ee667c3dc3e7220462c89b2ccf58a317.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 E-Learning Futures Professor J C Taylor Vice President (Academic & Global Learning) University of Southern Queensland Australia March 2004
E-Learning Futures Professor J C Taylor Vice President (Academic & Global Learning) University of Southern Queensland Australia March 2004
 Enrolled Students USQ 2003 § § All students On-campus Off-campus (Australia) Off-campus (Overseas) 25, 745 6, 204 13, 723 5, 818 Note: Students studying solely online (100%) (24%) (53%) (23%) 1, 064
Enrolled Students USQ 2003 § § All students On-campus Off-campus (Australia) Off-campus (Overseas) 25, 745 6, 204 13, 723 5, 818 Note: Students studying solely online (100%) (24%) (53%) (23%) 1, 064
 USQ’s International Students 2003 § § § Singapore 1, 598 Malaysia 2, 327 Hong Kong 565 South Africa 209 United Arab Emirates 114 Japan 93 Pacific Islands 180 India 18 Canada 98 China 195 Germany 188 Total, incl. students from 67 other countries 6, 976
USQ’s International Students 2003 § § § Singapore 1, 598 Malaysia 2, 327 Hong Kong 565 South Africa 209 United Arab Emirates 114 Japan 93 Pacific Islands 180 India 18 Canada 98 China 195 Germany 188 Total, incl. students from 67 other countries 6, 976
 Five Generations of Distance Education Technology § The Correspondence Model § The Multimedia Model § The Telelearning Model § The Flexible Learning Model § The Intelligent Flexible Learning Model
Five Generations of Distance Education Technology § The Correspondence Model § The Multimedia Model § The Telelearning Model § The Flexible Learning Model § The Intelligent Flexible Learning Model
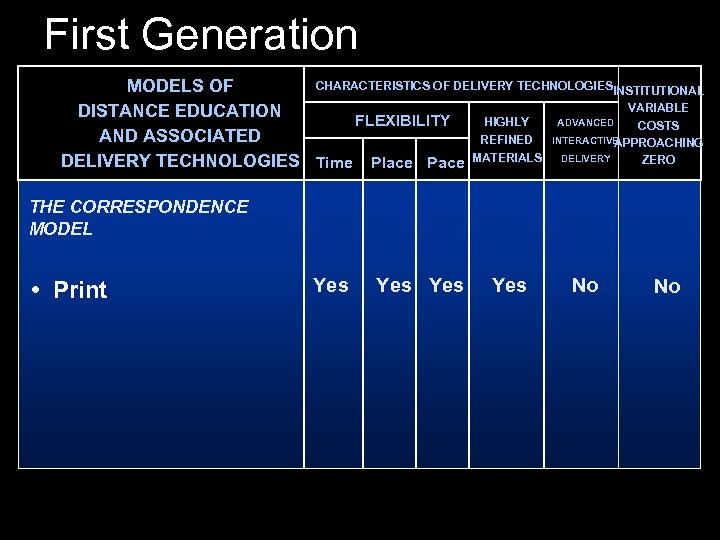 First Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE CORRESPONDENCE MODEL • Print Yes Yes No No
First Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE CORRESPONDENCE MODEL • Print Yes Yes No No
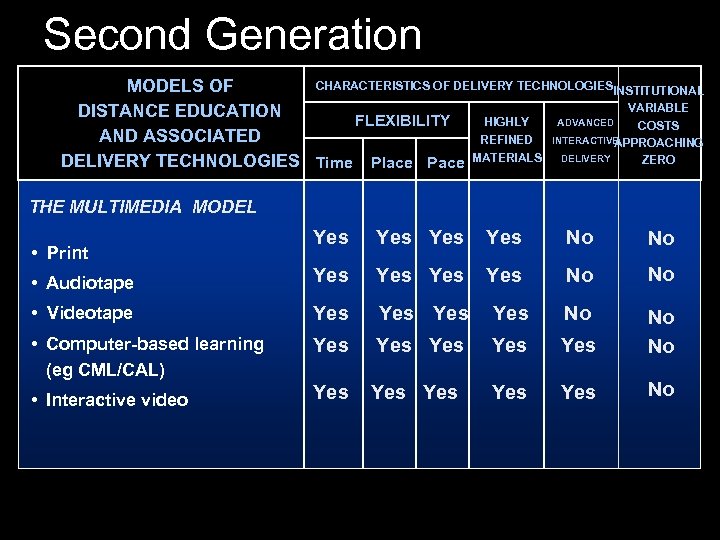 Second Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE MULTIMEDIA MODEL Yes Yes No No • Audiotape Yes Yes No No • Videotape Yes Yes No • Computer-based learning (eg CML/CAL) Yes Yes Yes No No • Interactive video Yes Yes Yes No • Print
Second Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE MULTIMEDIA MODEL Yes Yes No No • Audiotape Yes Yes No No • Videotape Yes Yes No • Computer-based learning (eg CML/CAL) Yes Yes Yes No No • Interactive video Yes Yes Yes No • Print
 Variable costs tend to increase or decrease directly (often linearly) with fluctuations in the volume of activity. In traditional distance education delivery, the distribution of packages of self-instructional materials (printed study guides, audiotapes, videotapes, etc) is a variable cost, which varies in direct proportion to the number of students enrolled.
Variable costs tend to increase or decrease directly (often linearly) with fluctuations in the volume of activity. In traditional distance education delivery, the distribution of packages of self-instructional materials (printed study guides, audiotapes, videotapes, etc) is a variable cost, which varies in direct proportion to the number of students enrolled.
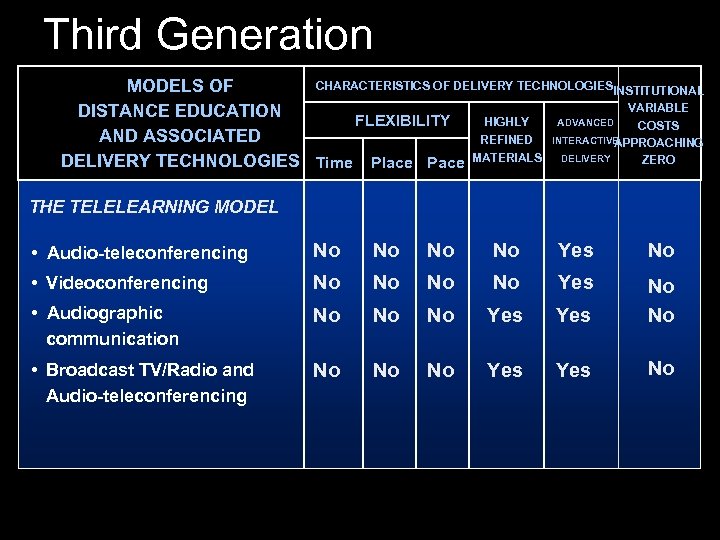 Third Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE TELELEARNING MODEL • Audio-teleconferencing No No Yes No • Videoconferencing No No Yes • Audiographic communication No No No Yes No No • Broadcast TV/Radio and Audio-teleconferencing No No No Yes No
Third Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE TELELEARNING MODEL • Audio-teleconferencing No No Yes No • Videoconferencing No No Yes • Audiographic communication No No No Yes No No • Broadcast TV/Radio and Audio-teleconferencing No No No Yes No
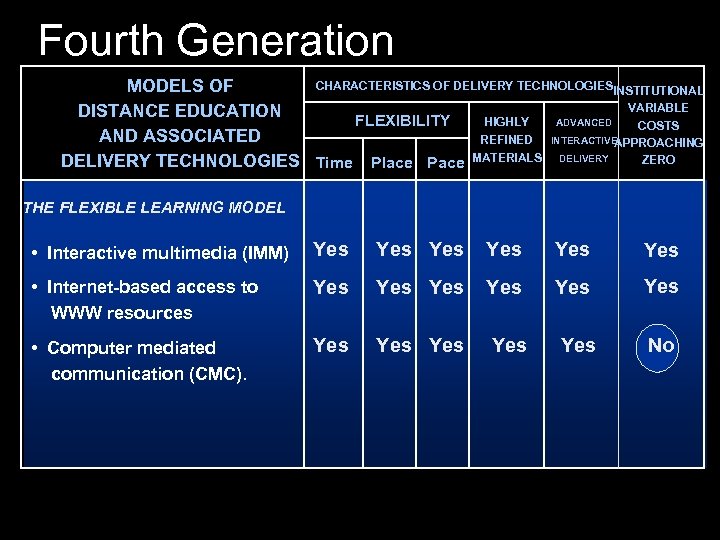 Fourth Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE FLEXIBLE LEARNING MODEL • Interactive multimedia (IMM) Yes Yes Yes • Internet-based access to WWW resources Yes Yes Yes • Computer mediated communication (CMC). Yes Yes Yes No
Fourth Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE FLEXIBLE LEARNING MODEL • Interactive multimedia (IMM) Yes Yes Yes • Internet-based access to WWW resources Yes Yes Yes • Computer mediated communication (CMC). Yes Yes Yes No
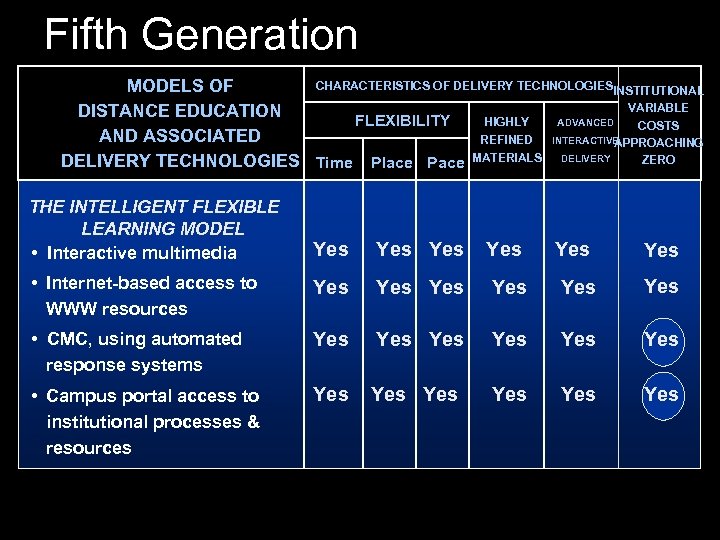 Fifth Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE INTELLIGENT FLEXIBLE LEARNING MODEL • Interactive multimedia Yes Yes Yes • Internet-based access to WWW resources Yes Yes Yes • CMC, using automated response systems Yes Yes Yes • Campus portal access to institutional processes & resources Yes Yes Yes
Fifth Generation CHARACTERISTICS OF DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIESINSTITUTIONAL MODELS OF VARIABLE DISTANCE EDUCATION HIGHLY ADVANCED FLEXIBILITY COSTS AND ASSOCIATED REFINED INTERACTIVE APPROACHING ZERO DELIVERY TECHNOLOGIES Time Place Pace MATERIALS DELIVERY THE INTELLIGENT FLEXIBLE LEARNING MODEL • Interactive multimedia Yes Yes Yes • Internet-based access to WWW resources Yes Yes Yes • CMC, using automated response systems Yes Yes Yes • Campus portal access to institutional processes & resources Yes Yes Yes
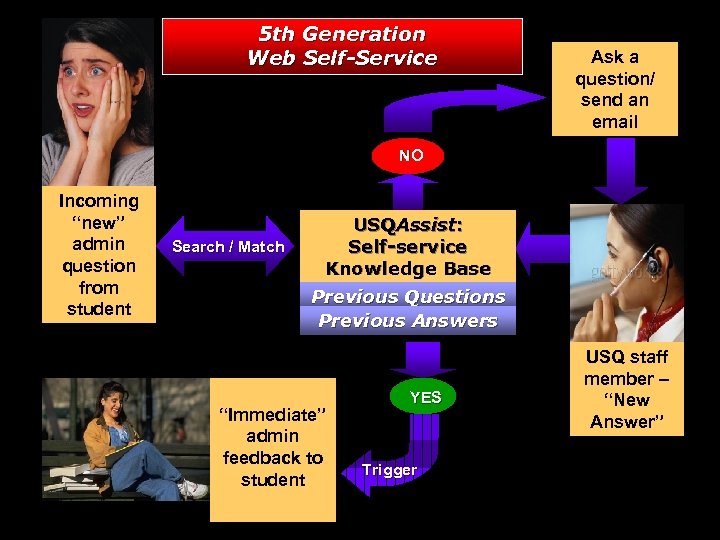 5 th Generation Web Self-Service Ask a question/ send an email NO Incoming “new” admin question from student Search / Match USQAssist: Self-service Knowledge Base Previous Questions Previous Answers “Immediate” admin feedback to student YES Trigger USQ staff member – “New Answer”
5 th Generation Web Self-Service Ask a question/ send an email NO Incoming “new” admin question from student Search / Match USQAssist: Self-service Knowledge Base Previous Questions Previous Answers “Immediate” admin feedback to student YES Trigger USQ staff member – “New Answer”
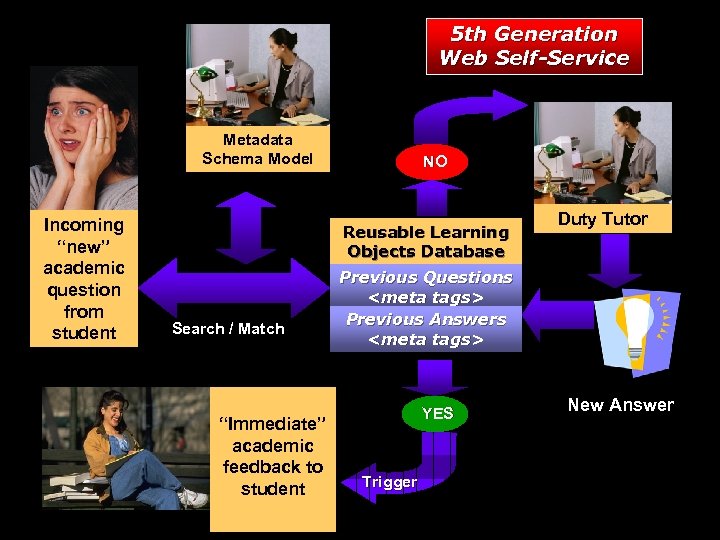 5 th Generation Web Self-Service Metadata Schema Model Incoming “new” academic question from student NO Reusable Learning Objects Database Search / Match “Immediate” academic feedback to student Duty Tutor Previous Questions Previous Answers YES Trigger New Answer
5 th Generation Web Self-Service Metadata Schema Model Incoming “new” academic question from student NO Reusable Learning Objects Database Search / Match “Immediate” academic feedback to student Duty Tutor Previous Questions Previous Answers YES Trigger New Answer


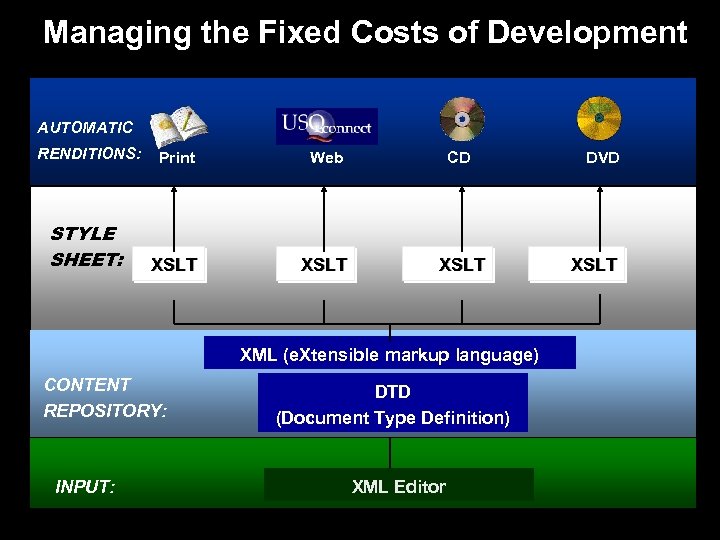 Managing the Fixed Costs of Development AUTOMATIC RENDITIONS: Print Web CD STYLE SHEET: XSLT XML (e. Xtensible markup language) CONTENT REPOSITORY: INPUT: DTD (Document Type Definition) XML Editor DVD XSLT
Managing the Fixed Costs of Development AUTOMATIC RENDITIONS: Print Web CD STYLE SHEET: XSLT XML (e. Xtensible markup language) CONTENT REPOSITORY: INPUT: DTD (Document Type Definition) XML Editor DVD XSLT

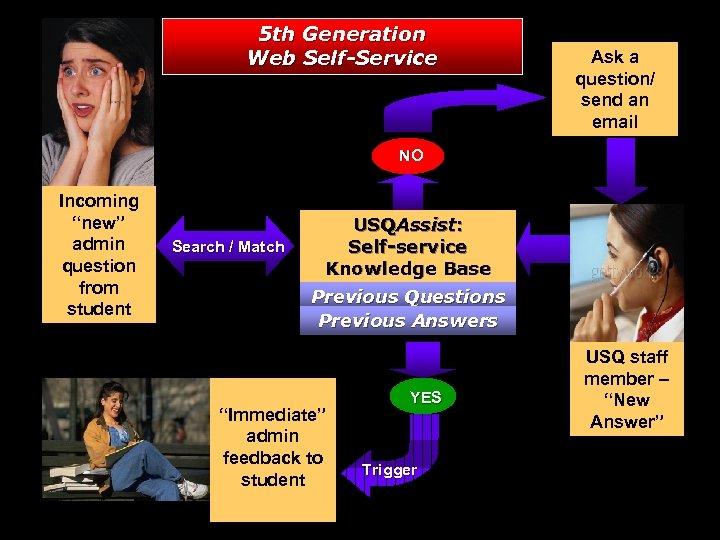 5 th Generation Web Self-Service Ask a question/ send an email NO Incoming “new” admin question from student Search / Match USQAssist: Self-service Knowledge Base Previous Questions Previous Answers “Immediate” admin feedback to student YES Trigger USQ staff member – “New Answer”
5 th Generation Web Self-Service Ask a question/ send an email NO Incoming “new” admin question from student Search / Match USQAssist: Self-service Knowledge Base Previous Questions Previous Answers “Immediate” admin feedback to student YES Trigger USQ staff member – “New Answer”
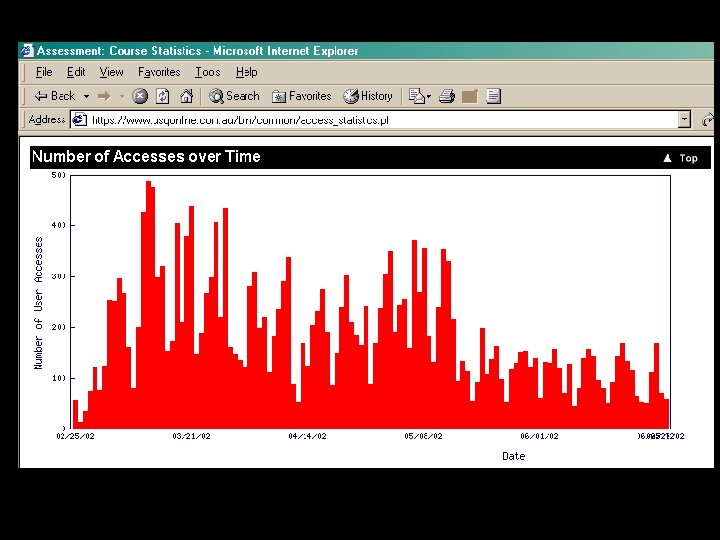
 USQAssist Self-Service Knowledge Base To 31 October 2003 the system received: § § § an average 10, 300 hits per week; 169, 000 student contacts; 106, 400 answers viewed; 42, 200 searches performed; 6, 190 questions using the “Ask a Question” facility. During S 2, the e-CRM also managed a further 67, 766 email queries.
USQAssist Self-Service Knowledge Base To 31 October 2003 the system received: § § § an average 10, 300 hits per week; 169, 000 student contacts; 106, 400 answers viewed; 42, 200 searches performed; 6, 190 questions using the “Ask a Question” facility. During S 2, the e-CRM also managed a further 67, 766 email queries.
 Managing the Variable Costs of Customer Contacts Face-to-face contact US $8. 00 Phone contact (average) Email Web Self-Service US $4. 00 - $6. 00 US $0. 50 - $2. 50 US $0. 24 Source: Gartner Group Inc.
Managing the Variable Costs of Customer Contacts Face-to-face contact US $8. 00 Phone contact (average) Email Web Self-Service US $4. 00 - $6. 00 US $0. 50 - $2. 50 US $0. 24 Source: Gartner Group Inc.

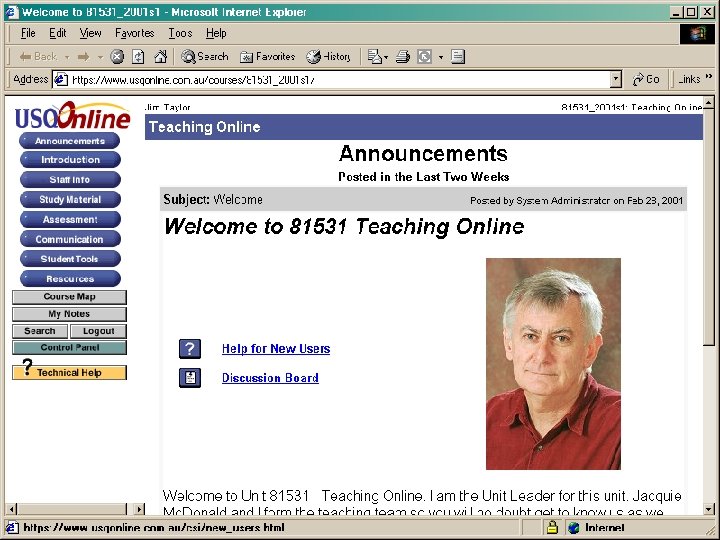
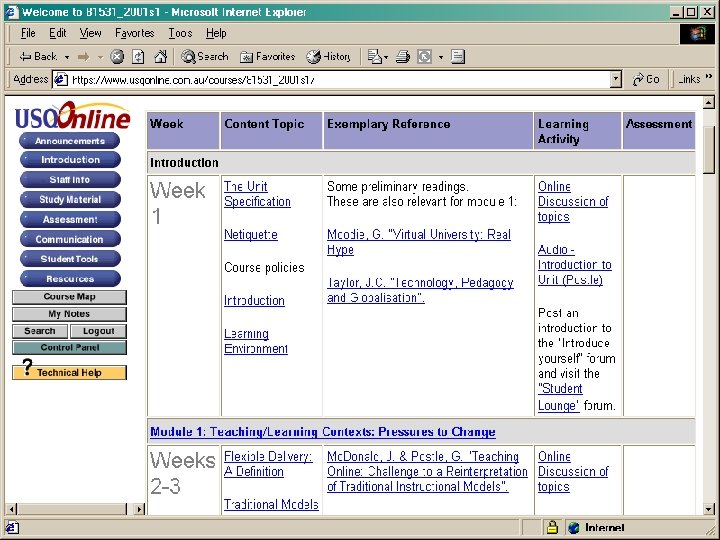
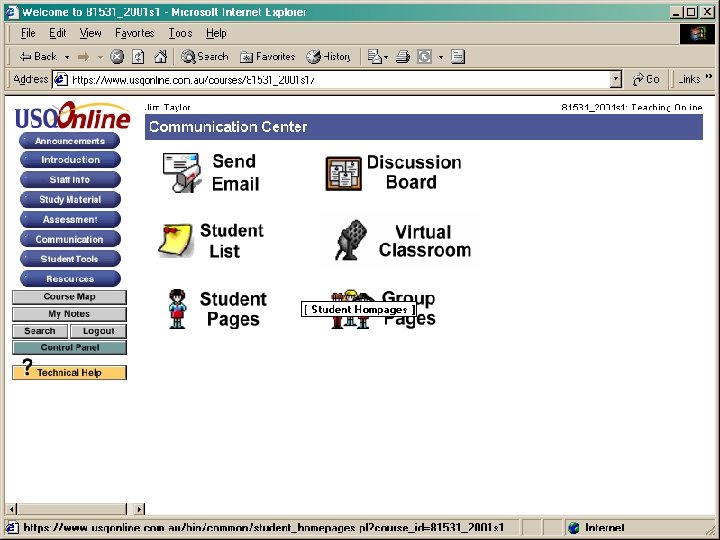
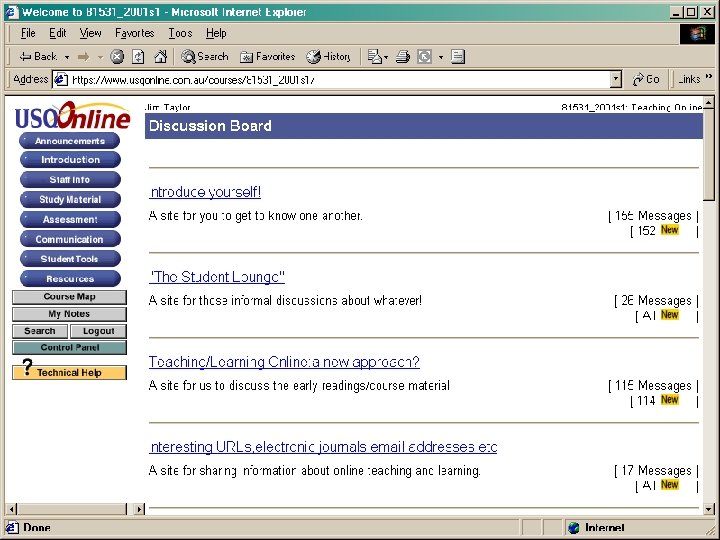
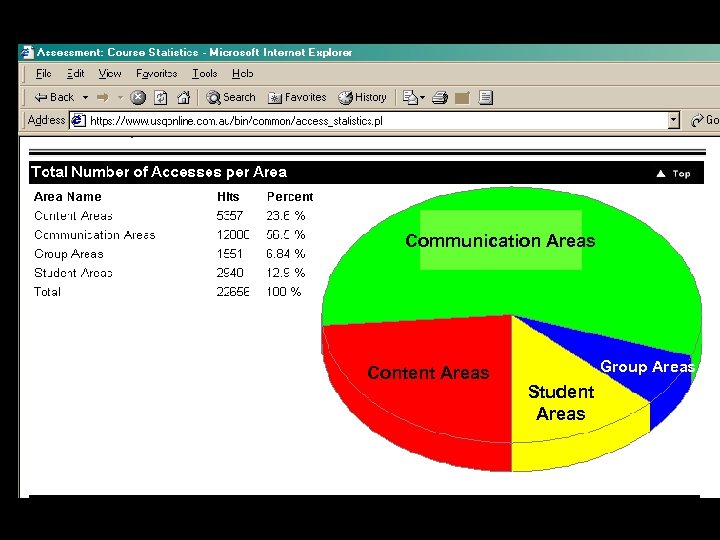 Communication Areas Content Areas Group Areas Student Areas
Communication Areas Content Areas Group Areas Student Areas
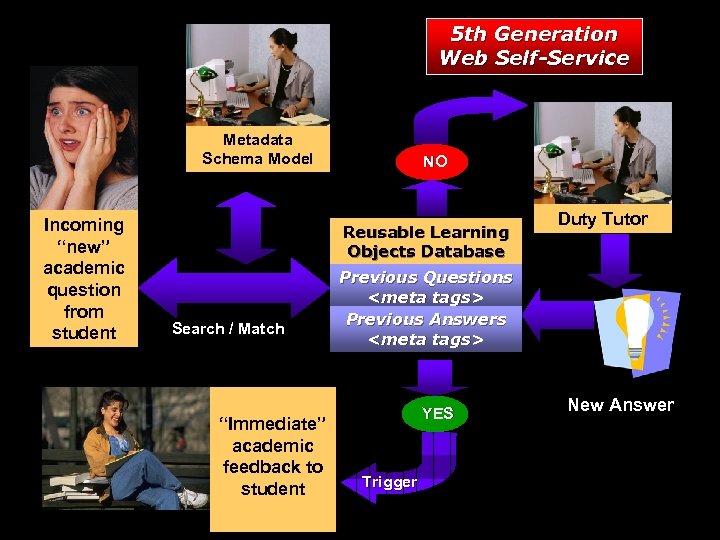 5 th Generation Web Self-Service Metadata Schema Model Incoming “new” academic question from student NO Reusable Learning Objects Database Search / Match “Immediate” academic feedback to student Duty Tutor Previous Questions Previous Answers YES Trigger New Answer
5 th Generation Web Self-Service Metadata Schema Model Incoming “new” academic question from student NO Reusable Learning Objects Database Search / Match “Immediate” academic feedback to student Duty Tutor Previous Questions Previous Answers YES Trigger New Answer
 The Potential of e-Learning § From transmission to transaction § From the independent learner to the inter-dependent learner
The Potential of e-Learning § From transmission to transaction § From the independent learner to the inter-dependent learner
 Brown & Duguid (2000) emphasised the importance of regarding learning as a social act: “Practice is an effective teacher, and community of practice an ideal learning environment. ”
Brown & Duguid (2000) emphasised the importance of regarding learning as a social act: “Practice is an effective teacher, and community of practice an ideal learning environment. ”
 Relevant Instructional Design Theories § ZPD: Zone of proximal development (Vygotsky, 1978; 1981) § Reflective practitioner (Schon, 1987) § Communities of practice (Brown, Collins & Duguid, 1989) § Situated cognition (Lave & Wenger, 1991)
Relevant Instructional Design Theories § ZPD: Zone of proximal development (Vygotsky, 1978; 1981) § Reflective practitioner (Schon, 1987) § Communities of practice (Brown, Collins & Duguid, 1989) § Situated cognition (Lave & Wenger, 1991)
 Lave & Wenger (1991) emphasised the importance of the social context in which the learner is immersed, and learning as legitimate peripheral participation in a community of practice.
Lave & Wenger (1991) emphasised the importance of the social context in which the learner is immersed, and learning as legitimate peripheral participation in a community of practice.
 In the online context, legitimate peripheral participation has become associated with the term “Lurker”. “One of the “silent majority” in an electronic forum; one who posts occasionally or not at all but is known to read the group's postings regularly. ” (The Jargon dictionary, 2002)
In the online context, legitimate peripheral participation has become associated with the term “Lurker”. “One of the “silent majority” in an electronic forum; one who posts occasionally or not at all but is known to read the group's postings regularly. ” (The Jargon dictionary, 2002)
 Student Participation Profiles § Proactive Workers § Peripheral Lurkers § Parsimonious Shirkers
Student Participation Profiles § Proactive Workers § Peripheral Lurkers § Parsimonious Shirkers
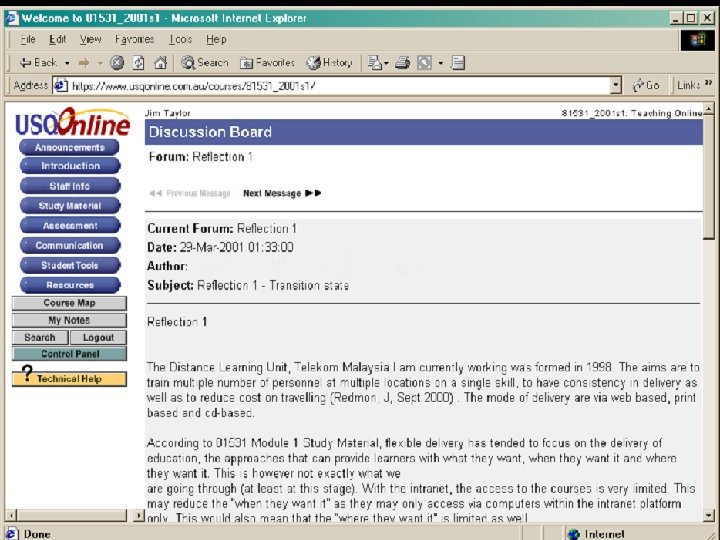
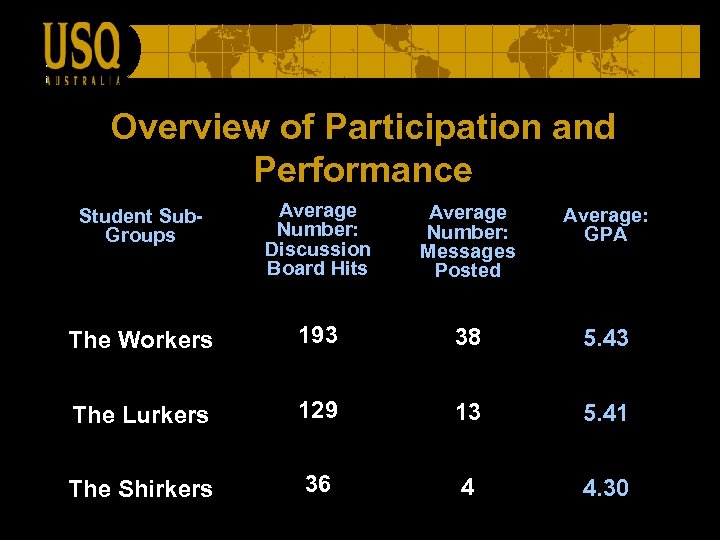 Overview of Participation and Performance Student Sub. Groups Average Number: Discussion Board Hits Average Number: Messages Posted Average: GPA The Workers 193 38 5. 43 The Lurkers 129 13 5. 41 The Shirkers 36 4 4. 30
Overview of Participation and Performance Student Sub. Groups Average Number: Discussion Board Hits Average Number: Messages Posted Average: GPA The Workers 193 38 5. 43 The Lurkers 129 13 5. 41 The Shirkers 36 4 4. 30
 Outcome The academic performance of the lurkers was on average not much less than that of the workers, thereby supporting the notion of learning as legitimate peripheral participation.
Outcome The academic performance of the lurkers was on average not much less than that of the workers, thereby supporting the notion of learning as legitimate peripheral participation.
 E-Learning Futures The success of the lurkers augurs well for the use of e-learning facilitated by intelligent databases and the flexibility inherent in interacting with virtual cohorts of students.
E-Learning Futures The success of the lurkers augurs well for the use of e-learning facilitated by intelligent databases and the flexibility inherent in interacting with virtual cohorts of students.
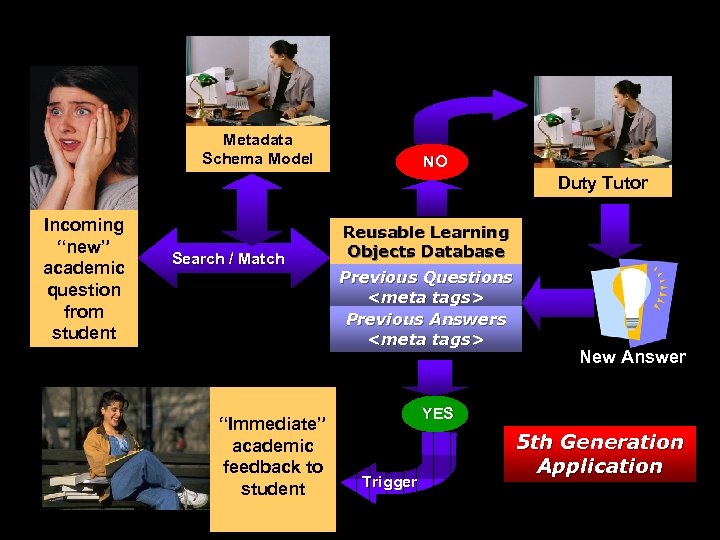 Metadata Schema Model NO Duty Tutor Incoming “new” academic question from student Search / Match “Immediate” academic feedback to student Reusable Learning Objects Database Previous Questions Previous Answers New Answer YES Trigger 5 th Generation Application
Metadata Schema Model NO Duty Tutor Incoming “new” academic question from student Search / Match “Immediate” academic feedback to student Reusable Learning Objects Database Previous Questions Previous Answers New Answer YES Trigger 5 th Generation Application
 5 th Generation In effect, fifth generation distance provides students with better quality tuition and more effective pedagogical and administrative support services at lower cost.
5 th Generation In effect, fifth generation distance provides students with better quality tuition and more effective pedagogical and administrative support services at lower cost.
 The e-Revolution “Any new technology environment eventually creates a totally new human environment”. Marshall Mc. Luhan
The e-Revolution “Any new technology environment eventually creates a totally new human environment”. Marshall Mc. Luhan


