943d3dced571c6afffb0759b3f82c621.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 E-Government Gateway Overview
E-Government Gateway Overview
 What is the Gateway? • A conduit for secure transactions between customers and government, covering Inputs, Outputs and Payments to Government; • Gateway does not host e-forms or applications that generate or consume transactions; • Gateway must communicate with front office and back office components to deliver an e-service.
What is the Gateway? • A conduit for secure transactions between customers and government, covering Inputs, Outputs and Payments to Government; • Gateway does not host e-forms or applications that generate or consume transactions; • Gateway must communicate with front office and back office components to deliver an e-service.
 What does the Gateway do? • • Single route into any government system; Processes and routes XML “e-forms”; Provides “single identity” access for users; Highly secure, resilient “always on” environment; Delivers outbound messages securely; Capacity to handle high volumes; Provides payment facilities.
What does the Gateway do? • • Single route into any government system; Processes and routes XML “e-forms”; Provides “single identity” access for users; Highly secure, resilient “always on” environment; Delivers outbound messages securely; Capacity to handle high volumes; Provides payment facilities.
 Who can use the Gateway? • Customers: – Citizens, businesses, intermediaries – Using ANY application, ANY device, ANY digital ID service that is t-Scheme approved • Government: – – Departments Local Authorities Agencies Devolved Administrations • Digital ID services. t-Scheme approved providers, currently are: – British Chambers of Commerce (using Royal Mail’s Via. Code) – Equifax • Software developers: – Software Vendors – Departments
Who can use the Gateway? • Customers: – Citizens, businesses, intermediaries – Using ANY application, ANY device, ANY digital ID service that is t-Scheme approved • Government: – – Departments Local Authorities Agencies Devolved Administrations • Digital ID services. t-Scheme approved providers, currently are: – British Chambers of Commerce (using Royal Mail’s Via. Code) – Equifax • Software developers: – Software Vendors – Departments
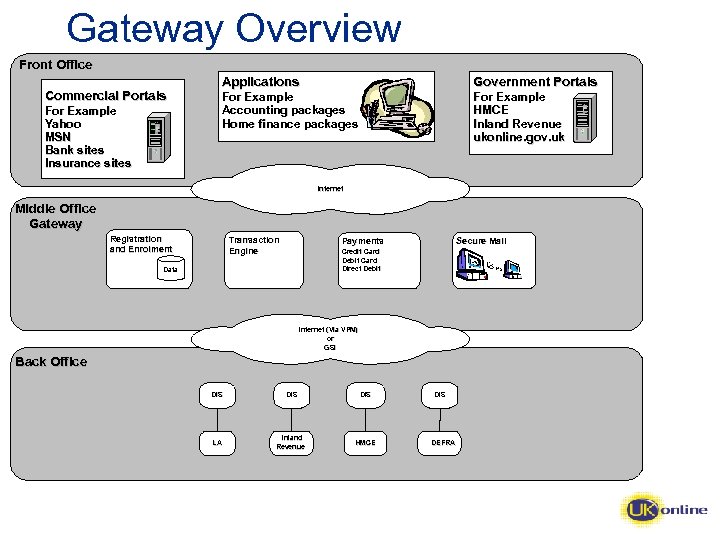 Gateway Overview Front Office Commercial Portals For Example Yahoo MSN Bank sites Insurance sites Applications Government Portals For Example Accounting packages Home finance packages For Example HMCE Inland Revenue ukonline. gov. uk ukonline. gov. Internet Middle Office Gateway Registration and Enrolment Transaction Engine Payments Secure Mail Credit Card Debit Card Direct Debit Data Internet (Via VPN) or GSI Back Office DIS DIS LA Inland Revenue HMCE DIS DEFRA
Gateway Overview Front Office Commercial Portals For Example Yahoo MSN Bank sites Insurance sites Applications Government Portals For Example Accounting packages Home finance packages For Example HMCE Inland Revenue ukonline. gov. uk ukonline. gov. Internet Middle Office Gateway Registration and Enrolment Transaction Engine Payments Secure Mail Credit Card Debit Card Direct Debit Data Internet (Via VPN) or GSI Back Office DIS DIS LA Inland Revenue HMCE DIS DEFRA
 Front Office • Encourage multiple channels for any transaction; • Open standards allow easy integration with applications using Uk. Gov. Talk compliant XML; • Support for Government portals with external authentication capability.
Front Office • Encourage multiple channels for any transaction; • Open standards allow easy integration with applications using Uk. Gov. Talk compliant XML; • Support for Government portals with external authentication capability.
 Middle Office • Gateway provides generic building blocks for creation of end-to-end services: – Registration and Enrolment engine for authentication – Transaction engine for routing – Payment Engine for payment of government related bills by credit, debit card or for setting up direct debits – Secure Mail system for secure communications between user and Government
Middle Office • Gateway provides generic building blocks for creation of end-to-end services: – Registration and Enrolment engine for authentication – Transaction engine for routing – Payment Engine for payment of government related bills by credit, debit card or for setting up direct debits – Secure Mail system for secure communications between user and Government
 Back Office • Department Interface Service (DIS) boxes provide off the shelf connectivity to Gateway; • DIS box can be used to transform XML messages into other formats when they reach departments.
Back Office • Department Interface Service (DIS) boxes provide off the shelf connectivity to Gateway; • DIS box can be used to transform XML messages into other formats when they reach departments.
 Registration & Enrolment • The R&E system: – enables users to have one account whilst having access to a diverse set of transactions and departments; – authenticates all incoming transactions; – remembers relationships between users and intermediaries (such as accountants).
Registration & Enrolment • The R&E system: – enables users to have one account whilst having access to a diverse set of transactions and departments; – authenticates all incoming transactions; – remembers relationships between users and intermediaries (such as accountants).
 Registration and Enrolment • Registration – this is the process of creating the user account, specifying passwords and providing information such as email address (optional); – the service that is being enrolled for will dictate the level of authentication required (either certificate or userid/password). • Enrolment – this is the process of enrolling for one or more services that the citizen or business wants to use. • Activation – Activation PINs are used to ensure the enroller is who they claim to be. PINS are sent to the name and address held by the back office system.
Registration and Enrolment • Registration – this is the process of creating the user account, specifying passwords and providing information such as email address (optional); – the service that is being enrolled for will dictate the level of authentication required (either certificate or userid/password). • Enrolment – this is the process of enrolling for one or more services that the citizen or business wants to use. • Activation – Activation PINs are used to ensure the enroller is who they claim to be. PINS are sent to the name and address held by the back office system.
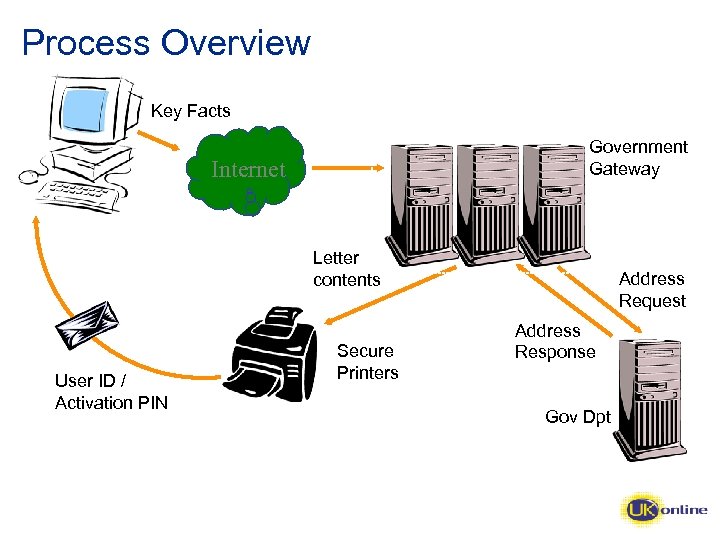 Process Overview Key Facts Government Gateway Internet Letter contents User ID / Activation PIN Secure Printers Address Request Address Response Gov Dpt
Process Overview Key Facts Government Gateway Internet Letter contents User ID / Activation PIN Secure Printers Address Request Address Response Gov Dpt
 What Does The Transaction Engine Do? • Authenticate – authentication of transactions from the Internet; – authentication of department connections over the Government Secure Intranet (GSI)/Virtual Private Network (VPN). • Consumes the transaction – apply a unique identifier and timestamp. • Validate – validate the content of the document header and check the structure. • Route – routing to departmental systems. • Audit – audit and logging; – transaction integrity.
What Does The Transaction Engine Do? • Authenticate – authentication of transactions from the Internet; – authentication of department connections over the Government Secure Intranet (GSI)/Virtual Private Network (VPN). • Consumes the transaction – apply a unique identifier and timestamp. • Validate – validate the content of the document header and check the structure. • Route – routing to departmental systems. • Audit – audit and logging; – transaction integrity.
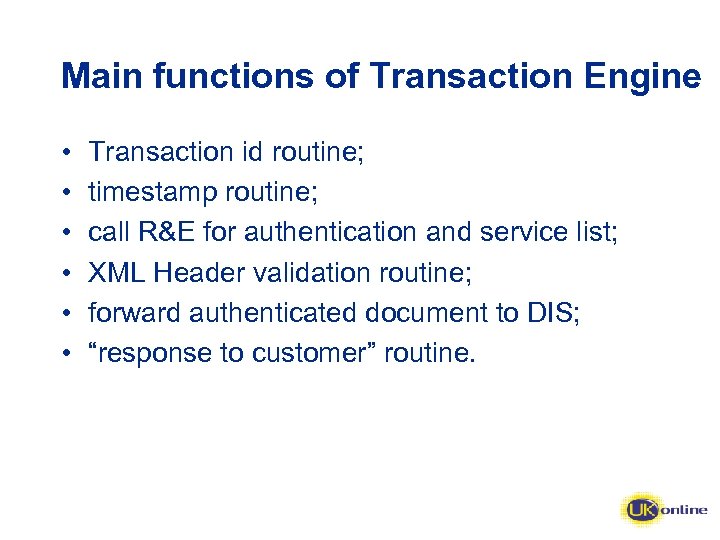 Main functions of Transaction Engine • • • Transaction id routine; timestamp routine; call R&E for authentication and service list; XML Header validation routine; forward authenticated document to DIS; “response to customer” routine.
Main functions of Transaction Engine • • • Transaction id routine; timestamp routine; call R&E for authentication and service list; XML Header validation routine; forward authenticated document to DIS; “response to customer” routine.
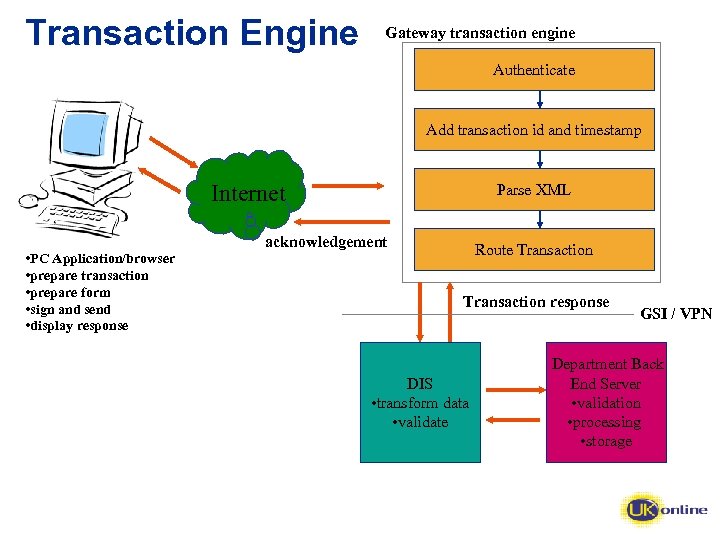 Transaction Engine Gateway transaction engine Authenticate Add transaction id and timestamp Internet • PC Application/browser • prepare transaction • prepare form • sign and send • display response Parse XML acknowledgement Route Transaction response DIS • transform data • validate GSI / VPN Department Back End Server • validation • processing • storage
Transaction Engine Gateway transaction engine Authenticate Add transaction id and timestamp Internet • PC Application/browser • prepare transaction • prepare form • sign and send • display response Parse XML acknowledgement Route Transaction response DIS • transform data • validate GSI / VPN Department Back End Server • validation • processing • storage
 XML • Platform independent; • XML allows the tagging of data; • language used to describe structure and/or content of a document; • makes data more portable and therefore is a keen enabler of Bto. B e-commerce; • does not provide presentation information - require XSL for this, which allows you to apply stylesheets to XML to present the information back to the user; • All transactions are submitted using HTTP Post to the Gateway URL using XML.
XML • Platform independent; • XML allows the tagging of data; • language used to describe structure and/or content of a document; • makes data more portable and therefore is a keen enabler of Bto. B e-commerce; • does not provide presentation information - require XSL for this, which allows you to apply stylesheets to XML to present the information back to the user; • All transactions are submitted using HTTP Post to the Gateway URL using XML.
 Scenarios • The following scenarios show the different modes of operation you can take advantage of when designing services
Scenarios • The following scenarios show the different modes of operation you can take advantage of when designing services
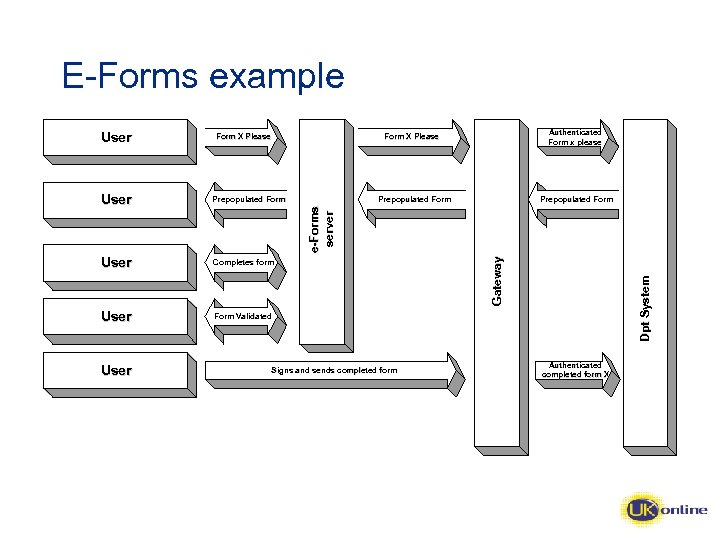 E-Forms example User Form X Please Authenticated Form x please Form X Please Prepopulated Form User Completes form User Form Validated User Prepopulated Form Signs and sends completed form Dpt System Gateway e-Forms server User Authenticated completed form X
E-Forms example User Form X Please Authenticated Form x please Form X Please Prepopulated Form User Completes form User Form Validated User Prepopulated Form Signs and sends completed form Dpt System Gateway e-Forms server User Authenticated completed form X
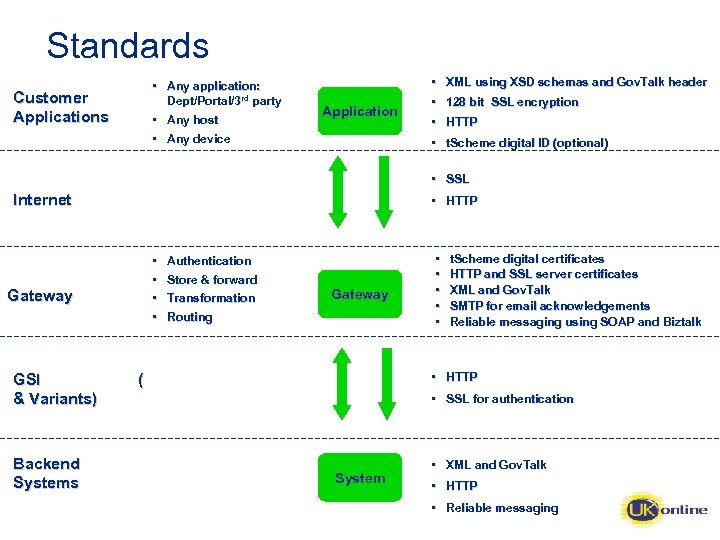 Standards • Any application: Dept/Portal/3 rd party Customer Applications • Any host • Any device • XML using XSD schemas and Gov. Talk header Application • 128 bit SSL encryption • HTTP • t. Scheme digital ID (optional) • SSL Internet • HTTP • • Gateway GSI & Variants) Backend Systems Authentication Store & forward Transformation Gateway Routing • • • t. Scheme digital certificates HTTP and SSL server certificates XML and Gov. Talk SMTP for email acknowledgements Reliable messaging using SOAP and Biztalk • HTTP ( • SSL for authentication System • XML and Gov. Talk • HTTP • Reliable messaging
Standards • Any application: Dept/Portal/3 rd party Customer Applications • Any host • Any device • XML using XSD schemas and Gov. Talk header Application • 128 bit SSL encryption • HTTP • t. Scheme digital ID (optional) • SSL Internet • HTTP • • Gateway GSI & Variants) Backend Systems Authentication Store & forward Transformation Gateway Routing • • • t. Scheme digital certificates HTTP and SSL server certificates XML and Gov. Talk SMTP for email acknowledgements Reliable messaging using SOAP and Biztalk • HTTP ( • SSL for authentication System • XML and Gov. Talk • HTTP • Reliable messaging
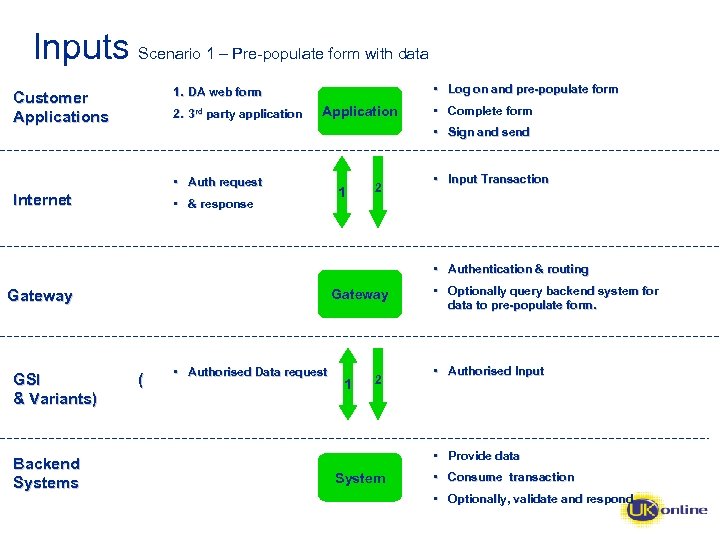 Inputs Scenario 1 – Pre-populate form with data • Log on and pre-populate form 1. DA web form Customer Applications 2. 3 rd party application Application • Complete form • Sign and send • Auth request Internet • & response 1 2 • Input Transaction • Authentication & routing Gateway GSI & Variants) Backend Systems ( • Authorised Data request 1 2 • Optionally query backend system for data to pre-populate form. • Authorised Input • Provide data System • Consume transaction • Optionally, validate and respond
Inputs Scenario 1 – Pre-populate form with data • Log on and pre-populate form 1. DA web form Customer Applications 2. 3 rd party application Application • Complete form • Sign and send • Auth request Internet • & response 1 2 • Input Transaction • Authentication & routing Gateway GSI & Variants) Backend Systems ( • Authorised Data request 1 2 • Optionally query backend system for data to pre-populate form. • Authorised Input • Provide data System • Consume transaction • Optionally, validate and respond
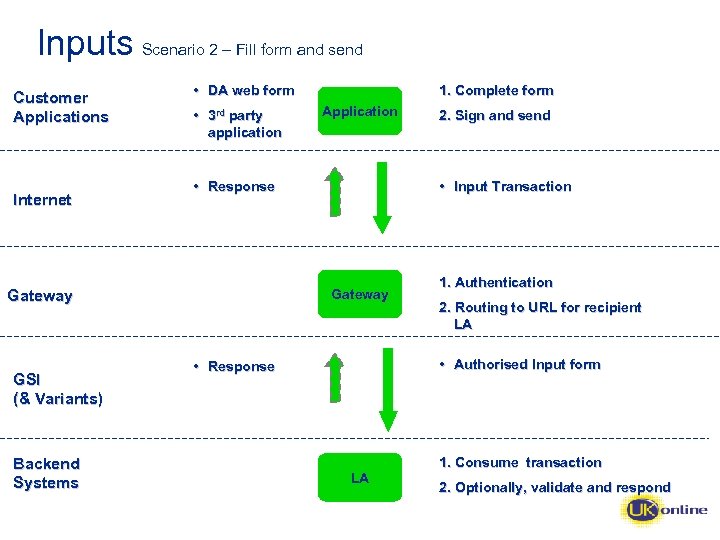 Inputs Scenario 2 – Fill form and send Customer Applications Internet • DA web form • 3 rd party application Backend Systems Application • Response 2. Sign and send • Input Transaction Gateway GSI (& Variants) 1. Complete form 1. Authentication 2. Routing to URL for recipient LA • Authorised Input form • Response LA LA 1. Consume transaction 2. Optionally, validate and respond
Inputs Scenario 2 – Fill form and send Customer Applications Internet • DA web form • 3 rd party application Backend Systems Application • Response 2. Sign and send • Input Transaction Gateway GSI (& Variants) 1. Complete form 1. Authentication 2. Routing to URL for recipient LA • Authorised Input form • Response LA LA 1. Consume transaction 2. Optionally, validate and respond
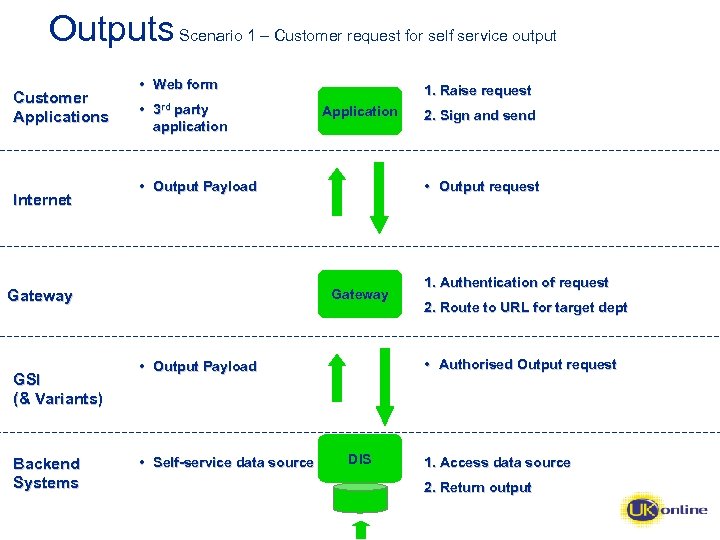 Outputs Scenario 1 – Customer request for self service output Customer Applications Internet • Web form • 3 rd party application Backend Systems Application • Output Payload 1. Authentication of request 2. Route to URL for target dept • Authorised Output request • Output Payload • Self-service data source 2. Sign and send • Output request Gateway GSI (& Variants) 1. Raise request DIS 1. Access data source 2. Return output
Outputs Scenario 1 – Customer request for self service output Customer Applications Internet • Web form • 3 rd party application Backend Systems Application • Output Payload 1. Authentication of request 2. Route to URL for target dept • Authorised Output request • Output Payload • Self-service data source 2. Sign and send • Output request Gateway GSI (& Variants) 1. Raise request DIS 1. Access data source 2. Return output
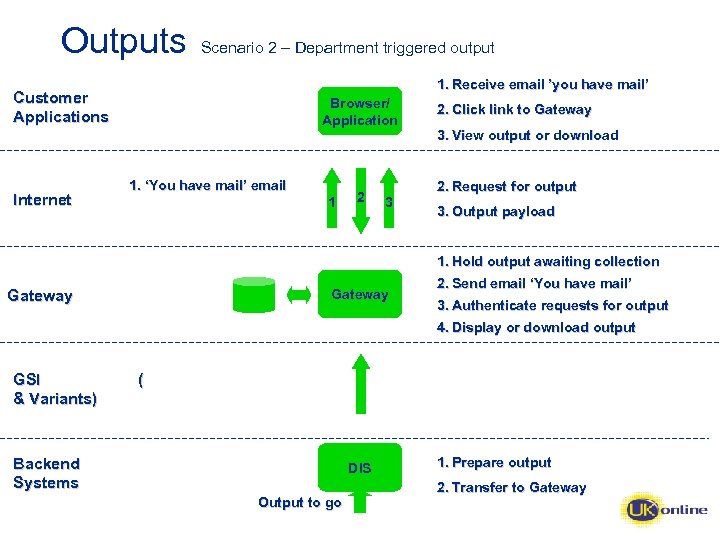 Outputs Scenario 2 – Department triggered output 1. Receive email ’you have mail’ Customer Applications Internet Browser/ Application 1. ‘You have mail’ email 1 3 Gateway GSI & Variants) 2 2. Click link to Gateway 3. View output or download 2. Request for output 3. Output payload 1. Hold output awaiting collection 2. Send email ‘You have mail’ 3. Authenticate requests for output 4. Display or download output ( Backend Systems DIS Output to go 1. Prepare output 2. Transfer to Gateway
Outputs Scenario 2 – Department triggered output 1. Receive email ’you have mail’ Customer Applications Internet Browser/ Application 1. ‘You have mail’ email 1 3 Gateway GSI & Variants) 2 2. Click link to Gateway 3. View output or download 2. Request for output 3. Output payload 1. Hold output awaiting collection 2. Send email ‘You have mail’ 3. Authenticate requests for output 4. Display or download output ( Backend Systems DIS Output to go 1. Prepare output 2. Transfer to Gateway
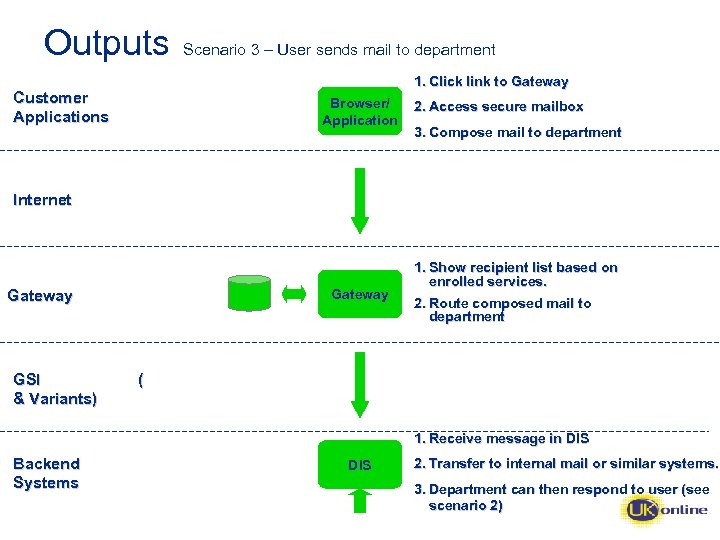 Outputs Scenario 3 – User sends mail to department 1. Click link to Gateway Customer Applications Browser/ Application 2. Access secure mailbox 3. Compose mail to department Internet Gateway GSI & Variants) 1. Show recipient list based on enrolled services. 2. Route composed mail to department ( 1. Receive message in DIS Backend Systems DIS 2. Transfer to internal mail or similar systems. 3. Department can then respond to user (see scenario 2)
Outputs Scenario 3 – User sends mail to department 1. Click link to Gateway Customer Applications Browser/ Application 2. Access secure mailbox 3. Compose mail to department Internet Gateway GSI & Variants) 1. Show recipient list based on enrolled services. 2. Route composed mail to department ( 1. Receive message in DIS Backend Systems DIS 2. Transfer to internal mail or similar systems. 3. Department can then respond to user (see scenario 2)
 Secure Mail • Provides a web based mail system for all users; • Allows Government to deliver correspondence into the users’ secure mailbox; • Users can send mail direct to Government departments whose services they have enrolled for.
Secure Mail • Provides a web based mail system for all users; • Allows Government to deliver correspondence into the users’ secure mailbox; • Users can send mail direct to Government departments whose services they have enrolled for.
 Payments Engine • Will allow bill payment with credit, debit card or direct debit (dept can specify which is acceptable for each service); • Payments can be taken as part of a transaction (Self Assessment transaction could contain a payment section) or via the payment web site; • User can receive bills via the secure mailbox and pay in the same session on the payment engine.
Payments Engine • Will allow bill payment with credit, debit card or direct debit (dept can specify which is acceptable for each service); • Payments can be taken as part of a transaction (Self Assessment transaction could contain a payment section) or via the payment web site; • User can receive bills via the secure mailbox and pay in the same session on the payment engine.
 Summary • Gateway provides a conduit for secure transactions between customers and government, covering Inputs, Outputs and Payments to Government; • Need to register with the Gateway and then enrol for specific services; • Transaction engine always ensures that there is a response to each request and assurance that government has received the transaction; • DIS boxes are housed at departments.
Summary • Gateway provides a conduit for secure transactions between customers and government, covering Inputs, Outputs and Payments to Government; • Need to register with the Gateway and then enrol for specific services; • Transaction engine always ensures that there is a response to each request and assurance that government has received the transaction; • DIS boxes are housed at departments.


