bd277049d7aaf7372dd9d0941fcc3378.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 E-Commerce Security COEN 351 Thomas Schwarz, S. J.
E-Commerce Security COEN 351 Thomas Schwarz, S. J.
 Amazon. com 1994: Bezos founds amazon. com 1995: Amazon opens for business; competes on prize, selection, convenience, service. Business model promises low overhead. 1999: Bezos is man of the year for Time magazine. 2000: 2. 7 B$ revenue, 1. 4 B$ loss starts search for profitability. 2002: First ever profits. 4 B$ revenue 2005: First quarter net revenue 1. 9 B$, net income 78 M$
Amazon. com 1994: Bezos founds amazon. com 1995: Amazon opens for business; competes on prize, selection, convenience, service. Business model promises low overhead. 1999: Bezos is man of the year for Time magazine. 2000: 2. 7 B$ revenue, 1. 4 B$ loss starts search for profitability. 2002: First ever profits. 4 B$ revenue 2005: First quarter net revenue 1. 9 B$, net income 78 M$
 E-Commerce n E-commerce n n Use of the internet to transact business. E-commerce I n n n 1995 – 2000: explosive growth, extraordinary innovation March 2000: dot. bust 2001 – today: solid growth, less hype
E-Commerce n E-commerce n n Use of the internet to transact business. E-commerce I n n n 1995 – 2000: explosive growth, extraordinary innovation March 2000: dot. bust 2001 – today: solid growth, less hype
 E-Commerce I n n Disintermediation Friction-free commerce n n Information equally distributed Transaction costs are low Prices are dynamically adjusted Goal of “First Mover” n Successful first mover becomes new intermediary $120 B$ capitalization for 12, 450 dot start-ups 10% survival rate, very few profitable
E-Commerce I n n Disintermediation Friction-free commerce n n Information equally distributed Transaction costs are low Prices are dynamically adjusted Goal of “First Mover” n Successful first mover becomes new intermediary $120 B$ capitalization for 12, 450 dot start-ups 10% survival rate, very few profitable
 E-Commerce II n n n Earning and profits emphasis Traditional Financing Stronger regulation and governance Strengthening intermediaries Imperfect markets Mixed “click and brick” strategies
E-Commerce II n n n Earning and profits emphasis Traditional Financing Stronger regulation and governance Strengthening intermediaries Imperfect markets Mixed “click and brick” strategies
 E-Commerce Business Model n n n n Value proposition (Why buy from you? ) Revenue model (How will you make money? ) Market opportunity Competitive environment Market strategy Organizational development Management team
E-Commerce Business Model n n n n Value proposition (Why buy from you? ) Revenue model (How will you make money? ) Market opportunity Competitive environment Market strategy Organizational development Management team
 E-Commerce Business Model n Revenue Model n n n Advertising revenue model Subscription revenue model Transaction fee revenue model Sales revenue model Affiliate revenue model
E-Commerce Business Model n Revenue Model n n n Advertising revenue model Subscription revenue model Transaction fee revenue model Sales revenue model Affiliate revenue model
 E-Commerce Business Model B 2 C n n Portals E-tailers n n Content provider Transaction broker Market creator n n n Competitive market because barrier to entry is low Brings buyers and sellers together Service Provider Community Provider
E-Commerce Business Model B 2 C n n Portals E-tailers n n Content provider Transaction broker Market creator n n n Competitive market because barrier to entry is low Brings buyers and sellers together Service Provider Community Provider
 E-Commerce Business Model B 2 B n n E-Distributor (Sales of goods) E-Procurement (Fees, supply chain management, fulfillment services) Exchanges (Fees, commissions on transactions) Industry Consortia
E-Commerce Business Model B 2 B n n E-Distributor (Sales of goods) E-Procurement (Fees, supply chain management, fulfillment services) Exchanges (Fees, commissions on transactions) Industry Consortia
 Emerging E-Commerce Business Models n n C 2 C: e. Bay P 2 P: Kazaa M-commerce (mobile commerce), uses wireless E-commerce enablers
Emerging E-Commerce Business Models n n C 2 C: e. Bay P 2 P: Kazaa M-commerce (mobile commerce), uses wireless E-commerce enablers
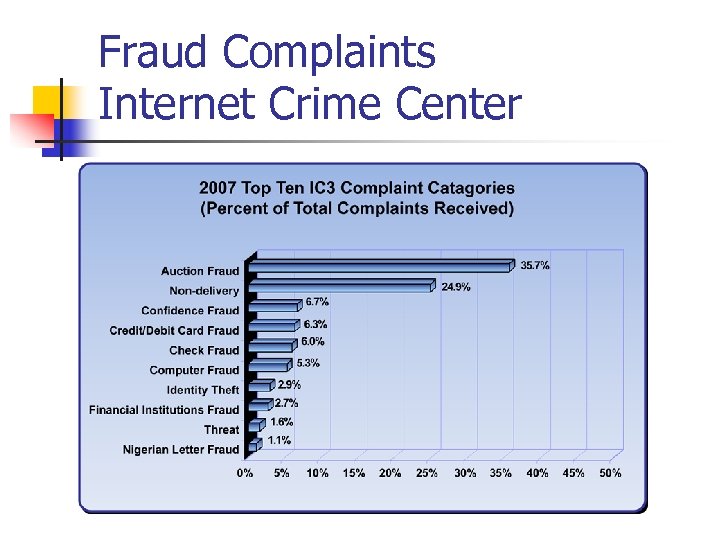
 Internet Fraud Complaints 2003 n n n n n Auction fraud 46. 1% Non-delivery 31. 3% Credit / Debit card fraud 11. 6% Investment fraud 1. 5% Business fraud 1. 3% Confidence fraud 1. 1% Identity theft 1. 0% Check fraud 0. 5% Nigerian letter fraud 0. 4% Communications fraud 0. 1%
Internet Fraud Complaints 2003 n n n n n Auction fraud 46. 1% Non-delivery 31. 3% Credit / Debit card fraud 11. 6% Investment fraud 1. 5% Business fraud 1. 3% Confidence fraud 1. 1% Identity theft 1. 0% Check fraud 0. 5% Nigerian letter fraud 0. 4% Communications fraud 0. 1%
 Fraud Complaints Internet Crime Center
Fraud Complaints Internet Crime Center
 Fraud Complaints Internet Crime Center
Fraud Complaints Internet Crime Center
 Fraud Complaints Internet Crime Center
Fraud Complaints Internet Crime Center
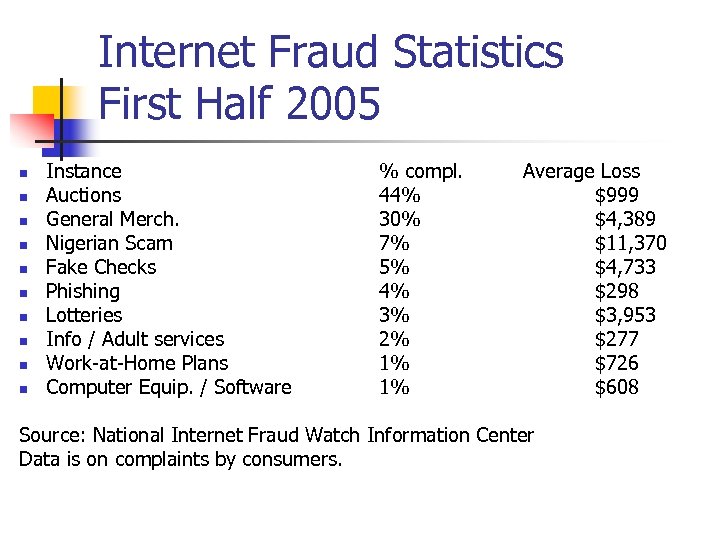 Internet Fraud Statistics First Half 2005 n n n n n Instance Auctions General Merch. Nigerian Scam Fake Checks Phishing Lotteries Info / Adult services Work-at-Home Plans Computer Equip. / Software % compl. 44% 30% 7% 5% 4% 3% 2% 1% 1% Average Loss $999 $4, 389 $11, 370 $4, 733 $298 $3, 953 $277 $726 $608 Source: National Internet Fraud Watch Information Center Data is on complaints by consumers.
Internet Fraud Statistics First Half 2005 n n n n n Instance Auctions General Merch. Nigerian Scam Fake Checks Phishing Lotteries Info / Adult services Work-at-Home Plans Computer Equip. / Software % compl. 44% 30% 7% 5% 4% 3% 2% 1% 1% Average Loss $999 $4, 389 $11, 370 $4, 733 $298 $3, 953 $277 $726 $608 Source: National Internet Fraud Watch Information Center Data is on complaints by consumers.
 E-Commerce Security n n n Integrity Non-repudiation Authenticity Confidentiality Privacy Availability
E-Commerce Security n n n Integrity Non-repudiation Authenticity Confidentiality Privacy Availability
 E-Commerce Security n Threats: n n n n Malicious Code Hacking, Cybervandalism Credit Card Fraud Spoofing Do. S, DDo. S Sniffing Insider Jobs
E-Commerce Security n Threats: n n n n Malicious Code Hacking, Cybervandalism Credit Card Fraud Spoofing Do. S, DDo. S Sniffing Insider Jobs


