dec2464b2bdfc7ab8be0f49a76212255.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 e-Courts Project Implementation Plan #
e-Courts Project Implementation Plan #
 Chronolgy n n NIC initiated computerised activities in the Indian Judiciary in 1990 by taking up the computeristaion of the Supreme Court of India. During 1992 -95 NIC took up the computerisation of all High Courts on the lines of the Supreme court computerisation program. During 1997 -99 NIC implemented IT activities in 430 District Courts primarily for creating awareness. In 2002 -05 implemented Metro & Capital city courts Since 2007 NIC has been implementing phase I of District & Subordinate courts project at a cost of Rs. 442 cr to be completed in 2 years #
Chronolgy n n NIC initiated computerised activities in the Indian Judiciary in 1990 by taking up the computeristaion of the Supreme Court of India. During 1992 -95 NIC took up the computerisation of all High Courts on the lines of the Supreme court computerisation program. During 1997 -99 NIC implemented IT activities in 430 District Courts primarily for creating awareness. In 2002 -05 implemented Metro & Capital city courts Since 2007 NIC has been implementing phase I of District & Subordinate courts project at a cost of Rs. 442 cr to be completed in 2 years #
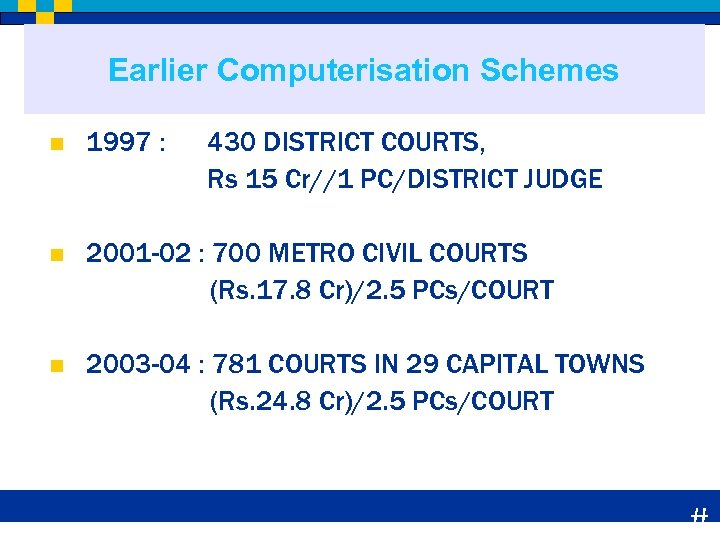 Earlier Computerisation Schemes n 1997 : 430 DISTRICT COURTS, Rs 15 Cr//1 PC/DISTRICT JUDGE n 2001 -02 : 700 METRO CIVIL COURTS (Rs. 17. 8 Cr)/2. 5 PCs/COURT n 2003 -04 : 781 COURTS IN 29 CAPITAL TOWNS (Rs. 24. 8 Cr)/2. 5 PCs/COURT #
Earlier Computerisation Schemes n 1997 : 430 DISTRICT COURTS, Rs 15 Cr//1 PC/DISTRICT JUDGE n 2001 -02 : 700 METRO CIVIL COURTS (Rs. 17. 8 Cr)/2. 5 PCs/COURT n 2003 -04 : 781 COURTS IN 29 CAPITAL TOWNS (Rs. 24. 8 Cr)/2. 5 PCs/COURT #
 Introduction: e. Courts MMP n n n Integrated Mission Mode Project Approved by CCEA on February 2, 2007 Cost Rs. 442 crores, Duration : 2 years Coverage n n 4 ICT enablement of District and Subordinate Courts Upgradation of ICT infrastructure of supreme court & high courts Implementing agency- NIC, Consultation & guidance of E-Committee #
Introduction: e. Courts MMP n n n Integrated Mission Mode Project Approved by CCEA on February 2, 2007 Cost Rs. 442 crores, Duration : 2 years Coverage n n 4 ICT enablement of District and Subordinate Courts Upgradation of ICT infrastructure of supreme court & high courts Implementing agency- NIC, Consultation & guidance of E-Committee #
 Public Interface applications 1. ● Causelists on Internet The Advocates & Litigants can get the Cause lists as soon as they are out in the Registry. ● No need to wait for the hardcopy to be delivered late in the evening. ● Advocates can easily locate/generate their own CLs 2. Daily Orders ● Litigants can get Daily Orders on Internet ● No need to approach the court ● No scope for any hassles ● It receives about 150, 000 hits a day #
Public Interface applications 1. ● Causelists on Internet The Advocates & Litigants can get the Cause lists as soon as they are out in the Registry. ● No need to wait for the hardcopy to be delivered late in the evening. ● Advocates can easily locate/generate their own CLs 2. Daily Orders ● Litigants can get Daily Orders on Internet ● No need to approach the court ● No scope for any hassles ● It receives about 150, 000 hits a day #
 Public Interface applications 3. Case status on Internet • Up-to-Date status of a case can be found out through the web • No need to contact either the Registry or the advocate • Litigants can keep track of their cases & maintain case records on their own • No chance for corruption in obtaining case related information #
Public Interface applications 3. Case status on Internet • Up-to-Date status of a case can be found out through the web • No need to contact either the Registry or the advocate • Litigants can keep track of their cases & maintain case records on their own • No chance for corruption in obtaining case related information #
 Public Interface applications 4. Judgments Information System • Contains about 60, 000 reported judgments of Apex court. • • Judgments are available on the net • Advocates can maintain their own Case law library without much expenditure Litigants can obtain relevant judgments as soon as they are delivered 5. Interactive Voice Response System Supreme court cases can be accessed on IVRS. Ph. No: 24357276 #
Public Interface applications 4. Judgments Information System • Contains about 60, 000 reported judgments of Apex court. • • Judgments are available on the net • Advocates can maintain their own Case law library without much expenditure Litigants can obtain relevant judgments as soon as they are delivered 5. Interactive Voice Response System Supreme court cases can be accessed on IVRS. Ph. No: 24357276 #
 Public Interface applications 6. Digitally Signed Certified Copies As the Digitally signed copies need not be cross checked with the original file, it can be served to the litigant on the spot with out time delay. • As there will be no delay in issuing Certified Copy, the dealing clerk has to provide the copy on the spot. • No chance for excuses • The litigant can even down load an electronically certified copy from the net with out contacting the court. #
Public Interface applications 6. Digitally Signed Certified Copies As the Digitally signed copies need not be cross checked with the original file, it can be served to the litigant on the spot with out time delay. • As there will be no delay in issuing Certified Copy, the dealing clerk has to provide the copy on the spot. • No chance for excuses • The litigant can even down load an electronically certified copy from the net with out contacting the court. #
 Public Interface applications 7. Indiacode • Contains all acts of parliament right from 1834 onwards. • Each Act contains: Short Title, Enactment dt. , Sections and Schedule. • Up-to-date Acts, Amendments, etc. , can be retrieved through the web • Judges & Librarians can maintain reliable & updated India code #
Public Interface applications 7. Indiacode • Contains all acts of parliament right from 1834 onwards. • Each Act contains: Short Title, Enactment dt. , Sections and Schedule. • Up-to-date Acts, Amendments, etc. , can be retrieved through the web • Judges & Librarians can maintain reliable & updated India code #
 Public Interface applications 8. e-Filing It envisages filing of cases by the advocates electronically from his/her office. The advocate gets a receipt under digital signature of court authority. The person filing cases electronically, is entitled to receive the proceedings of the court electronically. • It avoids litigants/advocates to visit the courts for filing their cases • Courts need not transfer the filed documents into electronic form • Convenient, reliable, easy and efficient #
Public Interface applications 8. e-Filing It envisages filing of cases by the advocates electronically from his/her office. The advocate gets a receipt under digital signature of court authority. The person filing cases electronically, is entitled to receive the proceedings of the court electronically. • It avoids litigants/advocates to visit the courts for filing their cases • Courts need not transfer the filed documents into electronic form • Convenient, reliable, easy and efficient #
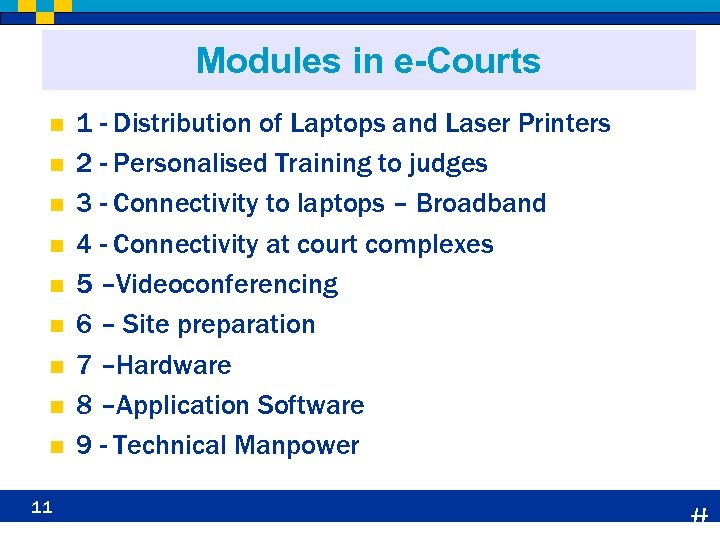 Modules in e-Courts n n n n n 11 1 - Distribution of Laptops and Laser Printers 2 - Personalised Training to judges 3 - Connectivity to laptops – Broadband 4 - Connectivity at court complexes 5 –Videoconferencing 6 – Site preparation 7 –Hardware 8 –Application Software 9 - Technical Manpower #
Modules in e-Courts n n n n n 11 1 - Distribution of Laptops and Laser Printers 2 - Personalised Training to judges 3 - Connectivity to laptops – Broadband 4 - Connectivity at court complexes 5 –Videoconferencing 6 – Site preparation 7 –Hardware 8 –Application Software 9 - Technical Manpower #
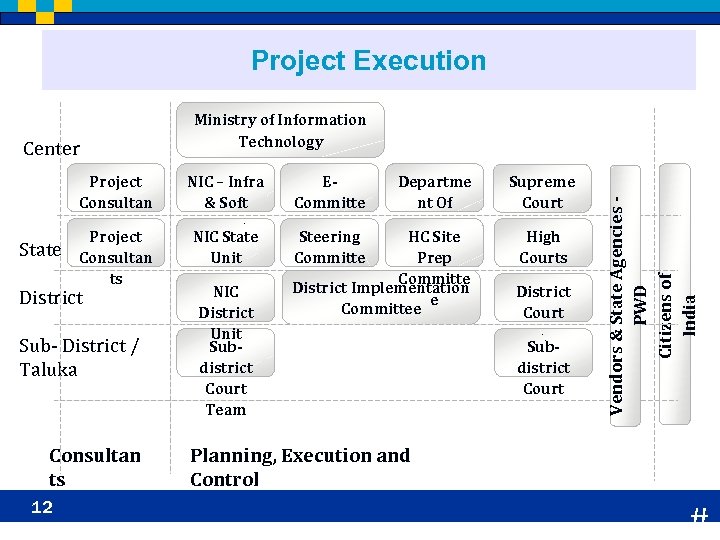 Project Execution State Project Consultan ts District Sub- District / Taluka Consultan ts 12 NIC – Infra & Soft Teams NIC State Unit NIC District Unit Subdistrict Court Team EDepartme Committe nt Of e Justice Steering HC Site Committe Prep e Committe District Implementation e Committee Supreme Court High Courts District Court (499) Subdistrict Court Vendors & State Agencies PWD Citizens of India Center Ministry of Information Technology Planning, Execution and Control #
Project Execution State Project Consultan ts District Sub- District / Taluka Consultan ts 12 NIC – Infra & Soft Teams NIC State Unit NIC District Unit Subdistrict Court Team EDepartme Committe nt Of e Justice Steering HC Site Committe Prep e Committe District Implementation e Committee Supreme Court High Courts District Court (499) Subdistrict Court Vendors & State Agencies PWD Citizens of India Center Ministry of Information Technology Planning, Execution and Control #
 Project Challenges – Site Preparation n Site Preparation Guidelines and Specifications circulated Formation of Site Preparation Committees at High Courts in progress Progress to be expedited on part of n n Workshop held on 9 th Jan, exclusively for Site Preparation n n 13 Engaging PWD and Vendor Identification Preparation of Cost Estimates Preparation of Layout diagrams Strong emphasis laid out on Site Preparation Urging High Courts to form Committees, submit Cost estimates #
Project Challenges – Site Preparation n Site Preparation Guidelines and Specifications circulated Formation of Site Preparation Committees at High Courts in progress Progress to be expedited on part of n n Workshop held on 9 th Jan, exclusively for Site Preparation n n 13 Engaging PWD and Vendor Identification Preparation of Cost Estimates Preparation of Layout diagrams Strong emphasis laid out on Site Preparation Urging High Courts to form Committees, submit Cost estimates #
 Site Preparation n n n n 14 Formation of Committee Identification of vendor Cost estimates and layout diagrams, to be approved by Committee NIC will release payment after receiving above Cost estimates should be around Rs. 2 Lakh/site Completion certificate to be vetted by High Courts and District Courts Site Preparation excludes LAN AC/DG sets procurement - central empanelment
Site Preparation n n n n 14 Formation of Committee Identification of vendor Cost estimates and layout diagrams, to be approved by Committee NIC will release payment after receiving above Cost estimates should be around Rs. 2 Lakh/site Completion certificate to be vetted by High Courts and District Courts Site Preparation excludes LAN AC/DG sets procurement - central empanelment
 Laser printers n Number of Laser Printers are equal to the number of Laptops n n 15 Stock Entry will be done at High Courts Procedure for stock entry, delivery, installation, and certification needs to be finalised Only one installation certificate should be sent per High court
Laser printers n Number of Laser Printers are equal to the number of Laptops n n 15 Stock Entry will be done at High Courts Procedure for stock entry, delivery, installation, and certification needs to be finalised Only one installation certificate should be sent per High court
 Email/Internet n n n 16 BSNL/MTNL is facility provider BSNL is provided with lists of address of judges vetted by HCs NIC is receiving lists directly from judges, not vetted by DJs or HCs Installation note to be signed by concerned judge All installation notes to be compiled together and vetted by respective High Courts before sending to NIC Change of addresses, phone nos. , transfers and retirement of judges – How to manage ?
Email/Internet n n n 16 BSNL/MTNL is facility provider BSNL is provided with lists of address of judges vetted by HCs NIC is receiving lists directly from judges, not vetted by DJs or HCs Installation note to be signed by concerned judge All installation notes to be compiled together and vetted by respective High Courts before sending to NIC Change of addresses, phone nos. , transfers and retirement of judges – How to manage ?
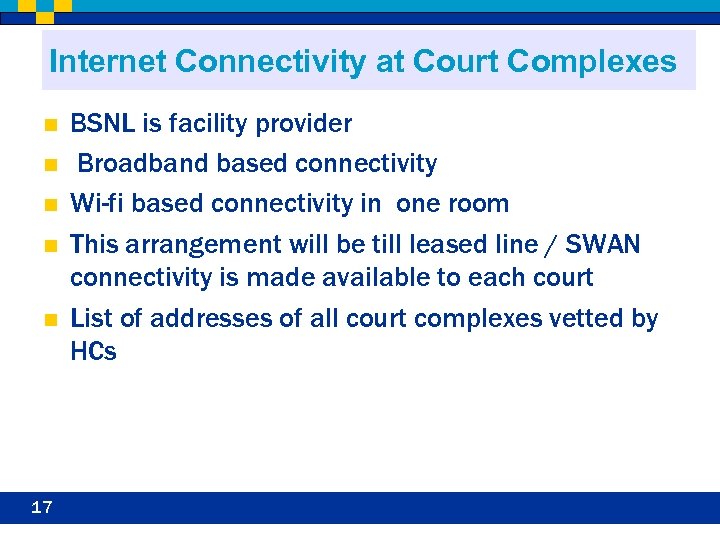 Internet Connectivity at Court Complexes n n n 17 BSNL is facility provider Broadband based connectivity Wi-fi based connectivity in one room This arrangement will be till leased line / SWAN connectivity is made available to each court List of addresses of all court complexes vetted by HCs
Internet Connectivity at Court Complexes n n n 17 BSNL is facility provider Broadband based connectivity Wi-fi based connectivity in one room This arrangement will be till leased line / SWAN connectivity is made available to each court List of addresses of all court complexes vetted by HCs
 Video Conferencing n n n 18 District court wise requirement of VC to be vetted by High Courts and sent to NIC Exclude sites where VC facility already exists VC will be based on VSAT technology At court end, complete VC facility will be made available. At Jail end , low end VC facility Procedure for stock entry, delivery, installation, and certification to be finalised
Video Conferencing n n n 18 District court wise requirement of VC to be vetted by High Courts and sent to NIC Exclude sites where VC facility already exists VC will be based on VSAT technology At court end, complete VC facility will be made available. At Jail end , low end VC facility Procedure for stock entry, delivery, installation, and certification to be finalised
 Hardware n n n 19 4 Computers (desktops and thin clients) with 3 printers will be given per court 2 computers in court, 1 in Judicial Service Centre (JSC), 1 for General purpose – Payroll, etc 3 Printers – 2 in Court, 1 in JSC/General Purpose All computers in a court complex will be networked to a server At each court complex one scanner will be provided Procedure for stock entry, delivery, installation, and certification to be discussed
Hardware n n n 19 4 Computers (desktops and thin clients) with 3 printers will be given per court 2 computers in court, 1 in Judicial Service Centre (JSC), 1 for General purpose – Payroll, etc 3 Printers – 2 in Court, 1 in JSC/General Purpose All computers in a court complex will be networked to a server At each court complex one scanner will be provided Procedure for stock entry, delivery, installation, and certification to be discussed
 Technical Manpower n n n 20 At each High Court – 1 Senior System Officer, 1 System Officer, 2 System Assistants At each District court – 1 System Officer, 2 System Assistants Deployed for 18 man-months Will report to High Court and District Court Judges as the case may be Whenever need arises, they will visit the subordinate courts TA/DA will be paid
Technical Manpower n n n 20 At each High Court – 1 Senior System Officer, 1 System Officer, 2 System Assistants At each District court – 1 System Officer, 2 System Assistants Deployed for 18 man-months Will report to High Court and District Court Judges as the case may be Whenever need arises, they will visit the subordinate courts TA/DA will be paid
 Project Monitoring System The web based e-Courts Project Monitoring System will enable in: n Monitoring progress at each court complex for n n Providing access to key project documents n n n Action Plans and Guidelines, Information on committees at each High Court Generating status reports at each level n n Site Preparation, Hardware, LAN, Training, etc Court Complex, District, and High Court Providing general information on n n Vendors Product Installation and Usage
Project Monitoring System The web based e-Courts Project Monitoring System will enable in: n Monitoring progress at each court complex for n n Providing access to key project documents n n n Action Plans and Guidelines, Information on committees at each High Court Generating status reports at each level n n Site Preparation, Hardware, LAN, Training, etc Court Complex, District, and High Court Providing general information on n n Vendors Product Installation and Usage
 Key Achievements n n 13000 laptops supplied to Judges ICT training of Judges/staff underway: n n n n 22 10853/ 13000 Judges 43412 / 60000 staff trained Broadband connection has been provided at 8717 Judge residences, 469 district courts and 896 taluka courts. Dial up connection has been provided at 971 judge residences, 17 district courts and 376 taluka courts. 13000 laser printers have been delivered to Judges. Project Monitoring Website launched SW standardization Committee’s first meeting was held on 26 th April 08. Engaging Project Consultants for Project Management and Process Reengineering
Key Achievements n n 13000 laptops supplied to Judges ICT training of Judges/staff underway: n n n n 22 10853/ 13000 Judges 43412 / 60000 staff trained Broadband connection has been provided at 8717 Judge residences, 469 district courts and 896 taluka courts. Dial up connection has been provided at 971 judge residences, 17 district courts and 376 taluka courts. 13000 laser printers have been delivered to Judges. Project Monitoring Website launched SW standardization Committee’s first meeting was held on 26 th April 08. Engaging Project Consultants for Project Management and Process Reengineering
 Key Achievements…. Site-preparation n Site preparation specifications and guidelines circulated. Site preparation estimates have been received out of about 2900 Court Complexes, from 1998 from the following states / UTs: n Andhra Pradesh, Andaman & Nicobar, Assam, Bihar, Chandigarh, Gujarat, Haryana, HP, J & K, Karnataka, Kerala, MP, Maharastra, Orissa, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil. Nadu, Tripura, UP, Uttrakhand, and West Bengal. n The Total Estmated Cost = Rs. 41. 7 Cr for 1998 Court Complexes.
Key Achievements…. Site-preparation n Site preparation specifications and guidelines circulated. Site preparation estimates have been received out of about 2900 Court Complexes, from 1998 from the following states / UTs: n Andhra Pradesh, Andaman & Nicobar, Assam, Bihar, Chandigarh, Gujarat, Haryana, HP, J & K, Karnataka, Kerala, MP, Maharastra, Orissa, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil. Nadu, Tripura, UP, Uttrakhand, and West Bengal. n The Total Estmated Cost = Rs. 41. 7 Cr for 1998 Court Complexes.
 HW items for District & sub-ordinate courts Depending on the requirement the District & Subordinate courts will be get the following items: n n n Rack Mount Server 1 U Rack Mount Server 2 U Thin Clients Slim PC 1 Mono Laser Printers 24 pin, 136 Column DMP Printer Scanner (Legal)-15 ppm Portable projector KVA On-line UPS with 120 min back up 2 KVA On-line UPS with 120 min back up 500 VA Line-Interactive UPS with 120 min backup LAN Items (Active & Passive)
HW items for District & sub-ordinate courts Depending on the requirement the District & Subordinate courts will be get the following items: n n n Rack Mount Server 1 U Rack Mount Server 2 U Thin Clients Slim PC 1 Mono Laser Printers 24 pin, 136 Column DMP Printer Scanner (Legal)-15 ppm Portable projector KVA On-line UPS with 120 min back up 2 KVA On-line UPS with 120 min back up 500 VA Line-Interactive UPS with 120 min backup LAN Items (Active & Passive)
 Activities in Queue n Videoconferencing – Bids to be received from vendors n Technical Manpower – Job orders are given to empanelled vendors n Hardware and Network – Technical evaluation is going on n Software Application Standardisation Version 1 n 25 Formation of Software Development Committees for Supreme Court, High Courts and Lower Courts – Completed
Activities in Queue n Videoconferencing – Bids to be received from vendors n Technical Manpower – Job orders are given to empanelled vendors n Hardware and Network – Technical evaluation is going on n Software Application Standardisation Version 1 n 25 Formation of Software Development Committees for Supreme Court, High Courts and Lower Courts – Completed
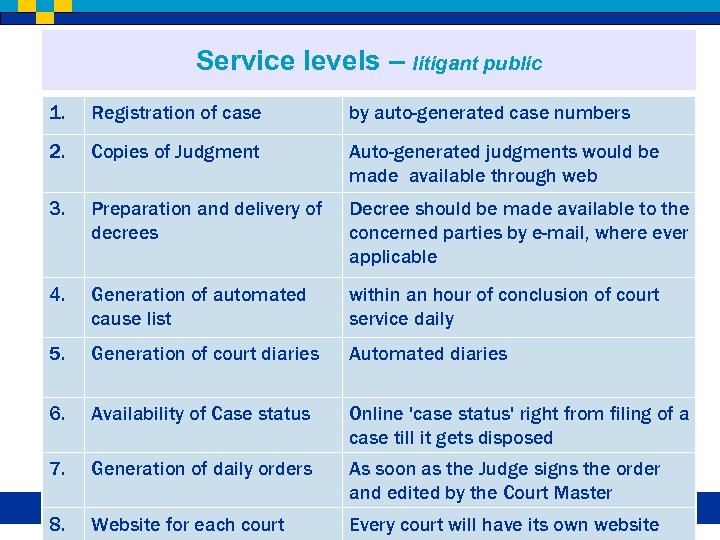 Service levels – litigant public 1. Registration of case by auto-generated case numbers 2. Copies of Judgment Auto-generated judgments would be made available through web 3. Preparation and delivery of decrees Decree should be made available to the concerned parties by e-mail, where ever applicable 4. Generation of automated cause list within an hour of conclusion of court service daily 5. Generation of court diaries Automated diaries 6. Availability of Case status Online 'case status' right from filing of a case till it gets disposed 7. Generation of daily orders As soon as the Judge signs the order and edited by the Court Master 8. Website for each court Every court will have its own website
Service levels – litigant public 1. Registration of case by auto-generated case numbers 2. Copies of Judgment Auto-generated judgments would be made available through web 3. Preparation and delivery of decrees Decree should be made available to the concerned parties by e-mail, where ever applicable 4. Generation of automated cause list within an hour of conclusion of court service daily 5. Generation of court diaries Automated diaries 6. Availability of Case status Online 'case status' right from filing of a case till it gets disposed 7. Generation of daily orders As soon as the Judge signs the order and edited by the Court Master 8. Website for each court Every court will have its own website
 Service levels - for Registry 1. Submission of report of Commissioner/ pleader appointed for recording evidence Tracking of submission of commissioners' report on a timely basis 2. Storing of documentary evidence Scanning and digitally capturing the cases in the database 3. Calculation of court fees due and paid for Automated calculation of court fee at the end of each transaction and report generated on a daily basis 4. Release of orders to the copying section as soon as the judgment is signed. 5. Filing of written statement by the defendant Tracking of generation of written statement - to be generated within 30 days of the date of summons or 90 days (if allowed to be extended by the court)
Service levels - for Registry 1. Submission of report of Commissioner/ pleader appointed for recording evidence Tracking of submission of commissioners' report on a timely basis 2. Storing of documentary evidence Scanning and digitally capturing the cases in the database 3. Calculation of court fees due and paid for Automated calculation of court fee at the end of each transaction and report generated on a daily basis 4. Release of orders to the copying section as soon as the judgment is signed. 5. Filing of written statement by the defendant Tracking of generation of written statement - to be generated within 30 days of the date of summons or 90 days (if allowed to be extended by the court)
 Project Acceleration Steps n n E-Committee, NIC & Do. J to play a key role in speeding up the implementation process Launch of Project Awareness Campaigns including n n n Conducting project awareness programmes to District judges at HCs Project Success Case Studies Project Films showcasing using of ICT in Judiciary Keeping in touch with HCs on project implementation issues Appointment of one Project Consultant at each High Court n n Will work towards successful implementation at High Court Level Reporting to E-Committee and NIC HQ and respective State Units
Project Acceleration Steps n n E-Committee, NIC & Do. J to play a key role in speeding up the implementation process Launch of Project Awareness Campaigns including n n n Conducting project awareness programmes to District judges at HCs Project Success Case Studies Project Films showcasing using of ICT in Judiciary Keeping in touch with HCs on project implementation issues Appointment of one Project Consultant at each High Court n n Will work towards successful implementation at High Court Level Reporting to E-Committee and NIC HQ and respective State Units
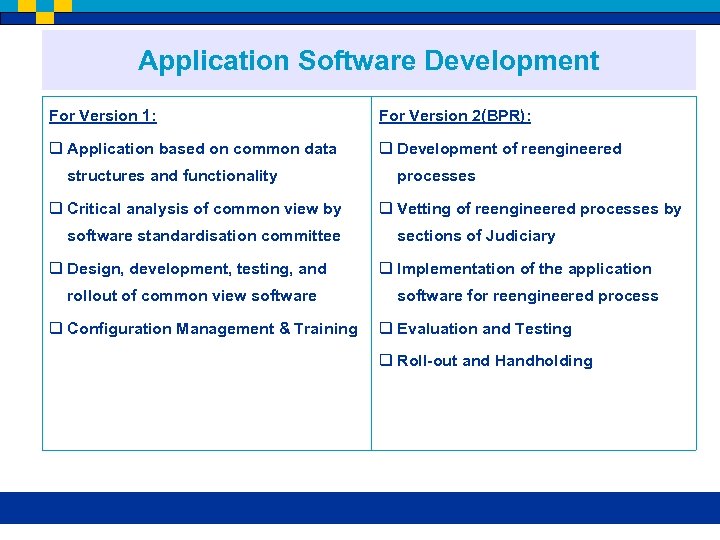 Application Software Development For Version 1: For Version 2(BPR): q Application based on common data q Development of reengineered structures and functionality q Critical analysis of common view by software standardisation committee q Design, development, testing, and rollout of common view software q Configuration Management & Training processes q Vetting of reengineered processes by sections of Judiciary q Implementation of the application software for reengineered process q Evaluation and Testing q Roll-out and Handholding
Application Software Development For Version 1: For Version 2(BPR): q Application based on common data q Development of reengineered structures and functionality q Critical analysis of common view by software standardisation committee q Design, development, testing, and rollout of common view software q Configuration Management & Training processes q Vetting of reengineered processes by sections of Judiciary q Implementation of the application software for reengineered process q Evaluation and Testing q Roll-out and Handholding
 General Issues n Site-preparation: n n n n 30 AC will be only for server room Furniture will be for Server room & JSC DG set would be procured locally Floor of JSC should be slightly elevated Hardware will be delivered directly at Court Complexes General mechanism for stock entry, delivery, installation, and certification Technical Manpower – a few will be deployed very shortly
General Issues n Site-preparation: n n n n 30 AC will be only for server room Furniture will be for Server room & JSC DG set would be procured locally Floor of JSC should be slightly elevated Hardware will be delivered directly at Court Complexes General mechanism for stock entry, delivery, installation, and certification Technical Manpower – a few will be deployed very shortly
 Site-preparation cost estimates n n n DC will consolidate all cost-estimates under its jurisdiction and forward it to HC HC will examine, if approved consolidate cost-estimates of DCs will forward to NIC for release of advance payment When the site is complete DC will issue consolidated work completion certificate for all court complexes HC will forward consolidated work completion certificates of all DCs to NIC. In the same way HCs will also forward fund utilization certificates to NIC for settlement of accounts
Site-preparation cost estimates n n n DC will consolidate all cost-estimates under its jurisdiction and forward it to HC HC will examine, if approved consolidate cost-estimates of DCs will forward to NIC for release of advance payment When the site is complete DC will issue consolidated work completion certificate for all court complexes HC will forward consolidated work completion certificates of all DCs to NIC. In the same way HCs will also forward fund utilization certificates to NIC for settlement of accounts
 Stock Entry – e-Courts Assets n n n n At the time of inspection 3 copies of lists of items with sr. nos & addresses of DCs/Taluka courts will be generated Two copies of lists will be sent to HCs Items will be directly delivered at respective court complex After delivery at each location judge in-charge will sign delivery challans All delivery challans will be collected by vendor and submitted to HC HC will cross check each delivery challan with the consolidated list and paste the same in the stock register HC will forward only one consolidated certified delivery challan to NIC Same procedure will be followed for installation and certification for bill clearance.
Stock Entry – e-Courts Assets n n n n At the time of inspection 3 copies of lists of items with sr. nos & addresses of DCs/Taluka courts will be generated Two copies of lists will be sent to HCs Items will be directly delivered at respective court complex After delivery at each location judge in-charge will sign delivery challans All delivery challans will be collected by vendor and submitted to HC HC will cross check each delivery challan with the consolidated list and paste the same in the stock register HC will forward only one consolidated certified delivery challan to NIC Same procedure will be followed for installation and certification for bill clearance.



