545d96bff515ce121af60126a20f8431.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Early Colonial Period §Virginia House of Burgesses, 1619 – First Representative House of Government in the Colonies §Mayflower Compact – Representative Voice in government

Early Colonial Period § § Virginia House of Burgesses, 1618 – First Representative House of Government in the Colonies. Only white, land owning males will be able to vote, establishment of slavery Mayflower Compact – Representative Voice in government Fundamental Orders of Connecticut – First Written State Constitution in the Colonies have limited rule from the King

Colonial and Government Relations Salutary Neglect – British allow the colonists limited rule as long as they are following the laws of the empire n Mercantilism – Resources and Raw Materials are sent back to England made into finished goods n The Navigation Acts – All colonial trade is to go through British ports for taxation n

French and Indian War n n The American colonists support the British crown in the fighting during the French and Indian War. It is their hope to gain cheap and abundant land. The colonists help the crown gain victory, but they do not want settlements West of the Appalachian Mountains. Albany Plan of the Union – First colonial attempt to unify the colonies, it fails, only six states sends delegates The Proclamation of 1763 forbids colonial expansion and this causes resentment to the King. Colonists want more land, English do not want to pay for fighting against the Indians.
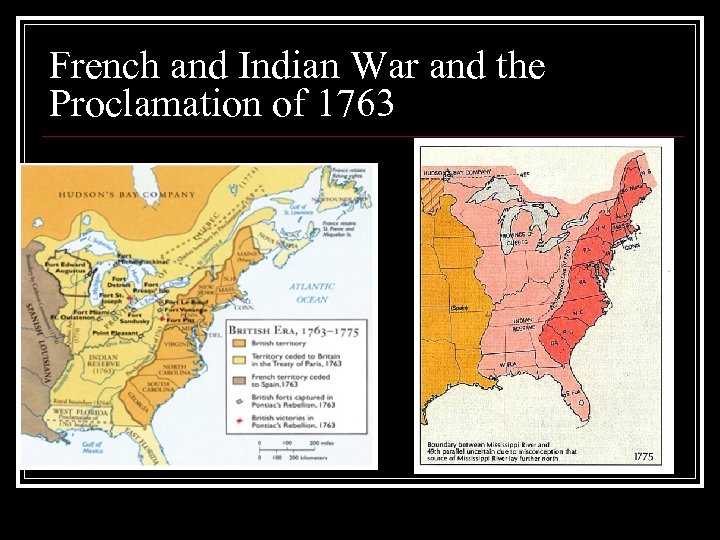
French and Indian War and the Proclamation of 1763

Causes of the Revolutionary War n n n n n Stamp Tax Sugar Tax Quartering Act Writs of Assistance Tea Act Intolerable Acts – Closing down of Boston Harbor and Town Hall Meetings French and Indian War Boston Massacre Boston Tea Party

Boston Massacre Boston Tea Party

Seeds of Resentment to the Crown 1754 – Albany Plan of the Union, 6 delegates n 1765 – Stamp Act Congress, 9 delegates n 1774 – First Continental Congress, 12 delegates – Increased support against the King/laws. n Lexington and Concord 1775 – Colonial fighting with British troops n

American patriotic beliefs and actions against the King • Belief in the natural rights of citizens that should be protected by a rightful government • Locke – Natural Rights Montesquieu – 3 Branches of government • Rousseau – Social Contract • Voltaire – Right to overthrow poor governments • Thomas Paine – Common Sense – A famous book on belief of American freedom against the British King • The colonies are a separate nation, economy and people away from the British

Declaration of Independence List of Grievances against the King n Not a framework of government n Seeking total independence for the colonies n The colonists fight the King with no framework of government in place n


Revolutionary War and the Articles of Confederation n n n General Washington loses more battles then he wins, but wins the key battles to survive Defeats the British at Yorktown and forces the King to free the Colonies Articles of Confederation does not create a strong central government All the power is given to the states The weaknesses of the Articles shows that our nation needs a strong government The government has no power to put down revolts (Shay’s Rebellion) and need a central authority

Federalists and Anti-Federalists n n Federalists – Strong central government, military and economy supported by Andrew Hamilton Anti-Federalists – Concerned over the powers of a strong government want a Bill of Rights to protect the people supported by Thomas Jefferson – Democratic Republicans Start of the political party system Federalist Papers – Series of documents that support the creation of the Constitution

Concerns over the Powers of Government n n n New Jersey Plan – Equal Representation based on smaller states – Senate Virginia Plan – Large scale Representation through population – House of Representatives Known as the Great Compromise through the creation of a Bi-Cameral Legislature 3/5’s Compromise – 3/5’s of all slave will be counted for taxation and representation Bill of Rights will protect the people, but the central government is the strongest power in the nation through the Constitution

The Signing of the Constitution

Interpretation of the Constitution n Strict Interpretation – Belief that you have to follow the Constitution and not deviate from its direction Loose Interpretation – Belief that times will change and there will be a need to have flexibility within the Constitution. Thomas Jefferson goes from strict to loose interpreter when he buys the Louisiana Purchase. No where in the Constitution does it state we can buy this land, Jefferson does it because it will benefit our nation

Checks and Balances of American Constitutional Power n n n Legislative Branch – Art. 1 – Makes the Laws Executive Branch – Art. 2 – Enforces the Laws Judicial Branch – Art. 3 – Interprets the Laws Elastic Clause – Article 1. Section 8 – The powers of the Legislative Branch to enforce the powers of the government. Amendment Process – The Constitution can be changed over time with flexibility through the addition of amendments Judicial Review – Marbury v. Madison – Power of the Supreme Court to interpret the Constitution and decide if government, military and civilians actions are correct

Powers of Government - Federalism n n n Federalism is the Constitutional distribution of power between the Federal, State and Local levels of government Delegate Powers – Federal Government powers Reserved Powers – State Government powers Concurrent Powers – Those powers that are shared between the State and Federal Government Implied Powers – Responsibilities that are not stated in the Constitution, but are given to government

The Unwritten Constitution Powers that were never stated in the Constitution, but help run government and the nation: n Judicial Review-Interpretation of the Constitution by the Supreme Court n Political party systems n The presidential cabinet n Swearing in of ambassadors n

Voting and the United States n n n n n Presidents will win their elections usually through gaining the majority of electoral votes It is possible for a President to win an election, by losing the popular vote 2000 Election Facts Outcome of race unknown for several weeks due to dispute over close vote totals in Florida Green Party candidate Ralph Nader received 2, 882, 728 votes, but no Electoral Votes Gore won DC; however one Elector did not cast a vote One of only 4 elections, and first in over 100 years (1824, 1876, 1888, 2000) where the popular vote winner was defeated Issues of the Day: Impeachment, Presidential ethics, Good economy 2000 George W. Bush (R) Electoral 271 Popular 50, 456, 062 Albert Gore, Jr. (D) Electoral 266 Popular 50, 996, 582 (R) = Republican (D) = Democratic

Electoral College and the 2000 Election n n n n It is possible for a President to win an election, by losing the popular vote 2000 Election Facts Outcome of race unknown for several weeks due to dispute over close vote totals in Florida Green Party candidate Ralph Nader received 2, 882, 728 votes, but no Electoral Votes Gore won DC; however one Elector did not cast a vote One of only 4 elections, and first in over 100 years (1824, 1876, 1888, 2000) where the popular vote winner was defeated Issues of the Day: Impeachment, Presidential ethics, Good economy 2000 George W. Bush (R) Electoral 271 Popular 50, 456, 062 Albert Gore, Jr. (D) Electoral 266 Popular 50, 996, 582 (R) = Republican (D) = Democratic

Electoral College and 1980 Victory 1980 Ronald Reagan (R) Electoral 489 Popular 43, 901, 812 Jimmy Carter (D) (I) Electoral 49 Popular 35, 483, 820 n (R) = Republican (D) = Democratic (I) = Incumbent n

Adams and the Alien and Sedition Acts n n Alien Act – Limitations on immigrants and the ease of their citizenship to our nation Sedition Acts – Limitations places on First Amendment rights of our citizens These acts were highly unpopular, but used to prevent the US from hurting our neutrality with fighting in British and French wars These acts are nullified and deemed to be unconstitutional

War of 1812 Embargo Act of 1807 n Intercourse Act n US declares war on England over impressments of sailors, trade violations and disrespect n Neither nation wins the war, US is weak, England fights a costly war. Both will never fight each other again n

Monroe Doctrine The United States is the main power in the Western Hemisphere n No new colonization in the Caribbean or Latin America n Dominant American Foreign Policy n Once a European nation is deposed, there is no new colonization n
545d96bff515ce121af60126a20f8431.ppt