b29cd497ec2bb1f67b579d579a8383de.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

E-Commerce

E-Commerce • Buying and selling, and marketing and servicing of products and services, and information via computer networks.

Broad Band & Economy • According to the study released by Connected Nation, A 7 percent increase in broadband adoption would: – create 2. 4 million jobs across the U. S; – save $6. 4 billion in vehicle mileage – U. S. residents would save 3. 8 billion hours a year by conducting transactions online, at a cost-savings of $35. 2 billion, according to the study.

E-Commerce Models • B 2 C: Storefront model – E-tailing (electronic retailing) – Shopping cart, on-line shopping mall • B 2 B: – Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) – Electronic Exchange: An electronic forum where manufacturers, suppliers, and competitors buy and sell goods. • Example: Global Sources and World. Wide Retail Exchange (WWRE) • http: //wwre. globalsources. com/ • C 2 C: – Auction model: e-Bay • Etc.
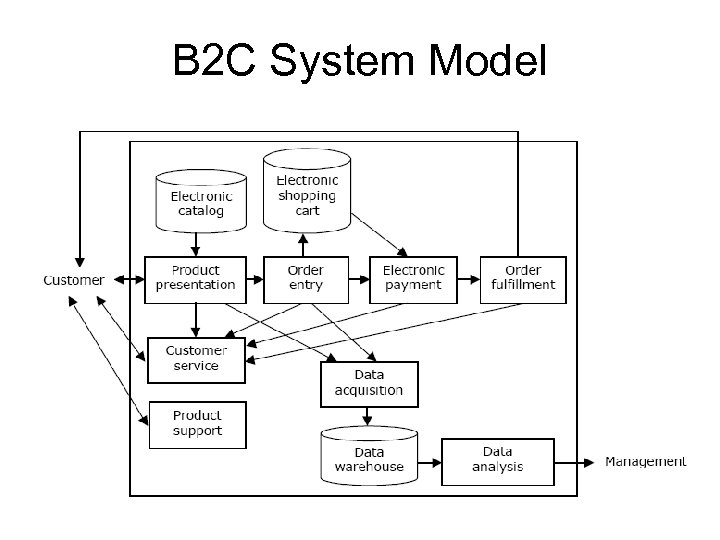
B 2 C System Model

E-Payment • Online credit card transaction: – Card-not-present transaction • Prepaid card: – Visa Reloadable Prepaid card • Pay. Pal: https: //www. paypal. com/ • Google Checkout: – https: //checkout. google. com/support/? hl=en_ US

M-Business • E-Business enabled by wireless communication. – Cell phone, PDA • WI-FI: Wireless local area network (WLAN) based on the IEEE 802. 11 specifications. – Hotspot

Location Based Services • Location-Identification Technologies: – Geocode: Longitude, latitude • Global Positioning System (GPS) • Cell phone – Angle of Arrival (AOA) • Location Based Services: – B 2 E (Employee) – B 2 C

Channel Conflict • For example, a manufacturing company may have a large, established dealer network. The channel conflict exists, when the companies tries to open another channel, such as an online store where customers can purchase goods directly from the company. This may alienate existing dealers, since they may feel that they are bypassed. • Example: Anthon Berg Chocolate • http: //toms. dk/default. aspx? Area. ID=25

E-Learning • Electronic learning or e. Learning is a general term used to refer to computer-enhanced learning. • Many higher education, for-profit institutions, now offer on-line classes. • The Sloan report, based on a poll of academic leaders, says that students generally appear to be at least as satisfied with their on-line classes as they are with traditional ones. • Example: GIS online course – http: //www. ruraltech. org/video/2005/acrview/index. asp

Technology Used in E-Learning • • • blogs collaborative software discussion boards e-mail educational animation learning management systems podcasts screencasts text chat virtual classrooms web-based teaching materials wiki

e-Government • It refers to government’s use of information technology to exchange information and services with citizens, businesses, and other arms of government.

e-Government Models • • Government-to-Citizen G 2 C Government-to-Business (G 2 B) Government-to-Government (G 2 G) Government-to-Employees (G 2 E). – http: //www. nbc. gov/egov/

Increase Traffic to Website • Search engine optimization: – http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Search_engine_optimization • Tips: – http: //www. 2 createawebsite. com/ebook/Traffic. Building. Tips. pdf • Grow your business with Google – Google Ad. Words • Yahoo!'s Open Search Platform – http: //tools. search. yahoo. com/newsearch/open. html

How Search Engines Work: Search Engine Relevancy Reviewed • http: //www. seobook. com/relevancy/

Internet Security • Authenticity: Is the sender of a message who they claim to be? • Privacy: Are the contents of a message secret and only known to the sender and receiver? • Integrity: Have the contents of a message been modified during transmission? • Nonrepudiation: Can the sender of a message deny that they actually sent the message?

Encryption (Cryptography) • Plain text: the original message in humanreadable form. • Ciphertext: the encrypted message • Encryption algorithm: the mathematical formula used to encrypt the plain text. • Key: the secret key used to encrypt and decrypt a message.
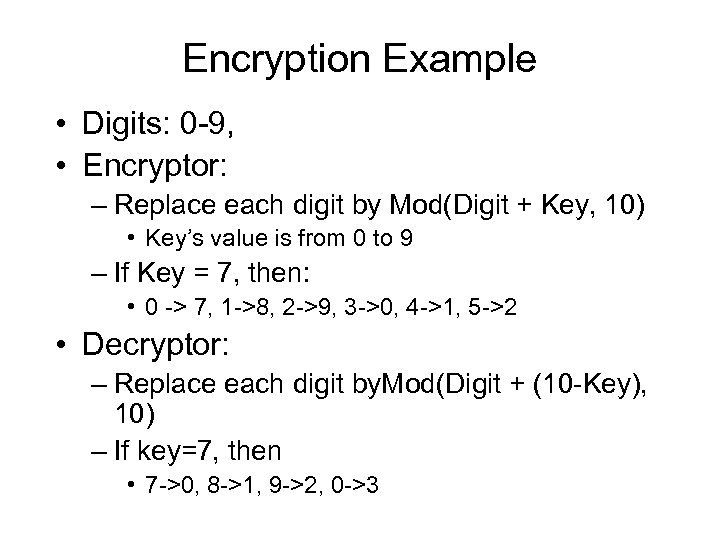
Encryption Example • Digits: 0 -9, • Encryptor: – Replace each digit by Mod(Digit + Key, 10) • Key’s value is from 0 to 9 – If Key = 7, then: • 0 -> 7, 1 ->8, 2 ->9, 3 ->0, 4 ->1, 5 ->2 • Decryptor: – Replace each digit by. Mod(Digit + (10 -Key), 10) – If key=7, then • 7 ->0, 8 ->1, 9 ->2, 0 ->3
Encryption Algorithms • Private key encryption – symmetric cryptography • Public key encryption – asymmetric cryptography • Digital signature • Digital certificate

Private Key (secret Key) Encryption • The same key is used by a sender (for encryption) and a receiver (for decryption) • The key must be transmitted to the receiver. • Example: – DES (Data Encryption Standard) algorithm with 56 -bit key

Public Key Encryption • Uses two different keys: a public and a private key. • Receiver’s public key must be delivered in advance. • Sender uses receiver’s public key to encrypt the message and receiver uses private key to decrypt the message (Sender can be sure the receiver is the true receiver) • Example: – RSA (Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman) algorithm with 512 -bit to 1024 -bit key. • Note: Although the two keys are mathematically related, deriving one from the other is “computationally infeasible”.

Digital Signature • It is used for the authentication and nonrepudiation of senders.

Certificate • A certificate is a digital document issued by a trusted third-party certificate authority (CA). • A certificate contains records such as a serial number, user’s name, owner’s public key, name of CA, etc. • Example of CA: Veri. Sign, U. S. Postal Service.

Online Transaction Security Protocol • Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) – Developed by Netscape – SSL implements public key technology using the RSA algorithm and digital certificate to authenticate the server in a transaction and protect private information.

• 1. A client sends a message to a server. • 2. The server sends its digital certificate to the client for authentication (authenticate the server) • 3. The client and server negotiate session keys to continue the transaction and use session keys and digital certificate for encryption.

Tech heavyweights join Open. ID Foundation board • IBM, Google, Microsoft, Yahoo and Veri. Sign have joined the board of the Open. ID Foundation, which puts consumers a little closer to being able to use a single sign-on when they surf the Web. • It is simpler: People no longer have to remember multiple passwords or re-enter their personal information every time they visit a new site. • It is also more secure because it protects against certain types of online attacks. • http: //openid. net/

Cookies • Designed to hold information about a user. • Created by a web site and saved on the visitor’s machine. • It contains: – Web site that sets the cookie. – One or more pieces of data. – Expiration date for this cookie. • Cookies directory: • Browser sends cookie with the URL when you visit the site that issued the cookie.

Excel’s Security • Use password to protect spreadsheet file: – Review/Protect Sheet – Review/Protect Workbook – Review/Share workbook • Protect spreadsheet content: – Home/Format/Protection • Protect sheet • Allow user to edit range • Hide data: – Home/Format/Cells/Number/Custom • Enter ; ; ; (three semicolons)

Database Security

Database Security • Database Security: Protection of the data against accidental or intentional loss, destruction, or misuse • Increased difficulty due to Internet access and client/server technologies

Threats to Data Security • Accidental losses attributable to: – People • Users: using another person’s means of access, viewing unauthorized data, introduction of viruses • Programmers/Operators • Database administrator: Inadequate security policy – Software failure • DBMS: security mechanism, privilege • Application software: program alteration – Hardware failure • Theft and fraud • Improper data access: – Loss of privacy (personal data) – Loss of confidentiality (corporate data) • Loss of availability (through, e. g. sabotage)

Countermeasures to Threats • Authorization – Authentication • • • Access controls: privileges Database views Back. Up and Recovery Enforcing integrity rules Encryption – Symmetric encryption: use same key for encryption and decryption – Asymmetric encryption: • Public key: for encryption • Private key: decryption • RAID

Authorization Rules • Controls incorporated in the data management system • Restrict: – access to data – actions that people can take on data • Authorization matrix for: – – Subjects Objects Actions Constraints
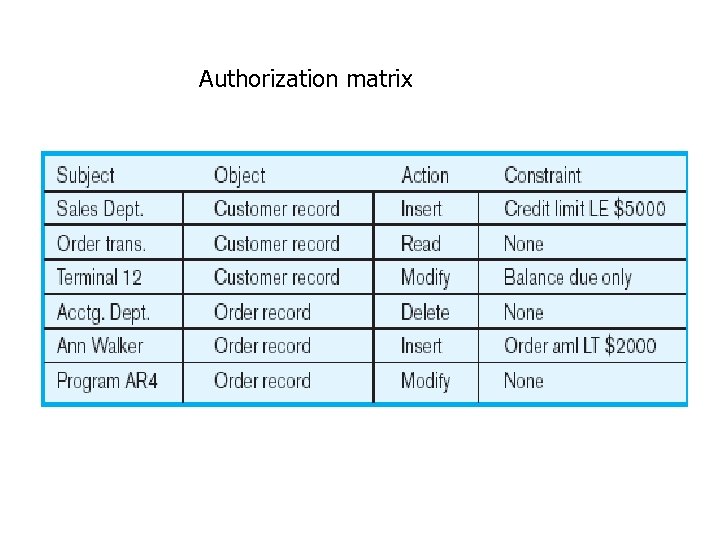
Authorization matrix
b29cd497ec2bb1f67b579d579a8383de.ppt