d38a076af6f48c4201cf05e8b5262edc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 e-Navigation & MSDI: The role of IHO, IMO and Developers “ARE THE PRINCIPLES AT ODDS WITH STRATEGIES FOR DELIVERY? ” MSDI Open Forum 3 rd March 2015 London
e-Navigation & MSDI: The role of IHO, IMO and Developers “ARE THE PRINCIPLES AT ODDS WITH STRATEGIES FOR DELIVERY? ” MSDI Open Forum 3 rd March 2015 London
 Edward Hosken Currently Head of Technical Engagement Previously Ph. D in GIS Chartered Surveyor Head of Hydrographic Data Services Head of ENC Production E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
Edward Hosken Currently Head of Technical Engagement Previously Ph. D in GIS Chartered Surveyor Head of Hydrographic Data Services Head of ENC Production E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 IHO, IMO The International Hydrographic Organization is an intergovernmental consultative and technical organization for the coordination of the activities of national hydrographic offices. Publishes hydrographic standards The International Maritime Organization is the United Nations specialized agency with responsibility for the safety and security of shipping and the prevention of marine pollution by ships. Responsible for international regulatory framework E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
IHO, IMO The International Hydrographic Organization is an intergovernmental consultative and technical organization for the coordination of the activities of national hydrographic offices. Publishes hydrographic standards The International Maritime Organization is the United Nations specialized agency with responsibility for the safety and security of shipping and the prevention of marine pollution by ships. Responsible for international regulatory framework E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 IHO, IMO E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
IHO, IMO E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 IHO, IMO S A L O S E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
IHO, IMO S A L O S E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 e-navigation … …“is the harmonised collection, integration, exchange, presentation and analysis of maritime information onboard and ashore by electronic means to enhance berth to berth navigation and related services, for safety and security at sea and protection of the marine environment” May 2006 e-navigation first mentioned at IMO Maritime Safety Committee (MSC 81) Nov 2008 MSC 85 approved the definition Nov 2014 MSC 94 approved the e-navigation Strategy Implementation Plan (SIP) yrs 9 Can it be delivered? E-navigation & MSDI: Who wants it? The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
e-navigation … …“is the harmonised collection, integration, exchange, presentation and analysis of maritime information onboard and ashore by electronic means to enhance berth to berth navigation and related services, for safety and security at sea and protection of the marine environment” May 2006 e-navigation first mentioned at IMO Maritime Safety Committee (MSC 81) Nov 2008 MSC 85 approved the definition Nov 2014 MSC 94 approved the e-navigation Strategy Implementation Plan (SIP) yrs 9 Can it be delivered? E-navigation & MSDI: Who wants it? The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
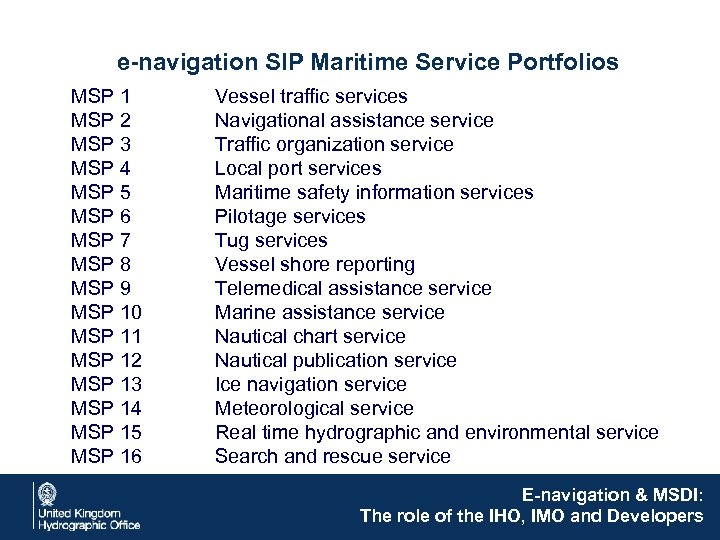 e-navigation SIP Maritime Service Portfolios MSP 1 MSP 2 MSP 3 MSP 4 MSP 5 MSP 6 MSP 7 MSP 8 MSP 9 MSP 10 MSP 11 MSP 12 MSP 13 MSP 14 MSP 15 MSP 16 Vessel traffic services Navigational assistance service Traffic organization service Local port services Maritime safety information services Pilotage services Tug services Vessel shore reporting Telemedical assistance service Marine assistance service Nautical chart service Nautical publication service Ice navigation service Meteorological service Real time hydrographic and environmental service Search and rescue service E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
e-navigation SIP Maritime Service Portfolios MSP 1 MSP 2 MSP 3 MSP 4 MSP 5 MSP 6 MSP 7 MSP 8 MSP 9 MSP 10 MSP 11 MSP 12 MSP 13 MSP 14 MSP 15 MSP 16 Vessel traffic services Navigational assistance service Traffic organization service Local port services Maritime safety information services Pilotage services Tug services Vessel shore reporting Telemedical assistance service Marine assistance service Nautical chart service Nautical publication service Ice navigation service Meteorological service Real time hydrographic and environmental service Search and rescue service E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 e-navigation projects MEH Marine Electronic Highway (Malacca and Singapore straits) ACCSEAS Accessibility for Shipping, Efficiency, Advantages and Sustainability (North Sea) Efficien. Sea 2 Efficient, Safe and Sustainable Traffic at Sea (Baltic) Monalisa 2 Motorways of the Sea (Baltic) STM Validation Sea Traffic Management (Baltic +) Sea. SHIFT Shift to short sea shipping (North Sea) E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
e-navigation projects MEH Marine Electronic Highway (Malacca and Singapore straits) ACCSEAS Accessibility for Shipping, Efficiency, Advantages and Sustainability (North Sea) Efficien. Sea 2 Efficient, Safe and Sustainable Traffic at Sea (Baltic) Monalisa 2 Motorways of the Sea (Baltic) STM Validation Sea Traffic Management (Baltic +) Sea. SHIFT Shift to short sea shipping (North Sea) E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
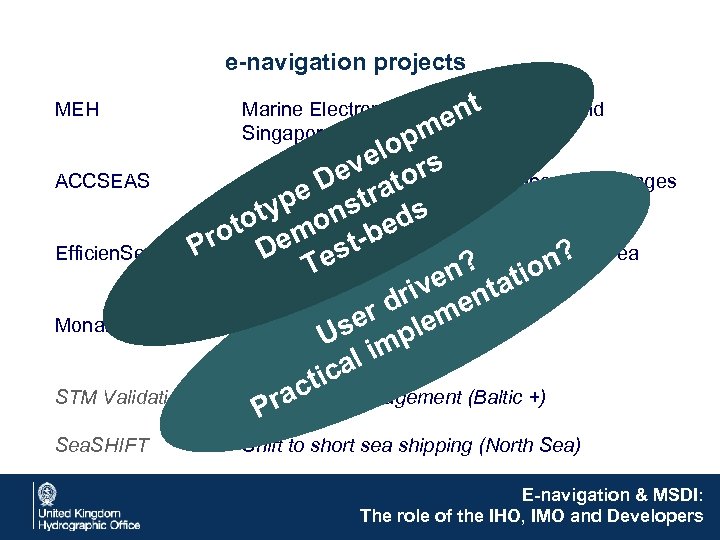 e-navigation projects MEH Marine Electronic Highway (Malacca and nt e Singapore straits) pm elo rs ev to Accessibility for Shipping, Efficiency, Advantages ACCSEAS e D stra (North Sea) and Sustainability s typ on ed oto em t-b r Efficient, Safe and Sustainable Traffic at Sea Efficien. Sea 2 P s D ? tion? Te (Baltic) en ta riv en r d. Sea m Motorways sethe le (Baltic) of Monalisa 2 U imp al tic Management (Baltic +) Sear. Traffic STM Validation ac P Sea. SHIFT Shift to short sea shipping (North Sea) E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
e-navigation projects MEH Marine Electronic Highway (Malacca and nt e Singapore straits) pm elo rs ev to Accessibility for Shipping, Efficiency, Advantages ACCSEAS e D stra (North Sea) and Sustainability s typ on ed oto em t-b r Efficient, Safe and Sustainable Traffic at Sea Efficien. Sea 2 P s D ? tion? Te (Baltic) en ta riv en r d. Sea m Motorways sethe le (Baltic) of Monalisa 2 U imp al tic Management (Baltic +) Sear. Traffic STM Validation ac P Sea. SHIFT Shift to short sea shipping (North Sea) E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 Hydrography – much more than … … just nautical charts Over 90% of the world’s trade travels by sea The seas, seabed and the sub-seabed, represent a vast resource for food, mineral resources, energy, water, biomedicines, and infrastructure. But they are hard to exploit safely, cost effectively and sustainably without knowing the depth of the water, the shape of the seafloor and the movement of the water. E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
Hydrography – much more than … … just nautical charts Over 90% of the world’s trade travels by sea The seas, seabed and the sub-seabed, represent a vast resource for food, mineral resources, energy, water, biomedicines, and infrastructure. But they are hard to exploit safely, cost effectively and sustainably without knowing the depth of the water, the shape of the seafloor and the movement of the water. E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 http: //imgs. xkcd. com/comics/desert_island. png
http: //imgs. xkcd. com/comics/desert_island. png
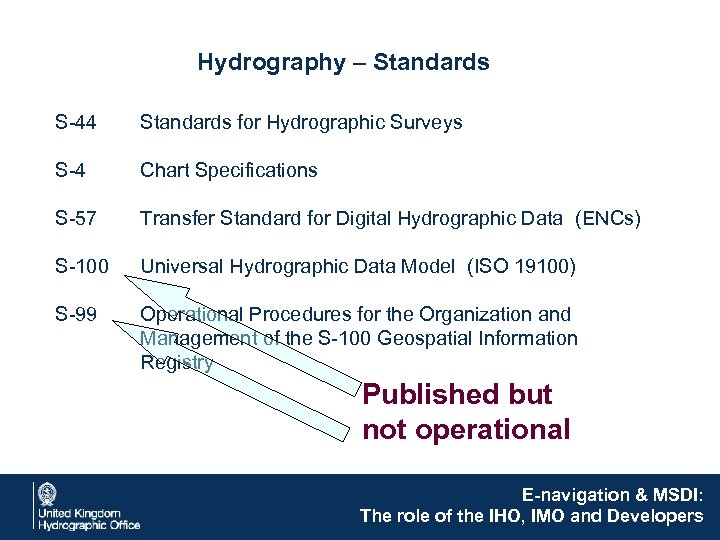 Hydrography – Standards S-44 Standards for Hydrographic Surveys S-4 Chart Specifications S-57 Transfer Standard for Digital Hydrographic Data (ENCs) S-100 Universal Hydrographic Data Model (ISO 19100) S-99 Operational Procedures for the Organization and Management of the S-100 Geospatial Information Registry Published but not operational E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
Hydrography – Standards S-44 Standards for Hydrographic Surveys S-4 Chart Specifications S-57 Transfer Standard for Digital Hydrographic Data (ENCs) S-100 Universal Hydrographic Data Model (ISO 19100) S-99 Operational Procedures for the Organization and Management of the S-100 Geospatial Information Registry Published but not operational E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 Hydrography – Standards ● IHO S-101 ENC ● IHO S-102 Bathymetric surface ● IHO S-103 Sub-surface navigation ● IHO S-111 Surface currents ● IHO S-112 Dynamic water level ● IHO S-121 Maritime limits and boundaries ● IHO S-124 Navigational warnings ● IALA S-201 Aids to Navigation Information ● IEHG S-401 Inland ENC ● JCOMM S-411 Sea ice ● JCOMM S-412 Met-ocean forecasts E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
Hydrography – Standards ● IHO S-101 ENC ● IHO S-102 Bathymetric surface ● IHO S-103 Sub-surface navigation ● IHO S-111 Surface currents ● IHO S-112 Dynamic water level ● IHO S-121 Maritime limits and boundaries ● IHO S-124 Navigational warnings ● IALA S-201 Aids to Navigation Information ● IEHG S-401 Inland ENC ● JCOMM S-411 Sea ice ● JCOMM S-412 Met-ocean forecasts E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
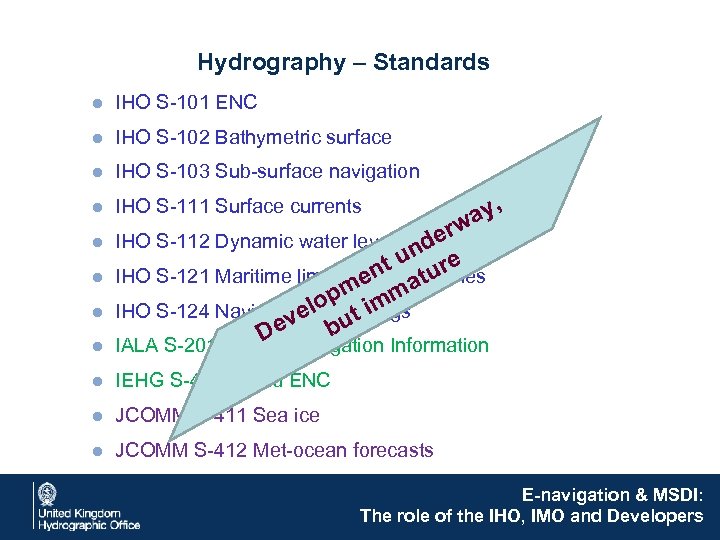 Hydrography – Standards ● IHO S-101 ENC ● IHO S-102 Bathymetric surface ● IHO S-103 Sub-surface navigation , ay rw ● IHO S-112 Dynamic water level nde u nt ature ● IHO S-121 Maritime limits and boundaries me m lop t im ● IHO S-124 Navigational warnings e ev bu D ● IHO S-111 Surface currents ● IALA S-201 Aids to Navigation Information ● IEHG S-401 Inland ENC ● JCOMM S-411 Sea ice ● JCOMM S-412 Met-ocean forecasts E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
Hydrography – Standards ● IHO S-101 ENC ● IHO S-102 Bathymetric surface ● IHO S-103 Sub-surface navigation , ay rw ● IHO S-112 Dynamic water level nde u nt ature ● IHO S-121 Maritime limits and boundaries me m lop t im ● IHO S-124 Navigational warnings e ev bu D ● IHO S-111 Surface currents ● IALA S-201 Aids to Navigation Information ● IEHG S-401 Inland ENC ● JCOMM S-411 Sea ice ● JCOMM S-412 Met-ocean forecasts E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 MSDI – C 17 “The IHO will support Member States in the identification, development and implementation of an appropriate role in national Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI) and MSDI initiatives. This will be achieved through: The development and maintenance of a Special Publication that will provide a definitive procedural guide to establishing the role of the national hydrographic authority in MSDI. ” EIHC Resolution K 4. 7 (2009) E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
MSDI – C 17 “The IHO will support Member States in the identification, development and implementation of an appropriate role in national Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI) and MSDI initiatives. This will be achieved through: The development and maintenance of a Special Publication that will provide a definitive procedural guide to establishing the role of the national hydrographic authority in MSDI. ” EIHC Resolution K 4. 7 (2009) E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
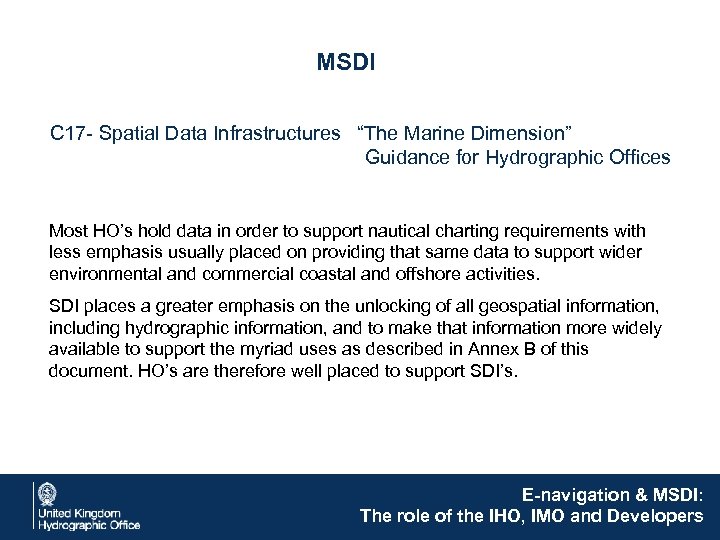 MSDI C 17 - Spatial Data Infrastructures “The Marine Dimension” Guidance for Hydrographic Offices Most HO’s hold data in order to support nautical charting requirements with less emphasis usually placed on providing that same data to support wider environmental and commercial coastal and offshore activities. SDI places a greater emphasis on the unlocking of all geospatial information, including hydrographic information, and to make that information more widely available to support the myriad uses as described in Annex B of this document. HO’s are therefore well placed to support SDI’s. E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
MSDI C 17 - Spatial Data Infrastructures “The Marine Dimension” Guidance for Hydrographic Offices Most HO’s hold data in order to support nautical charting requirements with less emphasis usually placed on providing that same data to support wider environmental and commercial coastal and offshore activities. SDI places a greater emphasis on the unlocking of all geospatial information, including hydrographic information, and to make that information more widely available to support the myriad uses as described in Annex B of this document. HO’s are therefore well placed to support SDI’s. E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 C 17 ANNEX B - Some uses of HO data for purposes other than navigation Habitat mapping & heritage assessment Conservation assessment & designation Site selection (e. g. renewable energy and oil & gas extraction) Route optimisation Vessel location and disposal monitoring Homeland security and defence Aggregates extraction Fisheries regulation Coastal protection & shoreline management Licensing & consent evaluation Emergency planning & management Survey planning & execution SP M
C 17 ANNEX B - Some uses of HO data for purposes other than navigation Habitat mapping & heritage assessment Conservation assessment & designation Site selection (e. g. renewable energy and oil & gas extraction) Route optimisation Vessel location and disposal monitoring Homeland security and defence Aggregates extraction Fisheries regulation Coastal protection & shoreline management Licensing & consent evaluation Emergency planning & management Survey planning & execution SP M
 Why is it important that an HO gets involved? By getting involved, the HO will gain a greater appreciation of the inherent value in its information which will lead to the wider use of hydrographic data and information in the development of new products and services. It would also demonstrate that the HO is a vital element of the national spatial data infrastructure and that it has a role to play. It will also allow the HO to work in cooperation with others to tackle some of the difficult issues affecting geospatial data at this time. C 17 FAQs E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
Why is it important that an HO gets involved? By getting involved, the HO will gain a greater appreciation of the inherent value in its information which will lead to the wider use of hydrographic data and information in the development of new products and services. It would also demonstrate that the HO is a vital element of the national spatial data infrastructure and that it has a role to play. It will also allow the HO to work in cooperation with others to tackle some of the difficult issues affecting geospatial data at this time. C 17 FAQs E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
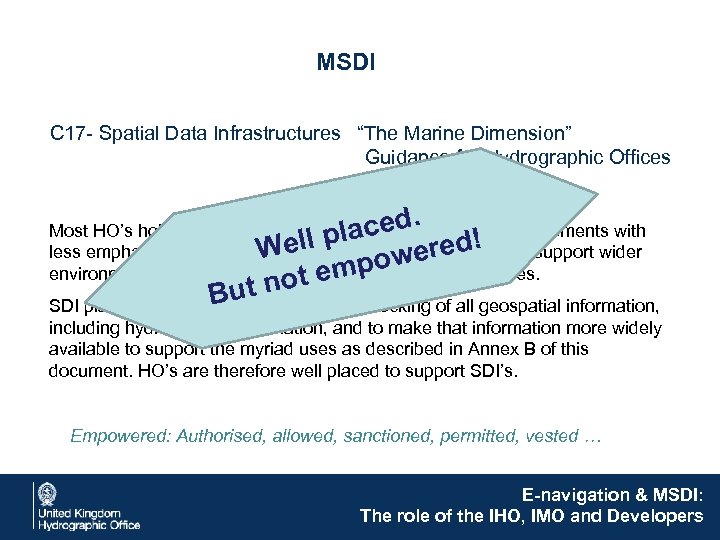 MSDI C 17 - Spatial Data Infrastructures “The Marine Dimension” Guidance for Hydrographic Offices ced. ell pla wered! W empo t not Bu Most HO’s hold data in order to support nautical charting requirements with less emphasis usually placed on providing that same data to support wider environmental and commercial coastal and offshore activities. SDI places a greater emphasis on the unlocking of all geospatial information, including hydrographic information, and to make that information more widely available to support the myriad uses as described in Annex B of this document. HO’s are therefore well placed to support SDI’s. Empowered: Authorised, allowed, sanctioned, permitted, vested … E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
MSDI C 17 - Spatial Data Infrastructures “The Marine Dimension” Guidance for Hydrographic Offices ced. ell pla wered! W empo t not Bu Most HO’s hold data in order to support nautical charting requirements with less emphasis usually placed on providing that same data to support wider environmental and commercial coastal and offshore activities. SDI places a greater emphasis on the unlocking of all geospatial information, including hydrographic information, and to make that information more widely available to support the myriad uses as described in Annex B of this document. HO’s are therefore well placed to support SDI’s. Empowered: Authorised, allowed, sanctioned, permitted, vested … E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
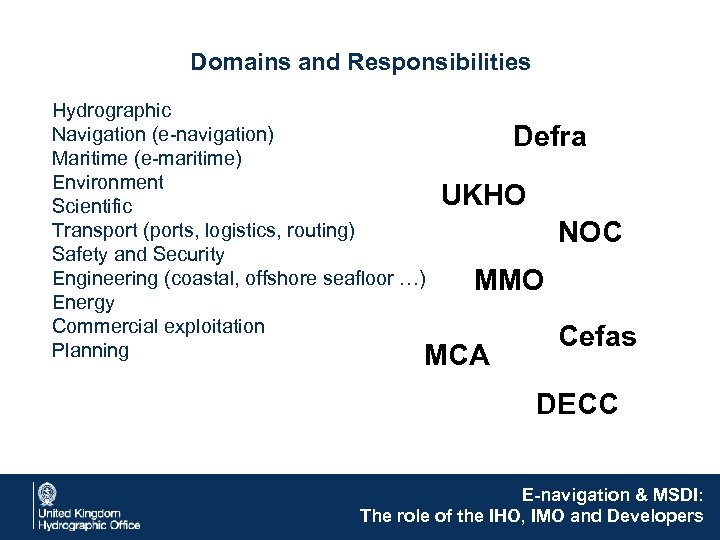 Domains and Responsibilities Hydrographic Navigation (e-navigation) Defra Maritime (e-maritime) Environment UKHO Scientific Transport (ports, logistics, routing) NOC Safety and Security Engineering (coastal, offshore seafloor …) MMO Energy Commercial exploitation Cefas Planning MCA DECC E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
Domains and Responsibilities Hydrographic Navigation (e-navigation) Defra Maritime (e-maritime) Environment UKHO Scientific Transport (ports, logistics, routing) NOC Safety and Security Engineering (coastal, offshore seafloor …) MMO Energy Commercial exploitation Cefas Planning MCA DECC E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 Domains and Responsibilities Hydrographic Navigation (e-navigation) Defra Maritime (e-maritime) Environment UKHO Scientific Transport (ports, logistics, routing) NOC Safety and Security Engineering (coastal, offshore seafloor …) n ? MMO o Energy ati din Commercial exploitation or Cefas o Planning C MCA DECC E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
Domains and Responsibilities Hydrographic Navigation (e-navigation) Defra Maritime (e-maritime) Environment UKHO Scientific Transport (ports, logistics, routing) NOC Safety and Security Engineering (coastal, offshore seafloor …) n ? MMO o Energy ati din Commercial exploitation or Cefas o Planning C MCA DECC E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 Obligations and Initiatives E-navigation INSPIRE EMODnet MSP - Maritime Spatial Planning ICZM - Integrated Coastal Zone Management IOC-UNESCO Open Government UN-GGIM ve d! loa r? er e ov liv ti DI de s? itia MS HO In n of Ca ole R E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
Obligations and Initiatives E-navigation INSPIRE EMODnet MSP - Maritime Spatial Planning ICZM - Integrated Coastal Zone Management IOC-UNESCO Open Government UN-GGIM ve d! loa r? er e ov liv ti DI de s? itia MS HO In n of Ca ole R E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 Challenges o Will users pay for e-navigation benefits? o MSDI benefits are wider than any one organisation can justify o Who is empowered to lead on benefits delivery? o Who will pay for development? o Who defines MSDI strategy? E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
Challenges o Will users pay for e-navigation benefits? o MSDI benefits are wider than any one organisation can justify o Who is empowered to lead on benefits delivery? o Who will pay for development? o Who defines MSDI strategy? E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
 Questions? Let’s see if we get further clarity during the day E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers
Questions? Let’s see if we get further clarity during the day E-navigation & MSDI: The role of the IHO, IMO and Developers


