017c48500ec19992e6ecb9ccb90c7b37.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

E-Commerce

E-Commerce • Buying and selling, and marketing and servicing of products and services, and information via computer networks.

Broad Band & Economy • According to the study released by Connected Nation, A 7 percent increase in broadband adoption would: – create 2. 4 million jobs across the U. S; – save $6. 4 billion in vehicle mileage – U. S. residents would save 3. 8 billion hours a year by conducting transactions online, at a cost-savings of $35. 2 billion, according to the study. • http: //www. connectednation. org/

E-Commerce Models • B 2 C: Storefront model – E-tailing (electronic retailing) – Shopping cart, on-line shopping mall • B 2 B: – Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) – Electronic Exchange: An electronic forum where manufacturers, suppliers, and competitors buy and sell goods. • Example: Global Sources and World. Wide Retail Exchange (WWRE) • http: //wwre. globalsources. com/ • C 2 C: – Auction model: e-Bay, Craig's List • C 2 B: A business model in which consumers (individuals) offer products and services to companies and the companies pay them. – http: //c 2 b. typepad. com/c 2 b_business_model/ – Amazon Affiliate program: https: //affiliate-program. amazon. com/ • Etc.

M-Business • E-Business enabled by wireless communication. – Cell phone, PDA

QR Code-Enabled Virtual Store • Tesco Subway virtual store: – http: //www. adverblog. com/2011/06/23/tescossubway-virtual-store/ • Well. ca Opens QR Code-Enabled Virtual Store in Downtown Toronto: – http: //www. delvinia. com/well-ca-opens-qrcode-enabled-virtual-store-in-downtoronto/

Location Based Services • Location-Identification Technologies: – Geocode: Longitude, latitude • Global Positioning System (GPS) • Cell phone – Angle of Arrival (AOA)

E-Payment • Online credit card transaction: – Card-not-present transaction • Pay. Pal: https: //www. paypal. com/ • Google Checkout: – https: //accounts. google. com/Service. Login? ser vice=sierra&continue=https: //checkout. google. com/main? upgrade%3 Dtrue&hl=en_US&nui= 1<mpl=default&sacu=1

Channel Conflict • For example, a manufacturing company may have a large, established dealer network. The channel conflict exists, when the companies tries to open another channel, such as an online store where customers can purchase goods directly from the company. This may alienate existing dealers, since they may feel that they are bypassed.

Increase Traffic to Website • Search engine optimization: – http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Search_engine_optimization – Search Engine Relevancy Reviewed – http: //www. seobook. com/relevancy • Tips: – http: //www. 2 createawebsite. com/ebook/Traffic. Building. Tips. pdf • Grow your business with Google – Google Ad. Words • Yahoo!'s Open Search Platform – http: //tools. search. yahoo. com/newsearch/open. html

Internet Security • Authenticity: Is the sender of a message who they claim to be? • Privacy: Are the contents of a message secret and only known to the sender and receiver? • Integrity: Have the contents of a message been modified during transmission? • Nonrepudiation: Can the sender of a message deny that they actually sent the message?

Encryption (Cryptography) • Plain text: the original message in humanreadable form. • Ciphertext: the encrypted message • Encryption algorithm: the mathematical formula used to encrypt the plain text. • Key: the secret key used to encrypt and decrypt a message.
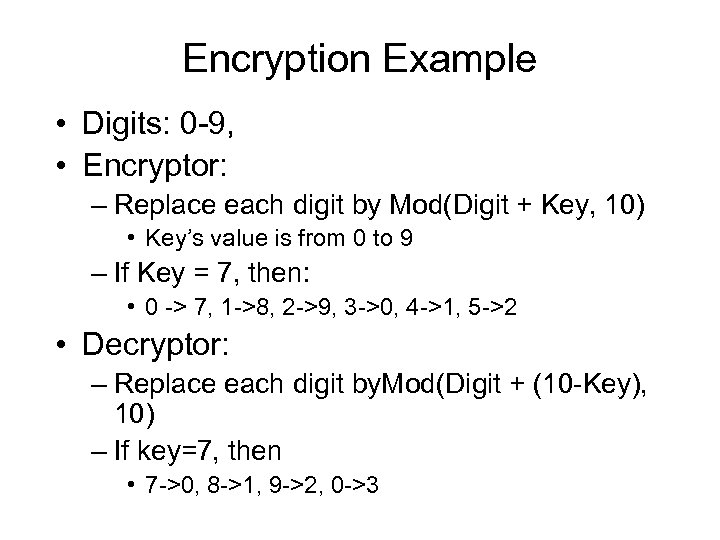
Encryption Example • Digits: 0 -9, • Encryptor: – Replace each digit by Mod(Digit + Key, 10) • Key’s value is from 0 to 9 – If Key = 7, then: • 0 -> 7, 1 ->8, 2 ->9, 3 ->0, 4 ->1, 5 ->2 • Decryptor: – Replace each digit by. Mod(Digit + (10 -Key), 10) – If key=7, then • 7 ->0, 8 ->1, 9 ->2, 0 ->3
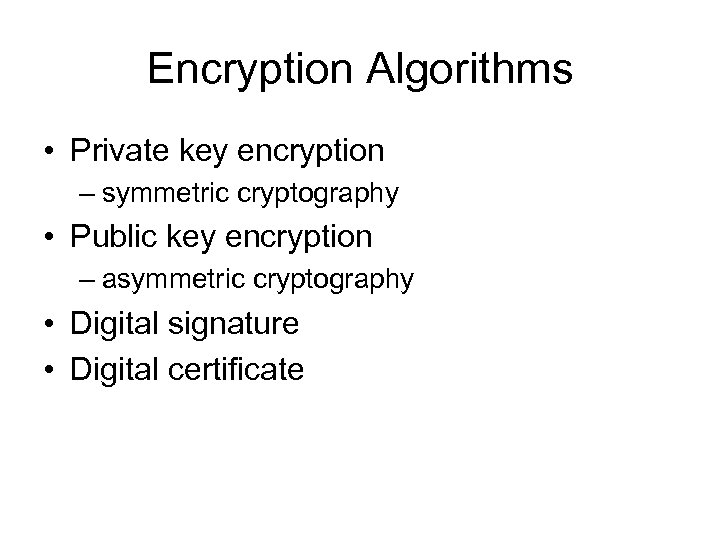
Encryption Algorithms • Private key encryption – symmetric cryptography • Public key encryption – asymmetric cryptography • Digital signature • Digital certificate

Private Key (secret Key) Encryption • The same key is used by a sender (for encryption) and a receiver (for decryption) • The key must be transmitted to the receiver. • Example: – DES (Data Encryption Standard) algorithm with 56 -bit key

Public Key Encryption • Uses two different keys: a public and a private key. • Receiver’s public key must be delivered in advance. • Sender uses receiver’s public key to encrypt the message and receiver uses private key to decrypt the message (Sender can be sure the receiver is the true receiver) • Example: – RSA (Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman) algorithm with 512 -bit to 1024 -bit key. • Note: Although the two keys are mathematically related, deriving one from the other is “computationally infeasible”.

Digital Signature • It is used for the authentication and nonrepudiation of senders.

Tech heavyweights join Open. ID Foundation board • IBM, Google, Microsoft, Yahoo and Veri. Sign have joined the board of the Open. ID Foundation, which puts consumers a little closer to being able to use a single sign-on when they surf the Web. • It is simpler: People no longer have to remember multiple passwords or re-enter their personal information every time they visit a new site. • It is also more secure because it protects against certain types of online attacks. • http: //openid. net/
017c48500ec19992e6ecb9ccb90c7b37.ppt