472744f2fef17db91c67991979d7f68c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Early Childhood Development. An Imperative for Sustainable Development Agenda OMEP World Congress, July 11 -13, 2013 - Shanghai Nurper Ulkuer, Ph. D.

• What is Sustainable Development Agenda? • Why ECD is an imperative? New Evidence • Where is the gap? So far? • What needs to be done?

What is Sustainable Development Agenda for post-2015? • Framework for post-2015 • How different from MDGs? • The process

Sustainable Development Agenda for Post-2015 • 2015 refers to the year that the current Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) will expire; • More inclusive of various stakeholders (Civil Society, Government, UN, Private Sector, Academia, Citizens); • Aims to be an agenda that building on the strengths of the MDGs, but also addresses their shortfalls, “the unfinished agenda” and neglected issues; • Various processes leading to 2015 (e. g. Rio+20, UN Task Team, High Level Panel, “Global Conversation”) will need to be integrated. 4

What is “Post-2015? ” Some roles and definitions (1) UN System Post-2015 Task Team: Designated by the UN Secretary-General in late 2011 and chaired by UNDESA and UNDP Rio+20: The UN Conference on Sustainable Development took place from 20 -22 June 2012 and now work will begin on how the outcomes of Rio will be integrated into the post-2015 process. 5

What is “Post-2015? ” Some roles and definitions (2) High Level Panel (HLP): A group eminent persons – likely drawn from leaders in political, academic, civil society and private sector fields -- selected by the Secretary-General to advise on the post-2015 development agenda and prepare inputs for the 2013 General Assembly. Three co-chairs appointed in May: Presidents of Indonesia and Liberia and the Prime Minister of the UK. Other appointments are expected to be announced by the SG in July 2012. The “Global Conversation”: A rather broad concept that aims to capture how various stakeholders will have their say. Specifically, this can be done through multiple country-level and global thematic consultations. It is also expected that there would be a significant “online” component to this -- leveraging social media to bring people in to the conversation. 6

What is “Post 2015? ” Country and Global Thematic Consultations Country Consultations: Multi-stakeholder consultations within countries on the post-2015 agenda to ensure a transparent process and meaningful participation from governments, NGOs, CSOs, etc. Catalyzed by UN Resident Coordinators and UNCTs within selected countries. Global Thematic Consultations: An additional 9 thematic multi-stakeholder consultations led or co-led by 2 -3 UN Organizations, covering the following. UNICEF will be co-lead on 3, with expected involvement in several others. • • • Inequalities (UNICEF, UN Women); Population (UNHABITAT, UNFPA); Health (WHO, UNICEF); Education (UNESCO, UNICEF); Growth & Employment (UNDP, ILO, UNCTAD); • Conflict & Fragility (UN PBSO, UNDP); • Governance (OHCHR, UNDP); • Environmental Sustainability (UNEP, UNDP); • Food Security and Nutrition (FAO, IFAD). 7
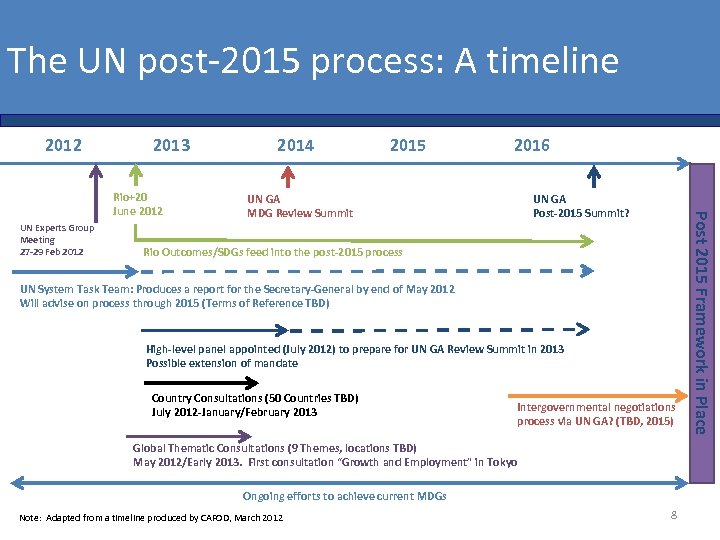
The UN post-2015 process: A timeline 2012 2013 UN Experts Group Meeting 27 -29 Feb 2012 2015 2016 UN GA MDG Review Summit UN GA Post-2015 Summit? Rio Outcomes/SDGs feed into the post-2015 process UN System Task Team: Produces a report for the Secretary-General by end of May 2012 Will advise on process through 2015 (Terms of Reference TBD) High-level panel appointed (July 2012) to prepare for UN GA Review Summit in 2013 Possible extension of mandate Country Consultations (50 Countries TBD) July 2012 -January/February 2013 Intergovernmental negotiations process via UN GA? (TBD, 2015) Global Thematic Consultations (9 Themes, locations TBD) May 2012/Early 2013. First consultation “Growth and Employment” in Tokyo Ongoing efforts to achieve current MDGs Note: Adapted from a timeline produced by CAFOD, March 2012 8 Post 2015 Framework in Place Rio+20 June 2012 2014

Sustainable Development Agenda “Realizing the future we want for all” June 2012 Source: UN System-wide report on Post 2015 for the UN SG, Pillars of Sustainable Development Economic Social Environmental Peace and Security 9

Transformative Shifts of the Agenda • Leave no one behind – equality and equity – not only the national averages, but inclusive of all • Put Sustainable Development at the core • Transform economies for jobs and inclusive growth • Build peace and effective, open and accountable institutions for all • Forge a global new partnership 10

Why is ECD an imperative? New Evidence • Helps achieving MDGs with equity and sustain the gains • Sets the foundation for the sustainable development and building peace, stable and resilient societies

Helps achieving and sustaining MDGs. . Source: Executive Summary- Early Childhood Development in Latin America: A Commitment with the Future of the Region www. earth. columbia. edu MDG Contribution of ECD 1. ERADICATION OF EXTREME Parenting programmes can improve nutrition outcomes, and ensure child cognitive social and emotional development, breaking inter-generational cycle of poverty and create enhanced human capital 2. UNIVERSAL PRIMARY EDUCATION Early stimulation programs and preschool education have shown a positive effect on performance and learning in primary schools with lower repetition and dropout rate. 3. GENDER EQUALITY Comprehensive early childhood development programs involve the parents of the child, family and community. The education of fathers and mothers alike has provided a sense of shared responsibility for the care and upbringing of children. POVERTY AND HUNGER 4. REDUCE CHILD MORTALITY Improved child care practices for survival, growth and development increases survival chances of children while ensuring their development. 12

Helps achieving and sustaining MDGs. . 2 Source: Executive Summary- Early Childhood Development in Latin America: A Commitment with the Future of the Region www. earth. columbia. edu MDG Contribution of ECD 5. IMPROVE MATERNAL HEALTH Programs, which include prenatal education and care of pregnant women contribute to better health and nutrition of the mother and, therefore, increases the probability of child survival through a specialized delivery care! Involvement of parents in ECD programs decreases the likelihood of maternal depression. 6. COMBAT HIV / AIDS, MALARIA AND OTHER DISEASES Health and nutrition programs decrease levels of vulnerability and malnutrition, improving the overall health of children infected by HIV / AIDS, malaria, tuberculosis and neglected tropical diseases. 7. ENSURE ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY More than one third of the burden of infant morbidity is due to modifiable environmental factors. The disease burden caused by environmental factors is much higher in the developing world than in developed countries. ! 8. DEVELOP A GLOBAL PARTNERSHIP FOR DEVELOPMENT International cooperation and allocation of resources for ECD programs in the region will contribute to universal access to comprehensive ECD services in order to reduce inequality. ! 13
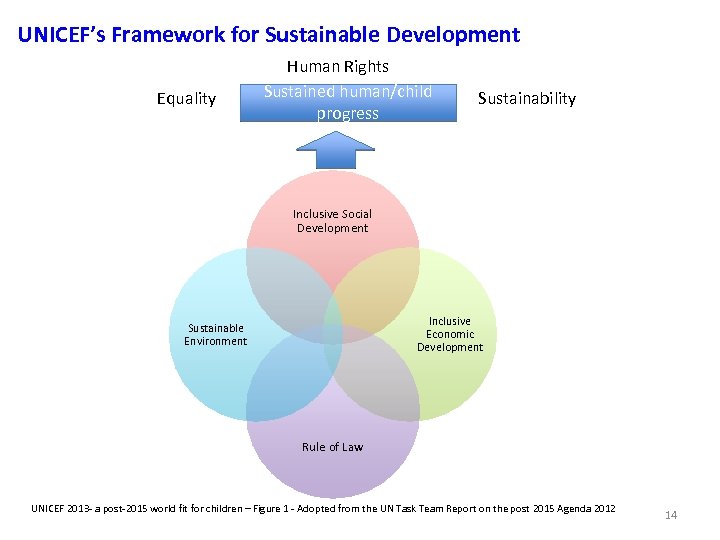
UNICEF’s Framework for Sustainable Development Equality Human Rights Sustained human/child progress Sustainability Inclusive Social Development Inclusive Economic Development Sustainable Environment Rule of Law UNICEF 2013 - a post-2015 world fit for children – Figure 1 - Adopted from the UN Task Team Report on the post 2015 Agenda 2012 14

UNICEF – May 2013 A post-2015 World Fit for Children • Sustainable Development starts with safe, healthy, and well educated children • Safe and sustainable societies are, in turn, essential for children • Children’s voices, choices and participation are critical for the sustainable future we want 15
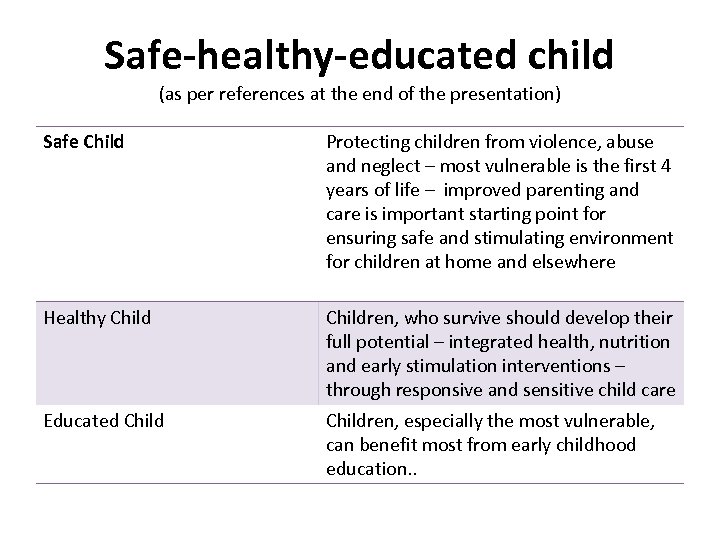
Safe-healthy-educated child (as per references at the end of the presentation) Safe Child Protecting children from violence, abuse and neglect – most vulnerable is the first 4 years of life – improved parenting and care is important starting point for ensuring safe and stimulating environment for children at home and elsewhere Healthy Children, who survive should develop their full potential – integrated health, nutrition and early stimulation interventions – through responsive and sensitive child care Educated Children, especially the most vulnerable, can benefit most from early childhood education. .
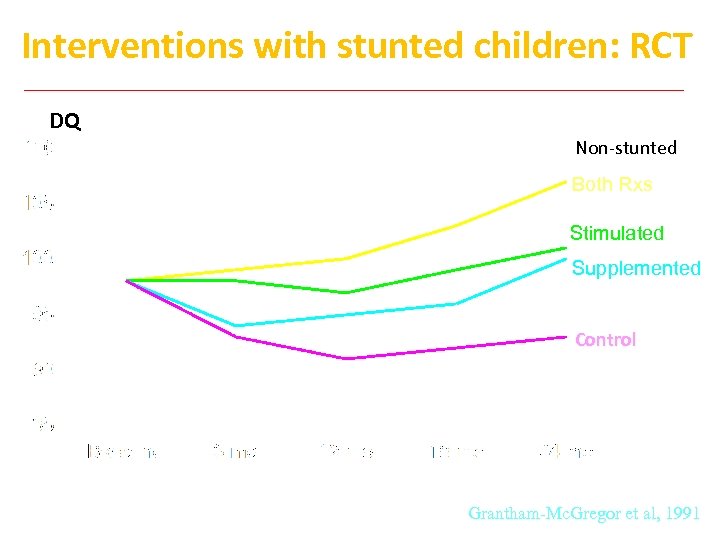
Interventions with stunted children: RCT DQ Non-stunted Both Rxs Stimulated Supplemented Control Grantham-Mc. Gregor et al, 1991
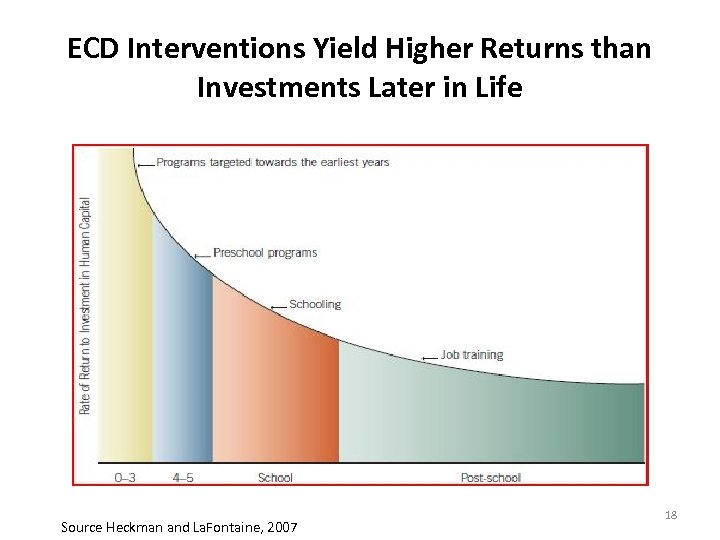
ECD Interventions Yield Higher Returns than Investments Later in Life Source Heckman and La. Fontaine, 2007 18
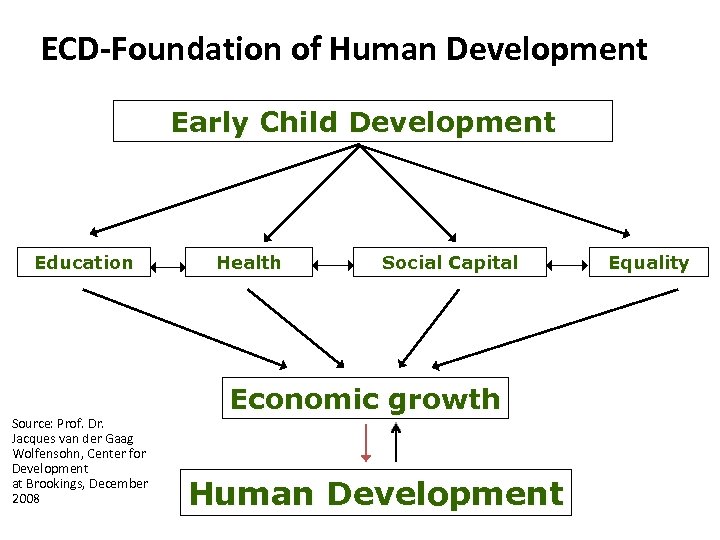
ECD-Foundation of Human Development Early Child Development Education Source: Prof. Dr. Jacques van der Gaag Wolfensohn, Center for Development at Brookings, December 2008 Health Social Capital Economic growth Human Development Equality

Modes of Effective ECD interventions • Integrated Health-Nutrition-Child Development Programmes for improved care and learning from the beginning – Parenting programmes • High quality early childhood education – home-community-center based • Social Protection Programmes – addressing inequities to eradicate poverty
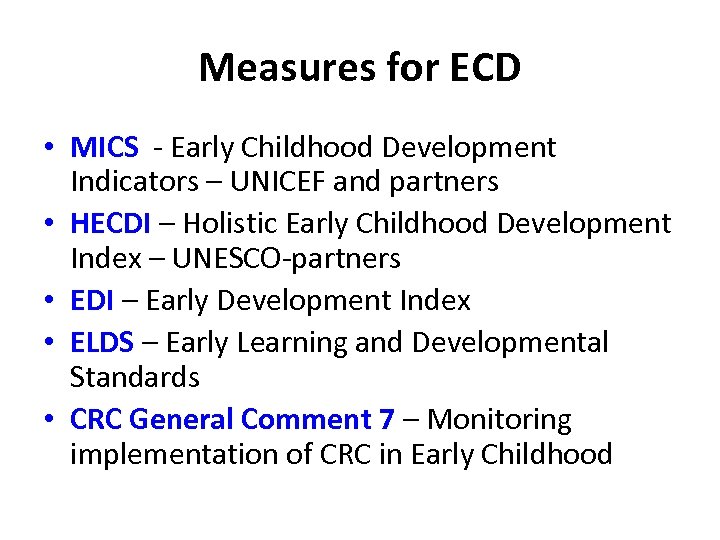
Measures for ECD • MICS - Early Childhood Development Indicators – UNICEF and partners • HECDI – Holistic Early Childhood Development Index – UNESCO-partners • EDI – Early Development Index • ELDS – Early Learning and Developmental Standards • CRC General Comment 7 – Monitoring implementation of CRC in Early Childhood

Where is the gap?

INEQUİTİES İN EARLY CHİLDHOOD PERSİST Children from poor income households are still at a greater risk of developing their full potential 23
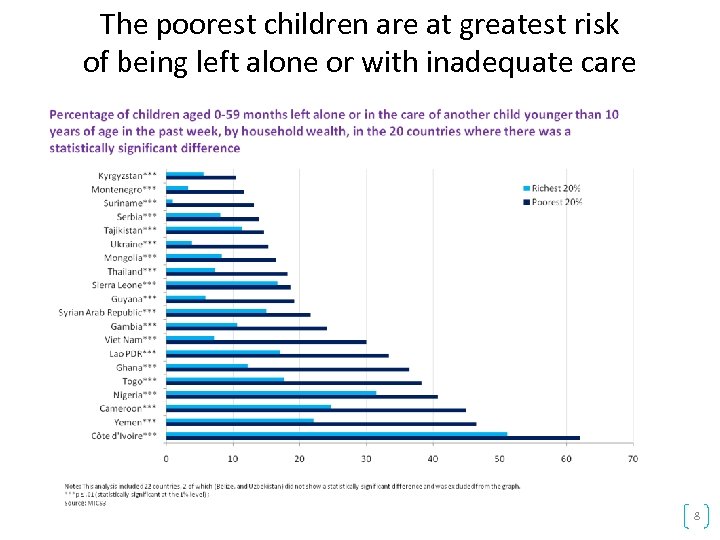
The poorest children are at greatest risk of being left alone or with inadequate care 8
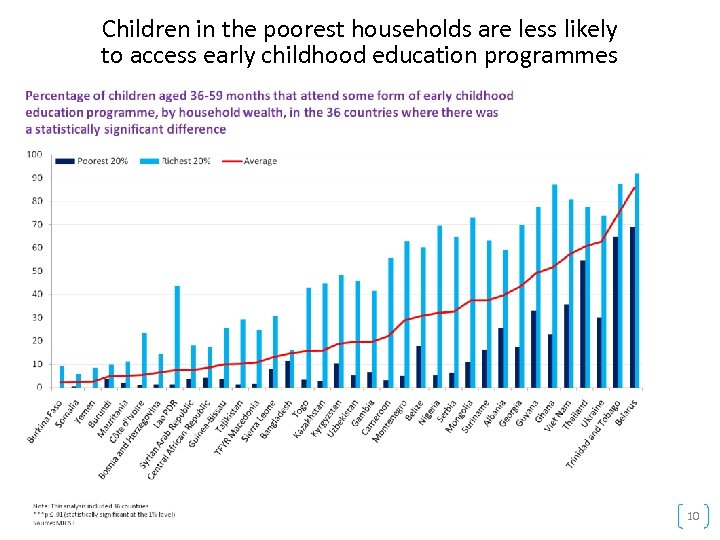
Children in the poorest households are less likely to access early childhood education programmes 10

Early Childhood Development is missing in the post-2015 discussion 26

UNICEF – May 2013 A post-2015 World Fit for Children • Sustainable Development starts with safe, healthy, and well educated children, includes early childhood development • Safe and sustainable societies are, in turn, essential for children - no reference • Children’s voices, choices and participation are critical for the sustainable future we want -starts late 27

Sustainable Development Solutions Network – June 2013 Proposes 10 Goals 1. End Extreme Poverty and Hunger – ECD should be here 2. Achieve development within planetary boundaries 3. Ensure Effective Learning for All children and Youth for Livelihood – starting with early childhood development 4. Gender Equality, social inclusion, 5. Achieve Health and Wellbeing at all ages (ECD to be included) 6. Improve agriculture 7. Resilient cities – should start with young children 8. Climate change – clean energy 9. Ecosystem-biodiversity 10. Good Governance 28

HLP – Report – June 2013 – Proposed Goals - targets • End Poverty – investing in ECD is an entry point – no mention. . • Empower Girls & Women and Achieve Gender Equality – child care and development – decent work needs attention • Provide Quality Education and Lifelong Learning – target for pre-school. . Not strong. • Ensure Healthy Lives – no mention of ECD • Ensure Food Security and Good Nutrition - no mention of ECD • Achieve Universal Access to Water and Sanitation • Secure Sustainable Energy • Create Jobs, Sustainable Livelihoods, and Equitable Growth • Manage Natural Resource Assets Sustainably • Ensure Good Governance and Effective Institutions • Ensure Stable and Peaceful Societies – starts in early childhood • Create a Global Enabling Environment and Catalyze Long-term Finance 29

Risks for not including ECD in Agenda • Children from poor households will not develop to their full potential. . AND this will in turn hinder • inclusive social and economic development • building safe and stable societies. .

What needs to be done? Early Childhood Development Goals and Targets should be placed on the post 2015 Agenda…

starting point ECD quality-integrated early childhood development most vulnerable…

OMEP has an important role to play…

Evidence for ECD. . • Aboud, E. F. 2007, J. Health Population and Nutrition, 2007 Mar. 25(1) • Aboud, E. F, Akhter, S. Pediatrics 2011: 127/5. • Role of cash in conditional cash transfer programmes for child health, growth, and development: an analysis of Mexico’s Oportunidades. Fernald, L. C. H. , Gertler, P. J. and Neufeld, L. M. (2008) Lancet, 371, pp. 828 -837. • Ferhald, L. C. H, and Hidrobo M. , Social Science and Medicine, 72 (2011) Effect of Ecuador’s cash transfer program (Bono de Desarrollo Humano) on child development in infants and toddlers: A randomized effectiveness trial, • Walker, (S. 2011) Early Childhood Stimulation Benefits Adult Competence and Reduces Violent Behavior, Walker, S. P. at. al, Pediatrics 2011: 127: 849 -857 -Jamaica

Evidence. . • • • Grantham Mc. Gregor, S. et al. , (2007). Developmental potential in the first 5 years for children in developing countries. The Lancet, 369: 60 -70. WHO and UNICEF. Care for Development. National Scientific Council on the Developing Child (2007). The Timing and Quality of Early Experiences Combine to Shape Brain Architecture: Working Paper #5. Chan, M. (2013). Linking child survival and child development for health, equity, and sustainable development. The Lancet. 381. Walker, S. et al. (2011) Inequality in early childhood: Risk and protective factors for early childhood development. The Lancet, 378 (9799). Engle, P. et al. (2011). Strategies for reducing inequalities and improving developmental outcomes for young children in low-income and middle-income countries. The Lancet, 378 (9799). Carneiro, P. M. and Heckman, J. J. (2003). Human Capital Policy. NBER Working Paper Series, vol. w 9495. The Heckman Equation. http: //www. heckmanequation. org/heckman-equation. National Scientific Council on the Developing Child. (2004). Young children develop in an environment of relationships: Working Paper Number 1. Retrieved from www. developingchild. harvard. edu
472744f2fef17db91c67991979d7f68c.ppt