1bdc54dce247fb011233f12702afbd47.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Early Civilizations
Early Civilizations
 Egyptians • Overview of Ancient Egypt • Early inhabitants (Neolithic's) called the land Kemet • Renamed Egypt by the Greeks • The Nile River Valley (annual floods) • World’s Longest River – flows from South to North
Egyptians • Overview of Ancient Egypt • Early inhabitants (Neolithic's) called the land Kemet • Renamed Egypt by the Greeks • The Nile River Valley (annual floods) • World’s Longest River – flows from South to North
 • Two Kingdoms by 4, 000 B. C. • Lower Kingdom in the North • Upper Kingdom in the South • 3000 B. C. – Narmer (Menes) invaded Lower Egypt • Marked the first Egyptian Dynasty
• Two Kingdoms by 4, 000 B. C. • Lower Kingdom in the North • Upper Kingdom in the South • 3000 B. C. – Narmer (Menes) invaded Lower Egypt • Marked the first Egyptian Dynasty
 Three Egyptian Dynasties • The Old Kingdom (2700 -2200 B. C. ) • Established a theocracy (god-king) • Built pyramids to honor god-kings (mummification) • The Middle Kingdom (2050 -1700 B. C. ) • Egypt was reunited after a time of upheaval • The capital was moved to Thebes • Were invaded by the Hyksos (from Western Asia) • The New Kingdom (1600 -1200 B. C. ) • Egyptians overthrew the Hyksos – led by Ahmose • Kings began to use the title Pharaoh
Three Egyptian Dynasties • The Old Kingdom (2700 -2200 B. C. ) • Established a theocracy (god-king) • Built pyramids to honor god-kings (mummification) • The Middle Kingdom (2050 -1700 B. C. ) • Egypt was reunited after a time of upheaval • The capital was moved to Thebes • Were invaded by the Hyksos (from Western Asia) • The New Kingdom (1600 -1200 B. C. ) • Egyptians overthrew the Hyksos – led by Ahmose • Kings began to use the title Pharaoh
 New Kingdom Pharaohs • Hatshepsut (1480 B. C. ) - female pharaoh • Ruled because her son was too young to rule • Extensive building projects • Thutmose III (Hatshepsut’s son) • Expanded the Dynasty to include Syria • Made an “empire” for Egypt – cultural diffusion • Amenhotep: (1370 B. C. ) – wife Nefertiti • Decided to make Egypt monotheistic (Aton) • Changed his name to Akhenaton • Moved the capital to central Egypt
New Kingdom Pharaohs • Hatshepsut (1480 B. C. ) - female pharaoh • Ruled because her son was too young to rule • Extensive building projects • Thutmose III (Hatshepsut’s son) • Expanded the Dynasty to include Syria • Made an “empire” for Egypt – cultural diffusion • Amenhotep: (1370 B. C. ) – wife Nefertiti • Decided to make Egypt monotheistic (Aton) • Changed his name to Akhenaton • Moved the capital to central Egypt
 • Tutankhamen (King Tut) • The boy king • Moved the capital back to Thebes • Ramses II (“the Great”) • Fought the Hittites for control of Syria • A. D. 1995, a tomb was uncovered that held 50 of Ramses 52 sons • Egypt weakened after Ramses’ death • Invasions by the Libyans and Kushites
• Tutankhamen (King Tut) • The boy king • Moved the capital back to Thebes • Ramses II (“the Great”) • Fought the Hittites for control of Syria • A. D. 1995, a tomb was uncovered that held 50 of Ramses 52 sons • Egypt weakened after Ramses’ death • Invasions by the Libyans and Kushites
 Egyptian Life • Social Order • Upper class; middle class; lower class • Women's’ rights improved btwn. Old & New Kingdoms • Religion: polytheistic (other than Akhenaton) • Gods were depicted as part human part animal • Writing System • • Hieroglyphics: carved picture symbols Hieratic: cursive for everyday use Rosetta Stone: part Greek and part Egyptian Book of the Dead
Egyptian Life • Social Order • Upper class; middle class; lower class • Women's’ rights improved btwn. Old & New Kingdoms • Religion: polytheistic (other than Akhenaton) • Gods were depicted as part human part animal • Writing System • • Hieroglyphics: carved picture symbols Hieratic: cursive for everyday use Rosetta Stone: part Greek and part Egyptian Book of the Dead
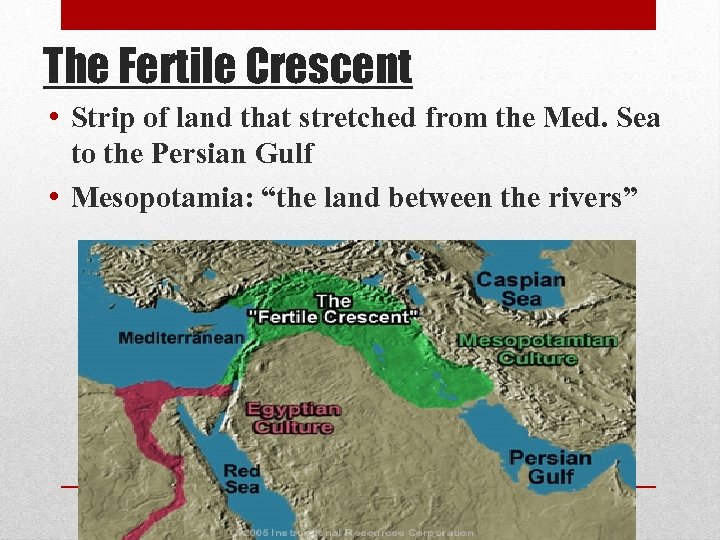 The Fertile Crescent • Strip of land that stretched from the Med. Sea to the Persian Gulf • Mesopotamia: “the land between the rivers”
The Fertile Crescent • Strip of land that stretched from the Med. Sea to the Persian Gulf • Mesopotamia: “the land between the rivers”
 The Sumerians • Settled in Mesopotamia in 3500 B. C. • Built the world’s first cities (Ur, Uruk, Eridu) • Built ziggurats – temples in each city-state • only priests could enter the temples
The Sumerians • Settled in Mesopotamia in 3500 B. C. • Built the world’s first cities (Ur, Uruk, Eridu) • Built ziggurats – temples in each city-state • only priests could enter the temples
 • Government: each city was independent • • A military leader was chosen to lead/protect 2700: military leaders were viewed as kings Leaders served as king and high priest The legal systems were not clear or consistent • Roles of Men and Women • Men had ultimate authority over families • Women possessed very few rights (buy/sell prop. ) • Writing System • Cuneiform: pictograms on wet clay • Gilgamesh was written @ 1850 B. C
• Government: each city was independent • • A military leader was chosen to lead/protect 2700: military leaders were viewed as kings Leaders served as king and high priest The legal systems were not clear or consistent • Roles of Men and Women • Men had ultimate authority over families • Women possessed very few rights (buy/sell prop. ) • Writing System • Cuneiform: pictograms on wet clay • Gilgamesh was written @ 1850 B. C
 • Religion: each god was over a natural force • The gods were viewed as unpredictable/angry • Inventions: • The wheel, 12 mo. Calendar, arch, and sundial • Developed bronze and metal plow
• Religion: each god was over a natural force • The gods were viewed as unpredictable/angry • Inventions: • The wheel, 12 mo. Calendar, arch, and sundial • Developed bronze and metal plow
 Mesopotamian Empires • Invaders dreamt of controlling an empire • Sargon I and the Akkadians • Came to power in the 2300 s B. C. • United the Mesopotamian city-states • Hammurabi’s Babylonian Empire • • Amorites overran Sumerian centers (Babylon) Hammurabi became the dominant ruler Increased Babylon's prosperity Law Code: “Made Justice Appear in the Land” • Law covered the entire region • 282 sections on Daily Life • Clear punishment for crimes
Mesopotamian Empires • Invaders dreamt of controlling an empire • Sargon I and the Akkadians • Came to power in the 2300 s B. C. • United the Mesopotamian city-states • Hammurabi’s Babylonian Empire • • Amorites overran Sumerian centers (Babylon) Hammurabi became the dominant ruler Increased Babylon's prosperity Law Code: “Made Justice Appear in the Land” • Law covered the entire region • 282 sections on Daily Life • Clear punishment for crimes
 • Babylonian Society • • Upper Class: Kings, priests, nobles Middle Class: artisans, merchants, scribes, farmers Lower Class: slaves (from war/had not paid debts) Borrowed ideas and techniques from Sumerians • Writing system, farming techniques, & religion
• Babylonian Society • • Upper Class: Kings, priests, nobles Middle Class: artisans, merchants, scribes, farmers Lower Class: slaves (from war/had not paid debts) Borrowed ideas and techniques from Sumerians • Writing system, farming techniques, & religion
 1. How did these ancient civilizations influence later civilizations prior to the modern era? 2. What elements of either the Ancient Egyptians or Middle Eastern Civilizations exist in our world today?
1. How did these ancient civilizations influence later civilizations prior to the modern era? 2. What elements of either the Ancient Egyptians or Middle Eastern Civilizations exist in our world today?
 The Early Israelites • Lived in Canaan (Abraham) • Monotheistic • Worshiped one God (Yahweh) • A divine covenant w/ Abraham • Lived as nomadic shepherds • Jacob and 12 sons • Joseph was sold into slavery • Fled to Egypt • Later enslaved • Moses and the Exodus from Egypt (Passover) • The Ten Commandments & “Promised Land”
The Early Israelites • Lived in Canaan (Abraham) • Monotheistic • Worshiped one God (Yahweh) • A divine covenant w/ Abraham • Lived as nomadic shepherds • Jacob and 12 sons • Joseph was sold into slavery • Fled to Egypt • Later enslaved • Moses and the Exodus from Egypt (Passover) • The Ten Commandments & “Promised Land”
 • Settling in Canaan: Joshua led them into Canaan • Fought against the Canaanites and Philistines • Judges led the Twelve Tribes of Israel • Saul (r. 1020 -1012 B. C. ): first Israelite king • David (r. 1012 -961 B. C. ) • Set up the capital in Jerusalem – economic prosperity • Solomon (r. 961 -922 B. C. ) • Built the Temple in Jerusalem • Very prosperous economically
• Settling in Canaan: Joshua led them into Canaan • Fought against the Canaanites and Philistines • Judges led the Twelve Tribes of Israel • Saul (r. 1020 -1012 B. C. ): first Israelite king • David (r. 1012 -961 B. C. ) • Set up the capital in Jerusalem – economic prosperity • Solomon (r. 961 -922 B. C. ) • Built the Temple in Jerusalem • Very prosperous economically
 • Israel’s Struggle • 10 northern tribes broke away from the southern 2 • The 2 southern tribes became Judah (Jews) • Exile of Kingdoms • Assyrians and Chaldeans invaded and enslaved Israel • Exile in Babylon – prophets (Jeremiah) rose up • Rebuilding Jerusalem • • 539 B. C. the Persians (Cyrus) conquered the Chaldeans Darius allowed the Jews to return to Jerusalem to rebuild The Torah was organized (first 5 books of the O. T. ) The Diaspora (the scattering) began
• Israel’s Struggle • 10 northern tribes broke away from the southern 2 • The 2 southern tribes became Judah (Jews) • Exile of Kingdoms • Assyrians and Chaldeans invaded and enslaved Israel • Exile in Babylon – prophets (Jeremiah) rose up • Rebuilding Jerusalem • • 539 B. C. the Persians (Cyrus) conquered the Chaldeans Darius allowed the Jews to return to Jerusalem to rebuild The Torah was organized (first 5 books of the O. T. ) The Diaspora (the scattering) began
 Lasting Legacy of the Israelites • Their view on occurrences • Everything happened according to God’s purpose • Believe that humans have an infinite worth • Humans are accountable for what goes on in the world b/c we work in a partnership with God
Lasting Legacy of the Israelites • Their view on occurrences • Everything happened according to God’s purpose • Believe that humans have an infinite worth • Humans are accountable for what goes on in the world b/c we work in a partnership with God
 The Persians • Settled in Iran in 2000 s B. C. • Cyrus II (540 s B. C. ) • • • Developed a strong military Conquered the Medes (expanded the empire) Took over land in Asia Minor (Lydia/Greek city-states) 525 B. C. – Cambyses conquered Egypt Persian Empire covered 3, 000 miles & 50 million people
The Persians • Settled in Iran in 2000 s B. C. • Cyrus II (540 s B. C. ) • • • Developed a strong military Conquered the Medes (expanded the empire) Took over land in Asia Minor (Lydia/Greek city-states) 525 B. C. – Cambyses conquered Egypt Persian Empire covered 3, 000 miles & 50 million people
 • Darius I (522 -486 B. C. ) • Empire’s best organizer (satraps and provinces) • “Eyes and Ears of the King” inspectors • Brought artisans in to build Persepolis
• Darius I (522 -486 B. C. ) • Empire’s best organizer (satraps and provinces) • “Eyes and Ears of the King” inspectors • Brought artisans in to build Persepolis
 • Imperial Rule • Treated conquered people fairly • Improved the network of roads • Religion and Culture • Strict moral code • Polytheistic until 500 s B. C. • Zoroaster: (Ahura Mazda & Ahriman) • Good vs. Evil – Good will win in the end Faravahar
• Imperial Rule • Treated conquered people fairly • Improved the network of roads • Religion and Culture • Strict moral code • Polytheistic until 500 s B. C. • Zoroaster: (Ahura Mazda & Ahriman) • Good vs. Evil – Good will win in the end Faravahar
 • Fall of Persia • Darius waged war with the Greeks for control of Asia Minor • 480 B. C. Xerxes lost to the Greeks
• Fall of Persia • Darius waged war with the Greeks for control of Asia Minor • 480 B. C. Xerxes lost to the Greeks
 1. What are some examples of cultural diffusion between the Ancient Persians and the Israelites? What were the modes of diffusion? 2. What lasting impact did any of the Ancient Middle Eastern civilizations have on later civilizations?
1. What are some examples of cultural diffusion between the Ancient Persians and the Israelites? What were the modes of diffusion? 2. What lasting impact did any of the Ancient Middle Eastern civilizations have on later civilizations?


