, 2009, ASCO -7501
Overall Survival by Treatment Arm Fig. 1 All Patients 5 yr: 67% vs 56% MST 94 m vs 72 m HR 0. 69 5 yr: 69% vs 54% MST 94 m vs 73 m Absolute improvement in 5 yr OS = 15% (69% vs 54%) Winton et al. NEJM 2005 Absolute improvement in 5 yr OS = 11% (67% vs 56%); benefit persists at 9+ yrs Vincent, Butts et al, 2009, ASCO -7501
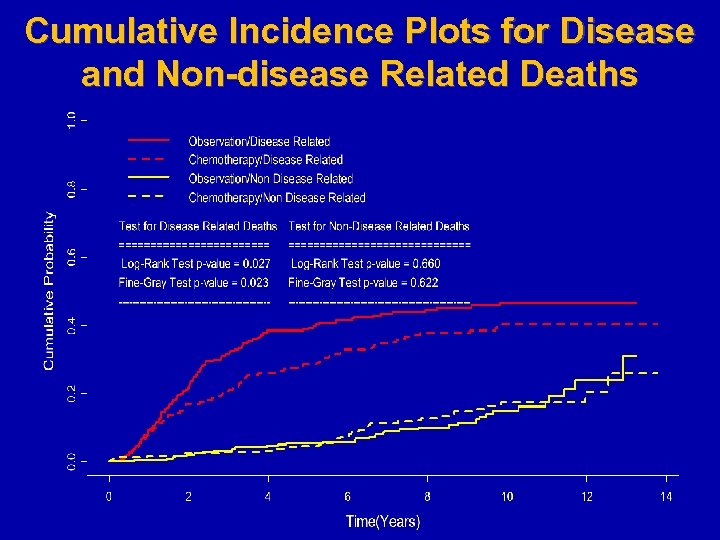 Cumulative Incidence Plots for Disease and Non-disease Related Deaths
Cumulative Incidence Plots for Disease and Non-disease Related Deaths
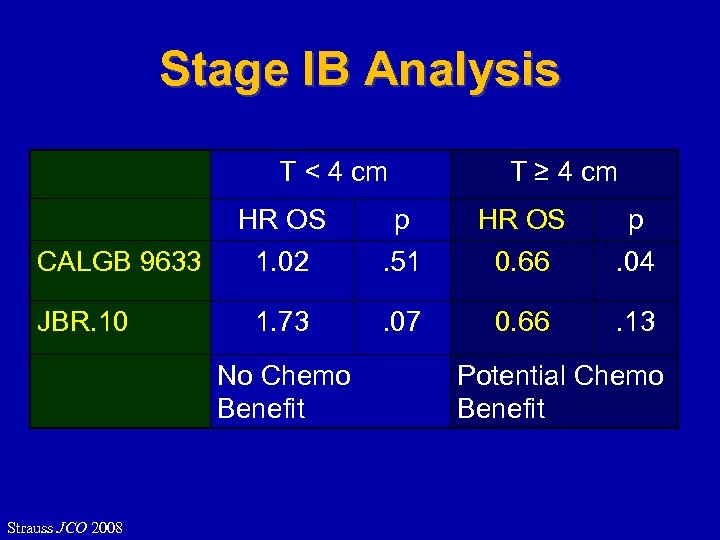 Stage IB Analysis T < 4 cm T ≥ 4 cm HR OS p CALGB 9633 1. 02 . 51 0. 66 . 04 JBR. 10 1. 73 . 07 0. 66 . 13 No Chemo Benefit Strauss JCO 2008 Potential Chemo Benefit
Stage IB Analysis T < 4 cm T ≥ 4 cm HR OS p CALGB 9633 1. 02 . 51 0. 66 . 04 JBR. 10 1. 73 . 07 0. 66 . 13 No Chemo Benefit Strauss JCO 2008 Potential Chemo Benefit
 ANITA - 840 pts, stage IB-IIIA • 1: 1 Randomization post-resection – Vinorelbine (30 mg/m 2) Q wk X 16 + Cisplatin 100 mg/m 2 Q 4 wks X 4 vs – Observation • Radiation therapy allowed • 8. 6% survival advantage at 5 years (persists at 7 yr) – 42. 6% vs 51. 2% alive • HR 0. 7 [0. 66 -0. 95], p =. 013 • Benefit only in stage II and IIIA Douillard Lancet Oncol. 7: 719, 2006
ANITA - 840 pts, stage IB-IIIA • 1: 1 Randomization post-resection – Vinorelbine (30 mg/m 2) Q wk X 16 + Cisplatin 100 mg/m 2 Q 4 wks X 4 vs – Observation • Radiation therapy allowed • 8. 6% survival advantage at 5 years (persists at 7 yr) – 42. 6% vs 51. 2% alive • HR 0. 7 [0. 66 -0. 95], p =. 013 • Benefit only in stage II and IIIA Douillard Lancet Oncol. 7: 719, 2006
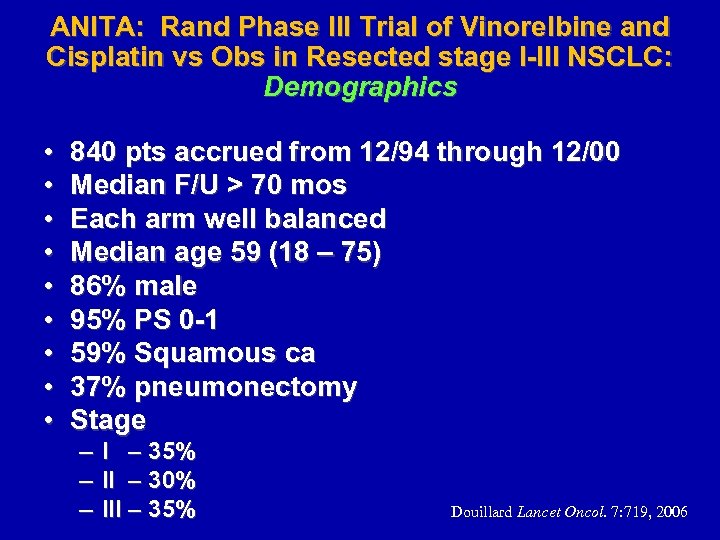 ANITA: Rand Phase III Trial of Vinorelbine and Cisplatin vs Obs in Resected stage I-III NSCLC: Demographics • • • 840 pts accrued from 12/94 through 12/00 Median F/U > 70 mos Each arm well balanced Median age 59 (18 – 75) 86% male 95% PS 0 -1 59% Squamous ca 37% pneumonectomy Stage – – – I – 35% II – 30% III – 35% Douillard Lancet Oncol. 7: 719, 2006
ANITA: Rand Phase III Trial of Vinorelbine and Cisplatin vs Obs in Resected stage I-III NSCLC: Demographics • • • 840 pts accrued from 12/94 through 12/00 Median F/U > 70 mos Each arm well balanced Median age 59 (18 – 75) 86% male 95% PS 0 -1 59% Squamous ca 37% pneumonectomy Stage – – – I – 35% II – 30% III – 35% Douillard Lancet Oncol. 7: 719, 2006
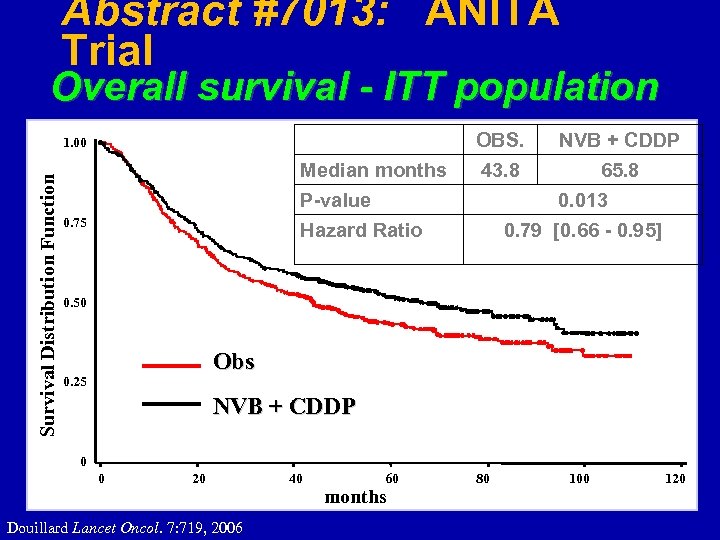 Abstract #7013: ANITA Trial Overall survival - ITT population OBS. Survival Distribution Function 1. 00 Median months NVB + CDDP 43. 8 65. 8 P-value 0. 75 0. 013 Hazard Ratio 0. 79 [0. 66 - 0. 95] 0. 50 Obs 0. 25 NVB + CDDP 0 0 20 Douillard Lancet Oncol. 7: 719, 2006 40 60 months 80 100 120
Abstract #7013: ANITA Trial Overall survival - ITT population OBS. Survival Distribution Function 1. 00 Median months NVB + CDDP 43. 8 65. 8 P-value 0. 75 0. 013 Hazard Ratio 0. 79 [0. 66 - 0. 95] 0. 50 Obs 0. 25 NVB + CDDP 0 0 20 Douillard Lancet Oncol. 7: 719, 2006 40 60 months 80 100 120
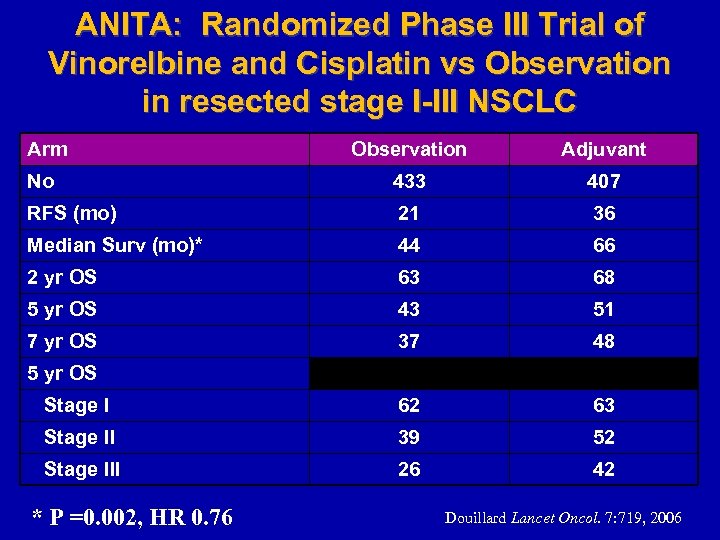 ANITA: Randomized Phase III Trial of Vinorelbine and Cisplatin vs Observation in resected stage I-III NSCLC Arm Observation Adjuvant No 433 407 RFS (mo) 21 36 Median Surv (mo)* 44 66 2 yr OS 63 68 5 yr OS 43 51 7 yr OS 37 48 Stage I 62 63 Stage II 39 52 Stage III 26 42 5 yr OS * P =0. 002, HR 0. 76 Douillard Lancet Oncol. 7: 719, 2006
ANITA: Randomized Phase III Trial of Vinorelbine and Cisplatin vs Observation in resected stage I-III NSCLC Arm Observation Adjuvant No 433 407 RFS (mo) 21 36 Median Surv (mo)* 44 66 2 yr OS 63 68 5 yr OS 43 51 7 yr OS 37 48 Stage I 62 63 Stage II 39 52 Stage III 26 42 5 yr OS * P =0. 002, HR 0. 76 Douillard Lancet Oncol. 7: 719, 2006
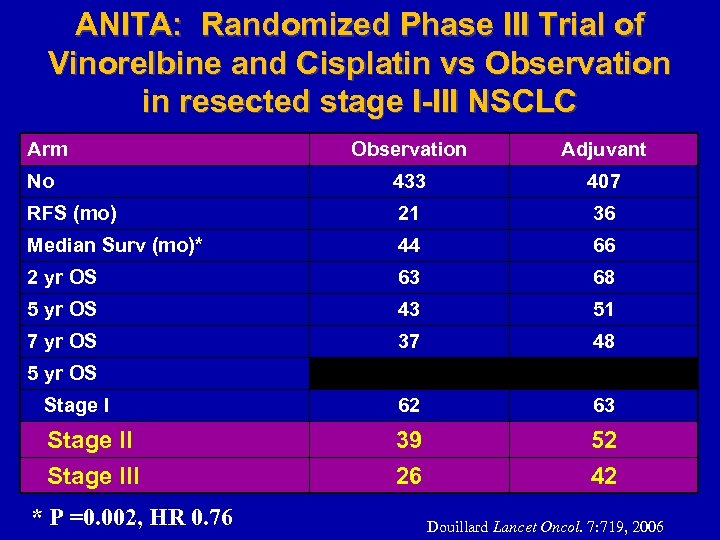 ANITA: Randomized Phase III Trial of Vinorelbine and Cisplatin vs Observation in resected stage I-III NSCLC Arm Observation Adjuvant No 433 407 RFS (mo) 21 36 Median Surv (mo)* 44 66 2 yr OS 63 68 5 yr OS 43 51 7 yr OS 37 48 Stage I 62 63 Stage III 39 26 52 42 5 yr OS * P =0. 002, HR 0. 76 Douillard Lancet Oncol. 7: 719, 2006
ANITA: Randomized Phase III Trial of Vinorelbine and Cisplatin vs Observation in resected stage I-III NSCLC Arm Observation Adjuvant No 433 407 RFS (mo) 21 36 Median Surv (mo)* 44 66 2 yr OS 63 68 5 yr OS 43 51 7 yr OS 37 48 Stage I 62 63 Stage III 39 26 52 42 5 yr OS * P =0. 002, HR 0. 76 Douillard Lancet Oncol. 7: 719, 2006
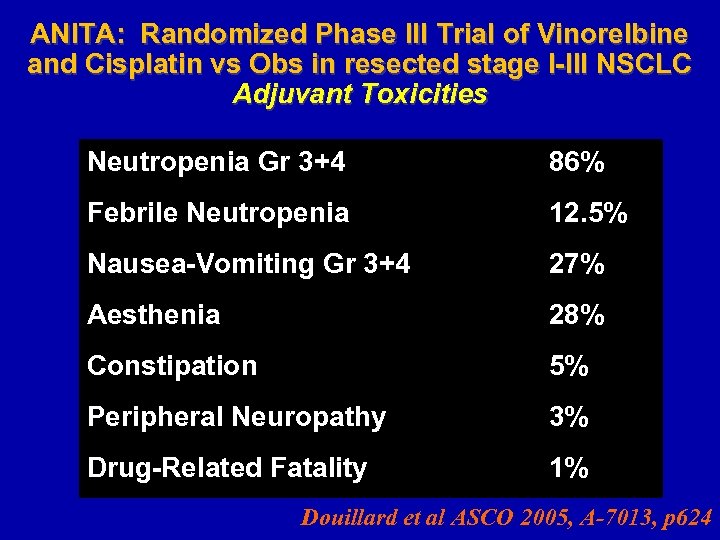 ANITA: Randomized Phase III Trial of Vinorelbine and Cisplatin vs Obs in resected stage I-III NSCLC Adjuvant Toxicities Neutropenia Gr 3+4 86% Febrile Neutropenia 12. 5% Nausea-Vomiting Gr 3+4 27% Aesthenia 28% Constipation 5% Peripheral Neuropathy 3% Drug-Related Fatality 1% Douillard et al ASCO 2005, A-7013, p 624
ANITA: Randomized Phase III Trial of Vinorelbine and Cisplatin vs Obs in resected stage I-III NSCLC Adjuvant Toxicities Neutropenia Gr 3+4 86% Febrile Neutropenia 12. 5% Nausea-Vomiting Gr 3+4 27% Aesthenia 28% Constipation 5% Peripheral Neuropathy 3% Drug-Related Fatality 1% Douillard et al ASCO 2005, A-7013, p 624
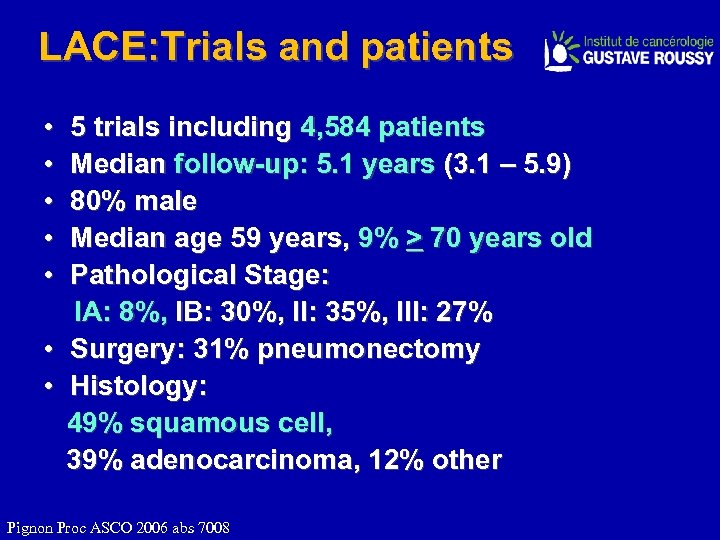 LACE: Trials and patients • 5 trials including 4, 584 patients • Median follow-up: 5. 1 years (3. 1 – 5. 9) • 80% male • Median age 59 years, 9% > 70 years old • Pathological Stage: IA: 8%, IB: 30%, II: 35%, III: 27% • Surgery: 31% pneumonectomy • Histology: 49% squamous cell, 39% adenocarcinoma, 12% other Pignon Proc ASCO 2006 abs 7008
LACE: Trials and patients • 5 trials including 4, 584 patients • Median follow-up: 5. 1 years (3. 1 – 5. 9) • 80% male • Median age 59 years, 9% > 70 years old • Pathological Stage: IA: 8%, IB: 30%, II: 35%, III: 27% • Surgery: 31% pneumonectomy • Histology: 49% squamous cell, 39% adenocarcinoma, 12% other Pignon Proc ASCO 2006 abs 7008
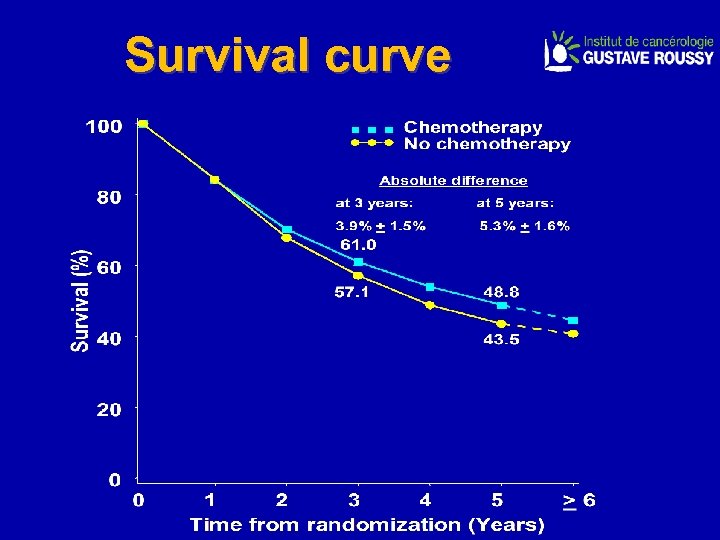 Survival curve
Survival curve
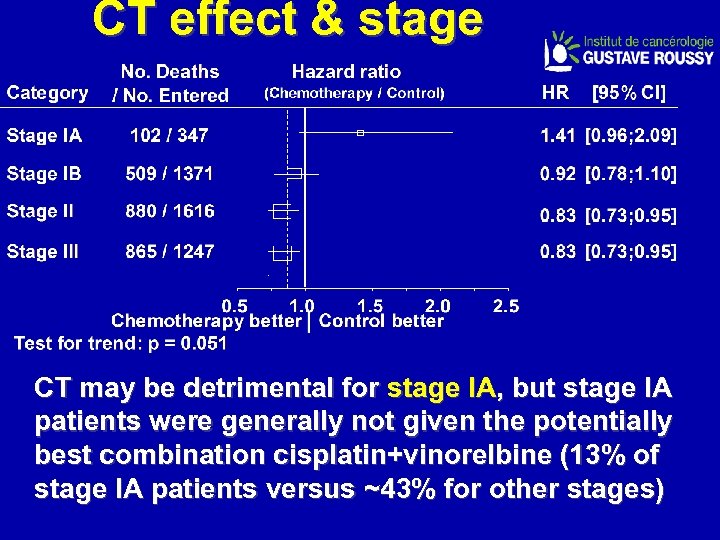 CT effect & stage CT may be detrimental for stage IA, but stage IA patients were generally not given the potentially best combination cisplatin+vinorelbine (13% of stage IA patients versus ~43% for other stages)
CT effect & stage CT may be detrimental for stage IA, but stage IA patients were generally not given the potentially best combination cisplatin+vinorelbine (13% of stage IA patients versus ~43% for other stages)
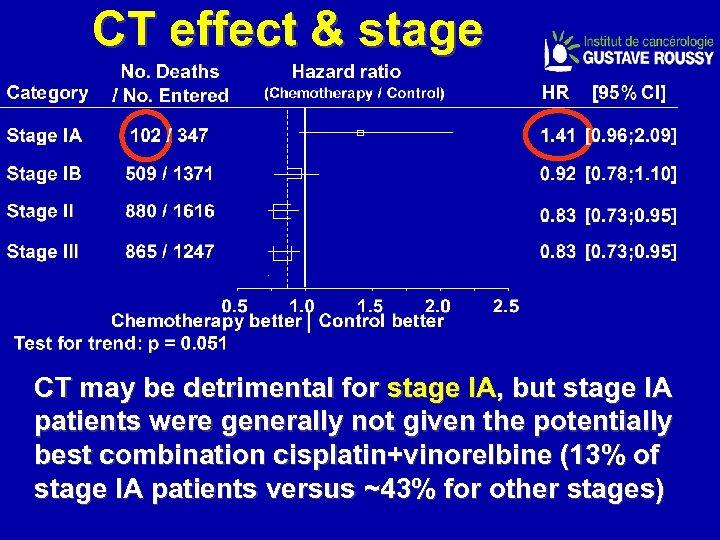 CT effect & stage CT may be detrimental for stage IA, but stage IA patients were generally not given the potentially best combination cisplatin+vinorelbine (13% of stage IA patients versus ~43% for other stages)
CT effect & stage CT may be detrimental for stage IA, but stage IA patients were generally not given the potentially best combination cisplatin+vinorelbine (13% of stage IA patients versus ~43% for other stages)
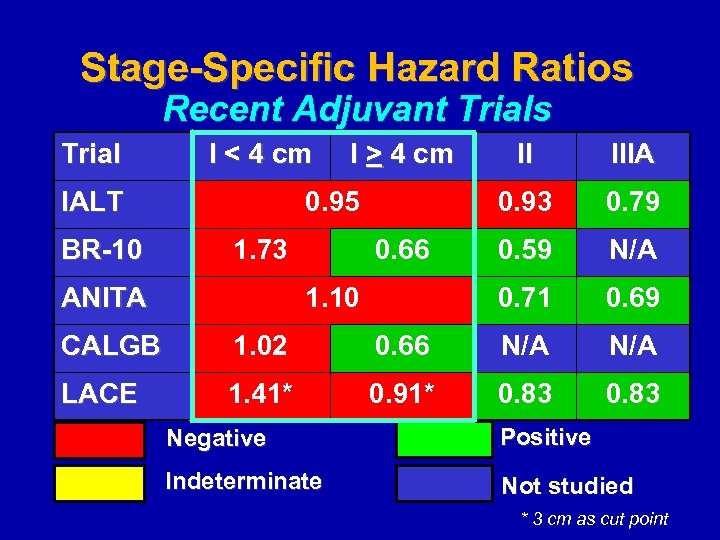 Stage-Specific Hazard Ratios Recent Adjuvant Trials Trial I < 4 cm IALT BR-10 I > 4 cm 1. 73 ANITA 1. 10 0. 79 0. 59 N/A 0. 71 0. 66 IIIA 0. 93 0. 95 II 0. 69 CALGB 1. 02 0. 66 N/A LACE 1. 41* 0. 91* 0. 83 Negative Positive Indeterminate Not studied * 3 cm as cut point
Stage-Specific Hazard Ratios Recent Adjuvant Trials Trial I < 4 cm IALT BR-10 I > 4 cm 1. 73 ANITA 1. 10 0. 79 0. 59 N/A 0. 71 0. 66 IIIA 0. 93 0. 95 II 0. 69 CALGB 1. 02 0. 66 N/A LACE 1. 41* 0. 91* 0. 83 Negative Positive Indeterminate Not studied * 3 cm as cut point
 Therapeutic Implications • Short course adjuvant, platinum-based therapy has emerged as standard practice in resected stage Ib-IIIa NSCLC • Ongoing controversies re: – – – – Molecular Selection Influence of Age on Outcome Ideal plating agent: carbo vs cisplatin Choice of partner agent Impact of Stage Role of targeted agents Utility of RT in IIIA (N 2)
Therapeutic Implications • Short course adjuvant, platinum-based therapy has emerged as standard practice in resected stage Ib-IIIa NSCLC • Ongoing controversies re: – – – – Molecular Selection Influence of Age on Outcome Ideal plating agent: carbo vs cisplatin Choice of partner agent Impact of Stage Role of targeted agents Utility of RT in IIIA (N 2)
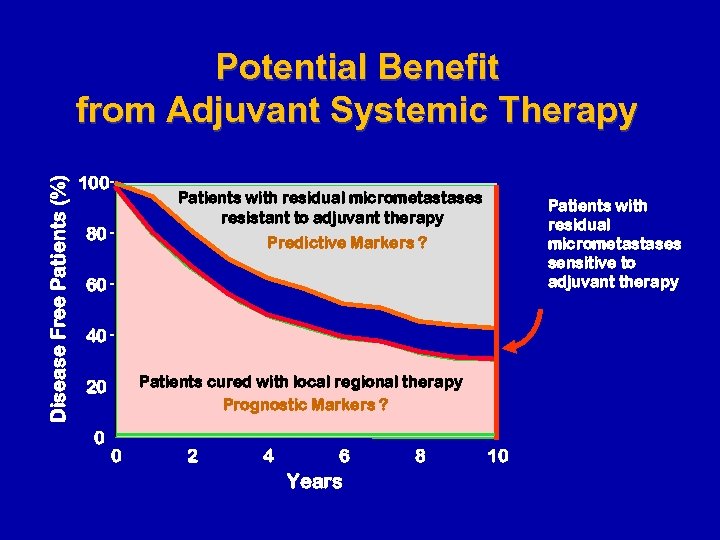 Disease Free Patients (%) Potential Benefit from Adjuvant Systemic Therapy 100 Patients with residual micrometastases resistant to adjuvant therapy 80 Patients with residual micrometastases sensitive to adjuvant therapy Predictive Markers ? 60 40 Patients cured with local regional therapy Prognostic Markers ? 20 0 0 2 4 6 Years 8 10
Disease Free Patients (%) Potential Benefit from Adjuvant Systemic Therapy 100 Patients with residual micrometastases resistant to adjuvant therapy 80 Patients with residual micrometastases sensitive to adjuvant therapy Predictive Markers ? 60 40 Patients cured with local regional therapy Prognostic Markers ? 20 0 0 2 4 6 Years 8 10
 Influence of Age on Outcome
Influence of Age on Outcome
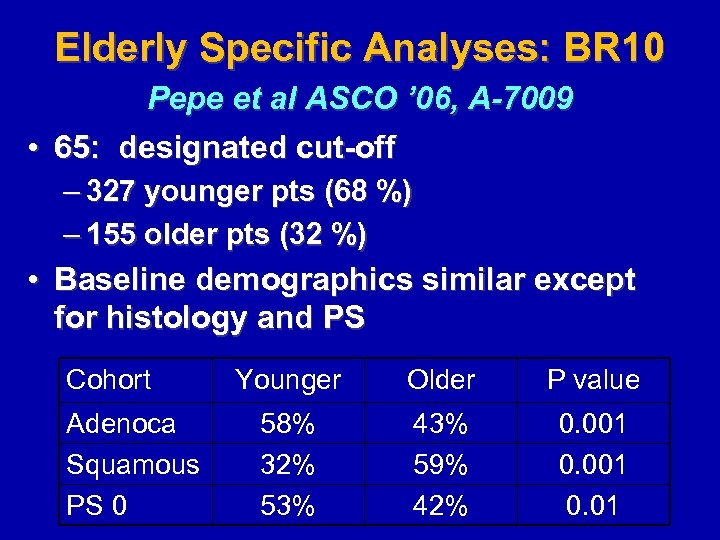 Elderly Specific Analyses: BR 10 Pepe et al ASCO ’ 06, A-7009 • 65: designated cut-off – 327 younger pts (68 %) – 155 older pts (32 %) • Baseline demographics similar except for histology and PS Cohort Adenoca Squamous PS 0 Younger Older P value 58% 32% 53% 43% 59% 42% 0. 001 0. 01
Elderly Specific Analyses: BR 10 Pepe et al ASCO ’ 06, A-7009 • 65: designated cut-off – 327 younger pts (68 %) – 155 older pts (32 %) • Baseline demographics similar except for histology and PS Cohort Adenoca Squamous PS 0 Younger Older P value 58% 32% 53% 43% 59% 42% 0. 001 0. 01
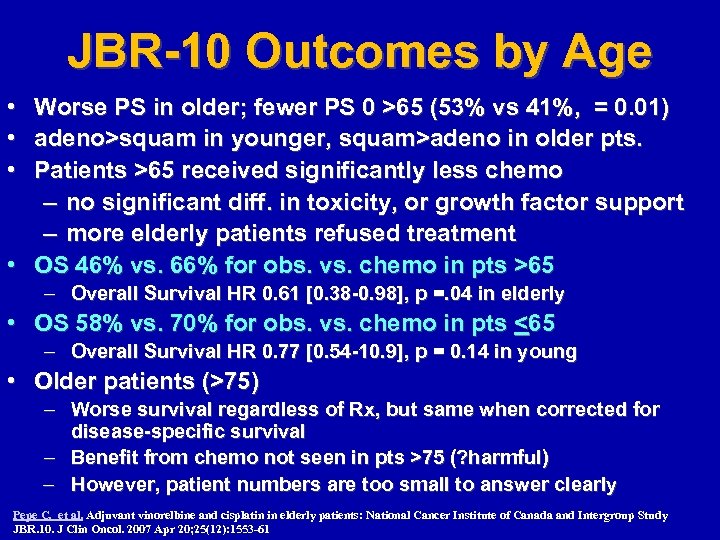 JBR-10 Outcomes by Age • Worse PS in older; fewer PS 0 >65 (53% vs 41%, = 0. 01) • adeno>squam in younger, squam>adeno in older pts. • Patients >65 received significantly less chemo – no significant diff. in toxicity, or growth factor support – more elderly patients refused treatment • OS 46% vs. 66% for obs. vs. chemo in pts >65 – Overall Survival HR 0. 61 [0. 38 -0. 98], p =. 04 in elderly • OS 58% vs. 70% for obs. vs. chemo in pts <65 – Overall Survival HR 0. 77 [0. 54 -10. 9], p = 0. 14 in young • Older patients (>75) – Worse survival regardless of Rx, but same when corrected for disease-specific survival – Benefit from chemo not seen in pts >75 (? harmful) – However, patient numbers are too small to answer clearly Pepe C, et al. Adjuvant vinorelbine and cisplatin in elderly patients: National Cancer Institute of Canada and Intergroup Study JBR. 10. J Clin Oncol. 2007 Apr 20; 25(12): 1553 -61
JBR-10 Outcomes by Age • Worse PS in older; fewer PS 0 >65 (53% vs 41%, = 0. 01) • adeno>squam in younger, squam>adeno in older pts. • Patients >65 received significantly less chemo – no significant diff. in toxicity, or growth factor support – more elderly patients refused treatment • OS 46% vs. 66% for obs. vs. chemo in pts >65 – Overall Survival HR 0. 61 [0. 38 -0. 98], p =. 04 in elderly • OS 58% vs. 70% for obs. vs. chemo in pts <65 – Overall Survival HR 0. 77 [0. 54 -10. 9], p = 0. 14 in young • Older patients (>75) – Worse survival regardless of Rx, but same when corrected for disease-specific survival – Benefit from chemo not seen in pts >75 (? harmful) – However, patient numbers are too small to answer clearly Pepe C, et al. Adjuvant vinorelbine and cisplatin in elderly patients: National Cancer Institute of Canada and Intergroup Study JBR. 10. J Clin Oncol. 2007 Apr 20; 25(12): 1553 -61
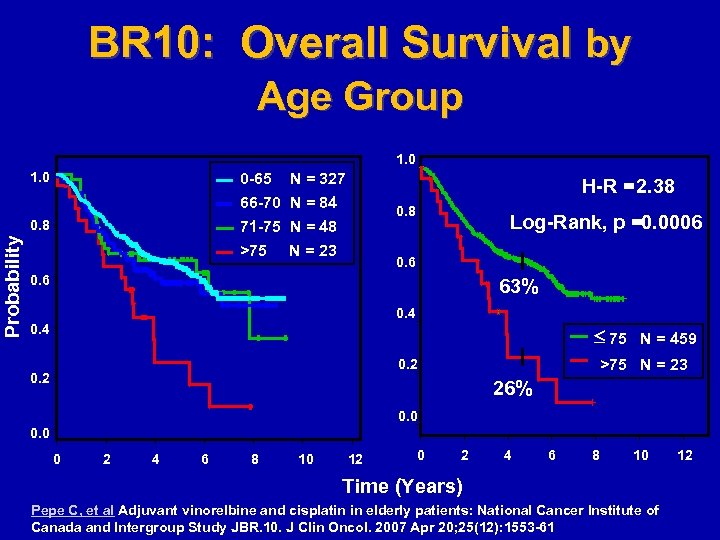 BR 10: Overall Survival by Age Group 1. 0 0 -65 N = 327 66 -70 N = 84 71 -75 N = 48 >75 N = 23 Probability 0. 8 H-R =2. 38 0. 8 Log-Rank, p =0. 0006 0. 6 63% 0. 4 75 N = 459 >75 N = 23 0. 2 26% 0. 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 0 2 4 6 8 10 Time (Years) Pepe C, et al Adjuvant vinorelbine and cisplatin in elderly patients: National Cancer Institute of Canada and Intergroup Study JBR. 10. J Clin Oncol. 2007 Apr 20; 25(12): 1553 -61 12
BR 10: Overall Survival by Age Group 1. 0 0 -65 N = 327 66 -70 N = 84 71 -75 N = 48 >75 N = 23 Probability 0. 8 H-R =2. 38 0. 8 Log-Rank, p =0. 0006 0. 6 63% 0. 4 75 N = 459 >75 N = 23 0. 2 26% 0. 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 0 2 4 6 8 10 Time (Years) Pepe C, et al Adjuvant vinorelbine and cisplatin in elderly patients: National Cancer Institute of Canada and Intergroup Study JBR. 10. J Clin Oncol. 2007 Apr 20; 25(12): 1553 -61 12
 Ideal Plating Agent
Ideal Plating Agent
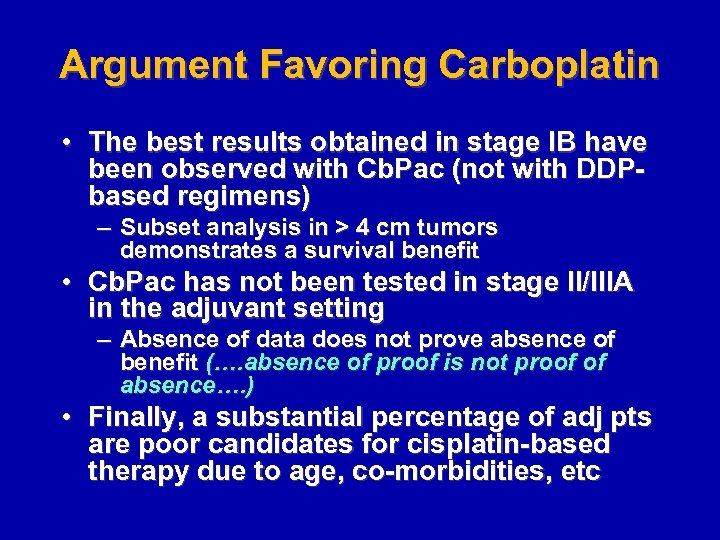 Argument Favoring Carboplatin • The best results obtained in stage IB have been observed with Cb. Pac (not with DDPbased regimens) – Subset analysis in > 4 cm tumors demonstrates a survival benefit • Cb. Pac has not been tested in stage II/IIIA in the adjuvant setting – Absence of data does not prove absence of benefit (…. absence of proof is not proof of absence…. ) • Finally, a substantial percentage of adj pts are poor candidates for cisplatin-based therapy due to age, co-morbidities, etc
Argument Favoring Carboplatin • The best results obtained in stage IB have been observed with Cb. Pac (not with DDPbased regimens) – Subset analysis in > 4 cm tumors demonstrates a survival benefit • Cb. Pac has not been tested in stage II/IIIA in the adjuvant setting – Absence of data does not prove absence of benefit (…. absence of proof is not proof of absence…. ) • Finally, a substantial percentage of adj pts are poor candidates for cisplatin-based therapy due to age, co-morbidities, etc
 Which Agents Partner Best with Platinum
Which Agents Partner Best with Platinum
 Randomized phase 2 Trial on Refinement of Early stage NSCLC Adjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin and pemetrexed (CPx) versus cisplatin and vinorelbine (CVb) - TREAT M. Kreuter, J. Vansteenkiste, J. Fischer, W. Eberhardt, H. Zabeck, J. Kollmeier, M. Serke, N. Frickhofen, M. Reck, W. Engel-Riedel, S. Neumann, M. Thomeer, C. Schumann, P. De Leyn, T. Graeter, G. Stamatis, I. Zuna, F. Griesinger and M. Thomas on behalf of the TREAT investigators
Randomized phase 2 Trial on Refinement of Early stage NSCLC Adjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin and pemetrexed (CPx) versus cisplatin and vinorelbine (CVb) - TREAT M. Kreuter, J. Vansteenkiste, J. Fischer, W. Eberhardt, H. Zabeck, J. Kollmeier, M. Serke, N. Frickhofen, M. Reck, W. Engel-Riedel, S. Neumann, M. Thomeer, C. Schumann, P. De Leyn, T. Graeter, G. Stamatis, I. Zuna, F. Griesinger and M. Thomas on behalf of the TREAT investigators
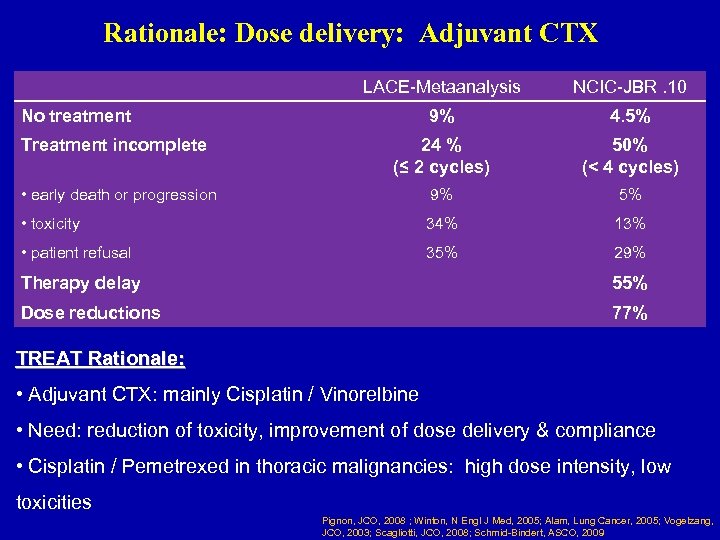 Rationale: Dose delivery: Adjuvant CTX LACE-Metaanalysis NCIC-JBR. 10 9% 4. 5% Treatment incomplete 24 % (≤ 2 cycles) 50% (< 4 cycles) • early death or progression 9% 5% • toxicity 34% 13% • patient refusal 35% 29% No treatment Therapy delay 55% Dose reductions 77% TREAT Rationale: • Adjuvant CTX: mainly Cisplatin / Vinorelbine • Need: reduction of toxicity, improvement of dose delivery & compliance • Cisplatin / Pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies: high dose intensity, low toxicities Pignon, JCO, 2008 ; Winton, N Engl J Med, 2005; Alam, Lung Cancer, 2005; Vogelzang, JCO, 2003; Scagliotti, JCO, 2008; Schmid-Bindert, ASCO, 2009
Rationale: Dose delivery: Adjuvant CTX LACE-Metaanalysis NCIC-JBR. 10 9% 4. 5% Treatment incomplete 24 % (≤ 2 cycles) 50% (< 4 cycles) • early death or progression 9% 5% • toxicity 34% 13% • patient refusal 35% 29% No treatment Therapy delay 55% Dose reductions 77% TREAT Rationale: • Adjuvant CTX: mainly Cisplatin / Vinorelbine • Need: reduction of toxicity, improvement of dose delivery & compliance • Cisplatin / Pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies: high dose intensity, low toxicities Pignon, JCO, 2008 ; Winton, N Engl J Med, 2005; Alam, Lung Cancer, 2005; Vogelzang, JCO, 2003; Scagliotti, JCO, 2008; Schmid-Bindert, ASCO, 2009
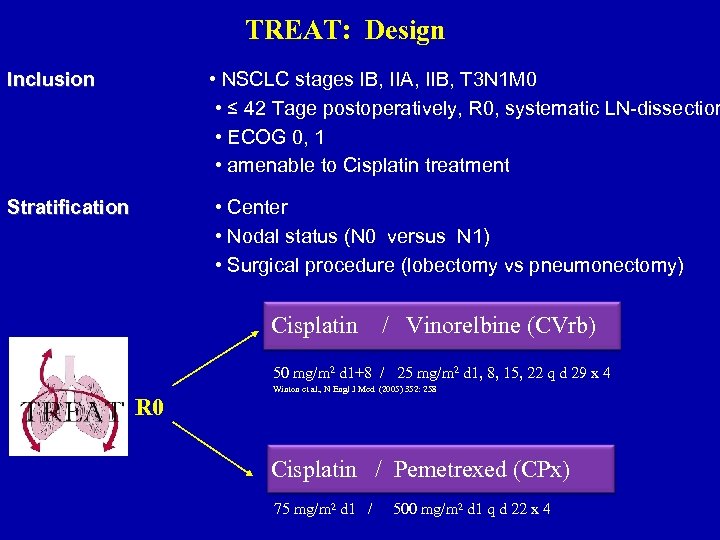 TREAT: Design Inclusion • NSCLC stages IB, IIA, IIB, T 3 N 1 M 0 • ≤ 42 Tage postoperatively, R 0, systematic LN-dissection • ECOG 0, 1 • amenable to Cisplatin treatment Stratification • Center • Nodal status (N 0 versus N 1) • Surgical procedure (lobectomy vs pneumonectomy) Cisplatin / Vinorelbine (CVrb) 50 mg/m 2 d 1+8 / 25 mg/m 2 d 1, 8, 15, 22 q d 29 x 4 R 0 Winton et al. , N Engl J Med (2005) 352: 258 Cisplatin / Pemetrexed (CPx) 75 mg/m 2 d 1 / 500 mg/m 2 d 1 q d 22 x 4
TREAT: Design Inclusion • NSCLC stages IB, IIA, IIB, T 3 N 1 M 0 • ≤ 42 Tage postoperatively, R 0, systematic LN-dissection • ECOG 0, 1 • amenable to Cisplatin treatment Stratification • Center • Nodal status (N 0 versus N 1) • Surgical procedure (lobectomy vs pneumonectomy) Cisplatin / Vinorelbine (CVrb) 50 mg/m 2 d 1+8 / 25 mg/m 2 d 1, 8, 15, 22 q d 29 x 4 R 0 Winton et al. , N Engl J Med (2005) 352: 258 Cisplatin / Pemetrexed (CPx) 75 mg/m 2 d 1 / 500 mg/m 2 d 1 q d 22 x 4
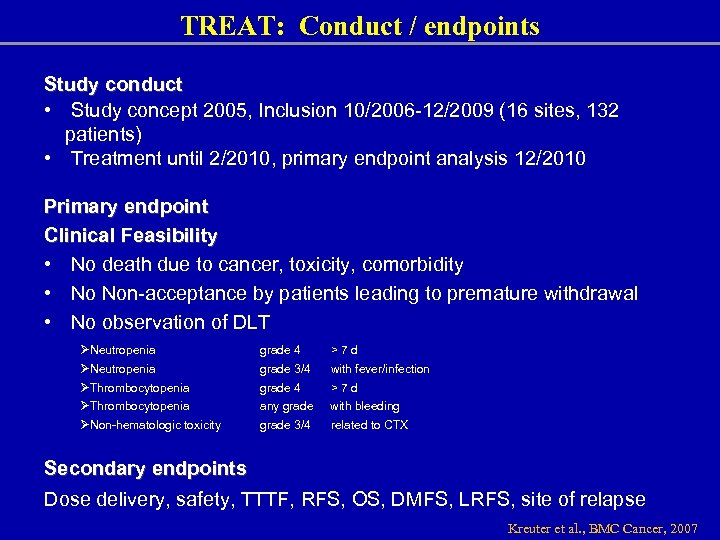 TREAT: Conduct / endpoints Study conduct • Study concept 2005, Inclusion 10/2006 -12/2009 (16 sites, 132 patients) • Treatment until 2/2010, primary endpoint analysis 12/2010 Primary endpoint Clinical Feasibility • No death due to cancer, toxicity, comorbidity • No Non-acceptance by patients leading to premature withdrawal • No observation of DLT ØNeutropenia ØThrombocytopenia ØNon-hematologic toxicity grade 4 >7 d grade 3/4 with fever/infection grade 4 >7 d any grade with bleeding grade 3/4 related to CTX Secondary endpoints Dose delivery, safety, TTTF, RFS, OS, DMFS, LRFS, site of relapse Kreuter et al. , BMC Cancer, 2007
TREAT: Conduct / endpoints Study conduct • Study concept 2005, Inclusion 10/2006 -12/2009 (16 sites, 132 patients) • Treatment until 2/2010, primary endpoint analysis 12/2010 Primary endpoint Clinical Feasibility • No death due to cancer, toxicity, comorbidity • No Non-acceptance by patients leading to premature withdrawal • No observation of DLT ØNeutropenia ØThrombocytopenia ØNon-hematologic toxicity grade 4 >7 d grade 3/4 with fever/infection grade 4 >7 d any grade with bleeding grade 3/4 related to CTX Secondary endpoints Dose delivery, safety, TTTF, RFS, OS, DMFS, LRFS, site of relapse Kreuter et al. , BMC Cancer, 2007
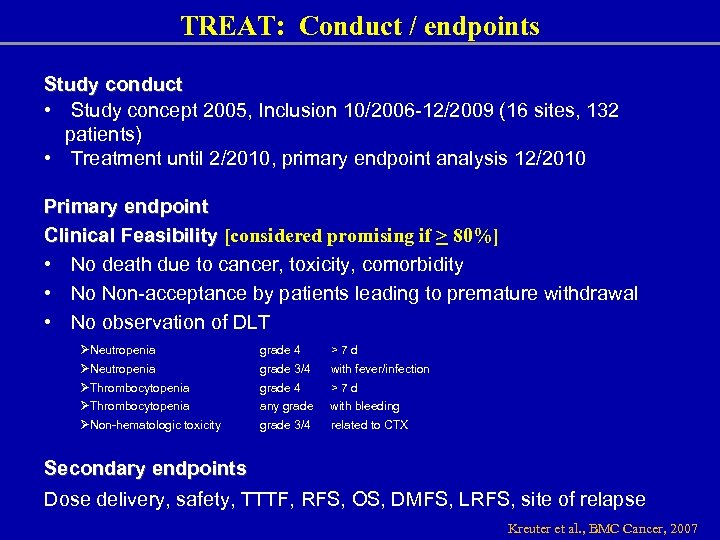 TREAT: Conduct / endpoints Study conduct • Study concept 2005, Inclusion 10/2006 -12/2009 (16 sites, 132 patients) • Treatment until 2/2010, primary endpoint analysis 12/2010 Primary endpoint Clinical Feasibility [considered promising if > 80%] • No death due to cancer, toxicity, comorbidity • No Non-acceptance by patients leading to premature withdrawal • No observation of DLT ØNeutropenia ØThrombocytopenia ØNon-hematologic toxicity grade 4 >7 d grade 3/4 with fever/infection grade 4 >7 d any grade with bleeding grade 3/4 related to CTX Secondary endpoints Dose delivery, safety, TTTF, RFS, OS, DMFS, LRFS, site of relapse Kreuter et al. , BMC Cancer, 2007
TREAT: Conduct / endpoints Study conduct • Study concept 2005, Inclusion 10/2006 -12/2009 (16 sites, 132 patients) • Treatment until 2/2010, primary endpoint analysis 12/2010 Primary endpoint Clinical Feasibility [considered promising if > 80%] • No death due to cancer, toxicity, comorbidity • No Non-acceptance by patients leading to premature withdrawal • No observation of DLT ØNeutropenia ØThrombocytopenia ØNon-hematologic toxicity grade 4 >7 d grade 3/4 with fever/infection grade 4 >7 d any grade with bleeding grade 3/4 related to CTX Secondary endpoints Dose delivery, safety, TTTF, RFS, OS, DMFS, LRFS, site of relapse Kreuter et al. , BMC Cancer, 2007
![TREAT: Characteristics Age (years [range]) Gender (%) • male • female Smoking status (%) TREAT: Characteristics Age (years [range]) Gender (%) • male • female Smoking status (%)](https://present5.com/presentation/e26c25e84c43960a5eb558435521d2f6/image-56.jpg) TREAT: Characteristics Age (years [range]) Gender (%) • male • female Smoking status (%) • Smoker • Ex-smoker • Non-smoker • Not available CPx CVb Total (n=67) (n=65) (n=132) 58 [40 -73] 60 [38 -74] 59 [38 -74] 72 28 77 23 74 26 33 61 6 0 26 71 1. 5 29 66 4 1 37 12 46 5 38 8 48 6 38 10 47 5 Stage (%) IB IIA IIB T 3 N 1
TREAT: Characteristics Age (years [range]) Gender (%) • male • female Smoking status (%) • Smoker • Ex-smoker • Non-smoker • Not available CPx CVb Total (n=67) (n=65) (n=132) 58 [40 -73] 60 [38 -74] 59 [38 -74] 72 28 77 23 74 26 33 61 6 0 26 71 1. 5 29 66 4 1 37 12 46 5 38 8 48 6 38 10 47 5 Stage (%) IB IIA IIB T 3 N 1
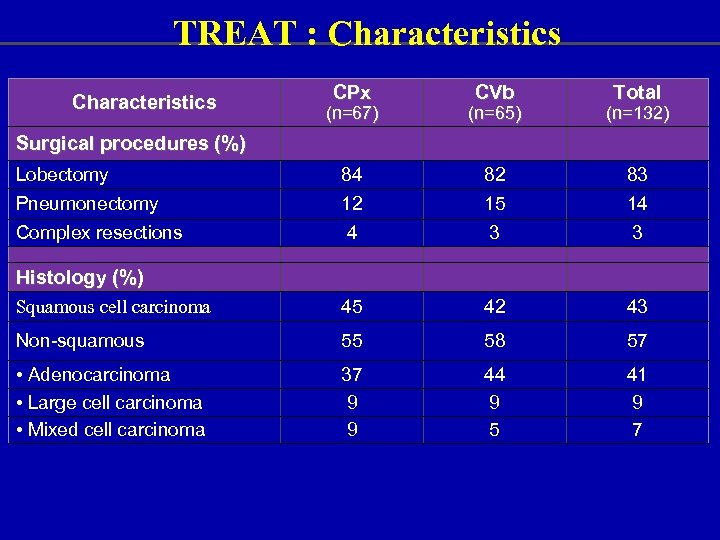 TREAT : Characteristics CPx CVb Total (n=67) (n=65) (n=132) Lobectomy 84 82 83 Pneumonectomy 12 15 14 Complex resections 4 3 3 Squamous cell carcinoma 45 42 43 Non-squamous 55 58 57 • Adenocarcinoma • Large cell carcinoma • Mixed cell carcinoma 37 9 9 44 9 5 41 9 7 Surgical procedures (%) Histology (%)
TREAT : Characteristics CPx CVb Total (n=67) (n=65) (n=132) Lobectomy 84 82 83 Pneumonectomy 12 15 14 Complex resections 4 3 3 Squamous cell carcinoma 45 42 43 Non-squamous 55 58 57 • Adenocarcinoma • Large cell carcinoma • Mixed cell carcinoma 37 9 9 44 9 5 41 9 7 Surgical procedures (%) Histology (%)
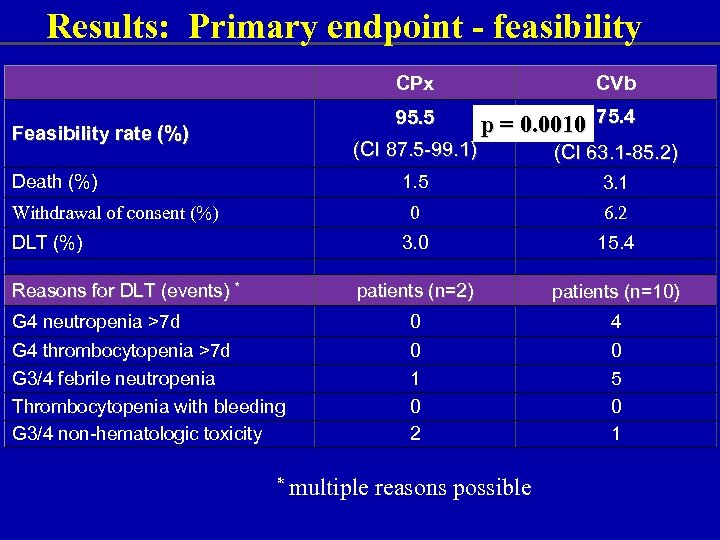 Results: Primary endpoint - feasibility CPx 95. 5 Feasibility rate (%) CVb p = 0. 0010 75. 4 (CI 87. 5 -99. 1) Death (%) (CI 63. 1 -85. 2) 1. 5 3. 1 0 6. 2 3. 0 15. 4 patients (n=2) patients (n=10) G 4 neutropenia >7 d 0 4 G 4 thrombocytopenia >7 d G 3/4 febrile neutropenia Thrombocytopenia with bleeding G 3/4 non-hematologic toxicity 0 1 0 2 0 5 0 1 Withdrawal of consent (%) DLT (%) Reasons for DLT (events) * * multiple reasons possible
Results: Primary endpoint - feasibility CPx 95. 5 Feasibility rate (%) CVb p = 0. 0010 75. 4 (CI 87. 5 -99. 1) Death (%) (CI 63. 1 -85. 2) 1. 5 3. 1 0 6. 2 3. 0 15. 4 patients (n=2) patients (n=10) G 4 neutropenia >7 d 0 4 G 4 thrombocytopenia >7 d G 3/4 febrile neutropenia Thrombocytopenia with bleeding G 3/4 non-hematologic toxicity 0 1 0 2 0 5 0 1 Withdrawal of consent (%) DLT (%) Reasons for DLT (events) * * multiple reasons possible
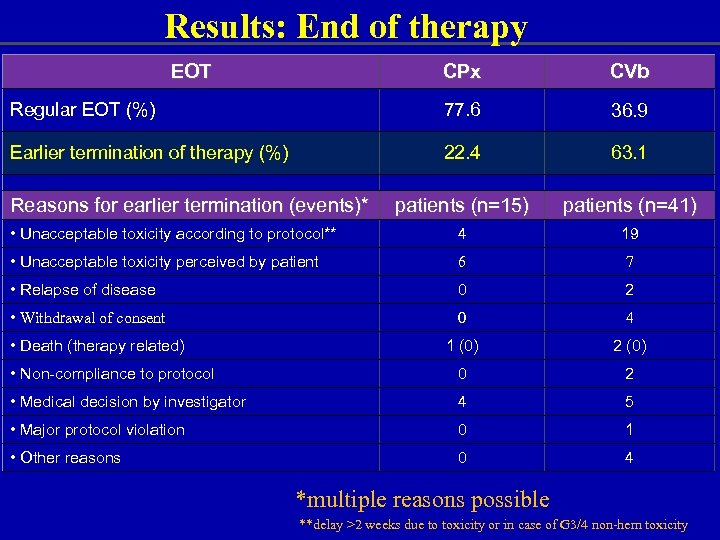 Results: End of therapy EOT CPx CVb Regular EOT (%) 77. 6 36. 9 Earlier termination of therapy (%) 22. 4 63. 1 patients (n=15) patients (n=41) • Unacceptable toxicity according to protocol** 4 19 • Unacceptable toxicity perceived by patient 6 7 • Relapse of disease 0 2 • Withdrawal of consent 0 4 1 (0) 2 (0) • Non-compliance to protocol 0 2 • Medical decision by investigator 4 5 • Major protocol violation 0 1 • Other reasons 0 4 Reasons for earlier termination (events)* • Death (therapy related) *multiple reasons possible **delay >2 weeks due to toxicity or in case of G 3/4 non-hem toxicity
Results: End of therapy EOT CPx CVb Regular EOT (%) 77. 6 36. 9 Earlier termination of therapy (%) 22. 4 63. 1 patients (n=15) patients (n=41) • Unacceptable toxicity according to protocol** 4 19 • Unacceptable toxicity perceived by patient 6 7 • Relapse of disease 0 2 • Withdrawal of consent 0 4 1 (0) 2 (0) • Non-compliance to protocol 0 2 • Medical decision by investigator 4 5 • Major protocol violation 0 1 • Other reasons 0 4 Reasons for earlier termination (events)* • Death (therapy related) *multiple reasons possible **delay >2 weeks due to toxicity or in case of G 3/4 non-hem toxicity
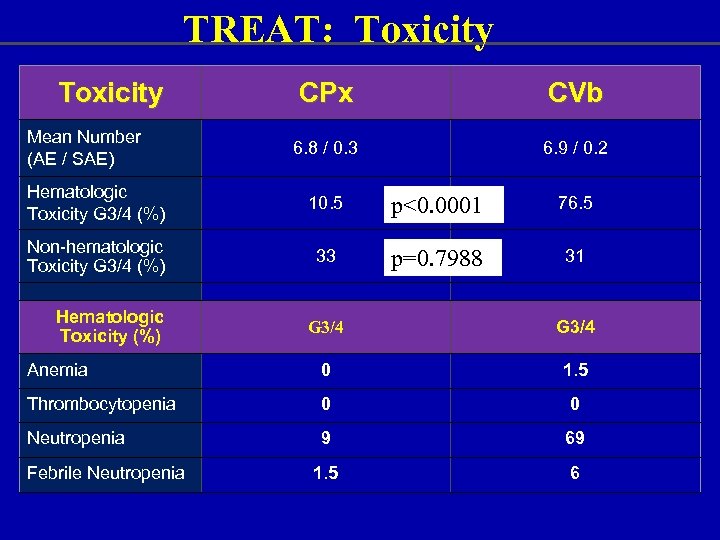 TREAT: Toxicity Mean Number (AE / SAE) CPx CVb 6. 8 / 0. 3 6. 9 / 0. 2 Hematologic Toxicity G 3/4 (%) 10. 5 p<0. 0001 76. 5 Non-hematologic Toxicity G 3/4 (%) 33 p=0. 7988 31 Hematologic Toxicity (%) G 3/4 Anemia 0 1. 5 Thrombocytopenia 0 0 Neutropenia 9 69 1. 5 6 Febrile Neutropenia
TREAT: Toxicity Mean Number (AE / SAE) CPx CVb 6. 8 / 0. 3 6. 9 / 0. 2 Hematologic Toxicity G 3/4 (%) 10. 5 p<0. 0001 76. 5 Non-hematologic Toxicity G 3/4 (%) 33 p=0. 7988 31 Hematologic Toxicity (%) G 3/4 Anemia 0 1. 5 Thrombocytopenia 0 0 Neutropenia 9 69 1. 5 6 Febrile Neutropenia
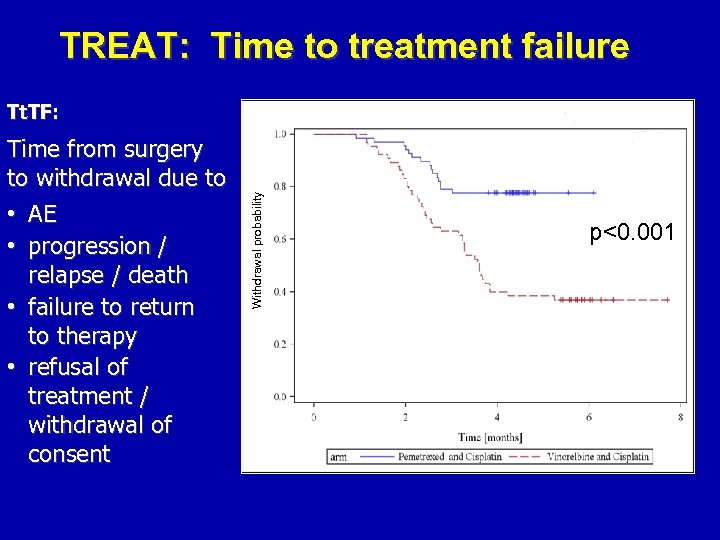 TREAT: Time to treatment failure Time from surgery to withdrawal due to • AE • progression / relapse / death • failure to return to therapy • refusal of treatment / withdrawal of consent Withdrawal probability Tt. TF: p<0. 001
TREAT: Time to treatment failure Time from surgery to withdrawal due to • AE • progression / relapse / death • failure to return to therapy • refusal of treatment / withdrawal of consent Withdrawal probability Tt. TF: p<0. 001
 TREAT: Conclusions • CPx safe and feasible Ø less toxicity compared to CVb Ø superior dose delivery compared to CVb Ø high dose density (mg/m 2/week) • Dose delivery failure in CVb mostly due to Vb (delivery d 15, d 22) • Efficacy: longer follow up to be awaited
TREAT: Conclusions • CPx safe and feasible Ø less toxicity compared to CVb Ø superior dose delivery compared to CVb Ø high dose density (mg/m 2/week) • Dose delivery failure in CVb mostly due to Vb (delivery d 15, d 22) • Efficacy: longer follow up to be awaited
 Molecular Selection
Molecular Selection
 Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining of the Excision Repair Cross-Complementing 1 (ERCC 1) Protein as Predictor of Benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy (CT) in the International Lung Cancer Trial (IALT) · 761 pts. (28 centers, 14 countries) evaluable for ERCC 1 expression · ERCC 1 repairs cisplatin-DNA adducts, so expression indicates platinum resistance · ERCC 1 a “double-edged sword”; worse prognosis of NSCLC if low expression, but more responsive to platinum Soria, Proc ASCO 2006 A#7010; Olaussen K et al. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 983 -991
Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining of the Excision Repair Cross-Complementing 1 (ERCC 1) Protein as Predictor of Benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy (CT) in the International Lung Cancer Trial (IALT) · 761 pts. (28 centers, 14 countries) evaluable for ERCC 1 expression · ERCC 1 repairs cisplatin-DNA adducts, so expression indicates platinum resistance · ERCC 1 a “double-edged sword”; worse prognosis of NSCLC if low expression, but more responsive to platinum Soria, Proc ASCO 2006 A#7010; Olaussen K et al. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 983 -991
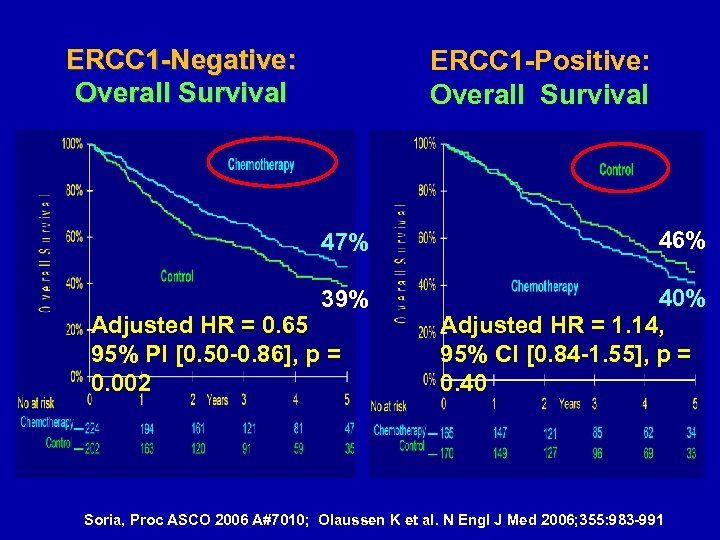 ERCC 1 -Negative: Overall Survival ERCC 1 -Positive: Overall Survival 47% 46% 39% 40% Adjusted HR = 1. 14, 95% CI [0. 84 -1. 55], p = 0. 40 Adjusted HR = 0. 65 95% PI [0. 50 -0. 86], p = 0. 002 Soria, Proc ASCO 2006 A#7010; Olaussen K et al. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 983 -991
ERCC 1 -Negative: Overall Survival ERCC 1 -Positive: Overall Survival 47% 46% 39% 40% Adjusted HR = 1. 14, 95% CI [0. 84 -1. 55], p = 0. 40 Adjusted HR = 0. 65 95% PI [0. 50 -0. 86], p = 0. 002 Soria, Proc ASCO 2006 A#7010; Olaussen K et al. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 983 -991
 IFCT-0801 TASTE TAilored post-Surgical Therapy in Early stage NSCLC Principal Investigator Jean-Charles SORIA Institut Gustave Roussy - Villejuif Biological Coordinator Marie Wislez Hôpital Tenon - Paris
IFCT-0801 TASTE TAilored post-Surgical Therapy in Early stage NSCLC Principal Investigator Jean-Charles SORIA Institut Gustave Roussy - Villejuif Biological Coordinator Marie Wislez Hôpital Tenon - Paris
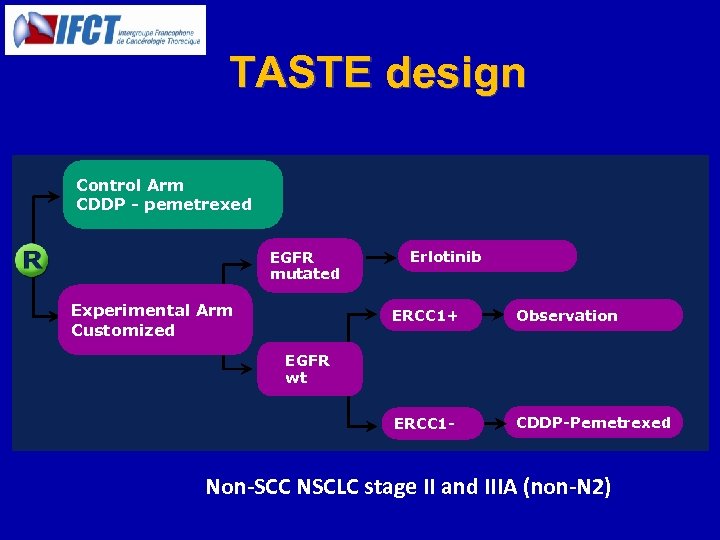 TASTE design Control Arm CDDP - pemetrexed EGFR mutated Experimental Arm Customized Erlotinib ERCC 1+ Observation ERCC 1 - CDDP-Pemetrexed EGFR wt Non-SCC NSCLC stage II and IIIA (non-N 2)
TASTE design Control Arm CDDP - pemetrexed EGFR mutated Experimental Arm Customized Erlotinib ERCC 1+ Observation ERCC 1 - CDDP-Pemetrexed EGFR wt Non-SCC NSCLC stage II and IIIA (non-N 2)
 TASTE Results • • • 150 pts randomized between May 2009 and July 2012, 74 in arm A (PEM/DDP) and 76 in arm B (Selected) Most pts were male (61%), > 60 years (51%), and smokers (91%) Pathological stage was IIA in 69 pt, IIB in 48 pt and IIIA in 32 pt. ERCC 1 was positive in 38 pts (19 in each arm) – only 25%, not 44% expected • EGFR mutation was identified in 10 pts (3 in arm A, 7 in arm B). – Arm A, all pts received CP. – Arm B, • 7 pts received erlotinib, • 53 pts received CP • 16 were observed • Median exposure time to erlotinib was 276 days (10 -365). • Out of 127 pts allocated to CP, 82% received the expected 4 cycles with a very good tolerability profile (no febrile neutropenia). • Success rate was 80% (120 out of 150 pts): appropriate Tx A-7505, ASCO ‘ 13 Soria J-C et al assignment 68
TASTE Results • • • 150 pts randomized between May 2009 and July 2012, 74 in arm A (PEM/DDP) and 76 in arm B (Selected) Most pts were male (61%), > 60 years (51%), and smokers (91%) Pathological stage was IIA in 69 pt, IIB in 48 pt and IIIA in 32 pt. ERCC 1 was positive in 38 pts (19 in each arm) – only 25%, not 44% expected • EGFR mutation was identified in 10 pts (3 in arm A, 7 in arm B). – Arm A, all pts received CP. – Arm B, • 7 pts received erlotinib, • 53 pts received CP • 16 were observed • Median exposure time to erlotinib was 276 days (10 -365). • Out of 127 pts allocated to CP, 82% received the expected 4 cycles with a very good tolerability profile (no febrile neutropenia). • Success rate was 80% (120 out of 150 pts): appropriate Tx A-7505, ASCO ‘ 13 Soria J-C et al assignment 68
 TASTE Conclusions • Met its primary end point for the phase II component, demonstrating feasibility of a national biology-driven trial in the adjuvant setting. • Nevertheless, the phase III was canceled due to the unexpected unreliability of the ERCC 1 IHC read-out. – Current commercial antibodies are unable to distinguish all isoforms of ERCC 1 TASTE Implications • TASTE Needs to be redone with accurate ERCC 1 IHC Ab • May have been responsible for the (-) Made. IT phase III trial in advanced NSCLC (relied on PCR m. RNA probes and AQUA) 69 Soria J-C et al A-7505, ASCO ‘ 13
TASTE Conclusions • Met its primary end point for the phase II component, demonstrating feasibility of a national biology-driven trial in the adjuvant setting. • Nevertheless, the phase III was canceled due to the unexpected unreliability of the ERCC 1 IHC read-out. – Current commercial antibodies are unable to distinguish all isoforms of ERCC 1 TASTE Implications • TASTE Needs to be redone with accurate ERCC 1 IHC Ab • May have been responsible for the (-) Made. IT phase III trial in advanced NSCLC (relied on PCR m. RNA probes and AQUA) 69 Soria J-C et al A-7505, ASCO ‘ 13
 Role of Targeted Therapy
Role of Targeted Therapy
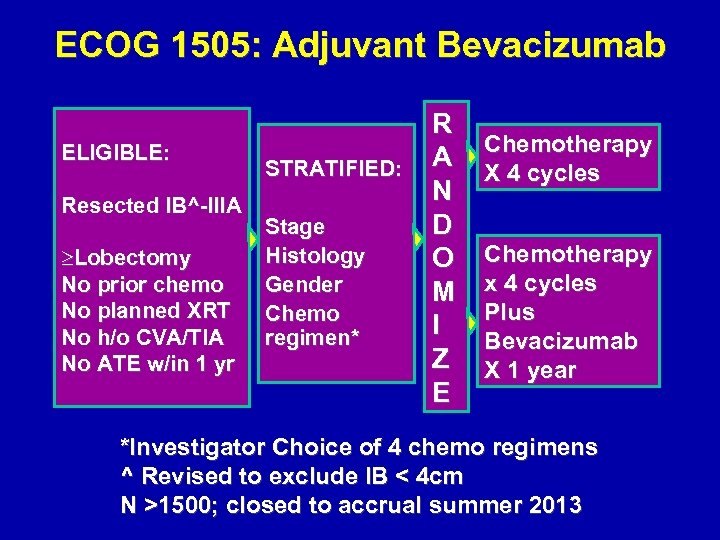 ECOG 1505: Adjuvant Bevacizumab ELIGIBLE: Resected IB^-IIIA ³Lobectomy No prior chemo No planned XRT No h/o CVA/TIA No ATE w/in 1 yr STRATIFIED: Stage Histology Gender Chemo regimen* R A N D O M I Z E Chemotherapy X 4 cycles Chemotherapy x 4 cycles Plus Bevacizumab X 1 year *Investigator Choice of 4 chemo regimens ^ Revised to exclude IB < 4 cm N >1500; closed to accrual summer 2013
ECOG 1505: Adjuvant Bevacizumab ELIGIBLE: Resected IB^-IIIA ³Lobectomy No prior chemo No planned XRT No h/o CVA/TIA No ATE w/in 1 yr STRATIFIED: Stage Histology Gender Chemo regimen* R A N D O M I Z E Chemotherapy X 4 cycles Chemotherapy x 4 cycles Plus Bevacizumab X 1 year *Investigator Choice of 4 chemo regimens ^ Revised to exclude IB < 4 cm N >1500; closed to accrual summer 2013
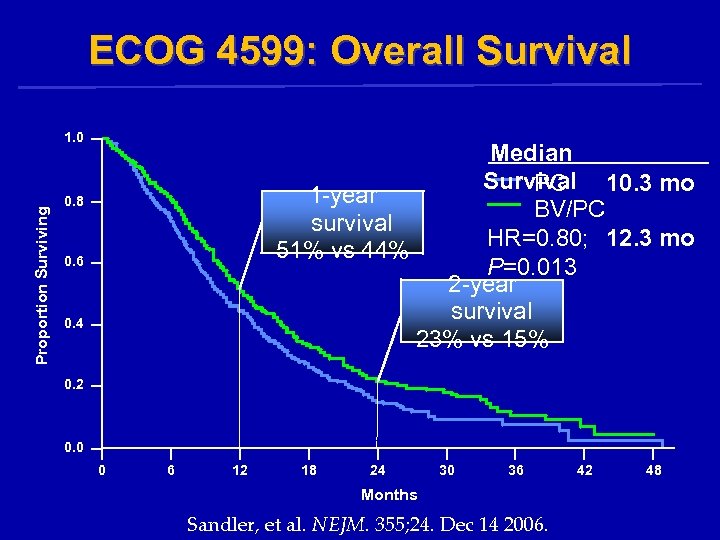 ECOG 4599: Overall Survival Proportion Surviving 1. 0 Median Survival 10. 3 mo PC 1 -year BV/PC survival HR=0. 80; 12. 3 mo 51% vs 44% P=0. 013 2 -year survival 23% vs 15% 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0. 0 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 Months Sandler, et al. NEJM. 355; 24. Dec 14 2006. 42 48
ECOG 4599: Overall Survival Proportion Surviving 1. 0 Median Survival 10. 3 mo PC 1 -year BV/PC survival HR=0. 80; 12. 3 mo 51% vs 44% P=0. 013 2 -year survival 23% vs 15% 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0. 0 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 Months Sandler, et al. NEJM. 355; 24. Dec 14 2006. 42 48
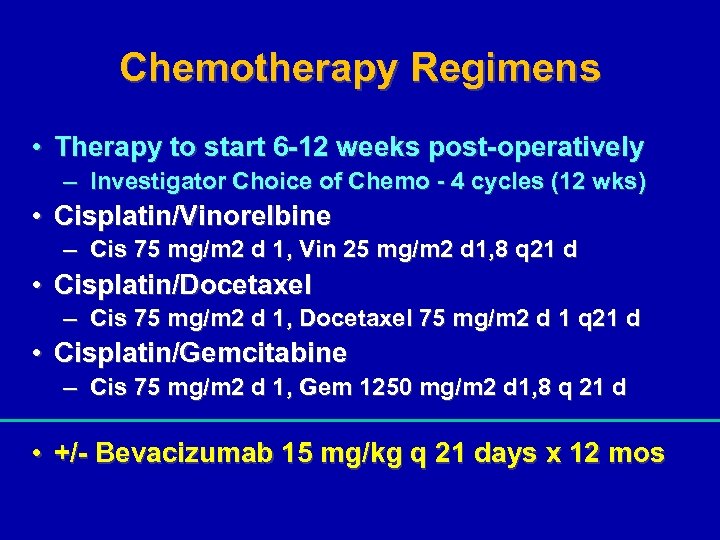 Chemotherapy Regimens • Therapy to start 6 -12 weeks post-operatively – Investigator Choice of Chemo - 4 cycles (12 wks) • Cisplatin/Vinorelbine – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Vin 25 mg/m 2 d 1, 8 q 21 d • Cisplatin/Docetaxel – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Docetaxel 75 mg/m 2 d 1 q 21 d • Cisplatin/Gemcitabine – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Gem 1250 mg/m 2 d 1, 8 q 21 d • +/- Bevacizumab 15 mg/kg q 21 days x 12 mos
Chemotherapy Regimens • Therapy to start 6 -12 weeks post-operatively – Investigator Choice of Chemo - 4 cycles (12 wks) • Cisplatin/Vinorelbine – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Vin 25 mg/m 2 d 1, 8 q 21 d • Cisplatin/Docetaxel – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Docetaxel 75 mg/m 2 d 1 q 21 d • Cisplatin/Gemcitabine – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Gem 1250 mg/m 2 d 1, 8 q 21 d • +/- Bevacizumab 15 mg/kg q 21 days x 12 mos
 Chemotherapy Regimens: amended 2010 • Therapy to start 6 -12 weeks post-operatively – Investigator Choice of Chemo - 4 cycles (12 wks) • Cisplatin/Pemetrexed – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Pemetrexed 500 mg/m 2 d 1 • Cisplatin/Vinorelbine – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Vin 25 mg/m 2 d 1, 8 q 21 d • Cisplatin/Docetaxel – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Docetaxel 75 mg/m 2 d 1 q 21 d • Cisplatin/Gemcitabine – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Gem 1250 mg/m 2 d 1, 8 q 21 d • +/- Bevacizumab 15 mg/kg q 21 days x 12 mos
Chemotherapy Regimens: amended 2010 • Therapy to start 6 -12 weeks post-operatively – Investigator Choice of Chemo - 4 cycles (12 wks) • Cisplatin/Pemetrexed – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Pemetrexed 500 mg/m 2 d 1 • Cisplatin/Vinorelbine – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Vin 25 mg/m 2 d 1, 8 q 21 d • Cisplatin/Docetaxel – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Docetaxel 75 mg/m 2 d 1 q 21 d • Cisplatin/Gemcitabine – Cis 75 mg/m 2 d 1, Gem 1250 mg/m 2 d 1, 8 q 21 d • +/- Bevacizumab 15 mg/kg q 21 days x 12 mos
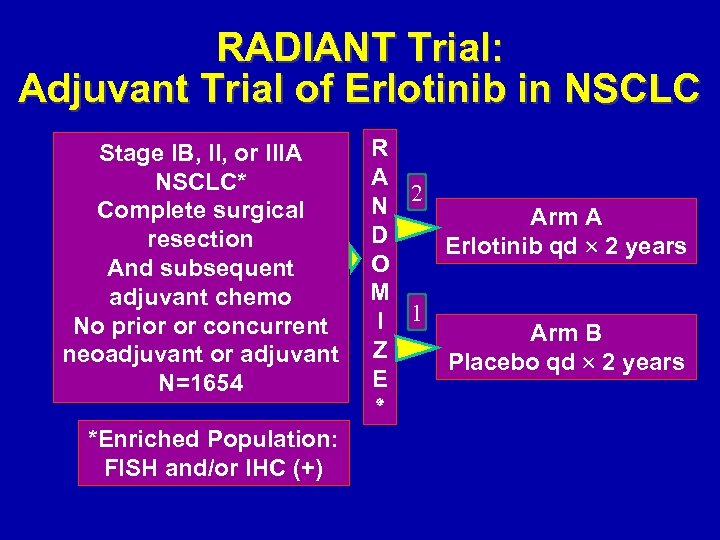 RADIANT Trial: Adjuvant Trial of Erlotinib in NSCLC Stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC* Complete surgical resection And subsequent adjuvant chemo No prior or concurrent neoadjuvant or adjuvant N=1654 *Enriched Population: FISH and/or IHC (+) R A 2 N Arm A D Erlotinib qd 2 years O M I 1 Arm B Z Placebo qd 2 years E ٭
RADIANT Trial: Adjuvant Trial of Erlotinib in NSCLC Stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC* Complete surgical resection And subsequent adjuvant chemo No prior or concurrent neoadjuvant or adjuvant N=1654 *Enriched Population: FISH and/or IHC (+) R A 2 N Arm A D Erlotinib qd 2 years O M I 1 Arm B Z Placebo qd 2 years E ٭
 RADIANT Trial: Adjuvant Trial of Erlotinib in NSCLC Stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC* Complete surgical resection And subsequent adjuvant chemo No prior or concurrent neoadjuvant or adjuvant N=1654 R A 2 N Arm A D Erlotinib qd 2 years O M I 1 Arm B Z Placebo qd 2 years E ٭ ted le mp Co al ru 10 cc A 20 il, pr A *Enriched Population: FISH and/or IHC (+)
RADIANT Trial: Adjuvant Trial of Erlotinib in NSCLC Stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC* Complete surgical resection And subsequent adjuvant chemo No prior or concurrent neoadjuvant or adjuvant N=1654 R A 2 N Arm A D Erlotinib qd 2 years O M I 1 Arm B Z Placebo qd 2 years E ٭ ted le mp Co al ru 10 cc A 20 il, pr A *Enriched Population: FISH and/or IHC (+)
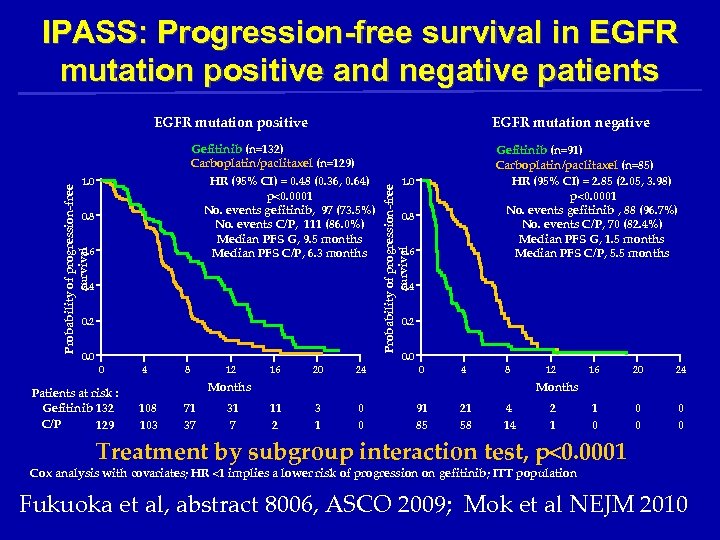 IPASS: Progression-free survival in EGFR mutation positive and negative patients EGFR mutation positive EGFR mutation negative Probability of progression-free survival 1. 0 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0. 0 Gefitinib (n=91) Carboplatin/paclitaxel (n=85) HR (95% CI) = 2. 85 (2. 05, 3. 98) p<0. 0001 No. events gefitinib , 88 (96. 7%) No. events C/P, 70 (82. 4%) Median PFS G, 1. 5 months Median PFS C/P, 5. 5 months Probability of progression-free survival Gefitinib (n=132) Carboplatin/paclitaxel (n=129) HR (95% CI) = 0. 48 (0. 36, 0. 64) p<0. 0001 No. events gefitinib, 97 (73. 5%) No. events C/P, 111 (86. 0%) Median PFS G, 9. 5 months Median PFS C/P, 6. 3 months 0. 2 0 Patients at risk : Gefitinib 132 C/P 129 4 8 12 16 20 24 0. 0 0 4 8 Months 108 103 71 37 31 7 12 16 20 24 1 0 0 0 Months 11 2 3 1 0 0 91 85 21 58 4 14 2 1 Treatment by subgroup interaction test, p<0. 0001 Cox analysis with covariates; HR <1 implies a lower risk of progression on gefitinib; ITT population Fukuoka et al, abstract 8006, ASCO 2009; Mok et al NEJM 2010
IPASS: Progression-free survival in EGFR mutation positive and negative patients EGFR mutation positive EGFR mutation negative Probability of progression-free survival 1. 0 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0. 0 Gefitinib (n=91) Carboplatin/paclitaxel (n=85) HR (95% CI) = 2. 85 (2. 05, 3. 98) p<0. 0001 No. events gefitinib , 88 (96. 7%) No. events C/P, 70 (82. 4%) Median PFS G, 1. 5 months Median PFS C/P, 5. 5 months Probability of progression-free survival Gefitinib (n=132) Carboplatin/paclitaxel (n=129) HR (95% CI) = 0. 48 (0. 36, 0. 64) p<0. 0001 No. events gefitinib, 97 (73. 5%) No. events C/P, 111 (86. 0%) Median PFS G, 9. 5 months Median PFS C/P, 6. 3 months 0. 2 0 Patients at risk : Gefitinib 132 C/P 129 4 8 12 16 20 24 0. 0 0 4 8 Months 108 103 71 37 31 7 12 16 20 24 1 0 0 0 Months 11 2 3 1 0 0 91 85 21 58 4 14 2 1 Treatment by subgroup interaction test, p<0. 0001 Cox analysis with covariates; HR <1 implies a lower risk of progression on gefitinib; ITT population Fukuoka et al, abstract 8006, ASCO 2009; Mok et al NEJM 2010
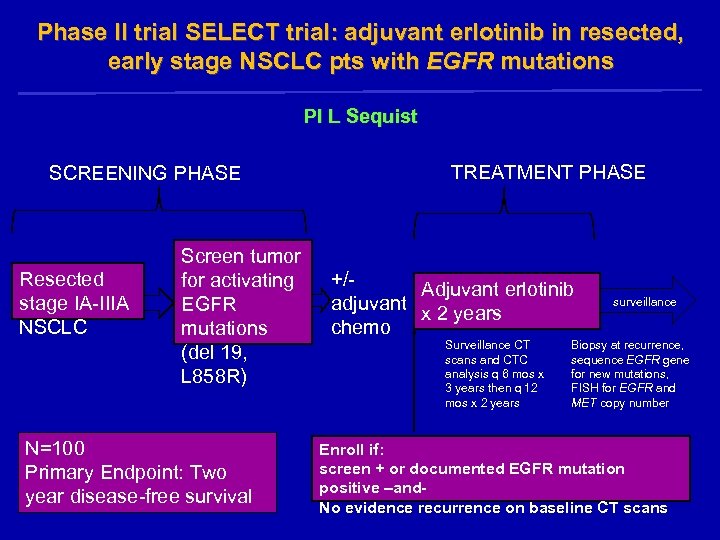 Phase II trial SELECT trial: adjuvant erlotinib in resected, early stage NSCLC pts with EGFR mutations PI L Sequist SCREENING PHASE Resected stage IA-IIIA NSCLC Screen tumor for activating EGFR mutations (del 19, L 858 R) N=100 Primary Endpoint: Two year disease-free survival TREATMENT PHASE +/Adjuvant erlotinib adjuvant x 2 years chemo Surveillance CT scans and CTC analysis q 6 mos x 3 years then q 12 mos x 2 years surveillance Biopsy at recurrence, sequence EGFR gene for new mutations, FISH for EGFR and MET copy number Enroll if: screen + or documented EGFR mutation positive –and. No evidence recurrence on baseline CT scans
Phase II trial SELECT trial: adjuvant erlotinib in resected, early stage NSCLC pts with EGFR mutations PI L Sequist SCREENING PHASE Resected stage IA-IIIA NSCLC Screen tumor for activating EGFR mutations (del 19, L 858 R) N=100 Primary Endpoint: Two year disease-free survival TREATMENT PHASE +/Adjuvant erlotinib adjuvant x 2 years chemo Surveillance CT scans and CTC analysis q 6 mos x 3 years then q 12 mos x 2 years surveillance Biopsy at recurrence, sequence EGFR gene for new mutations, FISH for EGFR and MET copy number Enroll if: screen + or documented EGFR mutation positive –and. No evidence recurrence on baseline CT scans
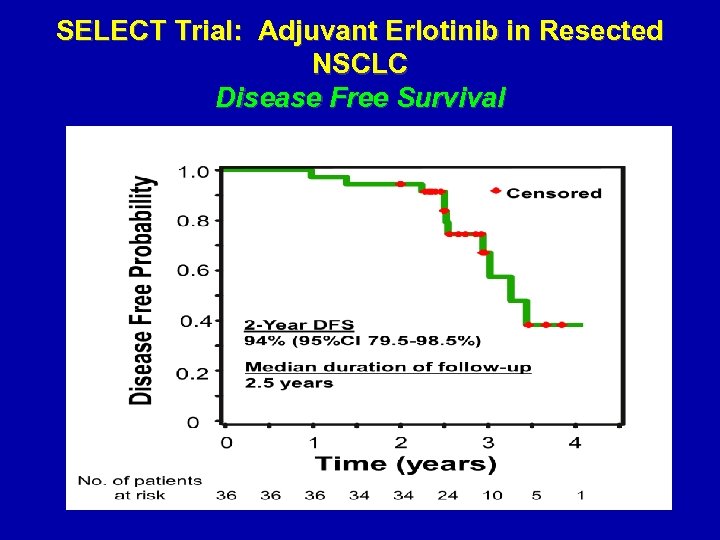 SELECT Trial: Adjuvant Erlotinib in Resected NSCLC Disease Free Survival
SELECT Trial: Adjuvant Erlotinib in Resected NSCLC Disease Free Survival
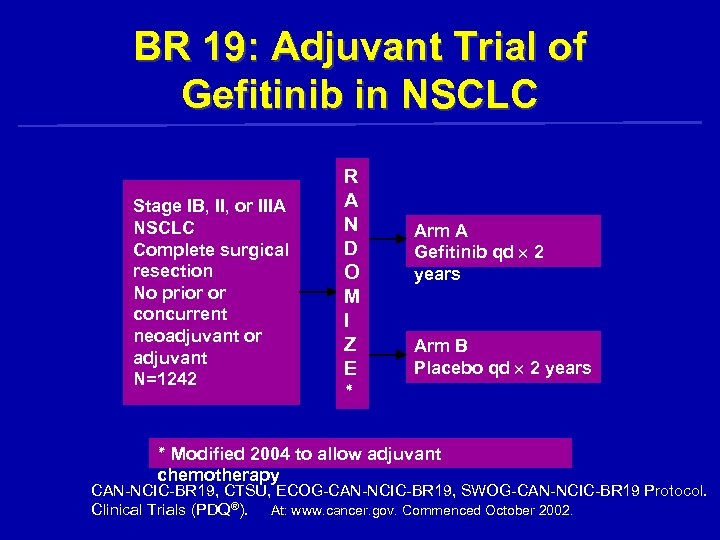 BR 19: Adjuvant Trial of Gefitinib in NSCLC Stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC Complete surgical resection No prior or concurrent neoadjuvant or adjuvant N=1242 R A N D O M I Z E ٭ Arm A Gefitinib qd 2 years Arm B Placebo qd 2 years ٭ Modified 2004 to allow adjuvant chemotherapy CAN-NCIC-BR 19, CTSU, ECOG-CAN-NCIC-BR 19, SWOG-CAN-NCIC-BR 19 Protocol. Clinical Trials (PDQ®). At: www. cancer. gov. Commenced October 2002.
BR 19: Adjuvant Trial of Gefitinib in NSCLC Stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC Complete surgical resection No prior or concurrent neoadjuvant or adjuvant N=1242 R A N D O M I Z E ٭ Arm A Gefitinib qd 2 years Arm B Placebo qd 2 years ٭ Modified 2004 to allow adjuvant chemotherapy CAN-NCIC-BR 19, CTSU, ECOG-CAN-NCIC-BR 19, SWOG-CAN-NCIC-BR 19 Protocol. Clinical Trials (PDQ®). At: www. cancer. gov. Commenced October 2002.
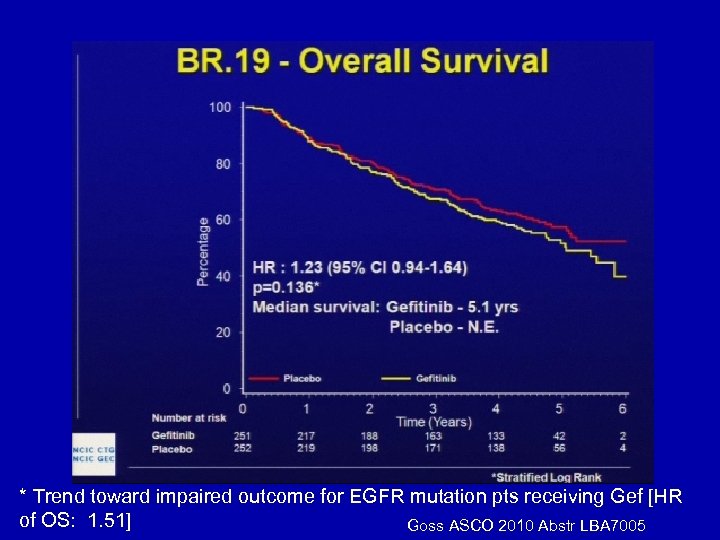 * Trend toward impaired outcome for EGFR mutation pts receiving Gef [HR of OS: 1. 51] Goss ASCO 2010 Abstr LBA 7005
* Trend toward impaired outcome for EGFR mutation pts receiving Gef [HR of OS: 1. 51] Goss ASCO 2010 Abstr LBA 7005
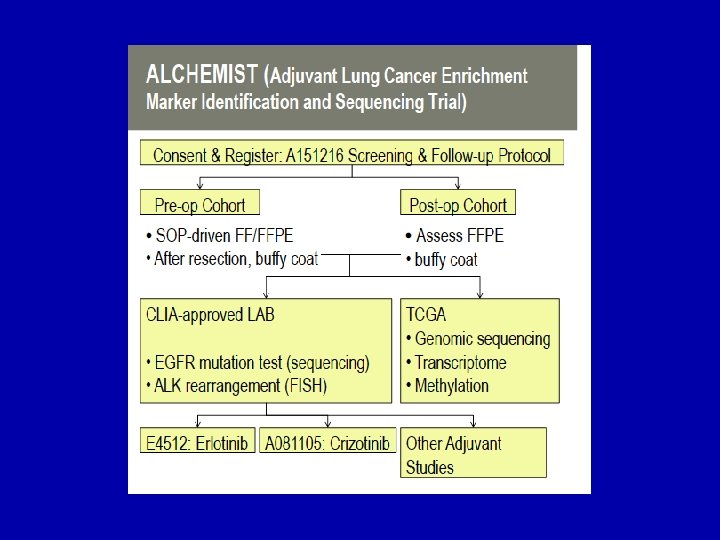
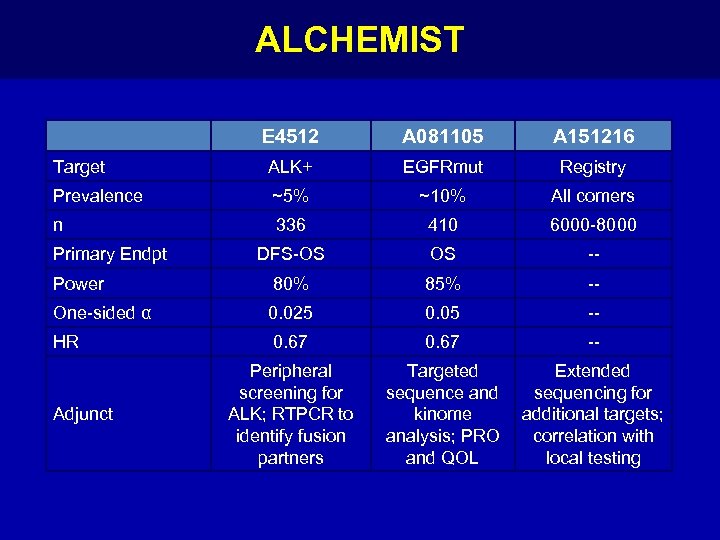 ALCHEMIST E 4512 A 081105 A 151216 Target ALK+ EGFRmut Registry Prevalence ~5% ~10% All comers n 336 410 6000 -8000 DFS-OS OS -- Power 80% 85% -- One-sided α 0. 025 0. 05 -- HR 0. 67 -- Peripheral screening for ALK; RTPCR to identify fusion partners Targeted sequence and kinome analysis; PRO and QOL Extended sequencing for additional targets; correlation with local testing Primary Endpt Adjunct
ALCHEMIST E 4512 A 081105 A 151216 Target ALK+ EGFRmut Registry Prevalence ~5% ~10% All comers n 336 410 6000 -8000 DFS-OS OS -- Power 80% 85% -- One-sided α 0. 025 0. 05 -- HR 0. 67 -- Peripheral screening for ALK; RTPCR to identify fusion partners Targeted sequence and kinome analysis; PRO and QOL Extended sequencing for additional targets; correlation with local testing Primary Endpt Adjunct
 Vaccines
Vaccines
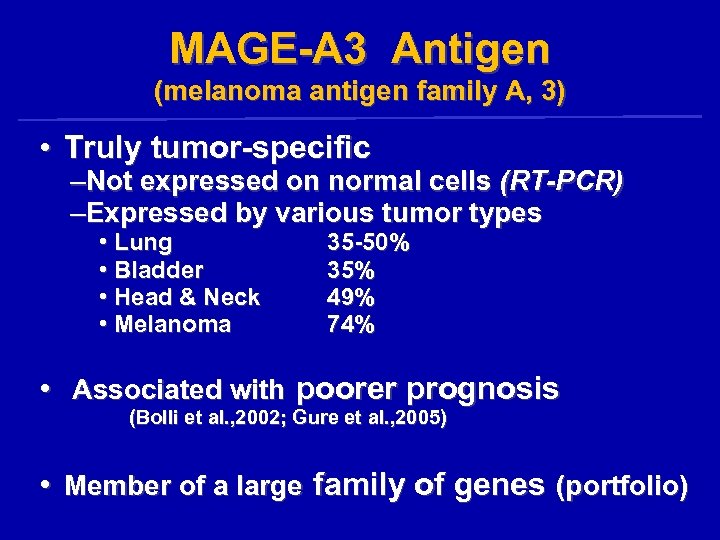 MAGE-A 3 Antigen (melanoma antigen family A, 3) • Truly tumor-specific –Not expressed on normal cells (RT-PCR) –Expressed by various tumor types • Lung • Bladder • Head & Neck • Melanoma 35 -50% 35% 49% 74% • Associated with poorer prognosis (Bolli et al. , 2002; Gure et al. , 2005) • Member of a large family of genes (portfolio)
MAGE-A 3 Antigen (melanoma antigen family A, 3) • Truly tumor-specific –Not expressed on normal cells (RT-PCR) –Expressed by various tumor types • Lung • Bladder • Head & Neck • Melanoma 35 -50% 35% 49% 74% • Associated with poorer prognosis (Bolli et al. , 2002; Gure et al. , 2005) • Member of a large family of genes (portfolio)
 MAGE A 3 ASCI* randomized phase II • Stage p. IB or p. II: double-blind, randomly assigned 2: 1 to postoperative MAGE-A 3 vaccination or placebo. • Vaccination was started >6 weeks after surgery, with 5 vaccinations at 3 -week intervals, followed by 8 vaccinations every 3 months. • Other anti-cancer adjuvant therapy was not allowed. • Primary endpoint was time-to-recurrence, other endpoints were recurrence rates at different times, and survival. * antigen-specific cancer immune therapeutic Vansteenkiste et al, ASCO 2006, abstract 7019
MAGE A 3 ASCI* randomized phase II • Stage p. IB or p. II: double-blind, randomly assigned 2: 1 to postoperative MAGE-A 3 vaccination or placebo. • Vaccination was started >6 weeks after surgery, with 5 vaccinations at 3 -week intervals, followed by 8 vaccinations every 3 months. • Other anti-cancer adjuvant therapy was not allowed. • Primary endpoint was time-to-recurrence, other endpoints were recurrence rates at different times, and survival. * antigen-specific cancer immune therapeutic Vansteenkiste et al, ASCO 2006, abstract 7019
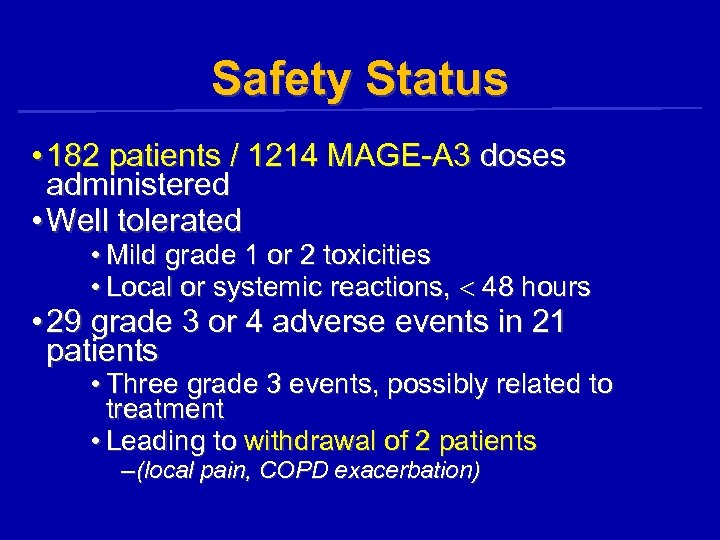 Safety Status • 182 patients / 1214 MAGE-A 3 doses administered • Well tolerated • Mild grade 1 or 2 toxicities • Local or systemic reactions, 48 hours • 29 grade 3 or 4 adverse events in 21 patients • Three grade 3 events, possibly related to treatment • Leading to withdrawal of 2 patients – (local pain, COPD exacerbation)
Safety Status • 182 patients / 1214 MAGE-A 3 doses administered • Well tolerated • Mild grade 1 or 2 toxicities • Local or systemic reactions, 48 hours • 29 grade 3 or 4 adverse events in 21 patients • Three grade 3 events, possibly related to treatment • Leading to withdrawal of 2 patients – (local pain, COPD exacerbation)
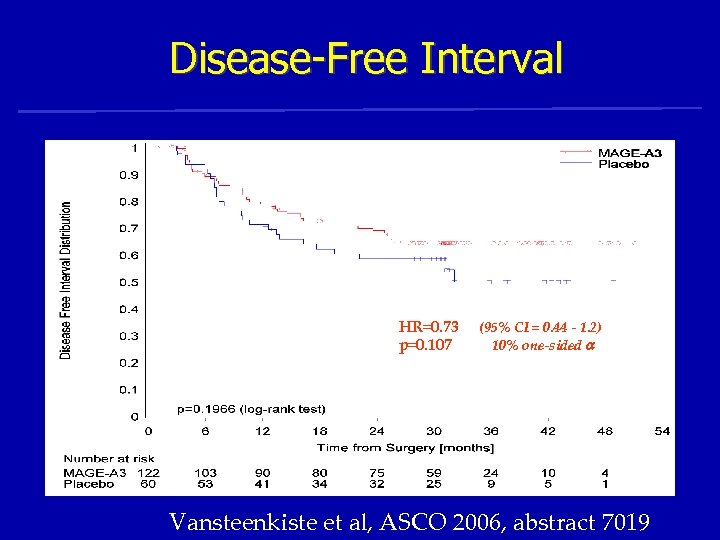 Disease-Free Interval HR=0. 73 p=0. 107 (95% CI = 0. 44 - 1. 2) 10% one-sided Vansteenkiste et al, ASCO 2006, abstract 7019
Disease-Free Interval HR=0. 73 p=0. 107 (95% CI = 0. 44 - 1. 2) 10% one-sided Vansteenkiste et al, ASCO 2006, abstract 7019
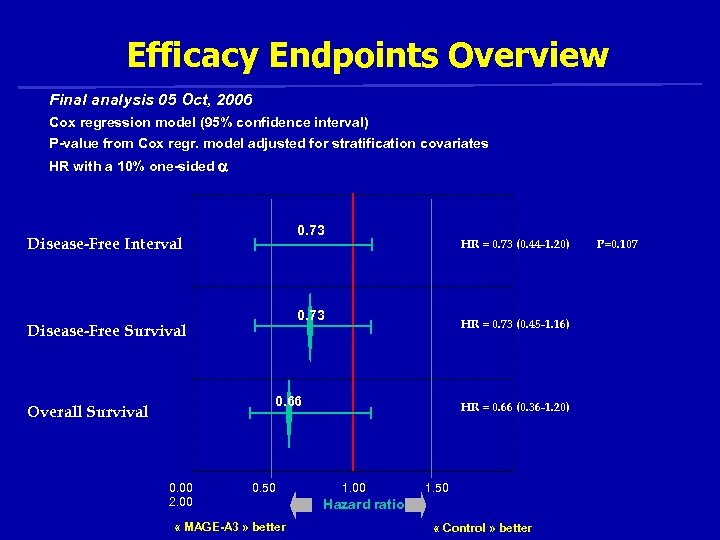 Efficacy Endpoints Overview Final analysis 05 Oct, 2006 Cox regression model (95% confidence interval) P-value from Cox regr. model adjusted for stratification covariates HR with a 10% one-sided 0. 73 Disease-Free Interval HR = 0. 73 (0. 44 -1. 20) 0. 73 Disease-Free Survival HR = 0. 73 (0. 45 -1. 16) 0. 66 Overall Survival 0. 00 2. 00 0. 50 « MAGE-A 3 » better HR = 0. 66 (0. 36 -1. 20) 1. 00 1. 50 Hazard ratio « Control » better P=0. 107
Efficacy Endpoints Overview Final analysis 05 Oct, 2006 Cox regression model (95% confidence interval) P-value from Cox regr. model adjusted for stratification covariates HR with a 10% one-sided 0. 73 Disease-Free Interval HR = 0. 73 (0. 44 -1. 20) 0. 73 Disease-Free Survival HR = 0. 73 (0. 45 -1. 16) 0. 66 Overall Survival 0. 00 2. 00 0. 50 « MAGE-A 3 » better HR = 0. 66 (0. 36 -1. 20) 1. 00 1. 50 Hazard ratio « Control » better P=0. 107
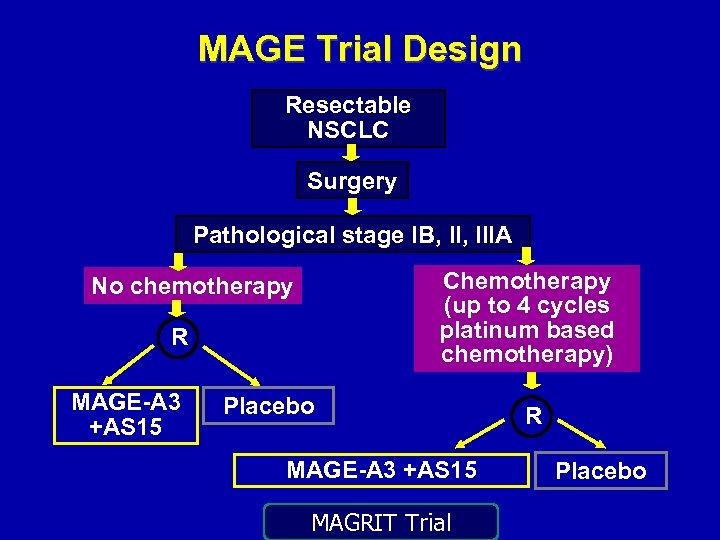 MAGE Trial Design Resectable NSCLC Surgery Pathological stage IB, IIIA Chemotherapy (up to 4 cycles platinum based chemotherapy) No chemotherapy R MAGE-A 3 +AS 15 Placebo MAGE-A 3 +AS 15 MAGRIT Trial R Placebo
MAGE Trial Design Resectable NSCLC Surgery Pathological stage IB, IIIA Chemotherapy (up to 4 cycles platinum based chemotherapy) No chemotherapy R MAGE-A 3 +AS 15 Placebo MAGE-A 3 +AS 15 MAGRIT Trial R Placebo
 MAGRIT: Phase III • • • Largest lung cancer study EVER Began in October 2007 Goal: 2270 patients from 400 centers in 33 countries in Europe, North and South America, Asia, Australia • 2289 ultimately enrolled
MAGRIT: Phase III • • • Largest lung cancer study EVER Began in October 2007 Goal: 2270 patients from 400 centers in 33 countries in Europe, North and South America, Asia, Australia • 2289 ultimately enrolled
 Role of Adjuvant RT in Stage II and Stage IIIA
Role of Adjuvant RT in Stage II and Stage IIIA
 Should the pt receive adj RT? 1) 2) 3) Yes No Maybe
Should the pt receive adj RT? 1) 2) 3) Yes No Maybe
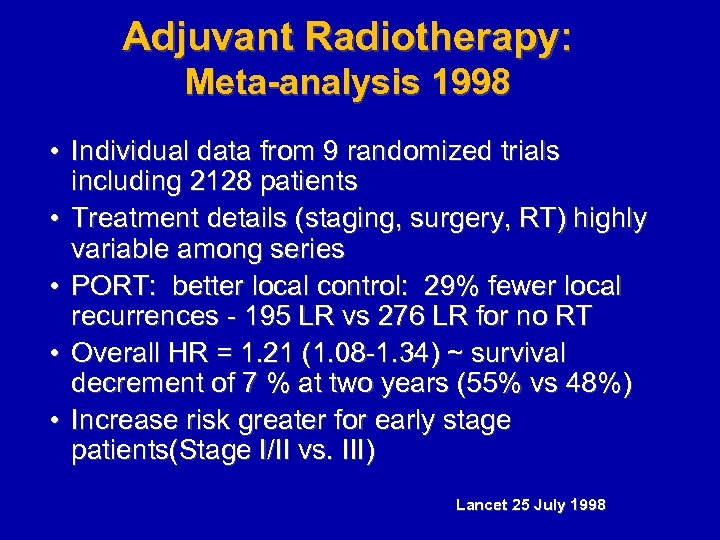 Adjuvant Radiotherapy: Meta-analysis 1998 • Individual data from 9 randomized trials including 2128 patients • Treatment details (staging, surgery, RT) highly variable among series • PORT: better local control: 29% fewer local recurrences - 195 LR vs 276 LR for no RT • Overall HR = 1. 21 (1. 08 -1. 34) ~ survival decrement of 7 % at two years (55% vs 48%) • Increase risk greater for early stage patients(Stage I/II vs. III) Lancet 25 July 1998
Adjuvant Radiotherapy: Meta-analysis 1998 • Individual data from 9 randomized trials including 2128 patients • Treatment details (staging, surgery, RT) highly variable among series • PORT: better local control: 29% fewer local recurrences - 195 LR vs 276 LR for no RT • Overall HR = 1. 21 (1. 08 -1. 34) ~ survival decrement of 7 % at two years (55% vs 48%) • Increase risk greater for early stage patients(Stage I/II vs. III) Lancet 25 July 1998
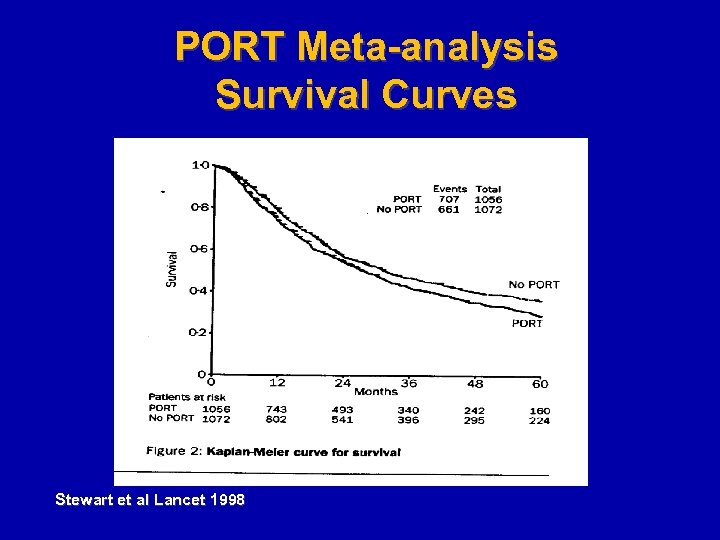 PORT Meta-analysis Survival Curves Stewart et al Lancet 1998
PORT Meta-analysis Survival Curves Stewart et al Lancet 1998
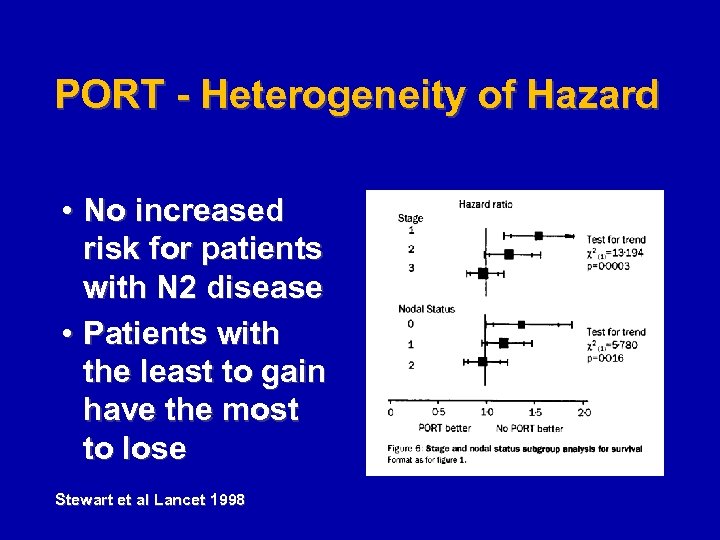 PORT - Heterogeneity of Hazard • No increased risk for patients with N 2 disease • Patients with the least to gain have the most to lose Stewart et al Lancet 1998
PORT - Heterogeneity of Hazard • No increased risk for patients with N 2 disease • Patients with the least to gain have the most to lose Stewart et al Lancet 1998
 PORT Meta-analysis Methodologic Flaws • Variable and unspecified staging • Variable and unspecified interval between resection and PORT • Inadequate RT – Suboptimal doses; large fields – Poor treatment planning – Outmoded techniques (e. g. : use of low-energy photons or 60 Co for a substantial proportion of patients) • • • Inclusion of N 0 patients Unpublished data (2 of 9 studies) Relatively short F/U (< 4 yrs) Stewart et al Lancet 1998
PORT Meta-analysis Methodologic Flaws • Variable and unspecified staging • Variable and unspecified interval between resection and PORT • Inadequate RT – Suboptimal doses; large fields – Poor treatment planning – Outmoded techniques (e. g. : use of low-energy photons or 60 Co for a substantial proportion of patients) • • • Inclusion of N 0 patients Unpublished data (2 of 9 studies) Relatively short F/U (< 4 yrs) Stewart et al Lancet 1998
 Risks of PORT with Modern Technology • Retrospective review – 202 patients treated with surgery and PORT for Stage II and III disease – Median dose 55 Gy – Actuarial rate of death from intercurrent disease was 13. 5% compared to expected rate of 10% Machtay et al JCO 2001
Risks of PORT with Modern Technology • Retrospective review – 202 patients treated with surgery and PORT for Stage II and III disease – Median dose 55 Gy – Actuarial rate of death from intercurrent disease was 13. 5% compared to expected rate of 10% Machtay et al JCO 2001
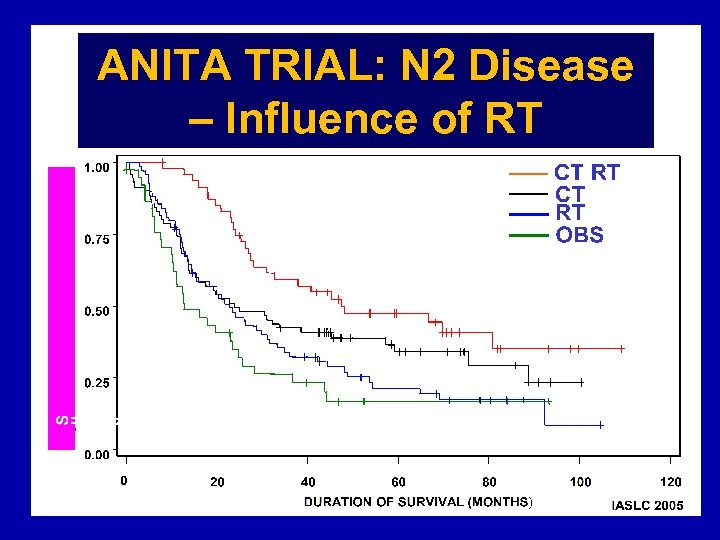 ANITA TRIAL: N 2 Disease – Influence of RT
ANITA TRIAL: N 2 Disease – Influence of RT
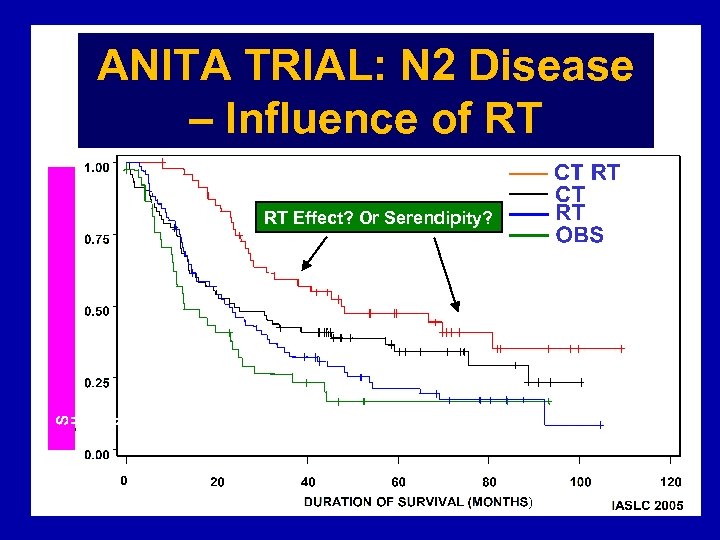 ANITA TRIAL: N 2 Disease – Influence of RT RT Effect? Or Serendipity?
ANITA TRIAL: N 2 Disease – Influence of RT RT Effect? Or Serendipity?
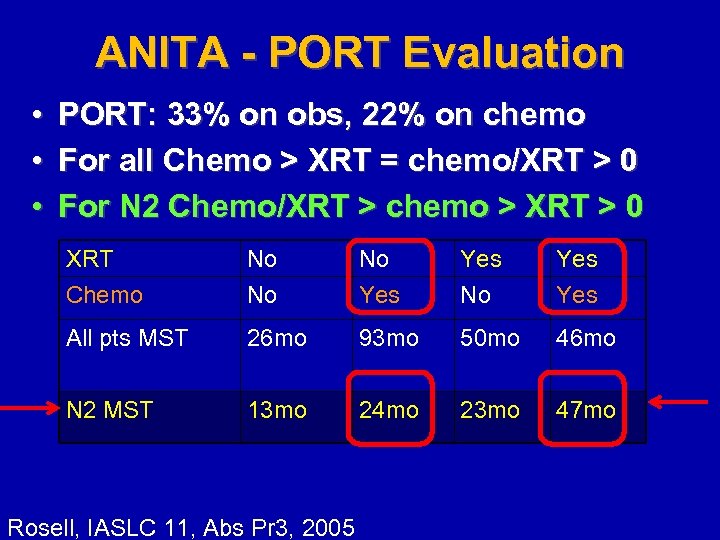 ANITA - PORT Evaluation • • • PORT: 33% on obs, 22% on chemo For all Chemo > XRT = chemo/XRT > 0 For N 2 Chemo/XRT > chemo > XRT > 0 XRT Chemo No No No Yes Yes All pts MST 26 mo 93 mo 50 mo 46 mo N 2 MST 13 mo 24 mo 23 mo 47 mo Rosell, IASLC 11, Abs Pr 3, 2005
ANITA - PORT Evaluation • • • PORT: 33% on obs, 22% on chemo For all Chemo > XRT = chemo/XRT > 0 For N 2 Chemo/XRT > chemo > XRT > 0 XRT Chemo No No No Yes Yes All pts MST 26 mo 93 mo 50 mo 46 mo N 2 MST 13 mo 24 mo 23 mo 47 mo Rosell, IASLC 11, Abs Pr 3, 2005
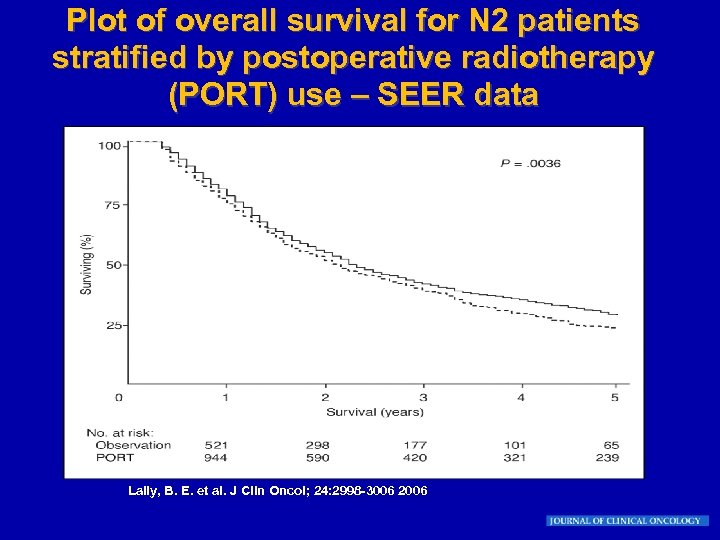 Plot of overall survival for N 2 patients stratified by postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) use – SEER data Lally, B. E. et al. J Clin Oncol; 24: 2998 -3006 2006
Plot of overall survival for N 2 patients stratified by postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) use – SEER data Lally, B. E. et al. J Clin Oncol; 24: 2998 -3006 2006
 PORT Conclusions • PORT has no role in N 0 or N 1 disease • Role of PORT in N 2 is controversial – Recent subset and retrospective analyses hint at benefit – Ongoing “Lung ART” trial in France • • • 700 pts with resected N 2 randomized to PORT or not Adjuvant chemo allowed 1 st Accrual sluggish
PORT Conclusions • PORT has no role in N 0 or N 1 disease • Role of PORT in N 2 is controversial – Recent subset and retrospective analyses hint at benefit – Ongoing “Lung ART” trial in France • • • 700 pts with resected N 2 randomized to PORT or not Adjuvant chemo allowed 1 st Accrual sluggish
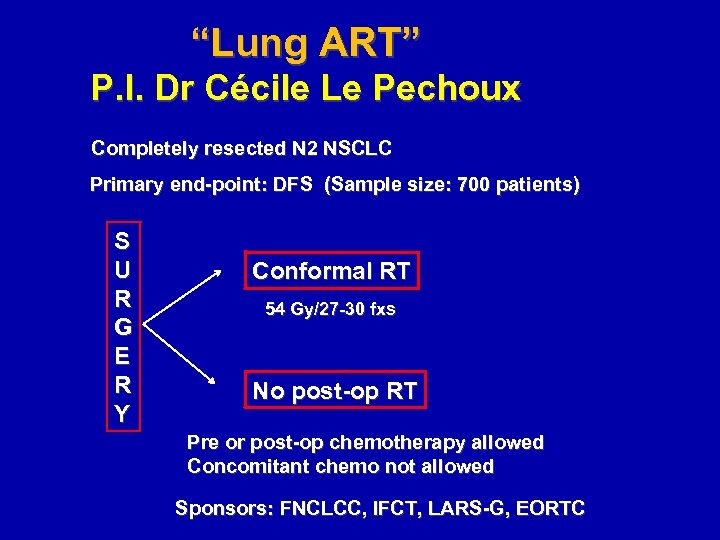 “Lung ART” P. I. Dr Cécile Le Pechoux Completely resected N 2 NSCLC Primary end-point: DFS (Sample size: 700 patients) S U R G E R Y Conformal RT 54 Gy/27 -30 fxs No post-op RT Pre or post-op chemotherapy allowed Concomitant chemo not allowed Sponsors: FNCLCC, IFCT, LARS-G, EORTC
“Lung ART” P. I. Dr Cécile Le Pechoux Completely resected N 2 NSCLC Primary end-point: DFS (Sample size: 700 patients) S U R G E R Y Conformal RT 54 Gy/27 -30 fxs No post-op RT Pre or post-op chemotherapy allowed Concomitant chemo not allowed Sponsors: FNCLCC, IFCT, LARS-G, EORTC
 Conclusions: Adjuvant Therapy • Adjuvant Platinum-based Chemotherapy is the Standard of Care for Resected Stage II-IIIA NSCLC – Improves OS 5%-15% at 5 years with newer drugs • Fit elderly patients (< 75 yrs) benefit as much as younger patients • Ongoing trials with molecularly determined Tx, erlotinib, bevacizumab, vaccines • Controversies – – Benefit in IB Neoadjuvant vs adjuvant therapy Which chemotherapy to use PORT
Conclusions: Adjuvant Therapy • Adjuvant Platinum-based Chemotherapy is the Standard of Care for Resected Stage II-IIIA NSCLC – Improves OS 5%-15% at 5 years with newer drugs • Fit elderly patients (< 75 yrs) benefit as much as younger patients • Ongoing trials with molecularly determined Tx, erlotinib, bevacizumab, vaccines • Controversies – – Benefit in IB Neoadjuvant vs adjuvant therapy Which chemotherapy to use PORT


