66c3f92e30d87af7ec6ddafc27f53aae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 E-Commerce
E-Commerce
 Internet • It is a network that follows the TCP/IP protocol. – Transmission Control Protocol – handles communications between applications. • A message is divided into pieces called packets. • Packets are numbered and may be transmitted by different routes. – Internet Protocol – handles communications between network addresses. • A computer on the internet is assigned an unique address, IP address, which consists of 4 numbers (each number is less than 256) separated by period. Example, 158. 104. 1. 10
Internet • It is a network that follows the TCP/IP protocol. – Transmission Control Protocol – handles communications between applications. • A message is divided into pieces called packets. • Packets are numbered and may be transmitted by different routes. – Internet Protocol – handles communications between network addresses. • A computer on the internet is assigned an unique address, IP address, which consists of 4 numbers (each number is less than 256) separated by period. Example, 158. 104. 1. 10
 E-Commerce • Buying and selling, and marketing and servicing of products and services, and information via computer networks.
E-Commerce • Buying and selling, and marketing and servicing of products and services, and information via computer networks.
 CISCO Internet Value Matrix
CISCO Internet Value Matrix
 The Four Quadrants • New Fundamentals: These companies are taking the low risk road. They use the Internet as a new channel for doing old things, for example streamline operations, to achieve cost saving. • Operational Excellence: Business in this section, are using the Internet technologies to improve management of customer services and for value innovation. • Breakthrough strategies (Early Movers): These are the bold players venturing into new markets, new channels and new products. Their focus is on competitive advantage through new ways of managing relationships and doing business. • Experimentation: These businesses want to become learning organizations. They are exploring the Internet and Intranet and funding small scale experiments. They experiment with new market segments, sources of revenue and ways of doing business but not in a way, which can compromise the main business activities.
The Four Quadrants • New Fundamentals: These companies are taking the low risk road. They use the Internet as a new channel for doing old things, for example streamline operations, to achieve cost saving. • Operational Excellence: Business in this section, are using the Internet technologies to improve management of customer services and for value innovation. • Breakthrough strategies (Early Movers): These are the bold players venturing into new markets, new channels and new products. Their focus is on competitive advantage through new ways of managing relationships and doing business. • Experimentation: These businesses want to become learning organizations. They are exploring the Internet and Intranet and funding small scale experiments. They experiment with new market segments, sources of revenue and ways of doing business but not in a way, which can compromise the main business activities.
 E-Commerce Models • B 2 C: Storefront model – E-tailing (electronic retailing) – Shopping cart, on-line shopping mall • B 2 B: – Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) – Electronic Exchange: An electronic forum where manufacturers, suppliers, and competitors buy and sell goods. • Example: World. Wide Retail Exchange (WWRE) • http: //www. worldwideretailexchange. org/cs/en/index. htm • C 2 C: – Auction model: e-Bay • Etc.
E-Commerce Models • B 2 C: Storefront model – E-tailing (electronic retailing) – Shopping cart, on-line shopping mall • B 2 B: – Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) – Electronic Exchange: An electronic forum where manufacturers, suppliers, and competitors buy and sell goods. • Example: World. Wide Retail Exchange (WWRE) • http: //www. worldwideretailexchange. org/cs/en/index. htm • C 2 C: – Auction model: e-Bay • Etc.
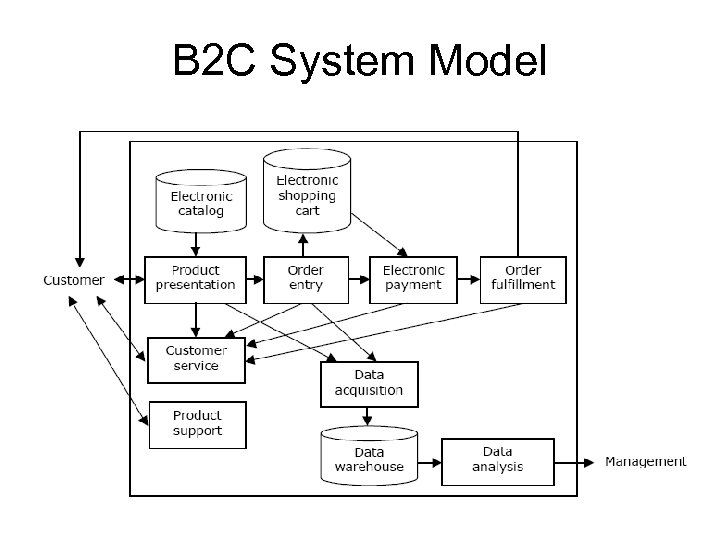 B 2 C System Model
B 2 C System Model
 E-Payment • Online credit card transaction: – Card-not-present transaction • Prepaid card: – Visa Reloadable Prepaid card • E-Wallet: Online wallets try to make Internet shopping easier by letting consumers register once to shop at multiple retail outlets. • Pay. Pal: https: //www. paypal. com/ – Click Merchants/demo
E-Payment • Online credit card transaction: – Card-not-present transaction • Prepaid card: – Visa Reloadable Prepaid card • E-Wallet: Online wallets try to make Internet shopping easier by letting consumers register once to shop at multiple retail outlets. • Pay. Pal: https: //www. paypal. com/ – Click Merchants/demo
 M-Business • E-Business enabled by wireless communication. – Cell phone, PDA • WI-FI: Wireless local area network (WLAN) based on the IEEE 802. 11 specifications. • Hotspot: A person with a Wi-Fi device, such as a computer, cell telephone, or personal digital assistant (PDA) can connect to the Internet when in proximity of an Access Point. The region covered by one or several access points is called a hotspot.
M-Business • E-Business enabled by wireless communication. – Cell phone, PDA • WI-FI: Wireless local area network (WLAN) based on the IEEE 802. 11 specifications. • Hotspot: A person with a Wi-Fi device, such as a computer, cell telephone, or personal digital assistant (PDA) can connect to the Internet when in proximity of an Access Point. The region covered by one or several access points is called a hotspot.
 Location Based Services • Location-Identification Technologies: – Geocode: Longitude, latitude • Global Positioning System (GPS) • Cell phone – Angle of Arrival (AOA) • Location Based Services: – B 2 E (Employee) – B 2 C
Location Based Services • Location-Identification Technologies: – Geocode: Longitude, latitude • Global Positioning System (GPS) • Cell phone – Angle of Arrival (AOA) • Location Based Services: – B 2 E (Employee) – B 2 C
 Internet Security • Authenticity: Is the sender of a message who they claim to be? • Privacy: Are the contents of a message secret and only known to the sender and receiver? • Integrity: Have the contents of a message been modified during transmission? • Nonrepudiation: Can the sender of a message deny that they actually sent the message?
Internet Security • Authenticity: Is the sender of a message who they claim to be? • Privacy: Are the contents of a message secret and only known to the sender and receiver? • Integrity: Have the contents of a message been modified during transmission? • Nonrepudiation: Can the sender of a message deny that they actually sent the message?
 Encryption (Cryptography) • Plain text: the original message in humanreadable form. • Ciphertext: the encrypted message • Encryption algorithm: the mathematical formula used to encrypt the plain text. • Key: the secret key used to encrypt and decrypt a message.
Encryption (Cryptography) • Plain text: the original message in humanreadable form. • Ciphertext: the encrypted message • Encryption algorithm: the mathematical formula used to encrypt the plain text. • Key: the secret key used to encrypt and decrypt a message.
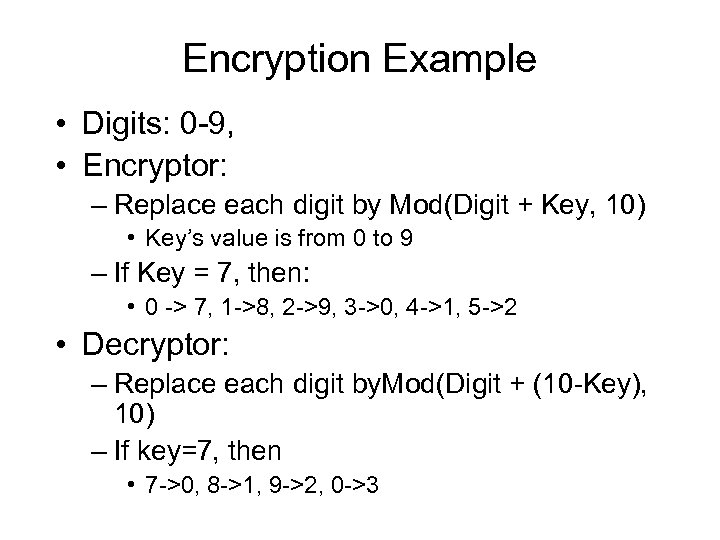 Encryption Example • Digits: 0 -9, • Encryptor: – Replace each digit by Mod(Digit + Key, 10) • Key’s value is from 0 to 9 – If Key = 7, then: • 0 -> 7, 1 ->8, 2 ->9, 3 ->0, 4 ->1, 5 ->2 • Decryptor: – Replace each digit by. Mod(Digit + (10 -Key), 10) – If key=7, then • 7 ->0, 8 ->1, 9 ->2, 0 ->3
Encryption Example • Digits: 0 -9, • Encryptor: – Replace each digit by Mod(Digit + Key, 10) • Key’s value is from 0 to 9 – If Key = 7, then: • 0 -> 7, 1 ->8, 2 ->9, 3 ->0, 4 ->1, 5 ->2 • Decryptor: – Replace each digit by. Mod(Digit + (10 -Key), 10) – If key=7, then • 7 ->0, 8 ->1, 9 ->2, 0 ->3
 Encryption Algorithms • Private key encryption – symmetric cryptography • Public key encryption – asymmetric cryptography • Digital signature • Digital certificate
Encryption Algorithms • Private key encryption – symmetric cryptography • Public key encryption – asymmetric cryptography • Digital signature • Digital certificate
 Private Key (secret Key) Encryption • The same key is used by a sender (for encryption) and a receiver (for decryption) • The key must be transmitted to the receiver. • Example: – DES (Data Encryption Standard) algorithm with 56 -bit key
Private Key (secret Key) Encryption • The same key is used by a sender (for encryption) and a receiver (for decryption) • The key must be transmitted to the receiver. • Example: – DES (Data Encryption Standard) algorithm with 56 -bit key
 Public Key Encryption • Uses two different keys: a public and a private key. • Receiver’s public key must be delivered in advance. • Sender uses receiver’s public key to encrypt the message and receiver uses private key to decrypt the message (Sender can be sure the receiver is the true receiver) • Example: – RSA (Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman) algorithm with 512 -bit to 1024 -bit key. • Note: Although the two keys are mathematically related, deriving one from the other is “computationally infeasible”.
Public Key Encryption • Uses two different keys: a public and a private key. • Receiver’s public key must be delivered in advance. • Sender uses receiver’s public key to encrypt the message and receiver uses private key to decrypt the message (Sender can be sure the receiver is the true receiver) • Example: – RSA (Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman) algorithm with 512 -bit to 1024 -bit key. • Note: Although the two keys are mathematically related, deriving one from the other is “computationally infeasible”.
 Digital Signature • It is used for the authentication and nonrepudiation of senders by applying public key encryption in reverse, and ensures the integrity of the message. • How digital signature works: – Sender: • Create message digest: Hash(original message) • Digital signature: Encrypt(Message digest, Sender’s private key) • Encrypted message: Encrypt(Original message, Receiver’s public key) • Send the hash function, digital signature, and the encrypted message to receiver. – Receiver: • Use receiver’s private key to decrypt the encrypted message to reveal the original message. • Use the sender’s public key to decrypt digital signature and reveal the message digest. • Apply the hash function to the original message. If the hash value matches the message digest in the digital signature, the message is intact.
Digital Signature • It is used for the authentication and nonrepudiation of senders by applying public key encryption in reverse, and ensures the integrity of the message. • How digital signature works: – Sender: • Create message digest: Hash(original message) • Digital signature: Encrypt(Message digest, Sender’s private key) • Encrypted message: Encrypt(Original message, Receiver’s public key) • Send the hash function, digital signature, and the encrypted message to receiver. – Receiver: • Use receiver’s private key to decrypt the encrypted message to reveal the original message. • Use the sender’s public key to decrypt digital signature and reveal the message digest. • Apply the hash function to the original message. If the hash value matches the message digest in the digital signature, the message is intact.
 Certificate • A certificate is a digital document issued by a trusted third-party certificate authority (CA). • A certificate contains records such as a serial number, user’s name, owner’s public key, name of CA, etc. • Example of CA: Veri. Sign, U. S. Postal Service.
Certificate • A certificate is a digital document issued by a trusted third-party certificate authority (CA). • A certificate contains records such as a serial number, user’s name, owner’s public key, name of CA, etc. • Example of CA: Veri. Sign, U. S. Postal Service.
 Online Transaction Security Protocol • Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) – Developed by Netscape – SSL implements public key technology using the RSA algorithm and digital certificate to authenticate the server in a transaction and protect private information.
Online Transaction Security Protocol • Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) – Developed by Netscape – SSL implements public key technology using the RSA algorithm and digital certificate to authenticate the server in a transaction and protect private information.
 • 1. A client sends a message to a server. • 2. The server sends its digital certificate to the client for authentication (authenticate the server) • 3. The client and server negotiate session keys to continue the transaction and use session keys and digital certificate for encryption.
• 1. A client sends a message to a server. • 2. The server sends its digital certificate to the client for authentication (authenticate the server) • 3. The client and server negotiate session keys to continue the transaction and use session keys and digital certificate for encryption.
 Cookies • Designed to hold information about a user. • Created by a web site and saved on the visitor’s machine. • It contains: – Web site that sets the cookie. – One or more pieces of data. – Expiration date for this cookie. • Cookies directory: • Browser sends cookie with the URL when you visit the site that issued the cookie.
Cookies • Designed to hold information about a user. • Created by a web site and saved on the visitor’s machine. • It contains: – Web site that sets the cookie. – One or more pieces of data. – Expiration date for this cookie. • Cookies directory: • Browser sends cookie with the URL when you visit the site that issued the cookie.
 Excel’s Security • Use password to protect spreadsheet file: – Tools/Option/Security • Password to open • Password to modify • Protect spreadsheet content: – Tools/Protection • Protect sheet • Allow user to edit range • Hide data: – Format/Cells/Number/Custom • Enter ; ; ; (three semicolons)
Excel’s Security • Use password to protect spreadsheet file: – Tools/Option/Security • Password to open • Password to modify • Protect spreadsheet content: – Tools/Protection • Protect sheet • Allow user to edit range • Hide data: – Format/Cells/Number/Custom • Enter ; ; ; (three semicolons)
 Database Security
Database Security
 Database Security • Database Security: Protection of the data against accidental or intentional loss, destruction, or misuse • Increased difficulty due to Internet access and client/server technologies
Database Security • Database Security: Protection of the data against accidental or intentional loss, destruction, or misuse • Increased difficulty due to Internet access and client/server technologies
 Threats to Data Security • Accidental losses attributable to: – People • Users: using another person’s means of access, viewing unauthorized data, introduction of viruses • Programmers/Operators • Database administrator: Inadequate security policy – Software failure • DBMS: security mechanism, privilege • Application software: program alteration – Hardware failure • Theft and fraud • Improper data access: – Loss of privacy (personal data) – Loss of confidentiality (corporate data) • Loss of availability (through, e. g. sabotage)
Threats to Data Security • Accidental losses attributable to: – People • Users: using another person’s means of access, viewing unauthorized data, introduction of viruses • Programmers/Operators • Database administrator: Inadequate security policy – Software failure • DBMS: security mechanism, privilege • Application software: program alteration – Hardware failure • Theft and fraud • Improper data access: – Loss of privacy (personal data) – Loss of confidentiality (corporate data) • Loss of availability (through, e. g. sabotage)
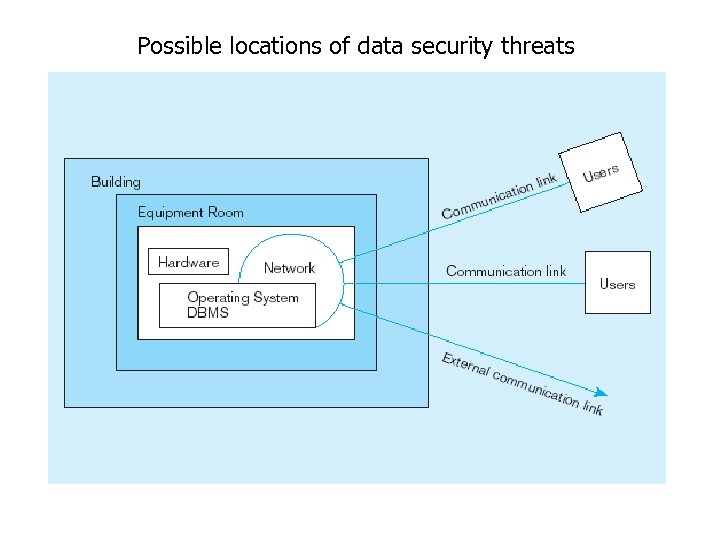 Possible locations of data security threats
Possible locations of data security threats
 Countermeasures to Threats • Authorization – Authentication • • • Access controls: privileges Database views Back. Up and Recovery Enforcing integrity rules Encryption – Symmetric encryption: use same key for encryption and decryption – Asymmetric encryption: • Public key: for encryption • Private key: decryption • RAID
Countermeasures to Threats • Authorization – Authentication • • • Access controls: privileges Database views Back. Up and Recovery Enforcing integrity rules Encryption – Symmetric encryption: use same key for encryption and decryption – Asymmetric encryption: • Public key: for encryption • Private key: decryption • RAID
 Authorization Rules • Controls incorporated in the data management system • Restrict: – access to data – actions that people can take on data • Authorization matrix for: – – Subjects Objects Actions Constraints
Authorization Rules • Controls incorporated in the data management system • Restrict: – access to data – actions that people can take on data • Authorization matrix for: – – Subjects Objects Actions Constraints
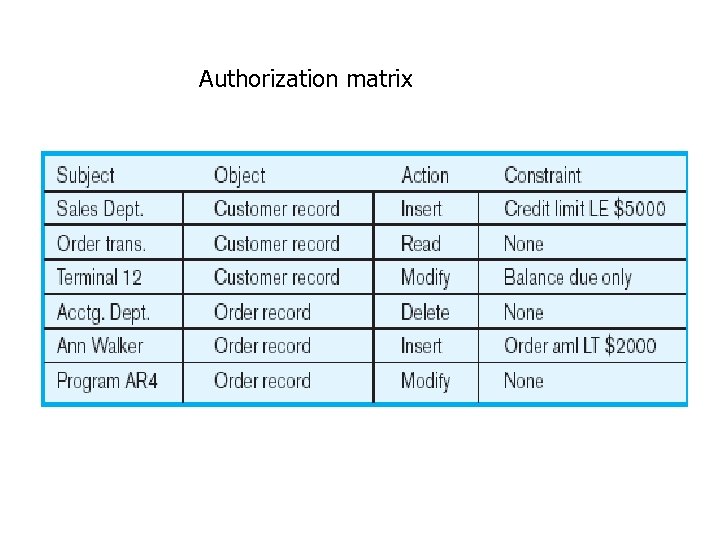 Authorization matrix
Authorization matrix
 SQL Injection • "SQL Injection" is an unverified/unsanitized user input vulnerability, and the idea is to convince the application to run SQL code that was not intended. • Exploits applications that use external input for database commands.
SQL Injection • "SQL Injection" is an unverified/unsanitized user input vulnerability, and the idea is to convince the application to run SQL code that was not intended. • Exploits applications that use external input for database commands.
 SQL Injection Demo • On a web page that takes customer ID entered in a textbox as input, then displays the customer’s data. • In the textbox, enter: ‘ OR 1=1 OR CID = ‘ SQLInjection. Demo Other SQL injection examples:
SQL Injection Demo • On a web page that takes customer ID entered in a textbox as input, then displays the customer’s data. • In the textbox, enter: ‘ OR 1=1 OR CID = ‘ SQLInjection. Demo Other SQL injection examples:
 Demo Protected Sub Button 1_Click(By. Val sender As Object, By. Val e As System. Event. Args) Handles Button 1. Click Dim str. Conn As String = "Provider=Microsoft. Jet. OLEDB. 4. 0; Data Source = c: sales. DB. mdb" Dim obj. Conn As New Ole. Db. Connection(str. Conn) Dim str. SQL As String = "select * from customer where cid = '" & Text. Box 1. Text & "'" Dim obj. Comm As New Ole. Db. Command(str. SQL, obj. Conn) Try obj. Conn. Open() Dim obj. Data. Reader As Ole. Db. Data. Reader obj. Data. Reader = obj. Comm. Execute. Reader() Grid. View 1. Data. Source = obj. Data. Reader Grid. View 1. Data. Bind() Catch except As System. Exception Response. Write(except. Message) End Try End Sub
Demo Protected Sub Button 1_Click(By. Val sender As Object, By. Val e As System. Event. Args) Handles Button 1. Click Dim str. Conn As String = "Provider=Microsoft. Jet. OLEDB. 4. 0; Data Source = c: sales. DB. mdb" Dim obj. Conn As New Ole. Db. Connection(str. Conn) Dim str. SQL As String = "select * from customer where cid = '" & Text. Box 1. Text & "'" Dim obj. Comm As New Ole. Db. Command(str. SQL, obj. Conn) Try obj. Conn. Open() Dim obj. Data. Reader As Ole. Db. Data. Reader obj. Data. Reader = obj. Comm. Execute. Reader() Grid. View 1. Data. Source = obj. Data. Reader Grid. View 1. Data. Bind() Catch except As System. Exception Response. Write(except. Message) End Try End Sub
 Access security • Database Password: – Must open the database exclusively • In the File/Open window, click Open button’s dropdown list and select: Open Exclusive – Tools/Security/Set database password • Tools/Security/Encode Decode • User group/User level security
Access security • Database Password: – Must open the database exclusively • In the File/Open window, click Open button’s dropdown list and select: Open Exclusive – Tools/Security/Set database password • Tools/Security/Encode Decode • User group/User level security


