958ca4917ab4f5449889a46a2fe417ae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 E-Governance: Success Stories from around the World Owino Magana E-governance Consultant, E-Kazi Africa 23 March 2004
E-Governance: Success Stories from around the World Owino Magana E-governance Consultant, E-Kazi Africa 23 March 2004
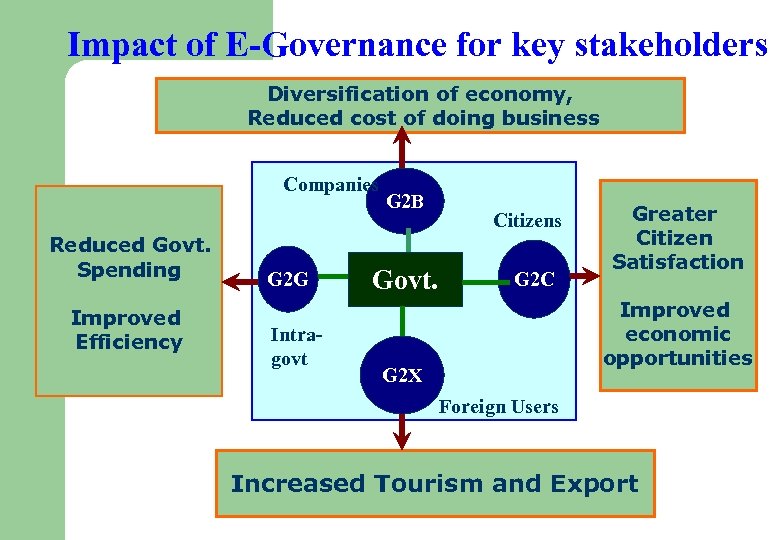 Impact of E-Governance for key stakeholders Diversification of economy, Reduced cost of doing business Companies Reduced Govt. Spending Improved Efficiency G 2 G Intragovt G 2 B Govt. Citizens G 2 C Greater Citizen Satisfaction Improved economic opportunities G 2 X Foreign Users Increased Tourism and Export
Impact of E-Governance for key stakeholders Diversification of economy, Reduced cost of doing business Companies Reduced Govt. Spending Improved Efficiency G 2 G Intragovt G 2 B Govt. Citizens G 2 C Greater Citizen Satisfaction Improved economic opportunities G 2 X Foreign Users Increased Tourism and Export
 Insanity is doing the same things the same way and expecting different results Stephen Haines
Insanity is doing the same things the same way and expecting different results Stephen Haines
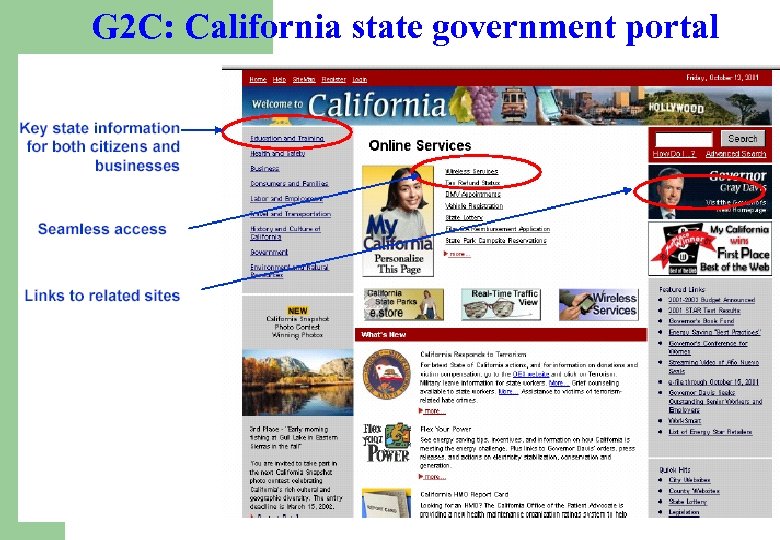 G 2 C: California state government portal
G 2 C: California state government portal
 G 2 B: Chile’s government e-procurement system Before No coherent inter-governmental procurement policy. Businesses had to deal with differing rules for each department and agency. After www. comprachile. cl e-system allowing storage, distribution and analyses of procurement information as well as generation of bidding Single registration as supplier for any government agency Transparency of outcomes of bidding process Benefits üGreater transparency, efficiency, and fairness üEstimated efficiency gains of $200 m a year, 1. 4% of total government expenditures!
G 2 B: Chile’s government e-procurement system Before No coherent inter-governmental procurement policy. Businesses had to deal with differing rules for each department and agency. After www. comprachile. cl e-system allowing storage, distribution and analyses of procurement information as well as generation of bidding Single registration as supplier for any government agency Transparency of outcomes of bidding process Benefits üGreater transparency, efficiency, and fairness üEstimated efficiency gains of $200 m a year, 1. 4% of total government expenditures!
 G 2 B: Philippine government electronic customs clearance system Online system to process clearance of imports, payment of duty, and delivery of release orders for shipments to leave the docks. Before: • Diversion of duty through banking system problematic. • Customs collecting officers ran away with their collections. • Process involved nearly 10 separate documents in multiple copies, over 90 • steps and more than 40 signatures and initials were involved. • Customs Bureau rated one of the most bureaucratic and corrupt
G 2 B: Philippine government electronic customs clearance system Online system to process clearance of imports, payment of duty, and delivery of release orders for shipments to leave the docks. Before: • Diversion of duty through banking system problematic. • Customs collecting officers ran away with their collections. • Process involved nearly 10 separate documents in multiple copies, over 90 • steps and more than 40 signatures and initials were involved. • Customs Bureau rated one of the most bureaucratic and corrupt
 After • Payment of duties and taxes are made to Authorized Agent Bank. • No cash is handled by any Customs Officer. • Nearly paperless system • . No paper Order of Payment, no Customs Invoice. Single electronic clearance document. Benefits üCargo is released within 4 hours to 2 days, down from 8 days üPayment reconciliation time down from 4 months to same day
After • Payment of duties and taxes are made to Authorized Agent Bank. • No cash is handled by any Customs Officer. • Nearly paperless system • . No paper Order of Payment, no Customs Invoice. Single electronic clearance document. Benefits üCargo is released within 4 hours to 2 days, down from 8 days üPayment reconciliation time down from 4 months to same day
 G 2 G: Intra-government activities • Common architectural framework and common standards for Governmentwide IT infrastructure • Common metadata format for sharing and exchange of data among government departments and with the private sector. • Aggregating data about citizens and businesses into common Repositories • Establishing regional alliances with other governments for purchasing, • Facilitating learning and collaboration among government employees
G 2 G: Intra-government activities • Common architectural framework and common standards for Governmentwide IT infrastructure • Common metadata format for sharing and exchange of data among government departments and with the private sector. • Aggregating data about citizens and businesses into common Repositories • Establishing regional alliances with other governments for purchasing, • Facilitating learning and collaboration among government employees
 G 2 X: International Constituents Government-to-government interactions • Co-operation on IT infrastructure projects with other states and Central government • Co-investment with other governments Trade, Investment & Tourism development Portals promoting the above • Online hotel booking, car rentals, etc. • 82% of Air Tickets in US bought online • Total annual value of Air Travel industry is US$ 3. 5 Trillion Expatriates Repatriation of earnings • Immigration and work permit filing
G 2 X: International Constituents Government-to-government interactions • Co-operation on IT infrastructure projects with other states and Central government • Co-investment with other governments Trade, Investment & Tourism development Portals promoting the above • Online hotel booking, car rentals, etc. • 82% of Air Tickets in US bought online • Total annual value of Air Travel industry is US$ 3. 5 Trillion Expatriates Repatriation of earnings • Immigration and work permit filing
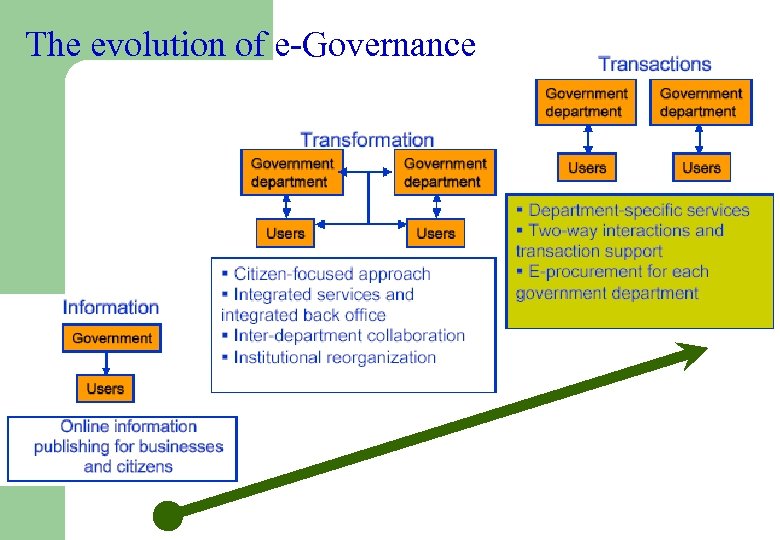 The evolution of e-Governance
The evolution of e-Governance
 How to pay for e-Governance initiatives ØCharging fees to citizens (There are hidden costs in poorly delivered free services) ØOptimization of Resource allocation ØIncreased tax revenues due to better compliance. ØRevenues from add-on services. ØSharing development and operating costs with private sector partners
How to pay for e-Governance initiatives ØCharging fees to citizens (There are hidden costs in poorly delivered free services) ØOptimization of Resource allocation ØIncreased tax revenues due to better compliance. ØRevenues from add-on services. ØSharing development and operating costs with private sector partners
 Problems with e-governance implementations v. Most governments have not changed their processes in any way, and instead have automated flawed processes v. There is a big gulf between a “pretty web site” and integrated service delivery v. Government budgets and administration tends to be in departmental silos, but e-government cuts across departments v. Too much attention to “citizen portals” has taken attention away from internal government functioning and govt. to business v. Even best in class state and local e-government solutions have not gained widespread adoption v. Governments often underestimate the security, infrastructure, and scalability requirements of their applications
Problems with e-governance implementations v. Most governments have not changed their processes in any way, and instead have automated flawed processes v. There is a big gulf between a “pretty web site” and integrated service delivery v. Government budgets and administration tends to be in departmental silos, but e-government cuts across departments v. Too much attention to “citizen portals” has taken attention away from internal government functioning and govt. to business v. Even best in class state and local e-government solutions have not gained widespread adoption v. Governments often underestimate the security, infrastructure, and scalability requirements of their applications
 Lessons: Clear justification for projects q Clarity about costs and benefits Balancing cost, payoff, and risk in implementation Use appropriate technology q Citizens are willing to pay, if they see real value Private sector involvement can defray costs q Use government experts with IT training, not IT experts Insource strategy; Outsource design and development q q Appropriate Sustainability Model q Institutional Framework q Project management q Think big, start small, scale fast q Celebrate early wins, celebrate reasoned failures q Focus on training and change management
Lessons: Clear justification for projects q Clarity about costs and benefits Balancing cost, payoff, and risk in implementation Use appropriate technology q Citizens are willing to pay, if they see real value Private sector involvement can defray costs q Use government experts with IT training, not IT experts Insource strategy; Outsource design and development q q Appropriate Sustainability Model q Institutional Framework q Project management q Think big, start small, scale fast q Celebrate early wins, celebrate reasoned failures q Focus on training and change management
 The only way to accurately predict the future…is to create it!! Peter Drucker, Management Guru
The only way to accurately predict the future…is to create it!! Peter Drucker, Management Guru


