bdd7da53cdbe323521c3b811055cb8a6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 e. Health Opportunities and Challenges Dr. R. S. Khandpur Director General, Pushpa Gujral Science City
e. Health Opportunities and Challenges Dr. R. S. Khandpur Director General, Pushpa Gujral Science City
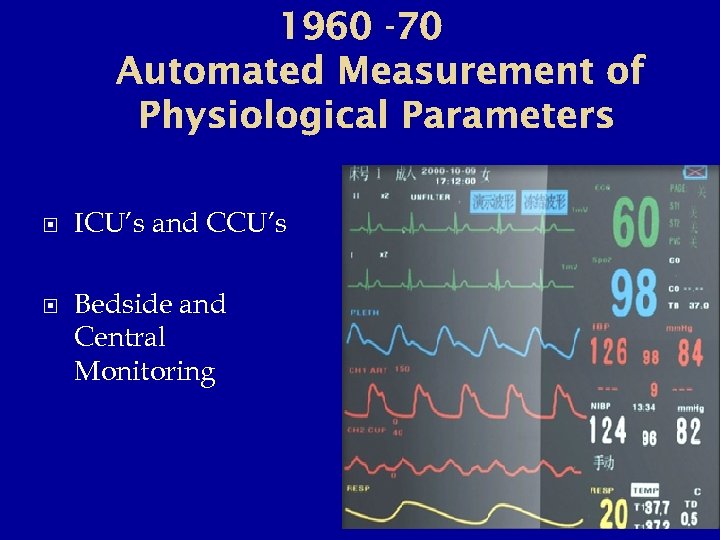 1960 -70 Automated Measurement of Physiological Parameters ICU’s and CCU’s Bedside and Central Monitoring
1960 -70 Automated Measurement of Physiological Parameters ICU’s and CCU’s Bedside and Central Monitoring
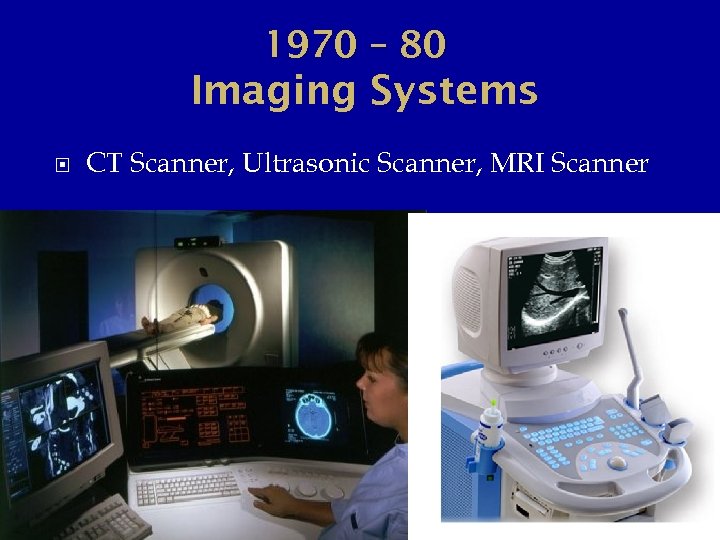 1970 – 80 Imaging Systems CT Scanner, Ultrasonic Scanner, MRI Scanner
1970 – 80 Imaging Systems CT Scanner, Ultrasonic Scanner, MRI Scanner
 1980 – 1990 Intelligent Instrumentation Use of Microprocessors and Micro-controllers
1980 – 1990 Intelligent Instrumentation Use of Microprocessors and Micro-controllers
 1990 – 2000 PC based Instrumentation (IT)
1990 – 2000 PC based Instrumentation (IT)
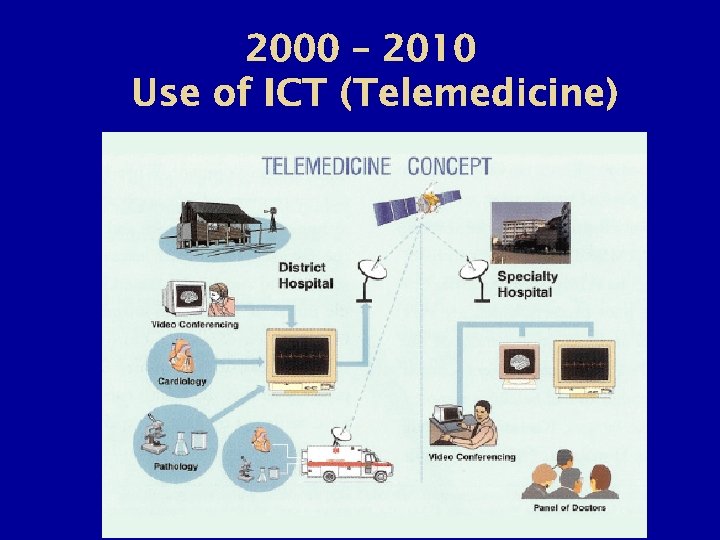 2000 – 2010 Use of ICT (Telemedicine)
2000 – 2010 Use of ICT (Telemedicine)
 2010 - - e-Health, m-Health, Home Care Devices, Wireless Monitors
2010 - - e-Health, m-Health, Home Care Devices, Wireless Monitors
 Role of ICT in Healthcare "The revolution in communication technology needs to be harnessed to deliver healthcare services in rural India. The need is to create an Health-care system that is both affordable and effective" – Former President Dr. A. P. J Abdul Kalam. ICT, specifically the internet enables people to get access to huge pool of information irrespective of caste, creed, race, sex, physical ability, location and social background.
Role of ICT in Healthcare "The revolution in communication technology needs to be harnessed to deliver healthcare services in rural India. The need is to create an Health-care system that is both affordable and effective" – Former President Dr. A. P. J Abdul Kalam. ICT, specifically the internet enables people to get access to huge pool of information irrespective of caste, creed, race, sex, physical ability, location and social background.
 Telemetry & Telemedicine Telemetry: means for monitoring and studying human and animal physiological functions from a remote site. Telemedicine: use of electronic information and communications technologies to provide and support health care when distance separates the patient and the doctor. In telemedicine. The expertise is transferred and not the patient.
Telemetry & Telemedicine Telemetry: means for monitoring and studying human and animal physiological functions from a remote site. Telemedicine: use of electronic information and communications technologies to provide and support health care when distance separates the patient and the doctor. In telemedicine. The expertise is transferred and not the patient.
 Tele. Health & e. Health Telehealth: use of electronic information and telecommunication technologies to support long-distance clinical health care, patient and professional health-related education, public health and health administration. Broadly includes: telemedicine, education and informatics. e-Health: refers to all forms of electronic health care delivered over the internet
Tele. Health & e. Health Telehealth: use of electronic information and telecommunication technologies to support long-distance clinical health care, patient and professional health-related education, public health and health administration. Broadly includes: telemedicine, education and informatics. e-Health: refers to all forms of electronic health care delivered over the internet
 What is e. Health? e. Health = Medicine + Communication + Information + Society e. Health is an emerging field of medical informatics. Refers to the delivery of health services and information using the Internet
What is e. Health? e. Health = Medicine + Communication + Information + Society e. Health is an emerging field of medical informatics. Refers to the delivery of health services and information using the Internet
 What is e. Health? Characterizes not only technical development, but a new way of working, an attitude and a commitment for networked, global thinking. Uses ICT to improve healthcare locally, regionally and worldwide.
What is e. Health? Characterizes not only technical development, but a new way of working, an attitude and a commitment for networked, global thinking. Uses ICT to improve healthcare locally, regionally and worldwide.
 e. Health Applications e. Health includes a range of services in medicine/healthcare and information technology. Electronic Health Records: enable easy communication of patient data between different healthcare professionals (GPs, specialists, care team, pharmacy) Telemedicine: includes all types of physical and psychological measurements that do not require a patient to travel to a specialist.
e. Health Applications e. Health includes a range of services in medicine/healthcare and information technology. Electronic Health Records: enable easy communication of patient data between different healthcare professionals (GPs, specialists, care team, pharmacy) Telemedicine: includes all types of physical and psychological measurements that do not require a patient to travel to a specialist.
 e. Health Consumer Health Informatics: both healthy individuals and patients want to be informed on medical topics. Health Knowledge Management : overview of latest medical journals, best practice guidelines or epidemiological tracking. Examples include physician resources such as Medscape and MDLinx. Virtual Healthcare Teams: consist of healthcare professionals who collaborate and share information on patients through digital means
e. Health Consumer Health Informatics: both healthy individuals and patients want to be informed on medical topics. Health Knowledge Management : overview of latest medical journals, best practice guidelines or epidemiological tracking. Examples include physician resources such as Medscape and MDLinx. Virtual Healthcare Teams: consist of healthcare professionals who collaborate and share information on patients through digital means
 e. Health m. Health: includes the use of mobile devices in collecting aggregate and patient level health data, providing healthcare information to practitioners and patients, real-time monitoring of patient vitals, and direct provision of care via mobile telemedicine. Healthcare Information Systems: refer to software solutions for appointment scheduling, patient data management, work schedule management and other administrative and financial tasks.
e. Health m. Health: includes the use of mobile devices in collecting aggregate and patient level health data, providing healthcare information to practitioners and patients, real-time monitoring of patient vitals, and direct provision of care via mobile telemedicine. Healthcare Information Systems: refer to software solutions for appointment scheduling, patient data management, work schedule management and other administrative and financial tasks.
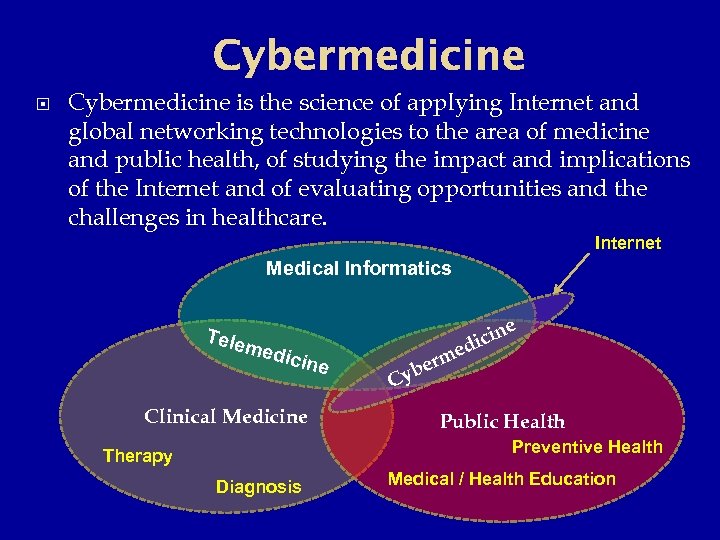 Cybermedicine is the science of applying Internet and global networking technologies to the area of medicine and public health, of studying the impact and implications of the Internet and of evaluating opportunities and the challenges in healthcare. Internet Medical Informatics Tele e icin d me r ybe med icine Clinical Medicine C Public Health Preventive Health Therapy Diagnosis Medical / Health Education
Cybermedicine is the science of applying Internet and global networking technologies to the area of medicine and public health, of studying the impact and implications of the Internet and of evaluating opportunities and the challenges in healthcare. Internet Medical Informatics Tele e icin d me r ybe med icine Clinical Medicine C Public Health Preventive Health Therapy Diagnosis Medical / Health Education
 Cybermedicine On-line Consultation On-line Information On-line Pharmacy
Cybermedicine On-line Consultation On-line Information On-line Pharmacy
 Sources used to Access Health Information
Sources used to Access Health Information
 Ethical Issues in Cybermedicine Healing yourself via You. Tube: The Amazing and Frightening future of Healthcare Tele-Consultation: Doctors credential, locating the cyber doctor in case of wrong medical advise, responsibility and privacy issues. Tele-Information: Validity of information, reliability and authenticity issues Tele-Pharmacy: Responsibility in case of side effects of drug, sale of unproved drugs, no doctor-patient relationship
Ethical Issues in Cybermedicine Healing yourself via You. Tube: The Amazing and Frightening future of Healthcare Tele-Consultation: Doctors credential, locating the cyber doctor in case of wrong medical advise, responsibility and privacy issues. Tele-Information: Validity of information, reliability and authenticity issues Tele-Pharmacy: Responsibility in case of side effects of drug, sale of unproved drugs, no doctor-patient relationship
 Hospital Management Information System Immediate On-line reports from Hospitals Tracking System for pregnant women and children Routine Immunization Monitoring System RFID smart cards for capturing patient and doctor data Video Conferencing System including teleeducation Employees Information System
Hospital Management Information System Immediate On-line reports from Hospitals Tracking System for pregnant women and children Routine Immunization Monitoring System RFID smart cards for capturing patient and doctor data Video Conferencing System including teleeducation Employees Information System

 TELEMEDICINE : WHAT ? “ Delivery of healthcare or exchange of medical information across distances using Information Technology. ” OBJECTIVE Move the information Instead of the patient.
TELEMEDICINE : WHAT ? “ Delivery of healthcare or exchange of medical information across distances using Information Technology. ” OBJECTIVE Move the information Instead of the patient.
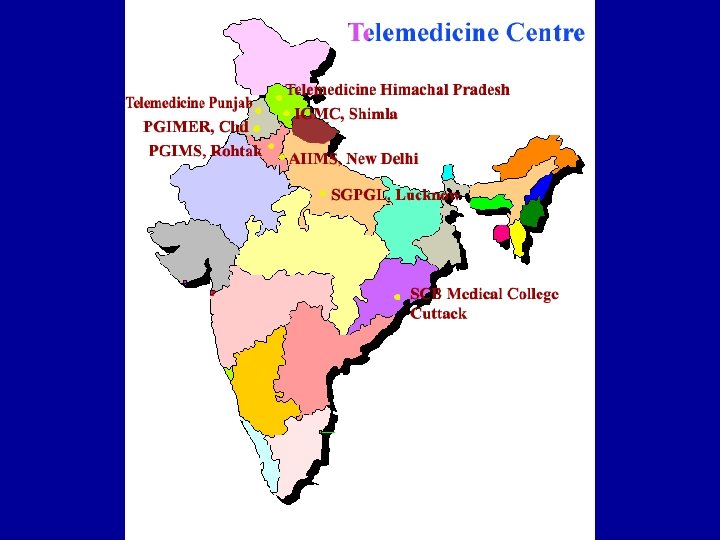
 TELE-MEDICINE at C-DAC, Mohali International Telemedicine Project (for Myanmar & Tanzania) Mo. U with Sehej for the e. Sanjeevani hosting on the CSCs under the Ne. GP Telemedicine project for Punjab Tele Ophthalmology Project from Mo. HFW Successfully implemented the pilot project Project sanctioned (C-DAC Mohali and Pune) Visualized 1998 1999 2002 2005 2007 2008
TELE-MEDICINE at C-DAC, Mohali International Telemedicine Project (for Myanmar & Tanzania) Mo. U with Sehej for the e. Sanjeevani hosting on the CSCs under the Ne. GP Telemedicine project for Punjab Tele Ophthalmology Project from Mo. HFW Successfully implemented the pilot project Project sanctioned (C-DAC Mohali and Pune) Visualized 1998 1999 2002 2005 2007 2008
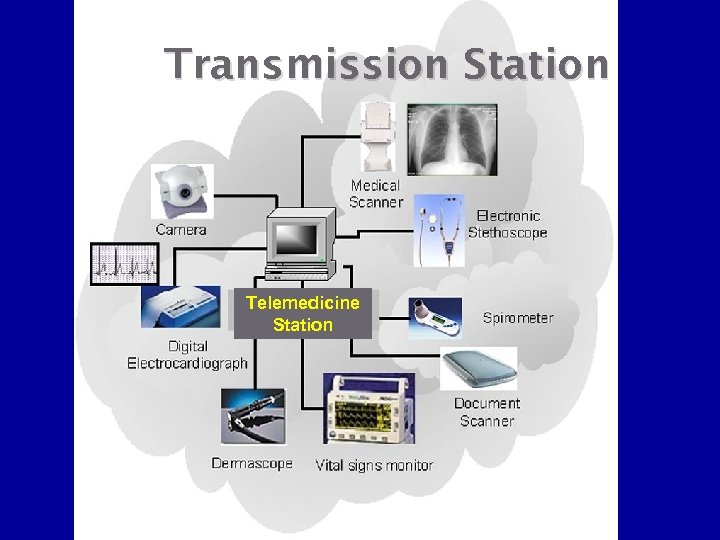 Transmission Station Telemedicine Station
Transmission Station Telemedicine Station
 WHY TELEMEDICINE ? Uneven geographic distribution of health care resources throughout the country – facilities and health manpower Inadequate access to health care on the part of certain segments of the population, including underprivileged, isolated Unabating rise in the cost of care, including the cost on transport Potential for improving the health status and quality of life gets limited Telemedicine proposed as a multifaceted response to address all the three problems simultaneously
WHY TELEMEDICINE ? Uneven geographic distribution of health care resources throughout the country – facilities and health manpower Inadequate access to health care on the part of certain segments of the population, including underprivileged, isolated Unabating rise in the cost of care, including the cost on transport Potential for improving the health status and quality of life gets limited Telemedicine proposed as a multifaceted response to address all the three problems simultaneously
 TELEMEDICINE • Telemedicine includes digital conversion and transmission of • Data • Still Images • Video • Audio - All patient related medical data Patient records / History Images; X-ray; CT, Ultrasound, MRI etc. Investigations Prescriptions etc.
TELEMEDICINE • Telemedicine includes digital conversion and transmission of • Data • Still Images • Video • Audio - All patient related medical data Patient records / History Images; X-ray; CT, Ultrasound, MRI etc. Investigations Prescriptions etc.
 TELEMEDICINE : HOW?
TELEMEDICINE : HOW?
 TELEMEDICINE : HOW? Transferring the information over the communication channels like : POTS, ISDN, ATM, VSAT, Internet etc. Getting back the views/opinion of the Specialist over the same channel.
TELEMEDICINE : HOW? Transferring the information over the communication channels like : POTS, ISDN, ATM, VSAT, Internet etc. Getting back the views/opinion of the Specialist over the same channel.
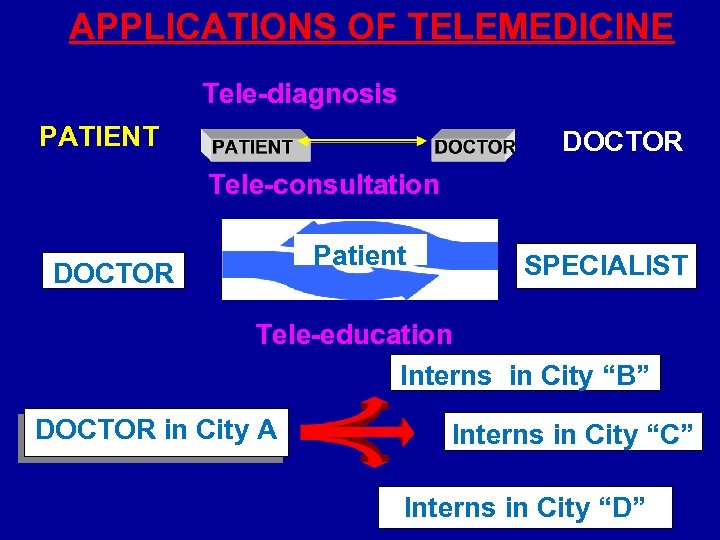 APPLICATIONS OF TELEMEDICINE Tele-diagnosis PATIENT DOCTOR Tele-consultation Patient DOCTOR SPECIALIST Tele-education Interns in City “B” DOCTOR in City A Interns in City “C” Interns in City “D”
APPLICATIONS OF TELEMEDICINE Tele-diagnosis PATIENT DOCTOR Tele-consultation Patient DOCTOR SPECIALIST Tele-education Interns in City “B” DOCTOR in City A Interns in City “C” Interns in City “D”
 TELEMEDICINE : TECHNIQUES EMPLOYED (Store & Forward Concept) Static Mode Pathology slides, physiological signals like ECG, EMG, Respiratory Rate etc. acquired/collected at patient’s end and transferred to the expert’s end. Still images and pictures scanned or directly acquired and communicated. (Real Time Concept) Dynamic Mode Regularly varying / condition dependant parameters like ECG, heart sounds & video clips transferred to the expert’s end online. Video Conferencing Desktop Video-conferencing.
TELEMEDICINE : TECHNIQUES EMPLOYED (Store & Forward Concept) Static Mode Pathology slides, physiological signals like ECG, EMG, Respiratory Rate etc. acquired/collected at patient’s end and transferred to the expert’s end. Still images and pictures scanned or directly acquired and communicated. (Real Time Concept) Dynamic Mode Regularly varying / condition dependant parameters like ECG, heart sounds & video clips transferred to the expert’s end online. Video Conferencing Desktop Video-conferencing.
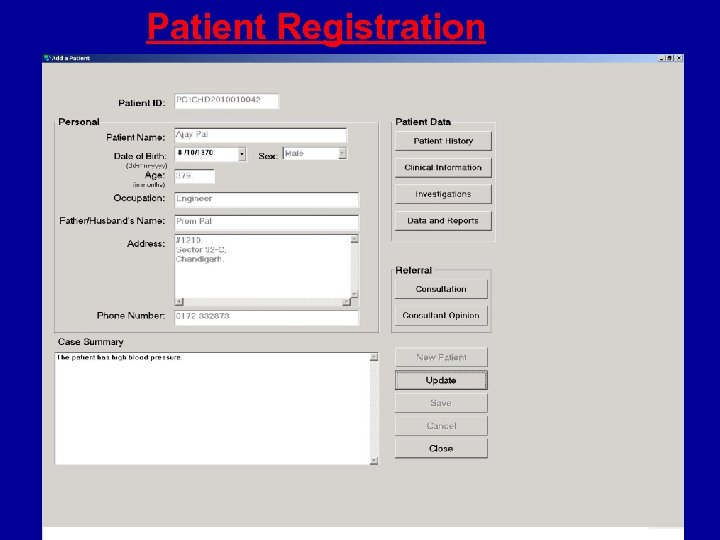 Patient Registration
Patient Registration
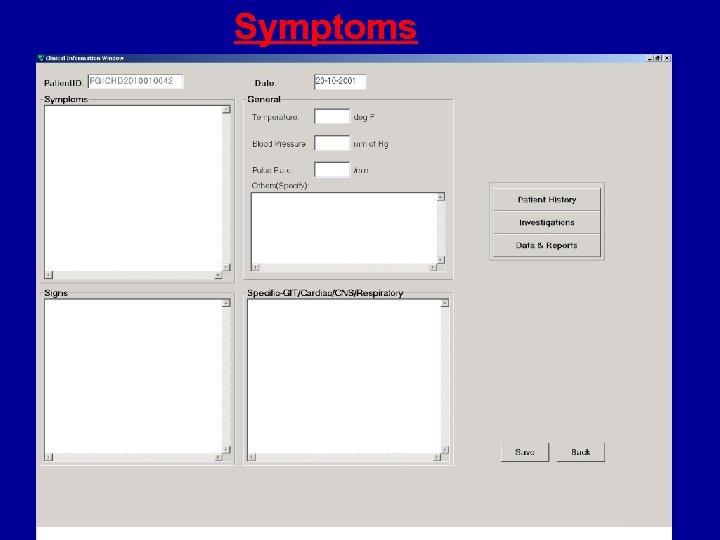 Symptoms
Symptoms
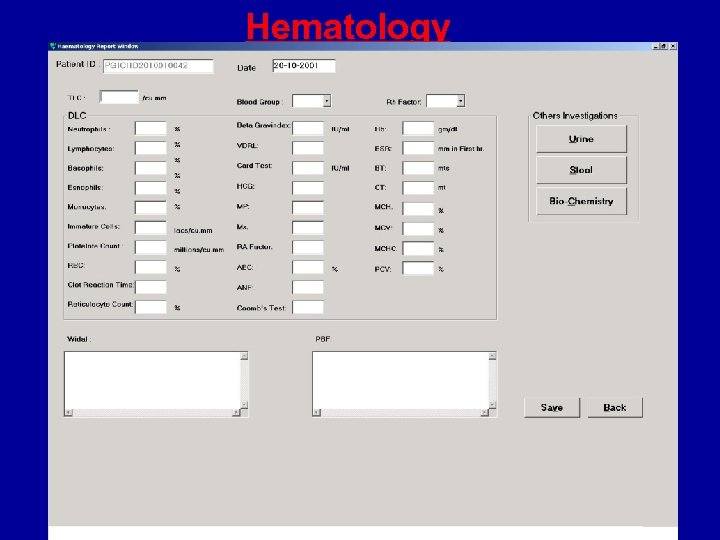 Hematology
Hematology
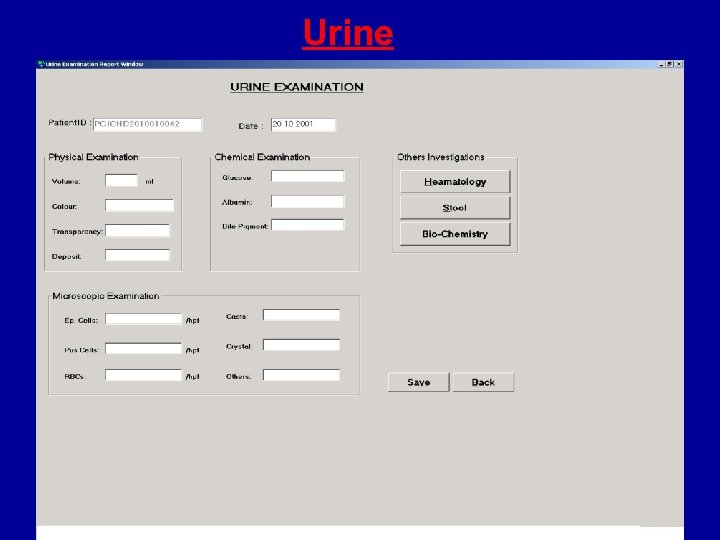 Urine
Urine
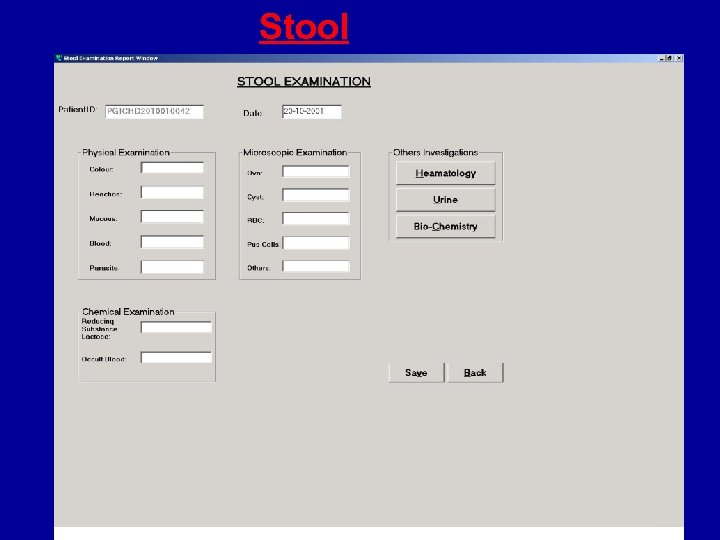 Stool
Stool
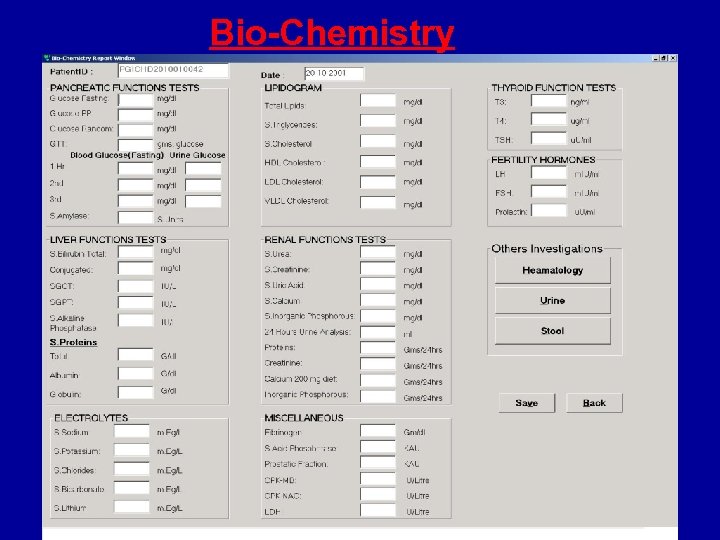 Bio-Chemistry
Bio-Chemistry
 Images
Images
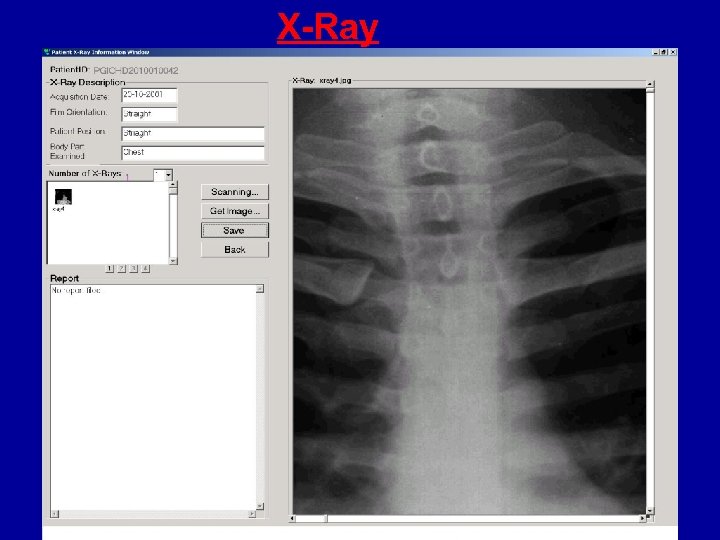 X-Ray
X-Ray
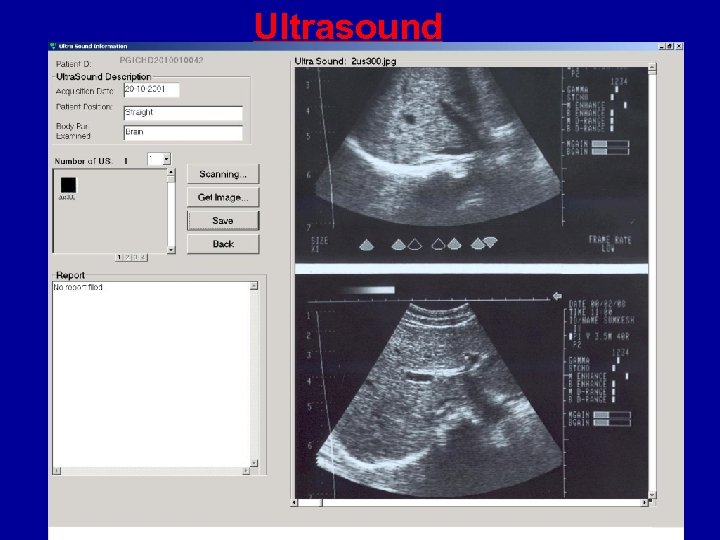 Ultrasound
Ultrasound
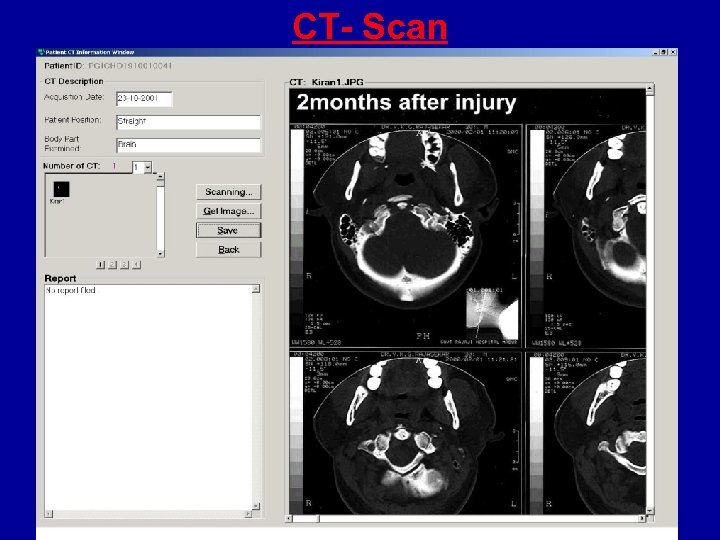 CT- Scan
CT- Scan
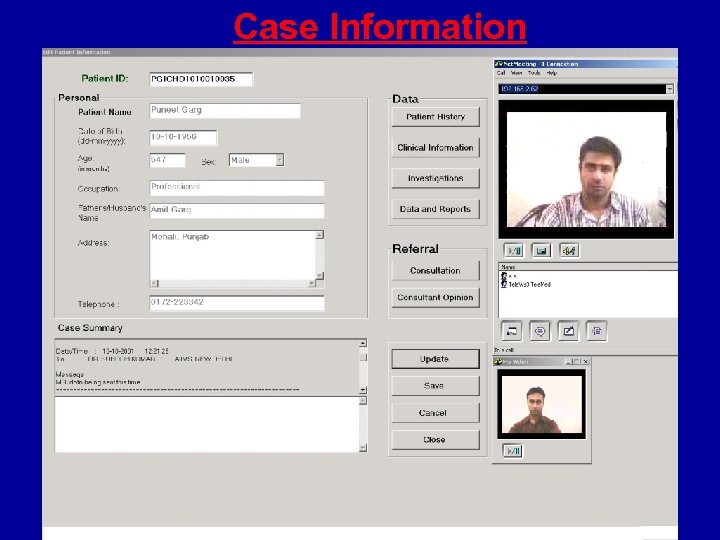 Case Information
Case Information
 TELEMEDICINE – GLOBAL MARKET Market of telemedicine increased from $ 4. 8 billion in 2006 to an expected level of $ 13. 9 billion by 2012. India with 70% population in rural areas has tremendous potential for telemedicine.
TELEMEDICINE – GLOBAL MARKET Market of telemedicine increased from $ 4. 8 billion in 2006 to an expected level of $ 13. 9 billion by 2012. India with 70% population in rural areas has tremendous potential for telemedicine.
 TELEMEDICINE – GLOBAL MARKET Tele-home market currently accounts for 22% of the market and is expected to 37% of the telemedicine 2012 capture market by Telemedicine service market is expected to grow from $ 3. 6 billion in 2007 to $ 8. 3 billion in 2012, mainly driven by tele-hospital service market.
TELEMEDICINE – GLOBAL MARKET Tele-home market currently accounts for 22% of the market and is expected to 37% of the telemedicine 2012 capture market by Telemedicine service market is expected to grow from $ 3. 6 billion in 2007 to $ 8. 3 billion in 2012, mainly driven by tele-hospital service market.
 Market Drivers for Telemedicine Need for better clinical outcome (preference) Increasing acceptance by patients Centralized EHR / EMR Improved technology infrastructure Increased focus of Companies on telemedicine as a key to market differentiator Rising e-Health Care Market Growing investments in Tele-medicine (particularly by developing world, developed world in exotic telemedicine)
Market Drivers for Telemedicine Need for better clinical outcome (preference) Increasing acceptance by patients Centralized EHR / EMR Improved technology infrastructure Increased focus of Companies on telemedicine as a key to market differentiator Rising e-Health Care Market Growing investments in Tele-medicine (particularly by developing world, developed world in exotic telemedicine)
 Tele - Cardiology Major components in Tele - Home Care Health Care Services using tele-cardiology for early detection of abnormalities Hospitals outsourcing cardiology image management to specialists Cardiac patients experience higher comfort level with tele-cardiology Larger number of cardiac patients being monitored remotely Mobile Emergency services opting for telecardiology
Tele - Cardiology Major components in Tele - Home Care Health Care Services using tele-cardiology for early detection of abnormalities Hospitals outsourcing cardiology image management to specialists Cardiac patients experience higher comfort level with tele-cardiology Larger number of cardiac patients being monitored remotely Mobile Emergency services opting for telecardiology
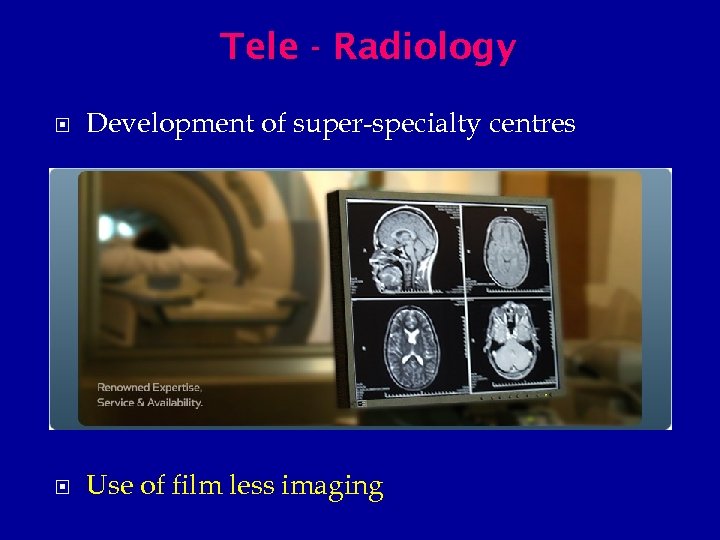 Tele - Radiology Development of super-specialty centres Use of film less imaging
Tele - Radiology Development of super-specialty centres Use of film less imaging
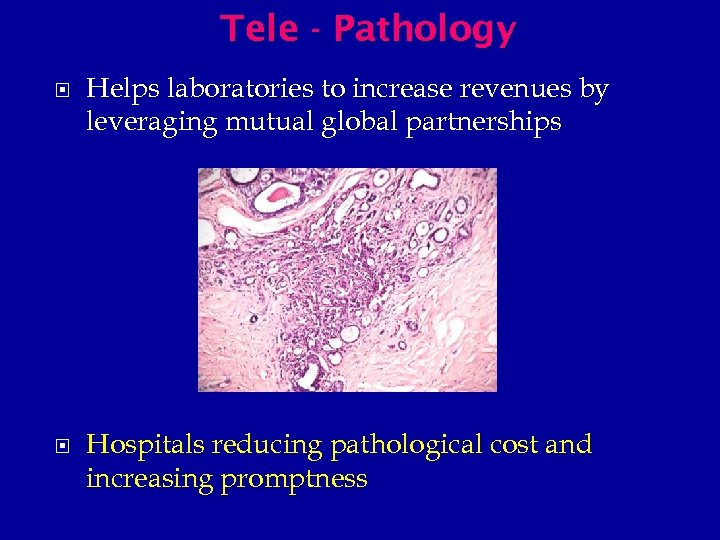 Tele - Pathology Helps laboratories to increase revenues by leveraging mutual global partnerships Hospitals reducing pathological cost and increasing promptness
Tele - Pathology Helps laboratories to increase revenues by leveraging mutual global partnerships Hospitals reducing pathological cost and increasing promptness
 m-Health and Mobile Telemedicine m-Health – Mobile health Information Technology refers to use of portable devices to create, store, retrieve and transmit data in real time between the end users (patients and doctors) 3. 5 billion mobile phones in use across the globe – number growing, more in developing countries offer great potential in tele-medicine.
m-Health and Mobile Telemedicine m-Health – Mobile health Information Technology refers to use of portable devices to create, store, retrieve and transmit data in real time between the end users (patients and doctors) 3. 5 billion mobile phones in use across the globe – number growing, more in developing countries offer great potential in tele-medicine.
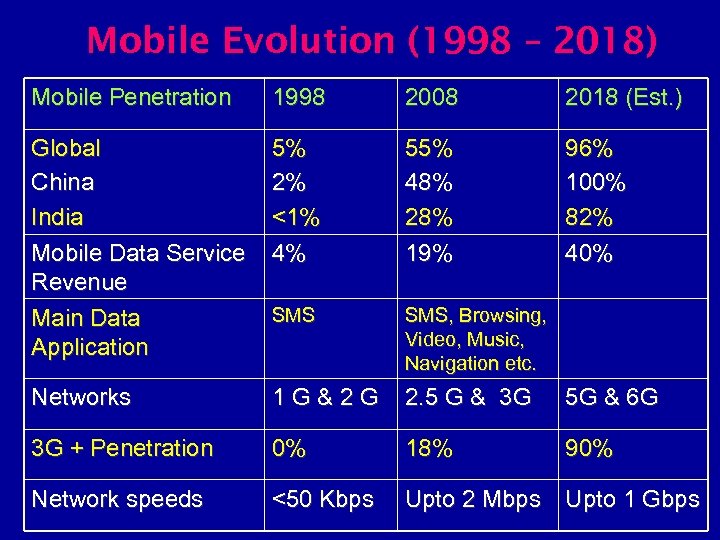 Mobile Evolution (1998 – 2018) Mobile Penetration 1998 2008 2018 (Est. ) Global China India Mobile Data Service Revenue Main Data Application 5% 2% <1% 4% 55% 48% 28% 19% 96% 100% 82% 40% SMS, Browsing, Video, Music, Navigation etc. Networks 1 G&2 G 2. 5 G & 3 G 5 G & 6 G 3 G + Penetration 0% 18% 90% Network speeds <50 Kbps Upto 2 Mbps Upto 1 Gbps
Mobile Evolution (1998 – 2018) Mobile Penetration 1998 2008 2018 (Est. ) Global China India Mobile Data Service Revenue Main Data Application 5% 2% <1% 4% 55% 48% 28% 19% 96% 100% 82% 40% SMS, Browsing, Video, Music, Navigation etc. Networks 1 G&2 G 2. 5 G & 3 G 5 G & 6 G 3 G + Penetration 0% 18% 90% Network speeds <50 Kbps Upto 2 Mbps Upto 1 Gbps
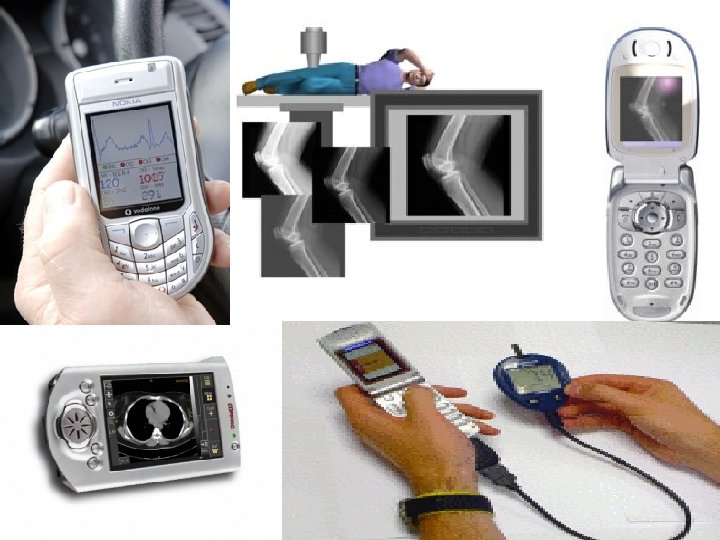
 Homeopathy on the Mobile Phone allows patients to Register Submit their case history Chat online with doctors Request or reschedule of appointments
Homeopathy on the Mobile Phone allows patients to Register Submit their case history Chat online with doctors Request or reschedule of appointments
 Homeopathy on the Mobile Phone allows patients to Commence or renew treatment plans Order medicines to be delivered at their homes Make secure payments Free consultation
Homeopathy on the Mobile Phone allows patients to Commence or renew treatment plans Order medicines to be delivered at their homes Make secure payments Free consultation
 KEY ISSUES * Common standards for sharing data i. e. DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine) developed by American College of Radiology. * Licensing for consultation via telemedicine. *Reimbursement of expenses for consultation on telemedicine. * Security of data : privacy and confidentiality. * Legal and regulatory issues. * Electronic signatures. * Exploitation of patients.
KEY ISSUES * Common standards for sharing data i. e. DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine) developed by American College of Radiology. * Licensing for consultation via telemedicine. *Reimbursement of expenses for consultation on telemedicine. * Security of data : privacy and confidentiality. * Legal and regulatory issues. * Electronic signatures. * Exploitation of patients.
 Key Technical Challenges Complex networks demanding standardization across integrated Telemedicine Systems Bench-marking global telemedicine particularly Tele-Home Care Units programmes, Reliability issues (Equipment & availability of Experts) Increasing speed and reliability of data transfer Increased Using use of wireless technologies in Telemedicine more computer based diagnosis Launching more user friendly technology
Key Technical Challenges Complex networks demanding standardization across integrated Telemedicine Systems Bench-marking global telemedicine particularly Tele-Home Care Units programmes, Reliability issues (Equipment & availability of Experts) Increasing speed and reliability of data transfer Increased Using use of wireless technologies in Telemedicine more computer based diagnosis Launching more user friendly technology
 Professional Challenges Need for a new breed of Healthcare Professionals, Healthcare Administrators and Healthcare Technologists Healthcare Industry is the last adopter of technology. In Healthcare Education even today the medical, dental, nursing, pharmacology do not have courses on IT. Requires immediate action to include in all courses related to Healthcare delivery.
Professional Challenges Need for a new breed of Healthcare Professionals, Healthcare Administrators and Healthcare Technologists Healthcare Industry is the last adopter of technology. In Healthcare Education even today the medical, dental, nursing, pharmacology do not have courses on IT. Requires immediate action to include in all courses related to Healthcare delivery.
 e. Health is the single most important revolution in Healthcare since the advent of modern medicine. Its growth is inevitable Thanks … www. pgsciencecity. org
e. Health is the single most important revolution in Healthcare since the advent of modern medicine. Its growth is inevitable Thanks … www. pgsciencecity. org


