1dd82383be80abfa1506842951e4c53a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

® e. Mail and Records Management with IBM Classification Module Jon Dellaria, IBM Certified ECM Information Technology Specialist © 2008 IBM Corporation

Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management What is Classification? Definition: Class. i. fic. a. tion [klas-uh-fi-key-shuhn] – n – the act of assigning an element (a document for example) to a category. © 2008 IBM Corporation

Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management IBM – Leadership in Text Analysis and Classification § IBM has a 50+ year history in text analysis and discovery – As early as 1957, IBM published pioneer research done on text classification (and related topics, such as text search, and automatic creation of text abstracts) § IBM invests ~$50 M annually in research and development for search and text analytics – 200 people actively engaged in R&D – IBM holds over 200 patents in information access with more each year © 2008 IBM Corporation
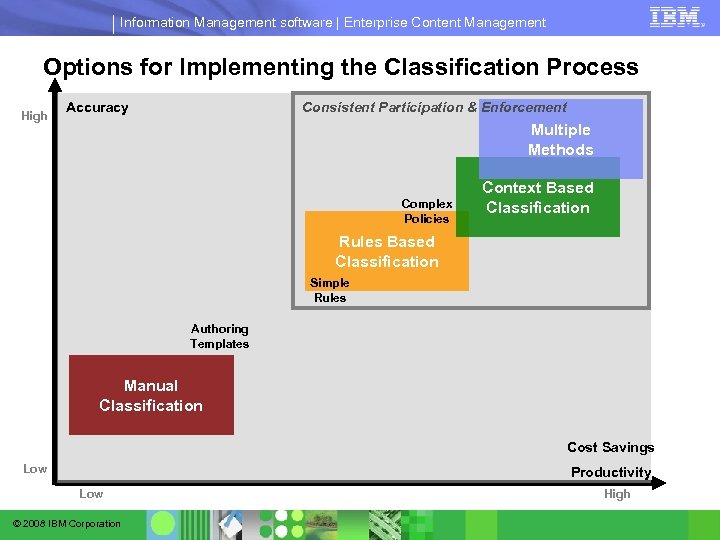
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Options for Implementing the Classification Process High Accuracy Consistent Participation & Enforcement Multiple Methods Complex Policies Context Based Classification Rules Based Classification Simple Rules Authoring Templates Manual Classification Cost Savings Low Productivity Low © 2008 IBM Corporation High
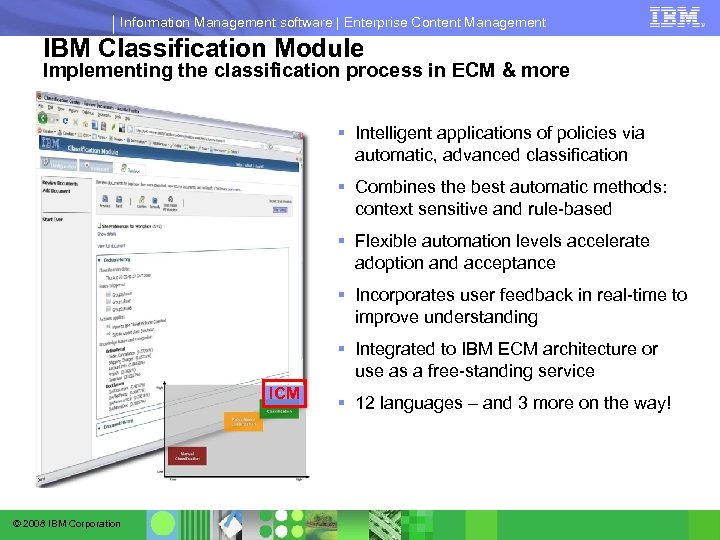
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management IBM Classification Module Implementing the classification process in ECM & more § Intelligent applications of policies via automatic, advanced classification § Combines the best automatic methods: context sensitive and rule-based § Flexible automation levels accelerate adoption and acceptance § Incorporates user feedback in real-time to improve understanding § Integrated to IBM ECM architecture or use as a free-standing service ICM © 2008 IBM Corporation § 12 languages – and 3 more on the way!
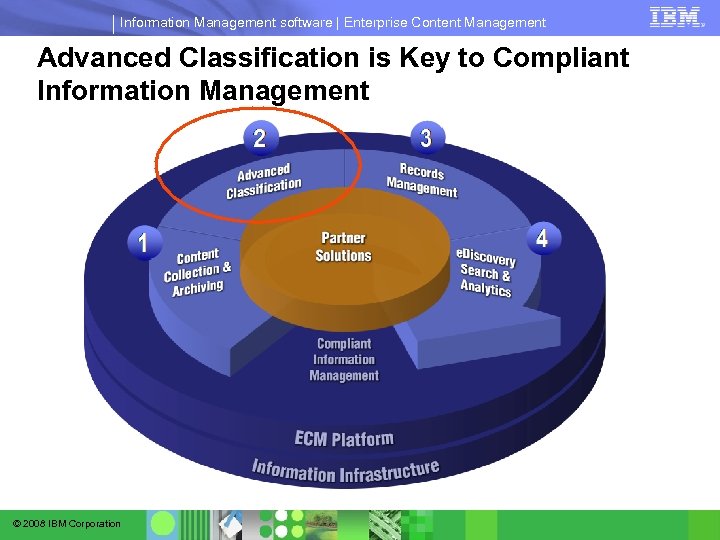
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Advanced Classification is Key to Compliant Information Management © 2008 IBM Corporation
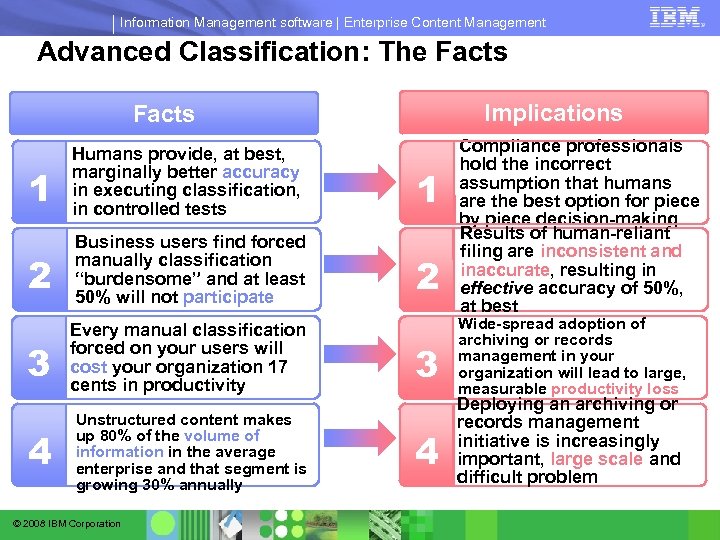
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Advanced Classification: The Facts Implications Facts 1 Humans provide, at best, marginally better accuracy in executing classification, in controlled tests 1 2 Business users find forced manually classification “burdensome” and at least 50% will not participate 2 3 Every manual classification forced on your users will cost your organization 17 cents in productivity 3 Unstructured content makes up 80% of the volume of information in the average enterprise and that segment is growing 30% annually 4 4 © 2008 IBM Corporation Compliance professionals hold the incorrect assumption that humans are the best option for piece by piece decision-making Results of human-reliant filing are inconsistent and inaccurate, resulting in effective accuracy of 50%, at best Wide-spread adoption of archiving or records management in your organization will lead to large, measurable productivity loss Deploying an archiving or records management initiative is increasingly important, large scale and difficult problem
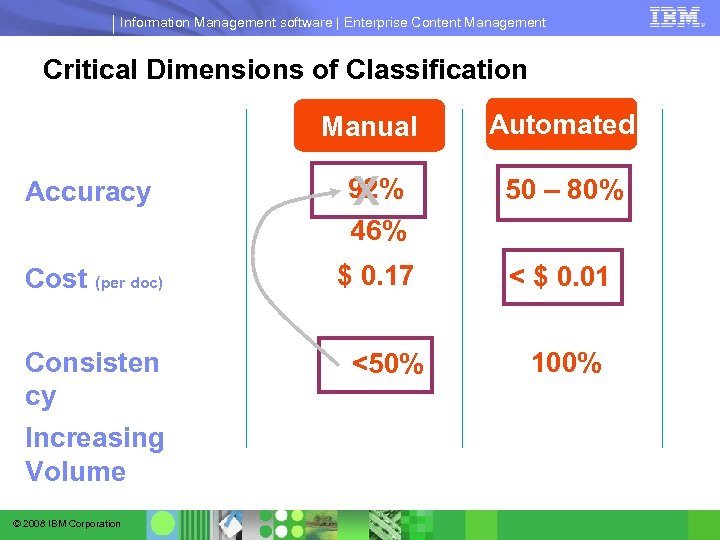
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Critical Dimensions of Classification Manual Automated Accuracy 92% X 46% 50 – 80% Cost (per doc) $ 0. 17 < $ 0. 01 Consisten cy Increasing Volume © 2008 IBM Corporation <50% 100%
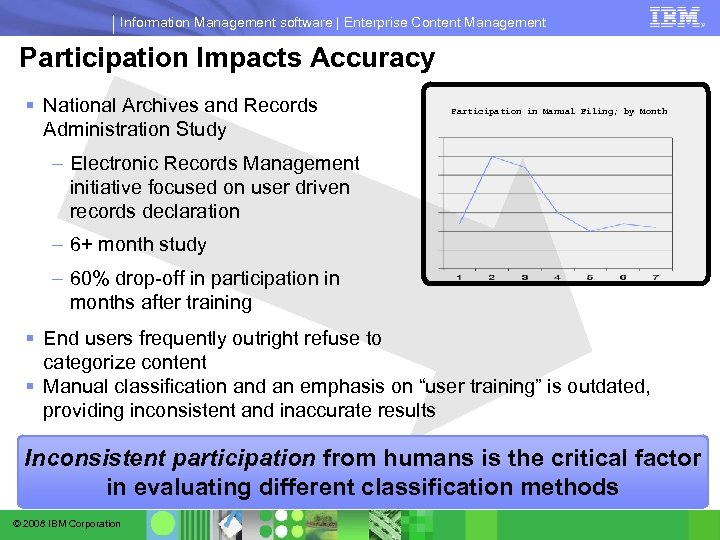
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Participation Impacts Accuracy § National Archives and Records Administration Study Participation in Manual Filing; by Month – Electronic Records Management initiative focused on user driven records declaration – 6+ month study – 60% drop-off in participation in months after training § End users frequently outright refuse to categorize content § Manual classification and an emphasis on “user training” is outdated, providing inconsistent and inaccurate results Inconsistent participation from humans is the critical factor in evaluating different classification methods © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Manual Classification With paper With rudimentary electronics Today’s advanced electronics © 2008 IBM Corporation
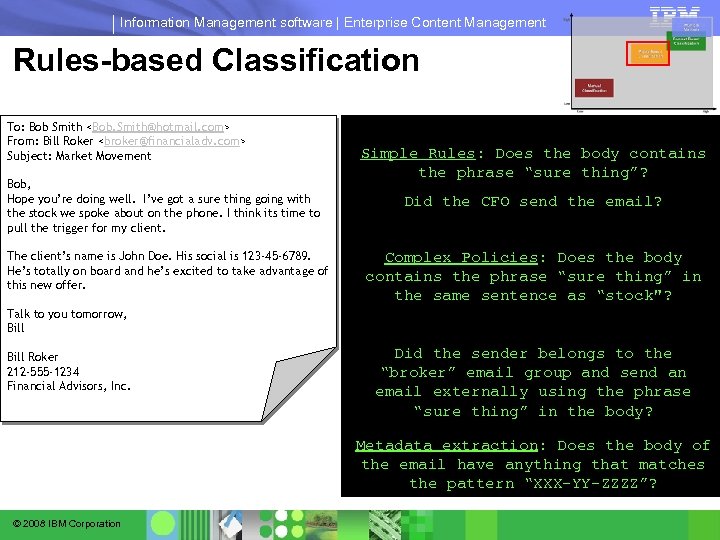
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Rules-based Classification To: Bob Smith <Bob. Smith@hotmail. com> From: Bill Roker <broker@financialadv. com> Subject: Market Movement Bob, Hope you’re doing well. I’ve got a sure thing going with the stock we spoke about on the phone. I think its time to pull the trigger for my client. The client’s name is John Doe. His social is 123 -45 -6789. He’s totally on board and he’s excited to take advantage of this new offer. Simple Rules: Does the body contains the phrase “sure thing”? Did the CFO send the email? Complex Policies: Does the body contains the phrase “sure thing” in the same sentence as “stock"? Talk to you tomorrow, Bill Roker 212 -555 -1234 Financial Advisors, Inc. Did the sender belongs to the “broker” email group and send an email externally using the phrase “sure thing” in the body? Metadata extraction: Does the body of the email have anything that matches the pattern “XXX-YY-ZZZZ”? © 2008 IBM Corporation
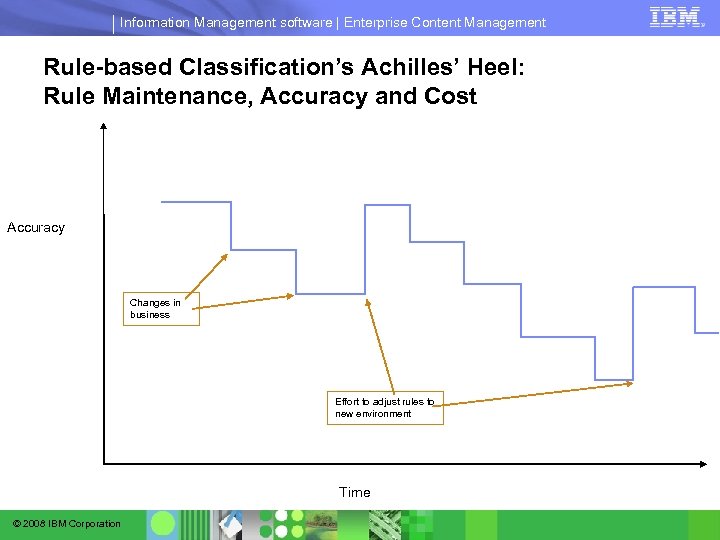
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Rule-based Classification’s Achilles’ Heel: Rule Maintenance, Accuracy and Cost Accuracy Changes in business Effort to adjust rules to new environment Time © 2008 IBM Corporation
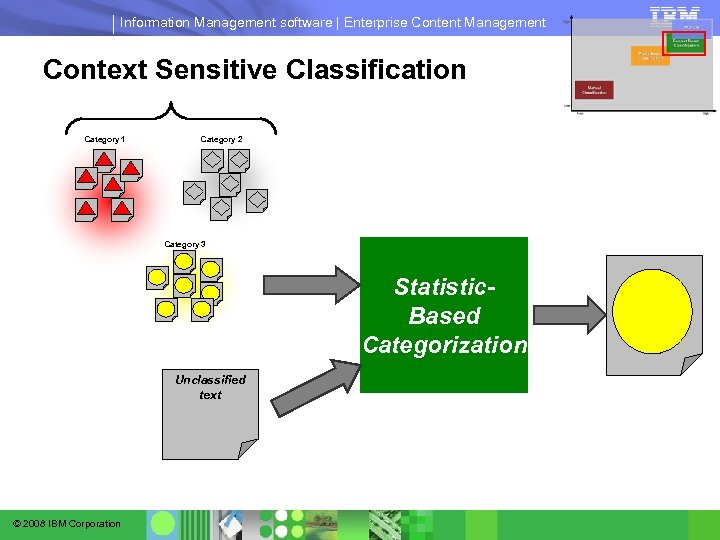
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Context Sensitive Classification Category 1 Category 2 Category 3 Statistic. Based Categorization Unclassified text © 2008 IBM Corporation
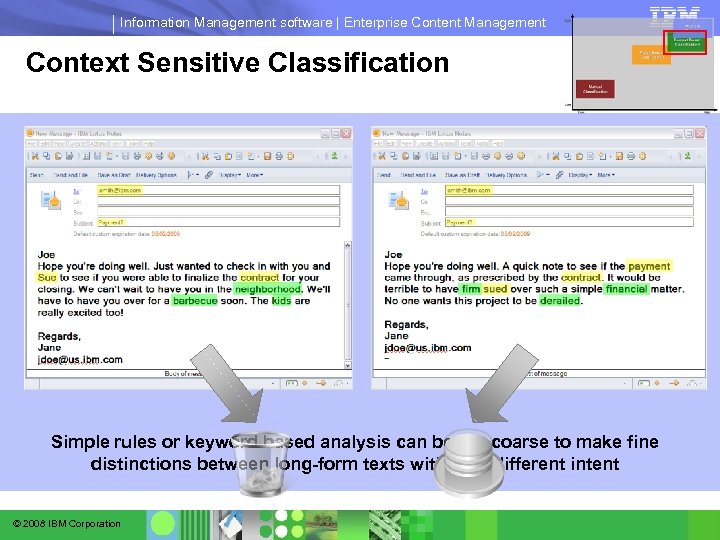
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Context Sensitive Classification Simple rules or keyword based analysis can be too coarse to make fine distinctions between long-form texts with very different intent © 2008 IBM Corporation
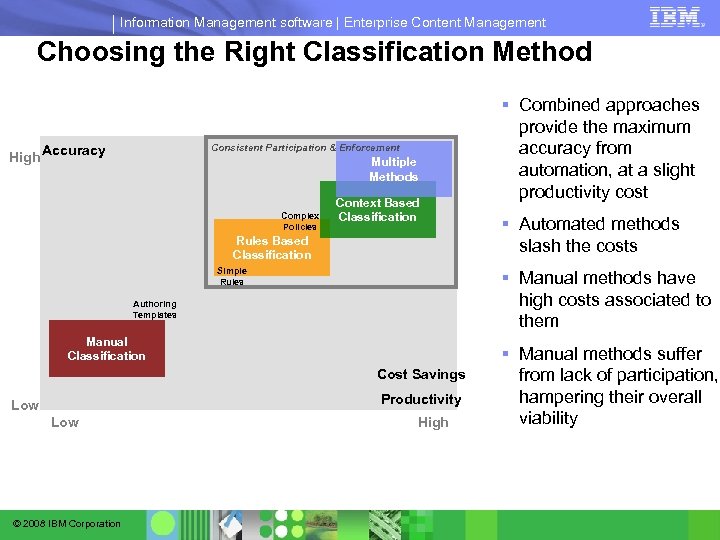
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Choosing the Right Classification Method Consistent Participation & Enforcement High Accuracy Multiple Methods Complex Policies Context Based Classification Rules Based Classification Simple Rules Manual Classification Cost Savings Productivity Low © 2008 IBM Corporation § Automated methods slash the costs § Manual methods have high costs associated to them Authoring Templates Low § Combined approaches provide the maximum accuracy from automation, at a slight productivity cost High § Manual methods suffer from lack of participation, hampering their overall viability
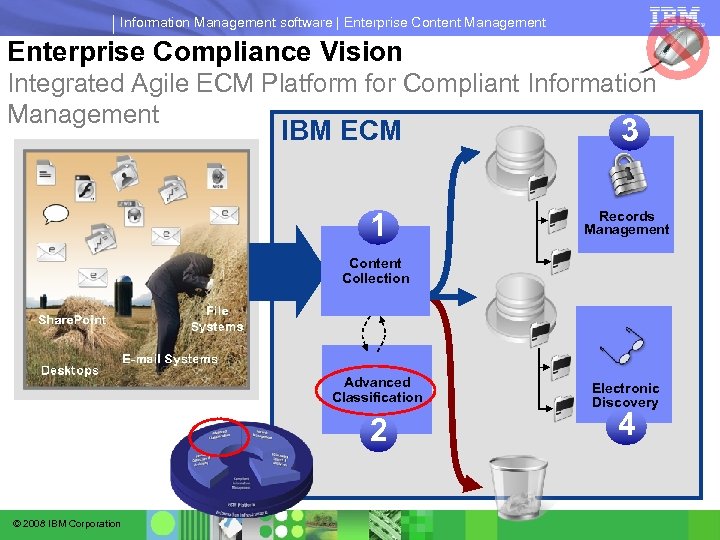
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Enterprise Compliance Vision Integrated Agile ECM Platform for Compliant Information Management IBM ECM 1 3 Records Management Content Collection Advanced Classification 2 © 2008 IBM Corporation Electronic Discovery 4
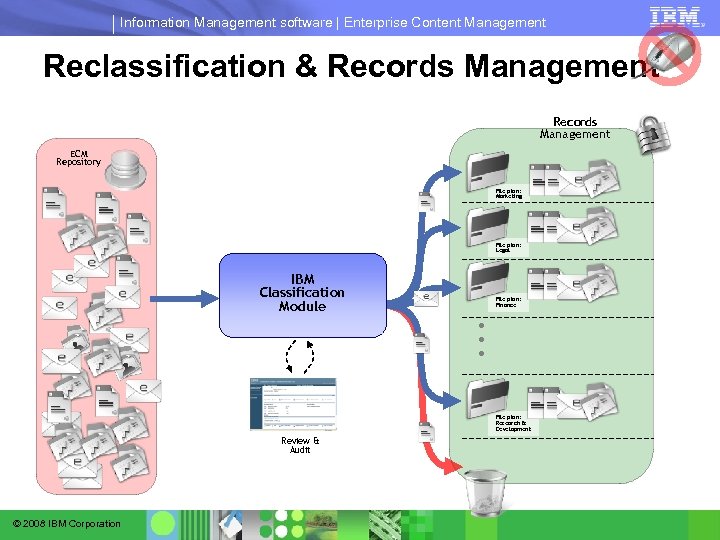
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Reclassification & Records Management ECM Repository File plan: Marketing File plan: Legal IBM Classification Module File plan: Finance . . . File plan: Research & Development Review & Audit © 2008 IBM Corporation

Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management US Army Email and Records Manager Pilot GOAL § Provide a means to address Army’s requirement for the successful records management of email – Challenges faced: • Lack of records management follow through from end users • Need to capture records and transactional activities from email • Need to capture records without user intervention 18 © 2008 IBM Corporation

Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management US Army Email and Records Manager Pilot Success Criteria for pilot: – Correctly capture and retrieve email provided – Ensure information is secure – Determine email can be accurately Auto Categorized by the IBM Categorization Module (ICM) • Goal of 90% or better accuracy • Show ICM learns and improves accuracy over time – Place categorized record emails under correct Army records disposition 19 © 2008 IBM Corporation
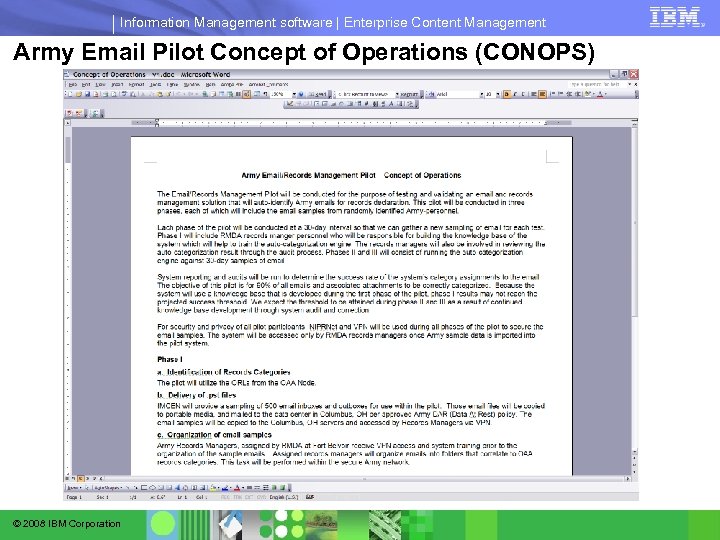
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Army Email Pilot Concept of Operations (CONOPS) © 2008 IBM Corporation
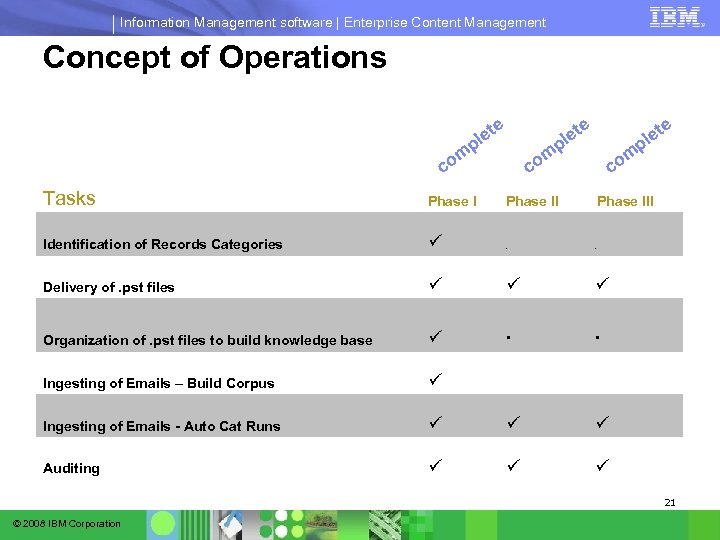
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Concept of Operations p m co e t le p m o e et l p om c c Tasks Phase III Identification of Records Categories ü Delivery of. pst files ü ü ü Organization of. pst files to build knowledge base ü Ingesting of Emails – Build Corpus ü Ingesting of Emails - Auto Cat Runs ü ü ü Auditing ü ü ü 21 © 2008 IBM Corporation

Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Pilot Phases § Pre-Phase Activity – Teach the system by building the knowledge base (Corpus) § Phase I – Process the first run of sample. pst files – Review and Audit the results § Phase II (30 days later) – Process the second run of sample. pst files – Review and Audit the results § Phase III (30 days later) – Process the third run of sample. pst files – Review and Audit the results © 2008 IBM Corporation
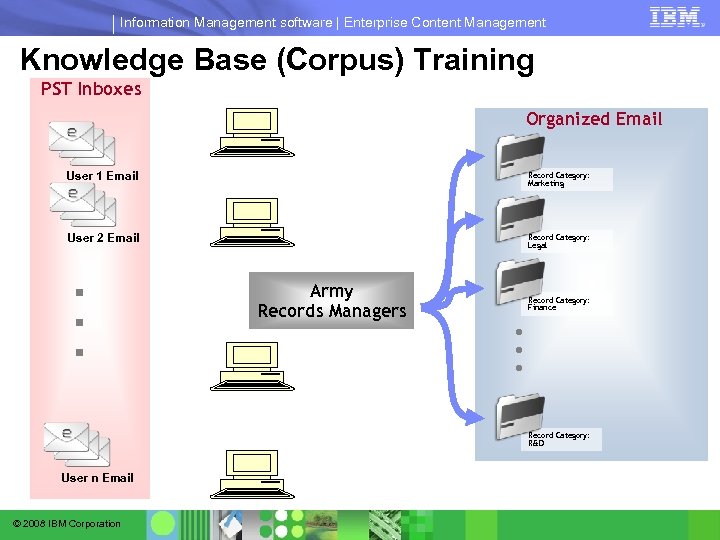
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Knowledge Base (Corpus) Training PST Inboxes Organized Email User 1 Email Record Category: Marketing User 2 Email Record Category: Legal Record Category: Finance . . . Army Records Managers Record Category: R&D User n Email © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Outlook Configuration © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Building the Knowledge Base for Email Categorization © 2008 IBM Corporation
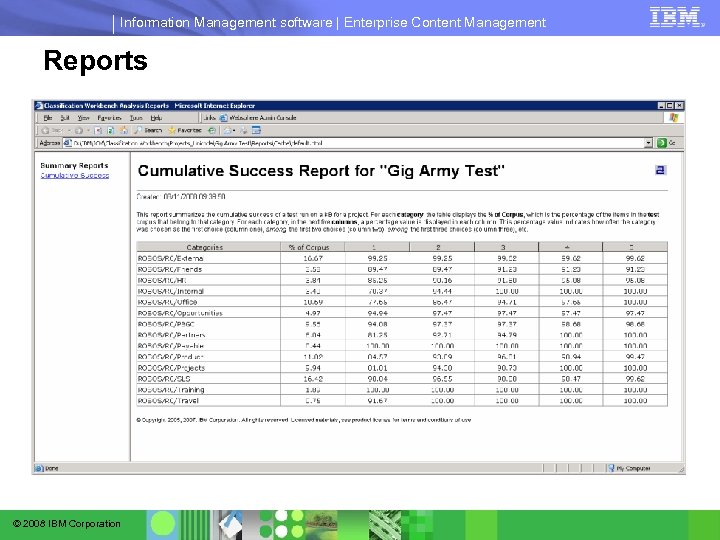
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Reports © 2008 IBM Corporation
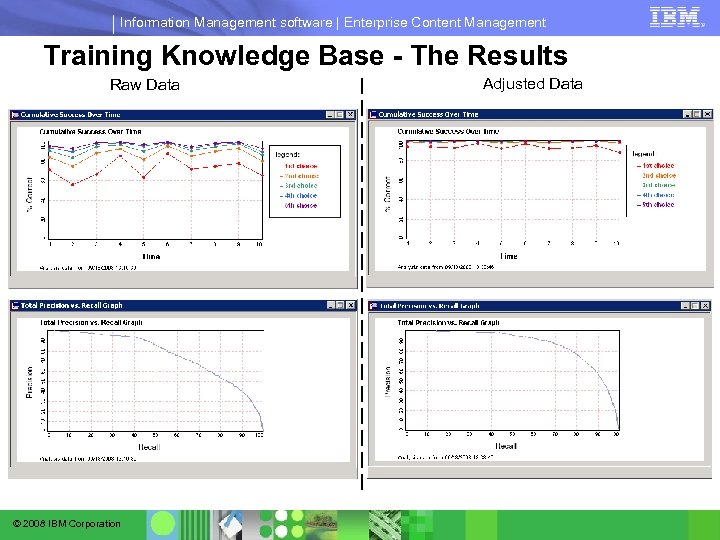
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Training Knowledge Base - The Results Raw Data © 2008 IBM Corporation Adjusted Data

Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Pilot Project Pre-Phase Activities Build Categorization Knowledge Base • Work with Army Records Managers to define the most appropriate records categories and identify example mails for them § Goal: – Find examples of email records for each of the record categories – Find 15 – 20 examples for each category § Results: – 54 records categories were identified as being associated with the assigned offices • 28 categories have 15 or more examples • 26 categories have 14 or less examples 28 © 2008 IBM Corporation
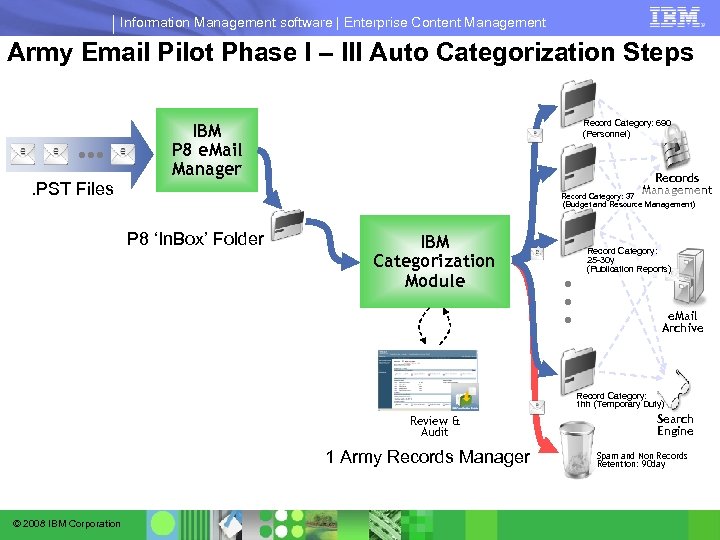
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Army Email Pilot Phase I – III Auto Categorization Steps . . PST Files Record Category: 690 (Personnel) IBM P 8 e. Mail Manager Records Management Record Category: 37 (Budget and Resource Management) P 8 ‘In. Box’ Folder Record Category: 25 -30 y (Publication Reports) . . . IBM Categorization Module e. Mail Archive Record Category: 1 hh (Temporary Duty) Review & Audit 1 Army Records Manager © 2008 IBM Corporation Search Engine Spam and Non Records Retention: 90 day

Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Pilot Project Phase I – III Activities First Pass of Categorization (process. pst files) § Take the Knowledgebase created by Army Records Managers and apply it to the bulk of email § Measure categorization results returned and begin Audit and Review process § Audit – Used to confirm the accuracy of categorization via a random sampling of categorized results. If necessary, the chosen category may be modified which serves to retrain the knowledgebase for the future § Review – items that do not meet the defined thresholds for categorization are available for further analysis and categorization by records personnel § The result of Audit and Review is improved the accuracy of the knowledgebase therefore improved categorization for future email ingest Post Audit/Review reprocessing of email to measure categorization improvements § Measure results for the completion of each Phase 30 © 2008 IBM Corporation

Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Pilot Project Activities § Focus on email from 16 different offices across Army • Demonstrate ability to categorize emails across Army enterprise § PST files from 398 pre-selected users • • 581, 634 emails in total in Phase I 581, 256 emails in total in Phase II 735, 333 emails in total in Phase III 1, 898, 232 total emails through Phase III § PST files transferred to the pilot system via secure connection 31 © 2008 IBM Corporation
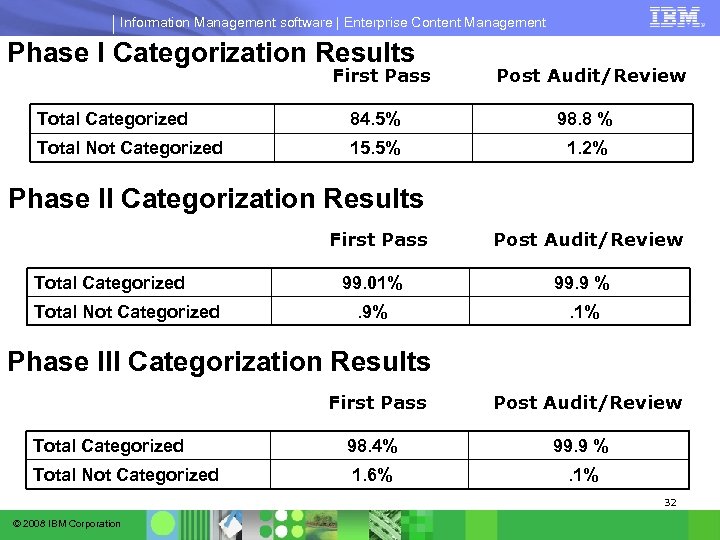
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Phase I Categorization Results First Pass Post Audit/Review Total Categorized 84. 5% 98. 8 % Total Not Categorized 15. 5% 1. 2% Phase II Categorization Results First Pass Total Categorized Total Not Categorized Post Audit/Review 99. 01% 99. 9 % . 9% . 1% Phase III Categorization Results First Pass Post Audit/Review Total Categorized 98. 4% 99. 9 % Total Not Categorized 1. 6% . 1% 32 © 2008 IBM Corporation

Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Army Records Manager Observations § As a records manager with a 25 -year background in federal and civilian records management, I believe the automatic categorization of information is the next logical evolution in managing the records of an organization. § The classifier correctly identifies categories of records based on information from office file plans. Since office file plans are incorporated within an agency records manual, the initial input for the system is nominal. The office file plan becomes the document classifier. § Because the classifier retains information on document retrieval activity, it may be appropriate for use in many other information management program areas, including the Freedom of Information and Privacy Act. © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Demo 34 © 2008 IBM Corporation

Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management Thank You 35 © 2008 IBM Corporation
Information Management software | Enterprise Content Management IBM Records Manager with Army File Plan © 2008 IBM Corporation
1dd82383be80abfa1506842951e4c53a.ppt