819a93284ecaf44a09db86f774ee73e9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Early Intervention: The International Perspective Paddy Power “A Stitch in Time Saves Nine”
Early Intervention: The International Perspective Paddy Power “A Stitch in Time Saves Nine”
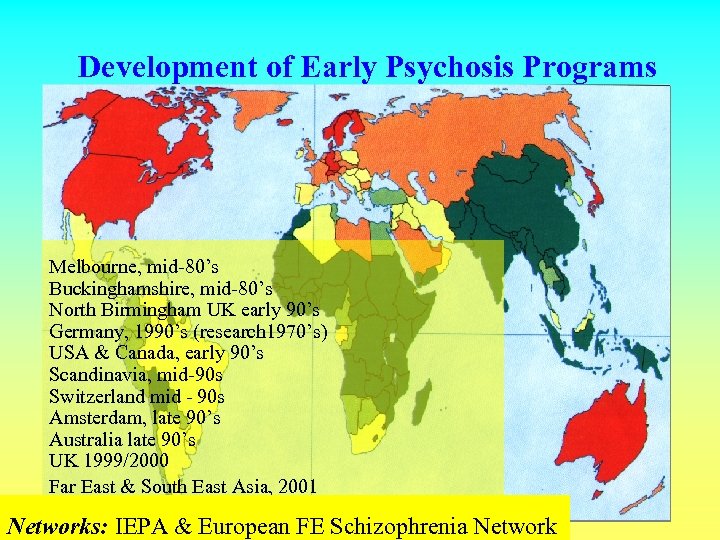 Development of Early Psychosis Programs Melbourne, mid-80’s Buckinghamshire, mid-80’s North Birmingham UK early 90’s Germany, 1990’s (research 1970’s) USA & Canada, early 90’s Scandinavia, mid-90 s Switzerland mid - 90 s Amsterdam, late 90’s Australia late 90’s UK 1999/2000 Far East & South East Asia, 2001 Networks: IEPA & European FE Schizophrenia Network
Development of Early Psychosis Programs Melbourne, mid-80’s Buckinghamshire, mid-80’s North Birmingham UK early 90’s Germany, 1990’s (research 1970’s) USA & Canada, early 90’s Scandinavia, mid-90 s Switzerland mid - 90 s Amsterdam, late 90’s Australia late 90’s UK 1999/2000 Far East & South East Asia, 2001 Networks: IEPA & European FE Schizophrenia Network
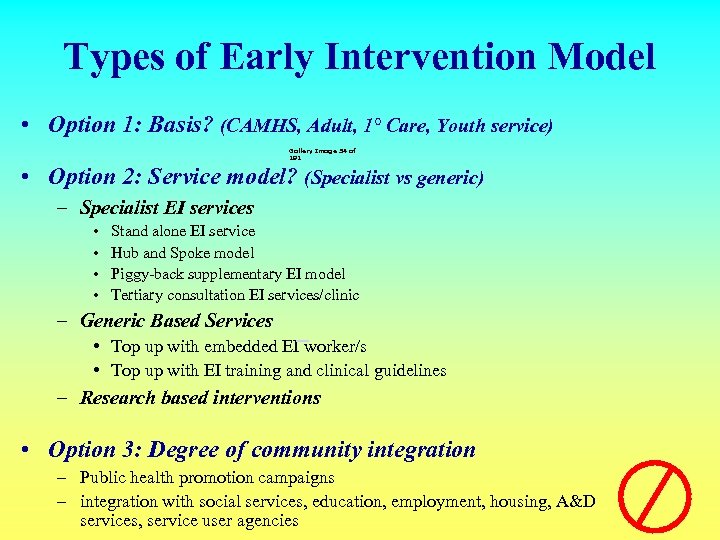 Types of Early Intervention Model • Option 1: Basis? (CAMHS, Adult, 1° Care, Youth service) Gallery Image 34 of 191 • Option 2: Service model? (Specialist vs generic) – Specialist EI services • • Stand alone EI service Hub and Spoke model Piggy-back supplementary EI model Tertiary consultation EI services/clinic – Generic Based Services • Top up with embedded EI worker/s • Top up with EI training and clinical guidelines – Research based interventions • Option 3: Degree of community integration – Public health promotion campaigns – integration with social services, education, employment, housing, A&D services, service user agencies
Types of Early Intervention Model • Option 1: Basis? (CAMHS, Adult, 1° Care, Youth service) Gallery Image 34 of 191 • Option 2: Service model? (Specialist vs generic) – Specialist EI services • • Stand alone EI service Hub and Spoke model Piggy-back supplementary EI model Tertiary consultation EI services/clinic – Generic Based Services • Top up with embedded EI worker/s • Top up with EI training and clinical guidelines – Research based interventions • Option 3: Degree of community integration – Public health promotion campaigns – integration with social services, education, employment, housing, A&D services, service user agencies
 Aims of an Early Intervention service • Reduce delays (& DUP) by: – promoting early detection and collaborative engagement in the community • Optimise assessment & diagnosis by: – Comprehensive Bio/psycho/social assessment • Maximise recovery by: – providing integrated bio/psycho/social community Rx – focus on functional as well as symptomatic factors – addressing co-morbidity and treatment resistance early • Prevent relapse by: – ensuring assertive followup and psychoed. during critical period
Aims of an Early Intervention service • Reduce delays (& DUP) by: – promoting early detection and collaborative engagement in the community • Optimise assessment & diagnosis by: – Comprehensive Bio/psycho/social assessment • Maximise recovery by: – providing integrated bio/psycho/social community Rx – focus on functional as well as symptomatic factors – addressing co-morbidity and treatment resistance early • Prevent relapse by: – ensuring assertive followup and psychoed. during critical period
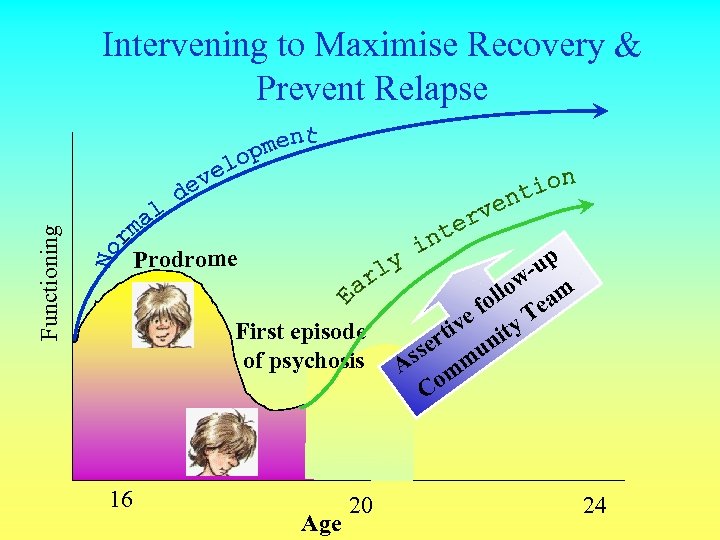 Functioning Intervening to Maximise Recovery & Prevent Relapse Prodrome First episode of psychosis 16 Age 20 p -u w llo eam fo T ive ity t er un ss m 2 nd episode A m Co of psychosis 24
Functioning Intervening to Maximise Recovery & Prevent Relapse Prodrome First episode of psychosis 16 Age 20 p -u w llo eam fo T ive ity t er un ss m 2 nd episode A m Co of psychosis 24
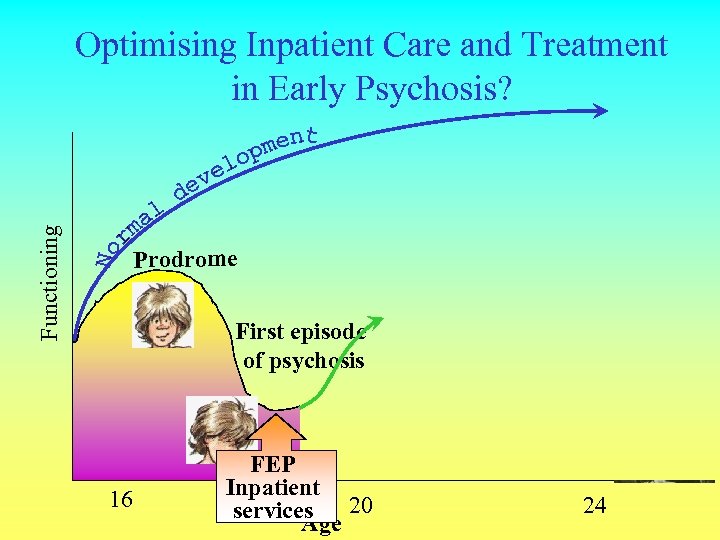 Functioning Optimising Inpatient Care and Treatment in Early Psychosis? Prodrome First episode of psychosis 16 FEP Inpatient 20 services Age 2 nd episode of psychosis 24
Functioning Optimising Inpatient Care and Treatment in Early Psychosis? Prodrome First episode of psychosis 16 FEP Inpatient 20 services Age 2 nd episode of psychosis 24
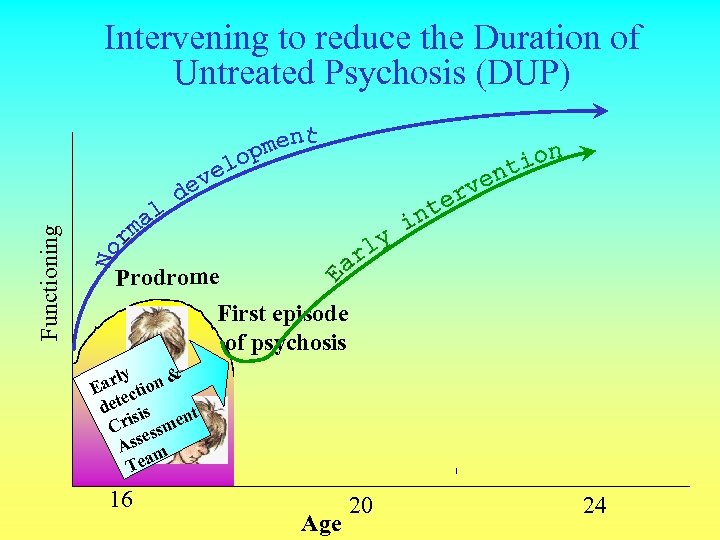 Functioning Intervening to reduce the Duration of Untreated Psychosis (DUP) Prodrome First episode of psychosis 2 nd episode of psychosis ly & Ear ction e det sis t ri smen C es Ass m Tea 16 Age 20 24
Functioning Intervening to reduce the Duration of Untreated Psychosis (DUP) Prodrome First episode of psychosis 2 nd episode of psychosis ly & Ear ction e det sis t ri smen C es Ass m Tea 16 Age 20 24
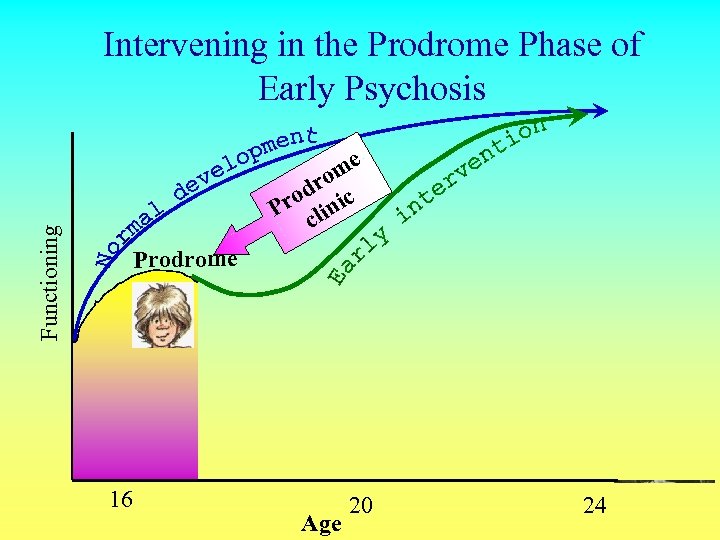 Functioning Intervening in the Prodrome Phase of Early Psychosis me o dr ic o Pr clin Prodrome First episode of psychosis 16 Age 20 2 nd episode of psychosis 24
Functioning Intervening in the Prodrome Phase of Early Psychosis me o dr ic o Pr clin Prodrome First episode of psychosis 16 Age 20 2 nd episode of psychosis 24
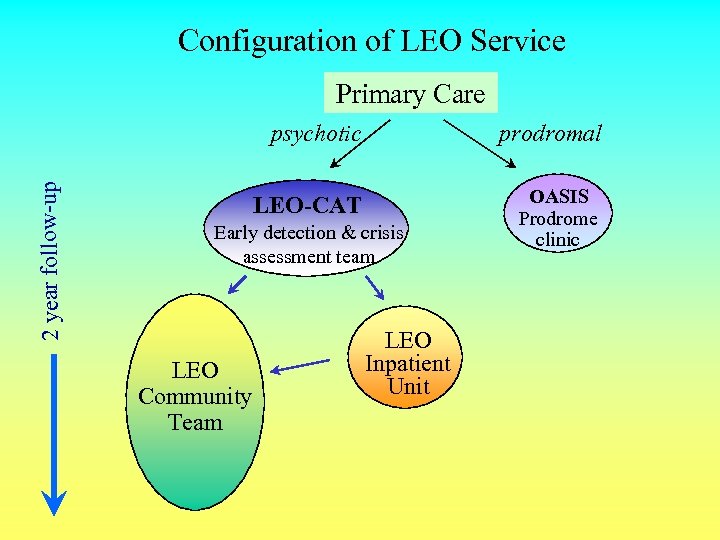 Configuration of LEO Service Primary Care 2 year follow-up psychotic prodromal LEO-CAT OASIS Prodrome clinic Early detection & crisis assessment team LEO Community Team LEO Inpatient Unit
Configuration of LEO Service Primary Care 2 year follow-up psychotic prodromal LEO-CAT OASIS Prodrome clinic Early detection & crisis assessment team LEO Community Team LEO Inpatient Unit
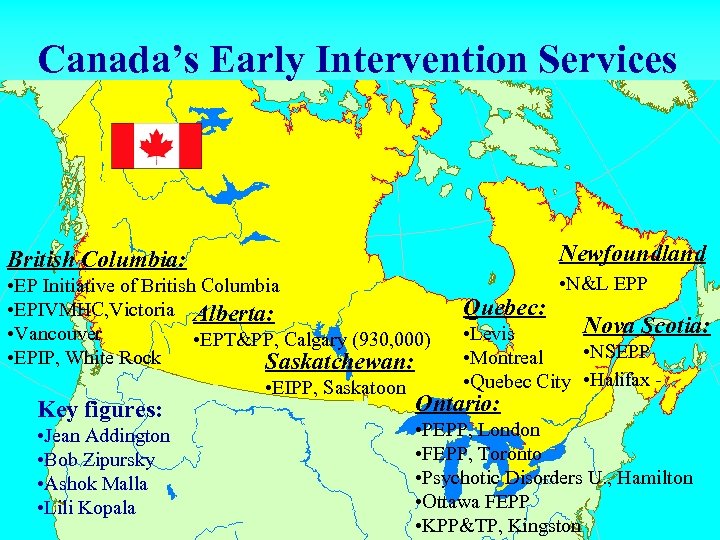 Canada’s Early Intervention Services British Columbia: • EP Initiative of British Columbia • EPIVMHC, Victoria Alberta: • Vancouver • EPT&PP, Calgary (930, 000) • EPIP, White Rock Saskatchewan: • EIPP, Saskatoon Key figures: • Jean Addington • Bob Zipursky • Ashok Malla • Lili Kopala Quebec: Newfoundland • N&L EPP Nova Scotia: • Levis • NSEPP • Montreal • Quebec City • Halifax - Ontario: • PEPP, London • FEPP, Toronto • Psychotic Disorders U. , Hamilton • Ottawa FEPP • KPP&TP, Kingston
Canada’s Early Intervention Services British Columbia: • EP Initiative of British Columbia • EPIVMHC, Victoria Alberta: • Vancouver • EPT&PP, Calgary (930, 000) • EPIP, White Rock Saskatchewan: • EIPP, Saskatoon Key figures: • Jean Addington • Bob Zipursky • Ashok Malla • Lili Kopala Quebec: Newfoundland • N&L EPP Nova Scotia: • Levis • NSEPP • Montreal • Quebec City • Halifax - Ontario: • PEPP, London • FEPP, Toronto • Psychotic Disorders U. , Hamilton • Ottawa FEPP • KPP&TP, Kingston
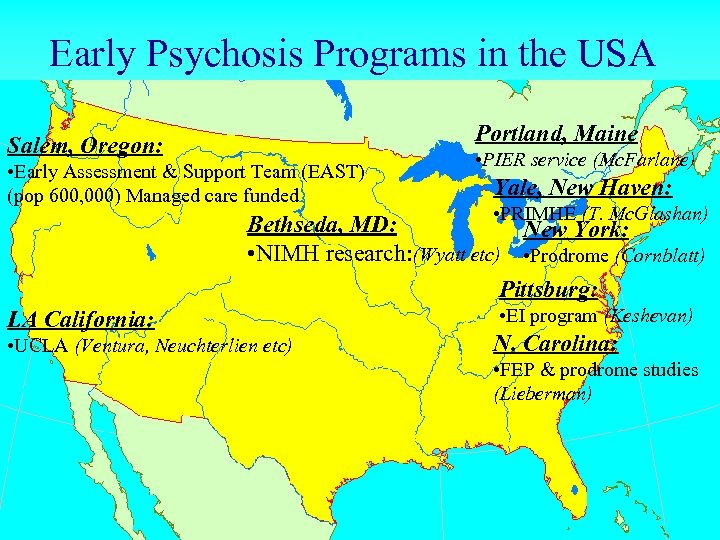 Early Psychosis Programs in the USA Portland, Maine Salem, Oregon: • Early Assessment & Support Team (EAST) (pop 600, 000) Managed care funded • PIER service (Mc. Farlane) Yale, New Haven: • PRIMHE (T. Mc. Glashan) Bethseda, MD: New York: • NIMH research: (Wyatt etc) • Prodrome (Cornblatt) Pittsburg: LA California: • UCLA (Ventura, Neuchterlien etc) • EI program (Keshevan) N. Carolina: • FEP & prodrome studies (Lieberman)
Early Psychosis Programs in the USA Portland, Maine Salem, Oregon: • Early Assessment & Support Team (EAST) (pop 600, 000) Managed care funded • PIER service (Mc. Farlane) Yale, New Haven: • PRIMHE (T. Mc. Glashan) Bethseda, MD: New York: • NIMH research: (Wyatt etc) • Prodrome (Cornblatt) Pittsburg: LA California: • UCLA (Ventura, Neuchterlien etc) • EI program (Keshevan) N. Carolina: • FEP & prodrome studies (Lieberman)
 New Zealand’s Early Intervention Services New Zealand National Early Intervention Group . . • Auckland: EPI Centre, Kari Centre, Taylor Centre, Manaaki CMHT - FEP, St Lukes FEP, Hartford House EPI, Campbell team . Lodge EI team • Wellington: Wellington EI service (400, 000) • Christchurch: Tatara House EIP service (380, 000) • Dunedin: Aspiring House EI service (150, 000)
New Zealand’s Early Intervention Services New Zealand National Early Intervention Group . . • Auckland: EPI Centre, Kari Centre, Taylor Centre, Manaaki CMHT - FEP, St Lukes FEP, Hartford House EPI, Campbell team . Lodge EI team • Wellington: Wellington EI service (400, 000) • Christchurch: Tatara House EIP service (380, 000) • Dunedin: Aspiring House EI service (150, 000)
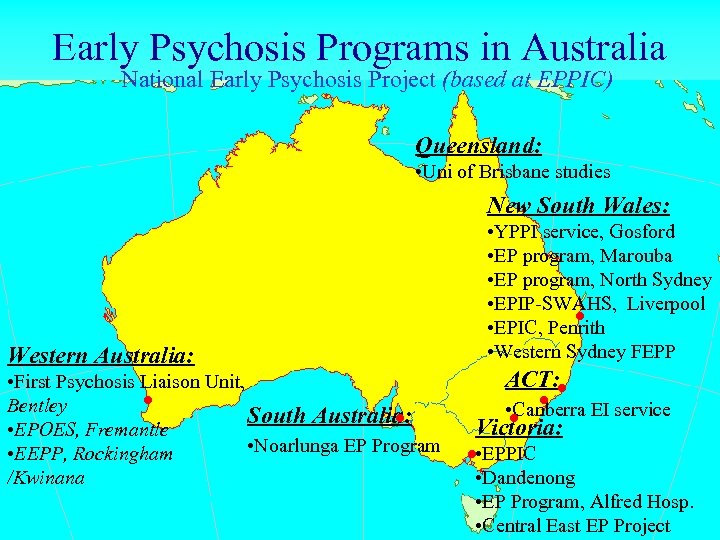 Early Psychosis Programs in Australia National Early Psychosis Project (based at EPPIC) Queensland: • Uni of Brisbane studies New South Wales: • YPPI service, Gosford • EP program, Marouba • EP program, North Sydney • EPIP-SWAHS, Liverpool • EPIC, Penrith • Western Sydney FEPP . . Western Australia: . . • First Psychosis Liaison Unit, Bentley South Australia: • EPOES, Fremantle • Noarlunga EP Program • EEPP, Rockingham /Kwinana . . . ACT: • Canberra EI service Victoria: • EPPIC • Dandenong • EP Program, Alfred Hosp. • Central East EP Project
Early Psychosis Programs in Australia National Early Psychosis Project (based at EPPIC) Queensland: • Uni of Brisbane studies New South Wales: • YPPI service, Gosford • EP program, Marouba • EP program, North Sydney • EPIP-SWAHS, Liverpool • EPIC, Penrith • Western Sydney FEPP . . Western Australia: . . • First Psychosis Liaison Unit, Bentley South Australia: • EPOES, Fremantle • Noarlunga EP Program • EEPP, Rockingham /Kwinana . . . ACT: • Canberra EI service Victoria: • EPPIC • Dandenong • EP Program, Alfred Hosp. • Central East EP Project
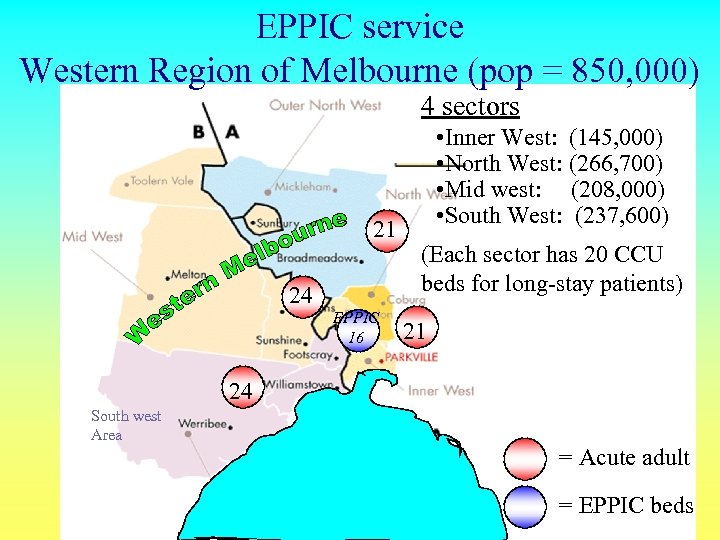 EPPIC service Western Region of Melbourne (pop = 850, 000) 4 sectors 21 24 EPPIC 16 • Inner West: (145, 000) • North West: (266, 700) • Mid west: (208, 000) • South West: (237, 600) (Each sector has 20 CCU beds for long-stay patients) 21 24 South west Area = Acute adult = EPPIC beds
EPPIC service Western Region of Melbourne (pop = 850, 000) 4 sectors 21 24 EPPIC 16 • Inner West: (145, 000) • North West: (266, 700) • Mid west: (208, 000) • South West: (237, 600) (Each sector has 20 CCU beds for long-stay patients) 21 24 South west Area = Acute adult = EPPIC beds
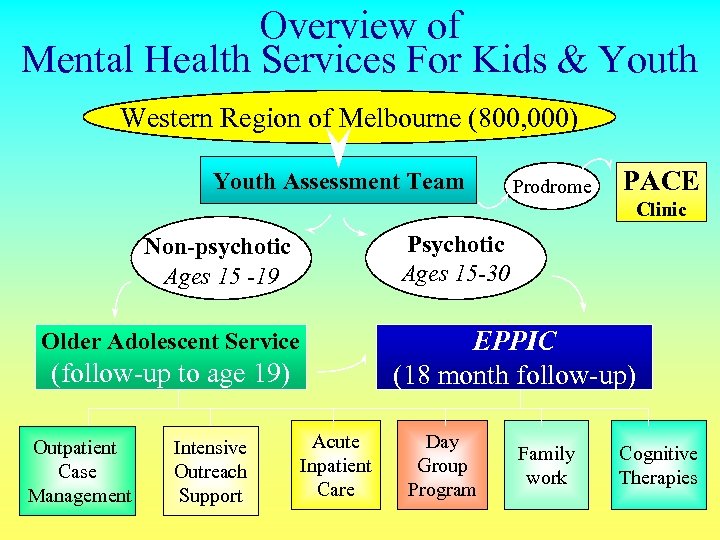 Overview of Mental Health Services For Kids & Youth Western Region of Melbourne (800, 000) Youth Assessment Team Prodrome PACE Clinic Non-psychotic Ages 15 -19 Psychotic Ages 15 -30 EPPIC (18 month follow-up) Older Adolescent Service (follow-up to age 19) Outpatient Case Management Intensive Outreach Support Acute Inpatient Care Day Group Program Family work Cognitive Therapies
Overview of Mental Health Services For Kids & Youth Western Region of Melbourne (800, 000) Youth Assessment Team Prodrome PACE Clinic Non-psychotic Ages 15 -19 Psychotic Ages 15 -30 EPPIC (18 month follow-up) Older Adolescent Service (follow-up to age 19) Outpatient Case Management Intensive Outreach Support Acute Inpatient Care Day Group Program Family work Cognitive Therapies
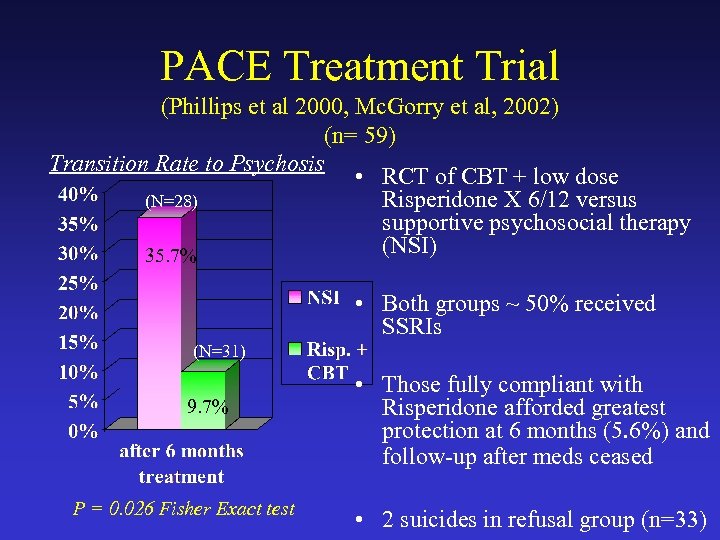 PACE Treatment Trial (Phillips et al 2000, Mc. Gorry et al, 2002) (n= 59) Transition Rate to Psychosis • RCT of CBT + low dose (N=28) Risperidone X 6/12 versus supportive psychosocial therapy (NSI) 35. 7% • Both groups ~ 50% received SSRIs (N=31) 9. 7% P = 0. 026 Fisher Exact test • Those fully compliant with Risperidone afforded greatest protection at 6 months (5. 6%) and follow-up after meds ceased • 2 suicides in refusal group (n=33)
PACE Treatment Trial (Phillips et al 2000, Mc. Gorry et al, 2002) (n= 59) Transition Rate to Psychosis • RCT of CBT + low dose (N=28) Risperidone X 6/12 versus supportive psychosocial therapy (NSI) 35. 7% • Both groups ~ 50% received SSRIs (N=31) 9. 7% P = 0. 026 Fisher Exact test • Those fully compliant with Risperidone afforded greatest protection at 6 months (5. 6%) and follow-up after meds ceased • 2 suicides in refusal group (n=33)
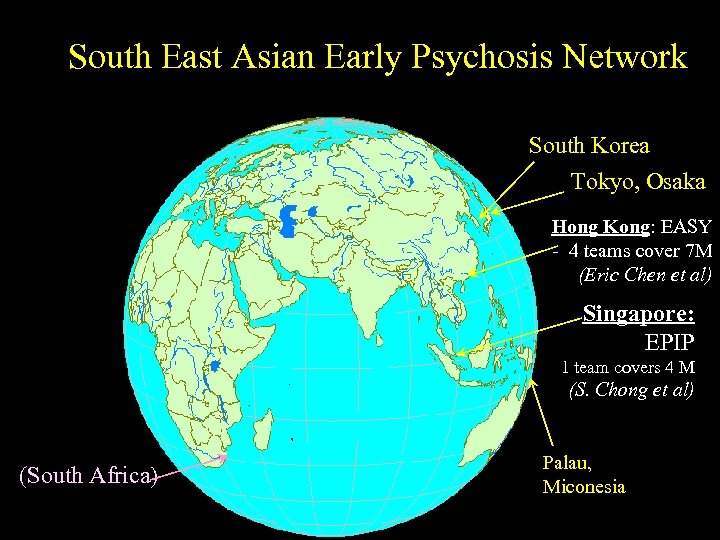 South East Asian Early Psychosis Network South Korea Tokyo, Osaka Hong Kong: EASY - 4 teams cover 7 M (Eric Chen et al) Singapore: EPIP 1 team covers 4 M (S. Chong et al) (South Africa) Palau, Miconesia
South East Asian Early Psychosis Network South Korea Tokyo, Osaka Hong Kong: EASY - 4 teams cover 7 M (Eric Chen et al) Singapore: EPIP 1 team covers 4 M (S. Chong et al) (South Africa) Palau, Miconesia
 Swiss Early Psychosis Programs Bern: • Uni Hosp. of Social & Comm. Psych. (Gekle) (Merlo - moved to Geneva) Basil: • Uni Hosp. Basil: Basil FEPSY screening study (Gschwandtner et al) Geneva & Zurich: Swiss Early Psychosis Project SWEPP (Simon, Umbricht & Merlo)
Swiss Early Psychosis Programs Bern: • Uni Hosp. of Social & Comm. Psych. (Gekle) (Merlo - moved to Geneva) Basil: • Uni Hosp. Basil: Basil FEPSY screening study (Gschwandtner et al) Geneva & Zurich: Swiss Early Psychosis Project SWEPP (Simon, Umbricht & Merlo)
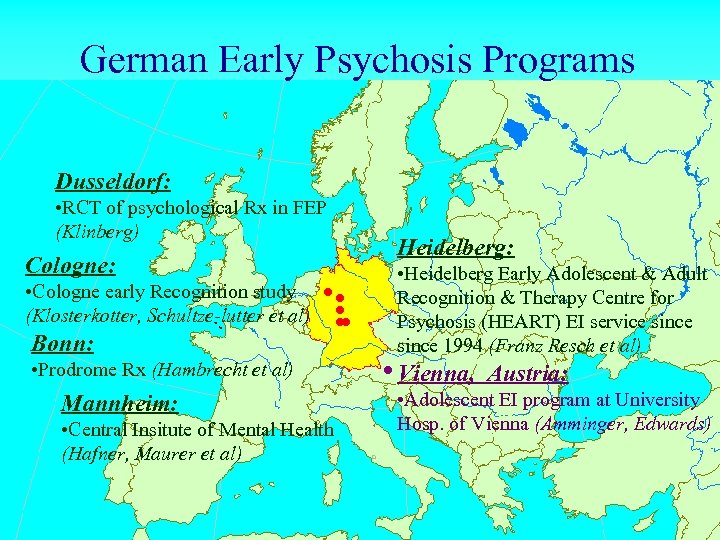 German Early Psychosis Programs Dusseldorf: • RCT of psychological Rx in FEP (Klinberg) Cologne: • Cologne early Recognition study (Klosterkotter, Schultze-lutter et al) Bonn: . . . • Prodrome Rx (Hambrecht et al) Mannheim: • Central Insitute of Mental Health (Hafner, Maurer et al) Heidelberg: . • Heidelberg Early Adolescent & Adult Recognition & Therapy Centre for Psychosis (HEART) EI service since 1994 (Franz Resch et al) Vienna, Austria: • Adolescent EI program at University Hosp. of Vienna (Amminger, Edwards)
German Early Psychosis Programs Dusseldorf: • RCT of psychological Rx in FEP (Klinberg) Cologne: • Cologne early Recognition study (Klosterkotter, Schultze-lutter et al) Bonn: . . . • Prodrome Rx (Hambrecht et al) Mannheim: • Central Insitute of Mental Health (Hafner, Maurer et al) Heidelberg: . • Heidelberg Early Adolescent & Adult Recognition & Therapy Centre for Psychosis (HEART) EI service since 1994 (Franz Resch et al) Vienna, Austria: • Adolescent EI program at University Hosp. of Vienna (Amminger, Edwards)
 Scandinavian Early Psychosis Services Norwegian Services: • TIPS - Roskilde/Stravanger (Larsen, Johannessen etc) DUP median (weeks) • UNA-projektet, Oslo • EOP, Skien Control Finland: • Turku: Detection of early Psychosis project (Suomela et al) Swedish Services: • Parachute Project (1. 5 M), Stockholm • Sodertalja Psykiatriska Sektor, Sodetalje • TUPP Project, Stockholm (Cleland)
Scandinavian Early Psychosis Services Norwegian Services: • TIPS - Roskilde/Stravanger (Larsen, Johannessen etc) DUP median (weeks) • UNA-projektet, Oslo • EOP, Skien Control Finland: • Turku: Detection of early Psychosis project (Suomela et al) Swedish Services: • Parachute Project (1. 5 M), Stockholm • Sodertalja Psykiatriska Sektor, Sodetalje • TUPP Project, Stockholm (Cleland)
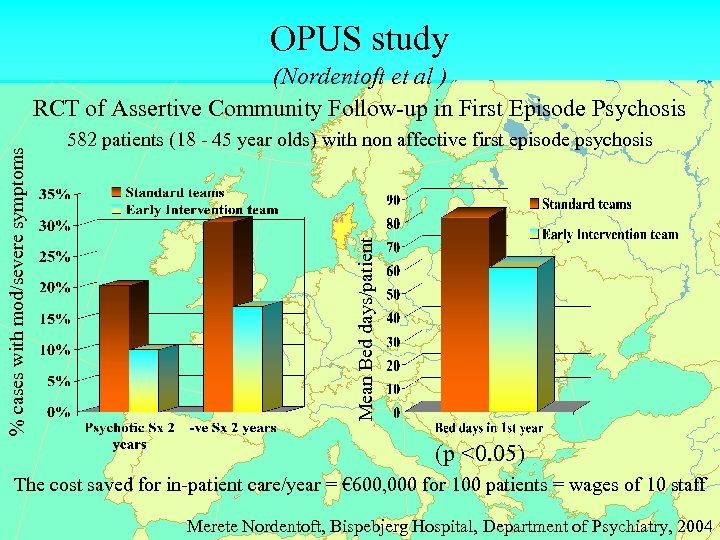 OPUS study 582 patients (18 - 45 year olds) with non affective first episode psychosis Mean Bed days/patient % cases with mod/severe symptoms (Nordentoft et al ) RCT of Assertive Community Follow-up in First Episode Psychosis (p <0. 05) The cost saved for in-patient care/year = € 600, 000 for 100 patients = wages of 10 staff Merete Nordentoft, Bispebjerg Hospital, Department of Psychiatry, 2004
OPUS study 582 patients (18 - 45 year olds) with non affective first episode psychosis Mean Bed days/patient % cases with mod/severe symptoms (Nordentoft et al ) RCT of Assertive Community Follow-up in First Episode Psychosis (p <0. 05) The cost saved for in-patient care/year = € 600, 000 for 100 patients = wages of 10 staff Merete Nordentoft, Bispebjerg Hospital, Department of Psychiatry, 2004
 Dutch & Belgian EI Programs Netherlands: Belgian Projects: • PECC (Janssen-Cilag) • Academic Medical Centre (Don Linszen) • University of Maastricht: NEMESIS (Van Os, J. ) • University Med Centre, Utrecht (Dutch Prediction of Psychosis Study- DUPS) Other European Projects: • European Prediction of Psychosis (EPOS) study (6 centres: Birmingham, Amsterdam, Cologne, Turku, Santander, Dannstadt) • Dublin: SJOG Hospital (E. O’Callaghan) • Bordeaux: (Helen Verdoux) • Barcelona, Madrid, Santander: 4 prodrome research programs • Lisbon: planning EI service • Eastern European, Russian & Middle East: research programs & plans for services
Dutch & Belgian EI Programs Netherlands: Belgian Projects: • PECC (Janssen-Cilag) • Academic Medical Centre (Don Linszen) • University of Maastricht: NEMESIS (Van Os, J. ) • University Med Centre, Utrecht (Dutch Prediction of Psychosis Study- DUPS) Other European Projects: • European Prediction of Psychosis (EPOS) study (6 centres: Birmingham, Amsterdam, Cologne, Turku, Santander, Dannstadt) • Dublin: SJOG Hospital (E. O’Callaghan) • Bordeaux: (Helen Verdoux) • Barcelona, Madrid, Santander: 4 prodrome research programs • Lisbon: planning EI service • Eastern European, Russian & Middle East: research programs & plans for services
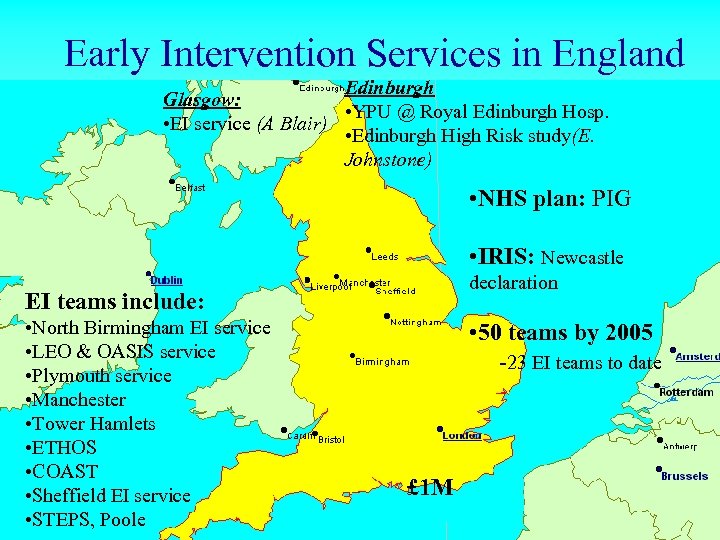 Early Intervention Services in England Edinburgh Glasgow: • YPU @ Royal Edinburgh Hosp. • EI service (A Blair) • Edinburgh High Risk study(E. Johnstone) • NHS plan: PIG • IRIS: Newcastle declaration EI teams include: • North Birmingham EI service • LEO & OASIS service • Plymouth service • Manchester • Tower Hamlets • ETHOS • COAST • Sheffield EI service • STEPS, Poole • 50 teams by 2005 -23 EI teams to date £ 1 M
Early Intervention Services in England Edinburgh Glasgow: • YPU @ Royal Edinburgh Hosp. • EI service (A Blair) • Edinburgh High Risk study(E. Johnstone) • NHS plan: PIG • IRIS: Newcastle declaration EI teams include: • North Birmingham EI service • LEO & OASIS service • Plymouth service • Manchester • Tower Hamlets • ETHOS • COAST • Sheffield EI service • STEPS, Poole • 50 teams by 2005 -23 EI teams to date £ 1 M
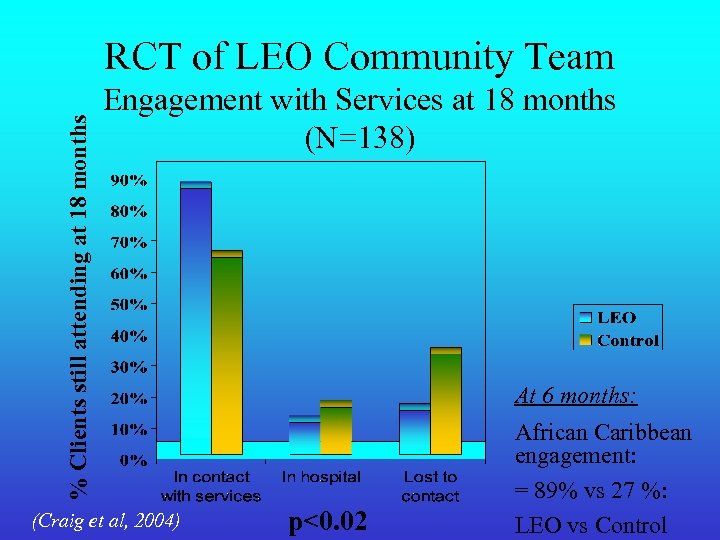 % Clients still attending at 18 months RCT of LEO Community Team Engagement with Services at 18 months (N=138) (Craig et al, 2004) At 6 months: p<0. 02 African Caribbean engagement: = 89% vs 27 %: LEO vs Control
% Clients still attending at 18 months RCT of LEO Community Team Engagement with Services at 18 months (N=138) (Craig et al, 2004) At 6 months: p<0. 02 African Caribbean engagement: = 89% vs 27 %: LEO vs Control
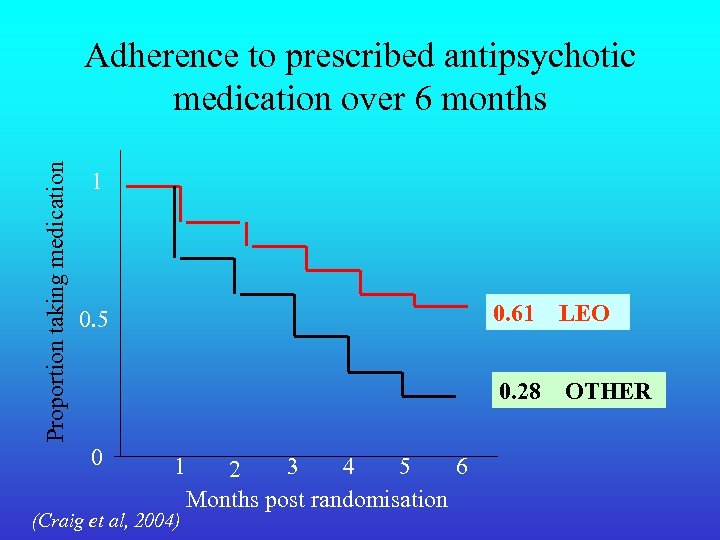 Proportion taking medication Adherence to prescribed antipsychotic medication over 6 months 1 0. 61 0 1 3 4 5 6 2 Months post randomisation (Craig et al, 2004) LEO 0. 28 0. 5 OTHER
Proportion taking medication Adherence to prescribed antipsychotic medication over 6 months 1 0. 61 0 1 3 4 5 6 2 Months post randomisation (Craig et al, 2004) LEO 0. 28 0. 5 OTHER
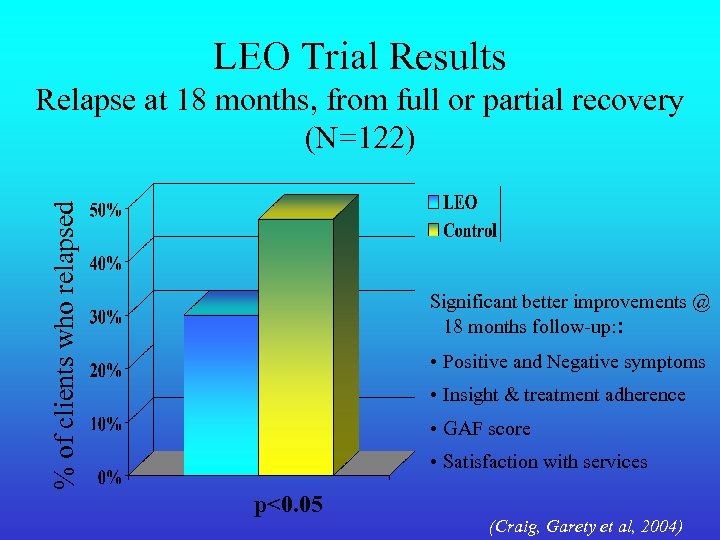 LEO Trial Results % of clients who relapsed Relapse at 18 months, from full or partial recovery (N=122) Significant better improvements @ 18 months follow-up: : • Positive and Negative symptoms • Insight & treatment adherence • GAF score • Satisfaction with services p<0. 05 (Craig, Garety et al, 2004)
LEO Trial Results % of clients who relapsed Relapse at 18 months, from full or partial recovery (N=122) Significant better improvements @ 18 months follow-up: : • Positive and Negative symptoms • Insight & treatment adherence • GAF score • Satisfaction with services p<0. 05 (Craig, Garety et al, 2004)
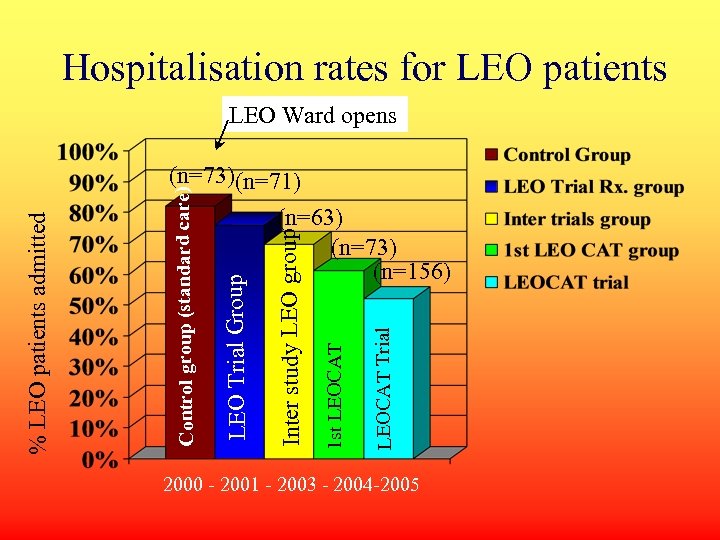 Hospitalisation rates for LEO patients LEO Ward opens LEOCAT Trial 1 st LEOCAT (n=63) (n=73) (n=156) Inter study LEO group LEO Trial Group Control group (standard care) % LEO patients admitted (n=73)(n=71) 2000 - 2001 - 2003 - 2004 -2005
Hospitalisation rates for LEO patients LEO Ward opens LEOCAT Trial 1 st LEOCAT (n=63) (n=73) (n=156) Inter study LEO group LEO Trial Group Control group (standard care) % LEO patients admitted (n=73)(n=71) 2000 - 2001 - 2003 - 2004 -2005
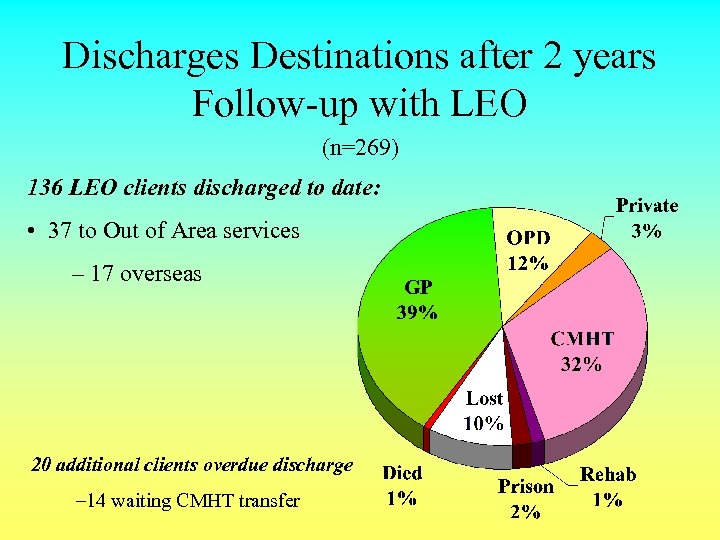 Discharges Destinations after 2 years Follow-up with LEO (n=269) 136 LEO clients discharged to date: • 37 to Out of Area services – 17 overseas 20 additional clients overdue discharge – 14 waiting CMHT transfer
Discharges Destinations after 2 years Follow-up with LEO (n=269) 136 LEO clients discharged to date: • 37 to Out of Area services – 17 overseas 20 additional clients overdue discharge – 14 waiting CMHT transfer
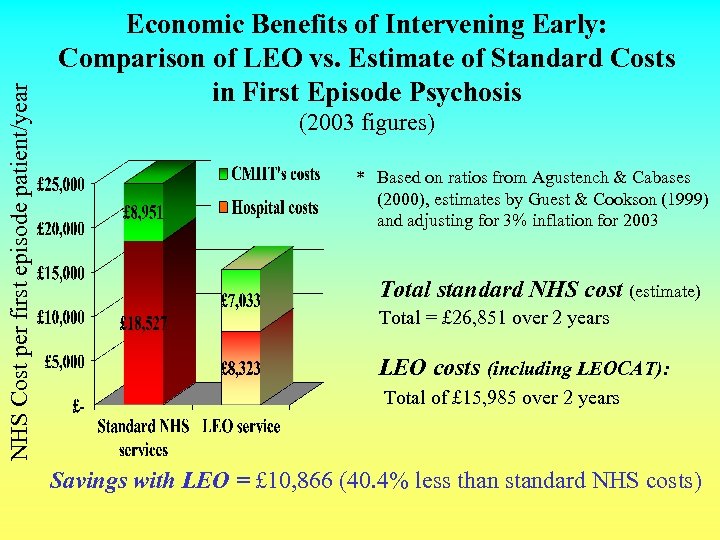 NHS Cost per first episode patient/year Economic Benefits of Intervening Early: Comparison of LEO vs. Estimate of Standard Costs in First Episode Psychosis (2003 figures) * Based on ratios from Agustench & Cabases (2000), estimates by Guest & Cookson (1999) and adjusting for 3% inflation for 2003 Total standard NHS cost (estimate) Total = £ 26, 851 over 2 years LEO costs (including LEOCAT): Total of £ 15, 985 over 2 years Savings with LEO = £ 10, 866 (40. 4% less than standard NHS costs)
NHS Cost per first episode patient/year Economic Benefits of Intervening Early: Comparison of LEO vs. Estimate of Standard Costs in First Episode Psychosis (2003 figures) * Based on ratios from Agustench & Cabases (2000), estimates by Guest & Cookson (1999) and adjusting for 3% inflation for 2003 Total standard NHS cost (estimate) Total = £ 26, 851 over 2 years LEO costs (including LEOCAT): Total of £ 15, 985 over 2 years Savings with LEO = £ 10, 866 (40. 4% less than standard NHS costs)


