6_lesson_ear_and_nose_tongue2.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Ear, nose and tongue
Ear, nose and tongue
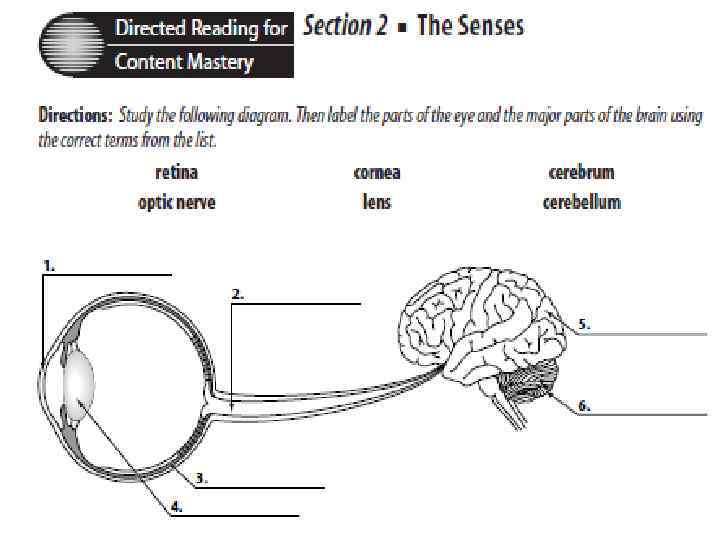
 • It has 2 sensory functions: • Hearing. • Maintaning balance or equilibrium.
• It has 2 sensory functions: • Hearing. • Maintaning balance or equilibrium.
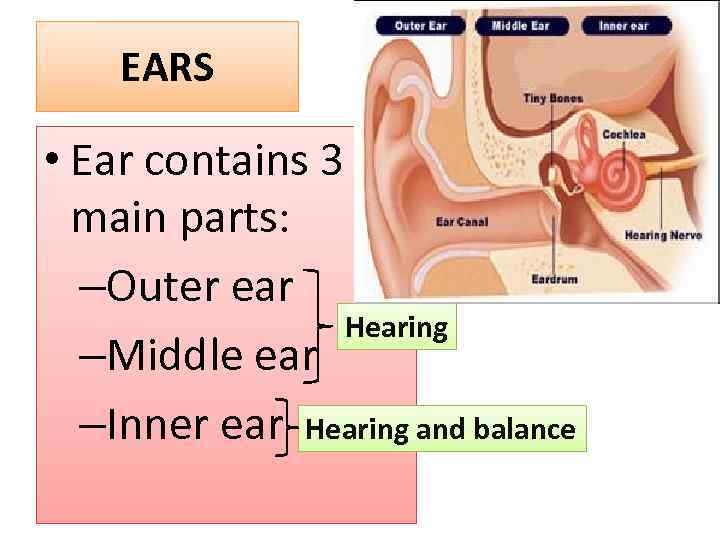 EARS • Ear contains 3 main parts: –Outer ear Hearing –Middle ear –Inner ear Hearing and balance
EARS • Ear contains 3 main parts: –Outer ear Hearing –Middle ear –Inner ear Hearing and balance
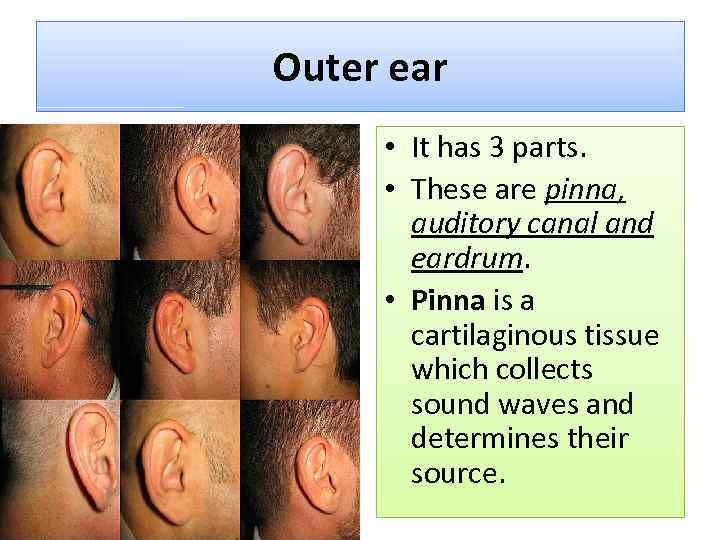 Outer ear • It has 3 parts. • These are pinna, auditory canal and eardrum. • Pinna is a cartilaginous tissue which collects sound waves and determines their source.
Outer ear • It has 3 parts. • These are pinna, auditory canal and eardrum. • Pinna is a cartilaginous tissue which collects sound waves and determines their source.
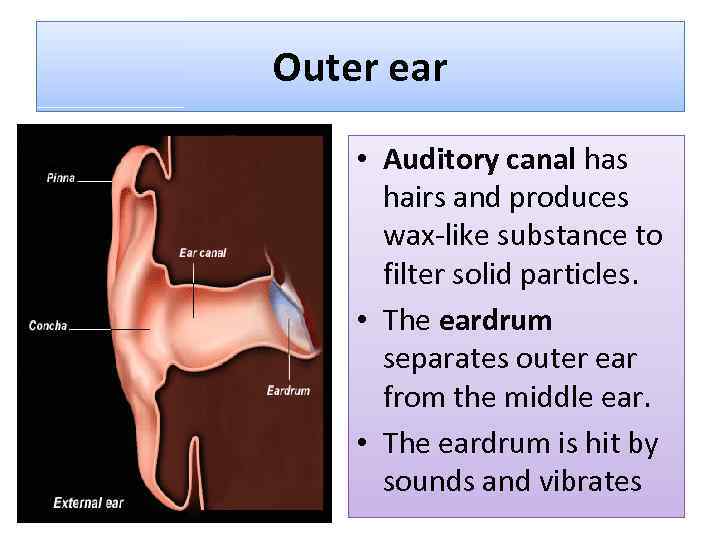 Outer ear • Auditory canal has hairs and produces wax-like substance to filter solid particles. • The eardrum separates outer ear from the middle ear. • The eardrum is hit by sounds and vibrates
Outer ear • Auditory canal has hairs and produces wax-like substance to filter solid particles. • The eardrum separates outer ear from the middle ear. • The eardrum is hit by sounds and vibrates
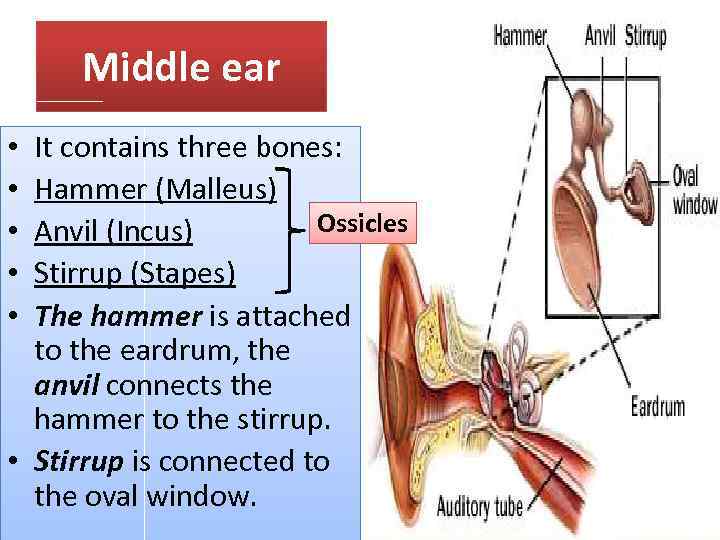 Middle ear It contains three bones: Hammer (Malleus) Ossicles Anvil (Incus) Stirrup (Stapes) The hammer is attached to the eardrum, the anvil connects the hammer to the stirrup. • Stirrup is connected to the oval window. • • •
Middle ear It contains three bones: Hammer (Malleus) Ossicles Anvil (Incus) Stirrup (Stapes) The hammer is attached to the eardrum, the anvil connects the hammer to the stirrup. • Stirrup is connected to the oval window. • • •
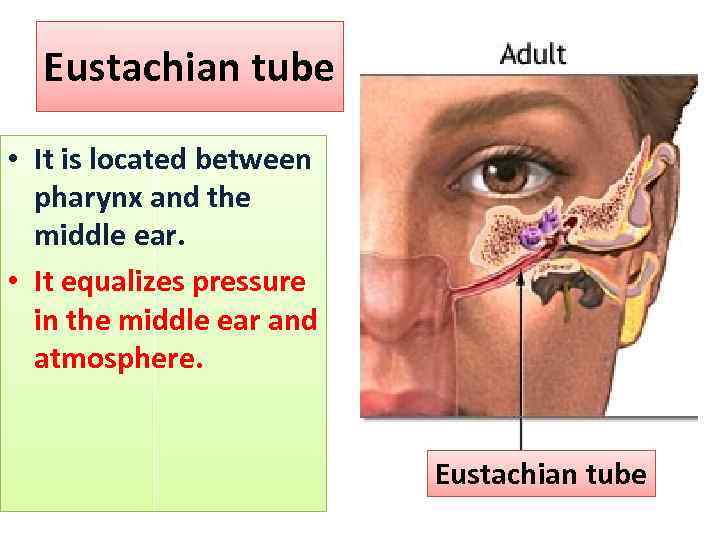 Eustachian tube • It is located between pharynx and the middle ear. • It equalizes pressure in the middle ear and atmosphere. Eustachian tube
Eustachian tube • It is located between pharynx and the middle ear. • It equalizes pressure in the middle ear and atmosphere. Eustachian tube
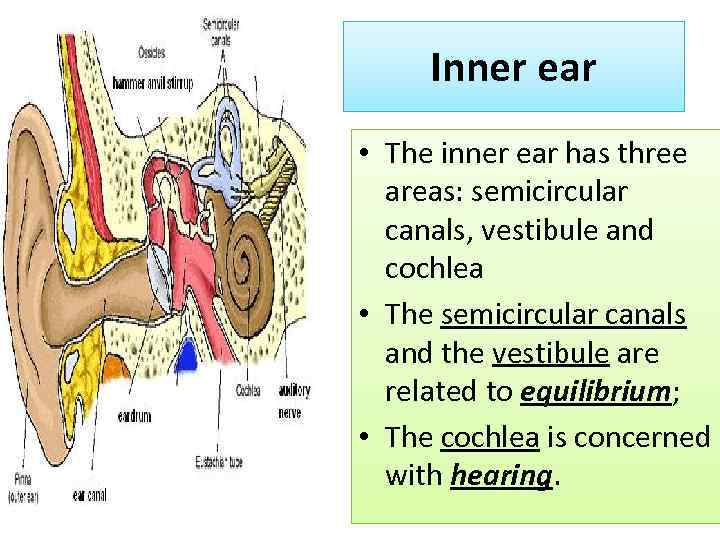 Inner ear • The inner ear has three areas: semicircular canals, vestibule and cochlea • The semicircular canals and the vestibule are related to equilibrium; • The cochlea is concerned with hearing.
Inner ear • The inner ear has three areas: semicircular canals, vestibule and cochlea • The semicircular canals and the vestibule are related to equilibrium; • The cochlea is concerned with hearing.
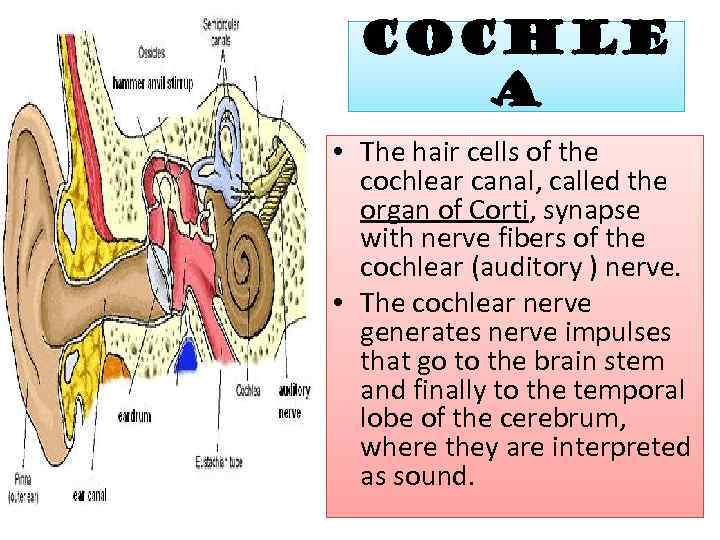 Cochle a • The hair cells of the cochlear canal, called the organ of Corti, synapse with nerve fibers of the cochlear (auditory ) nerve. • The cochlear nerve generates nerve impulses that go to the brain stem and finally to the temporal lobe of the cerebrum, where they are interpreted as sound.
Cochle a • The hair cells of the cochlear canal, called the organ of Corti, synapse with nerve fibers of the cochlear (auditory ) nerve. • The cochlear nerve generates nerve impulses that go to the brain stem and finally to the temporal lobe of the cerebrum, where they are interpreted as sound.
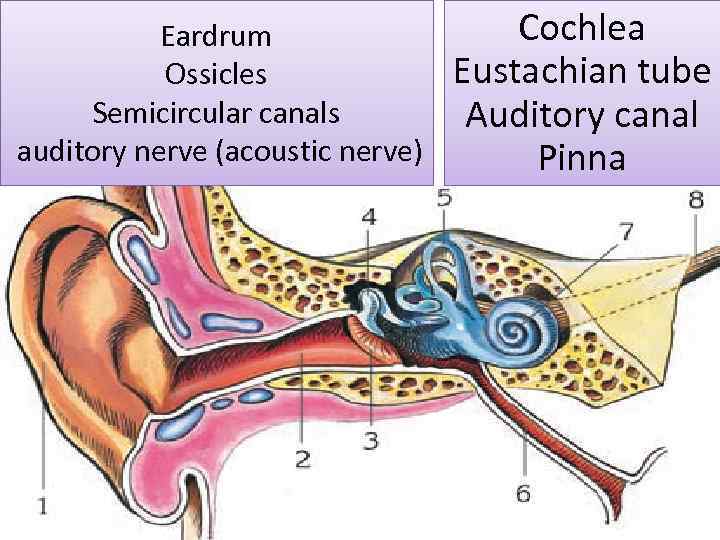 Eardrum Ossicles Semicircular canals auditory nerve (acoustic nerve) Cochlea Eustachian tube Auditory canal Pinna
Eardrum Ossicles Semicircular canals auditory nerve (acoustic nerve) Cochlea Eustachian tube Auditory canal Pinna
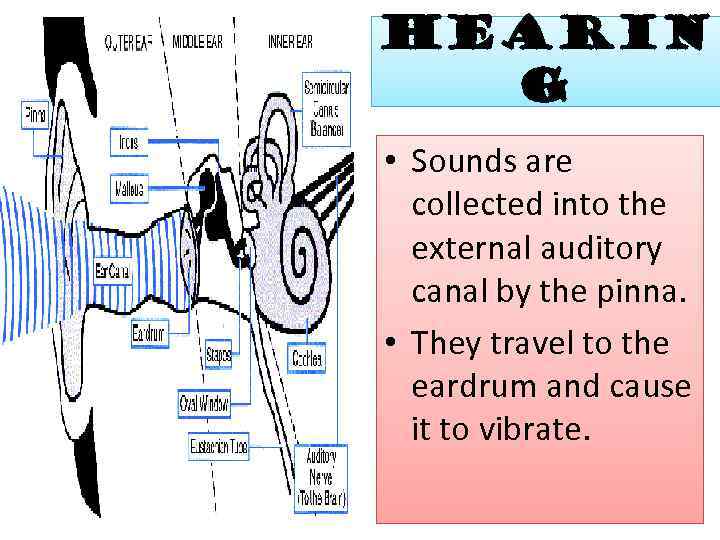 Hearin g • Sounds are collected into the external auditory canal by the pinna. • They travel to the eardrum and cause it to vibrate.
Hearin g • Sounds are collected into the external auditory canal by the pinna. • They travel to the eardrum and cause it to vibrate.
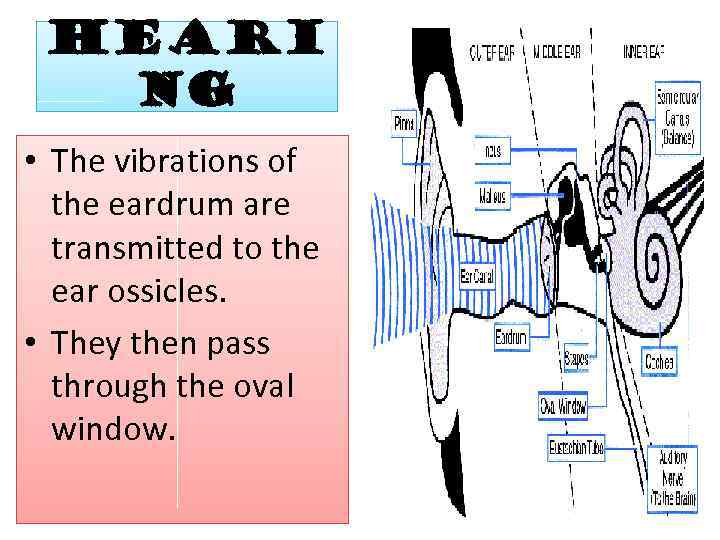 Heari ng • The vibrations of the eardrum are transmitted to the ear ossicles. • They then pass through the oval window.
Heari ng • The vibrations of the eardrum are transmitted to the ear ossicles. • They then pass through the oval window.
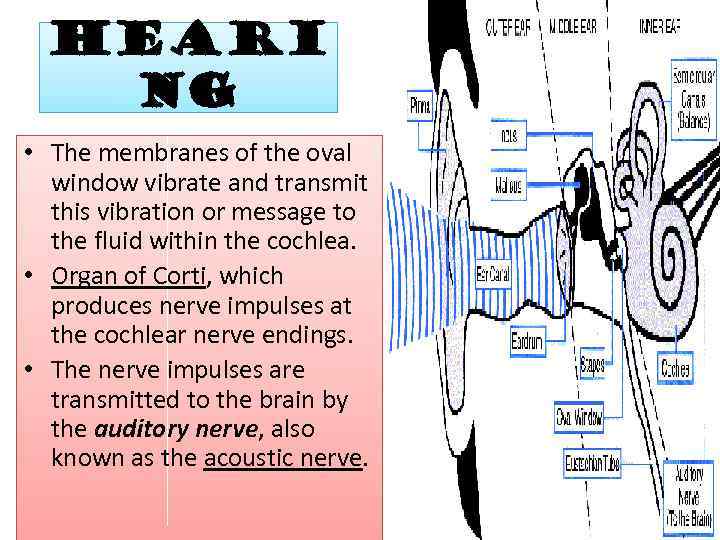 Heari ng • The membranes of the oval window vibrate and transmit this vibration or message to the fluid within the cochlea. • Organ of Corti, which produces nerve impulses at the cochlear nerve endings. • The nerve impulses are transmitted to the brain by the auditory nerve, also known as the acoustic nerve.
Heari ng • The membranes of the oval window vibrate and transmit this vibration or message to the fluid within the cochlea. • Organ of Corti, which produces nerve impulses at the cochlear nerve endings. • The nerve impulses are transmitted to the brain by the auditory nerve, also known as the acoustic nerve.

 Nose • Nose is the organ of the body involved in both respiration and smell. • The reception of smell takes place in chemoreceptors located in nasal cavity.
Nose • Nose is the organ of the body involved in both respiration and smell. • The reception of smell takes place in chemoreceptors located in nasal cavity.
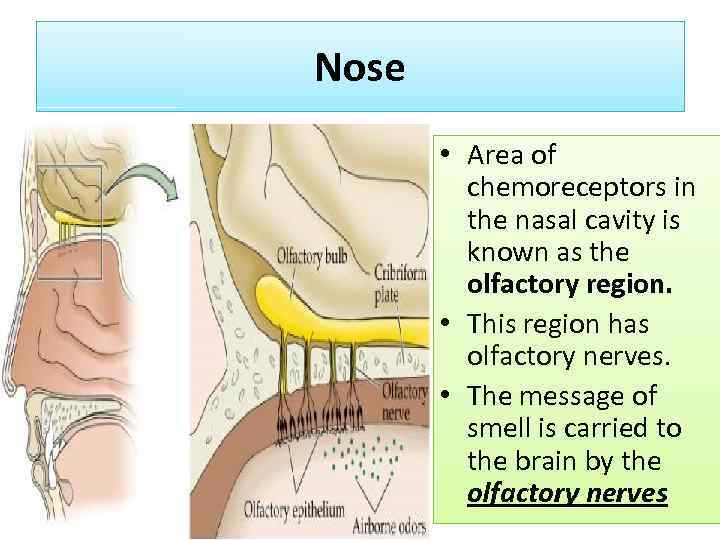 Nose • Area of chemoreceptors in the nasal cavity is known as the olfactory region. • This region has olfactory nerves. • The message of smell is carried to the brain by the olfactory nerves
Nose • Area of chemoreceptors in the nasal cavity is known as the olfactory region. • This region has olfactory nerves. • The message of smell is carried to the brain by the olfactory nerves
 Tongue • The tongue is one of the most important organs of speech and nutrition
Tongue • The tongue is one of the most important organs of speech and nutrition
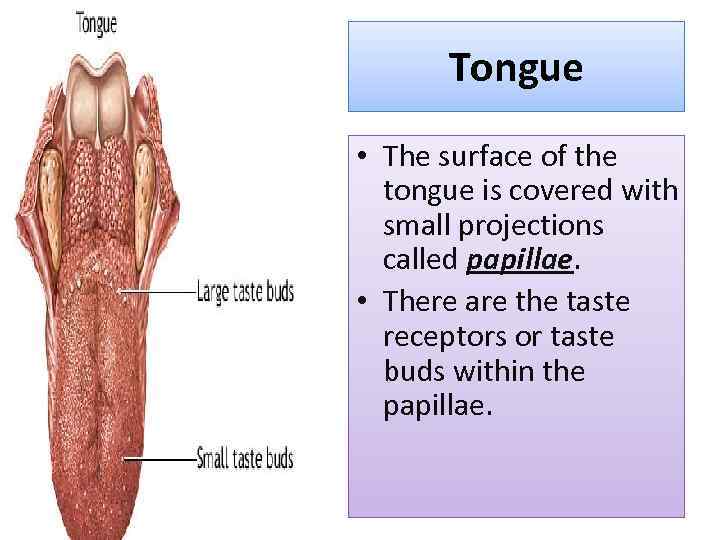 Tongue • The surface of the tongue is covered with small projections called papillae. • There are the taste receptors or taste buds within the papillae.
Tongue • The surface of the tongue is covered with small projections called papillae. • There are the taste receptors or taste buds within the papillae.
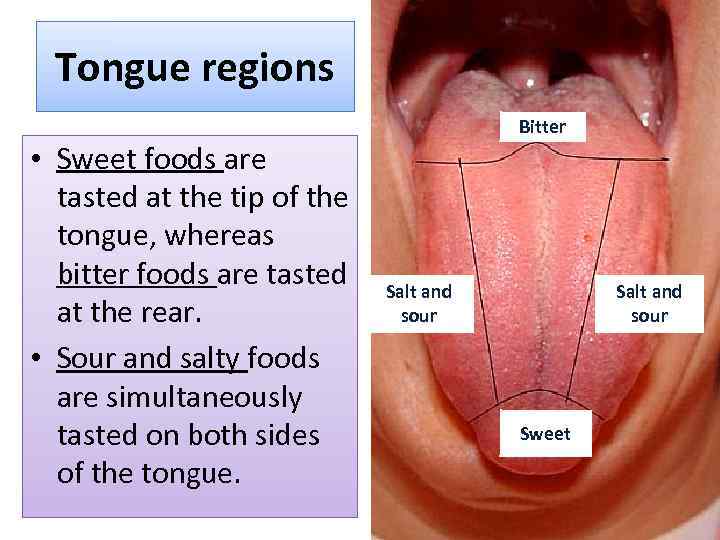 Tongue regions • Sweet foods are tasted at the tip of the tongue, whereas bitter foods are tasted at the rear. • Sour and salty foods are simultaneously tasted on both sides of the tongue. Bitter Salt and sour Sweet
Tongue regions • Sweet foods are tasted at the tip of the tongue, whereas bitter foods are tasted at the rear. • Sour and salty foods are simultaneously tasted on both sides of the tongue. Bitter Salt and sour Sweet
 THANKS!!!
THANKS!!!


