b2631f8a52d8c188c3e3e85ae2f4093f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 e. Services for ALL: the i 2010 Initiative Jean-Francois Junger European Commission DG Information Society 1
e. Services for ALL: the i 2010 Initiative Jean-Francois Junger European Commission DG Information Society 1
 Presentation outline 1. CIP 2. FP 7 – ICT Work Programme – Challenges, FETs, Horizontal Support – ICT Calls for Proposal 3. D-Space and e. Learning 2
Presentation outline 1. CIP 2. FP 7 – ICT Work Programme – Challenges, FETs, Horizontal Support – ICT Calls for Proposal 3. D-Space and e. Learning 2
 CIP - ICT Policy Support Programme 3
CIP - ICT Policy Support Programme 3
 ICT policy framework: i 2010 initiative • Comprehensive and holistic approach for EU Information Society • Three priorities • Legislation, regulation • Coordination, consensus-building and Media policies – Completing the Single European Information Space – Strengthening innovation and investment in research – Achieving an Inclusive European Information society – From Plan to delivery, less political talk; more implementation • Financial support – ICT in CIP: To drive forward innovation through the adoption and best use of ICTs – ICT in FP 7: To strengthen Europe’s leadership role in mastering and shaping the development of ICTs – In addition, Cohesion & Structural Funds 4
ICT policy framework: i 2010 initiative • Comprehensive and holistic approach for EU Information Society • Three priorities • Legislation, regulation • Coordination, consensus-building and Media policies – Completing the Single European Information Space – Strengthening innovation and investment in research – Achieving an Inclusive European Information society – From Plan to delivery, less political talk; more implementation • Financial support – ICT in CIP: To drive forward innovation through the adoption and best use of ICTs – ICT in FP 7: To strengthen Europe’s leadership role in mastering and shaping the development of ICTs – In addition, Cohesion & Structural Funds 4
 CIP : 3 specific programmes 3621 M€ for 2007 – 2013 (current prices) EIP committee ICT committee IEE committee 5
CIP : 3 specific programmes 3621 M€ for 2007 – 2013 (current prices) EIP committee ICT committee IEE committee 5
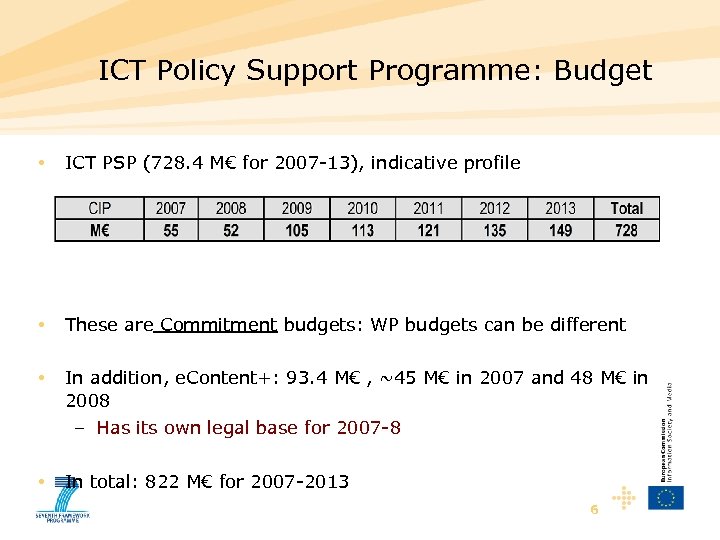 ICT Policy Support Programme: Budget • ICT PSP (728. 4 M€ for 2007 -13), indicative profile • These are Commitment budgets: WP budgets can be different • In addition, e. Content+: 93. 4 M€ , ~45 M€ in 2007 and 48 M€ in 2008 – Has its own legal base for 2007 -8 • In total: 822 M€ for 2007 -2013 6
ICT Policy Support Programme: Budget • ICT PSP (728. 4 M€ for 2007 -13), indicative profile • These are Commitment budgets: WP budgets can be different • In addition, e. Content+: 93. 4 M€ , ~45 M€ in 2007 and 48 M€ in 2008 – Has its own legal base for 2007 -8 • In total: 822 M€ for 2007 -2013 6
 ICT PSP: general objectives • Accelerate the development of a sustainable, competitive, innovative and inclusive Information Society • By : – developing the single information space – ensuring wider uptake and better use of ICT – enabling an inclusive Information Society • Building on the experience of e. Content(+); e. Ten ; Modinis 7
ICT PSP: general objectives • Accelerate the development of a sustainable, competitive, innovative and inclusive Information Society • By : – developing the single information space – ensuring wider uptake and better use of ICT – enabling an inclusive Information Society • Building on the experience of e. Content(+); e. Ten ; Modinis 7
 Developing the Single Information Space • ensuring seamless access to electronic services – mainly studies, analysis, benchmarks, . . • improving the conditions for the development of digital content – Important part of the budget, – e. Content + in 2007 -08 • monitoring the European Information Society – mainly studies, analysis, benchmarks, . . 8
Developing the Single Information Space • ensuring seamless access to electronic services – mainly studies, analysis, benchmarks, . . • improving the conditions for the development of digital content – Important part of the budget, – e. Content + in 2007 -08 • monitoring the European Information Society – mainly studies, analysis, benchmarks, . . 8
 Innovation, adoption and investment in ICT • Wider uptake of innovative ICT – ICT uptake in processes, products and services (in particular SMEs) • Facilitating public and private interaction/partnerships – for accelerating innovation and investments in ICTs • Promoting and raising awareness 9
Innovation, adoption and investment in ICT • Wider uptake of innovative ICT – ICT uptake in processes, products and services (in particular SMEs) • Facilitating public and private interaction/partnerships – for accelerating innovation and investments in ICTs • Promoting and raising awareness 9
 An inclusive IS with better services in areas of public interest • Services in areas of public interest showing the way – demand-led innovation • Improving quality, efficiency and effectiveness of ICT-based services in areas of public interest – enabling European enterprises (SMEs) to benefit from the wide business opportunities offered by ICT-based services in areas of public interest • Benefits to all citizens – widening ICT accessibility and digital literacy • An important part of the budget 10
An inclusive IS with better services in areas of public interest • Services in areas of public interest showing the way – demand-led innovation • Improving quality, efficiency and effectiveness of ICT-based services in areas of public interest – enabling European enterprises (SMEs) to benefit from the wide business opportunities offered by ICT-based services in areas of public interest • Benefits to all citizens – widening ICT accessibility and digital literacy • An important part of the budget 10
 ICT PSP – activities • Pilot projects • thematic networks (including best practice actions) • Policy analyses, development and coordination with participating countries • Promotion, communication, information sharing and dissemination • possibly Projects of common interest (public procurement based on commonly agreed specification) – as an option within the programme, this is not foreseen in 2007 11
ICT PSP – activities • Pilot projects • thematic networks (including best practice actions) • Policy analyses, development and coordination with participating countries • Promotion, communication, information sharing and dissemination • possibly Projects of common interest (public procurement based on commonly agreed specification) – as an option within the programme, this is not foreseen in 2007 11
 ICT PSP WP 2007: Approach • Focus: given the limited budget – To maximise impact • Providing means to measure impact – In a particular field or theme, on a particular constituency • Balance between – Activities building on, and strengthening Member States actions – Activities stimulating new actions in public and private sector 12
ICT PSP WP 2007: Approach • Focus: given the limited budget – To maximise impact • Providing means to measure impact – In a particular field or theme, on a particular constituency • Balance between – Activities building on, and strengthening Member States actions – Activities stimulating new actions in public and private sector 12
 WP 2007: Themes and Horizontal actions (still under discussion) • Selection of main themes – policy priority areas as expressed in the i 2010 initiative – need for financial intervention at EU level – expected impact on the CIP objectives – readiness of the stakeholders to engage in an action when appropriate • For 2007, three main themes proposed – e. Government, e. ID, Ageing and inclusion, e. Health Horizontal and other actions – SMEs related actions – Networking and consensus building actions (intelligent cars, sustainable growth, privacy) – Promotion actions, Benchmarking, studies on Information society • development 13
WP 2007: Themes and Horizontal actions (still under discussion) • Selection of main themes – policy priority areas as expressed in the i 2010 initiative – need for financial intervention at EU level – expected impact on the CIP objectives – readiness of the stakeholders to engage in an action when appropriate • For 2007, three main themes proposed – e. Government, e. ID, Ageing and inclusion, e. Health Horizontal and other actions – SMEs related actions – Networking and consensus building actions (intelligent cars, sustainable growth, privacy) – Promotion actions, Benchmarking, studies on Information society • development 13
 WP 2007: Structure • WP focused on a set of themes and horizontal actions – The theme defines the ultimate socio-economic goals • Themes and horizontal actions are addressed through a set of objectives – To be achieved through community contribution and their impact • • • An objective is supported with Pilot (s) A or B Thematic Network (s) • Awareness, benchmarking, conferences, Studies, Details defined in the workprogramme – Through Calls for applications – Through Calls for tenders (details defined in the tender pack) or grants (without call for applications, according to EU financial rules) 14
WP 2007: Structure • WP focused on a set of themes and horizontal actions – The theme defines the ultimate socio-economic goals • Themes and horizontal actions are addressed through a set of objectives – To be achieved through community contribution and their impact • • • An objective is supported with Pilot (s) A or B Thematic Network (s) • Awareness, benchmarking, conferences, Studies, Details defined in the workprogramme – Through Calls for applications – Through Calls for tenders (details defined in the tender pack) or grants (without call for applications, according to EU financial rules) 14
 Type A pilots in 2007 (still under discussion) Goal: ……… service pilots with interoperability as the central theme aiming to demonstrate a “federated” solution and borderless operation of national systems Outcome: …. to implement an open, common interoperable solution with results widely disseminated and available to all member states Duration: …. typically 36 months with a pilot service operating for 12 months Response: … a proposal embracing existing national activities and evaluated to the published evaluation criteria Scale: ……… implementation in at least 6 Member States but with the potential to scale up to all member states Participants: National administrations (relevant National Competence Centres), service providers, industrial stakeholders & users Funding: …. . supports up to 50% of cost of the effort to achieve interoperability Community contribution available is 5 -10 M€ / pilot) 15
Type A pilots in 2007 (still under discussion) Goal: ……… service pilots with interoperability as the central theme aiming to demonstrate a “federated” solution and borderless operation of national systems Outcome: …. to implement an open, common interoperable solution with results widely disseminated and available to all member states Duration: …. typically 36 months with a pilot service operating for 12 months Response: … a proposal embracing existing national activities and evaluated to the published evaluation criteria Scale: ……… implementation in at least 6 Member States but with the potential to scale up to all member states Participants: National administrations (relevant National Competence Centres), service providers, industrial stakeholders & users Funding: …. . supports up to 50% of cost of the effort to achieve interoperability Community contribution available is 5 -10 M€ / pilot) 15
 Type B pilots in 2007 (still under discussion) Goal: ……… a first implementation of an ICT based innovative service carried out under realistic conditions Outcome: …. operational pilot service demonstrating significant impact potential and the engagement of a complete value-chain of stakeholders Duration: …. typically 24 -36 months with a pilot service operating for 12 months Response: … competing proposals addressing a workprogramme objective and evaluated to the published evaluation criteria Scale: ……… implemented in at least 4 Member States and with potential to scale to all member states Participants: relevant public authorities (sustaining partners), service providers, industrial stakeholders and users Funding: …. . supports (up to 50%) of the costs of implementing the pilot service Community contribution available is 2 -3 M€ / pilot) 16
Type B pilots in 2007 (still under discussion) Goal: ……… a first implementation of an ICT based innovative service carried out under realistic conditions Outcome: …. operational pilot service demonstrating significant impact potential and the engagement of a complete value-chain of stakeholders Duration: …. typically 24 -36 months with a pilot service operating for 12 months Response: … competing proposals addressing a workprogramme objective and evaluated to the published evaluation criteria Scale: ……… implemented in at least 4 Member States and with potential to scale to all member states Participants: relevant public authorities (sustaining partners), service providers, industrial stakeholders and users Funding: …. . supports (up to 50%) of the costs of implementing the pilot service Community contribution available is 2 -3 M€ / pilot) 16
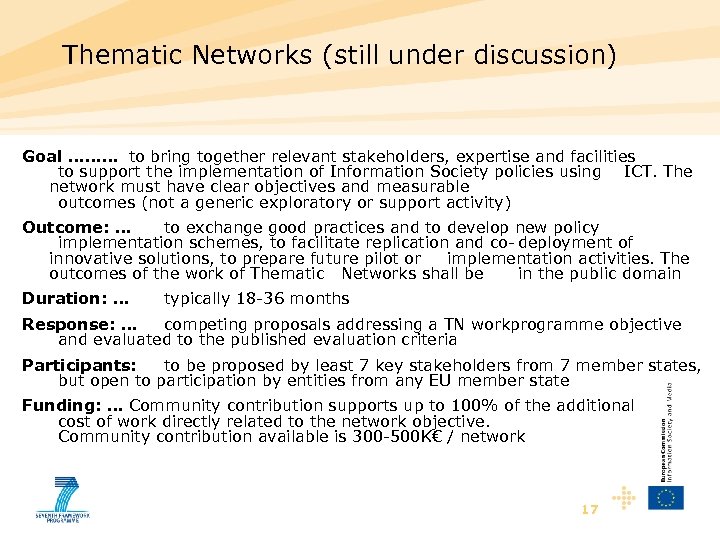 Thematic Networks (still under discussion) Goal ……… to bring together relevant stakeholders, expertise and facilities to support the implementation of Information Society policies using ICT. The network must have clear objectives and measurable outcomes (not a generic exploratory or support activity) Outcome: … to exchange good practices and to develop new policy implementation schemes, to facilitate replication and co- deployment of innovative solutions, to prepare future pilot or implementation activities. The outcomes of the work of Thematic Networks shall be in the public domain Duration: … typically 18 -36 months Response: … competing proposals addressing a TN workprogramme objective and evaluated to the published evaluation criteria Participants: to be proposed by least 7 key stakeholders from 7 member states, but open to participation by entities from any EU member state Funding: … Community contribution supports up to 100% of the additional cost of work directly related to the network objective. Community contribution available is 300 -500 K€ / network 17
Thematic Networks (still under discussion) Goal ……… to bring together relevant stakeholders, expertise and facilities to support the implementation of Information Society policies using ICT. The network must have clear objectives and measurable outcomes (not a generic exploratory or support activity) Outcome: … to exchange good practices and to develop new policy implementation schemes, to facilitate replication and co- deployment of innovative solutions, to prepare future pilot or implementation activities. The outcomes of the work of Thematic Networks shall be in the public domain Duration: … typically 18 -36 months Response: … competing proposals addressing a TN workprogramme objective and evaluated to the published evaluation criteria Participants: to be proposed by least 7 key stakeholders from 7 member states, but open to participation by entities from any EU member state Funding: … Community contribution supports up to 100% of the additional cost of work directly related to the network objective. Community contribution available is 300 -500 K€ / network 17
 WP time table • Preparation of the work-programme rules, contracts and user guides • Opinion by Committee • Guide for proposers • Commission decision on WP • First Call • Evaluation, negotiation • Projects start on going March 07 Feb-March 07 end April 07 May 07 Autumn 07 early 2008 18
WP time table • Preparation of the work-programme rules, contracts and user guides • Opinion by Committee • Guide for proposers • Commission decision on WP • First Call • Evaluation, negotiation • Projects start on going March 07 Feb-March 07 end April 07 May 07 Autumn 07 early 2008 18
 More information about the entire CIP programme http: //ec. europa. eu/enterprise_policy/cip/index_en. htm about ICT Policy support programme http: //europa. eu/ICT_PSP (soon available) 19
More information about the entire CIP programme http: //ec. europa. eu/enterprise_policy/cip/index_en. htm about ICT Policy support programme http: //europa. eu/ICT_PSP (soon available) 19
 1. ICT Work Programme 2007 -2008 and beyond • Work programme 2007 -2008 has – 3 major calls – FET Open call – Joint call with the Security theme • Yet no detailed planning beyond 2008 • In practice we would anticipate two calls per year! 20
1. ICT Work Programme 2007 -2008 and beyond • Work programme 2007 -2008 has – 3 major calls – FET Open call – Joint call with the Security theme • Yet no detailed planning beyond 2008 • In practice we would anticipate two calls per year! 20
 1. ICT Work Programme Approach and structure • A limited set of Challenges that – respond to well-identified industry and technology needs and/or – target specific socio-economic goals • A Challenge is addressed through a limited set of Objectives that form the basis of Calls for Proposals • An Objective is described in terms of – target outcome - in terms of characteristics – expected impact - in terms of industrial competitiveness, societal goal, technology progress • A total of 25 Objectives expressed within 7 Challenges 21
1. ICT Work Programme Approach and structure • A limited set of Challenges that – respond to well-identified industry and technology needs and/or – target specific socio-economic goals • A Challenge is addressed through a limited set of Objectives that form the basis of Calls for Proposals • An Objective is described in terms of – target outcome - in terms of characteristics – expected impact - in terms of industrial competitiveness, societal goal, technology progress • A total of 25 Objectives expressed within 7 Challenges 21
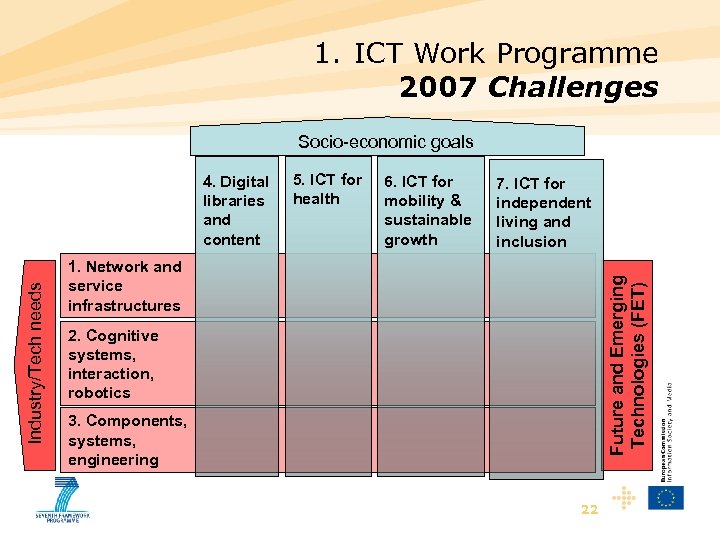 1. ICT Work Programme 2007 Challenges Socio-economic goals 5. ICT for health 6. ICT for mobility & sustainable growth 7. ICT for independent living and inclusion 1. Network and service infrastructures Future and Emerging Technologies (FET) Industry/Tech needs 4. Digital libraries and content 2. Cognitive systems, interaction, robotics 3. Components, systems, engineering 22
1. ICT Work Programme 2007 Challenges Socio-economic goals 5. ICT for health 6. ICT for mobility & sustainable growth 7. ICT for independent living and inclusion 1. Network and service infrastructures Future and Emerging Technologies (FET) Industry/Tech needs 4. Digital libraries and content 2. Cognitive systems, interaction, robotics 3. Components, systems, engineering 22
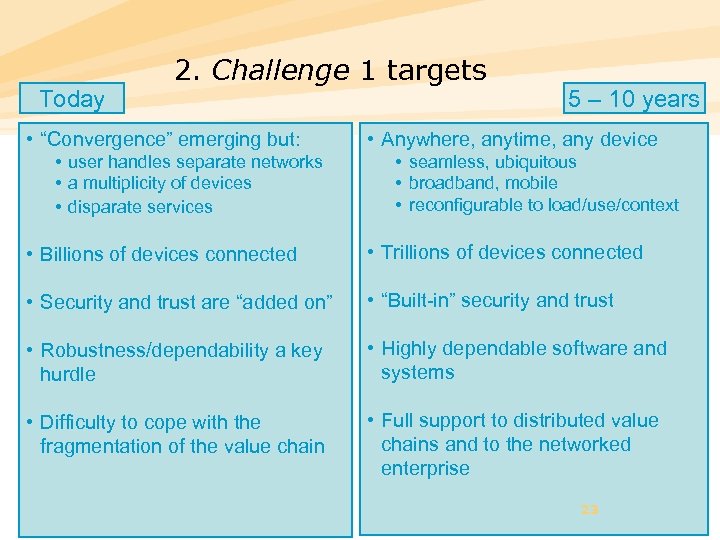 Today 2. Challenge 1 targets • “Convergence” emerging but: • user handles separate networks • a multiplicity of devices • disparate services 5 – 10 years • Anywhere, anytime, any device • seamless, ubiquitous • broadband, mobile • reconfigurable to load/use/context • Billions of devices connected • Trillions of devices connected • Security and trust are “added on” • “Built-in” security and trust • Robustness/dependability a key hurdle • Highly dependable software and systems • Difficulty to cope with the fragmentation of the value chain • Full support to distributed value chains and to the networked enterprise 23
Today 2. Challenge 1 targets • “Convergence” emerging but: • user handles separate networks • a multiplicity of devices • disparate services 5 – 10 years • Anywhere, anytime, any device • seamless, ubiquitous • broadband, mobile • reconfigurable to load/use/context • Billions of devices connected • Trillions of devices connected • Security and trust are “added on” • “Built-in” security and trust • Robustness/dependability a key hurdle • Highly dependable software and systems • Difficulty to cope with the fragmentation of the value chain • Full support to distributed value chains and to the networked enterprise 23
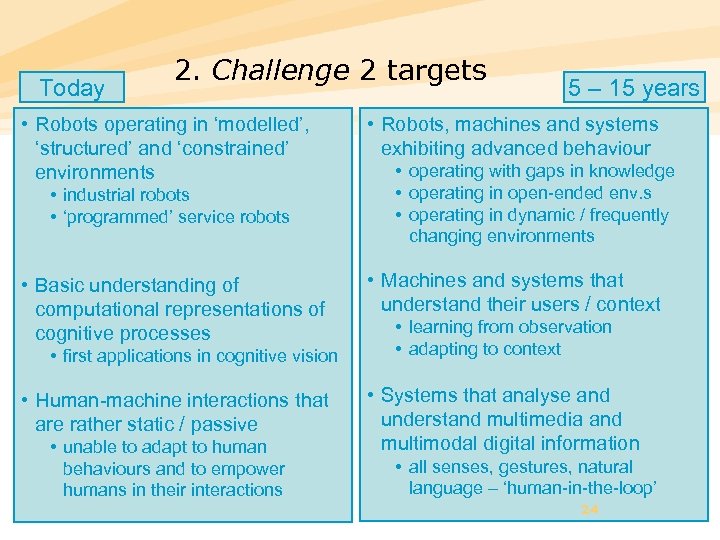 Today 2. Challenge 2 targets • Robots operating in ‘modelled’, ‘structured’ and ‘constrained’ environments • industrial robots • ‘programmed’ service robots • Basic understanding of computational representations of cognitive processes • first applications in cognitive vision • Human-machine interactions that are rather static / passive • unable to adapt to human behaviours and to empower humans in their interactions 5 – 15 years • Robots, machines and systems exhibiting advanced behaviour • operating with gaps in knowledge • operating in open-ended env. s • operating in dynamic / frequently changing environments • Machines and systems that understand their users / context • learning from observation • adapting to context • Systems that analyse and understand multimedia and multimodal digital information • all senses, gestures, natural language – ‘human-in-the-loop’ 24
Today 2. Challenge 2 targets • Robots operating in ‘modelled’, ‘structured’ and ‘constrained’ environments • industrial robots • ‘programmed’ service robots • Basic understanding of computational representations of cognitive processes • first applications in cognitive vision • Human-machine interactions that are rather static / passive • unable to adapt to human behaviours and to empower humans in their interactions 5 – 15 years • Robots, machines and systems exhibiting advanced behaviour • operating with gaps in knowledge • operating in open-ended env. s • operating in dynamic / frequently changing environments • Machines and systems that understand their users / context • learning from observation • adapting to context • Systems that analyse and understand multimedia and multimodal digital information • all senses, gestures, natural language – ‘human-in-the-loop’ 24
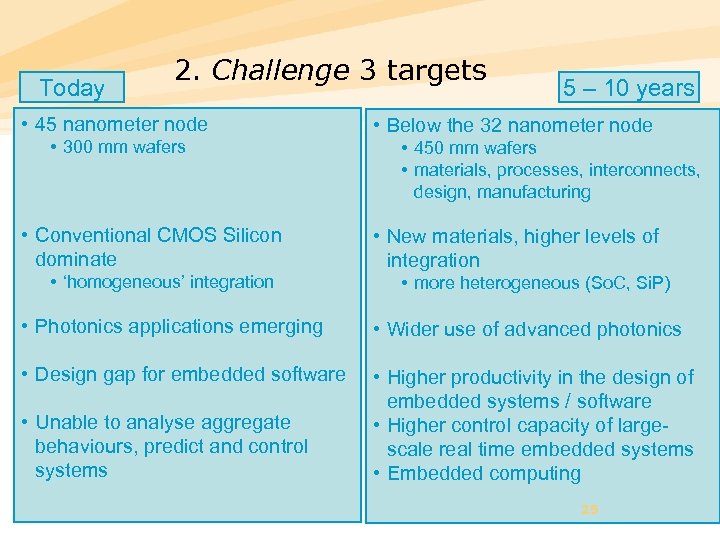 Today 2. Challenge 3 targets • 45 nanometer node • 300 mm wafers • Conventional CMOS Silicon dominate • ‘homogeneous’ integration 5 – 10 years • Below the 32 nanometer node • 450 mm wafers • materials, processes, interconnects, design, manufacturing • New materials, higher levels of integration • more heterogeneous (So. C, Si. P) • Photonics applications emerging • Wider use of advanced photonics • Design gap for embedded software • Higher productivity in the design of embedded systems / software • Higher control capacity of largescale real time embedded systems • Embedded computing • Unable to analyse aggregate behaviours, predict and control systems 25
Today 2. Challenge 3 targets • 45 nanometer node • 300 mm wafers • Conventional CMOS Silicon dominate • ‘homogeneous’ integration 5 – 10 years • Below the 32 nanometer node • 450 mm wafers • materials, processes, interconnects, design, manufacturing • New materials, higher levels of integration • more heterogeneous (So. C, Si. P) • Photonics applications emerging • Wider use of advanced photonics • Design gap for embedded software • Higher productivity in the design of embedded systems / software • Higher control capacity of largescale real time embedded systems • Embedded computing • Unable to analyse aggregate behaviours, predict and control systems 25
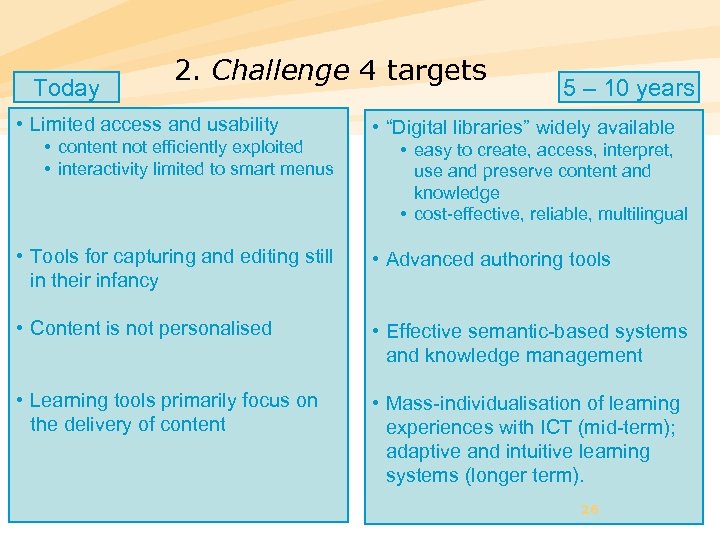 Today 2. Challenge 4 targets • Limited access and usability • content not efficiently exploited • interactivity limited to smart menus 5 – 10 years • “Digital libraries” widely available • easy to create, access, interpret, use and preserve content and knowledge • cost-effective, reliable, multilingual • Tools for capturing and editing still in their infancy • Advanced authoring tools • Content is not personalised • Effective semantic-based systems and knowledge management • Learning tools primarily focus on the delivery of content • Mass-individualisation of learning experiences with ICT (mid-term); adaptive and intuitive learning systems (longer term). 26
Today 2. Challenge 4 targets • Limited access and usability • content not efficiently exploited • interactivity limited to smart menus 5 – 10 years • “Digital libraries” widely available • easy to create, access, interpret, use and preserve content and knowledge • cost-effective, reliable, multilingual • Tools for capturing and editing still in their infancy • Advanced authoring tools • Content is not personalised • Effective semantic-based systems and knowledge management • Learning tools primarily focus on the delivery of content • Mass-individualisation of learning experiences with ICT (mid-term); adaptive and intuitive learning systems (longer term). 26
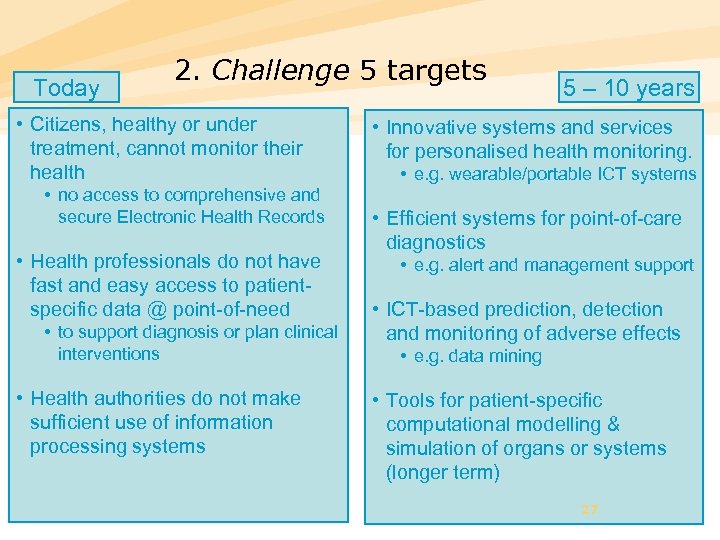 Today 2. Challenge 5 targets • Citizens, healthy or under treatment, cannot monitor their health • no access to comprehensive and secure Electronic Health Records • Health professionals do not have fast and easy access to patientspecific data @ point-of-need • to support diagnosis or plan clinical interventions • Health authorities do not make sufficient use of information processing systems 5 – 10 years • Innovative systems and services for personalised health monitoring. • e. g. wearable/portable ICT systems • Efficient systems for point-of-care diagnostics • e. g. alert and management support • ICT-based prediction, detection and monitoring of adverse effects • e. g. data mining • Tools for patient-specific computational modelling & simulation of organs or systems (longer term) 27
Today 2. Challenge 5 targets • Citizens, healthy or under treatment, cannot monitor their health • no access to comprehensive and secure Electronic Health Records • Health professionals do not have fast and easy access to patientspecific data @ point-of-need • to support diagnosis or plan clinical interventions • Health authorities do not make sufficient use of information processing systems 5 – 10 years • Innovative systems and services for personalised health monitoring. • e. g. wearable/portable ICT systems • Efficient systems for point-of-care diagnostics • e. g. alert and management support • ICT-based prediction, detection and monitoring of adverse effects • e. g. data mining • Tools for patient-specific computational modelling & simulation of organs or systems (longer term) 27
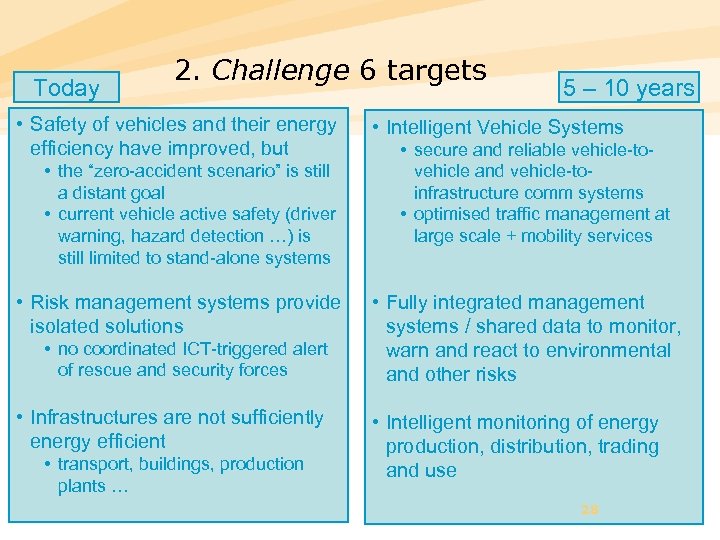 Today 2. Challenge 6 targets • Safety of vehicles and their energy efficiency have improved, but • the “zero-accident scenario” is still a distant goal • current vehicle active safety (driver warning, hazard detection …) is still limited to stand-alone systems • Risk management systems provide isolated solutions • no coordinated ICT-triggered alert of rescue and security forces • Infrastructures are not sufficiently energy efficient • transport, buildings, production plants … 5 – 10 years • Intelligent Vehicle Systems • secure and reliable vehicle-tovehicle and vehicle-toinfrastructure comm systems • optimised traffic management at large scale + mobility services • Fully integrated management systems / shared data to monitor, warn and react to environmental and other risks • Intelligent monitoring of energy production, distribution, trading and use 28
Today 2. Challenge 6 targets • Safety of vehicles and their energy efficiency have improved, but • the “zero-accident scenario” is still a distant goal • current vehicle active safety (driver warning, hazard detection …) is still limited to stand-alone systems • Risk management systems provide isolated solutions • no coordinated ICT-triggered alert of rescue and security forces • Infrastructures are not sufficiently energy efficient • transport, buildings, production plants … 5 – 10 years • Intelligent Vehicle Systems • secure and reliable vehicle-tovehicle and vehicle-toinfrastructure comm systems • optimised traffic management at large scale + mobility services • Fully integrated management systems / shared data to monitor, warn and react to environmental and other risks • Intelligent monitoring of energy production, distribution, trading and use 28
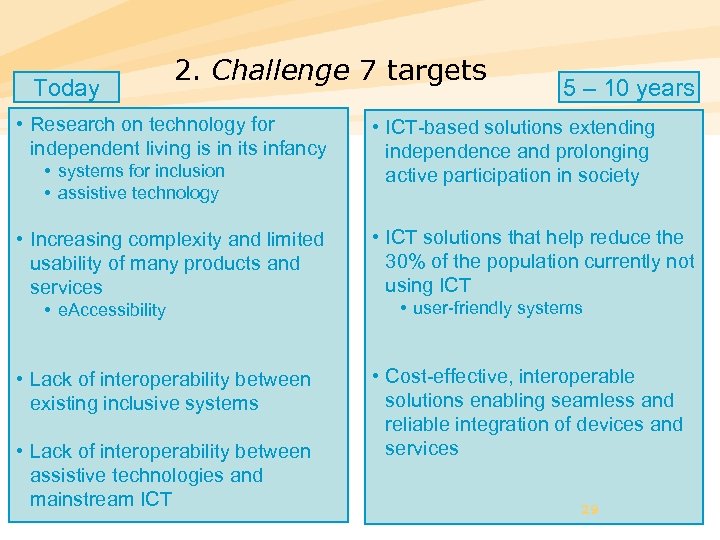 Today 2. Challenge 7 targets • Research on technology for independent living is in its infancy • systems for inclusion • assistive technology • Increasing complexity and limited usability of many products and services • e. Accessibility • Lack of interoperability between existing inclusive systems • Lack of interoperability between assistive technologies and mainstream ICT 5 – 10 years • ICT-based solutions extending independence and prolonging active participation in society • ICT solutions that help reduce the 30% of the population currently not using ICT • user-friendly systems • Cost-effective, interoperable solutions enabling seamless and reliable integration of devices and services 29
Today 2. Challenge 7 targets • Research on technology for independent living is in its infancy • systems for inclusion • assistive technology • Increasing complexity and limited usability of many products and services • e. Accessibility • Lack of interoperability between existing inclusive systems • Lack of interoperability between assistive technologies and mainstream ICT 5 – 10 years • ICT-based solutions extending independence and prolonging active participation in society • ICT solutions that help reduce the 30% of the population currently not using ICT • user-friendly systems • Cost-effective, interoperable solutions enabling seamless and reliable integration of devices and services 29
 2. Future and Emerging Technologies Objective • To lay foundations of the ICT innovations of tomorrow • To foster trans-disciplinary research excellence in emerging ICT-related research domains • To help emerging research communities to organise and structure their research agenda Impact • Pathfinder role: prepare for future ICT directions in the WP • Create new long-term competitive options for ICT • Avoid ‘tunnel vision’ in FP 7, by exploring unconventional ‘minority’ options and opportunities off the beaten track 30
2. Future and Emerging Technologies Objective • To lay foundations of the ICT innovations of tomorrow • To foster trans-disciplinary research excellence in emerging ICT-related research domains • To help emerging research communities to organise and structure their research agenda Impact • Pathfinder role: prepare for future ICT directions in the WP • Create new long-term competitive options for ICT • Avoid ‘tunnel vision’ in FP 7, by exploring unconventional ‘minority’ options and opportunities off the beaten track 30
 Horizontal support actions • International cooperation – To pave the way for strategic partnerships in view of developing global standards and interoperable solutions and strengthening EU competitiveness – To widen the diffusion of the information society, especially in developing countries and strengthened the EU policy for development • Trans-national co-operation among National Contact Points – One proposal including officially appointed NCPs – To improve NCP service across Europe – To help to simplify access to FP 7 calls – To lower the entry barriers for newcomers – To raise the quality of submitted proposals 31
Horizontal support actions • International cooperation – To pave the way for strategic partnerships in view of developing global standards and interoperable solutions and strengthening EU competitiveness – To widen the diffusion of the information society, especially in developing countries and strengthened the EU policy for development • Trans-national co-operation among National Contact Points – One proposal including officially appointed NCPs – To improve NCP service across Europe – To help to simplify access to FP 7 calls – To lower the entry barriers for newcomers – To raise the quality of submitted proposals 31
 3. ICT Calls for Proposal 1 Open: ~Jan 2007 - Close: 24 April 2007 Note: Budget allocations are indicative, implementation issues still under discussion 32
3. ICT Calls for Proposal 1 Open: ~Jan 2007 - Close: 24 April 2007 Note: Budget allocations are indicative, implementation issues still under discussion 32
 3. ICT Calls for Proposal 1: ~Jan-Apr 2007+ FET Open – continuous, close 31 Dec 2008 33
3. ICT Calls for Proposal 1: ~Jan-Apr 2007+ FET Open – continuous, close 31 Dec 2008 33
 3. ICT Calls for Proposal Open: May/Jun 2007 - Close: Sep/Oct 2007 34 Note: Budget allocations are indicative, implementation issues still under discussion
3. ICT Calls for Proposal Open: May/Jun 2007 - Close: Sep/Oct 2007 34 Note: Budget allocations are indicative, implementation issues still under discussion
 3. ICT Calls for Proposal Open: Dec 2007 - Close: Mar 2008 35 Note: Budget allocations are indicative, implementation issues still under discussion
3. ICT Calls for Proposal Open: Dec 2007 - Close: Mar 2008 35 Note: Budget allocations are indicative, implementation issues still under discussion
 3. ICT Calls for Proposal FP 7 Capacities Programme ICT-related Research Infrastructures • ICT based research e-infrastructures – high-capacity and high-performance communication and grid empowered infrastructures, distributed supercomputing facilities, data storage and advanced visualisation facilities – Calls early + late 2007 • Integrating Activities – To provide research services for ICT experience and application research, nano-electronics and integrated micro -/nano-systems research, and embedded systems research – Call late 2007 36
3. ICT Calls for Proposal FP 7 Capacities Programme ICT-related Research Infrastructures • ICT based research e-infrastructures – high-capacity and high-performance communication and grid empowered infrastructures, distributed supercomputing facilities, data storage and advanced visualisation facilities – Calls early + late 2007 • Integrating Activities – To provide research services for ICT experience and application research, nano-electronics and integrated micro -/nano-systems research, and embedded systems research – Call late 2007 36
 Where does D-Space Fit? • Comes out of IST and e. TEN • Gives access to all to an unreachable universe 37
Where does D-Space Fit? • Comes out of IST and e. TEN • Gives access to all to an unreachable universe 37
 Thank you! Just do it! 38
Thank you! Just do it! 38


